Isolation and Genomic Analysis of Escherichia coli Phage AUBRB02: Implications for Phage Therapy in Lebanon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of Escherichia coli Phage
2.2. Phage Host Range Determination
2.3. Phage One-Step Growth and Adsorption Rate
2.4. Bacteriolytic Activity
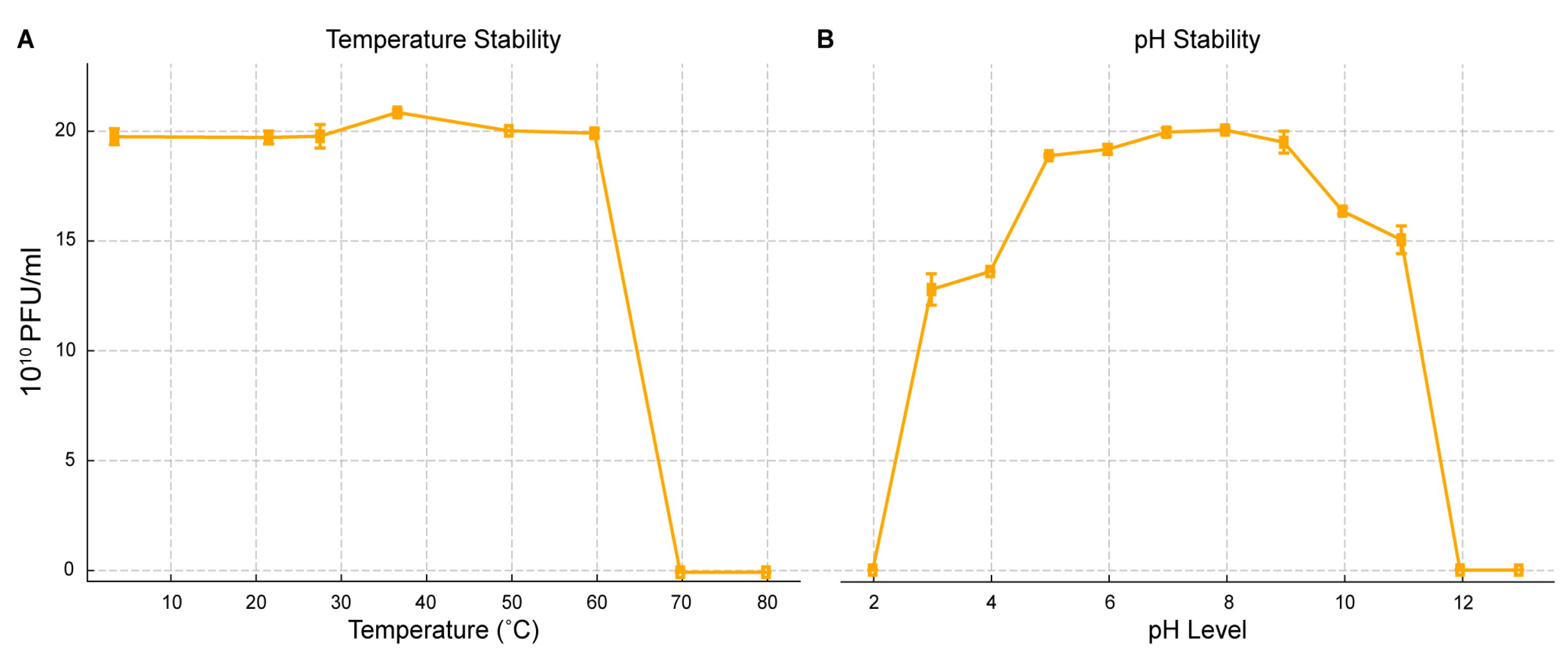
2.5. pH and Thermal Stability
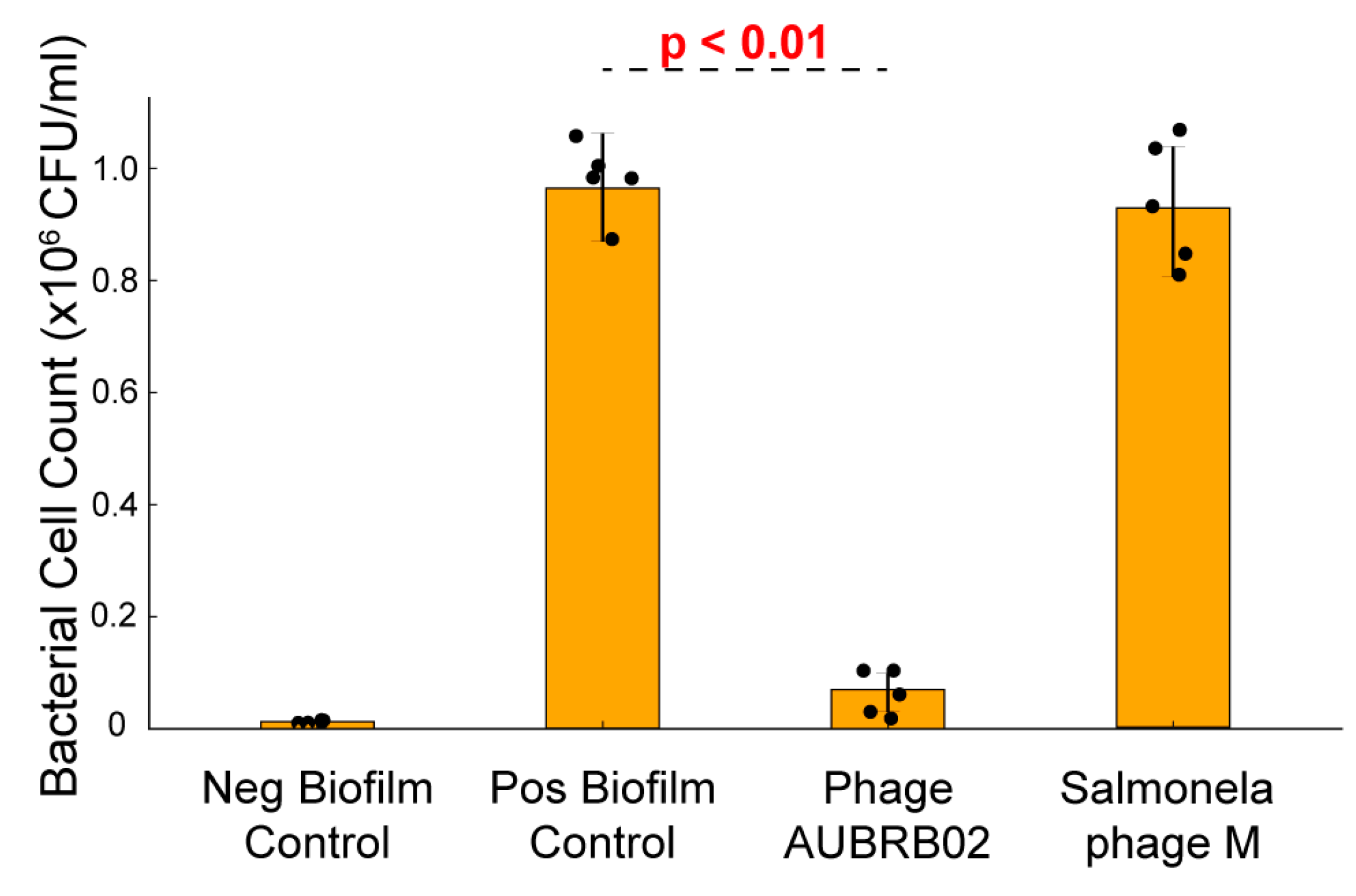
2.6. Biofilm Elimination Potential of AUBRB02
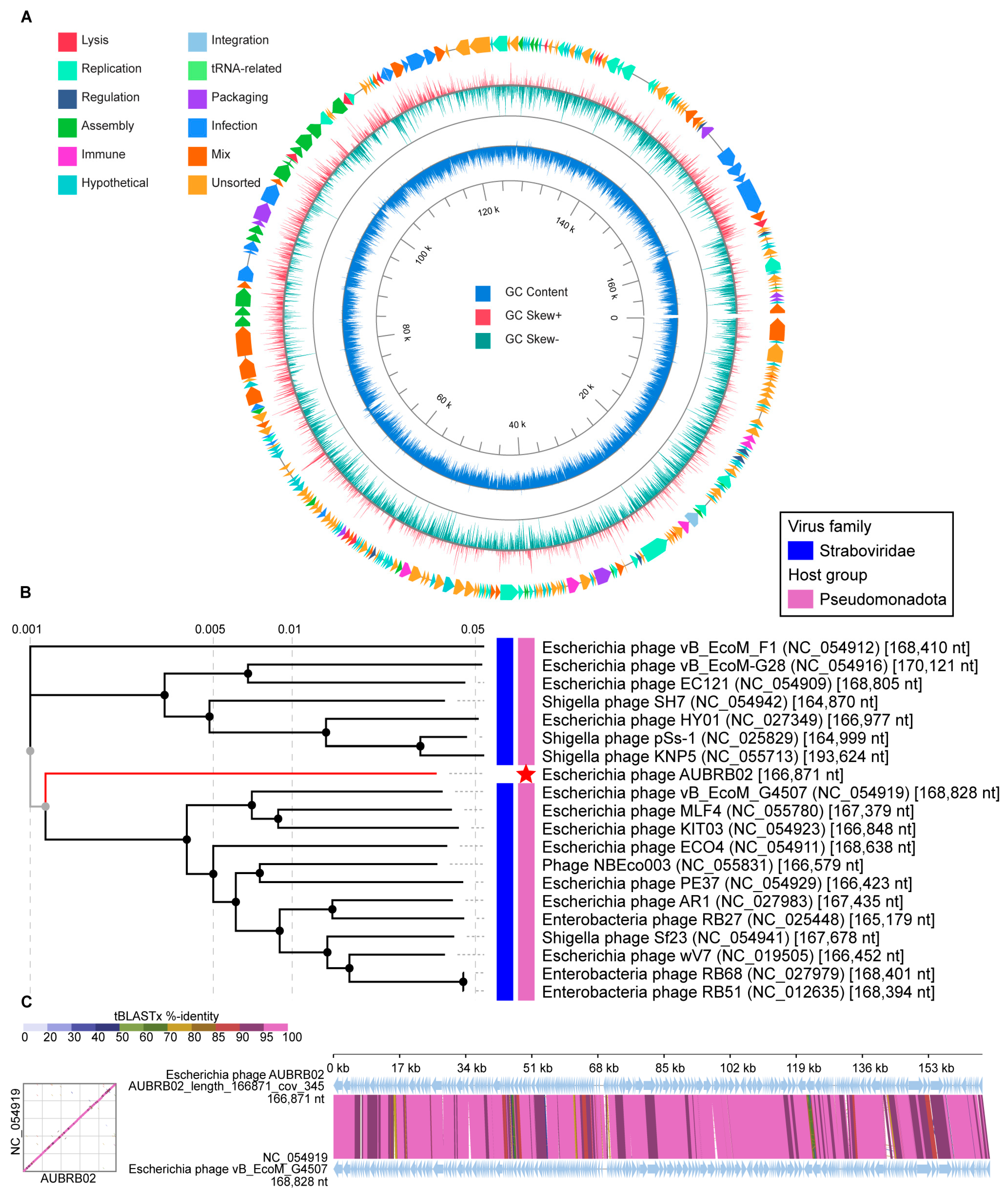
2.7. Whole Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Sewage Sample Collection
4.3. Phage Isolation
4.4. Phage Purification and Enrichment
4.5. Host Range Assay
4.6. One-Step Growth Curve
4.7. Adsorption Rate Assay
4.8. Bacteriolytic Activity Assay
4.9. Phage pH and Thermal Stability
4.10. Biofilm Elimination Assay
4.11. DNA Extraction
4.12. Phage Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.13. Bacterial Pangenome Analysis
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Raw Data Availability
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoon, S.H.; Jeong, H.; Kwon, S.-K.; Kim, J.F. Genomics, biological features, and biotechnological applications of Escherichia coli B: “Is B for better?!”. In Systems Biology and Biotechnology of Escherichia coli; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrollahian, S.; Graham, J.P.; Halaji, M. A review of the mechanisms that confer antibiotic resistance in pathotypes of E. coli. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1387497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.J. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pormohammad, A.; Nasiri, M.J.; Azimi, T. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli strains simultaneously isolated from humans, animals, food, and the environment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, S.; Dahdouh, E.; Daoud, Z. Resistance of Gram-Negative Bacilli in Lebanon. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 759208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaeta, M.; Sanfilippo, G.; Fraix, A.; Sortino, G.; Barcellona, M.; Oliveri Conti, G.; Fragalà, M.E.; Ferrante, M.; Purrello, R.; D’Urso, A. Photodegradation of Antibiotics by Noncovalent Porphyrin-Functionalized TiO2 in Water for the Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance Risk Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otrock, Z.K.; Oghlakian, G.O.; Salamoun, M.M.; Haddad, M.; Bizri, A.R.N. Incidence of urinary tract infection following transrectal ultrasound guided prostate biopsy at a tertiary-care medical center in Lebanon. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2004, 25, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanafani, Z.A.; Kara, L.; Hayek, S.; Kanj, S.S. Ventilator-associated pneumonia at a tertiary-care center in a developing country: Incidence, microbiology, and susceptibility patterns of isolated microorganisms. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2003, 24, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dagher, L.A.; Hassan, J.; Kharroubi, S.; Jaafar, H.; Kassem, I.I. Nationwide Assessment of Water Quality in Rivers Across Lebanon by Quantifying Fecal Indicators Densities and Profiling Antibiotic Resistance of Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, J.; Abboud, E.; Tokajian, S. The dissemination of antimicrobial resistance determinants in surface water sources in Lebanon. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiab113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Magrini, N.; Kahlmeter, G.; Singh, N. Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 27, pp. 318–327. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Lack of New Antibiotics Threatens Global Efforts to Contain Drug-Resistant Infections; New Release, 17 January 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kasman, L.M.; Porter, L.D. Bacteriophages. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, T.A.; Houjeiry, S.E.; Kanj, S.S.; Matar, G.M.; Saba, E.S. From forgotten cure to modern medicine: The resurgence of bacteriophage therapy. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 39, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dion, M.B.; Oechslin, F.; Moineau, S. Phage diversity, genomics and phylogeny. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszak, T.; Latka, A.; Roszniowski, B.; Valvano, M.A.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. Phage life cycles behind bacterial biodiversity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3987–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wood, T.K. Cryptic prophages as targets for drug development. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 27, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, P. The Bacteriophage Head-to-Tail Interface. In Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 88, pp. 305–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yin, S.; Li, G.; Wang, J.; Huang, G.; Jiang, B.; You, B.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Luo, X. Global transcriptomic analysis of the interactions between phage φAbp1 and extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. mSystems 2019, 4, e00068-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Gutiérrez, D.; García, P.; Rodríguez, A. The perfect bacteriophage for therapeutic applications—A quick guide. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, R.M. Phage therapy: Past history and future prospects. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp.-Engl. Ed. 1999, 47, 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Abedon, S.T.; Thomas-Abedon, C. Phage therapy pharmacology. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2010, 11, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliźniewicz, M.; Miłek, D.; Olszewska, P.; Czajkowski, A.; Serwin, N.; Cecerska-Heryć, E.; Dołęgowska, B.; Grygorcewicz, B. Advances in bacteriophage-mediated strategies for combating polymicrobial biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1320345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak, N.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Roszak, M.; Bochentyn, B.; Piechowicz, L. Comparative Assessment of Bacteriophage and Antibiotic Activity Against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lu, H.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Q. Phages against Pathogenic Bacterial Biofilms and Biofilm-Based Infections: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grygiel, I.; Bajrak, O.; Wójcicki, M.; Krusiec, K.; Jończyk-Matysiak, E.; Górski, A.; Majewska, J.; Letkiewicz, S. Comprehensive Approaches to Combatting Acinetobacter baumannii Biofilms: From Biofilm Structure to Phage-Based Therapies. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukman, C.; Yonathan, C.; Magdalena, S.; Waturangi, D.E. Isolation and characterization of pathogenic Escherichia coli bacteriophages from chicken and beef offal. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbaraj, S.; Angappan, M.; Thomas, P.; Kumar, M.; Irungbam, K.; Verma, M.R.; Viswas, K.N.; Abhishek; Rawat, M.; Chaudhuri, P. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophage Ib_pec2 against shigatoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Basic Microbiol. 2023, 63, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, M.; Trotereau, A.; Culot, A.; Moodley, A.; Atterbury, R.; Wagemans, J.; Lavigne, R.; Velge, P.; Schouler, C. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Phage Collection Against Avian-Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e04296-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Mansilla, J.; Sánchez, P.; Silva-Valenzuela, C.A.; Molina-Quiroz, R.C. Isolation and characterization of novel lytic phages infecting multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01678-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artawinata, P.C.; Lorraine, S.; Waturangi, D.E. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages from soil against food spoilage and foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, P.; Tamhankar, A.J.; Lundborg, C.S.; Ramesh, N. Isolation, characterization and in vivo efficacy of Escherichia phage myPSH1131. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, S.B.; Green, S.I.; Liu, C.G.; Salazar, K.C.; Clark, J.R.; Terwilliger, A.L.; Kaplan, H.B.; Maresso, A.W.; Trautner, B.W.; Ramig, R.F. Constructing and characterizing bacteriophage libraries for phage therapy of human infections. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, P. Phages for phage therapy: Isolation, characterization, and host range breadth. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.; Ward, S.; Hyman, P. More is better: Selecting for broad host range bacteriophages. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, P.; Abedon, S.T. Bacteriophage host range and bacterial resistance. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 70, 217–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olawade, D.B.; Fapohunda, O.; Egbon, E.; Ebiesuwa, O.A.; Usman, S.O.; Faronbi, A.O.; Fidelis, S.C. Phage therapy: A targeted approach to overcoming antibiotic resistance. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 197, 107088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yehl, K.; Lemire, S.; Yang, A.C.; Ando, H.; Mimee, M.; Torres, M.T.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Lu, T.K. Engineering Phage Host-Range and Suppressing Bacterial Resistance Through Phage Tail Fiber Mutagenesis. Cell 2019, 179, 459–469.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.K.; Sistrom, M.; Wertz, J.E.; Kortright, K.E.; Narayan, D.; Turner, P.E. Phage selection restores antibiotic sensitivity in MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, J.J.; Gill, J.J. The habits of highly effective phages: Population dynamics as a framework for identifying therapeutic phages. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, H.M.; Son, H.M.; Honjoh, K.-i.; Miyamoto, T. Isolation and application of bacteriophages to reduce Salmonella contamination in raw chicken meat. LWT 2018, 91, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegini, Z.; Khoshbayan, A.; Taati Moghadam, M.; Farahani, I.; Jazireian, P.; Shariati, A. Bacteriophage therapy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: A review. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaki, S.; Omachi, T.; Kawai, Y.; Yamazaki, K. Characterization of a novel Morganella morganii bacteriophage FSP1 isolated from river water. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 359, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Y.; Ong, S.L.; Hu, J.Y.; Tan, X.L.; Ng, W.J. Effects of pH and temperature on the survival of coliphages MS2 and Qβ. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montso, P.K.; Mlambo, V.; Ateba, C.N. Efficacy of novel phages for control of multi-drug resistant Escherichia coli O177 on artificially contaminated beef and their potential to disrupt biofilm formation. Food Microbiol. 2021, 94, 103647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, R.; Lamas-Samanamud, G.R. Inhibition of biofilm formation by T7 bacteriophages producing quorum-quenching enzymes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5340–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.C.; Heckmann, E.R.; Green, S.I.; Clark, J.R.; Kaplan, H.B.; Ramig, R.F.; Hines-Munson, C.; Skelton, F.; Trautner, B.W.; Maresso, A.W. Development of Phage Cocktails to Treat E. coli Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection and Associated Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 796132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, S.; O’Grady, M.C.; Corcoran, D.; Finn, K.; Lucey, B. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Biofilm-Forming Capabilities Are Not Predictable from Clinical Details or from Colonial Morphology. Diseases 2020, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, W.K.; Welch, G.S.; Williams, A.C.; Damron, A.J.; Northcut, W.O.; Rumbaugh, K.P. Efficacy and safety of biofilm dispersal by glycoside hydrolases in wounds. Biofilm 2021, 3, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrie, S.J.; Samson, J.E.; Moineau, S. Bacteriophage resistance mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, O.I.; Brown, E.D. Phage-antibiotic combinations: A promising approach to constrain resistance evolution in bacteria. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1496, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanegas, D.; Abril-Novillo, A.; Khachatryan, A.; Jerves-Andrade, L.; Peñaherrera, E.; Cuzco, N.; Wilches, I.; Calle, J.; León-Tamariz, F. Validation of a method of broth microdilution for the determination of antibacterial activity of essential oils. BMC Res. Notes 2021, 14, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozahra, R.; Shlkamy, D.; Abdelhamid, S.M. Isolation and characterization of ΦEcM-vB1 bacteriophage targeting multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli. BMC Res. Notes 2025, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.; Menon, K.V.; Latha, C.; Sunil, B.; Sethulekshmi, C.; Jolly, D. Isolation of Listeria-specific bacteriophage from three different towns in Kerala, India. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 667–669. [Google Scholar]
- Svensson, U.; Christiansson, A. Methods for phage monitoring. Bull. Int. Dairy Fed. 1991, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Salifu, S.P.; Casey, S.C.; Foley, S. Isolation and characterization of soilborne virulent bacteriophages infecting the pathogen Rhodococcus equi. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, D.; Yang, S.; Almeida, A.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, L.; Wang, D. Bacteriophage potential against Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilms. Food Control 2019, 98, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadas, H.; Einav, M.; Fishov, I.; Zaritsky, A. Bacteriophage T4 development depends on the physiology of its host Escherichia coli. Microbiology 1997, 143 Pt 1, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, F.; Sun, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, W.; Zou, L.; Pan, Q.; Ren, H. Isolation and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage vB_SauS_SA2. AIMS Microbiol. 2019, 5, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprouffske, K.; Wagner, A. Growthcurver: An R package for obtaining interpretable metrics from microbial growth curves. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sada, T.S.; Tessema, T.S. Isolation and characterization of lytic bacteriophages from various sources in Addis Ababa against antimicrobial-resistant diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains and evaluation of their therapeutic potential. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, S.; Dong, Y.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages against virulent Aeromonas hydrophila. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerkan, G.; Witsø, E.; Bergh, K. Sonication is superior to scraping for retrieval of bacteria in biofilm on titanium and steel surfaces in vitro. Acta Orthop. 2009, 80, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.H.; Yang, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, S.C. PhageScope: A well-annotated bacteriophage database with automatic analyses and visualizations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 52, D756–D761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraru, C.; Varsani, A.; Kropinski, A.M. VIRIDIC—A novel tool to calculate the intergenomic similarities of prokaryote-infecting viruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohwer, F.; Edwards, R. The Phage Proteomic Tree: A genome-based taxonomy for phage. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 4529–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
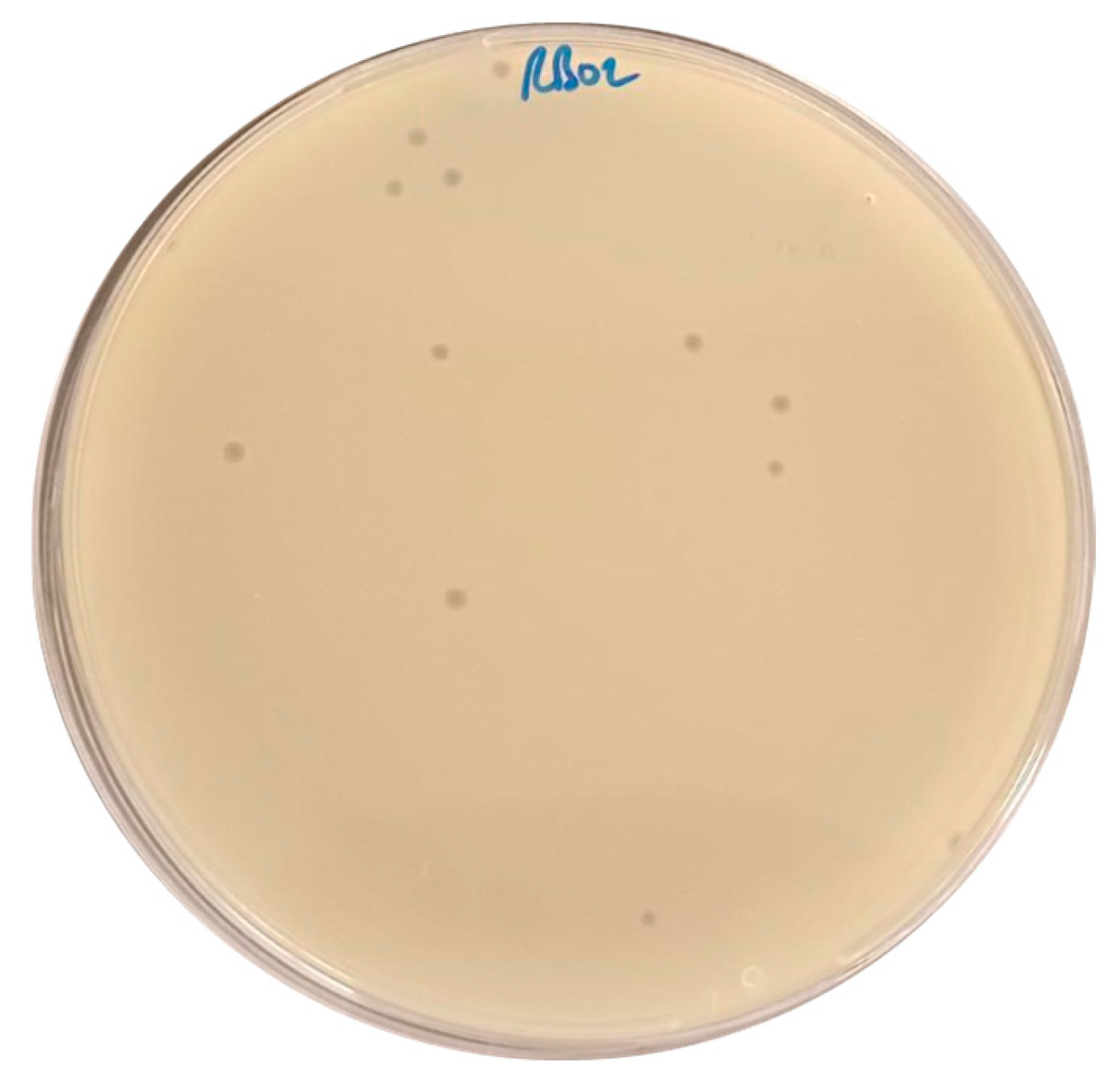
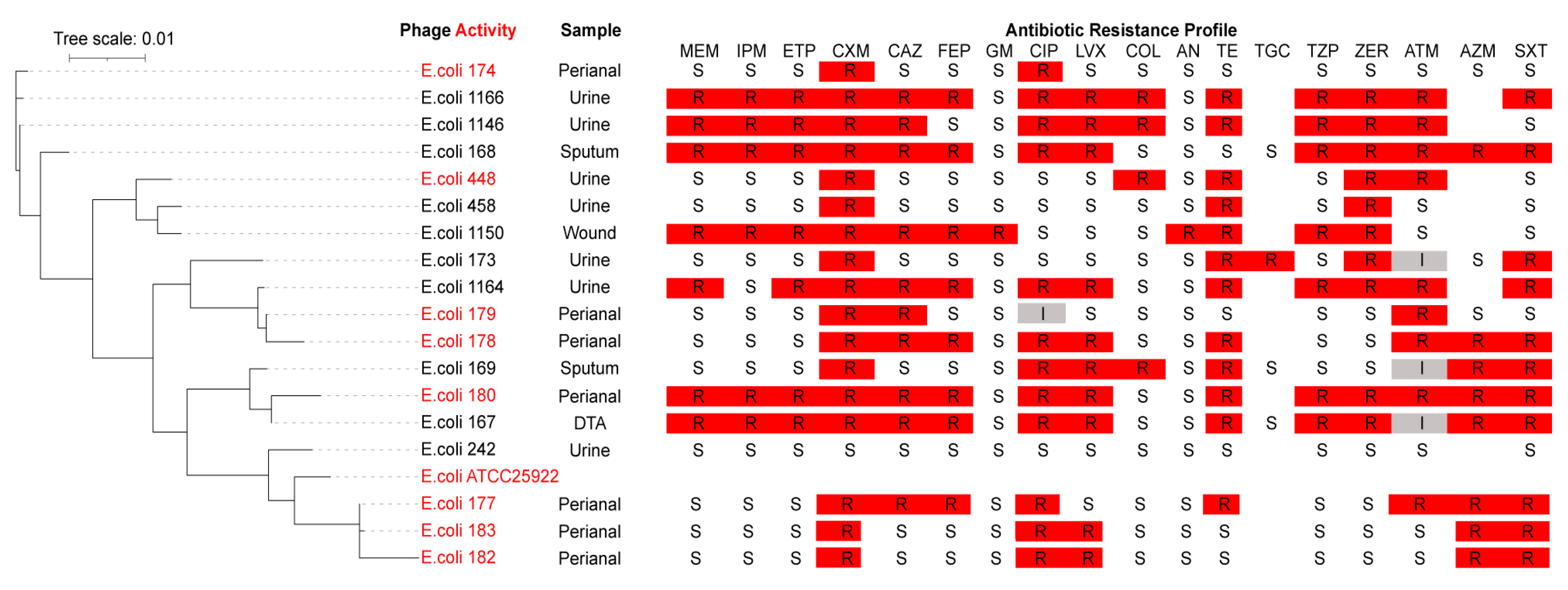
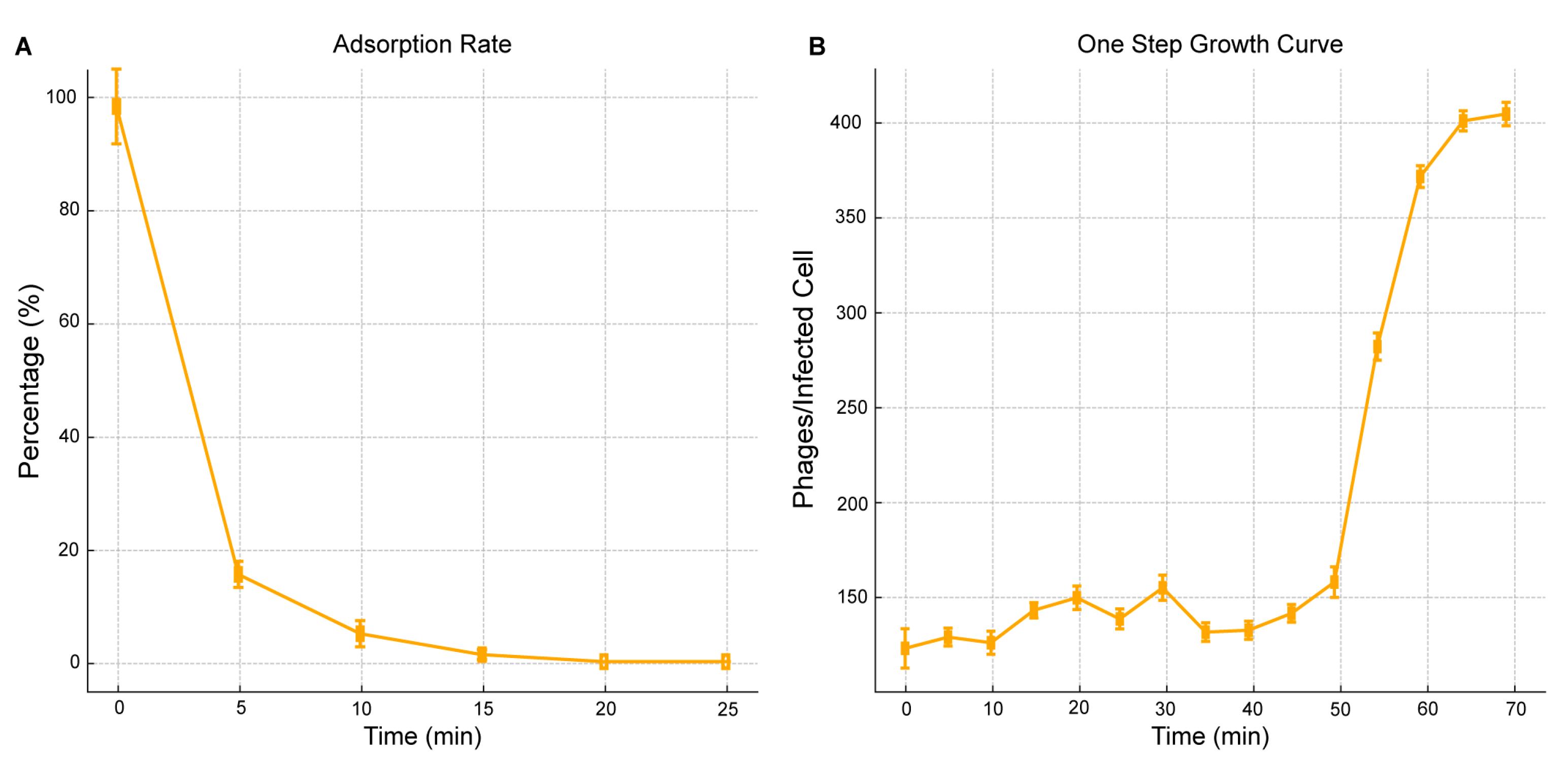
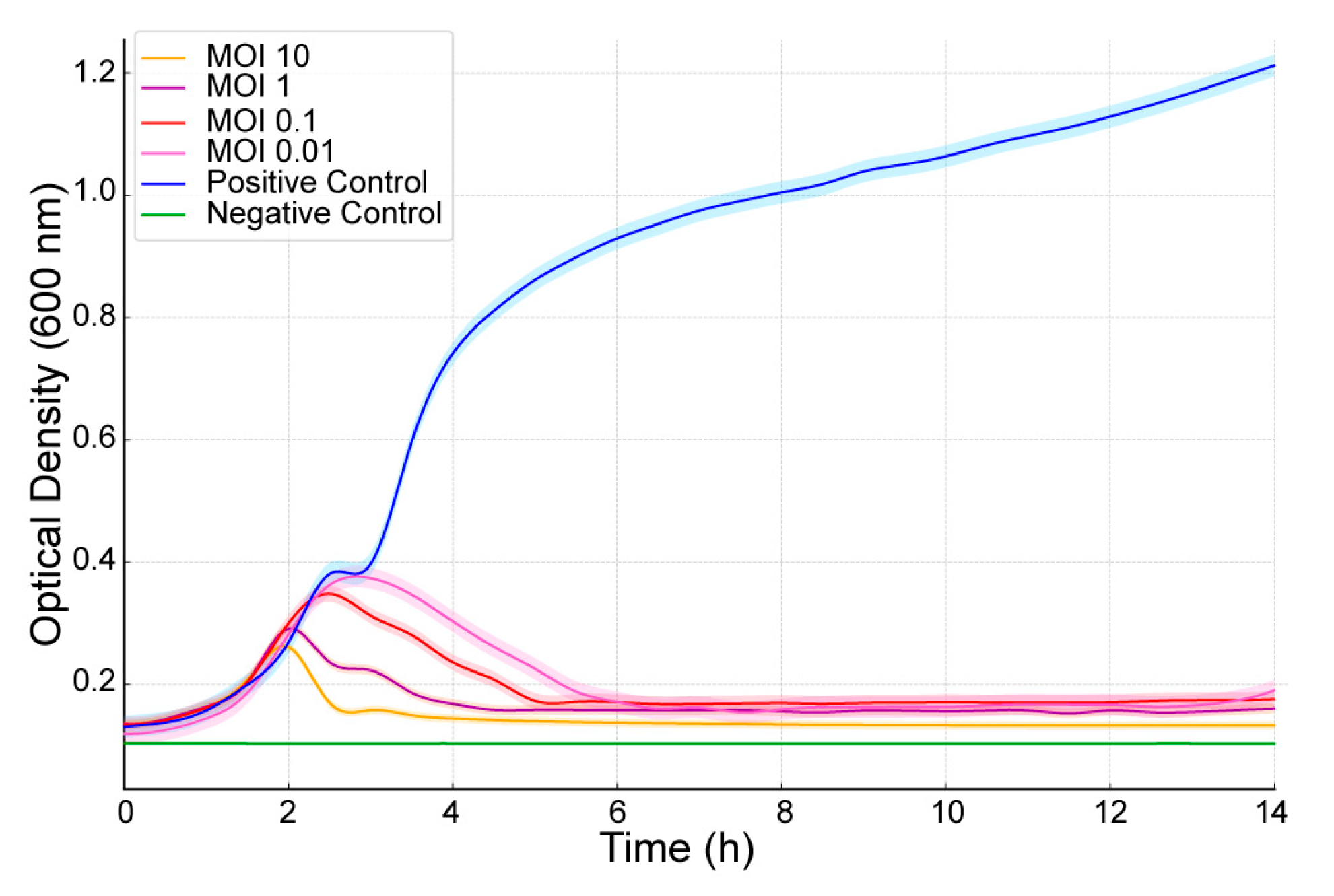
| E. coli Clinical Strain | AUBRB02 EOP |
|---|---|
| 174 | Avirulent but active (0.000001) |
| 1166 | - |
| 1146 | - |
| 168 | - |
| 448 | High (1) |
| 458 | - |
| 1150 | - |
| 173 | - |
| 1164 | - |
| 179 | Avirulent but active (0.000001) |
| 178 | Avirulent but active (0.00001) |
| 169 | - |
| 180 | Avirulent but active (0.0000001) |
| 167 | - |
| 242 | - |
| 177 | Slight (0.002) |
| 183 | Avirulent but active (0.0001) |
| 182 | Avirulent but active (0.0001) |
| Bacterial Strain | Source and Other Characteristics |
|---|---|
| E. coli Laboratory Strains | |
| ATCC® 25922™ | Serotype 06, Biotype 01 |
| E. coli Clinical Strains | |
| 1146 | Urine |
| 1150 | Wound |
| 1164 | Urine |
| 1166 | Urine |
| 242 | Urine |
| 448 | Urine |
| 458 | Urine |
| 167 | DTA |
| 168 | Sputum |
| 169 | Sputum |
| 173 | Urine |
| 174 | Perianal |
| 177 | Perianal |
| 178 | Perianal |
| 179 | Perianal |
| 180 | Perianal |
| 182 | Perianal |
| 183 | Perianal |
| 1146 | Urine |
| S. infantis | |
| 122,131 | Stool |
| P. aeruginosa | |
| 44 | Urine |
| A. baumannii | |
| 1 | Sputum |
| K. pneumoniae | |
| 12 | Urine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdo Ahmad, T.A.; El Houjeiry, S.A.; Abou Fayad, A.; Kanj, S.S.; Matar, G.M.; Saba, E.S. Isolation and Genomic Analysis of Escherichia coli Phage AUBRB02: Implications for Phage Therapy in Lebanon. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050458
Abdo Ahmad TA, El Houjeiry SA, Abou Fayad A, Kanj SS, Matar GM, Saba ES. Isolation and Genomic Analysis of Escherichia coli Phage AUBRB02: Implications for Phage Therapy in Lebanon. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(5):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050458
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdo Ahmad, Tasnime A., Samar A. El Houjeiry, Antoine Abou Fayad, Souha S. Kanj, Ghassan M. Matar, and Esber S. Saba. 2025. "Isolation and Genomic Analysis of Escherichia coli Phage AUBRB02: Implications for Phage Therapy in Lebanon" Antibiotics 14, no. 5: 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050458
APA StyleAbdo Ahmad, T. A., El Houjeiry, S. A., Abou Fayad, A., Kanj, S. S., Matar, G. M., & Saba, E. S. (2025). Isolation and Genomic Analysis of Escherichia coli Phage AUBRB02: Implications for Phage Therapy in Lebanon. Antibiotics, 14(5), 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050458







