Whole-Genome Analysis of Escherichia coli from One Health Sources: Evaluating Genetic Relatedness and Antimicrobial Resistance Carriage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequencing
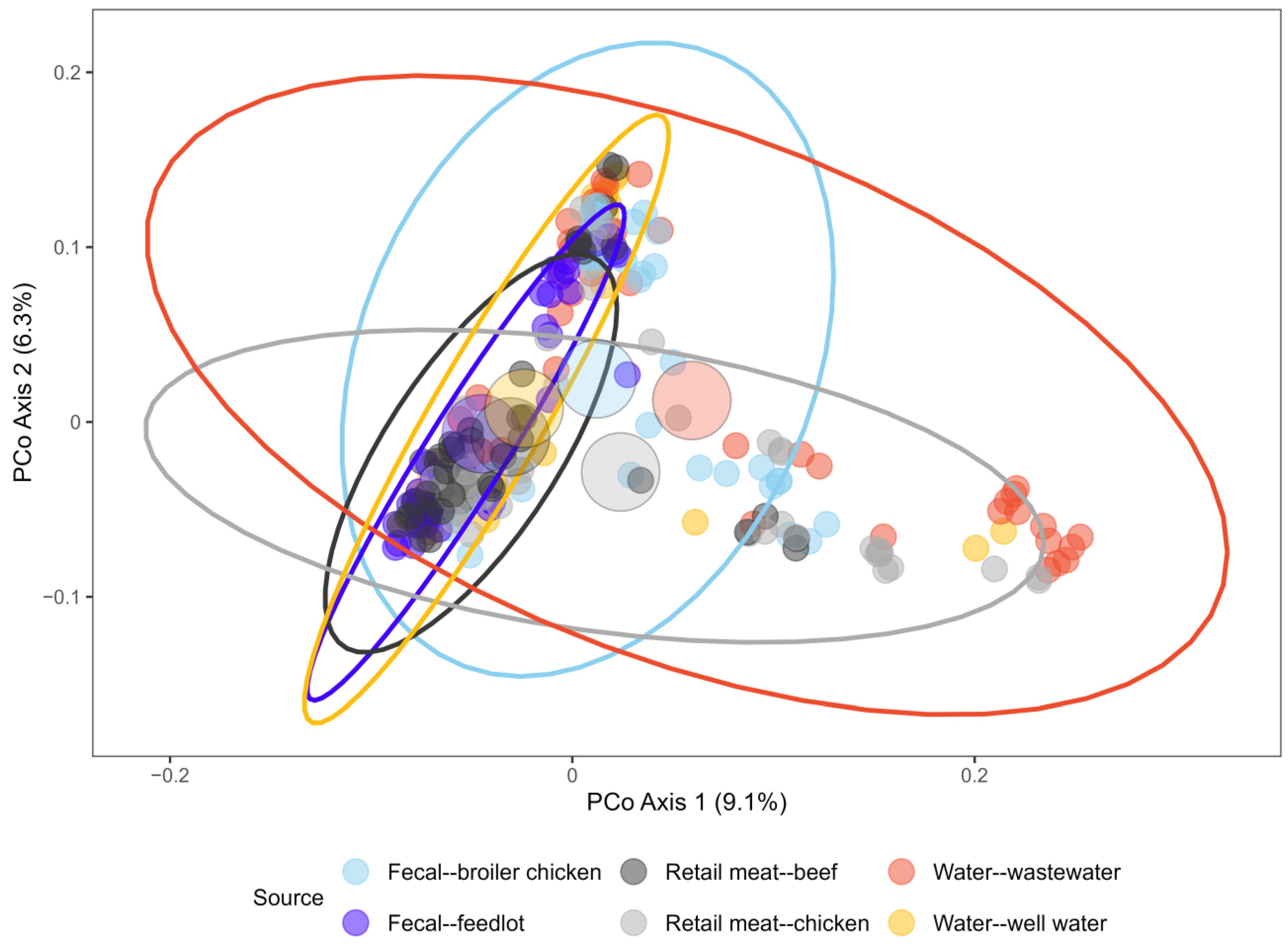
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
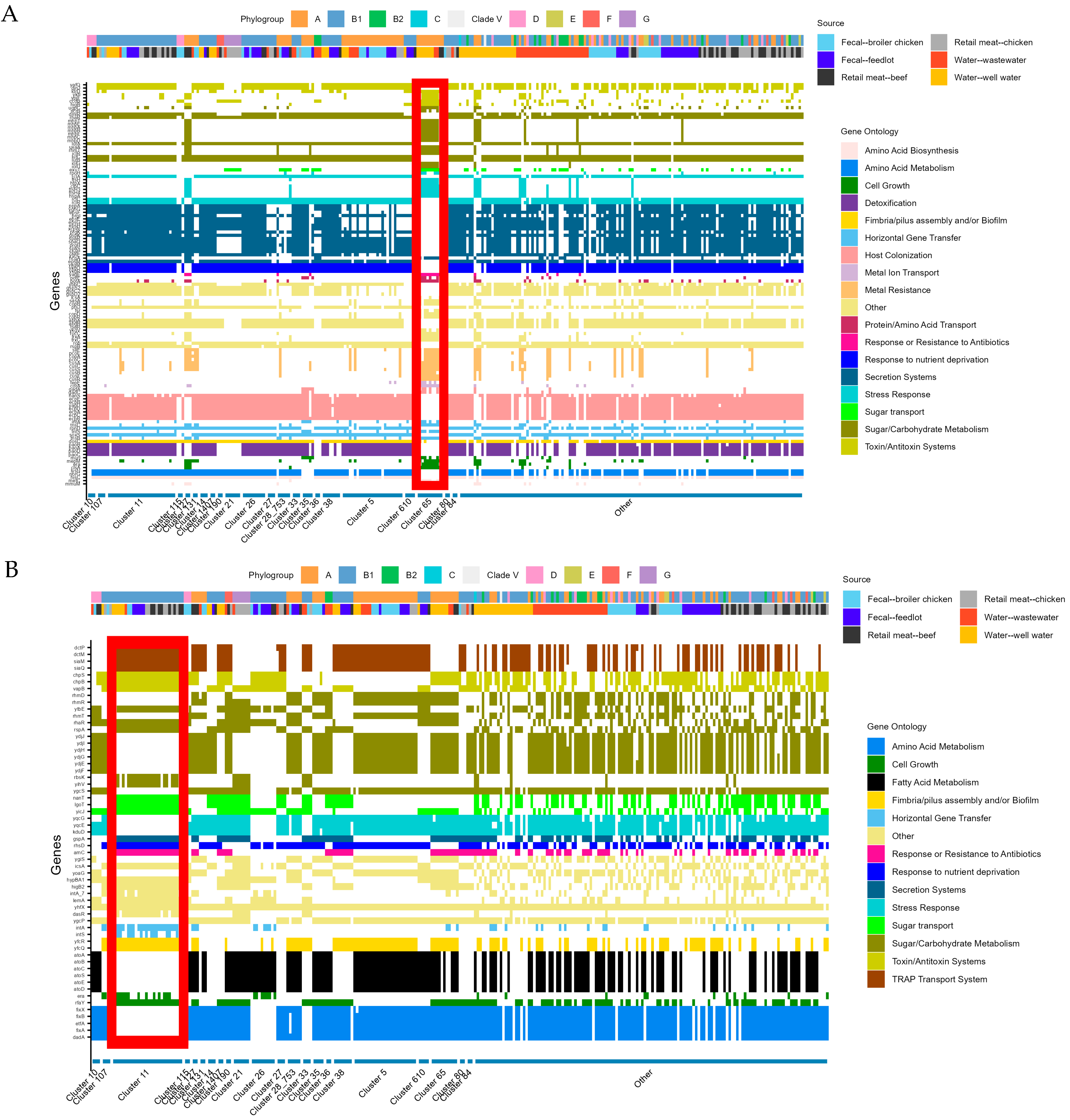
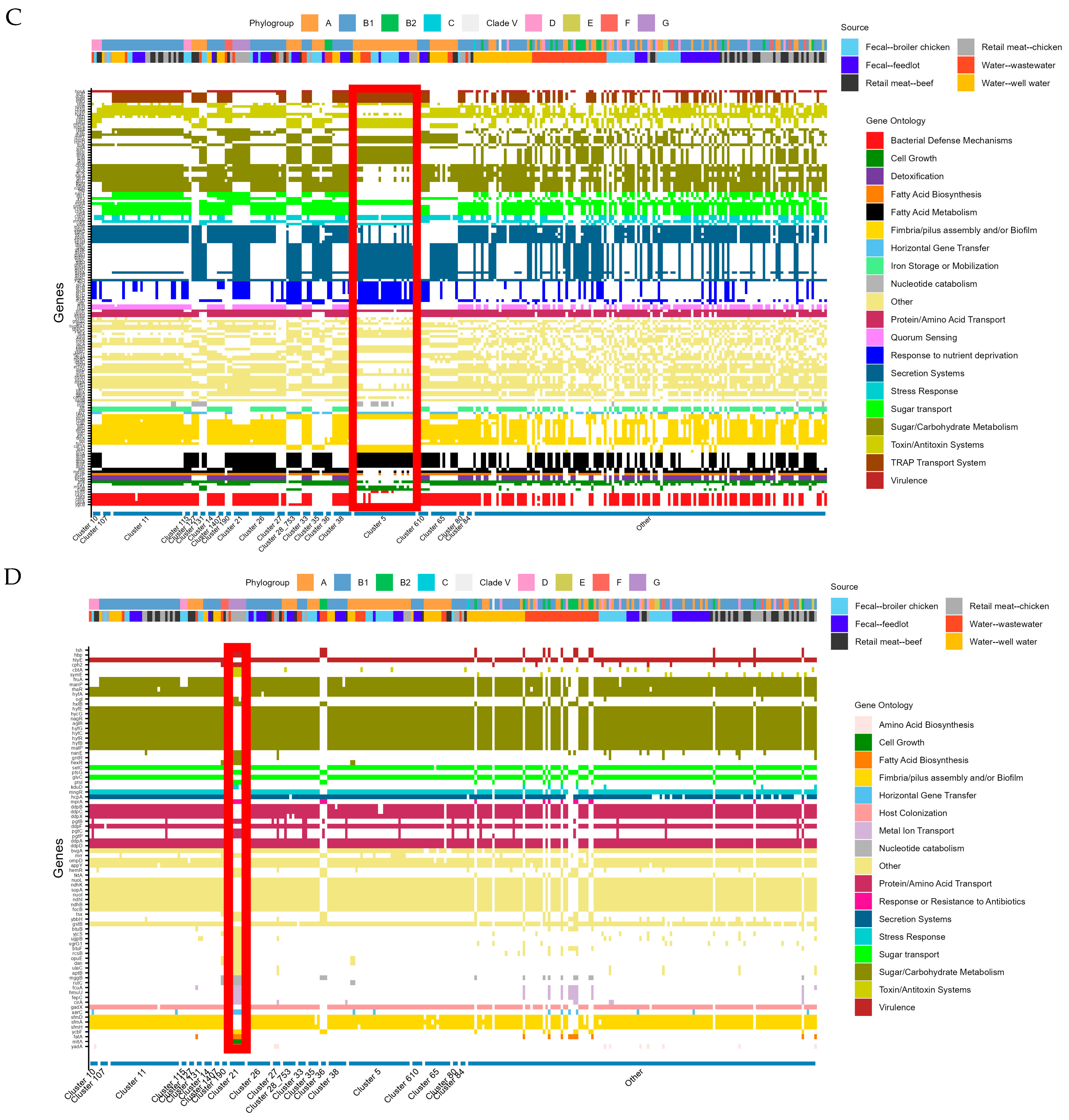
2.3. Gene Presence/Absence by Source
2.4. Cluster Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Bacterial Isolation, Identification, and Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Whole Genome Sequencing
4.4. Bioinformatics
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| APEC | Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli |
| CIPARS | Canadian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| EMB | Eosin-methylene blue |
| ExPEC | Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli |
| LB | Luria–Bertani |
| Mb | Megabasepairs (1,000,000 base pairs) |
| NARMS | National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring Systems (USA) |
| NML | National Microbiology Lab |
| PCoA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational analysis of variance |
| ST | Sequence type |
| TSB | Tryptic soy broth |
References
- World Health Organization. Call to Action on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.W.; Cha, C.J. Antibiotic resistome from the One-Health perspective: Understanding and controlling antimicrobial resistance transmission. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Meza, M.E.; Galarde-Lopez, M.; Carrillo-Quiroz, B.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.M. Antimicrobial resistance: One Health approach. Vet. World 2022, 15, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, H.; Spinner, K.; Crump, L.; Kuenzli, E.; Schuepbach, G.; Zinsstag, J. State of Knowledge on the Acquisition, Diversity, Interspecies Attribution and Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance between Humans, Animals and the Environment: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geurtsen, J.; de Been, M.; Weerdenburg, E.; Zomer, A.; McNally, A.; Poolman, J. Genomics and pathotypes of the many faces of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 46, fuac031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denamur, E.; Clermont, O.; Bonacorsi, S.; Gordon, D. The population genetics of pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, B.; Fekete, P.Z. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in veterinary medicine. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 295, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Hur, H.G.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Byappanahalli, M.N.; Yan, T.; Ishii, S. Environmental Escherichia coli: Ecology and public health implications-a review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.; Ksoll, W.B.; Hicks, R.E.; Sadowsky, M.J. Presence and growth of naturalized Escherichia coli in temperate soils from Lake Superior watersheds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devane, M.L.; Moriarty, E.; Weaver, L.; Cookson, A.; Gilpin, B. Fecal indicator bacteria from environmental sources; strategies for identification to improve water quality monitoring. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludden, C.; Raven, K.E.; Jamrozy, D.; Gouliouris, T.; Blane, B.; Coll, F.; de Goffau, M.; Naydenova, P.; Horner, C.; Hernandez-Garcia, J.; et al. One Health Genomic Surveillance of Escherichia coli Demonstrates Distinct Lineages and Mobile Genetic Elements in Isolates from Humans versus Livestock. mBio 2019, 10, e02693-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adator, E.H.; Narvaez-Bravo, C.; Zaheer, R.; Cook, S.R.; Tymensen, L.; Hannon, S.J.; Booker, C.W.; Church, D.; Read, R.R.; McAllister, T.A. A One Health Comparative Assessment of Antimicrobial Resistance in Generic and Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporin-Resistant Escherichia coli from Beef Production, Sewage and Clinical Settings. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, S.; Banting, G.; Stothard, P.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Checkley, S.; Meyer, K.; Otto, S.; Neumann, N.F. Evidence for the evolution, clonal expansion and global dissemination of water treatment-resistant naturalized strains of Escherichia coli in wastewater. Water Res. 2019, 156, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Stothard, P.; Neumann, N.F. Emergence of potentially disinfection-resistant, naturalized Escherichia coli populations across food- and water-associated engineered environments. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Tran, F.; Zhang, P.; Wang, H. Genomic and Phenotypic Analysis of Heat and Sanitizer Resistance in Escherichia coli from Beef in Relation to the Locus of Heat Resistance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0157421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymensen, L.D.; Pyrdok, F.; Coles, D.; Koning, W.; McAllister, T.A.; Jokinen, C.C.; Dowd, S.E.; Neumann, N.F. Comparative accessory gene fingerprinting of surface water Escherichia coli reveals genetically diverse naturalized population. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Walk, S.T.; Gordon, D.M.; Feldgarden, M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Genome sequencing of environmental Escherichia coli expands understanding of the ecology and speciation of the model bacterial species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7200–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenaillon, O.; Skurnik, D.; Picard, B.; Denamur, E. The population genetics of commensal Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, S.; Diancourt, L.; Laouenan, C.; Vigan, M.; Caro, V.; Arlet, G.; Drieux, L.; Leflon-Guibout, V.; Mentre, F.; Jarlier, V.; et al. Phylogenetic distribution of CTX-M- and non-extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli isolates: Group B2 isolates, except clone ST131, rarely produce CTX-M enzymes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2974–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchon, M.; Perrin, A.; de Sousa, J.A.M.; Vangchhia, B.; Burn, S.; O’Brien, C.L.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.; Rocha, E.P. Phylogenetic background and habitat drive the genetic diversification of Escherichia coli. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.F.; Mohamed, K.; Fan, Y.; Agama Study, G.; Achtman, M. The EnteroBase user’s guide, with case studies on Salmonella transmissions, Yersinia pestis phylogeny, and Escherichia core genomic diversity. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loayza, F.; Graham, J.P.; Trueba, G. Factors Obscuring the Role of E. coli from Domestic Animals in the Global Antimicrobial Resistance Crisis: An Evidence-Based Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, E.P.C. Neutral Theory, Microbial Practice: Challenges in Bacterial Population Genetics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathayat, D.; Lokesh, D.; Ranjit, S.; Rajashekara, G. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC): An Overview of Virulence and Pathogenesis Factors, Zoonotic Potential, and Control Strategies. Pathogens 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, J.A.; Harris, S.R.; Tonkin-Hill, G.; Gladstone, R.A.; Lo, S.W.; Weiser, J.N.; Corander, J.; Bentley, S.D.; Croucher, N.J. Fast and flexible bacterial genomic epidemiology with PopPUNK. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muloi, D.M.; Wee, B.A.; McClean, D.M.H.; Ward, M.J.; Pankhurst, L.; Phan, H.; Ivens, A.C.; Kivali, V.; Kiyong’a, A.; Ndinda, C.; et al. Population genomics of Escherichia coli in livestock-keeping households across a rapidly developing urban landscape. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Johansson, M.H.K.; Munk, P.; Malorny, B.; Skarzynska, M.; Wadepohl, K.; Moyano, G.; Hesp, A.; Veldman, K.T.; Bossers, A.; et al. Genomic evolution of antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.A.-O.; Chau, K.A.-O.X.; Kavanagh, J.A.-O.; AbuOun, M.A.-O.; Stubberfield, E.A.-O.; Gweon, H.A.-O.; Barker, L.; Rodger, G.A.-O.; Bowes, M.A.-O.; Hubbard, A.T.M.; et al. Niche and local geography shape the pangenome of wastewater- and livestock-associated Enterobacteriaceae. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, 2375–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, D.; Bervoets, I. Regulation of arginine biosynthesis, catabolism and transport in Escherichia coli. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 1103–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.N.; Anderson, M.T.; Bachman, M.A.; Mobley, H.L.T. The ArcAB Two-component system Function in metabolism redox control and infection. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2022, 86, e0011021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, M.V.; Mihailovskaya, V.S.; Remezovskaya, N.B.; Starcic Erjavec, M. Bacteriocin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from the Gastrointestinal Tract of Farm Animals: Prevalence, Molecular Characterization and Potential for Application. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Paramo, P.; Le Menac’h, A.; Le Gall, T.; Amorin, C.; Gouriou, S.; Picard, B.; Skurnik, D.; Denamur, E. Identification of forces shaping the commensal Escherichia coli genetic structure by comparing animal and human isolates. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, P.; Dhakal, S.; Dozois, C.M. The Diversity of Escherichia coli Pathotypes and Vaccination Strategies against This Versatile Bacterial Pathogen. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stromberg, Z.R.; Johnson, J.R.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Kilbourne, J.; Van Goor, A.; Curtiss, R.R.; Mellata, M. Evaluation of Escherichia coli isolates from healthy chickens to determine their potential risk to poultry and human health. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, M.M.; Thakur, S.; Almeida, R.N.D.; Wang, P.W.; Weir, B.S.; Guttman, D.S. Recombination of ecologically and evolutionarily significant loci maintains genetic cohesion in the Pseudomonas syringae species complex. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidenberg, A.B.S.; Edslev, S.M.; Hallstrøm, S.; Rasmussen, A.; Park, D.E.; Aziz, M.; Dos Santos Queiroz, B.; Baptista, A.A.S.; Barbosa, F.; Rocha, V.G.P.; et al. Escherichia coli ST117: Exploring the zoonotic hypothesis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0046624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Jiang, M.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhuge, X.; Dai, J. Complete genomic analysis of ST117 lineage extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) to reveal multiple genetic determinants to drive its global transmission: ST117 E. coli as an emerging multidrug-resistant foodborne ExPEC with zoonotic potential. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 3256–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Ma, P.P.; Liu, W.S.; Liang, X.; Li, X.Y.; Li, Y.Z.; Liu, B.T. Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance Characteristics of Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli among Healthy Chickens from Farms and Live Poultry Markets in China. Animals 2021, 11, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delago, J.; Miller, E.A.; Flores-Figueroa, C.; Munoz-Aguayo, J.; Cardona, C.; Smith, A.H.; Johnson, T.J. Survey of clinical and commensal Escherichia coli from commercial broilers and turkeys, with emphasis on high-risk clones using APECTyper. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Rehman, M.A.; Yin, X.; Carrillo, C.D.; Wang, Q.I.; Yang, C.; Gong, J.; Diarra, M.S. Antimicrobial Resistance Phenotypes and Genotypes of Escherichia coli Isolates from Broiler Chickens Fed Encapsulated Cinnamaldehyde and Citral. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, S.; Li, Q.; Yasui, Y.; Edge, T.; Topp, E.; Neumann, N.F. Assessing host-specificity of Escherichia coli using a supervised learning logic-regression-based analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms in intergenic regions. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 92, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Banting, G.; Neumann, N.F. A review of the taxonomy, genetics, and biology of the genus Escherichia and the type species Escherichia coli. Can. J. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 553–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Vargas, G.; Bergsveinson, J.; Lawrence, J.R.; Korber, D.R. Environmental Biofilms as Reservoirs for Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 766242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthe, T.; Ratajczak, M.; Clermont, O.; Denamur, E.; Petit, F. Evidence for coexistence of distinct Escherichia coli populations in various aquatic environments and their survival in estuary water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4684–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skurnik, D.; Clermont, O.; Guillard, T.; Launay, A.; Danilchanka, O.; Pons, S.; Diancourt, L.; Lebreton, F.; Kadlec, K.; Roux, D.; et al. Emergence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Escherichia coli of Animal Origin Spreading in Humans. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 898–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Walk, S.T.; Alm, E.W.; Calhoun, L.M.; Mladonicky, J.M.; Whittam, T.S. Genetic diversity and population structure of Escherichia coli isolated from freshwater beaches. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2274–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropea, E.; Hynds, P.; McDermott, K.; Brown, R.S.; Majury, A. Environmental adaptation of E. coli within private groundwater sources in southeastern Ontario: Implications for groundwater quality monitoring and human health. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cookson, A.L.; Devane, M.; Marshall, J.C.; Moinet, M.; Gardner, A.; Collis, R.M.; Rogers, L.; Biggs, P.J.; Pita, A.B.; Cornelius, A.J.; et al. Population structure and pathogen interaction of Escherichia coli in freshwater: Implications of land-use for water quality and public health in Aotearoa New Zealand. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2024, 16, e13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monday, S.R.; Whittam, T.S.; Feng, P.C. Genetic and evolutionary analysis of mutations in the gusA gene that cause the absence of beta-glucuronidase activity in Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C. The Spatiotemporal Occurrence and Recovery of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) in Well-Sourced Drinking Water from Southern Alberta, Canada. Master’s Thesis, Uniersity of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Butters, A.; Jovel, J.; Gow, S.; Liljebjelke, K.; Waldner, C.; Checkley, S.L. PmrB Y358N, E123D amino acid substitutions are not associated with colistin resistance but with phylogeny in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0053224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, T.J.; Scriver, L.; Lam, L.; Duong, M.; Peirano, G.; Lynch, T.; Dong, T.; Pitout, J.D.D.; DeVinney, R. A Comprehensive Account of Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131 in Wastewater Reveals an Abundance of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Clade A Strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01913-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Government of Canada. Canadian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (CIPARS) 2018: Design and Methods; Government of Canada: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2020.
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; CLSI supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; Posit Software, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Aronesty, E. ea-utils: “Command-Line Tools for Processing Biological Sequencing Data”. 2011. Available online: https://github.com/ExpressionAnalysis/ea-utils (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes De Novo Assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikheenko, A.; Prjibelski, A.; Saveliev, V.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A. Versatile genome assembly evaluation with QUAST-LG. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i142–i150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C. BIGSdb: Scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghain, J.; Bridier-Nahmias, A.; Le Nagard, H.; Denamur, E.; Clermont, O. ClermonTyping: An easy-to-use and accurate in silico method for Escherichia genus strain phylotyping. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin-Hill, G.; MacAlasdair, N.; Ruis, C.; Weimann, A.; Horesh, G.; Lees, J.A.; Gladstone, R.A.; Lo, S.; Beaudoin, C.; Floto, R.A.; et al. Producing polished prokaryotic pangenomes with the Panaroo pipeline. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, C.; Pires, M.M.; Stoppe, N.C.; Hachich, E.M.; Sato, M.I.; Gomes, T.A.; Amaral, L.A.; Ottoboni, L.M. Escherichia coli phylogenetic group determination and its application in the identification of the major animal source of fecal contamination. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez, R.L.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zankari, E.; Allesoe, R.; Joensen, K.G.; Cavaco, L.M.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. PointFinder: A novel web tool for WGS-based detection of antimicrobial resistance associated with chromosomal point mutations in bacterial pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snipen, L.; Liland, K.H. micropan: Microbial Pan-Genome Analysis, Version 2.1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=micropan (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Szoecs, E.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package, Version 2.6-4; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brynildsrud, O.; Bohlin, J.; Scheffer, L.; Eldholm, V. Rapid scoring of genes in microbial pan-genome-wide association studies with Scoary. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Source | Sequence Types | Number of Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| Broiler chicken fecal | 10 | 6 |
| 189 | 3 | |
| 720 | 3 | |
| 752 | 3 | |
| 155 | 2 | |
| 2705 | 2 | |
| 328 | 2 | |
| 40 | 2 | |
| Singletons | 25 | |
| Feedlot cattle fecal | 10 | 7 |
| 1080 | 3 | |
| 10,895 | 3 | |
| 6488 | 3 | |
| - | 2 | |
| 155 | 2 | |
| 20 | 2 | |
| 278 | 2 | |
| 336 | 2 | |
| 58 | 2 | |
| 6617 | 2 | |
| Singletons | 18 | |
| Retail chicken meat | 117 | 6 |
| 58 | 4 | |
| 10 | 3 | |
| 295 | 3 | |
| - | 2 | |
| 101 | 2 | |
| 602 | 2 | |
| 648 | 2 | |
| Singletons | 24 | |
| Retail beef | 58 | 4 |
| 109 | 3 | |
| 155 | 3 | |
| 607 | 3 | |
| 10 | 2 | |
| 399 | 2 | |
| 56 | 2 | |
| 847 | 2 | |
| Singletons | 26 | |
| Wastewater | - | 4 |
| 10 | 3 | |
| 998 | 3 | |
| Singletons | 38 | |
| Well water | 399 | 6 |
| 1086 | 3 | |
| 58 | 3 | |
| 10 | 2 | |
| 442 | 2 | |
| 635 | 2 | |
| Singletons | 30 |
| Cluster | Number of Isolates | Sources (n) | Phylo-Group | Sequence Types (n) | AMR Strata (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster 65 | 12 | Water—well water (8) | A | 399 (9) | Pan susceptible (11) |
| Water—Wastewater (2) | 635 (3) | Resistant to 1 or 2 classes (1) | |||
| Retail meat—beef (2) | |||||
| Cluster 11 | 28 | Water—well water (5) | 58 (13) | Pan susceptible (8) | |
| Water—wastewater (1) | B1 | 155 (10) | Resistant to 1 or 2 classes (7) | ||
| Fecal—broiler chicken (2) | 616 (1) | Resistant to 3 or more classes (13) | |||
| Fecal—feedlot cattle (5) | 683 (1) | ||||
| Retail meat—chicken (7) | 5565 (1) | ||||
| Retail meat—beef (8) | Not typed (2) | ||||
| Cluster 5 | 25 | Water—well water (3) | A | 10 (14) | Pan susceptible (7) |
| Water—wastewater (4) | 43 (2) | Resistant to 1 or 2 classes (11) | |||
| Fecal—broiler chicken (10) | 744 (1) | Resistant to 3 or more classes (7) | |||
| Fecal—feedlot (5) | 752 (3) | ||||
| Retail meat—chicken (3) | 1141 (1) | ||||
| 5265 (1) | |||||
| 6617 (2) | |||||
| Not typed (1) | |||||
| Cluster 21 | 7 | Water—wastewater (1) | G | 117 (7) | Pan susceptible (2) |
| Retail meat—chicken (6) | Resistant to 1 or 2 classes (2) | ||||
| Resistant to 3 or more classes (3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Butters, A.; Jovel, J.; Gow, S.; Waldner, C.; Checkley, S.L. Whole-Genome Analysis of Escherichia coli from One Health Sources: Evaluating Genetic Relatedness and Antimicrobial Resistance Carriage. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111151
Butters A, Jovel J, Gow S, Waldner C, Checkley SL. Whole-Genome Analysis of Escherichia coli from One Health Sources: Evaluating Genetic Relatedness and Antimicrobial Resistance Carriage. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(11):1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111151
Chicago/Turabian StyleButters, Alyssa, Juan Jovel, Sheryl Gow, Cheryl Waldner, and Sylvia L. Checkley. 2025. "Whole-Genome Analysis of Escherichia coli from One Health Sources: Evaluating Genetic Relatedness and Antimicrobial Resistance Carriage" Antibiotics 14, no. 11: 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111151
APA StyleButters, A., Jovel, J., Gow, S., Waldner, C., & Checkley, S. L. (2025). Whole-Genome Analysis of Escherichia coli from One Health Sources: Evaluating Genetic Relatedness and Antimicrobial Resistance Carriage. Antibiotics, 14(11), 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111151






