Widespread Distribution of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella spp. in Clinical and Environmental Settings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sample Collection, Detection Rates, and Species Identification
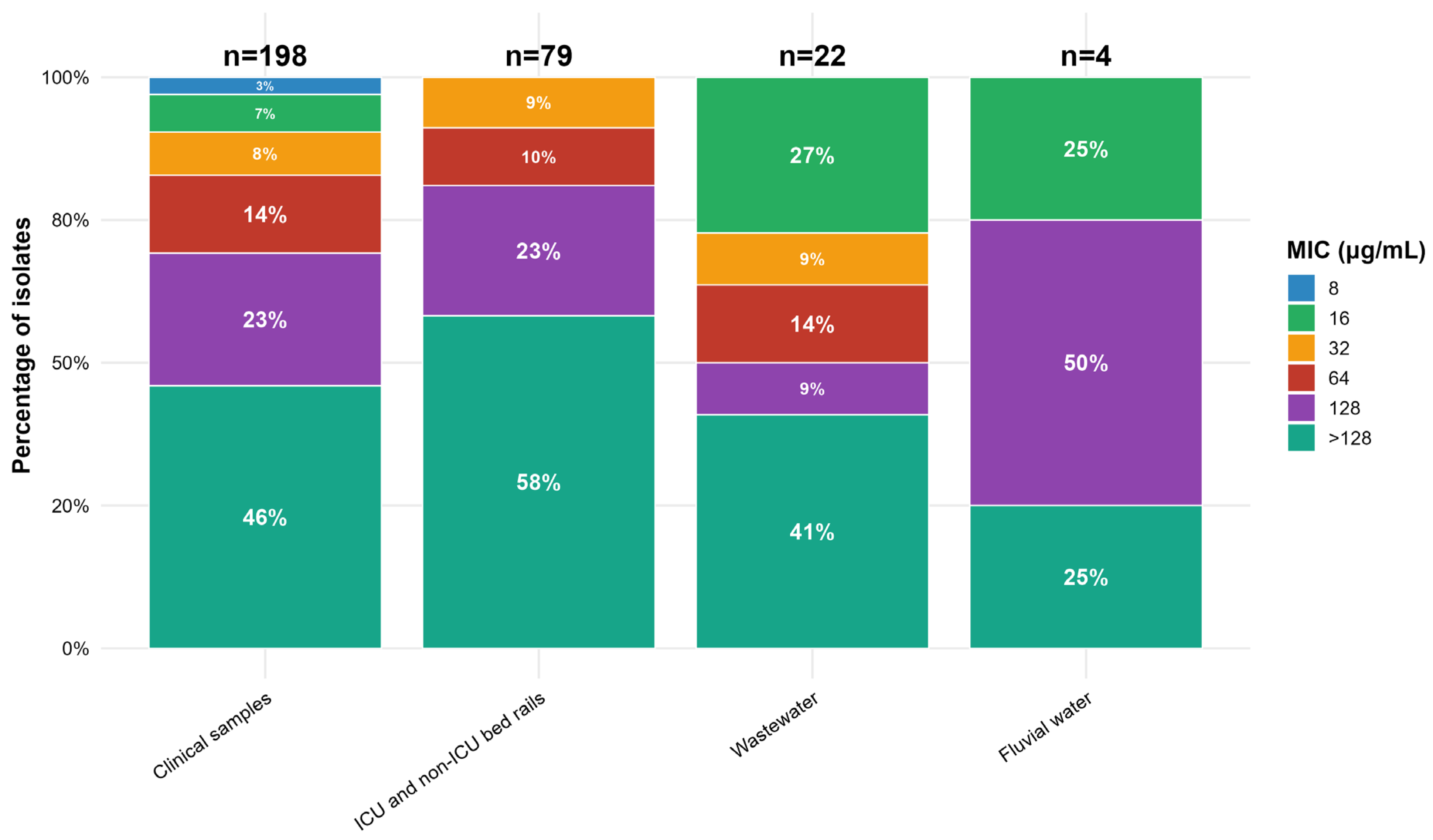
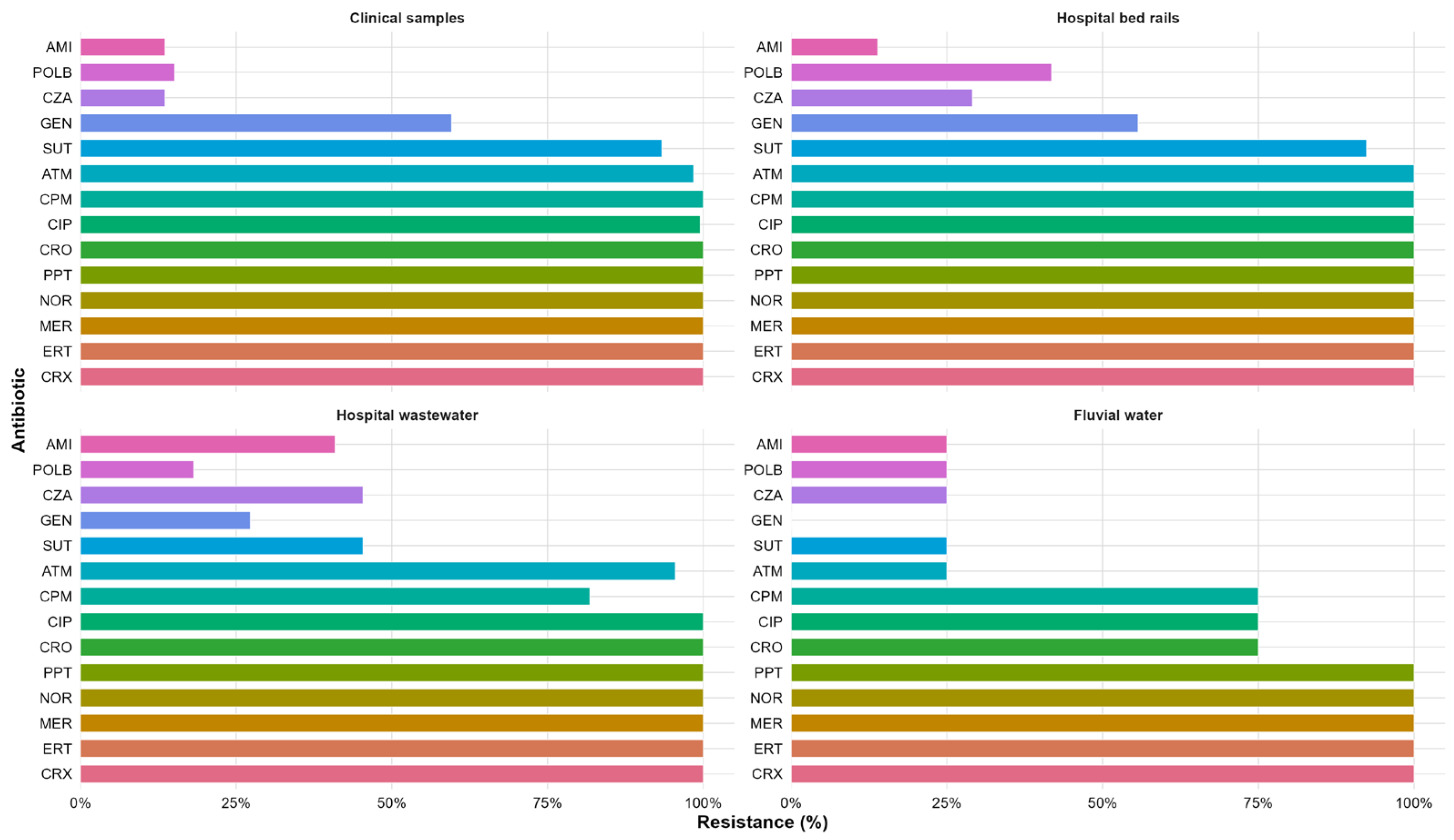
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
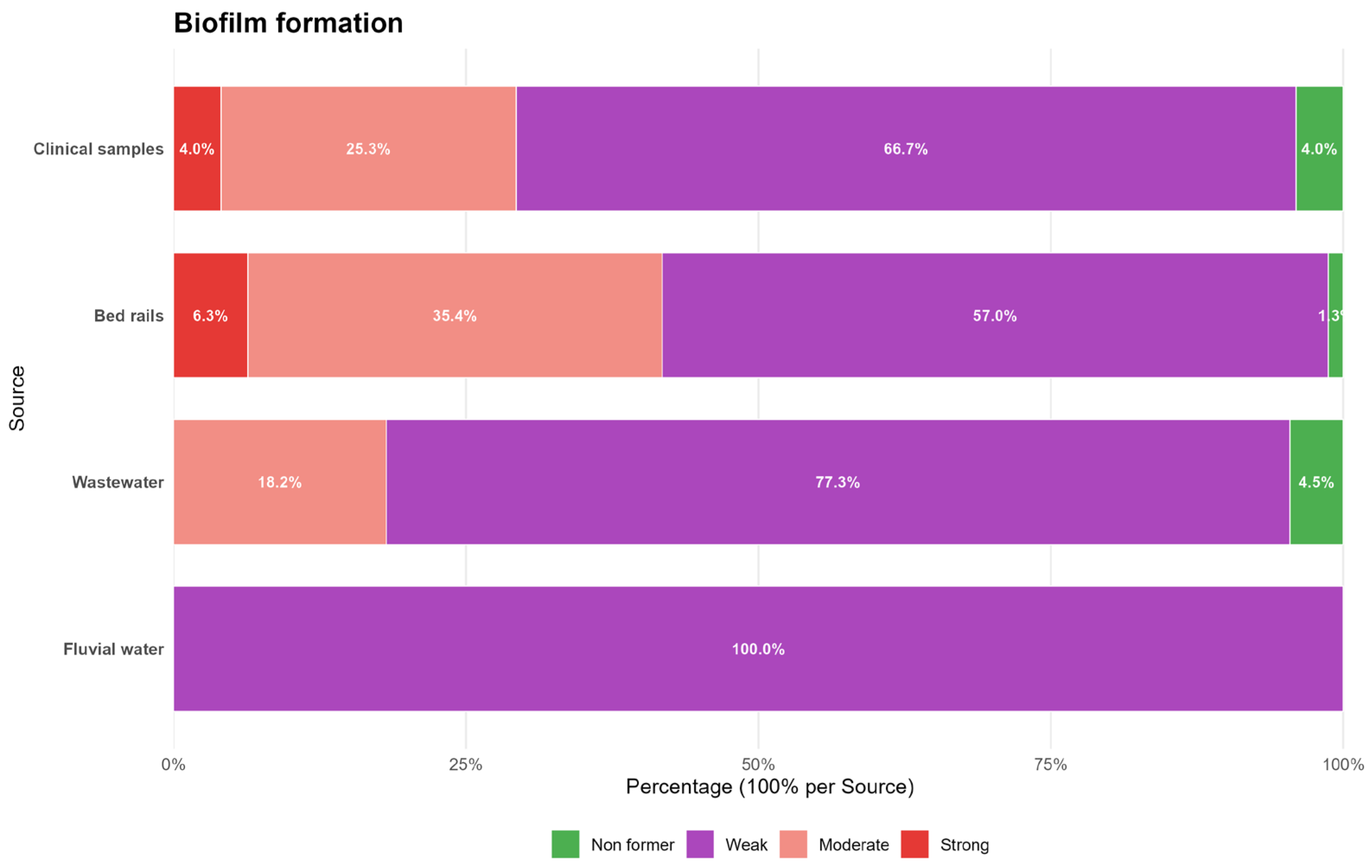
2.3. Biofilm Formation
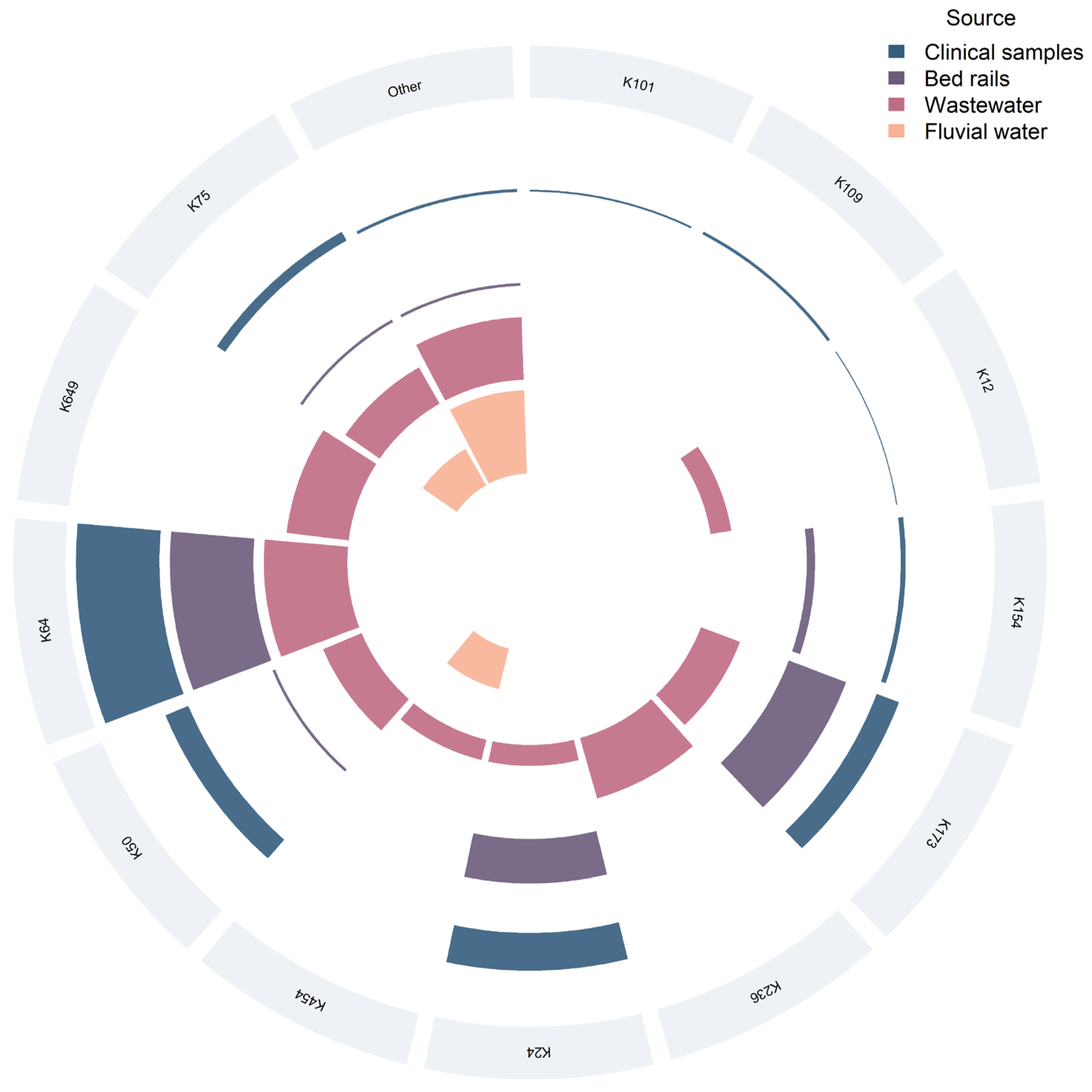
2.4. K Typing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical Setting
4.2. Sampling in the Hospital Environment
4.3. Water Sample Collections
4.4. Clinical Isolates
4.5. Identification of Bacterial Isolates
4.6. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.7. Determination of the Ability to Form Biofilm
4.8. Capsular Typing
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial Resistance |
| AMRO | Americas Regional Office |
| ARG | Antibiotic resistance gene |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| BigDye | BigDye Terminator Sequencing Chemistry |
| CMY-2 | Cephamycinase type 2 |
| CRE | Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteria |
| CRKP | Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| CZA | Ceftazidime–avibactam |
| DHA-1 | Dhahran Hospital AmpC type 1 |
| ESBL | Extended-spectrum β-lactamase |
| EUCAST | European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
| Fiocruz | Fundação Oswaldo Cruz |
| gyrA | DNA gyrase subunit A gene |
| HAI | Healthcare-Associated Infection |
| HGT | Horizontal Gene Transfer |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| INCQS | Instituto Nacional de Controle de Qualidade em Saúde |
| KPC | Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase |
| K-type | Capsular type |
| L-Ara4N | 4-Amino-4-Deoxy-L-Arabinose |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MALDI-TOF | Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization—Time of Flight |
| mcr-1 | Mobilized colistin resistance gene-1 |
| MDR | Multi-drug-resistant |
| MGE | Mobile Genetic Element |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MTB_autoX | An automated acquisition method used in MALDI-TOF for microbial identification, ensuring standardized spectral data collection |
| NDM | New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase |
| OD | Optical Density |
| OXA-48 | Oxacillinase-48 |
| PAHO | Pan American Health Organization |
| parC | DNA topoisomerase IV subunit C gene |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PDR | Pan-drug-resistant |
| PhoPQ | Two-Component Regulatory System PhoPQ |
| PmrAB | Two-Component Regulatory System PmrAB |
| POLB | Polymyxin B |
| PPT | Piperacillin–tazobactam |
| qnr | Quinolone resistance gene |
| ReLAVRA | Latin American Network for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance |
| SciPy | Scientific Python |
| STX | Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim |
| TAE | Tris-Acetate-EDTA Buffer |
| TSI | Triple Sugar Iron |
| XDR | Extensively drug-resistant |
References
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles Aguilar, G.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Weaver, N.D.; Ikuta, K.S.; Mestrovic, T.; Gray, A.P.; Chung, E.; Wool, E.E.; Han, C.; Hayoon, A.G.; et al. The burden of antimicrobial resistance in the Americas in 2019: A cross-country systematic analysis. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2023, 25, 100561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan American Health Organization. Magnitude and Trends of Antimicrobial Resistance in Latin America: ReLAVRA 2014–2016; PAHO: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Available online: https://www.paho.org/en/documents/magnitude-and-trends-antimicrobial-resistance-latin-america-relavra-2014-2015-2016 (accessed on 7 October 2025).
- Fabre, V.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Secaira, C.; Tapia Torrez, J.C.; Lessa, F.C.; Patel, T.S.; Quiros, R.; Caceres, D.H.; Perz, J.F.; Cardo, D.; et al. Antimicrobial stewardship in Latin America: Past, present, and future. Antimicrob. Steward. Healthc. Epidemiol. 2022, 2, e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillonetto, M.; Wink, P.L.; Melano, R.G.; Jiménez-Pearson, M.A.; Melgarejo Touchet, N.L.; Saavedra Rojas, S.Y.; Kulek, D.N.O.; Abreu, A.L.; Peral, R.T.; Miorando, R.; et al. Carbapenemases producing gram-negative bacteria surveillance in Latin America and the Caribbean: A retrospective observational study from 2015 to 2020. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2025, 49, 101185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics are Urgently Needed. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/detail/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Assefa, M.; Amare, A. Biofilm-Associated Multi-Drug Resistance in Hospital-Acquired Infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 5061–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, J.Y.; Centeleghe, I. How biofilm changes our understanding of cleaning and disinfection. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2023, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, K. Special Issue: Microbial Biofilms in Healthcare: Formation, prevention and treatment. Materials 2019, 12, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirwati, H.; Sinanjung, K.; Fahrunissa, F.; Wijaya, F.; Napitupulu, S.; Hati, V. Biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from clinical samples in a tertiary care hospital, Klaten, Indonesia. BMC Proc. 2019, 13, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkemngong, C.; Teska, P. Biofilms, mobile genetic elements and the persistence of pathogens on environmental surfaces in healthcare and food processing environments. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1405428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Ahmad, W.; Andleeb, S.; Jalil, F.; Imran, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Ali, M.; Rafiq, M.; Kamil, M.A.; et al. Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.E.S.; Destro, G.; Vieira, B.; Lima, A.S.; Ferraz, L.F.C.; Hakansson, A.P.; Darrieux, M.; Converso, T.R. Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms and their role in disease pathogenesis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 877995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, M.; Gudina, E.K.; Tadesse, W.; Froeschl, G.; Ali, S.; Seeholzer, T.; Kroidl, A.; Wieser, A. Hospital wastes as potential sources for multidrug-resistant ESBL-producing bacteria at a tertiary hospital in Ethiopia. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Almotiri, A.; AlZeyadi, Z.A. Antimicrobial resistance and β-lactamase production in clinically significant Gram-negative bacteria isolated from hospital and municipal wastewater. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura-Silva, R.; Dias, L.L.; Sousa, R.C.; Fujimoto, R.Y.; Pitondo-Silva, A. Multidrug-resistant and potentially pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae found in a tertiary hospital sewage in southeastern Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidova-Gerzova, L.; Lausova, J.; Sukkar, I.; Nesporova, K.; Nechutna, L.; Vlkova, K.; Chudejova, K.; Krutova, M.; Palkovicova, J.; Kaspar, J.; et al. Hospital and community wastewater as a source of multidrug-resistant ESBL-producing Escherichia coli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1184081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkman, A.; Do, T.T.; Walsh, F.; Virta, M.P.J. Antibiotic-resistance genes in waste water. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvi, K.; Mangayarkarasi, V.; Balakrishnan, D.; Chitraleka, V. Survival of antibacterial resistance microbes in hospital-generated recycled wastewater. J. Water Health 2016, 14, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashurst, J.V.; Dawson, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519004/ (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Bush, K. β-lactam antibiotics. In Antibiotic and Chemotherapy, 9th ed.; Finch, R.G., Greenwood, D., Norrby, S.R., Whitley, R.J., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2010; pp. 200–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opal, S.M.; Pop-Vicas, A. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 8th ed.; Bennett, J.E., Dolin, R., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 235–251.e3. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9781455748013000187 (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Rawat, D.; Nair, D. Extended-spectrum β-lactamases in gram negative bacteria. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2010, 2, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavagnoli, L.S.; Bassetti, B.R.; Kaiser, T.D.L.; Kutz, K.M.; Cerutti Junior, C. Factors associated with acquisition of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 2017, 25, e2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Epidemiology and diagnostics of carbapenem resistance in gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, S521–S528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.L.C.; Romano, M.; Kerry, L.E.; Kwong, H.-S.; Low, W.-W.; Brett, S.J.; Clements, A.; Beis, K.; Frankel, G. OmpK36-mediated carbapenem resistance attenuates ST258 Klebsiella pneumoniae in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, G.A. AmpC β-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, J.; Walters, L.; Leong, L.E.X.; Smith, K.; Amato, M.; Chen, X.; Turra, M.; Warner, M.S.; Papanicolas, L.E. Characterizing Escherichia coli carrying plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamases to optimize detection in a diagnostic laboratory setting. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0093324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimble, M.J.; Mlynárčik, P.; Kolář, M.; Hancock, R.E.W. Polymyxin: Alternative mechanisms of action and resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, K.E.D.; Rossato, L.; Leite, A.F.; Simionatto, S. Overview of polymyxin resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2022, 55, e0349-2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaara, M. Polymyxins and their potential next generation as therapeutic antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, J.H.; Harper, M.; Boyce, J.D. Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance. In Polymyxin Antibiotics: From Laboratory Bench to Bedside; Li, J., Nation, R.L., Kaye, K.S., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 1145, pp. 55–71. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-030-16373-0_5 (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.-X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, S.W.; Figueiredo, T.P.; Bessa, M.C.; Pagnussatti, V.E.; Ferreira, C.A.; Oliveira, S.D. Isolation and characterization of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates from a Brazilian hospital. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raro, O.H.F.; Gallo, S.W.; Ferreira, C.A.S.; Oliveira, S.D. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii contamination in an intensive care unit. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2017, 50, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampatakis, T.; Tsergouli, K.; Behzadi, P. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Virulence factors, molecular epidemiology and latest updates in treatment options. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galani, I.; Nafplioti, K.; Adamou, P.; Karaiskos, I.; Giamarellou, H.; Souli, M. Nationwide epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from Greek hospitals, with regards to plazomicin and aminoglycoside resistance. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolleti, F.; Seco, B.M.S.; Capuzzo dos Santos, C.; Felipe, C.B.; Lemo, M.E.B.; Alves, T.S.; Passadore, L.F.; Mimica, M.J.; Sampaio, S.C.F.; Zavascki, A.P.; et al. Polymyxin B resistance in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, São Paulo, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1849–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiesh, B.M.; Natsheh, M.; Amar, M.; AbuTaha, S.; Qadi, M.; AbuTaha, A.; Sabateen, A.; Zyoud, S.H. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of patients with healthcare-acquired multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacilli: A retrospective study from a tertiary care hospital. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Xie, W.; Jing, C. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections in Chinese children: In vitro activities of ceftazidime–avibactam and aztreonam–avibactam against carbapenemase-producing strains in a two-center study. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1545999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lin, D.; Wu, N. Analysis of the prevalence, drug resistance genes and evolution of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Lishui, China from 2015 to 2024. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2025, 18, e157871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.D.; Meghdadi, H.; Saki, M.; Bakhtiyariniya, P.; Heidari, R.; Akrami, S.; Rahbar, M.; Soltani, F.; Shahi, F.; Moosavian, M.; et al. Molecular identification of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes among Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates from southwest Iran. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Ahmad, N.; Saeed, N.K.; Shadab, M.; Joji, R.M.; Al-Mahmeed, A.; Bindayna, K.M.; Yusuf, M.A.; Qureshi, A.; Al Maslamani, M.; et al. Clinical carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates simultaneously harboring blaNDM-1, blaOXA types and qnrS genes from the Kingdom of Bahrain: Resistance profile and genetic environment. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1033305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livermore, D.M.; Meunier, D.; Hopkins, K.L.; Doumith, M.; Hill, R.; Pike, R.; Woodford, N. Activity of ceftazidime/avibactam against problem Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the UK, 2015–2016. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.B.; Asghar, A.H.; Bamaga, M.; Bahwerth, F.S.; Ibrahim, M.E.; Alghamdi, M.S.; Alzahrani, A.S.; Al-Hakami, A.M.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Alshareef, W.A.; et al. Characterization of aminoglycoside resistance genes in multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae collected from tertiary hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Dong, N.; Zhou, H.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, R.; Xu, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. Increasing polymyxin resistance in clinical carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains in China between 2000 and 2023. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceição-Neto, O.C.; da Costa, B.S.; Pontes, L.D.S.; Silveira, M.C.; Justo-da-Silva, L.H.; de Oliveira Santos, I.C.; Silva, R.F.; Reis, C.M.F.; Carvalho-Assef, A.P.D.; Asensi, M.D.; et al. Polymyxin resistance in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Brazil: Update on molecular mechanisms, clonal dissemination and relationship with KPC-producing strains. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 898125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Rosado, M.; Sands, K.; Portal, E.A.R.; Thomson, K.M.; Carvalho, M.J.; Mathias, J.; Phee, L.M.; Kinsman, T.; Smith, C.; Mathur, S.; et al. Colonisation of hospital surfaces from low- and middle-income countries by extended spectrum β-lactamase- and carbapenemase-producing bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Junior, A.G.; Ferreira, A.M.; Frota, O.P.; Rigotti, M.A.; Barcelos, L.D.S.; Lopes de Sousa, A.F.; Oliveira, A.C. Effectiveness of surface cleaning and disinfection in a Brazilian healthcare facility. Open Nurs. J. 2018, 12, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kampf, G. Adaptive bacterial response to low level chlorhexidine exposure and its implications for hand hygiene. Microb. Cell 2019, 6, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Element, S.J.; Moran, R.A.; Beattie, E.; Hall, R.J.; van Schaik, W.; Buckner, M.M.C. Growth in a biofilm promotes conjugation of a blaNDM-1-bearing plasmid between Klebsiella pneumoniae strains. mSphere 2023, 8, e00170-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Prentice, E.L.; Webber, M.A. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in biofilms. NPJ Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeleghe, I.; Norville, P.; Hughes, L.; Maillard, J.Y. Klebsiella pneumoniae survives on surfaces as a dry biofilm. Am. J. Infect. Control 2023, 51, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Vivas, J.; Chapartegui-González, I.; Fernández-Martínez, M.; González-Rico, C.; Fortún, J.; Escudero, R.; Marco, F.; Linares, L.; Montejo, M.; Aranzamendi, M.; et al. Biofilm formation by multidrug resistant Enterobacteriaceae strains isolated from solid organ transplant recipients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico, E.G.; Cavallo, I.; Sivori, F.; Marchesi, F.; Prignano, G.; Pimpinelli, F.; Sperduti, I.; Pelagalli, L.; Di Salvo, F.; Celesti, I.; et al. Biofilm production by carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae significantly increases the risk of death in oncological patients. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 561741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, C.; Grohmann, E. Horizontal gene transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in biofilms. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.C.; Baveye, P.; Neu, T.R.; Stoodley, P.; Szewzyk, U.; Wingender, J. Who put the film in biofilm? The migration of a term from wastewater engineering to medicine and beyond. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, R.; Nair, A.V.; Parmar, K.; Rajmani, R.S.; Chakravortty, D.; Das, D.; De, U.C.; Majumdar, S.; Pati, S.; Mukherjee, A.; et al. Combating biofilm-associated Klebsiella pneumoniae infections using a bovine microbial enzyme. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Falgenhauer, L.; Falgenhauer, J.; Heinmüller, P.; Domann, E.; Chakraborty, T. Plasmid-mediated spread of carbapenem resistance in Enterobacterales: A three-year genome-based survey. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Ouyang, P.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Kang, H.; et al. Evolution of hypervirulence in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in China: A multicentre, molecular epidemiological analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, H.A.; Booton, R.; Kallonen, T.; Gibbon, M.J.; Couto, N.; Passet, V.; López-Fernández, S.; Rodrigues, C.; Matthews, L.; Mitchell, S.; et al. A large-scale genomic snapshot of Klebsiella spp. isolates in Northern Italy reveals limited transmission between clinical and non-clinical settings. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 2054–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xia, X.; Yuan, T.; Zhu, J.; Shen, Z.; Li, M. Molecular epidemiology of antimicrobial resistance, virulence and capsular serotypes of carbapenemase-carrying Klebsiella pneumoniae in China. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Watts, S.C.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. A genomic surveillance framework and genotyping tool for Klebsiella pneumoniae and its related species complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez Pearson, M.A.; Galas, M.; Corso, A.; Hormazábal, J.C.; Duarte Valderrama, C.; Salgado Marcano, N.; Castañeda, N.; Pasterán, F.; Petroni, A.; López, C.; et al. Consenso latinoamericano para definir, categorizar y notificar patógenos multirresistentes, con resistencia extendida o panresistentes. Rev. Panam. Salud Pública 2019, 43, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlet, J.; Jarlier, V.; Harbarth, S.; Voss, A.; Goossens, H.; Pittet, D.; Pulcini, C.; Kluytmans, J.; Rice, L.B.; Struelens, M.J.; et al. Ready for a world without antibiotics? The pensières antibiotic resistance call to action. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2012, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgalel, R.R.; Ibrahem, R.A.; Mohamed, D.S.; Ahmed, A.B.F. Multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli in wastewater sources: A comparative study and identification of resistance hotspots. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartley, P.S.; Domitrovic, T.N.; Moretto, V.T.; Santos, C.S.; Ponce-Terashima, R.; Reis, M.G.; Riley, L.W. Antibiotic resistance in Enterobacteriaceae from surface waters in urban Brazil highlights the risks of poor sanitation. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Elena, A.X.; Kunath, M.A.; Berendonk, T.U.; Klümper, U. Reduced selection for antibiotic resistance in community context is maintained despite pressure by additional antibiotics. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, M.C.; Maugeri, A.; Favara, G.; La Mastra, C.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Barchitta, M.; Agodi, A. The impact of wastewater on antimicrobial resistance: A scoping review of transmission pathways and contributing factors. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassoun-Kheir, N.; Stabholz, Y.; Kreft, J.U.; De La Cruz, R.; Romalde, J.L.; Nesme, J.; Graham, D.W.; Paul, M.; Ploy, M.C.; Wuijts, S.; et al. Comparison of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes abundance in hospital and community wastewater: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagui, G.S.; Tonani, K.A.A.; Fregonesi, B.M.; Machado, G.P.; Silva, T.V.; Andrade, L.N.; Darini, A.L.C.; Oliveira-Pinto, C.; Rocha, D.J.P.G.; Ribeiro, R.A.; et al. Tertiary hospital sewage as reservoir of bacteria expressing MDR phenotype in Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 82, e234471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontoura, N.; Brun, G.; Figueira, C.; Frankeberg, C.; dos Santos, F.; Campos, M.; Silva, R.; Souza, T.; Almeida, P.; Vieira, L.; et al. Diagnóstico e Monitoramento Ambiental do Arroio Dilúvio (eixo Ipiranga); Instituto do Meio Ambiente da PUCRS: Porto Alegre, Brazil; Available online: https://www.pucrs.br/ima/projetos/projetos-concluidos/diagnostico-e-monitoramento-ambiental-do-arroio-diluvio-eixo-ipiranga/ (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Mills, M.; Wittum, T.; Lee, J. Dynamic microbiome and mobile resistome are revealed in river biofilms from a multi-use watershed through long-read sequencing. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1440635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedeño-Muñoz, J.S.; Aransiola, S.A.; Reddy, K.V.; Ranjit, P.; Victor-Ekwebelem, M.O.; Oyedele, O.J.; Adeola, O.; Ajiboye, T.; Ibe, C.; Eze, C.; et al. Antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes as contaminants of emerging concern: Occurrences, impacts, mitigations and future guidelines. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, K.; McDonald, W.; McNamara, P. Antibiotic resistance in urban stormwater: A review of the dissemination of resistance elements, their impact, and management opportunities. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2023, 9, 2188–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, K.A.; Garner, E.; Joshi, S.; Ahmed, W.; Ashbolt, N.; Medema, G.; Graham, D.W.; Rose, J.B.; Wuijts, S.; Manaia, C.M.; et al. Antimicrobial-resistant microorganisms and their genetic determinants in stormwater: A systematic review. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 16, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Héritier, C.; Nordmann, P. Chromosome-encoded Ambler class D β-lactamase of Shewanella oneidensis as a progenitor of carbapenem-hydrolyzing oxacillinase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allkja, J.; Van Charante, F.; Aizawa, J.; Reigada, I.; Guarch-Pérez, C.; Vazquez-Rodriguez, J.A.; Shainheit, M.G.; Anwar, S.; Giske, C.G.; Martínez, J.L.; et al. Interlaboratory study for the evaluation of three microtiter plate-based biofilm quantification methods. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, K.N.; Alhede, M.; Kvich, L.; Bjarnsholt, T. Into the well—A close look at the complex structures of a microtiter biofilm and the crystal violet assay. Biofilm 2019, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Rahdar, H.; Shiri Malekabad, E.; Dadashi, A.R.; Takei, E.; Keikha, M.; Kazemian, H.; Mohammadi, F.; Goudarzi, M.; Goudarzi, H.; Heidary, M.; et al. Correlation between biofilm formation and carbapenem resistance among clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2019, 29, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusumano, J.A.; Caffrey, A.R.; Daffinee, K.E.; Luther, M.K.; Lopes, V.; LaPlante, K.L. Weak biofilm formation among carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 95, 114877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.X.; Lin, Z.W.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Lin, F.J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Qu, T.; Wang, L.; et al. Biofilm formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia strains was found to be associated with CC23 and the presence of wcaG. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Gao, X.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Yu, J.; et al. Relationship between biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae and updates on antibiofilm therapeutic strategies. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1324895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqueira, I. Morfometria Comparativa de Três Arroios Afluentes ao Lago Guaíba no Município de Porto Alegre/RS/Brasil, com Uso da Tecnologia Sistema de Informações Geográficas (SIG); Instituto de Pesquisas Hidráulicas, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2019; Available online: https://professor.ufrgs.br/sites/default/files/collischonn/files/artigo_isabel.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Drescher, S.P.M.; Gallo, S.W.; Ferreira, P.M.A.; Ferreira, C.A.S.; Oliveira, S.D.D. Salmonella enterica persister cells form unstable small colony variants after in vitro exposure to ciprofloxacin. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Dakić, I.; Savić, B.; Švabić-Vlahović, M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 40, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Haugaard, A.B.; Babosan, A.; Kassis-Chikhani, N.; Struve, C.; Decré, D. wzi gene sequencing, a rapid method for determination of capsular type for Klebsiella strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 4073–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maldonado, K.V.M.; Pereira, J.M.; Costa, T.N.d.; Buss, G.L.; Almeida Pereira, K.N.d.; Silva, A.B.d.; Corção, G.; Souza, Â.C.d.; Martins, A.S.; Falci, D.R.; et al. Widespread Distribution of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella spp. in Clinical and Environmental Settings. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111140
Maldonado KVM, Pereira JM, Costa TNd, Buss GL, Almeida Pereira KNd, Silva ABd, Corção G, Souza ÂCd, Martins AS, Falci DR, et al. Widespread Distribution of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella spp. in Clinical and Environmental Settings. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(11):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111140
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaldonado, Karla Vanessa Molina, Julia Marchese Pereira, Tamires Nascimento da Costa, Gabriel Lemos Buss, Kethlen Natiele de Almeida Pereira, Anelise Baptista da Silva, Gertrudes Corção, Ândrea Celestino de Souza, Amanda Silva Martins, Diego Rodrigues Falci, and et al. 2025. "Widespread Distribution of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella spp. in Clinical and Environmental Settings" Antibiotics 14, no. 11: 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111140
APA StyleMaldonado, K. V. M., Pereira, J. M., Costa, T. N. d., Buss, G. L., Almeida Pereira, K. N. d., Silva, A. B. d., Corção, G., Souza, Â. C. d., Martins, A. S., Falci, D. R., Monteiro, A. B., Flores, C., Bianco, K., Clementino, M. M., Ferreira, C. A. S., Medina-Silva, R., & Oliveira, S. D. d. (2025). Widespread Distribution of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella spp. in Clinical and Environmental Settings. Antibiotics, 14(11), 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111140




