Exploring the Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Salmonella typhi and Its Clinical Burden
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Population
2.2. S. typhi-Confirmed Cases
2.3. Logistic Regression Model Using Typhoid Cases (Negative/Positive) as the Dependent Variable and Its Association with Other Covariates
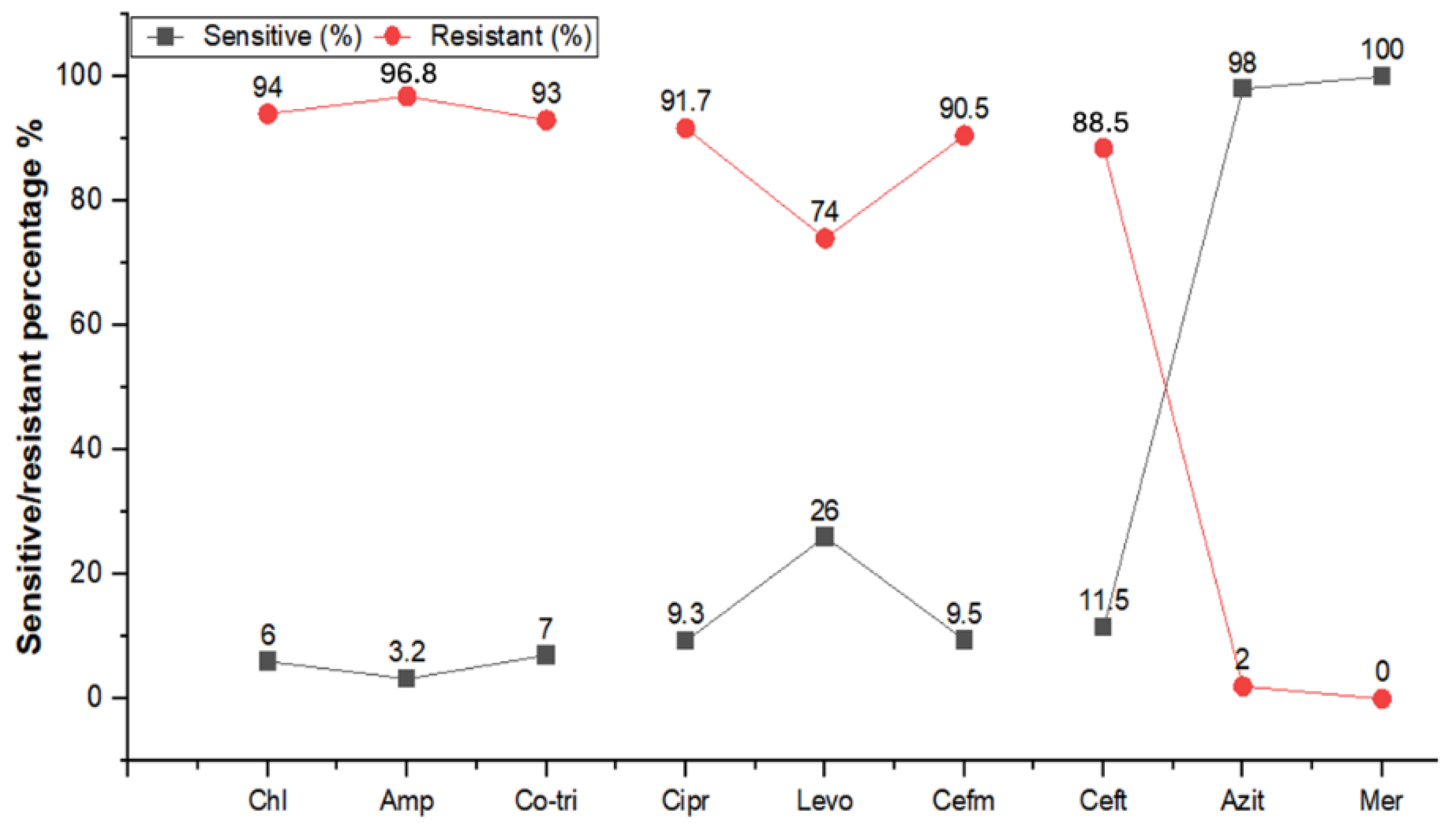
2.4. Antibiogram of S. typhi Isolates
3. Discussion
3.1. Prevalence and Geographic Variations
3.2. Vaccination Status, Socioeconomic Factors, Antibiotic Resistance, and Clinical Data
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
4.3. Data Collection
4.4. Sample Collection and Processing
4.5. Description of Bacterial Culture, Controls, Chemical Compositions of Media, and Antibiotics
4.6. Phenotypic and Genotypic Identification
4.7. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (AST)
4.8. Epidemiological and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeed, M.; Rasool, M.H.; Rasheed, F.; Saqalein, M.; Nisar, M.A.; Imran, A.A.; Tariq, S.; Amir, A.; Ikram, A.; Khurshid, M. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases producing extensively drug-resistant Salmonella typhi in Punjab, Pakistan. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2020, 14, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, M.E.; MacWright, W.R.; Im, J.; Meiring, J.E.; Gibani, M.M.; Park, S.E.; Longley, A.; Jeon, H.J.; Hemlock, C.; Yu, A.T.; et al. The Surveillance for Enteric Fever in Asia Project (SEAP), Severe Typhoid Fever Surveillance in Africa (SETA), Surveillance of Enteric Fever in India (SEFI), and Strategic Typhoid Alliance Across Africa and Asia (STRATAA) Population-based Enteric Fever Studies: A Review of Methodological Similarities and Differences. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71 (Suppl. S2), S102–S110. [Google Scholar]
- Meiring, J.E.; Shakya, M.; Khanam, F.; Voysey, M.; Phillips, M.T.; Tonks, S.; Thindwa, D.; Darton, T.C.; Dongol, S.; Karkey, A.; et al. Burden of enteric fever at three urban sites in Africa and Asia: A multicentre population-based study. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e1688–e1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B.; Raha, A. Typhoid and enteric fevers in intensive care unit. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 25 (Suppl. S2), S144. [Google Scholar]
- Informatics, G.; Berger, S.; G.S. Team. Infectious Diseases of China; GIDEON Informatics Inc.: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Crump, J.A.; Sjölund-Karlsson, M.; Gordon, M.A.; Parry, C.M. Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Laboratory Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Antimicrobial Management of Invasive Salmonella Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 901–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougan, G.; Baker, S. Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi and the Pathogenesis of Typhoid Fever. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 68, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutta, Z.A.; Naqvi, S.H.; Razzaq, R.A.; Farooqui, B.J. Multidrug-Resistant Typhoid in Children: Presentation and Clinical Features. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1991, 13, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaramis, A.; Yildirim, I.; Katar, S.; Ozbek, M.N.; Yalçin, I.; Tas, M.A.; Hosoglu, S. Clinical laboratory presentation of typhoid, fever. Int. Pediatr. 2001, 16, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Kariuki, S. Typhoid fever in sub-Saharan Africa: Challenges of diagnosis and management of infections. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2008, 2, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, J.; Khan, A.S.; Khan, H.A.; Gilani, S.A.; Akram, S.J.; Ahmad, F.J.; Mehboob, R. Extensively Drug-Resistant (XDR) Typhoid: Evolution, Prevention, and Its Management. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6432580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.H.; Saleem, A.; Javed, S.O.; Ullah, I.; Rehman, M.U.; Islam, N.; Tahir, M.A.; Malik, T.; Hafeez, S.; Hafeez, S. Rising XDR-typhoid fever cases in Pakistan: Are we heading back to the preantibiotic era? Front. Public Health 2022, 9, 794868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqui, A.; Khan, A.; Kazmi, S.U. Investigation of a community outbreak of typhoid fever associated with drinking water. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-A.; Chong, A.; Song, J. Why Is Eradicating Typhoid Fever So Challenging: Implications for Vaccine and Therapeutic Design. Vaccines 2018, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.M.; Simon, R. The gathering storm: Is untreatable typhoid fever on the way? mBio 2018, 9, 00482-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qamar, F.N.; Yousafzai, M.T.; Khalid, M.; Kazi, A.M.; Lohana, H.; Karim, S.; Khan, A.; Hotwani, A.; Qureshi, S.; Kabir, F.; et al. Outbreak investigation of ceftriaxone-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi and its risk factors among the general population in Hyderabad, Pakistan: A matched case-control study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousafzai, M.T.; Qamar, F.N.; Shakoor, S.; Saleem, K.; Lohana, H.; Karim, S.; Hotwani, A.; Qureshi, S.; Masood, N.; Rauf, M.; et al. Ceftriaxone-resistant Salmonella typhi outbreak in Hyderabad City of Sindh, Pakistan: High time for the introduction of typhoid conjugate vaccine. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68 (Suppl. S1), S16–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizamuddin, S.; Ching, C.; Kamal, R.; Zaman, M.H.; Sultan, F. Continued Outbreak of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhi across Pakistan and Assessment of Knowledge and Practices among Healthcare Workers. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, E.J.; Shakoor, S.; Page, A.J.; Qamar, F.N.; Judge, K.; Saeed, D.K.; Wong, V.K.; Dallman, T.J.; Nair, S.; Baker, S.; et al. Emergence of an Extensively Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Clone Harboring a Promiscuous Plasmid Encoding Resistance to Fluoroquinolones and Third-Generation Cephalosporins. mBio 2018, 9, 00105-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, J.; von Seidlein, L.; Andersen, F.; Elle, N.; White, N.J.; Lubell, Y. Community-acquired bacterial bloodstream infections in developing countries in south and southeast Asia: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskery, B.; Ochiai, R.L.; Lee, J.S.; Mogasale, V.V.; Ramani, E.; Kim, Y.E.; Park, J.K.; Wierzba, T.F. Burden of typhoid fever in low-income and middle-income countries: A systematic, literature-based update with risk-factor adjustment. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e570–e580. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, M.; Kumar, S.; Hussain, M.; Memon, N.M.; Vighio, A.; Syed, M.A.; Chaudhry, A.; Hussain, Z.; Baig, Z.I.; Baig, M.A.; et al. Morbidity and Mortality Associated with Typhoid Fever Among Hospitalized Patients in Hyderabad District, Pakistan, 2017–2018: Retrospective Record Review. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2021, 7, e27268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwani, Z.H.; Kumar, P.; Salman, Y.; Islam, Z.; Ahmad, S.; Essar, M.Y. Typhoid in Pakistan: Challenges, efforts, and recommendations. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 2523–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareen, A.M. Prevalence of Typhoid Fever in General Population of District Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan. J. Appl. Emerg. Sci. 2016, 5, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Sur, D.; von Seidlein, L.; Manna, B.; Dutta, S.; Deb, A.K.; Sarkar, B.L.; Kanungo, S.; Deen, J.L.; Ali, M.; Kim, D.R.; et al. The malaria and typhoid fever Burden in the slums of Kolkata, India: Data from a prospective community-based study. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 100, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Salman, M.; Malik, M.A.; Umair, M.; Rehman, P.; Khan, M. Current Antibiotics Resistance Patterns of Salmonella typhi in District Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Curr. Trends OMICS 2022, 2, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, F.; Hussain, S.Z.; Batool, D.; Usman, A.; Khalid, U.; Yaqoob, U.; Shahzad, H. study of sociodemographic factors affecting the prevalence of typhoid. Morb. Mortal. 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Dewan, A.M.; Corner, R.; Hashizume, M.; Ongee, E.T. Typhoid fever and its association with environmental factors in the Dhaka metropolitan area of Bangladesh: A spatial and time-series approach. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amicizia, D.; Micale, R.T.; Pennati, B.M.; Zangrillo, F.; Iovine, M.; Lecini, E.; Marchini, F.; Lai, P.L.; Panatto, D. Burden of typhoid fever and cholera: Similarities and differences. Prevention strategies for European travelers to endemic/epidemic areas. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2019, 60, E271. [Google Scholar]
- Israr, M.; Jadoon, A.; Ullah, M.J.; Rashid, F.; Maroof, L.; Qazi, N.U.; Ahmad, Z.; Ullah, S. Prevalance and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns of Salmonella typhi and Escherichia Coli in Drinking Water of Sub-Division Hassan Khel Peshawar. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2022, 26, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.A.A.; Nadeem, M.; Syed, S.A.; Abidi, S.T.F.; Khan, N.; Bano, N. Antimicrobial Sensitivity Pattern of Salmonella typhi: Emergence of Resistant Strains. Cureus 2020, 12, e11778. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Rahman, N.; Adeeb, H.; Ullah, I. Frequency and antimicrobial resistance profile of Salmonella typhi isolated from district buner. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 30, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakir, M.; Khan, M.; Umar, M.I.; Murtaza, G.; Ashraf, M.; Shamim, S. Emerging Trends of Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) and Extensively Drug-Resistant (XDR) Salmonella typhi in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Lahore, Pakistan. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, F.; Saeed, M.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Baker, D.; Khurshid, M.; Ainsworth, E.V.; Turner, A.K.; Imran, A.A.; Rasool, M.H.; Saqalein, M.; et al. Emergence of Resistance to Fluoroquinolones and Third-Generation Cephalosporins in Salmonella typhi in Lahore, Pakistan. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abro, A.H.; Abdou, A.M.; Gangwani, J.L.; Ustadi, A.M.; Younis, N.J.; Hussaini, H.S. Hematological and biochemical changes in typhoid fever. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 25, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Rasoulinezhad, M.; Esmailpour, B.N.; Mogbel, A.B. Salmonella hepatitis (analysis of hepatic involvement in 107 patients with typhoid fever). Acta Medica Iran. 2003, 41, 161–163. [Google Scholar]
- James, J.; Jayanthi, S.; Dutta, T.K. Correlation of clinical and hematologic profiles with bone marrow responses in typhoid fever. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 57, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsadraee, M.; Shirdel, A.; Roknee, F. Typhoid myopathy or typhoid hepatitis: A matter of debate. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 25, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgenstern, R.; Hayes, P.C. The liver in typhoid fever: Always affected, not just a complication. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1991, 86, 1235. [Google Scholar]
- Wahid, R.; Simon, R.; Zafar, S.J.; Levine, M.M.; Sztein, M.B. Live Oral Typhoid Vaccine Ty21a Induces Cross-Reactive Humoral Immune Responses against Salmonella enterica Serovar Paratyphi A and S. Paratyphi B in Humans. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.E.; Davis, T.M.E.; Henry, R.L.; Chan, L.P. Serum C-reactive protein concentrations in Malaysian children with enteric fever. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2001, 47, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shin, E.; Park, J.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, A.K.; Na, K.; Lee, H.; Chun, J.; Hwang, K.J.; Kim, C.J.; Kim, J. Emerging high-level ciprofloxacin-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar typhi haplotype H58 in travelers returning to the Republic of Korea from India. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M100: Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 32nd ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023; CLSI Supplement M100.
| Variable | Categories | Population (%) | S. typhi Infection Status | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative N (%) | Positive N (%) | ||||
| Gender | Male | 3235 (56.4) | 2788 (55.3) | 447 (64.7) | 0.001 |
| Female | 2500 (43.6) | 2256 (44.7) | 244 (35.3) | ||
| Age groups | Childhood (0–11 years) | 2747 (47.9) | 2318 (46.0) | 429 (62.1) | 0.001 |
| Adolescence (12–18 years) | 896 (15.6) | 786 (15.6) | 110 (15.9) | ||
| Adulthood (19–59 years) | 1830 (31.9) | 1684 (33.4) | 146 (21.1) | ||
| Older Adults (60+ years) | 262 (4.6) | 256 (5.1) | 6 (0.9) | ||
| Geographic distribution | Peshawar | 5033 (87.8) | 4424 (87.7) | 609 (88.1) | 0.014 |
| Hangu | 264 (4.6) | 232 (4.6) | 32 (4.6) | ||
| Malakand | 150 (2.6) | 136 (2.7) | 14 (2.0) | ||
| Mardan | 174 (3.0) | 146 (2.9) | 28 (4.1) | ||
| Bannu | 34 (0.6) | 28 (0.6) | 6 (0.9) | ||
| Kohat | 80 (1.4) | 78 (1.5) | 2 (0.3) | ||
| Locality | Urban | 2522 (44.0) | 2264 (44.9) | 258 (37.3) | 0.002 |
| Rural | 3163 (55.2) | 2732 (54.2) | 431 (62.4) | ||
| Peri-Urban | 50 (0.9%) | 48 (1.0) | 2 (0.3) | ||
| Water Source | Municipality | 4771 (83.2) | 4154 (82.4) | 617 (89.3) | 0.001 |
| Ground Water | 964 (16.8) | 890 (17.6) | 74 (10.7) | ||
| TCV Vaccination Status | No | 4807 (83.2) | 4134 (82.0) | 673 (97.4) | 0.002 |
| Yes | 928 (16.2) | 910 (18.0) | 18 (2.6) | ||
| History of Fever | Three or >3 days | 4128 (72.0) | 3505 (69.5) | 623 (90.1) | 0.002 |
| Recent Travel | 1607 (28.0) | 1539 (30.5) | 68 (9.9) | ||
| Leucopenia | Normal cases (4000–11,000/cm) | 5670 (98.9) | 5044 (100) | 626 (90.6) | 0.002 |
| Abnormal cases (<4000/cm) | 65 (1.1) | 0 (0) | 65 (9.4) | ||
| Thrombocytopenia | Normal cases (150,000–450,000/cm) | 5605 (97.7) | 5044 (100) | 561 (81.2) | 0.001 |
| Mild (50,000–149,000/cm) | 103 (1.8) | 0 (0.0) | 103 (14.9) | ||
| Moderate (30,000–50,000/cm) | 27 (0.50) | 0 (0.0) | 27 (3.9) | ||
| ALT/SGPT | Normal cases (<45 U/L) | 5333 (93.0) | 5044 (100) | 289 (41.8) | 0.001 |
| Abnormal cases (>45 U/L) | 402 (7.0) | 0 (0) | 402 (58.2) | ||
| CRP | Normal cases (up to 5 mg/dl) | 5045 (88.0) | 5044 (100) | 1 (0.1) | 0.002 |
| Abnormal cases (>5 mg/dl) | 690 (12.0) | 0 (0) | 690 (99.9) | ||
| Characteristics | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95%CI | p-Value | OR | 95%CI | p-Value | |
| Age group (in years) | ||||||
| 12–18 (adolescence) vs. child * | 0.75 | 0.60–0.94 | 0.001 | 0.52 | 0.419–0.664 | 0.001 |
| 19–59 (adulthood) vs. child * | 0.46 | 0.38–0.57 | 0.001 | 0.30 | 0.252–0.378 | 0.001 |
| >60 (old age) vs. child * | 0.12 | 0.05–0.28 | 0.003 | 0.08 | 0.035–0.181 | 0.001 |
| Gender | ||||||
| Female vs. male | 0.67 | 0.57–0.79 | 0.001 | 0.67 | 0.56–0.80 | 0.002 |
| Locality | ||||||
| Rural vs. urban | 1.38 | 1.17–1.63 | 0.001 | 1.38 | 1.16–1.63 | 0.001 |
| Peri-urban vs. urban | 0.36 | 0.08–1.51 | 0.366 | 0.26 | 0.06–1.11 | 0.007 |
| Water source | ||||||
| Groundwater vs. municipal | 0.56 | 0.43–0.72 | 0.001 | 0.56 | 0.43–0.73 | 0.002 |
| TCV vaccination status | ||||||
| Yes vs. no | 0.12 | 0.07–0.19 | 0.001 | 0.07 | 0.04–0.11 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asghar, M.; Khan, T.A.; Séraphin, M.N.; Schimke, L.F.; Cabral-Marques, O.; Haq, I.U.; Farooqi, Z.-u.-R.; Campino, S.; Ullah, I.; Clark, T.G. Exploring the Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Salmonella typhi and Its Clinical Burden. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080765
Asghar M, Khan TA, Séraphin MN, Schimke LF, Cabral-Marques O, Haq IU, Farooqi Z-u-R, Campino S, Ullah I, Clark TG. Exploring the Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Salmonella typhi and Its Clinical Burden. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(8):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080765
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsghar, Muhammad, Taj Ali Khan, Marie Nancy Séraphin, Lena F. Schimke, Otavio Cabral-Marques, Ihtisham Ul Haq, Zia-ur-Rehman Farooqi, Susana Campino, Ihsan Ullah, and Taane G. Clark. 2024. "Exploring the Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Salmonella typhi and Its Clinical Burden" Antibiotics 13, no. 8: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080765
APA StyleAsghar, M., Khan, T. A., Séraphin, M. N., Schimke, L. F., Cabral-Marques, O., Haq, I. U., Farooqi, Z.-u.-R., Campino, S., Ullah, I., & Clark, T. G. (2024). Exploring the Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Salmonella typhi and Its Clinical Burden. Antibiotics, 13(8), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080765








