The Many Lives of Auranofin: How an Old Anti-Rheumatic Agent May Become a Promising Antimicrobial Drug
Abstract
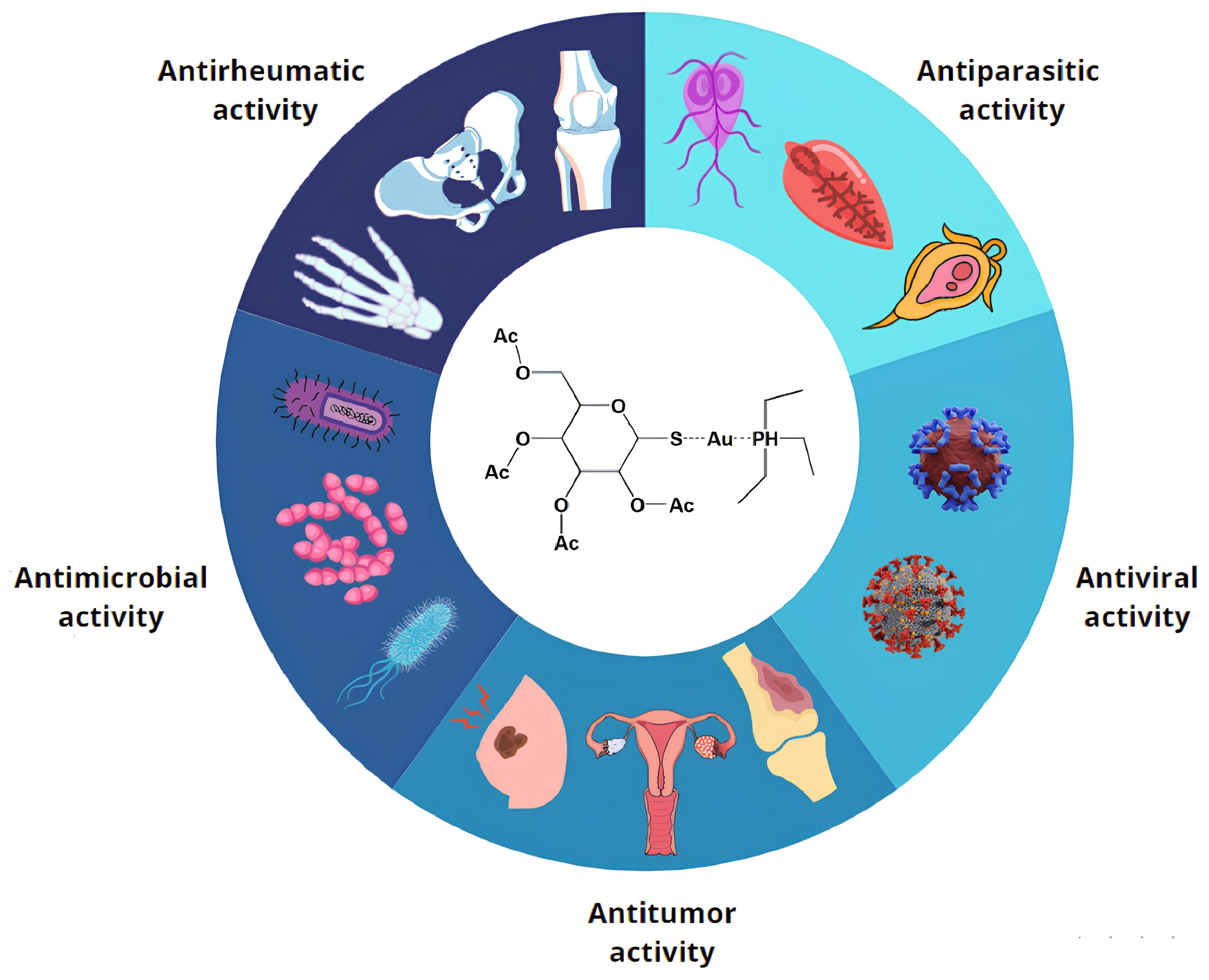
1. Introduction
2. Antimicrobial Activity of Auranofin
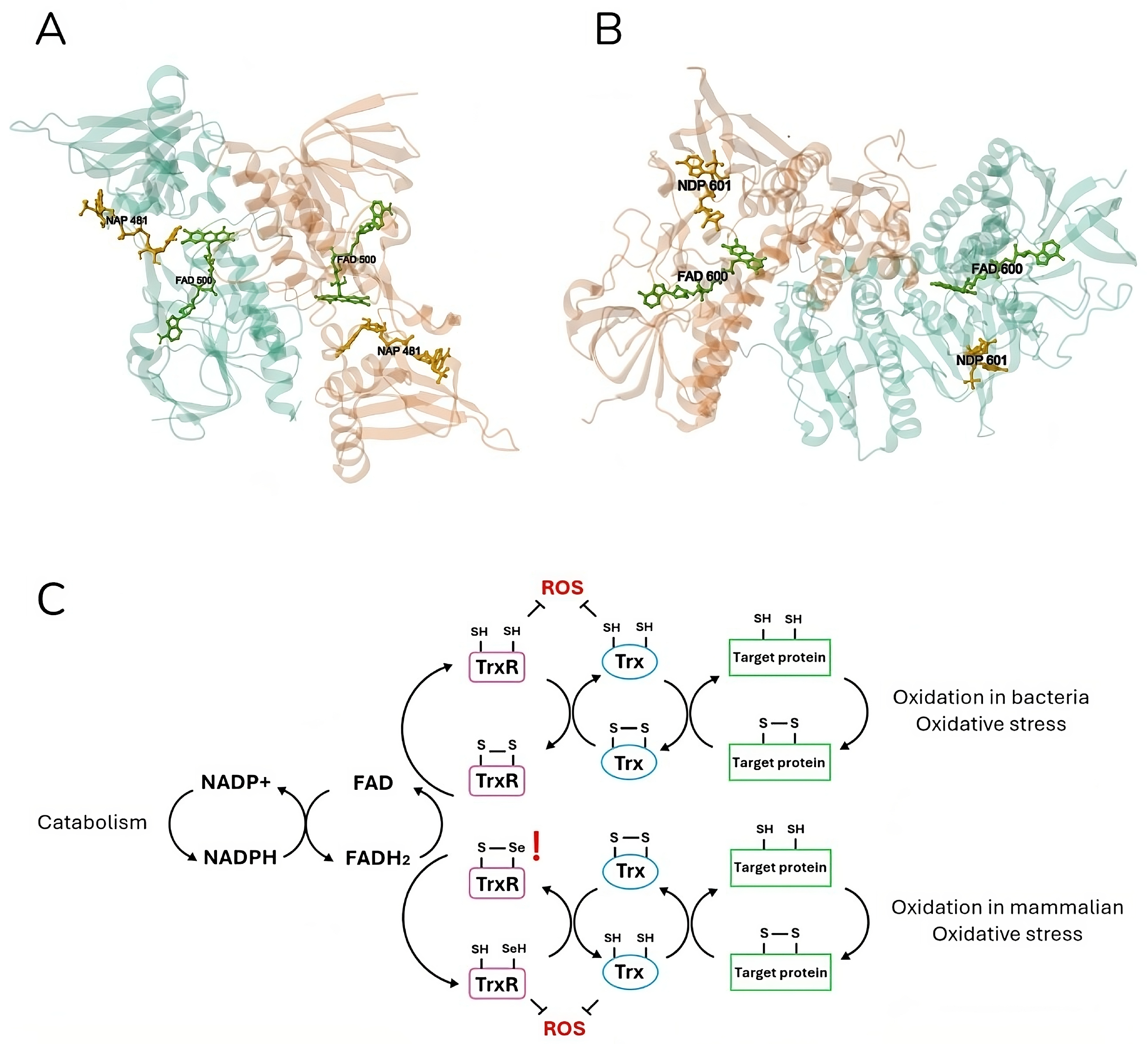
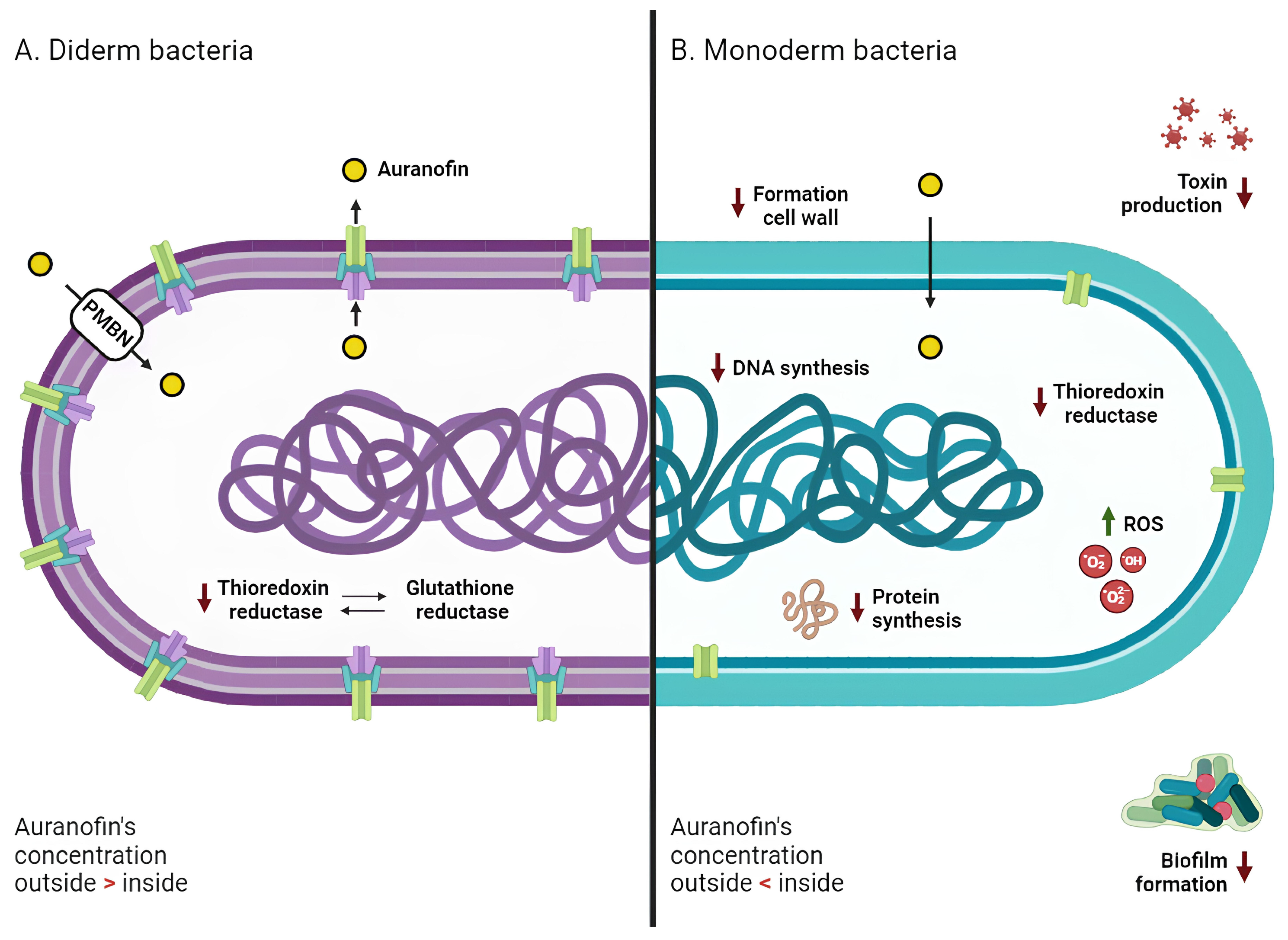
3. Mechanism of Action
3.1. Monoderm Bacteria
3.2. Diderm Bacteria
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cirri, D.; Fabbrini, M.G.; Pratesi, A.; Ciofi, L.; Massai, L.; Marzo, T.; Messori, L. The Leading Established Metal-Based Drugs: A Revisitation of Their Relevant Physico-Chemical Data. Biometals 2019, 32, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Shen, J.; Luo, Z.; Wang, F.; Min, J. Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications of the Gold Drug Auranofin. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 493, 215323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landini, I.; Massai, L.; Cirri, D.; Gamberi, T.; Paoli, P.; Messori, L.; Mini, E.; Nobili, S. Structure-Activity Relationships in a Series of Auranofin Analogues Showing Remarkable Antiproliferative Properties. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 208, 111079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannella, A.R.; Casini, A.; Gabbiani, C.; Messori, L.; Bilia, A.R.; Vincieri, F.F.; Majori, G.; Severini, C. New Uses for Old Drugs. Auranofin, a Clinically Established Antiarthritic Metallodrug, Exhibits Potent Antimalarial Effects in Vitro: Mechanistic and Pharmacological Implications. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M. Auranofin: Past to Present, and Repurposing. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, W.F.; Hart, L.; Buchanan, W.W. Auranofin. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 36, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonzogni-Desautels, K.; Ndao, M. Will Auranofin Become a Golden New Treatment Against COVID-19? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 683694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmeron, G.; Lipsky, P.E. Modulation of Human Immune Responsiveness in Vitro by Auranofin. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1982, 8, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug Repurposing: Progress, Challenges and Recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, H.; Saulnier, P.; Ramadan, A.A.; Cassisa, V.; Guillet, C.; Eveillard, M.; Umerska, A. Antibacterial Activity of Antipsychotic Agents, Their Association with Lipid Nanocapsules and Its Impact on the Properties of the Nanocarriers and on Antibacterial Activity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B.M.; Fazly Bazzaz, B.S. A Review and New Insights to Antimicrobial Action of Local Anesthetics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Antimicrobial Effects of Antipyretics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02268-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nakeeb, M.A.; Abou-Shleib, H.M.; Khalil, A.M.; Omar, H.G.; El-Halfawy, O.M. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Some Antihistaminics Belonging to Different Groups against Multi-Drug Resistant Clinical Isolates. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masadeh, M.; Mhaidat, N.; Alzoubi, K.; Al-azzam, S.; Alnasser, Z. Antibacterial Activity of Statins: A Comparative Study of Atorvastatin, Simvastatin, and Rosuvastatin. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2012, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jampilek, J. Drug Repurposing to Overcome Microbial Resistance. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 2028–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, J.E.; Stevens-Cullinane, L.; Siebenmann, L.; Hess, J. Recent Advances in the Development of Metal Complexes as Antibacterial Agents with Metal-Specific Modes of Action. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2023, 75, 102347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.; Kavanagh, K.A. Evaluation of Metal-Based Antimicrobial Compounds for the Treatment of Bacterial Pathogens. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 001363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Xia, Z. Antimicrobial Effect of Gallium Nitrate against Bacteria Encountered in Burn Wound Infections. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 52266–52273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domalaon, R.; Ammeter, D.; Brizuela, M.; Gorityala, B.K.; Zhanel, G.G.; Schweizer, F. Repurposed Antimicrobial Combination Therapy: Tobramycin-Ciprofloxacin Hybrid Augments Activity of the Anticancer Drug Mitomycin C Against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.C.S.; Imperi, F.; Minandri, F.; Visca, P. In Vitro and In Vivo Antimicrobial Activities of Gallium Nitrate against Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 5961–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Wood, T.L.; Martínez-Vázquez, M.; García-Contreras, R.; Wood, T.K. DNA-crosslinker Cisplatin Eradicates Bacterial Persister Cells. Biotech. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roder, C.; Thomson, M.J. Auranofin: Repurposing an Old Drug for a Golden New Age. Drugs R. D 2015, 15, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Pomel, S.; Latre de Late, P.; Taravaud, A.; Loiseau, P.M.; Maes, L.; Cho-Ngwa, F.; Bulman, C.A.; Fischer, C.; Sakanari, J.A.; et al. Repurposing Auranofin and Evaluation of a New Gold(I) Compound for the Search of Treatment of Human and Cattle Parasitic Diseases: From Protozoa to Helminth Infections. Molecules 2020, 25, 5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsonage, D.; Sheng, F.; Hirata, K.; Debnath, A.; McKerrow, J.H.; Reed, S.L.; Abagyan, R.; Poole, L.B.; Podust, L.M. X-ray Structures of Thioredoxin and Thioredoxin Reductase from Entamoeba Histolytica and Prevailing Hypothesis of the Mechanism of Auranofin Action. J. Struct. Biol. 2016, 194, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peroutka-Bigus, N.; Bellaire, B.H. Antiparasitic Activity of Auranofin against Pathogenic Naegleria Fowleri. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2019, 66, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manhas, R.; Gowri, V.S.; Madhubala, R. Leishmania Donovani Encodes a Functional Selenocysteinyl-tRNA Synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1203–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelucci, F.; Sayed, A.A.; Williams, D.L.; Boumis, G.; Brunori, M.; Dimastrogiovanni, D.; Miele, A.E.; Pauly, F.; Bellelli, A. Inhibition of Schistosoma Mansoni Thioredoxin-Glutathione Reductase by Auranofin: Structural and Kinetic Aspects. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 28977–28985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejman-Yarden, N.; Miyamoto, Y.; Leitsch, D.; Santini, J.; Debnath, A.; Gut, J.; McKerrow, J.H.; Reed, S.L.; Eckmann, L. A Reprofiled Drug, Auranofin, Is Effective against Metronidazole-Resistant Giardia Lamblia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.S.; Shytaj, I.L.; Giron, L.B.; Obermaier, B.; Della Libera, E.; Galinskas, J.; Dias, D.; Hunter, J.; Janini, M.; Gosuen, G.; et al. Potential Impact of the Antirheumatic Agent Auranofin on Proviral HIV-1 DNA in Individuals under Intensified Antiretroviral Therapy: Results from a Randomised Clinical Trial. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haß, C.; Belz, K.; Schoeneberger, H.; Fulda, S. Sensitization of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells for LCL161-Induced Cell Death by Targeting Redox Homeostasis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 105, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landini, I.; Lapucci, A.; Pratesi, A.; Massai, L.; Napoli, C.; Perrone, G.; Pinzani, P.; Messori, L.; Mini, E.; Nobili, S. Selection and Characterization of a Human Ovarian Cancer Cell Line Resistant to Auranofin. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 96062–96078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; McGrath, K.L.; Di Trapani, G.; Charoentong, P.; Shah, F.; King, M.M.; Clarke, F.M.; Tonissen, K.F. The Thioredoxin System in Breast Cancer Cell Invasion and Migration. Redox Biol. 2016, 8, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massai, L.; Cirri, D.; Marzo, T.; Messori, L. Auranofin and Its Analogs as Prospective Agents for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steers, G.J.; Chen, G.Y.; O’Leary, B.R.; Du, J.; Van Beek, H.; Cullen, J.J. Auranofin and Pharmacologic Ascorbate as Radiomodulators in the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance: A Rundown of a Global Crisis. IDR 2018, 11, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, M.A.; Brown, E.D. Drug Repurposing for Antimicrobial Discovery. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangamani, S.; Mohammad, H.; Abushahba, M.F.N.; Sobreira, T.J.P.; Hedrick, V.E.; Paul, L.N.; Seleem, M.N. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action of Auranofin against Multi-Drug Resistant Bacterial Pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silhavy, T.J.; Kahne, D.; Walker, S. The Bacterial Cell Envelope. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megrian, D.; Taib, N.; Witwinowski, J.; Beloin, C.; Gribaldo, S. One or Two Membranes? Diderm Firmicutes Challenge the Gram-positive/Gram-negative Divide. Mol. Microbiol. 2020, 113, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson-Rosario, S.; Cowart, D.; Myers, A.; Tarrien, R.; Levine, R.L.; Scott, R.A.; Self, W.T. Auranofin Disrupts Selenium Metabolism in Clostridium Difficile by Forming a Stable Au-Se Adduct. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 14, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdelKhalek, A.; Abutaleb, N.S.; Mohammad, H.; Seleem, M.N. Antibacterial and Antivirulence Activities of Auranofin against Clostridium Difficile. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbut, M.B.; Vilchèze, C.; Luo, X.; Hensler, M.E.; Guo, H.; Yang, B.; Chatterjee, A.K.; Nizet, V.; Jacobs, W.R.; Schultz, P.G.; et al. Auranofin Exerts Broad-Spectrum Bactericidal Activities by Targeting Thiol-Redox Homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, B.B.; RajaMuthiah, R.; Souza, A.C.R.; Eatemadpour, S.; Rossoni, R.D.; Santos, D.A.; Junqueira, J.C.; Rice, L.B.; Mylonakis, E. Inhibition of Bacterial and Fungal Pathogens by the Orphaned Drug Auranofin. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.; Karge, B.; Misgeld, R.; Prokop, A.; Brönstrup, M.; Ott, I. Biscarbene Gold(i) Complexes: Structure–Activity-Relationships Regarding Antibacterial Effects, Cytotoxicity, TrxR Inhibition and Cellular Bioavailability. Med. Chem. Commun. 2017, 8, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzo, T.; Cirri, D.; Pollini, S.; Prato, M.; Fallani, S.; Cassetta, M.I.; Novelli, A.; Rossolini, G.M.; Messori, L. Auranofin and Its Analogues Show Potent Antimicrobial Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens: Structure-Activity Relationships. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 2448–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, P.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, L.; Luo, Z.; Wu, Y. Synergistic Microbicidal Effect of Auranofin and Antibiotics Against Planktonic and Biofilm-Encased S. Aureus and E. Faecalis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruth, M.M.; van Rossum, M.; Koeken, V.A.C.M.; Pennings, L.J.; Svensson, E.M.; Ruesen, C.; Bowles, E.C.; Wertheim, H.F.L.; Hoefsloot, W.; van Ingen, J. Auranofin Activity Exposes Thioredoxin Reductase as a Viable Drug Target in Mycobacterium Abscessus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00449-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokai, Y.; Jurkowicz, B.; Fernández-Gallardo, J.; Zakirkhodjaev, N.; Sanaú, M.; Muth, T.R.; Contel, M. Auranofin and Related Heterometallic Gold(I)-Thiolates as Potent Inhibitors of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacterial Strains. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 138, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. The Thioredoxin Antioxidant System. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguinagalde, L.; Díez-Martínez, R.; Yuste, J.; Royo, I.; Gil, C.; Lasa, Í.; Martín-Fontecha, M.; Marín-Ramos, N.I.; Ardanuy, C.; Liñares, J.; et al. Auranofin Efficacy against MDR Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus Infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 2608–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yang, X.; Yan, M. Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationship Study of Antimicrobial Auranofin against ESKAPE Pathogens. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7751–7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.A.; Leitão, J.H.; Silva, R.A.L.; Belo, D.; Santos, I.C.; Guerreiro, J.F.; Martins, M.; Fontinha, D.; Prudêncio, M.; Almeida, M.; et al. On the Path to Gold: Monoanionic Au Bisdithiolate Complexes with Antimicrobial and Antitumor Activities. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 202, 110904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.-I.; Eom, Y.-B. Repurposing Auranofin to Combat Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Biofilms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassetta, M.I.; Marzo, T.; Fallani, S.; Novelli, A.; Messori, L. Drug Repositioning: Auranofin as a Prospective Antimicrobial Agent for the Treatment of Severe Staphylococcal Infections. Biometals 2014, 27, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, B.N.; Myers, J.N.; Muruato, L.A.; Tapia, D.; Torres, A.G. Evaluating New Compounds to Treat Burkholderia Pseudomallei Infections. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maydaniuk, D.T.; Martens, B.; Iqbal, S.; Hogan, A.M.; Lorente Cobo, N.; Motnenko, A.; Truong, D.; Liyanage, S.H.; Yan, M.; Prehna, G.; et al. The Mechanism of Action of Auranofin Analogs in B. Cenocepacia Revealed by Chemogenomic Profiling. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0320123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owings, J.P.; McNair, N.N.; Mui, Y.F.; Gustafsson, T.N.; Holmgren, A.; Contel, M.; Goldberg, J.B.; Mead, J.R. Auranofin and N-Heterocyclic Carbene Gold-Analogs Are Potent Inhibitors of the Bacteria Helicobacter Pylori. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkashif, A.; Seleem, M.N. Investigation of Auranofin and Gold-Containing Analogues Antibacterial Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.-I.; Eom, Y.-B. Antibiofilm and Antibacterial Activities of Repurposing Auranofin against Bacteroides Fragilis. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, A.; Ndao, M.; Reed, S.L. Reprofiled Drug Targets Ancient Protozoans: Drug Discovery for Parasitic Diarrheal Diseases. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntz, A.N.; Davioud-Charvet, E.; Sayed, A.A.; Califf, L.L.; Dessolin, J.; Arnér, E.S.J.; Williams, D.L. Thioredoxin Glutathione Reductase from Schistosoma Mansoni: An Essential Parasite Enzyme and a Key Drug Target. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.H.; Arscott, L.D.; Müller, S.; Lennon, B.W.; Ludwig, M.L.; Wang, P.; Veine, D.M.; Becker, K.; Schirmer, R.H. Thioredoxin Reductase: Two Modes of Catalysis Have Evolved. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 6110–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waksman, G.; Krishna, T.S.R.; Williams, C.H.; Kuriyan, J. Crystal Structure of Escherichia Coli Thioredoxin Reductase Refined at 2 Å Resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 236, 800–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandalova, T.; Zhong, L.; Lindqvist, Y.; Holmgren, A.; Schneider, G. Three-Dimensional Structure of a Mammalian Thioredoxin Reductase: Implications for Mechanism and Evolution of a Selenocysteine-Dependent Enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9533–9538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustacich, D.; Powis, G. Thioredoxin Reductase. Biochem. J. 2000, 346 Pt 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccoccia, F.; Angelucci, F.; Boumis, G.; Carotti, D.; Desiato, G.; Miele, A.; Bellelli, A. Thioredoxin Reductase and Its Inhibitors. CPPS 2014, 15, 621–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Vlamis-Gardikas, A.; Kandasamy, K.; Zhao, R.; Gustafsson, T.N.; Engstrand, L.; Hoffner, S.; Engman, L.; Holmgren, A. Inhibition of Bacterial Thioredoxin Reductase: An Antibiotic Mechanism Targeting Bacteria Lacking Glutathione. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eweas, A.F.; Allam, G. Targeting Thioredoxin Glutathione Reductase as a Potential Antischistosomal Drug Target. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2018, 225, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, M.A.; Holman, M.A.; Self, W.T. Inhibition of Selenoprotein Synthesis Is Not the Mechanism by Which Auranofin Inhibits Growth of Clostridioides Difficile. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Lu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, L.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, G.; Dong, W.; Tan, C.; et al. Auranofin Has Advantages over First-Line Drugs in the Treatment of Severe Streptococcus Suis Infections. Antibiotics 2020, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharmalingam, N.; Ribeiro, N.Q.; da Silva, D.L.; Naik, M.T.; Cruz, L.I.; Kim, W.; Shen, S.; Dos Santos, J.D.; Ezikovich, K.; D’Agata, E.M.; et al. Auranofin Is an Effective Agent against Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, L.; Mylonakis, E.; Fuchs, B.B. Thioredoxin Reductase Is a Valid Target for Antimicrobial Therapeutic Development Against Gram-Positive Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 663481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangamani, S.; Mohammad, H.; Abushahba, M.F.N.; Sobreira, T.J.P.; Seleem, M.N. Repurposing Auranofin for the Treatment of Cutaneous Staphylococcal Infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An Emergent Form of Bacterial Life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciofu, O.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Høiby, N. Tolerance and Resistance of Microbial Biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, F.; Luo, Z.; Wu, Y. Antibiofilm Efficacy of the Gold Compound Auranofin on Dual Species Biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus and Candida sp. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, J.; Hobbs, G.; Nakouti, I. Persister Cells: Formation, Resuscitation and Combative Therapies. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 5899–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetri, S. The Culmination of Multidrug-Resistant Efflux Pumps vs. Meager Antibiotic Arsenal Era: Urgent Need for an Improved New Generation of EPIs. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1149418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanjan, P.; Bose, V. Efflux-Mediated Multidrug Resistance in Critical Gram-Negative Bacteria and Natural Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Curr. Drug Res. Rev. 2024, 16, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloke, C.; Achilonu, I. Coping with the ESKAPE Pathogens: Evolving Strategies, Challenges and Future Prospects. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 175, 105963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, R.S.K.; Mistry, V.; Dholaria, M.; Rana, A.; Devgon, I.; Ali, I.; Iqbal, J.; Eldin, S.M.; Mohammad Said Al-Tawaha, A.R.; Bawazeer, S.; et al. Overcoming Mycobacterium tuberculosis Drug Resistance: Novel Medications and Repositioning Strategies. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 32244–32257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.Q.; Heo, B.E.; Jeon, S.; Ash, A.; Lee, H.; Moon, C.; Jang, J. Exploring Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms in Mycobacterium Abscessus for Enhanced Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1331508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auda, I.G.; Ali Salman, I.M.; Odah, J.G. Efflux Pumps of Gram-Negative Bacteria in Brief. Gene Rep. 2020, 20, 100666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coscione, F.; Zineddu, S.; Vitali, V.; Fondi, M.; Messori, L.; Perrin, E. The Many Lives of Auranofin: How an Old Anti-Rheumatic Agent May Become a Promising Antimicrobial Drug. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070652
Coscione F, Zineddu S, Vitali V, Fondi M, Messori L, Perrin E. The Many Lives of Auranofin: How an Old Anti-Rheumatic Agent May Become a Promising Antimicrobial Drug. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(7):652. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070652
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoscione, Francesca, Stefano Zineddu, Valentina Vitali, Marco Fondi, Luigi Messori, and Elena Perrin. 2024. "The Many Lives of Auranofin: How an Old Anti-Rheumatic Agent May Become a Promising Antimicrobial Drug" Antibiotics 13, no. 7: 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070652
APA StyleCoscione, F., Zineddu, S., Vitali, V., Fondi, M., Messori, L., & Perrin, E. (2024). The Many Lives of Auranofin: How an Old Anti-Rheumatic Agent May Become a Promising Antimicrobial Drug. Antibiotics, 13(7), 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070652








