Antimicrobial Properties of Newly Developed Silver-Enriched Red Onion–Polymer Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
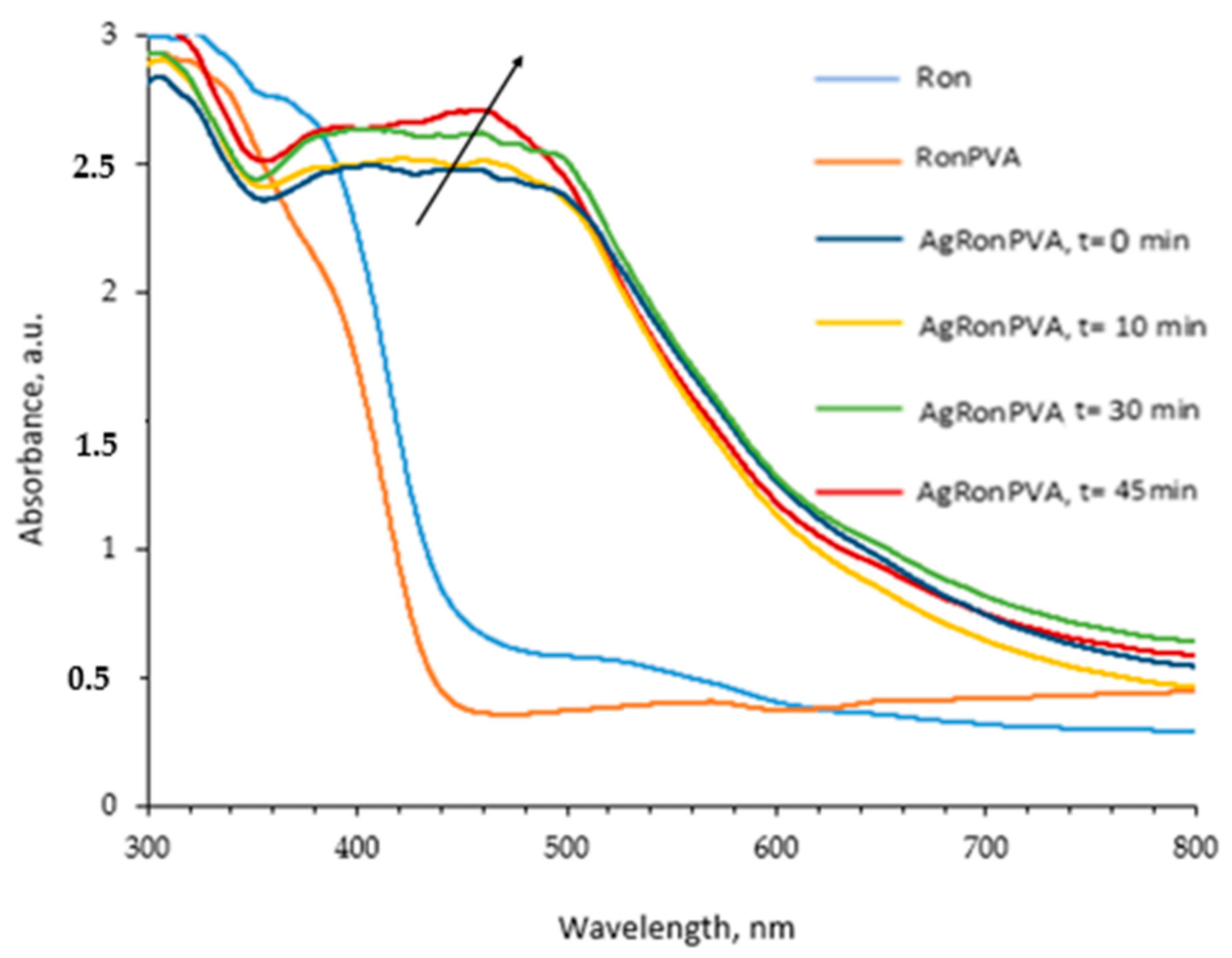
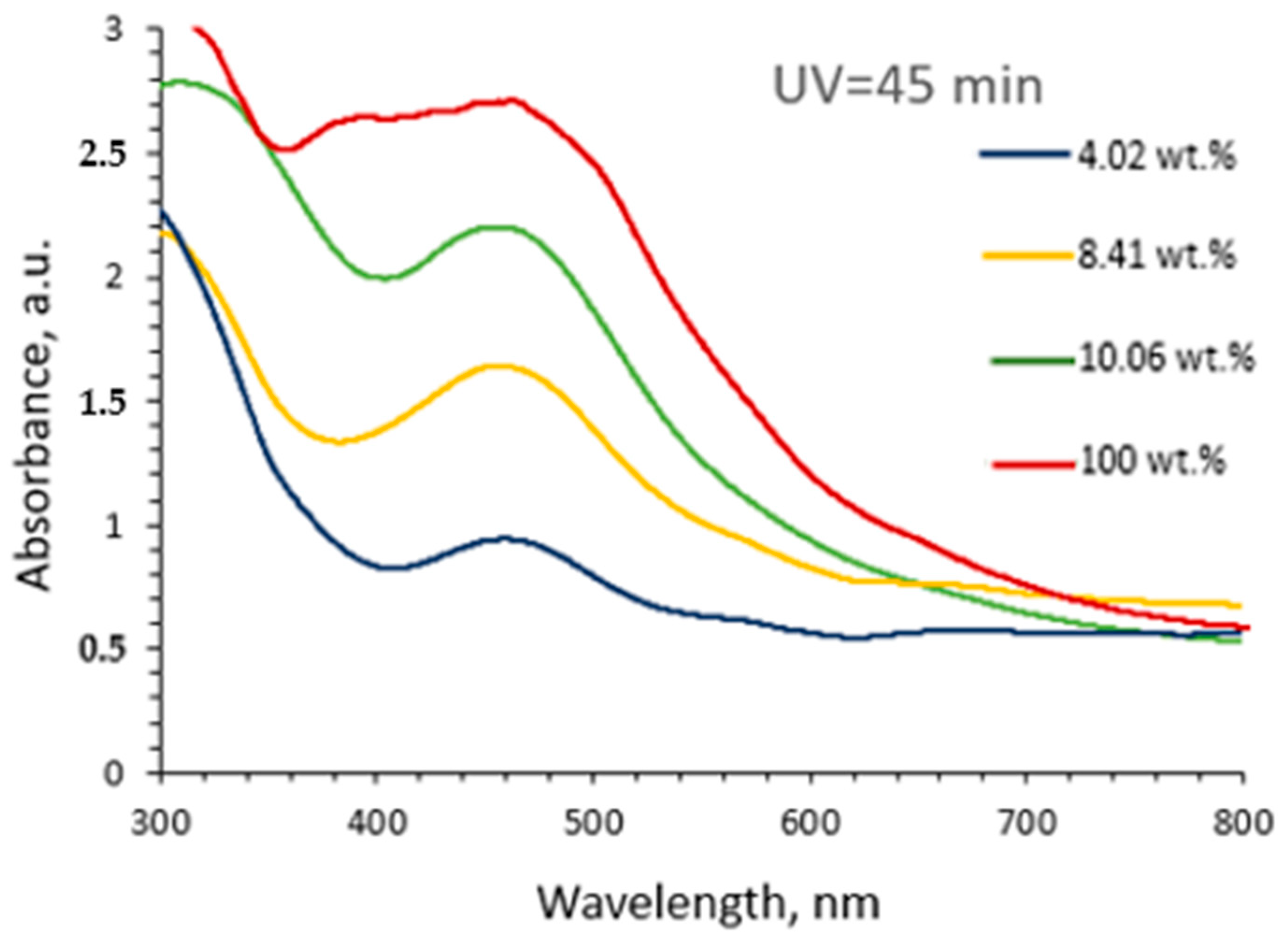
2.1. Optical Properties of Red Onion Peel–PVA Gels Containing Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles
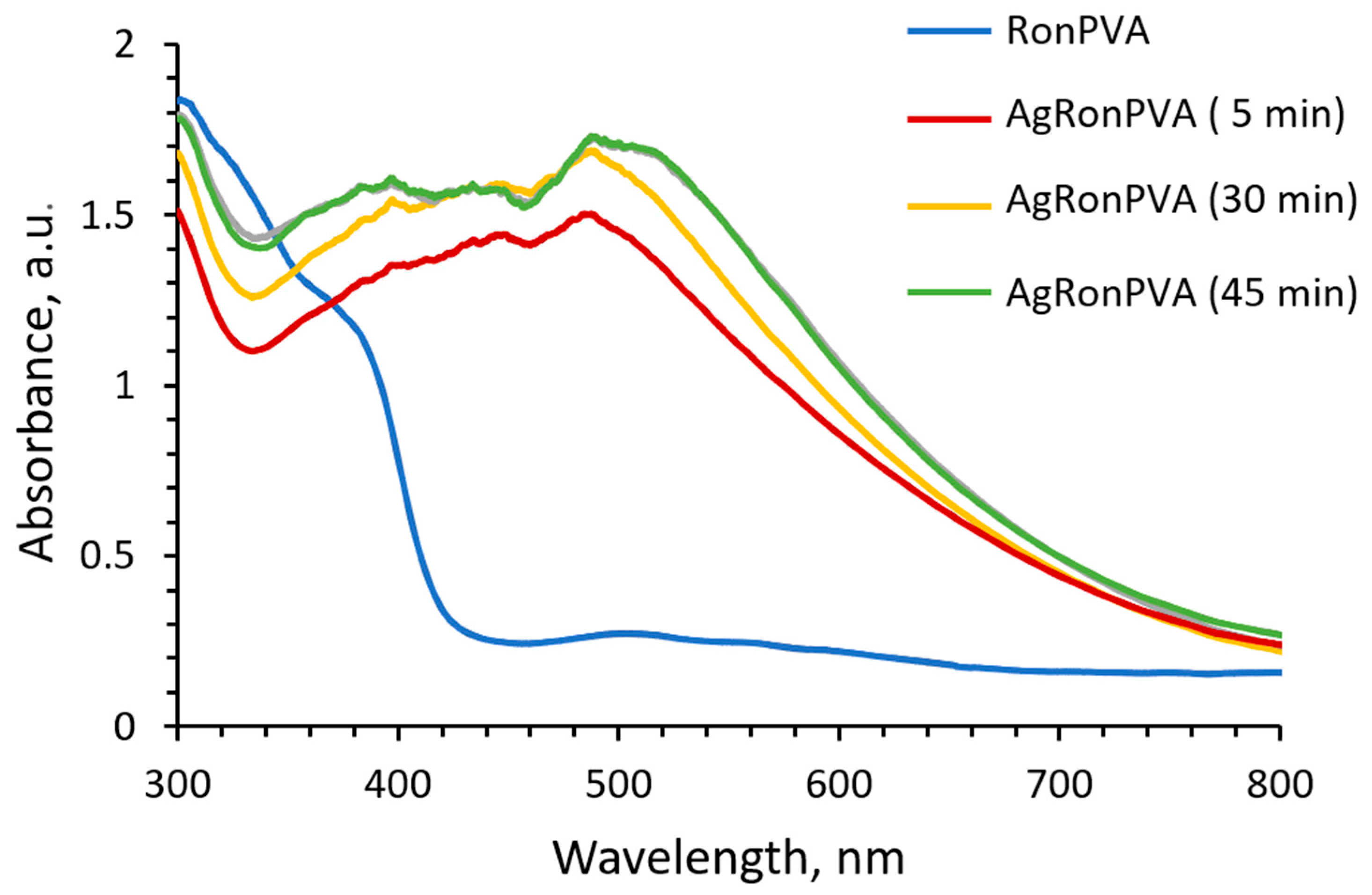
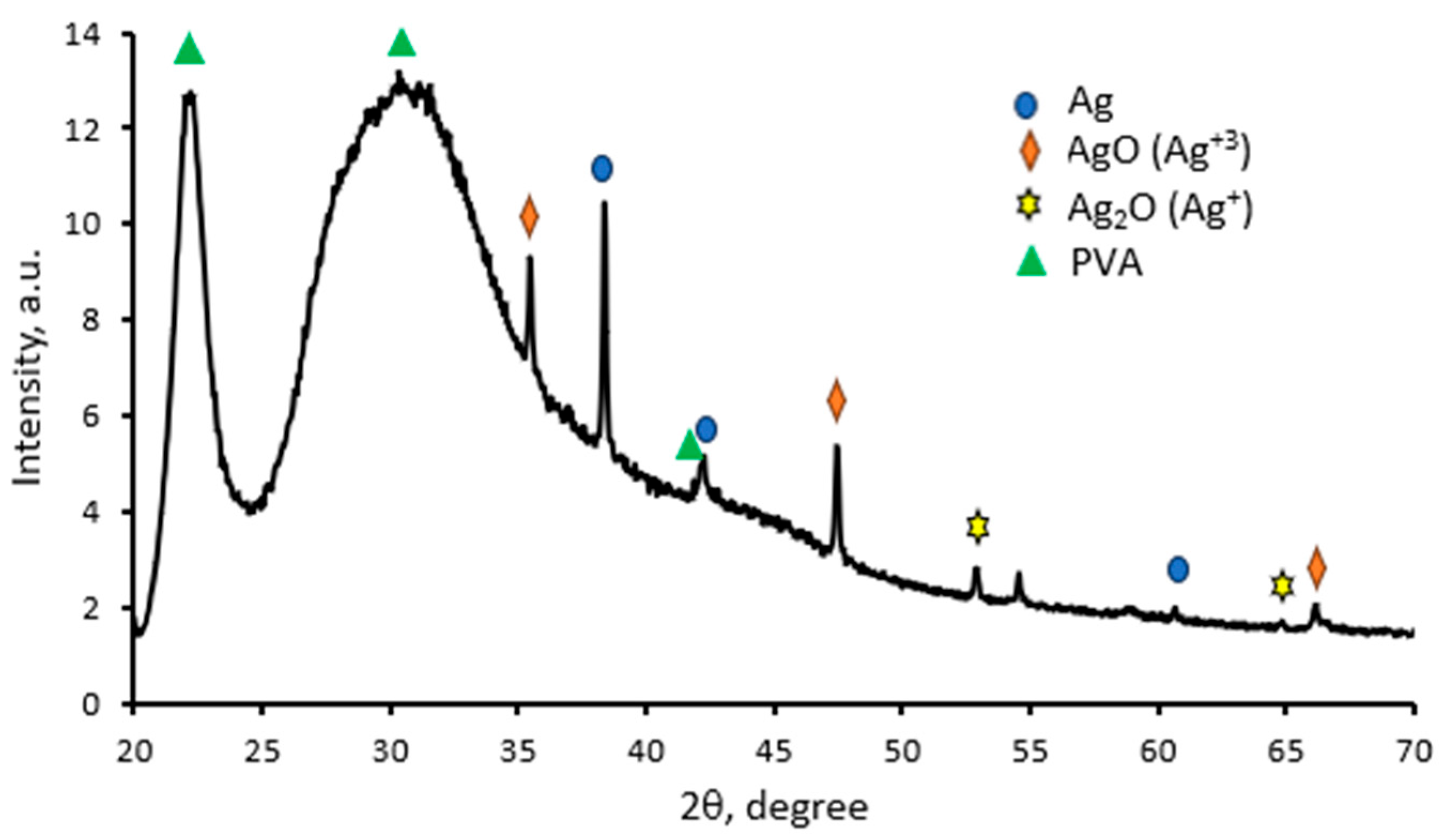
2.2. Optical Properties of Red Onion Peel–PVA Films Containing Silver Nanoparticles
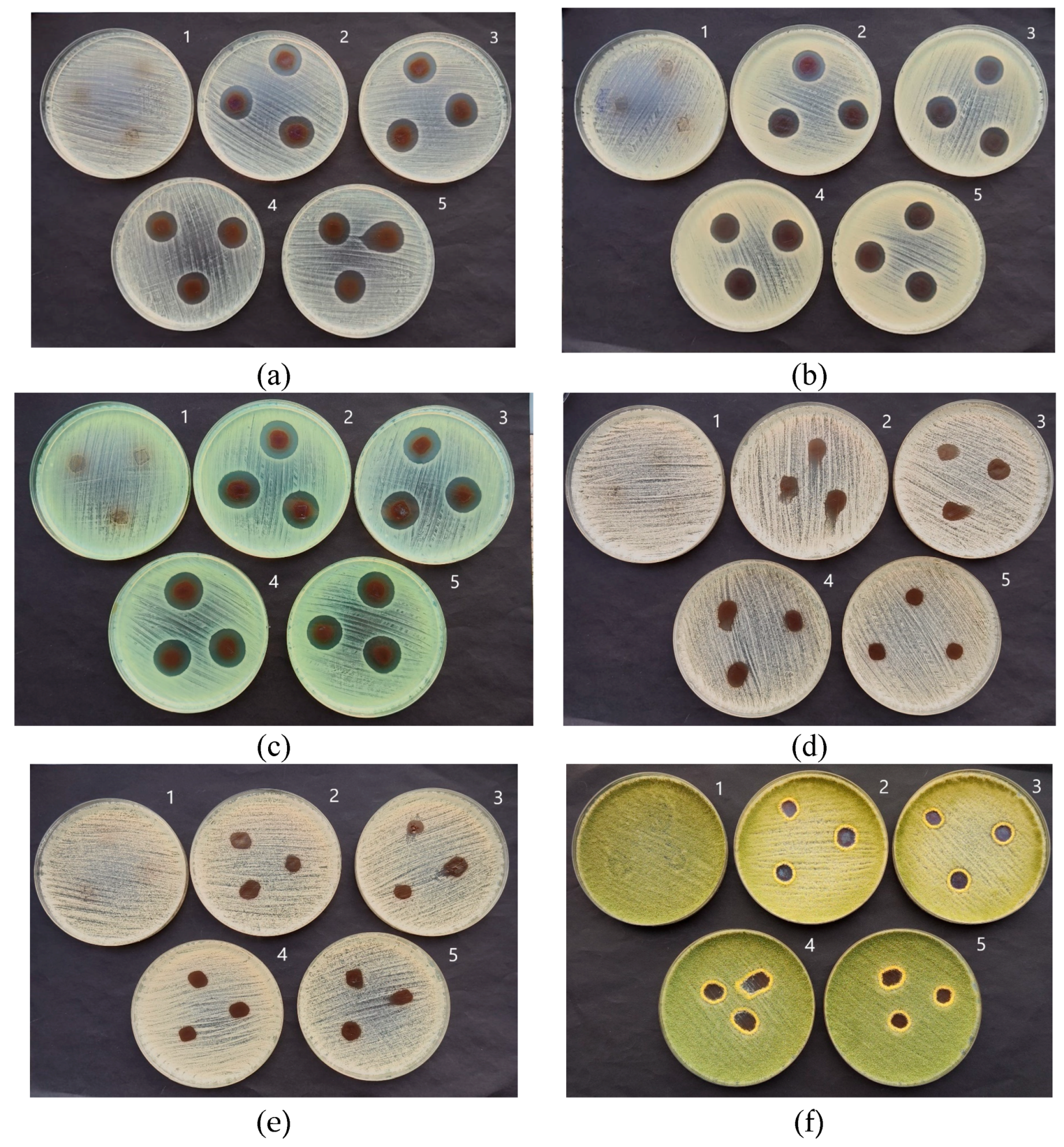
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity of the AgRonPVA Films Containing Silver Nanoparticles
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of AgRonPVA Gel
3.2. Synthesis of AgNPs in RonPVA Gels
3.3. Preparation of AgRonPVA Films
3.4. Characterization of the AgRonPVA Gels and Films
3.5. Microorganisms and Inoculum Preparation
3.6. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of the AgRonPVA Films Containing Silver Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sivam, G.P. Protection against Helicobacter pylori and other bacterial infections by garlic. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 1106S–1108S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, M.M. Plant products as antimicrobial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassagne, F.; Samarakoon, T.; Porras, G.; Lyles, J.T.; Dettweiler, M.; Marquez, L.; Salam, A.M.; Shabih, S.; Farrokhi, D.R.; Quave, C.L. A Systematic Review of Plants with Antibacterial Activities: A Taxonomic and Phylogenetic Perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 586548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzotti, V. The analysis of onion and garlic. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1112, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.L.; Dai, D.H.; Hu, W.L. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the essential oil from onion (Allium cepa L.). Food Control 2013, 30, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, M.Y.; Choi, S.D.; Kahng, G.G.; Nam, S.H.; Sung, N.J. Antimutagenic, antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of ethyl acetate extracts from white, yellow and red onions. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, N.A.; Pareek, S.; Benkeblia, N.; Xiao, J. Onion (Allium cepa L.) bioactives: Chemistry, pharmacotherapeutic functions, and industrial applications. Food Front. 2022, 3, 380–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, F.A.; Takaishi, Y.; Shirotori, M.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Shibata, H.; Higuti, T.; Tadokoro, T.; Takeuchi, M. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of quercetin oxidation products from yellow onion (Allium cepa) skin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3551–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škerget, M.; Majhenič, L.; Bezjak, M.; Knez, Ž. Antioxidant, Radical Scavenging and Antimicrobial Activities of Red Onion (Allium cepa L) Skin and Edible Part Extracts. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2009, 23, 435–444. [Google Scholar]
- Roldán, E.; Sánchez-Moreno, C.; de Ancos, B.; Cano, M.P. Characterisation of onion (Allium cepa L.) by-products as food ingredients with antioxidant and antibrowning properties. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Mahato, N.; Nile, S.H.; Lee, E.T.; Lee, Y.R. Economical and environmentally-friendly approaches for usage of onion (Allium cepa L.) waste. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3354–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, B.; Arias Calvo, A.; Gullón, B.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T.; González-García, S. Production of flavonol quercetin and fructooligosaccharides from onion (Allium cepa L.) waste: An environmental life cycle approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 392, 123772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celano, R.; Docimo, T.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Gazzerro, P.; Tucci, M.; Di Sanzo, R.; Carabetta, S.; Campone, L.; Russo, M.; Rastrelli, L. Onion Peel: Turning a Food Waste into a Resource. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Gomes, D.; Esteruelas, G.; Bonilla, L.; Lopez-Machado, A.L.; Galindo, R.; Cano, A.; Espina, M.; Ettcheto, M.; Camins, A.; et al. Metal-Based Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agents: An Overview. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.; Chu, C.H. The Antibacterial Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Application in Dentistry. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shanmuganathan, R.; Karuppusamy, I.; Saravanan, M.; Muthukumar, H.; Ponnuchamy, K.; Ramkumar, V.S.; Pugazhendhi, A. Synthesis of Silver nanoparticles and their biomedical applications—A comprehensive review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2650–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisan, C.M.; Mocan, T.; Manolea, M.; Lasca, L.I.; Tăbăran, F.-A.; Mocan, L. Review on Silver Nanoparticles as a Novel Class of Antibacterial Solutions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A Review of the Antibacterial Effects of Silver Nanomaterials and Potential Implications for Human Health and the Environment. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Yasmin, R.; Asif, R.; Ambreen, A.; Mustafa, M.; Umbreen, S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs), Structural Characterization, and their Antibacterial Potential. Dose Response 2022, 20, 15593258221088709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen, A.; Rao, R.A.K. A review on biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biocidal properties. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.K.; Jena, B.; Biswal, B.; Pradhan, A.K.; Arakha, M.; Acharya, S.; Acharya, L. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Eugenia roxburghii DC. extract and activity against biofilm-producing bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, H.S.T.S.H.; Asseri, S.N.A.R.M.; Mohamad, W.N.K.W.; Kan, S.-Y.; Azmi, A.A.; Julius, F.S.Y.; Chia, P.W. Green synthesis, characterization and applications of silver nanoparticle mediated by the aqueous extract of red onion peel. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, M.F.; Keskin, C.; Baran, A.; Hatipoğlu, A.; Yildiztekin, M.; Küçükaydin, S.; Kurt, K.; Hoşgören, H.; Sarker, M.M.R.; Sufianov, A.; et al. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Allium cepa L. Peel Extract, Their Antioxidant, Antipathogenic, and Anticholinesterase Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puišo, J.; Paškevičius, A.; Žvirgždas, J.; Dimitrova, T.L.; Litvakas, A.; Adliene, D. Application of Red Onion Peel Extract for Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in Hydrogels Exhibiting Antimicrobial Properties. Gels 2023, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.-M.; Liu, X. Advancing biomaterials of human origin for tissue engineering. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 53, 86–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, K.; Fabra, G.T.; Bozkurt, Y.; Pandit, A. Bioactive potential of natural biomaterials: Identification, retention and assessment of biological properties. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, A.B.; Kim, D.; Kim, D.; Park, H.; Lee, S.-H. Engineering and functionalization of gelatin biomaterials: From cell culture to medical applications. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2020, 26, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauzi, M.; Lokanathan, Y.; Aminuddin, B.; Ruszymah, B.; Chowdhury, S. Ovine tendon collagen: Extraction, characterisation and fabrication of thin films for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulkiflee, I.; Fauzi, M.B. Gelatin-Polyvinyl Alcohol Film for Tissue Engineering: A Concise Review. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djagny, K.B.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S. Gelatin: A valuable protein for food and pharmaceutical industries. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2001, 41, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidenko, N.; Schuster, C.F.; Bax, D.V.; Farndale, R.W.; Hamaia, S.; Best, S.M.; Cameron, R.E. Evaluation of cell binding to collagen and gelatin: A study of the effect of 2D and 3D architecture and surface chemistry. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.R.; Varaprasad, K.; Sadiku, R.; Ramam, K.; Reddy, G.V.S.; Raju, K.M.; Reddy, N.S. Development of gelatin based inorganic nanocomposite hydrogels for inactivation of bacteria. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2013, 23, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandri, A.; Nordin, A.; Hwei, N.M.; Chin, K.-Y.; Abd Aziz, I.; Fauzi, M.B. Natural 3D-Printed Bioinks for Skin Regeneration and Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Liu, W.; Cui, L.; Cao, Y. Tissue engineering of blood vessel. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2007, 11, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutolf, M.; Hubbell, J. Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.; Netravali, A.N. A composting study of membrane-like polyvinyl alcohol based resins and nanocomposites. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barui, A. Polymeric Gels; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 55–90. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar, M.S.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Jahan, Z.; Ahmad, T.; Hussain, A. Preparation and characterization of PVA/nanocellulose/Ag nanocomposite films for antimicrobial food packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gaikwad, K.K.; Lee, Y.S. Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of polyvinyl alcohol bio composite films containing seaweed extracted cellulose nano-crystal and basil leaves extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannat, S.; Jethwa, T.; Sawant, K.; Chawla, S. PVA-Gelatin films incorporated with tomato pulp: A potential primary food packaging film. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Meshram, J.; Koli, V.; Phadatare, M.R.; Pawar, S. Anti-microbial surfaces: An approach for deposition of ZnO nanoparticles on PVA-Gelatin composite film by screen printing technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, R.; Cao, J.; Jiang, X.; Rogachev, A.V. Prolonged release of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride from chitosan/gelatin/poly (vinyl alcohol) composite films. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, D.; Gong, W.; Zheng, A.; Guan, Y. Hydrogen-Bond Assembly of Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Polyhexamethylene Guanidine for Nonleaching and Transparent Antimicrobial Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 37535–37543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutha, Y.; Pathak, J.L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, X. Antibacterial and wound healing properties of chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol)/zinc oxide beads (CS/PVA/ZnO). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganthi, S.; Vignesh, S.; Sundar, J.K.; Raj, V. Fabrication of PVA polymer films with improved antibacterial activity by fine-tuning via organic acids for food packaging applications. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ren, Y.-Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Preparation and antibacterial activities of Ag/Ag+/Ag3+ nanoparticle composites made by pomegranate (Punica granatum) rind extract. Results Phys. 2016, 6, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaltianos, N.G.; Perrie, W.; Romani, S.; Potter, R.J.; Dearden, G.; Watkins, K.G. Polymer-nanoparticle composites composed of PEDOT: PSS and nanoparticles of Ag synthesised by laser ablation. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.O.; Ogawa, T.; Ono, K. Use of ozone to prepare silver oxides. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 2033–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajti, C.L.; Sattari, R.; Chichkov, B.N.; Barcikowski, S. Gram scale synthesis of pure ceramic nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid. J. Phys. Chem. 2010, 114, 2421–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.S.; Zaman, Q.; da Costa, K.Q.; Dmitriev, V.; Pandoli, O.; Fontes, G.; Del Rosso, T. Limits of the Effective Medium Theory in Particle Amplified Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy Biosensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šileikaitė, A.; Prosyčevas, I.; Puišo, J.; Juraitis, A.; Guobienė, A. Analysis of Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Chemical Reduction of Silver Salt Solution. Mater. Sci. 2006, 12, 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Tziolas, N.; Ordoudi, S.A.; Tavlaridis, A.; Karyotis, K.; Zalidis, G.; Mourtzinos, I. Rapid Assessment of Anthocyanins Content of Onion Waste through Visible-Near-Short-Wave and Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning Techniques. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdieh, M.; Zo-lanvari, A.; Azimee, A.S.; Mahdieh, M. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Spirulina platen-sis. Sci. Iran. 2012, 19, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The “MiePlot” Software, Version 4.6; Philip Laven: Bradenton, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: http://www.philiplaven.com/mieplot.htm (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Mostafa, A.M.; Menazea, A.A. Polyvinyl Alcohol/Silver nanoparticles film prepared via pulsed laser ablation: An eco-friendly nano-catalyst for 4-nitrophenol degradation. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1212, 128125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Jiao, C.; Peng, X.; Chen, Y.-N.; Chen, Y.; He, C.; Liu, R.; Wang, H. Super-strong and tough poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(acrylic acid) hydrogels reinforced by hydrogen bonding. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 8105–8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, A.; Bari, L.; Salem, K.S. Morphology, Thermal Stability, Electrical, and Mechanical Properties of Graphene Incorporated Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Gelatin Nanocomposites. Int. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 6, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, M.M.; Taha, E.O.; AbdelReheem, A.M. Nitrogen plasma effect on the structural, thermal, and dynamic mechanical properties of PVA/starch/graphene oxide nanocomposite. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aji, M.M.; Bijaksana, S.; Khairurrijal, K.; Abdullah, M. A General Formula for Ion Concentration-Dependent Electrical Conductivities in Polymer Electrolytes. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 9, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.A.M.; Ben Ahmed, A.; Al-Ahmed, H.I. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles for reducing the damage to sperm parameters in diabetic compared to metformin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2256, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Prathna, T.C.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Raichur, A.M.; Mukherjee, A. Biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Citrus limon (lemon) aqueous extract and theoretical prediction of particle size. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 82, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XRD Crystallite (Grain) Size Calculator (Scherrer Equation)—InstaNANO. Available online: https://instanano.com/all/characterization/xrd/crystallite-size/ (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Santhosh, A.; Theertha, V.; Prakash, P.; Chandran, S. From waste to a value added product: Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from onion peels together with its diverse applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 46, 4460–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraheni, I.P.A.; Widyastika, D.; Maulida, S.; Susilowati, H.; Jonarta, A.L. Effect of Red Onion (Allium cepa var ascalonicum) Skin Ethanolic Extract on the Motility and the Adhesion Index of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Macrophage Phagocytosis Index. Maj. Obat Tradis. 2019, 24, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genatrika, E.; Sundhani, E.; Oktaviana, M.I. Gel Potential of Red Onion (Allium cepa L.) Ethanol Extract as Antifungal Cause Tinea Pedis. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2020, 12, S733–S736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Albandary, A. Phenolic compounds content, antioxdidant, antibacterial and antifungal activities of red onions skin. Iraq J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 54, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, R.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y. Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3311–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Rong, K.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, R. Size-dependent antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles against oral anaerobic pathogenic bacteria. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivask, A.; Elbadawy, A.; Kaweeteerawat, C.; Boren, D.; Fischer, H.; Ji, Z.; Chang, C.H.; Liu, R.; Tolaymat, T.; Telesca, D.; et al. Toxicity mechanisms in Escherichia coli vary for silver nanoparticles and differ from ionic silver. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seil, J.T.; Webster, T.J. Antimicrobial applications of nanotechnology: Methods and literature. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2767–2781. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.R.; Xie, X.B.; Shi, Q.S.; Zeng, H.Y.; Ou-Yang, Y.S.; Chen, Y. Ben Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Silver nanoparticles as an antimicrobial agent: A case study on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli as models for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinteros, M.A.; Cano Aristizábal, V.; Dalmasso, P.R.; Paraje, M.G.; Páez, P.L. Oxidative stress generation of silver nanoparticles in three bacterial genera and its relationship with the antimicrobial activity. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 36, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Immobilized silver nanoparticles enhance contact killing and show highest efficacy: Elucidation of the mechanism of bactericidal action of silver. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7328–7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.; Ferreira, S.; Ramírez-Rodríguez, G.B.; Alves, N.; Sousa, Â.; Valente, J.F.A. Silver and Antimicrobial Polymer Nanocomplexes to Enhance Biocidal Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


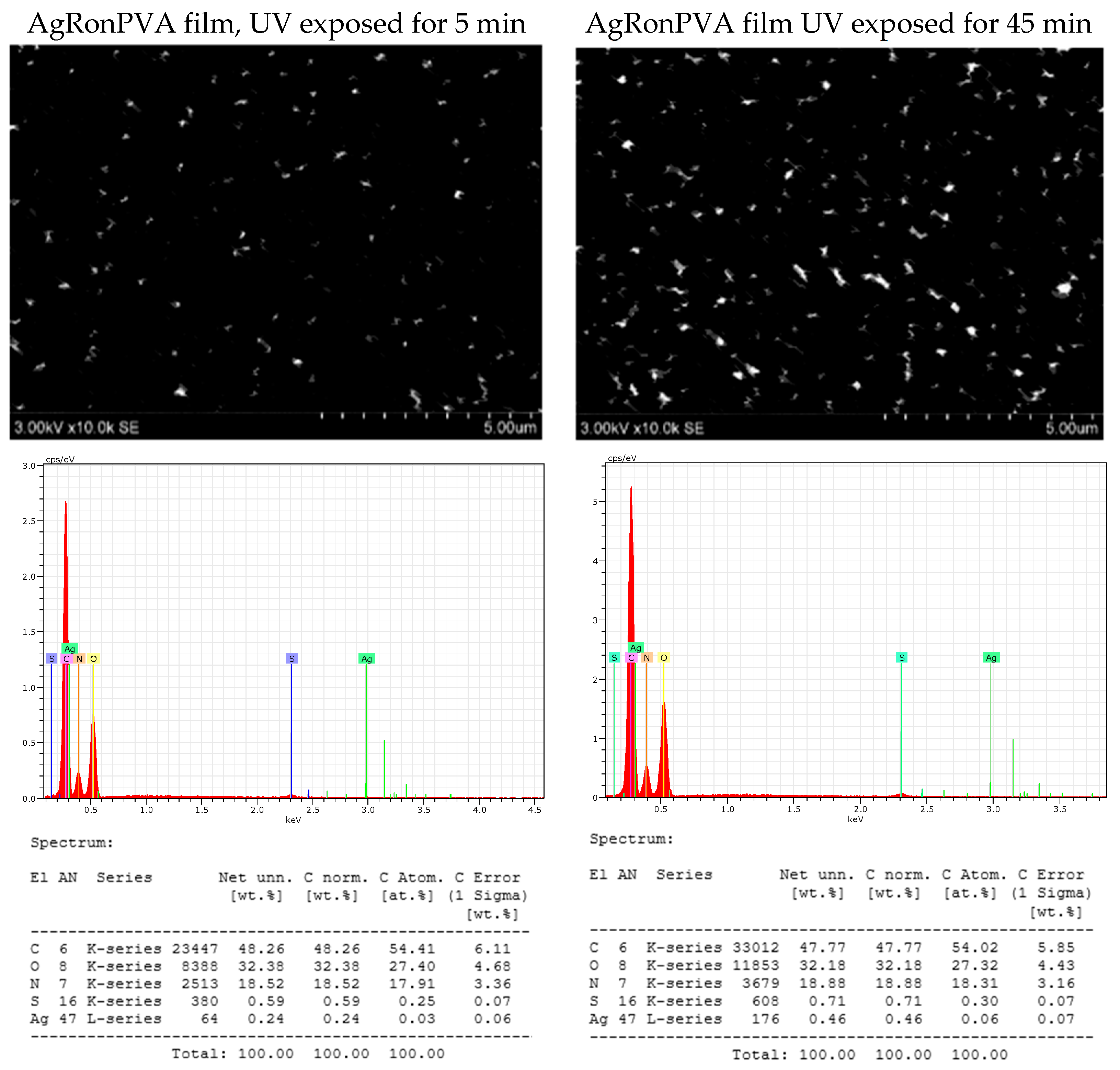
| Microorganism | Films | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| RonPVA (Control) | AgRonPVA (UV 5 min) | AgRonPVA (UV 10 min) | AgRonPVA (UV 30 min) | AgRonPVA (UV 45 min) | |
| Zone Diameter, mm | |||||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 0 | 20.0 ± 1.0 | 19.7 ± 0.6 | 18.7 ± 0.6 | 18.7 ± 0.6 |
| Acinetobacter baumannii BAA 747 | 0 | 18.3 ± 0.6 | 18.0 ± 0.0 | 18.0 ± 0.0 | 18.0 ± 0.0 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 15442 | 0 | 21.0 ± 0.0 | 20.7 ± 0.6 | 20.7 ± 0.6 | 19.7 ± 0.6 |
| Candida parapsilosis CBS 8836 | 0 | 10.7 ± 0.4 | 11.3 ± 0.5 | 9.3 ± 0.4 | 9.5 ± 0.3 |
| Candida albicans ATCC 90028 | 0 | 9.7 ± 0.4 | 9.3 ± 0.3 | 9.7 ± 0.4 | 9.3 ± 0.4 |
| Aspergillus flavus BTL G-33 | 0 | 13.0 ± 0.5 | 12.7 ± 0.6 | 12.0 ± 0.0 | 12.6 ± 0.4 |
| Aspergillus fumigatus BTL G-38 | 0 | 16.0 ± 0.0 | 13.3 ± 0.6 | 14.3 ± 0.6 | 11.7 ± 0.5 |
| Solutions | AgRonPVA (Gel) |
|---|---|
| Red onion extract, wt.% | 4.99 |
| PVA gel wt.% | 94.73 |
| 1 M AgNO3, wt.% | 0.28 |
| Total, wt.% | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puišo, J.; Žvirgždas, J.; Paškevičius, A.; Arslonova, S.; Adlienė, D. Antimicrobial Properties of Newly Developed Silver-Enriched Red Onion–Polymer Composites. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050441
Puišo J, Žvirgždas J, Paškevičius A, Arslonova S, Adlienė D. Antimicrobial Properties of Newly Developed Silver-Enriched Red Onion–Polymer Composites. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(5):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050441
Chicago/Turabian StylePuišo, Judita, Jonas Žvirgždas, Algimantas Paškevičius, Shirin Arslonova, and Diana Adlienė. 2024. "Antimicrobial Properties of Newly Developed Silver-Enriched Red Onion–Polymer Composites" Antibiotics 13, no. 5: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050441
APA StylePuišo, J., Žvirgždas, J., Paškevičius, A., Arslonova, S., & Adlienė, D. (2024). Antimicrobial Properties of Newly Developed Silver-Enriched Red Onion–Polymer Composites. Antibiotics, 13(5), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050441








