Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Isavuconazole: Serum Concentration Variability and Success Rates for Reaching Target in Comparison with Voriconazole
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Clinical Data and Definitions
2.3. Chemicals and Standards
2.4. Quantification of Azole Plasma Concentrations
2.5. Instruments and Chromatographic Conditions
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Data
3.2. Serum Concentrations
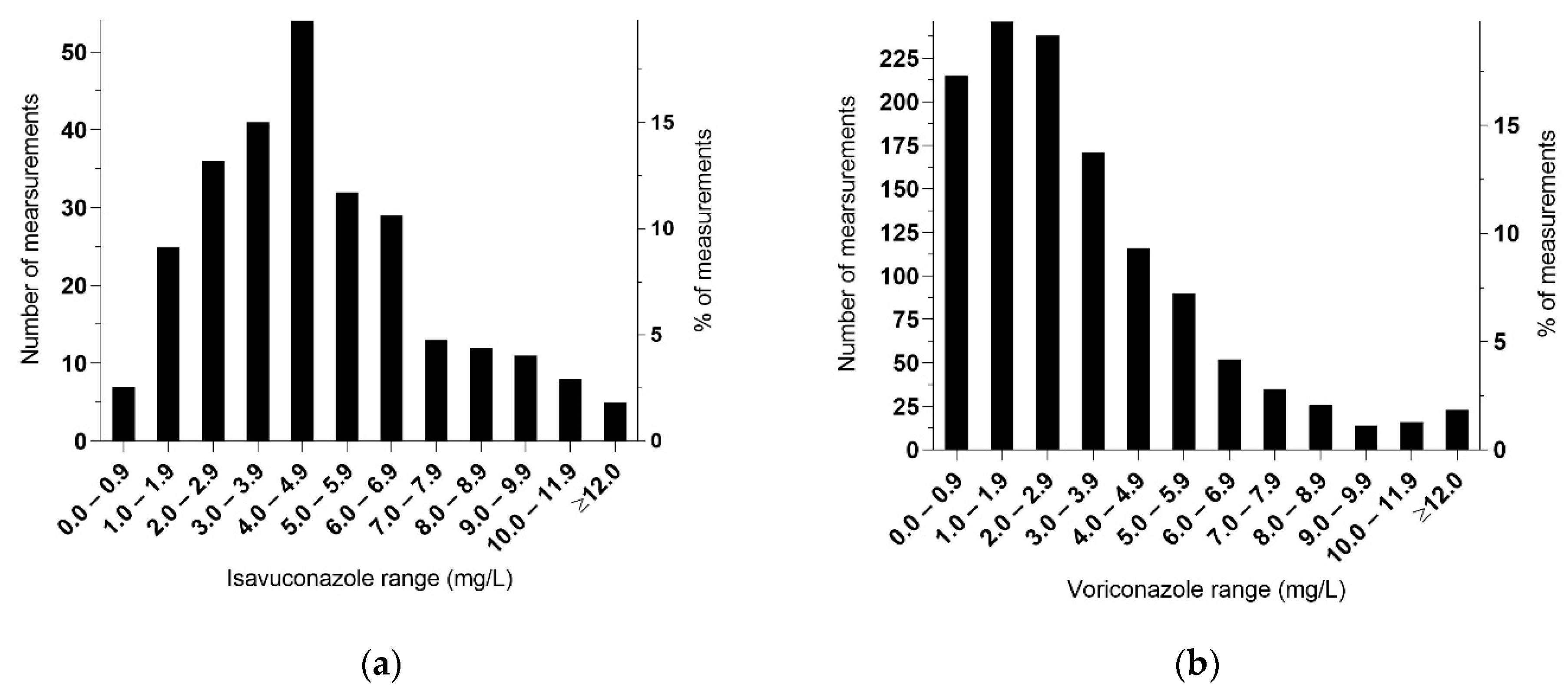
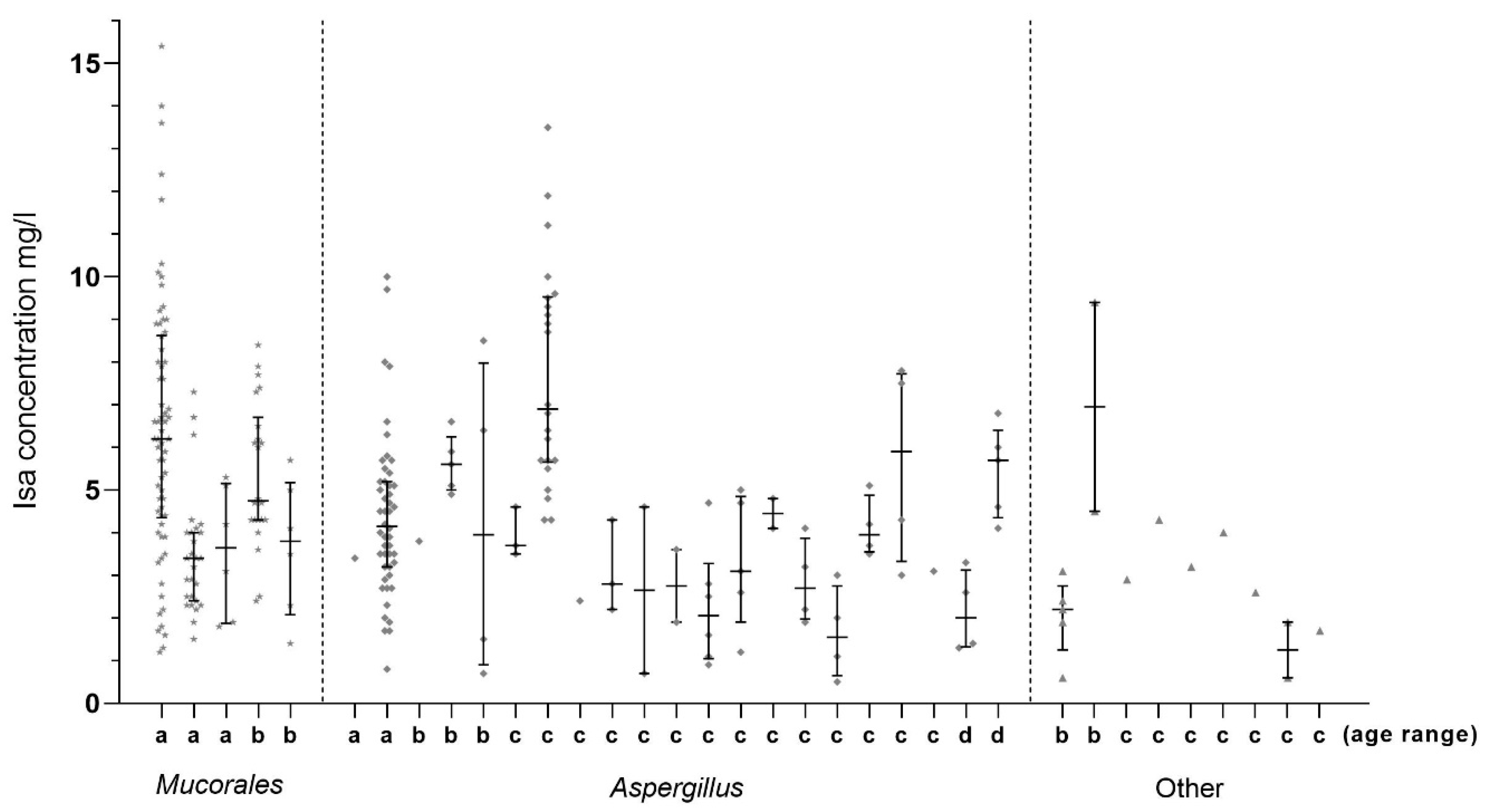
3.2.1. Serum Isavuconazole
3.2.2. Serum Voriconazole
3.3. Adverse Events
3.4. Breakthrough Fungal Infection
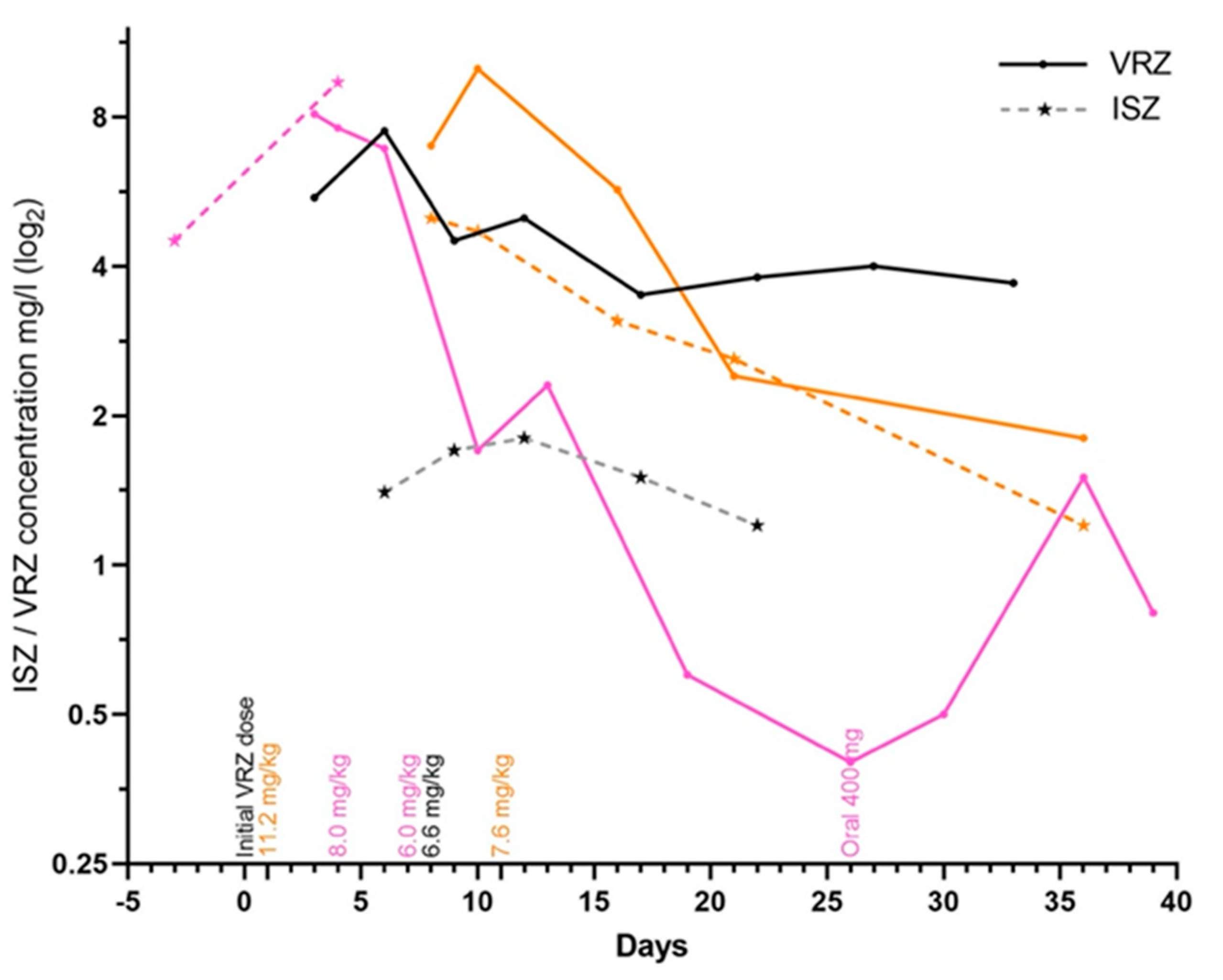
3.5. Drug–Drug Interactions
3.6. Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornely, O.A.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Arenz, D.; Chen, S.C.; Dannaoui, E.; Hochhegger, B.; Hoenigl, M.; Jensen, H.E.; Lagrou, K.; Lewis, R.E.; et al. Global guideline for the diag-nosis and management of mucormycosis: An initiative of the European Confederation of Medical Mycology in cooperation with the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e405–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualotto, A.C.; Falci, D.R. Profile of isavuconazole and its potential in the treatment of severe invasive fungal infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2013, 6, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miceli, M.H.; Kauffman, C.A. Isavuconazole: A New Broad-Spectrum Triazole Antifungal Agent. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marty, F.M.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Cornely, O.A.; Mullane, K.M.; Perfect, J.R.; Thompson, G.R.; Alangaden, G.J.; Brown, J.M.; Fredricks, D.N.; Heinz, W.J.; et al. Isavuconazole treatment for mucormycosis: A single-arm open-label trial and case-control analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, J.A.; Raad, I.I.; Marr, K.A.; Patterson, T.F.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Cornely, O.A.; Bow, E.J.; Rahav, G.; Neofytos, D.; Aoun, M.; et al. Isavuconazole versus voriconazole for primary treatment of invasive mould disease caused by Aspergillus and other filamentous fungi (SECURE): A phase 3, ran-domised-controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullberg, B.J.; Viscoli, C.; Pappas, P.G.; Vazquez, J.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Rotstein, C.; Sobel, J.D.; Herbrecht, R.; Rahav, G.; Jaruratanasirikul, S.; et al. Isavuconazole Versus Caspofungin in the Treatment of Candidemia and Other Invasive Candida Infections: The ACTIVE Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, P.; McCue, D.; Wurster, S.; Wiederhold, N.P.; Konopleva, M.; Kadia, T.M.; Borthakur, G.; Ravandi, F.; Masarova, L.; Takahashi, K.; et al. Isavuconazole as Primary Anti-Fungal Prophy-laxis in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia or Myelodysplastic Syndrome: An Open-Label, Prospective, Phase II Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, A.; Su, Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, S.; Shaffer, B.; Tamari, R.; Gyurkocza, B.; Barker, J.; Bogler, Y.; Giralt, S.; et al. A Single-Center, Open-Label Trial of Isavuconazole Prophylaxis against Invasive Fungal Infection in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Isavuconazole for Antifungal Prophylaxis following HCT. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, L.; Perlin, D.S.; Zhao, Y.; Noble, B.N.; Lewis, J.S.; Strasfeld, L.; Hakki, M. Isavuconazole Prophylaxis in Patients With Hematologic Malignancies and Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, C.A.; Rana, M.M.; Jacobs, S.E.; Saunders-Hao, P. Isavuconazole for the prophylaxis and treatment of invasive fungal disease: A single-center experience. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2020, e13469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, P.; Clancy, C.J.; Marini, R.V.; Rivosecchi, R.M.; McCreary, E.K.; Shields, R.K.; Falcione, B.A.; Viehman, A.; Sacha, L.; Kwak, E.J.; et al. Isavuconazole Is as Effective as and Bet-ter Tolerated Than Voriconazole for Antifungal Prophylaxis in Lung Transplant Recipients. Clin. Infect Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decembrino, N.; Perruccio, K.; Zecca, M.; Colombini, A.; Calore, E.; Muggeo, P.; Soncini, E.; Comelli, A.; Molinaro, M.; Goffredo, B.M.; et al. A Case Series and Literature Review of Isavuconazole Use in Pediatric Patients with Hemato-oncologic Diseases and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongomin, F.; Maguire, N.; Moore, C.B.; Felton, T.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R. Isavuconazole and voriconazole for the treatment of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: A retrospective comparison of rates of adverse events. Mycoses 2018, 62, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmidis, C.; Out, A.; Moore, C.B.; Richardson, M.D.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R. Isavuconazole therapeutic drug monitoring dur-ing long-term treatment for chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 65, e01511-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Daele, R.; Spriet, I.; Wauters, J.; Maertens, J.; Mercier, T.; Van Hecke, S.; Brüggemann, R. Antifungal drugs: What brings the future? Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, S328–S343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.V.; Kovanda, L.L.; Hope, W.W.; Andes, D.; Mouton, J.W.; Kowalski, D.L.; Townsend, R.W.; Mujais, S.; Bonate, P.L. Exposure-response relationships for isavuconazole in patients with invasive aspergillosis and other filamentous fungi. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01034-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furfaro, E.; Signori, A.; Di Grazia, C.; Dominietto, A.; Raiola, A.M.; Aquino, S.; Ghiggi, C.; Ghiso, A.; Ungaro, R.; Angelucci, E.; et al. Serial monitoring of isavuconazole blood levels during prolonged antifungal therapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2341–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statens Serum Institut. Voriconazole (Serumconcentration). Available online: https://www.ssi.dk/produkter-og-ydelser/diagnostik (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Jørgensen, R.; Andersen, S.R.; Astvad, K.M.T.; Arendrup, M.C. Implementation of isavuconazole in a fluorescence-based highper-formance liquid chromatography kit allowing simultaneous detection of all four currently licensed mold-active triazoles. Msphere 2017, 2, e00098-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risum, M.; Helweg-Larsen, J.; Petersen, S.L.; Kampmann, P.; Overgaard, U.M.; El Fassi, D.; Nielsen, O.J.; Brabrand, M.; Rubek, N.; Munksgaard, L.; et al. Introduction of a Comprehensive Diagnostic and Interdisciplinary Management Approach in Haematological Patients with Mucormycosis: A Pre and Post-Intervention Analysis. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, R.; Risum, M.; Arendrup, M.C. Therapeutic drug monitoring of isavuconazole in patients undergoing antifungal treatment in Denmark. In Proceedings of the 30th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Paris, France, 18–21 April 2020; p. 7419. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, J.P.; Chen, S.C.; Kauffman, C.A.; Steinbach, W.J.; Baddley, J.W.; Verweij, P.E.; Clancy, C.J.; Wingard, J.R.; Lockhart, S.R.; Groll, A.H.; et al. Revision and Update of the Consensus Definitions of Invasive Fungal Disease From the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the My-coses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaindl, T.; Andes, D.; Engelhardt, M.; Saulay, M.; Larger, P.; Groll, A.H. Variability and exposure–response relationships of isavuconazole plasma concentrations in the Phase 3 SECURE trial of patients with invasive mould diseases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andes, D.; Kovanda, L.; Desai, A.; Kitt, T.; Zhao, M.; Walsh, T.J. Isavuconazole Concentration in Real-World Practice: Consistency with Results from Clinical Trials. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00585-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurl, C.; Waller, M.; Schwameis, F.; Muhr, T.; Bauer, N.; Zollner-Schwetz, I.; Valentin, T.; Meinitzer, A.; Ullrich, E.; Wunsch, S.; et al. Isavuconazole treatment in a mixed patient co-hort with invasive fungal infections: Outcome, tolerability and clinical implications of isavuconazole plasma concentra-tions. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borman, A.; Hughes, J.M.; Oliver, D.; Fraser, M.; Sunderland, J.; Noel, A.R.; Johnson, E.M. Lessons from isavuconazole therapeutic drug monitoring at a United Kingdom Reference Center. Med. Mycol. 2020, 58, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreary, E.K.; Bayless, M.; Van, A.P.; Lepak, A.J.; Wiebe, D.A.; Schulz, L.T.; Andes, D.R. Impact of Triazole Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Availability and Timing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier-Veyret, E.; Bolcato, L.; Roustit, M.; Weiss, S.; Tonini, J.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.-P.; Cornet, M.; Thiebaut-Bertrand, A.; Stanke-Labesque, F. Treatment by Posaconazole Tablets, Compared to Posaconazole Suspension, Does Not Reduce Variability of Posaconazole Trough Concentrations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongomin, F.; Rodriguez-Goncer, I.; Lorden, C.; Otu, A.; Bazaz, R. Late-onset isavuconazole-induced liver injury. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2018, 22, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassouna, H.; Brizendine, K.; Athans, V. Real-World Use—Isavuconazole at a Large Academic Medical Center. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2017, 4, S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cattaneo, C.; Busca, A.; Gramegna, D.; Farina, F.; Candoni, A.; Piedimonte, M.; Fracchiolla, N.; Pagani, C.; Del Principe, M.I.; Tisi, M.C.; et al. Isavuconazole in Hematological Patients: Results of a Real-Life Multicentre Observational Seifem Study. HemaSphere 2019, 3, e320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, M.; Schwartz, B.S.; Doernberg, S.B.; Langelier, C.; Lo, M.; Graff, L.; Tan, M.; Logan, A.C.; Chin-Hong, P.; Babik, J.M. Breakthrough Invasive Fungal Infections on Isavuconazole Prophylaxis and Treatment: What Is Happening in the Real-World Setting? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 1142–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, C.R.; DiPippo, A.J.; Bose, P.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Breakthrough Fungal Infections in Patients with Leukemia Receiving Isavuconazole. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 1610–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Selleslag, D.; Mullane, K.; Cornely, O.A.; Hope, W.; Lortholary, O.; Croos-Dabrera, R.; Lademacher, C.; Engelhardt, M.; Patterson, T.F. Impact of unresolved neutropenia in patients with neutropenia and invasive aspergillosis: A post hoc analysis of the SECURE trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groll, A.H.; Desai, A.; Han, D.; Howieson, C.; Kato, K.; Akhtar, S.; Kowalski, D.; Lademacher, C.; Lewis, W.; Pearlman, H.; et al. Pharmacokinetic Assessment of Drug-Drug Interactions of Isavuconazole With the Immunosuppressants Cyclosporine, Mycophenolic Acid, Prednisolone, Sirolimus, and Tacrolimus in Healthy Adults. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2016, 6, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieu, V.; Jhangiani, K.; Dadwal, S.; Nakamura, R.; Pon, D. Effect of isavuconazole on tacrolimus and sirolimus serum concentra-tions in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients: A drug-drug interaction study. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2019, 21, e13007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornely, O.A.; Mullane, K.M.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Maher, R.M.; Croos-Dabrera, R.; Lu, Q.; Lademacher, C.; Perfect, J.R.; Oren, I.; Schmitt-Hoffmann, A.-H.; et al. Isavuconazole for treatment of rare invasive fungal diseases. Mycoses 2018, 61, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornely, O.A.; Böhme, A.; Schmitt-Hoffmann, A.; Ullmann, A.J. Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Isavuconazole as Antifungal Prophylaxis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients with Neutropenia: Results of a Phase 2, Dose Escalation Study. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2078–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Male/Female | 17/19 |
|---|---|
| Median age and range (years) | 60 (7–80) |
| Median weight and range (kg) | 68 (24–97) |
| Median length and range of antifungal treatment in observation period and range (days) * | 49 (5–584) |
| TDM level median and range (mg/L) | 4.3 (0.5–15.4) |
| Time from ISZ initiation to first measurement median and range (days) ** | 7 (0–34) |
| First TDM measurement median and range (mg/L) ** | 3 (0.6–6.7) |
| Underlying disease (n) | |
| Hematological disease | 16 |
| Pulmonary disorder | 13 |
| Infectious diseases | 4 |
| Solid organ transplant | 2 |
| Other | 1 |
| Indication for ISZ treatment (n) | |
| Aspergillosis *** (2 proven, 3 probably, 0 possible, 15 unclassifiable) | 20 |
| Mucormycosis (5 proven) | 5 |
| Empirical (0 proven, 0 probable, 1 possible, 5 unclassifiable) | 6 |
| Empirical until identification of fungal infection for which VRZ was preferred (1 proven aspergillosis, 1 probably aspergillosis and 1 proven other mold infection) | 3 |
| Hyphae identified, but no species identification | 1 |
| Other fungal infection | 1 |
| Patients (n) receiving co-medication with potential drug–drug interactions | |
| Vincristine | 2 |
| Calcineurin inhibitors | 5 |
| Macrolides | 4 |
| Statins | 3 |
| Other CYP3A4 interacting drugs | 3 |
| Outcome at day 42 (n) | |
| Alive | 33 |
| Dead | 2 |
| Unknown | 1 |
| TDM and Dosages | |
|---|---|
| Patients/samples who received increased dosages incl. patients with Mucorales (n) * | 12/199 |
| -TDM level total samples. Median and range (mg/L) | 4.3 (0.6–15.4) |
| Patients/samples who received increased dosages excl. Mucorales patients (n) | 7/72 |
| -TDM level total samples. Median and range (mg/L) | 3.6 (0.6–10) |
| Patients/samples who did not receive increased dosages (n) | 22/73 |
| -TDM level total samples. Median and range (mg/L) | 4.6 (0.5–13.5) |
| Prior VRZ treatment (n) | 15/36 |
| Shifted to ISZ due to intolerance to VRZ | 9/15 |
| Adverse events reported due to ISZ | |
| Abdominal malaise/nausea/emesis (n) | 5 |
| Constipation (n) ** | 2 |
| Elevated liver enzymes (n) | 3 |
| Fatigue (n) | 2 |
| Palpitations (n) | 1 |
| Neuropathy (n) ** | 1 |
| Leg pain (n) ** | 1 |
| Patients with adverse events (n) | 12 |
| -TDM level total samples. Median and range (mg/L) | 5 (0.6–15.4) |
| -Samples > 5 mg/L (n) | 50/102 |
| Patients with adverse events closely related to the use of ISZ (n) | 7 |
| -TDM level total samples. Median and range (mg/L) | 3.6 (1.7–7.8) |
| -Samples > 5 mg/L (n) | 2/22 |
| Patients without adverse events (n) | 23 |
| -TDM level total samples. Median and range (mg/L) | 4.1 (0.5–13.5) |
| -Samples > 5 mg/L (n) | 55/171 |
| Clinical Data and TDM | ISZ | VRZ |
| Median age and range (years) | 60 (7–80) | 65 (0–86) |
| Patients ≤ 16 years | 6% (2/36) | 7% (21/283) |
| TDM median and range (mg/L) | 4.3 (0.5–15.4) | 2.6 (0.2–21.9) |
| Successful target rate of measurements | 83% (227/273) | 67% (827/1242) |
| Coefficient of variation (CV%) | ISZ | VRZ |
| CV-interindividual | 54.8% | 83.3% |
| Patients (n) * | 35 | 283 |
| CV median intraindividual | 43.4% | 53.2% |
| Patients (n) | 25 | 192 |
| CV median intraindividual | 43.7% | 63.3% |
| Patients (n) (Same patients who received ISZ and VRZ during the study period) | 9 | 9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Risum, M.; Vestergaard, M.-B.; Weinreich, U.M.; Helleberg, M.; Vissing, N.H.; Jørgensen, R. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Isavuconazole: Serum Concentration Variability and Success Rates for Reaching Target in Comparison with Voriconazole. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050487
Risum M, Vestergaard M-B, Weinreich UM, Helleberg M, Vissing NH, Jørgensen R. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Isavuconazole: Serum Concentration Variability and Success Rates for Reaching Target in Comparison with Voriconazole. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(5):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050487
Chicago/Turabian StyleRisum, Malene, Mai-Britt Vestergaard, Ulla Møller Weinreich, Marie Helleberg, Nadja Hawwa Vissing, and René Jørgensen. 2021. "Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Isavuconazole: Serum Concentration Variability and Success Rates for Reaching Target in Comparison with Voriconazole" Antibiotics 10, no. 5: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050487
APA StyleRisum, M., Vestergaard, M.-B., Weinreich, U. M., Helleberg, M., Vissing, N. H., & Jørgensen, R. (2021). Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Isavuconazole: Serum Concentration Variability and Success Rates for Reaching Target in Comparison with Voriconazole. Antibiotics, 10(5), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050487







