Allergic Diseases Caused by Aspergillus Species in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
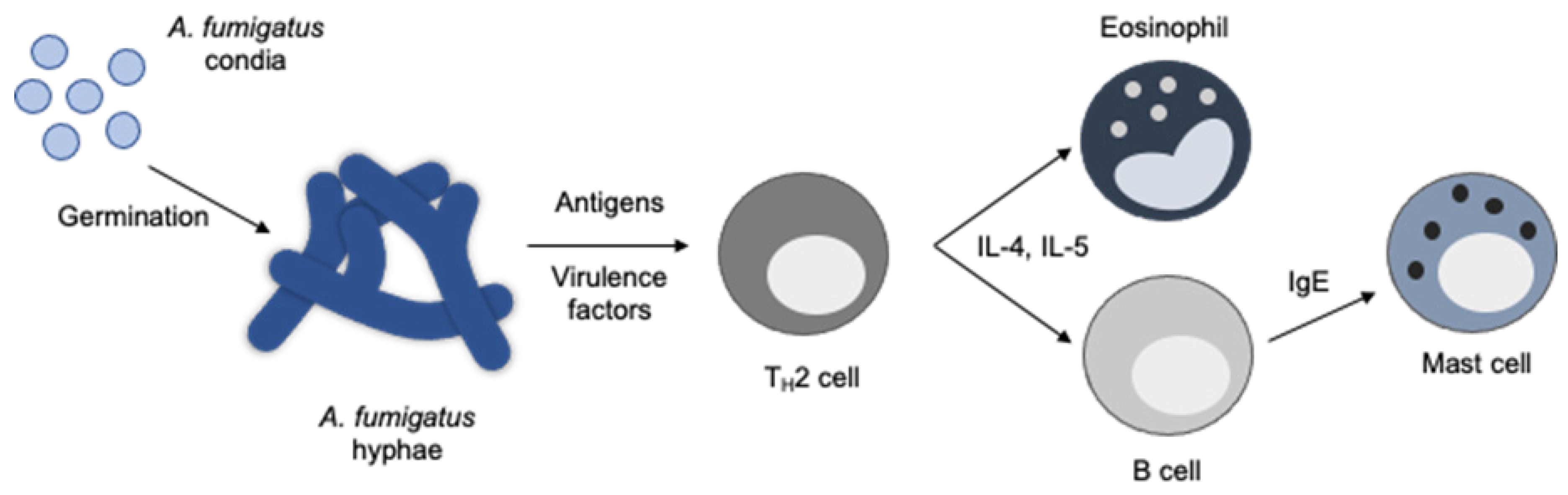
1. Pulmonary Aspergillus Infections
2. Prevalence and Diagnosis of Aspergillus Infections in Patients with CF
3. Aspergillus ssp. and Bacterial Interactions in the Pathogenesis of Disease
4. Treatment of ABPA with Approved Therapies
4.1. Oral Corticosteroids
4.2. Anti-Fungal Therapy
5. New Therapies to Treat ABPA and Fungal Infections
6. PUR1900: Inhaled Itraconazole
6.1. Inhaled Voriconazole
6.2. PC945: A Novel Inhaled Azole
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kousha, M.; Tadi, R.; Soubani, A.O. Pulmonary aspergillosis: A clinical review. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2011, 20, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagenais, T.R.T.; Keller, N.P. Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in Invasive Aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeghen, T.; Kibbler, C.C.; Prentice, H.G.; Berger, L.A.; Wallesby, R.K.; McWhinney, P.H.M.; Lampe, F.C.; Gillespie, S. Management of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Hematology Patients: A Review of 87 Consecutive Cases at a Single Institution. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, T.; Boeckh, M.; Carter, R.A.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Maris, M.B.; Maloney, D.G.; Martin, P.J.; Storb, R.F.; Marr, K.A. Risks and outcomes of invasive fungal infections in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell trans-plants after nonmyeloablative conditioning. Blood 2003, 102, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denning, D.W.; Cadranel, J.; Beigelman-Aubry, C.; Ader, F.; Chakrabarti, A.; Blot, S.; Ullmann, A.J.; Dimopoulos, G.; Lange, C. Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: Rationale and clinical guidelines for diagnosis and management. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 47, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; Pashley, C.; Hartl, D.; Wardlaw, A.; Godet, C.; Del Giacco, S.; Delhaes, L.; Sergejeva, S. Fungal allergy in asthma–state of the art and research needs. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2014, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Sehgal, I.S.; Dhooria, S.; Muthu, V.; Prasad, K.T.; Bal, A.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Chakrabarti, A. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 151, 529–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, G.; Greenberger, P.A. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019, 40, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwabara, K.; Hirose, M.; Kato, K.; Yokoi, T.; Shiga, M.; Kondo, R.; Nakamura, M.; Matsunaga, K.; Horiguchi, T. Serological analysis of sensitization in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: A study on allergen components and interspecies relationships. J. Asthma 2019, 57, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickmeier, O.; Zissler, U.M.; Wittschorek, J.; Unger, F.; Schmitt-Grohé, S.; Schubert, R.; Herrmann, E.; Zielen, S. Clinical relevance of Aspergillus fumigatus sensitization in cystic fibrosis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 50, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, R.B. Treatment options in severe fungal asthma and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, K.; Strek, M.E. Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2010, 7, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, C.G.; Dunn, G.; Jones, A.M.; Webb, K.; Gore, R.; Richardson, M.D.; Denning, D.W. Novel immunologic classification of aspergillosis in adult cystic fibrosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 560–566.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; Pleuvry, A.; Cole, D.C. Global burden of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with asthma and its complication chronic pulmonary aspergillosis in adults. Med. Mycol. 2013, 51, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.A.; Moss, R.B.; Kurup, V.P.; Knutsen, A.P.; Greenberger, P.; Judson, M.A.; Denning, D.W.; Crameri, R.; Brody, A.S.; Light, M.; et al. Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis in Cystic Fibrosis—State of the Art: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Conference. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37 (Suppl. 3), S225–S264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, M.; Mortezaee, V.; Hassanzad, M.; Mahdaviani, S.A.; Poorabdollah, M.; Mehrian, P.; Behnampour, N.; Mirenayat, M.S.; Abastabar, M.; Tavakoli, M.; et al. Prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis patients using two different diagnos-tic criteria. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 52, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, R.; Dupuis, A.; Aaron, S.D.; Ratjen, F. The Effect of Chronic Infection with Aspergillus fumigatus on Lung Function and Hospitalization in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Chest 2010, 137, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vrankrijker, A.M.M.; van der Ent, C.K.; van Berkhout, F.T.; Stellato, R.K.; Willems, R.J.L.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Wolfs, T.F.W. Aspergillus fumigatus colonization in cystic fibrosis: Implications for lung function? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihet, M.; Carrere, J.; Cimon, B.; Chabasse, D.; Delhaes, L.; Symoens, F.; Bouchara, J.-P. Occurrence and relevance of filamentous fungi in respiratory secretions of patients with cystic fibrosis—A review. Med Mycol. 2009, 47, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabino, R.; Ferreira, J.A.; Moss, R.B.; Valente, J.; Veríssimo, C.; Carolino, E.; Clemons, K.V.; Everson, C.; Banaei, N.; Penner, J.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Aspergillus collected from cystic fibrosis patients. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2015, 14, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipuma, J.J. The Changing Microbial Epidemiology in Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargon, J.; Dauletbaev, N.; Köhler, B.; Wolf, M.; Posselt, H.-G.; Wagner, T. Prophylactic antibiotic therapy is associated with an increased prevalence of Aspergillus colonization in adult cystic fibrosis patients. Respir. Med. 1999, 93, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, O.; Schultz, A.; Turkovic, L.; De Klerk, N.; Keil, A.D.; Brennan, S.; Harrison, J.; Robertson, C.; Robinson, P.J.; Sly, P.D.; et al. Changing Prevalence of Lower Airway Infections in Young Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.V.; Modha, D.E.; Claydon, A.; Gaillard, E.A. Chronic Aspergillus fumigatus colonization of the pediatric cystic fibrosis airway is common and may be associated with a more rapid decline in lung function. Med. Mycol. 2016, 54, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, K.A.; Hart, E.; Turkovic, L.; Padros-Goossens, M.; Stick, S.M.; Ranganathan, S.C. Respiratory infection rates differ between geographically distant paediatric cystic fibrosis cohorts. ERJ Open Res. 2016, 2, 00014–02016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillaux, J.; Brémont, F.; Murris, M.; Cassaing, S.; Rittié, J.-L.; Tétu, L.; Segonds, C.; Abbal, M.; Bieth, E.; Berry, A.; et al. Assessment of Aspergillus sensitization or persistent carriage as a factor in lung function impairment in cystic fibrosis patients. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 44, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noni, M.; Katelari, A.; Dimopoulos, G.; Doudounakis, S.-E.; Tzoumaka-Bakoula, C.; Spoulou, V. Aspergillus fumigatus chronic colonization and lung function decline in cystic fibrosis may have a two-way relationship. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 2235–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, G.; Alby, K.; Ng, S.C.; Fleck, V.; Kubrak, C.; Rubenstein, R.C.; Dorgan, D.J.; Kawut, S.M.; Hadjiliadis, D. The presence of Aspergillus fumigatus is associated with worse respiratory quality of life in cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangell, C.; Gard, S.; Douglas, T.; Park, J.; De Klerk, N.; Keil, T.; Brennan, S.; Ranganathan, S.; Robins-Browne, R.; Sly, P.D.; et al. Inflammatory Responses to Individual Microorganisms in the Lungs of Children With Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuer, O.; Schultz, A.; Garratt, L.W.; Turkovic, L.; Rosenow, T.; Murray, C.P.; Karpievitch, Y.V.; Akesson, L.; Dalton, S.; Sly, P.D.; et al. Aspergillus Infections and Progression of Structural Lung Disease in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harun, S.N.; Wainwright, C.E.; Grimwood, K.; Hennig, S. Aspergillus and progression of lung disease in children with cystic fibrosis. Thorax 2019, 74, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Chakrabarti, A.; Shah, A.; Gupta, D.; Meis, J.F.; Guleria, R.; Moss, R.; Denning, D.W.; ABPA Complicating Asthma ISHAM Working Group. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: Review of literature and proposal of new diagnostic and classifica-tion criteria. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 850–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, E.; McClean, S.; Greally, P.; Renwick, J. The prevalence of Aspergillus fumigatus in early cystic fibrosis disease is underestimated by culture-based diagnostic methods. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 164, 105683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraczek, M.G.; Kirwan, M.B.; Moore, C.B.; Morris, J.; Denning, D.W.; Richardson, M.D. Volume dependency for culture of fungi from respiratory secretions and increased sensitivity of Asper-gillus quantitative PCR. Mycoses 2014, 57, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstead, J.; Morris, J.; Denning, D.W. Multi-Country Estimate of Different Manifestations of Aspergillosis in Cystic Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briard, B.; Mislin, G.L.A.; Latgé, J.-P.; Beauvais, A. Interactions between Aspergillus fumigatus and Pulmonary Bacteria: Current State of the Field, New Data, and Future Perspective. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granchelli, A.M.; Adler, F.R.; Keogh, R.H.; Kartsonaki, C.; Cox, D.R.; Liou, T.G. Microbial Interactions in the Cystic Fibrosis Airway. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esther, C.R., Jr.; Esserman, D.A.; Gilligan, P.; Kerr, A.; Noone, P.G. Chronic Mycobacterium abscessus infection and lung function decline in cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2010, 9, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monin, L.; Mehta, S.; Elsegeiny, W.; Gopal, R.; McAleer, J.P.; Oury, T.D.; Kolls, J.; Khader, S.A. Aspergillus fumigatus Preexposure Worsens Pathology and Improves Control of Mycobacterium abscessus Pulmonary Infection in Mice. Infect. Immun. 2017, 86, e00859-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sass, G.; Nazik, H.; Penner, J.; Shah, H.; Ansari, S.R.; Clemons, K.V.; Groleau, M.-C.; Dietl, A.-M.; Visca, P.; Haas, H.; et al. Aspergillus-Pseudomonas interaction, relevant to competition in airways. Med Mycol. 2019, 57 (Suppl. 2), S228–S232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowat, E.; Rajendran, R.; Williams, C.; McCulloch, E.; Jones, B.; Lang, S.; Ramage, G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their small diffusible extracellular molecules inhibit Aspergillus fumigatus biofilm formation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 313, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidler, M.J.; Salvenmoser, S.; Muller, F.M. Aspergillus fumigatus forms biofilms with reduced antifungal drug susceptibil-ity on bronchial epithelial cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 4130–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.C.; Bilton, D. Bugs, biofilms, and resistance in cystic fibrosis. Respir. Care 2009, 54, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirazi, F.; Ferreira, J.A.G.; Stevens, D.A.; Clemons, K.V.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Biofilm Filtrates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains Isolated from Cystic Fibrosis Patients Inhibit Preformed Aspergillus fumigatus Biofilms via Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, G.; Nazik, H.; Penner, J.; Shah, H.; Ansari, S.R.; Clemons, K.V.; Groleau, M.C.; Dietl, A.M.; Visca, P.; Haas, H.; et al. Studies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mutants Indicate Pyoverdine as the Central Factor in Inhibition of As-pergillus fumigatus Biofilm. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 200, e00345-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melloul, E.; Luiggi, S.; Anaïs, L.; Arné, P.; Costa, J.-M.; Fihman, V.; Briard, B.; Dannaoui, E.; Guillot, J.; Decousser, J.-W.; et al. Characteristics of Aspergillus fumigatus in Association with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in an In Vitro Model of Mixed Biofilm. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roisin, L.; Melloul, E.; Woerther, P.-L.; Royer, G.; Decousser, J.-W.; Guillot, J.; Dannaoui, E.; Botterel, F. Modulated Response of Aspergillus fumigatus and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia to Antimicrobial Agents in Polymicrobial Biofilm. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 574028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberger, P.A.; Bush, R.K.; Demain, J.G.; Luong, A.; Slavin, R.G.; Knutsen, A.P. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2014, 2, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Dhooria, S.; Sehgal, I.S.; Garg, M.; Saikia, B.; Behera, D.; Chakrabarti, A. A randomised trial of glucocorticoids in acute-stage allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis complicating asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 47, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracy, M.C.; Okorie, C.U.A.; Foley, E.A.; Moss, R.B. Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Fungi 2016, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.K.; Chandr, A.; Gautam, P.B. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis—A clinical review. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2012, 60, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Dhooria, S.; Sehgal, I.S.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Garg, M.; Saikia, B.; Behera, D.; Chakrabarti, A. A Randomized Trial of Itraconazole vs Prednisolone in Acute-Stage Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergil-losis Complicating Asthma. Chest 2018, 153, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wark, P.A.B.; Hensley, M.J.; Saltos, N.; Boyle, M.J.; Toneguzzi, R.C.; Epid, G.D.C.; Simpson, J.L.; McElduff, P.; Gibson, P.G. Anti-inflammatory effect of itraconazole in stable allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, D.A.; Schwartz, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Moskovitz, B.L.; Jerome, D.C.; Catanzaro, A.; Bamberger, D.M.; Weinmann, A.J.; Tuazon, C.U.; Judson, M.A.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Itraconazole in Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Dhooria, S.; Sehgal, I.S.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Garg, M.; Saikia, B.; Chakrabarti, A. A randomised trial of voriconazole and prednisolone monotherapy in acute-stage allergic bronchopulmo-nary aspergillosis complicating asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1801159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chishimba, L.; Langridge, P.; Powell, G.; Niven, R.M.; Denning, D.W. Efficacy and safety of nebulised amphotericin B (NAB) in severe asthma with fungal sensitisation (SAFS) and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA). J. Asthma 2014, 52, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmiel, J.F.; Konstan, M.W. Anti-inflammatory medications for cystic fibrosis lung disease: Selecting the most appropriate agent. Treat. Respir. Med. 2005, 4, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Ahmet, A.; Ward, L.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Mandelcorn, E.D.; Leigh, R.; Brown, J.P.; Cohen, A.; Kim, H. A practical guide to the monitoring and management of the complications of systemic corticosteroid therapy. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.B. Treating allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: The way forward. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairs, A.; Agbetile, J.; Hargadon, B.; Bourne, M.; Monteiro, W.R.; Brightling, C.E.; Bradding, P.; Green, R.H.; Mutalithas, K.; Desai, D.; et al. IgE Sensitization toAspergillus fumigatusIs Associated with Reduced Lung Function in Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimanianda, V.; Bayry, J.; Bozza, S.; Kniemeyer, O.; Perruccio, K.; Elluru, S.R.; Clavaud, C.; Paris, S.; Brakhage, A.A.; Kaveri, S.V.; et al. Surface hydrophobin prevents immune recognition of airborne fungal spores. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 460, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.J.; Mitakakis, T.Z.; Tovey, E.R. Allergen detection from 11 fungal species before and after germination. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurup, V.P.; Knutsen, A.P.; Moss, R.B.; Bansal, N.K. Specific antibodies to recombinant allergens of Aspergillus fumigatus in cystic fibrosis patients with ABPA. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2006, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.S.; Silva, D.; Ferreira, A.R.; Delgado, L. Antifungal treatment in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with and without cystic fibrosis: A sys-tematic review. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 1210–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrant, J.; Brice, H.; Fowler, S.; Niven, R. Fungal sensitisation in severe asthma is associated with the identification of Aspergillus fumigatus in spu-tum. J. Asthma 2016, 53, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowen, L.E.; Steinbach, W.J. Stress, Drugs, and Evolution: The Role of Cellular Signaling in Fungal Drug Resistance. Eukaryot. Cell 2008, 7, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrdle, A.; Mustakim, S.; Bright-Thomas, R.J.; Baxter, C.G.; Felton, T.; Denning, D.W. Aspergillus bronchitis without significant immunocompromise. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1272, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denning, D.W.; Van Wye, J.E.; Lewiston, N.J.; Stevens, D.A. Adjunctive Therapy of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis with Itraconazole. Chest 1991, 100, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; Park, S.; Lass-Florl, C.; Fraczek, M.G.; Kirwan, M.; Gore, R.; Smith, J.; Bueid, A.; Moore, C.B.; Bowyer, P.; et al. High-frequency Triazole Resistance Found in Nonculturable Aspergillus fumigatus from Lungs of Patients with Chronic Fungal Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, K.M.; Guinea, J.; Meletiadis, J.; Hare, R.K.; Arendrup, M.C. Revision of EUCAST breakpoints: Consequences for susceptibility of contemporary Danish mould isolates to isavuconazole and comparators. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Jimenez, I.; Lucio, J.; Amich, J.; Cuesta, I.; Arroyo, R.S.; Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Mellado, E. A Cyp51B Mutation Contributes to Azole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepomuceno, I.B.; Esrig, S.; Moss, R.B. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis: Role of atopy and re-sponse to itraconazole. Chest 1999, 115, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chishimba, L.; Niven, R.M.; Cooley, J.; Denning, D.W. Voriconazole and Posaconazole Improve Asthma Severity in Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis and Severe Asthma with Fungal Sensitization. J. Asthma 2012, 49, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Popple, S.; Claydon, A.; Modha, D.E.; Gaillard, E.A. Posaconazole therapy in children with cystic fibrosis and Aspergillus-related lung disease. Med. Mycol. 2019, 58, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilliard, T.; Edwards, S.; Buchdahl, R.; Francis, J.; Rosenthal, M.; Balfour-Lynn, I.; Bush, A.; Davies, J. Voriconazole therapy in children with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2005, 4, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periselneris, J.; Nwankwo, L.; Schelenz, S.; Shah, A.; Armstrong-James, D. Posaconazole for the treatment of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with cystic fibro-sis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 1701–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigen, H.; Rosenstein, B.J.; FitzSimmons, S.; Schidlow, D.V. A multicenter study of alternate-day prednisone therapy in patients with cystic fibrosis. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Prednisone Trial Group. J. Pediatr. 1995, 126, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhudhikanok, G.S.; Lim, J.; Marcus, R.; Harkins, A.; Moss, R.B.; Bachrach, L.K. Correlates of osteopenia in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics 1996, 97, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Batista, M.; Costa, S.; Shikanai-Yasuda, M.; Moss, R. Current treatment options for invasive aspergillosis. Drugs Today 2013, 49, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, B.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Dhooria, S.; Sehgal, I.S.; Garg, M.; Behera, D.; Chakrabarti, A.; Agarwal, R. A pilot randomized trial of nebulized amphotericin in patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J. Asthma 2016, 53, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otu, A.A.; Langridge, P.; Denning, D.W. An evaluation of nebulised amphotericin B deoxycholate (Fungizone©) for treatment of pulmonary aspergillosis in the UK National Aspergillosis Centre. Mycoses 2019, 62, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, S.J.; Tsai, M. IgE and mast cells in allergic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsokera, A.; Corriveau, S.; Sykes, J.; Coriati, A.; Cortes, D.; Vadas, P.; Chaparro, C.; McIntyre, K.; Tullis, E.; Stephenson, A.L. Omalizumab for asthma and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in adults with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, G.F.; Portale, A.; Papale, M.; Tardino, L.; Rotolo, N.; Licari, A.; Leonardi, S. Successful treatment with omalizumab of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with cystic fibrosis: Case reports and literature review. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1636–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perisson, C.; Destruys, L.; Grenet, D.; Bassinet, L.; Derelle, J.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Thumerelle, C.; Prevotat, A.; Rosner, V.; Clement, A.; et al. Omalizumab treatment for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in young patients with cystic fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2017, 133, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkenazi, M.; Sity, S.; Sarouk, I.; Aluma, B.e.; Dagan, A.; Bezalel, Y.; Bentur, L.; de Boeck, K.; Efrati, O. Omalizumab in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Asthma Allergy 2018, 11, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, A.G.; Glasmacher, A. Making sense of itraconazole pharmacokinetics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56 (Suppl. 1), i17–i22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Lesne-Hulin, A.; Lenoir, G.; Singlas, E.; Berche, P.; Hennequin, C. Sputum Itraconazole Concentrations in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1937–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaron, S.D.; Vandemheen, K.L.; Freitag, A.; Pedder, L.; Cameron, W.; Lavoie, A.; Paterson, N.; Wilcox, P.; Rabin, H.; Tullis, E.; et al. Treatment of Aspergillus fumigatus in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbotsford, J.; Foley, D.A.; Goff, Z.; Bowen, A.C.; Blyth, C.C.; Yeoh, D.K. Clinical experience with SUBA-itraconazole at a tertiary paediatric hospital. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Ravi, A.; Kane, K.; Schmalbach, T.; Hava, D.L. The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tolerability of PUR0200, a novel tiotropium formulation, in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hava, D.L.; Tan, L.; Johnson, P.; Curran, A.K.; Perry, J.; Kramer, S.; Kane, K.; Bedwell, P.; Layton, G.; Swann, C.; et al. A phase 1/1b study of PUR1900, an inhaled formulation of itraconazole, in healthy volunteers and asthmat-ics to study safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caponetti, G.; Maggi, L.; Sardina, M.; Castegini, F.; Raiteri, L.; Salerio, I.; Kottakis, I.; van Holsbeke, C.; De Backer, J.; Vos, W. EDRY® an Innovative Dry Powder Technology Evaluated via Functional Respiratory Imaging. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, PA958. [Google Scholar]
- Beinborn, N.A.; Du, J.; Wiederhold, N.P.; Smyth, H.D.; Williams, R.O. Dry powder insufflation of crystalline and amorphous voriconazole formulations produced by thin film freezing to mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beinborn, N.A.; Lirola, H.L.; Williams, R.O. Effect of process variables on morphology and aerodynamic properties of voriconazole formulations produced by thin film freezing. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 429, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colley, T.; Alanio, A.; Kelly, S.L.; Sehra, G.; Kizawa, Y.; Warrilow, A.G.S.; Parker, J.E.; Kelly, D.E.; Kimura, G.; Anderson-Dring, L.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Antifungal Profile of a Novel and Long-Acting Inhaled Azole, PC945, on Aspergillus fumigatus Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02280-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cass, L.; Murray, A.; Davis, A.; Woodward, K.; Albayaty, M.; Ito, K.; Strong, P.; Ayrton, J.; Brindley, C.; Prosser, J.; et al. Safety and nonclinical and clinical pharmacokinetics of PC945, a novel inhaled triazole antifungal agent. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2021, 9, e00690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Drug | Dose | Design | N | Duration | Primary Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prednisolone | 0.5mg/kg * 0.75mg/kg * | Randomized, controlled | 92 | 6 to 8 weeks followed by taper for up to 10 months | Exacerbation rate Steroid-dependent ABPA | [49] |
| Itraconazole Prednisolone | 200mg BID 0.5mg/kg * | Randomized, controlled | 131 | 16 weeks | Composite clinical response Decline in IgE Exacerbation rate | [52] |
| Itraconazole | 400mg QD | Randomized, double blind, placebo controlled | 29 | 16 weeks | Sputum eosinophil count | [53] |
| Itraconazole | 200mg BID | Randomized, double blind, placebo controlled | 55 | 16 weeks | Composite clinical response | [54] |
| Voriconazole Prednisolone | 200mg BID 0.5mg/kg * | Randomized, controlled, unblinded | 50 | 16 weeks | Composite clinical response Exacerbation rate | [55] |
| Inhaled amphotericin B | 10mg BID | Randomized, controlled | 21 | 16 weeks | Time to first exacerbation | [56] |
| Omalizumab | 600 mg | Randomized, double blind, placebo controlled | 14 ** | 24 weeks | Requirement for rescue corticosteroids | NCT00787917 |
| Product | Company | Formulation | Drug | Clinical Trials | Primary Indication | Development Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUR1900 | Pulmatrix | Dry Powder | Itraconazole | NCT03479411 NCT03960606 | ABPA | Phase 2 |
| ZP-059 | Zambon | Dry Powder | Voriconazole | NCT04229303 | IPA | Phase 1 |
| TFF-Vori | TFF | Dry Powder | Voriconazole | NCT04576325 | ABPA | Phase 1 |
| PC945 | Pulmocide | Liquid Nebulization | Novel Azole | NCT02715570 | IPA | Phase 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Curran, A.K.; Hava, D.L. Allergic Diseases Caused by Aspergillus Species in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040357
Curran AK, Hava DL. Allergic Diseases Caused by Aspergillus Species in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(4):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040357
Chicago/Turabian StyleCurran, Aidan K., and David L. Hava. 2021. "Allergic Diseases Caused by Aspergillus Species in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis" Antibiotics 10, no. 4: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040357
APA StyleCurran, A. K., & Hava, D. L. (2021). Allergic Diseases Caused by Aspergillus Species in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Antibiotics, 10(4), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040357






