Abstract
Wild animals are potential vectors of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the environment. The present study aimed to investigate the occurrence of antimicrobial resistance among Salmonella serovars isolated from wildlife and the environment in Italy. A total of 164 Salmonella isolates were analyzed, and six different subspecies and 64 serovars were detected. High proportions of Salmonella isolates proved resistant to streptomycin (34.1%), followed by trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (23.2%), tetracycline (17.7%), ciprofloxacin (14.63%) and ampicillin (11.59%). By source, the lowest level of resistance was observed in Salmonella serovars isolated from a water environment, while antimicrobial resistance was frequent in strains collected from shellfish, reptiles and birds. Multidrug-resistant strains were recovered from seafood (n = 11), mammals (n = 3) and water (n = 1). Three S. Typhimurium monophasic variant strains showed asimultaneous resistance to ampicillin, streptomycin, tetracycline and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, which represents a recognized alert resistance profile for this serovar. These data indicate the environmental dissemination of resistant strains due to anthropogenic activities, which, in southern Italy, probably have a higher impact on marine ecosystems than on terrestrial ones. Moreover, as most of the animals considered in the present study are usually consumed by humans, the presence of resistant bacteria in them is a matter of great concern.
1. Introduction
Salmonella are Gram-negative bacteria belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family. The genus Salmonella includes two species, Salmonella (S.) bongori and S. enterica, and six subspecies: S. enterica subsp. arizonae, S. enterica subsp. diarizonae, S. enterica subsp. enterica, S. enterica subsp. houtenae, S. enterica subsp. indica and S. enterica subsp. salamae [1]. Moreover, the subspecies enterica, according to its surface antigens (O and H), can be divided into over 2600 serovars [2].
Salmonella is an enteric pathogen that colonizes the intestinal tract of a wide range of animals, including not only primates, livestock, birds and pets, but also cold-blooded animals and wild fauna [3]. Wildlife plays a complex and important role in the maintenance and transmission of this pathogen and those that cause other endemic diseases [4,5]. Although animals may develop diseases such as enteritis and septicemia, and suffer abortion, Salmonella infections in animals are generally asymptomatic [6]. Infected animals may excrete Salmonella bacteria in large numbers, spreading the pathogen to other habitats, such as water, foodstuffs and the environment, in which it can survive for a long period [7]. It has been reported that wild animals can act as reservoirs of different Salmonella serotypes [3], which may be transmitted both to domestic animals and to humans [8]. The transmission of Salmonella among humans, domestic animals and wildlife mainly occurs through direct contact with live animals or the consumption of contaminated food or water [9]. Salmonella infection in humans is usually associated with raw eggs and inadequately cooked meat. Although the consumption of wild animals (mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians) is still far lower than that of domestic animals, it is increasing worldwide [10]. Thus, the presence of Salmonella in wild animals may constitute a great risk for public health.
Moreover, the impact of Salmonella infections has increased in recent decades because of the rapid emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) worldwide. Over the years, the extensive use and misuse of antibiotics in human and veterinary medicine, agriculture and aquaculture has led to the spread of resistant bacteria, which already cause 700,000 deaths each year [11,12]. Salmonellosis is one of the most common zoonoses in humans in the European Union (EU) [13], and is the leading food-borne disease in Italy. In humans, infections are generally self-limiting and do not require antimicrobial treatment [14], but in rare cases the infection can be more serious, necessitating the use of antimicrobial agents. However, owing to the increased resistance of Salmonella spp., severe infections are often difficult to treat.
Wildlife may spread ARB in the environment via their feces [9]. The spread of resistant Salmonella strains in the natural environment constitutes a potential hazard for both humans and animals [15].
Italy is a densely populated country with considerable biodiversity and wildlife populations. Few data are available on the distribution of Salmonella serovars and the occurrence of antimicrobial resistance among them in wild animals, except for a few species (such as some birds and wild boars) [6,15]. Monitoring Salmonella-resistant strains in wild animals may constitute an important means of determining the level of dissemination of resistant strains in the environment. The present study therefore aimed to investigate the occurrence of antimicrobial resistance among Salmonella serovars isolated from wildlife.
2. Results
2.1. Serotyping
The isolates were assigned to the species Salmonella enterica and to the subspecies: enterica (82.3%), diarizonae (9.1%), salamae (5.5%), houtenae (1.2%), arizonae (1.2%) and indica (0.6%) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Number and distribution of Salmonella subspecies detected from amphibians (frogs), birds, the environment, mammals, shellfish, reptiles and snails.
Shellfish, snails and amphibians harbored strains belonging exclusively to a single Salmonella subspecies, while the remaining sources harbored Salmonella isolates belonging to three to six subspecies (Table 1). The number of S. enterica strains isolated from cold-blooded animals (amphibians, snails and reptiles) was significantly lower than the number isolated from warm-blooded animals (birds and mammals) and shellfish (p < 0.05). Serotyping identified 64 serovars (Table 2); S. Napoli was the most frequently detected (13 isolates), followed by S. Typhimurium (11 isolates), S. Enteritidis, S. Rissen (9 isolates each), and S. Derby (8 isolates).

Table 2.
Salmonella serovars or antigenic profiles identified within the subspecies enterica, diarizonae, salamae, houtenae, S. arizonae and indica isolated from wild animals and the environment.
2.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility
Overall, 60 isolates (36.6%) showed susceptibility to all antibiotics tested. The number of isolates susceptible to all antibiotics was significantly lower among the strains belonging to non-enterica subspecies than among those belonging to the enterica subspecies (p < 0.05), but with an average number of resistances of 2.13 and 1.6 for S. enterica and S. non-enterica, respectively. High levels of resistance were observed against aminoglycosides (35.9%), followed by quinolones (20.7%) and beta-lactams (15.8%) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Overall occurrence (n.) and percentage (%) of resistance to 11 antibiotics (ampicillin (Amp), cefotaxime (Cef), ceftazidime (Caz), nalidixic acid (Nal), ciprofloxacin (Cip), gentamicin (Gen), streptomycin (Str), chloramphenicol (Clo), colistin sulfate (Cl), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Sul) and tetracycline (Tet)) in Salmonella spp. from amphibians (frogs), birds, environment, mammals, shellfish, reptiles and snails.
Among the single antimicrobial agents tested, the highest frequency of resistance was toward streptomycin (34.1%), followed by trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (23.2%), tetracycline (17.7%), ciprofloxacin (14.63%) and ampicillin (11.59%), while the lowest levels of resistance were against ceftazidime (1.8%) and colistin sulfate (1.2%) (Table 3). In total, 54 of the resistant strains (32.79%) were resistant to only one antibiotic; 22 strains (13.4%) showed resistance to two antibiotics, and the remaining strains showed resistance to three to six antibiotics (Figure 1).
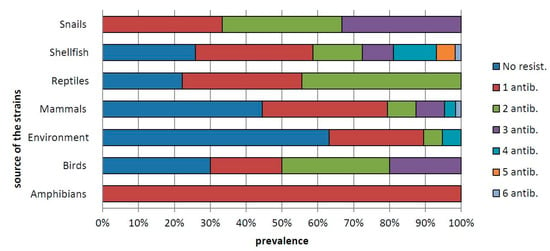
Figure 1.
Percentage of Salmonella strains resistant to one or more (up to six) antibiotics in isolates from amphibians (frogs), birds, environment, mammals, shellfish, reptiles and snails.
By source, the lowest level of resistance was observed in Salmonella serovars isolated from water (environment), while antimicrobial resistance was frequent in strains collected from shellfish, reptiles and birds (Table 3). On comparing the occurrence of resistant and susceptible strains in the various sources, the number of strains resistant to one or more antimicrobial agents was significantly higher in shellfish (p < 0.05). In particular, the strains detected in shellfish showed significantly higher resistance toward ampicillin and tetracycline (p < 0.05). Overall, 43 resistance profiles (R-types) were detected (Table 4).

Table 4.
Occurrence (n.) of resistance profiles observed within the subspecies enterica, diarizonae, salamae, houtenae, S. arizonae and indica isolated from wildlife and the environment.
Four profiles of antibiotic resistance were common to several subspecies of Salmonella. In total, 37 of these R-types were found in isolates of Salmonella subspecies enterica (27.41%), 7 R-types in S. salamae (77.78%), 5 in S. diarizonae (33.33%), 2 in S. houtenae (100%), and 1 R-type each in S. arizonae (50%) and S. indica (100%). Among the enterica subspecies, 13 strains showed simultaneous resistance to ampicillin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, 11 to ampicillin, tetracycline and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, 7 to ampicillin, streptomycin, tetracycline and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, 3 to ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid, and 2 to ceftazidime and cefotaxime. In total, 15 (9.15%) Salmonella isolates were classified as multidrug-resistant (MDR); these belonged to S. Infantis (n = 3), S. Rissen (n = 3), S. Typhimurium M.V. (n = 3), S. Brandenburg (n = 2), S. Typhimurium (n = 2), S. Manhattan (n = 1) and S. Virchow (n = 1) (Table 5). MDR strains were recovered from shellfish (n = 11), mammals (n = 3) and water (n = 1). Specifically, 7 of the 15 strains displayed simultaneous resistance to ampicillin, streptomycin, tetracycline and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (ASSuT). Three of the seven S. Typhimurium monophasic variant strains showed an ASSuT profile (Table 5).

Table 5.
Source of isolation of Salmonella serovars resistant to at least three antibiotic classes (multidrug-resistant; MDR).
3. Discussion
In the present study, a total of 164 Salmonella isolates collected in southern Italy from wild animals and the environment were analyzed and several subspecies were detected. Enterica was the dominant subspecies and was isolated in all animals except frogs. Enterica was the only subspecies detected in shellfish, as already reported by [16], while in the other samples, five non-enterica subspecies were found. In contrast to the study in [6], the prevalence of enterica subspecies in mammals was higher than that of non-enterica subspecies. However, the results of the present study are in line with those reported by [17], in which all Salmonella strains isolated from wild boar killed in the Campania region belonged to the subspecies enterica. Moreover, the results of the present study also agree with those reported in other studies, in which the dominant subspecies isolated from other mammals (Vulpus vulpes, Martes spp. and Meles meles) was enterica [18,19].
The subspecies enterica is principally associated with warm-blooded animals, but can also be found in cold-blooded animals [20]. Indeed, in the present study, two strains isolated from reptiles belonged to this subspecies. However, cold-blooded animals are more associated with non-enterica subspecies [20], and isolates collected from frogs, snails and reptiles mainly belonged to subspecies other than enterica. Among these, the subspecies diarizonae was frequently detected; this subspecies is increasingly associated with infections in humans, particularly after direct contact with reptiles or after the consumption of mutton [21], though the prevalence of this infection in Europe is still low. Other non-enterica subspecies were also detected (S. salamae, S. arizonae, S. hountenae and S. indica); although S. salamae, S. arizonae, S. hountenae and S. indica have a poor ability to invade host cells, it has been reported that they can cause infection in immunosuppressed subjects [20].
Serotyping identified 64 serovars. S. Napoli, S. Typhimurium, S. Enteritidis, S. Rissen and S. Derby were the most frequently found. S. Napoli is frequently detected in southern Italy and has been associated with human outbreaks [22]. Moreover, S. Typhimurium, S. Enteritidis and S. Derby, along with monophasic S. Typhimurium, S. Infantis, S. Newport, S. Stanley, S. Kentucky and S. Virchow, which were also detected in the present study, are frequently reported in human cases in Europe [13]. By contrast, S. Rissen is frequently reported in human infections in the United States of America and Asia [23], but not in the European Union.
The various Salmonella isolates were tested against 11 antibiotics, in order to evaluate the occurrence of resistant and multidrug-resistant strains. A total of 104 bacterial strains (63.41%) proved resistant to at least one antibiotic. The highest levels of resistance were found against streptomycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin and ampicillin. These drugs are used as first-line treatments for infections in humans and animals. High levels of resistance against streptomycin have also been reported in swine [24]. Streptomycin is categorized by the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) as a “veterinary critically important antimicrobial agent” [25], and therefore its use should be limited; however, it remains important for therapy in animals when there are no alternative antimicrobials [26]. Moreover, high levels of resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, tetracycline and ampicillin, which are widely used in veterinary medicine as first-line treatments in animal infections, are commonly reported among domestic animals [14,24]. However, as expected, the proportions of resistance to these antibiotics observed among strains isolated from domestic animals are higher than those observed in wild animals in the present study [14]. Moreover, 13 strains showed simultaneous resistance to ampicillin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, which are used as second-line therapies in humans who fail to respond to first-line antibiotics (e.g., in the case of infection caused by resistant bacteria) [27].
As fluoroquinolones constitute the gold standard for the treatment of invasive salmonellosis in humans, the resistance to ciprofloxacin that we observed is of particular concern. The level of resistance to ciprofloxacin was even higher than the levels commonly reported in human isolates [14,28]. Moreover, Salmonella serovars also showed resistance to nalidixic acid. Fortunately, however, co-resistance to both fluoroquinolones proved to be rare (1.83%). Co-resistance to the third-generation cephalosporins (cefotaxime and ceftazidime) was also low; the importance of this result lies in the fact that these antibiotics are used to treat human infections when fluoroquinolones are not recommended (e.g., during childhood infection).
High levels of resistance to sulfonamides, tetracyclines and ampicillin are also frequently reported in human Salmonella isolates [14], while these, along with resistance to fluoroquinolones, are also frequently reported in foodstuffs of animal origin [29,30].
In terms of source, 29 Salmonella serovars (50.88%) recovered from mammals were resistant to at least one antibiotic. The highest levels of resistance were found against trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, streptomycin and ciprofloxacin. In comparison with the results reported by [6], we found higher levels of resistance to streptomycin (28.07% vs. 8.5%), cefotaxime (7.02% vs. 1.8%) and nalidixic acid (5.26% vs. 1.8%), but lower levels of resistance to gentamicin (3.51% vs. 5.5%) and ampicillin (1.75% vs. 3.7%). The results of the present study are also in contrast with those of [31], who found a lower level of resistance in wild boars. The discrepancy between the different studies could be attributed to different serovars hosted by different wild boar populations [17].
In shellfish, the highest levels of antimicrobial resistance were observed not only to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, streptomycin and ciprofloxacin, but also to ampicillin and tetracycline. The presence of resistant Salmonella isolates in shellfish may indicate the spread of antibiotic-resistant strains from human or animal feces to aquatic ecosystems [32]. The low occurrence of resistant strains in water, as detected in the present study, does not contradict this hypothesis. Indeed, shellfish, being filter-feeding organisms, can concentrate unicellular algae, bacteria and other contaminants diluted in the environment; for this reason, they are often used for a more accurate analysis of water pollution [33].
Moreover, 11 strains isolated from shellfish, 3 strains isolated from mammals, and 1 isolated from water showed a profile of MDR. Furthermore, three S. Typhimurium monophasic variant strains from shellfish displayed the ASSuT profile, which is a recognized alert resistance profile for this serovar [1]. These results are of particular concern because shellfish and wild boars are commonly eaten by humans, to whom resistant Salmonella strains may therefore be transferred, causing infections that are hard to treat [9].
The evaluation of the occurrence of antimicrobial-resistant strains in wild birds is of great importance, as the long-distance migrations of some birds can spread resistant bacteria to different environments [9,15]. Around 70% of Salmonella strains isolated from birds were resistant to at least one antibiotic. These results are in contrast with those of [34], in which none of the isolates from wild birds exhibited phenotypic resistance.
In the present study, the occurrence of Salmonella strains displaying resistance, especially to streptomycin, was also found in isolates from amphibians, snails and reptiles. Some reptiles, besides being kept as pets, are also consumed by humans, and in recent years, the demand for their meat has increased in the EU. As reptiles carry a variety of pathogens, direct contact with these animals and the consumption of their meat may constitute a public health risk [35]. Thus, evaluation of the prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of the pathogens hosted by reptiles is essential in order to understand the magnitude of the risk associated with contact with reptiles or the consumption of their meat.
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
A total of 164 Salmonella strains isolated from 2014 to 2019 in the Campania and Calabria regions of southern Italy were collected and serotyped at the Salmonella Typing Centre of the Campania Region (Ce.Ti.Sa.; Department of Food Microbiology, Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale del Mezzogiorno, Portici, NA, Italy). The strains originated from: mammals (Sus scrofa, n = 48; Vulpes vulpes, n = 8; Martes martes, n = 4; Meles meles, n = 2; unidentified species, n = 1), shellfish (Mytilus spp., n = 40; Solen marginatus, n = 12; Tapes decussatus, n = 5; Donax spp., n = 1), birds (Anatidae, n = 3; Ardeidae, n = 3; birds of prey, n = 3; pigeons, n = 1), reptiles (snakes, n = 2; lizard, n = 1; Caretta caretta, n = 1; Testudo spp. n = 1; unspecified species, n = 4), land snails (n = 3), frogs (n = 2) and environment (waters, n = 19). Isolates were collected from the intestine, spleen, liver and/or lymph nodes of (i) animals (Sus scrofa) shot by official hunters and (ii) animals recovered dead from the environment by veterinary practitioners, owners, or law enforcement and presented to the Istituto Zooprofilattico del Mezzogiorno (IZSM) for diagnostic investigation. Those collected from water were isolated during environmental monitoring. Strains were stored at −20 °C in Microbanks™ (Pro-Lab Diagnostics, Neston, UK) until the analysis.
The strains were cultured in Trypticase Soy Agar 5% (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) and incubated for 24 h at 36 °C. Biochemical identification by means of a Vitek device (bioMerieux, Craponne, France) and PCR for the detection of the invA gene were carried out for confirmatory purposes [36,37].
4.2. Serotyping
Serotyping was performed in accordance with the Kauffman–White scheme [38] by means of agglutination with specific anti-sera for O (Statens Serum Institute–DK) and H antigens (Difco, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Salmonella enterica subspecies Typhimurium and Blockley, provided by the National Reference Laboratory for Salmonellosis (IZS, Padua, Italy), were used as quality control strains. The serological identification of the S. Typhimurium monophasic variant was confirmed through molecular assays [39].
4.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
The antimicrobial susceptibility of the isolates was determined by means of the disk diffusion method, in accordance with the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) recommendations. The following antibiotics (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK, and Becton Dickinson, Mississauga, ON, Canada) were used: nalidixic acid (NAL, 30 μg ), ampicillin (AMP, 10 μg), chloramphenicol (CLO, 30 μg), gentamicin (GEN, 10 μg), tetracycline (TET, 30 μg), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SUL, 25 μg), ciprofloxacin (CIP, 5 μg), colistin sulfate (CL, 10 μg), ceftazidime (CAZ, 10 μg), streptomycin (STR, 10 μg) and cefotaxime (CEF, 30 μg).
A quality-control strain (Escherichia coli ATCC 25922) was included in the test. The breakpoint for the interpretation of resistance or susceptibility to each antibiotic was that of the CLSI standards. In the evaluation of the results, strains displaying intermediate resistance were regarded as resistant, while those displaying resistance to at least three antibiotic classes were considered multidrug-resistant (MDR) [40].
4.4. Statistical Analysis
The significance of the differences in the resistance of the Salmonella strains recovered from the various sources was assessed by means of the chi-square test (χ²) through the EpiInfo 7 software package (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA, USA).
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, ARB are widespread in wildlife and the environment in Italy. Indeed, we found resistant and MDR Salmonella strains among the serovars isolated from wild animals and the environment. Specifically, the highest levels of resistance were observed toward streptomycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin and ampicillin, antibiotics that are commonly used as first-line treatments for infections in humans and animals. The occurrence of resistant strains in animals without a history of previous exposure reinforces the idea that resistant strains and/or antibiotic residues are spread to the environment from animal-rearing facilities. Shellfish exhibited the highest levels of resistant strains, indicating that anthropogenic activities in southern Italy probably have a higher impact on marine ecosystems than on terrestrial ones. Moreover, as most of the animals considered in the present study are usually eaten by humans, the presence of ARB in them is a matter of great concern. However, further research on the molecular profiles of these ARB is needed in order to define the association among domestic animals, wildlife and humans with regard to the occurrence of resistant bacteria and resistant genes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.C. (Federico Capuano), I.L.T. and M.F.P.; methodology, D.C.(Daniela Cristiano); software, F.C. (Federico Capuano); validation, I.L.T. and M.R.C.; formal analysis, I.L.T., N.D., F.C. (Francesco Casalinuovo) and F.D.N.; investigation, M.R.C., D.C. (Daniela Cristiano), D.C. (Davide Cardinale), F.C. (Federico Capuano); resources, F.C. (Federico Capuano); data curation, M.F.P.; writing—original draft preparation, I.L.T.; writing—review and editing, M.F.P.; visualization, D.C. (Daniela Cristiano); supervision, F.D.N.; project administration, F.C. (Federico Capuano); funding acquisition, F.C. (Federico Capuano). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Graziani, C.; Losasso, C.; Luzzi, I.; Ricci, A.; Scavia, G.; Pasquali, P. Salmonella, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780123850072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mąka, Ł.; Popowska, M. Antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella spp. isolated from food. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2016, 67, 343–358. [Google Scholar]
- De Iovine, R.O.; Dejuste, C.; Miranda, F.; Filoni, C.; Bueno, M.G.; de Carvalho, V.M. Isolation of escherichia coli and salmonella spp. from free-ranging wild animals. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Levy, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.M.J.; Hill-Cawthorne, G.A.; Ward, M.P.; Mor, S.M. Diversity of Salmonella serotypes from humans, food, domestic animals and wildlife in New South Wales, Australia 05 Environmental Sciences 0502 Environmental Science and Management 07 Agricultural and Veterinary Sciences 0707 Veterinary Sciences. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zottola, T.; Montagnaro, S.; Magnapera, C.; Sasso, S.; De Martino, L.; Bragagnolo, A.; D’Amici, L.; Condoleo, R.; Pisanelli, G.; Iovane, G.; et al. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella in European wild boar (Sus scrofa); Latium Region -Italy. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 36, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegegne, F.M. Epidemiology of Salmonella and its serotypes in human, food animals, foods of animal origin, animal feed and environment. J. Food Nutr. Heatlh 2019, 2, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gortázar, C.; Ferroglio, E.; Höfle, U.; Frölich, K.; Vicente, J. Diseases shared between wildlife and livestock: A European perspective. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2007, 53, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Imtiaz, M.A.; Sayeed, M.A.; Shaikat, A.H.; Hassan, M.M. Antimicrobial resistance pattern in domestic animal—Wildlife-environmental niche via the food chain to humans with a Bangladesh perspective; A systematic review. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehlenbein, M.P. Disease and Human/Animal Interactions. Annu. Rev. Anthropol. 2016, 45, 395–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caniça, M.; Manageiro, V.; Abriouel, H.; Moran-Gilad, J.; Franz, C.M.A.P. Antibiotic resistance in foodborne bacteria. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, D.; Torres, R.T.; Kronvall, G.; Fonseca, C.; Mendo, S.; Caetano, T. Assessment of antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli isolates and screening of Salmonella spp. in wild ungulates from Portugal. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food, E.; Authority, S. The European Union One Health 2018 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food, E.; Authority, S. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2017/2018. EFSA J. 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacopello, C.; Foti, M.; Mascetti, A.; Grosso, F.; Ricciardi, D.; Fisichella, V.; Lo Piccolo, F. Antibiotico resistenza in ceppi di Enterobacteriaceae isolati da avifauna europea ricoverata presso un centro di recupero per la fauna selvatica. Vet. Ital. 2016, 52, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamon, S.; Piras, F.; Meloni, D.; Agus, V.; Porcheddu, G.; Pes, M.; Cambula, M.G.; Fois, F.; Consolati, G.; Mureddu, A. Enumeration of Escherichia coli and determination of Salmonella spp. and verotoxi- genic Escherichia coli in shellfish (Mytilus galloprovin-cialis and Ruditapes decussat-us) harvested in Sardinia, Italy. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzy, M.F.; Murru, N.; Yu, Z.; Kerkhof, P.; Neola, B.; Joossens, M.; Proroga, Y.T.R.; Houf, K. Assessment of microbial communities on freshly killed wild boar meat by MALDI-TOF MS and 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 301, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakiewicz, A.; Zieba, P.; Ziółkowska, G.; Gnat, S.; Muszyńska, M.; Tomczuk, K.; Dziedzic, B.M.; Ulbrych, Ł.; Trościańczyk, A. Free-living species of carnivorous mammals in Poland: Red fox, beech marten, and raccoon as a potential reservoir of Salmonella, Yersinia, Listeria spp. and coagulase-positive Staphylococcus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millán, J.; Aduriz, G.; Moreno, B.; Juste, R.A.; Barral, M. Salmonella isolates from wild birds and mammals in the Basque Country (Spain). OIE Rev. Sci. Technol. 2004, 23, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, A.; Miranda, J.M.; Regal, P.; Vázquez, B.; Franco, C.M.; Cepeda, A. A comprehensive review of non-enterica subspecies of Salmonella enterica. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 206, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner-Lamia, J.; Vinuesa, P.; Betancor, L.; Silva, C.; Bisio, J.; Soleto, L.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Puente, J.L.; Soncini, F.C.; García-Vescovi, E.; et al. Genome analysis of Salmonella enterica subsp. diarizonae isolates from invasive human infections reveals enrichment of virulence-related functions in lineage ST1256. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, F.; Mancusi, A.; Capparelli, R.; Esposito, S.; Proroga, Y.T. Characterization of drug resistance and virulotypes of Salmonella strains isolated from food and humans. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, L.; Pinto, M.; Isidro, J.; Pista, Â.; Themudo, P.; Vieira, L.; Machado, J.; Gomes, J.P. Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Rissen Clusters Detected in Azores Archipelago, Portugal. Int. J. Genom. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, H.N.; Pham, T.; Turchi, B.; Fratini, F.; Ebani, V.V.; Cerri, D.; Bertelloni, F. Characterization of Salmonella spp. Isolates from Swine: Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance. Animals 2020, 10, 2418. [Google Scholar]
- Agency, E.M. Answer to the request from the European Commission for updating the scientific advice on the impact on public health and animal health of the use of antibiotics in animals-Categorisation of antimicrobials Answer to the request from the European Commissi. Eur. Med. Agency 2019, 44, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella, C.; Ricci, A.; DiGiannatale, E.; Luzzi, I.; Carattoli, A. Tetracycline and Streptomycin Resistance Genes, Transposons, and Plasmids in Salmonella enterica Isolates from Animals in Italy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Chon, J.W.; Lim, J.S.; Song, B.R.; Seo, K.H.; Heo, E.J.; Park, H.J.; Wee, S.H.; Oh, D.H.; Moon, J.S. Traceback Investigation for Salmonella Contamination at Egg Processing Plants in South Korea: Prevalence, Antibiotic Resistance, and Epidemiological Tracing by Rep-PCR Fingerprinting. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, M759–M764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proroga, Y.T.R.; Capuano, F.; Capparelli, R.; Bilei, S.; Bernardo, M.; Cocco, M.P.; Campagnuolo, R.; Pasquale, V. Characterization of non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica strains of human origin in central and southern Italy Medicine of the Lazio and Tuscany. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proroga, Y.T.R.; Capuano, F.; Carullo, M.R.; Tela, I.L.; Capparelli, R.; Barco, L.; Pasquale, V. Occurrenceand antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella strains from food of animal origin in southern Italy. Folia Microbiol. 2016, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peruzy, M.F.; Capuano, F.; Proroga, Y.T.R.; Cristiano, D.; Carullo, M.R.; Murru, N. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing for salmonella serovars isolated from food samples: Five-year monitoring (2015–2019). Antibiotics 2020, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonardi, S.; Bolzoni, L.; Zanoni, R.G.; Morganti, M.; Corradi, M.; Gilioli, S.; Pongolini, S. Limited Exchange of Salmonella Among Domestic Pigs and Wild Boars in Italy. Ecohealth 2019, 16, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaldone, G.; Marrone, R.; Cappiello, S.; Martin, G.A.; Oliva, G.; Cortesi, M.L.; Anastasio, A. Occurrence of antibiotic resistance in bacteria isolated from seawater organisms caught in Campania Region: Preliminary study. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, T.K.; Conn, D.B. Molecular markers and sentinel organisms for environmental monitoring. Parasite 2008, 15, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, K.T.; Chen, H.J.; Chau, M.L.; Yap, G.; Lim, X.F.; Humaidi, M.; Chua, C.; Yeo, G.; Yap, H.M.; Oh, J.Q.; et al. Salmonella in retail food and wild birds in singapore—Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and sequence types. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnino, S.; Colin, P.; Dei-Cas, E.; Madsen, M.; McLauchlin, J.; Nöckler, K.; Prieto Maradona, M.; Tsigarida, E.; Vanopdenbosch, E.; Van Peteghem, C. Biological risks associated with consumption of reptile products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 134, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennant, S.M.; Diallo, S.; Levy, H.; Livio, S.; Sow, S.O.; Tapia, M.; Fields, P.I.; Mikoleit, M.; Tamboura, B.; Kotloff, K.L.; et al. Identification by PCR of non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica serovars associated with invasive infections among febrile patients in Mali. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, L.; Lettini, A.A.; Ramon, E.; Longo, A.; Saccardin, C.; Pozza, M.C.D.; Ricci, A. A rapid and sensitive method to identify and differentiate Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium and Salmonella enterica serotype 4, [5],12:i:-by combining traditional serotyping and multiplex polymerase Chain reaction. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formulae, A.; The, O.F. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars; WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Proroga, Y.T.R.; Mancusi, A.; Peruzy, M.F.; Carullo, M.R.; Montone, A.M.I.; Fulgione, A.; Capuano, F. Characterization of Salmonella Typhimurium and its monophasic variant 1,4, [5],12:i:-isolated from different sources. Folia Microbiol. 2019, 64, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.T.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.T.; Giske, C.T.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbial. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).