Reducing Duration of Antibiotic Use for Presumed Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis in Greek NICUs. A “Low-Hanging Fruit” Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
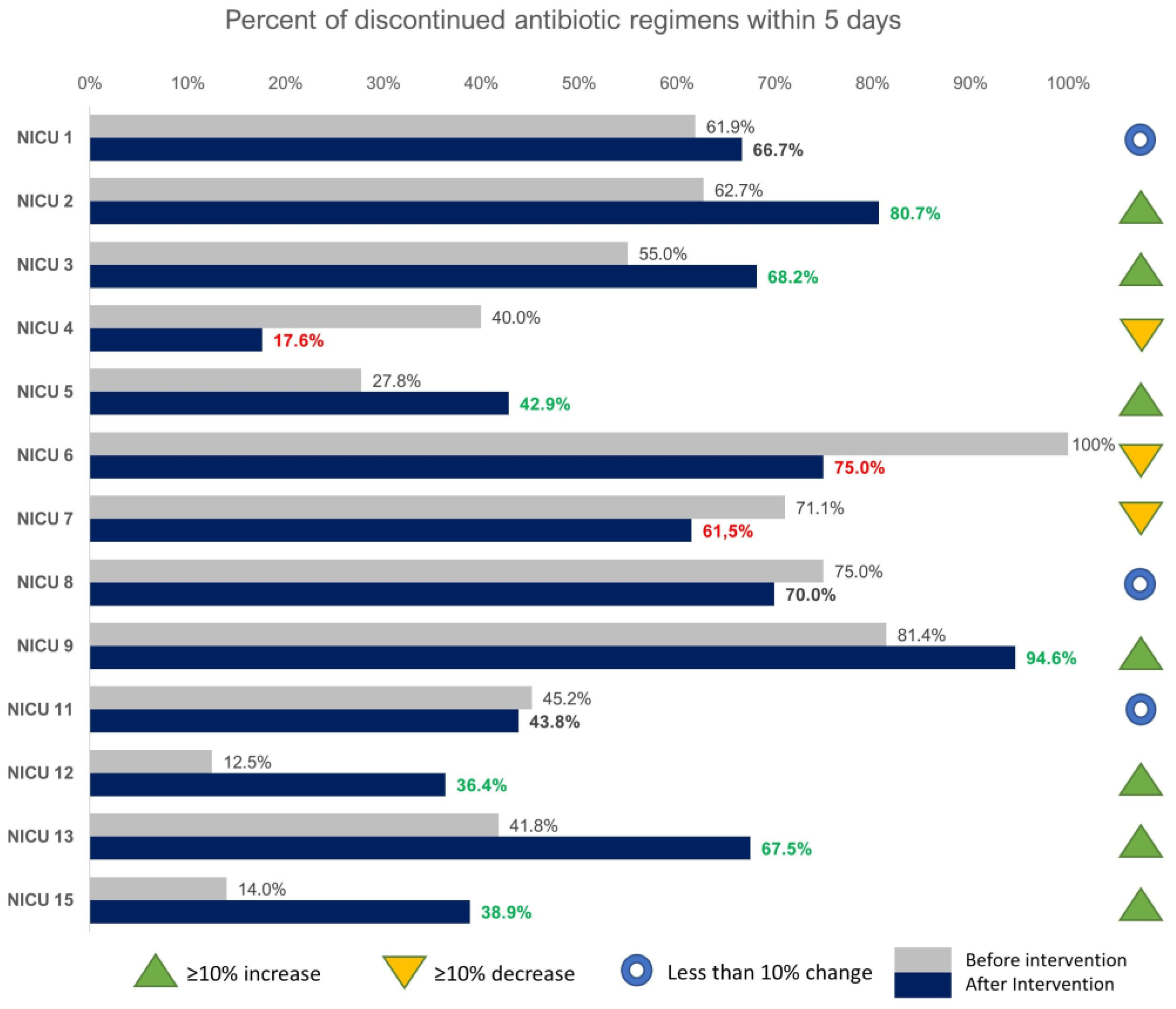
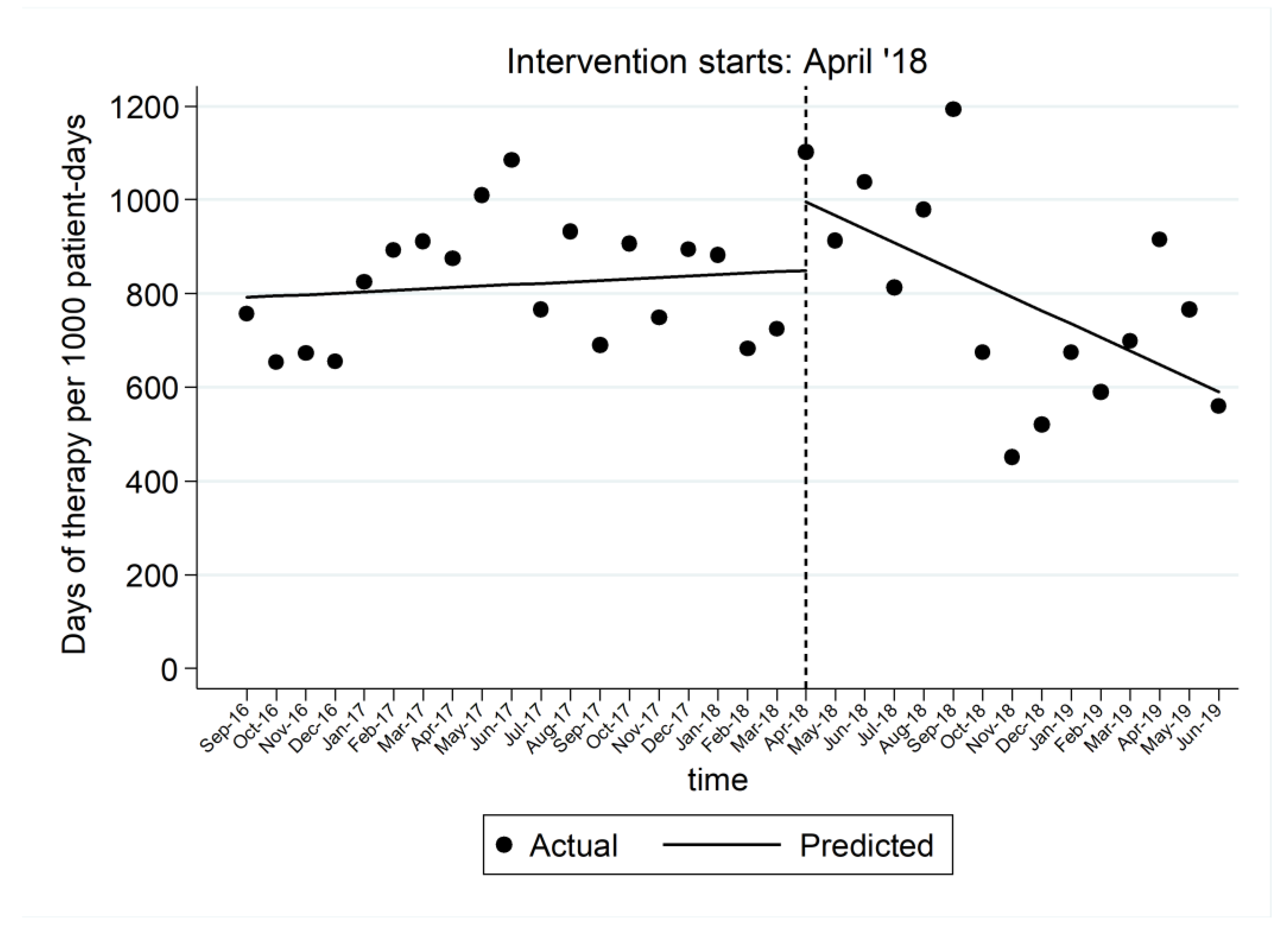
2.1. Impact on Length of Therapy and on Discontinuation in 5 Days or Less
2.2. Prescribing Patterns, Length of Stay and Mortality
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Population
4.2. Intervention
4.3. Evaluation of Impact
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goossens, H.; Ferech, M.; Vanderstichele, R.; Elseviers, M. Outpatient Antibiotic Use in Europe and Association with Resistance: A Cross-National Database Study. Lancet 2005, 365, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachouras, D.; Kavatha, D.; Antoniadou, A.; Giannitsioti, E.; Poulakou, G.; Kanellakopoulou, K.; Giamarellou, H. Dispensing of Antibiotics without Prescription in Greece, 2008: Another Link in the Antibiotic Resistance Chain. Eurosurveillance 2010, 15, 19488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Resistance in the EU/EEA (EARS-Net)—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2019; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Miyakis, S.; Pefanis, A.; Tsakris, A. The Challenges of Antimicrobial Drug Resistance in Greece. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Attributable Deaths and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years Caused by Infections with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A Population-Level Modelling Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkentzi, D.; Dimitriou, G. Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: An Update. CPR 2019, 15, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, J.; Profit, J.; Lee, H.C.; Dueñas, G.; Bennett, M.V.; Parucha, J.; Jocson, M.A.L.; Gould, J.B. Variations in Neonatal Antibiotic Use. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20180115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotten, C.M.; Taylor, S.; Stoll, B.; Goldberg, R.N.; Hansen, N.I.; Sanchez, P.J.; Ambalavanan, N.; Benjamin, D.K.; for the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Prolonged Duration of Initial Empirical Antibiotic Treatment Is Associated with Increased Rates of Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Death for Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantey, J.B.; Patel, S.J. Antimicrobial Stewardship in the NICU. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 28, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esaiassen, E.; Fjalstad, J.W.; Juvet, L.K.; van den Anker, J.N.; Klingenberg, C. Antibiotic Exposure in Neonates and Early Adverse Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1858–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantey, J.B.; Wozniak, P.S.; Pruszynski, J.E.; Sánchez, P.J. Reducing Unnecessary Antibiotic Use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (SCOUT): A Prospective Interrupted Time-Series Study. Lancet Infecti. Dis. 2016, 16, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjalstad, J.W.; Stensvold, H.J.; Bergseng, H.; Simonsen, G.S.; Salvesen, B.; Rønnestad, A.E.; Klingenberg, C. Early-Onset Sepsis and Antibiotic Exposure in Term Infants: A Nationwide Population-Based Study in Norway. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.B.; Sharland, M.; Heath, P.T. Improving Antibiotic Prescribing in Neonatal Units: Time to Act. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal. Ed. 2012, 97, F141–F146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, D.A.; Bauer, K.A.; Reed, E.E.; Stevenson, K.B.; Taylor, J.J.; West, J.E. Is the “Low-Hanging Fruit” Worth Picking for Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, C.; Kornelisse, R.F.; Buonocore, G.; Maier, R.F.; Stocker, M. Culture-Negative Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis—At the Crossroad between Efficient Sepsis Care and Antimicrobial Stewardship. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo da Silva, A.R.; Marques, A.; Di Biase, C.; Faitanin, M.; Murni, I.; Dramowski, A.; Hübner, J.; Zingg, W. Effectiveness of Antimicrobial Stewardship Programmes in Neonatology: A Systematic Review. Arch. Dis. Child 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.-H.; Michelow, I.C.; Cronin, J.; Ringer, S.A.; Ferris, T.G.; Puopolo, K.M. Effectiveness of a Guideline to Reduce Vancomycin Use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, J.Y.; Paquette, V.; Ng, K.; Lisonkova, S.; Hait, V.; Shivanada, S.; Tilley, P.; Osiovich, H.; Roberts, A. Reduction of Inappropriate Antimicrobial Prescriptions in a Tertiary Neonatal Intensive Care Unit After Antimicrobial Stewardship Care Bundle Implementation. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzegwu, N.I.; Rychalsky, M.R.; Nallu, L.A.; Song, X.; Deng, Y.; Natusch, A.M.; Baltimore, R.S.; Paci, G.R.; Bizzarro, M.J. Implementation of an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2017, 38, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Fishman, N.O.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Morales, K.H.; Weiner, M.G.; Synnestvedt, M.; Nachamkin, I.; Lautenbach, E. Risk Factors for Fluconazole-Resistant Candida Glabrata Bloodstream Infections. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassiouny, D.M.; Hassan, R.M.; Shalaby, A.; Halim, M.M.A.; Wassef, M.A. Establishment of an Antimicrobial Stewardship Strategy on the Surgical NICU at Cairo University Specialized Pediatric Hospital. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 55, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolia, V.; Desai, S.; Qin, H.; Rayburn, P.; Poon, G.; Murthy, K.; Ellsbury, D.; Chiruvolu, A. Implementation of an Automatic Stop Order and Initial Antibiotic Exposure in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Am. J. Perinatol. 2016, 34, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, H.; Wang, L. Implementation of the Smart Use of Antibiotics Program to Reduce Unnecessary Antibiotic Use in a Neonatal ICU: A Prospective Interrupted Time-Series Study in a Developing Country. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baky, R.M.A.; Senosy, E.M.; Omara, W.; Mohamed, D.S.; Ibrahim, R.A. The Impact of the Implementation of Culture-Based Antibiotic Policy on the Incidence of Nosocomial Infections in Neonates Hospitalized in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit in a General Egyptian Hospital in Upper Egypt, 2016–2018. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 1879–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thampi, N.; Shah, P.S.; Nelson, S.; Agarwal, A.; Steinberg, M.; Diambomba, Y.; Morris, A.M. Prospective Audit and Feedback on Antibiotic Use in Neonatal Intensive Care: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, L.; Lindquist, S.; Elfvin, A.; Hentz, E.; Studahl, M. Reduced Antibiotic Use in Extremely Preterm Infants with an Antimicrobial Stewardship Intervention. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2020, 4, e000872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dretvik, T.; Solevåg, A.L.; Finvåg, A.; Størdal, E.H.; Størdal, K.; Klingenberg, C. Active Antibiotic Discontinuation in Suspected but Not Confirmed Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis—A Quality Improvement Initiative. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyar, O.J.; Tebano, G.; Pulcini, C. Managing Responsible Antimicrobial Use: Perspectives across the Healthcare System. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, P.; Fung, T.; Killion, A.; Terrin, N.; Barza, M. Favorable Impact of a Multidisciplinary Antibiotic Management Program Conducted During 7 Years. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2003, 24, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchet, F.; Le Moing, V.; Dirand, D.; Cros, F.; Lienard, A.; Reynes, J.; Giraudon, L.; Morquin, D. Effectiveness and Acceptance of Multimodal Antibiotic Stewardship Program: Considering Progressive Implementation and Complementary Strategies. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, R.F.; Bhattarai, S.; Basu, S.K.; Hahn, A.; Stone, B.; Sadler, E.D.; Hammer, B.M.; Galiote, J.; Slomkowski, J.; Casto, A.M.; et al. Reducing Vancomycin Use in a Level IV NICU. Pediatrics 2020, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astorga, M.C.; Piscitello, K.J.; Menda, N.; Ebert, A.M.; Ebert, S.C.; Porte, M.A.; Kling, P.J. Antibiotic Stewardship in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: Effects of an Automatic 48-Hour Antibiotic Stop Order on Antibiotic Use. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2019, 8, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puopolo, K.M.; Benitz, W.E.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Committee on Fetus and Newborn; Committee on Infectious Diseases. Management of Neonates Born at ≥35 0/7 Weeks’ Gestation with Suspected or Proven Early-Onset Bacterial Sepsis. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20182894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, J.; Dimand, R.J.; Lee, H.C.; Duenas, G.V.; Bennett, M.V.; Gould, J.B. Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Antibiotic Use. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, A.R.; Kirkby, S.; Kornhauser, M. Practice Variation in Suspected Neonatal Sepsis: A Costly Problem in Neonatal Intensive Care. J. Perinatol. 2005, 25, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.; Dukhovny, D.; Zupancic, J.A.F.; Goldmann, D.A.; Horbar, J.D.; Pursley, D.M. Choosing Wisely in Newborn Medicine: Five Opportunities to Increase Value. Pediatrics 2015, 136, e482–e489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, J.S.; Prasad, P.A.; Fiks, A.G.; Localio, A.R.; Bell, L.M.; Keren, R.; Zaoutis, T.E. Durability of Benefits of an Outpatient Antimicrobial Stewardship Intervention After Discontinuation of Audit and Feedback. JAMA 2014, 312, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogrinc, G.; Davies, L.; Goodman, D.; Batalden, P.; Davidoff, F.; Stevens, D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): Revised Publication Guidelines from a Detailed Consensus Process. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2016, 25, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Number of Neonates & | Pre-Intervention | Post-Intervention | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 507 | 518 | ||
| Sex | N (%) | N (%) | |
| Male | 311 (61.3) | 329 (63.5) | 0.473 |
| Female | 196 (38.7) | 189 (36.5) | |
| Delivery | |||
| Vaginal | 145 (28.7) | 144 (27.9) | 0.790 |
| Caesarean | 361 (71.3) | 372 (72.1) | |
| Group B Streptococcus status | |||
| Negative | 151 (29.8) | 132 (25.6) | 0.803 * |
| Positive | 20 (4.0) | 16 (3.1) | |
| Unknown | 335 (66.2) | 367 (71.3) | |
| Chorioamnionitis | |||
| No | 476 (94.1) | 413 (80.3) | 0.849 * |
| Yes | 4 (0.8) | 3 (0.6) | |
| Unknown | 26 (5.1) | 98 (19.1) | |
| Rupture of Membranes (>18 h) | |||
| No | 461 (91.1) | 393 (97.3) | 0.194 * |
| Yes | 21 (4.2) | 11 (2.7) | |
| Unknown | 24 (4.7) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | ||
| Gestational Age (weeks) | 38 (37–39) | 38 (37–39) | 0.413 |
| Birth Weight (grams) | 3100 (2755–3420) | 3140 (2800–3420) | 0.275 |
| Unit | N1 | Mean1 (SD) | Median (IQR) | N2 | Mean2 (SD) | Median (IQR) | Difference of Mean AB Duration before and after the Intervention | Calculated total Difference of Antibiotic Administration Days * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NICU 1 | 21 | 5.7 (4) | 5 (3–6) | 12 | 4.6 (1.7) | 5 (3–5) | −1.1 | −13.2 |
| NICU 2 | 51 | 5.5 (3.4) | 4 (3–7) | 88 | 4.2 (1.5) | 4 (3–5) | −1.3 | −114.4 |
| NICU 3 | 20 | 5.9 (2.3) | 5 (4–7) | 22 | 5.5 (2.4) | 5 (4–6) | −0.4 | −8.4 |
| NICU 4 | 30 | 7.8 (6.9) | 7 (5–9) | 17 | 6.4 (1.8) | 8 (5–9) | −1.4 | −23.8 |
| NICU 5 | 18 | 10.5 (8.4) | 7 (5–10) | 21 | 7.6 (3.6) | 6 (5–11) | −2.9 | −60.9 |
| NICU 6 | 10 | 2.6 (1) | 2 (2–3) | 12 | 3.6 (1.3) | 3 (3–4.5) | 1 | 12 |
| NICU 7 | 38 | 5 (2.4) | 4 (3–6) | 65 | 5.1 (2.6) | 5 (3–7) | 0.1 | 6.5 |
| NICU 8 | 32 | 4.4 (1.8) | 4 (3–5.5) | 30 | 5.1 (3.6) | 4 (3–7) | 0.7 | 21 |
| NICU 9 | 70 | 4.4 (3.1) | 4 (3–5) | 37 | 3.4 (1.7) | 3 (2–4) | −1 | −37 |
| NICU 10 ^ | 55 | 5 (1.8) | 5 (3–6) | − | − | − | − | − |
| NICU 11 | 84 | 7.7 (5.6) | 7 (4–10) | 73 | 8.7 (6.8) | 7 (5–10) | 1 | 73 |
| NICU 12 | 16 | 7.8 (2.2) | 7.5 (7–9.5) | 11 | 8 (3.3) | 6 (5–9) | 0.2 | 2.2 |
| NICU 13 | 67 | 6.4 (2.7) | 6 (5–7) | 77 | 5.1 (2.3) | 4 (3–6) | −1.3 | −100.1 |
| NICU 14 ^ | 43 | 4.7 (2.6) | 4 (3–5) | − | − | − | − | − |
| NICU 15 | 50 | 8.7 (4.2) | 7.5 (6–10) | 54 | 7.3 (3.9) | 6 (5–7) | −1.4 | −75.6 |
| Total | 605 | 6.2 (4.2) | 5 (4–7) | 518 | 5.8 (3.9) | 5 (3–7) | −318.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopsidas, I.; Tsopela, G.-C.; Molocha, N.-M.; Bouza, E.; Chorafa, E.; Chorianopoulou, E.; Giapros, V.; Gkentzi, D.; Gkouvas, T.; Kapetanaki, A.; et al. Reducing Duration of Antibiotic Use for Presumed Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis in Greek NICUs. A “Low-Hanging Fruit” Approach. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030275
Kopsidas I, Tsopela G-C, Molocha N-M, Bouza E, Chorafa E, Chorianopoulou E, Giapros V, Gkentzi D, Gkouvas T, Kapetanaki A, et al. Reducing Duration of Antibiotic Use for Presumed Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis in Greek NICUs. A “Low-Hanging Fruit” Approach. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(3):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030275
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopsidas, Ioannis, Grammatiki-Christina Tsopela, Nafsika-Maria Molocha, Eleni Bouza, Elisavet Chorafa, Evangelia Chorianopoulou, Vasileios Giapros, Despoina Gkentzi, Theodoros Gkouvas, Anastasia Kapetanaki, and et al. 2021. "Reducing Duration of Antibiotic Use for Presumed Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis in Greek NICUs. A “Low-Hanging Fruit” Approach" Antibiotics 10, no. 3: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030275
APA StyleKopsidas, I., Tsopela, G.-C., Molocha, N.-M., Bouza, E., Chorafa, E., Chorianopoulou, E., Giapros, V., Gkentzi, D., Gkouvas, T., Kapetanaki, A., Karachristou, K., Karavana, G., Kourkouni, E., Kourlaba, G., Lithoxopoulou, M., Papaevangelou, V., Polychronaki, M., Roilides, E., Siahanidou, T., ... Preventing Hospital-Acquired Infections in Greece (PHiG) Investigators. (2021). Reducing Duration of Antibiotic Use for Presumed Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis in Greek NICUs. A “Low-Hanging Fruit” Approach. Antibiotics, 10(3), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030275







