Abstract
Efforts to develop and pair novel oral β-lactamase inhibitors with existing β-lactam agents to treat extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales are gaining ground. Ceftibuten is an oral third-generation cephalosporin capable of achieving high urine concentrations; however, there are no robust data describing its pharmacodynamic profile. This study characterizes ceftibuten pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in a neutropenic murine thigh infection model. Enterobacterales isolates expressing no known clinically-relevant enzymatic resistance (n = 7) or harboring an ESBL (n = 2) were evaluated. The ceftibuten minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were 0.03–4 mg/L. Nine ceftibuten regimens, including a human-simulated regimen (HSR) equivalent to clinical ceftibuten doses of 300 mg taken orally every 8 h, were utilized to achieve various fT > MICs. A sigmoidal Emax model was fitted to fT > MIC vs. change in log10 CFU/thigh to determine the requirements for net stasis and 1-log10 CFU/thigh bacterial burden reduction. The growth of the 0 h and 24 h control groups was 5.97 ± 0.37 and 8.51 ± 0.84 log10 CFU/thigh, respectively. Ceftibuten HSR resulted in a -0.49 to -1.43 log10 CFU/thigh bacterial burden reduction at 24 h across the isolates. Stasis and 1-log10 CFU/thigh reduction were achieved with a fT > MIC of 39% and 67%, respectively. The fT > MIC targets identified can be used to guide ceftibuten dosage selection to optimize the likelihood of clinical efficacy.
1. Introduction
Gram-negative Enterobacterales that harbor extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) and carbapenemases continue to be a burden on healthcare [1,2,3]. ESBLs, in particular, are frequent causes of infection in both hospitalized and community-dwelling patients [1,3]. Few oral therapeutic options exist, resulting in the use of intravenous broad-spectrum antibiotics (i.e., carbapenems) with the potential for further resistance development [4,5]. Moreover, infections caused by ESBL-harboring Enterobacterales are associated with an approximately two-fold increase in the cost of hospitalization and the length of stay compared with β-lactamase naïve infections [6].
The clear need for carbapenem-sparing antibiotics that can effectively treat ESBL-harboring Enterobacterales has spurred numerous oral drug development efforts over the past several years [7]. Additionally, the availability of an effective oral agent targeting these challenging organisms would provide a significant therapeutic breakthrough for patients treated outside the institutional setting. Thus, repurposing older and infrequently utilized oral β-lactam agents, such as ceftibuten, cefixime, and cefpodoxime, to be paired with investigational β-lactamase inhibitors (BLIs), has become an attractive option.
Ceftibuten has been explored as a β-lactam (BL) backbone because of its excellent bioavailability (75–90%) and high fractional excretion in urine [8,9]. In addition, ceftibuten demonstrates improved in vitro stability against ESBLs compared with other oral third-generation cephalosporins [8,9]. Ceftibuten’s pharmacodynamic driver is free drug time above MIC (fT > MIC). The fT > MIC requirements that best correlate with cephalosporin efficacy vary from 40–50%, as reported by the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) scientific committee [10], to as high as 50–70% [11,12]. However, a formal ceftibuten pharmacodynamic assessment against clinically-relevant Enterobacterales has never been performed. Previously published studies have focused on the activity of ceftibuten in combination with BLIs, with a focus on understanding BLI exposure requirements for efficacy [13,14]. Thus, ceftibuten-specific pharmacodynamic profiling is needed in order to better understand the scope and potential utility of a range of exposures prior to their combination with a novel BLI. Herein, we describe a pharmacodynamic assessment of ceftibuten in a neutropenic murine thigh infection model.
2. Results
2.1. Murine Pharmacokinetic Studies
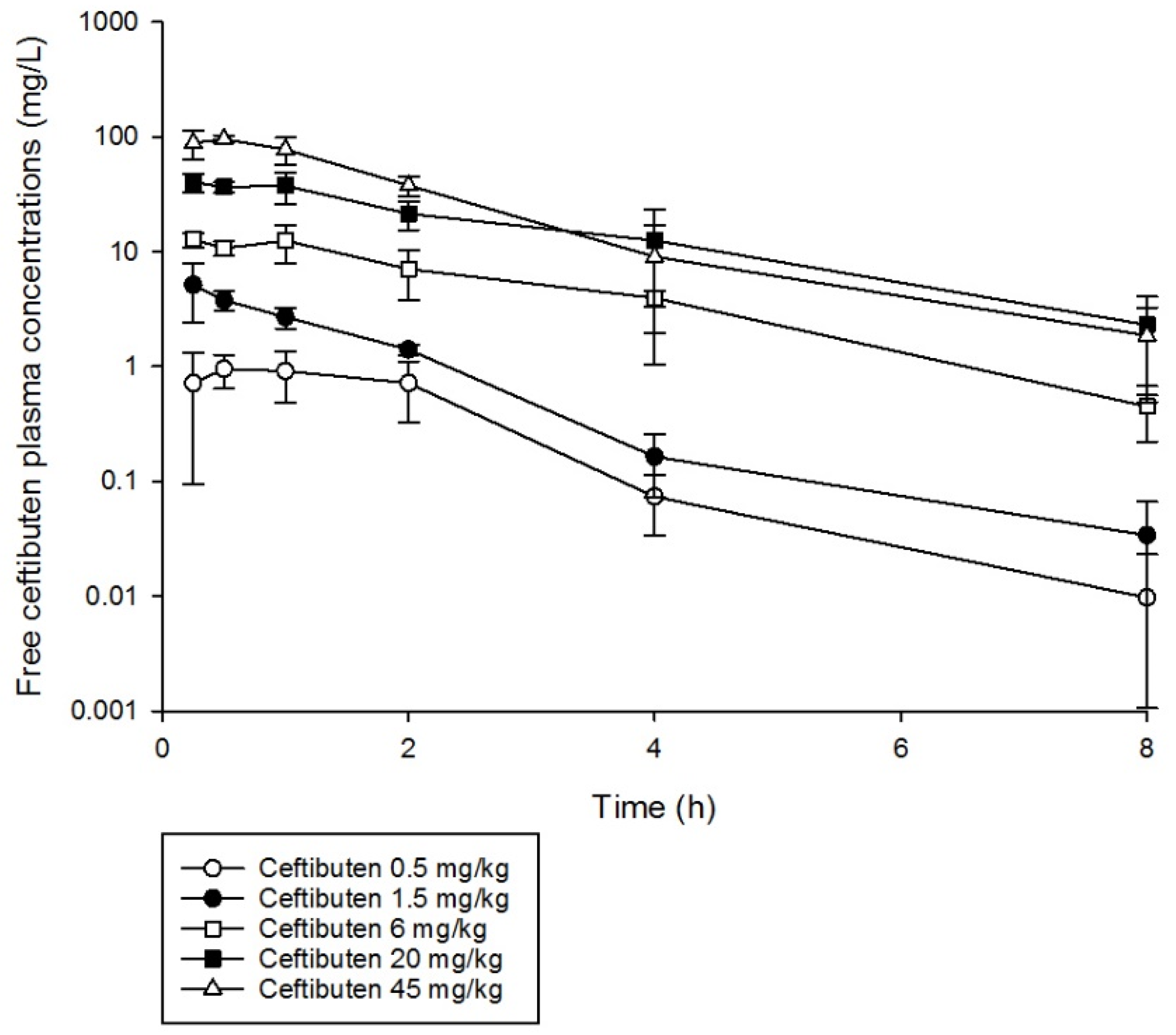
Ceftibuten single doses were well characterized using a uniform one-compartment model with first-order absorption and elimination (Figure 1). Furthermore, the pharmacokinetics of ceftibuten were relatively linear (area under the curve (AUC) R2 0.98) over the single doses administered using non-compartmental analysis (Table 1). The elimination half-life ranged from 1.0 to 1.8 h. The mean (± standard deviation (SD)) pharmacokinetic parameters, namely, volume of distribution (Vd), 0.342 ± 0.09 (L/kg); absorption constant (Ka), 5.45 ± 2.46 (1/h); and elimination constant (Ke), 0.60 ± 0.17 (1/h), were used to simulate ceftibuten regimens and obtain concentration–time profiles. Comparisons of the %fT > MIC values achieved with ceftibuten at MICs ranging between 0.03 and 4 mg/L, as well as the area under the concentration–time curve from 0 to 24 h for the free, unbound fraction of the drug (fAUC0–24), in mice receiving the selected regimens are presented in Table 2.
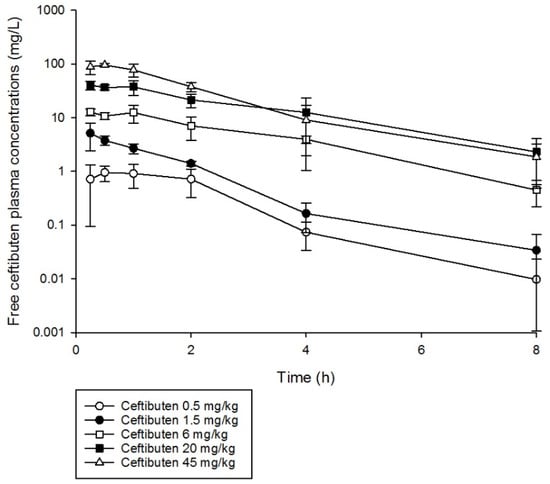
Figure 1.
Ceftibuten free plasma concentration–time profiles in a neutropenic mouse thigh infection model following the administration of single subcutaneous doses (0.5–45 mg/kg).

Table 1.
Comparison of single dose ceftibuten regimens in mice using non-compartmental analysis.

Table 2.
Comparison of the %fT > MIC values achieved with ceftibuten regimens at different MICs in humans and the murine thigh infection model.
2.2. Pharmacodynamic Studies
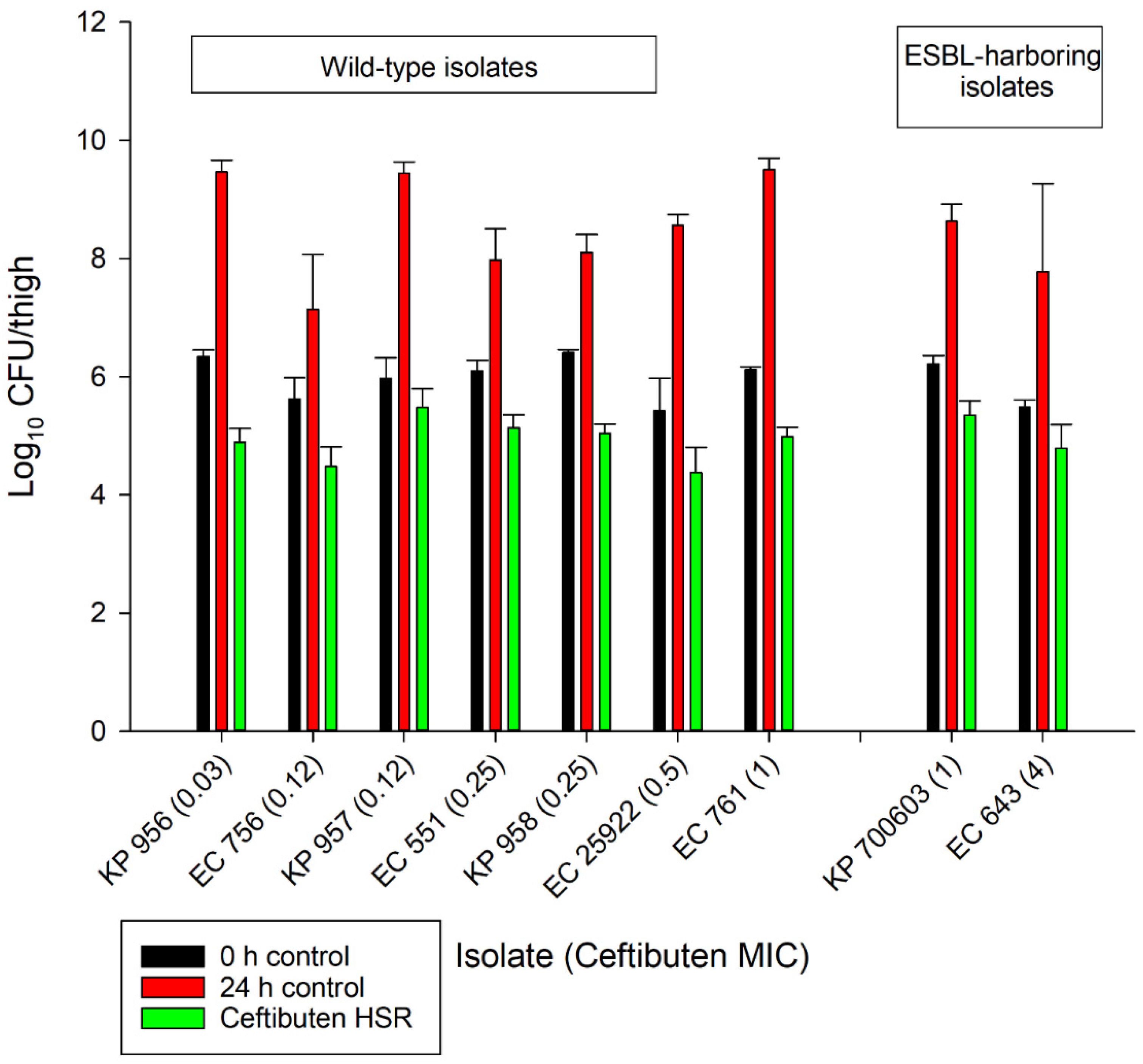
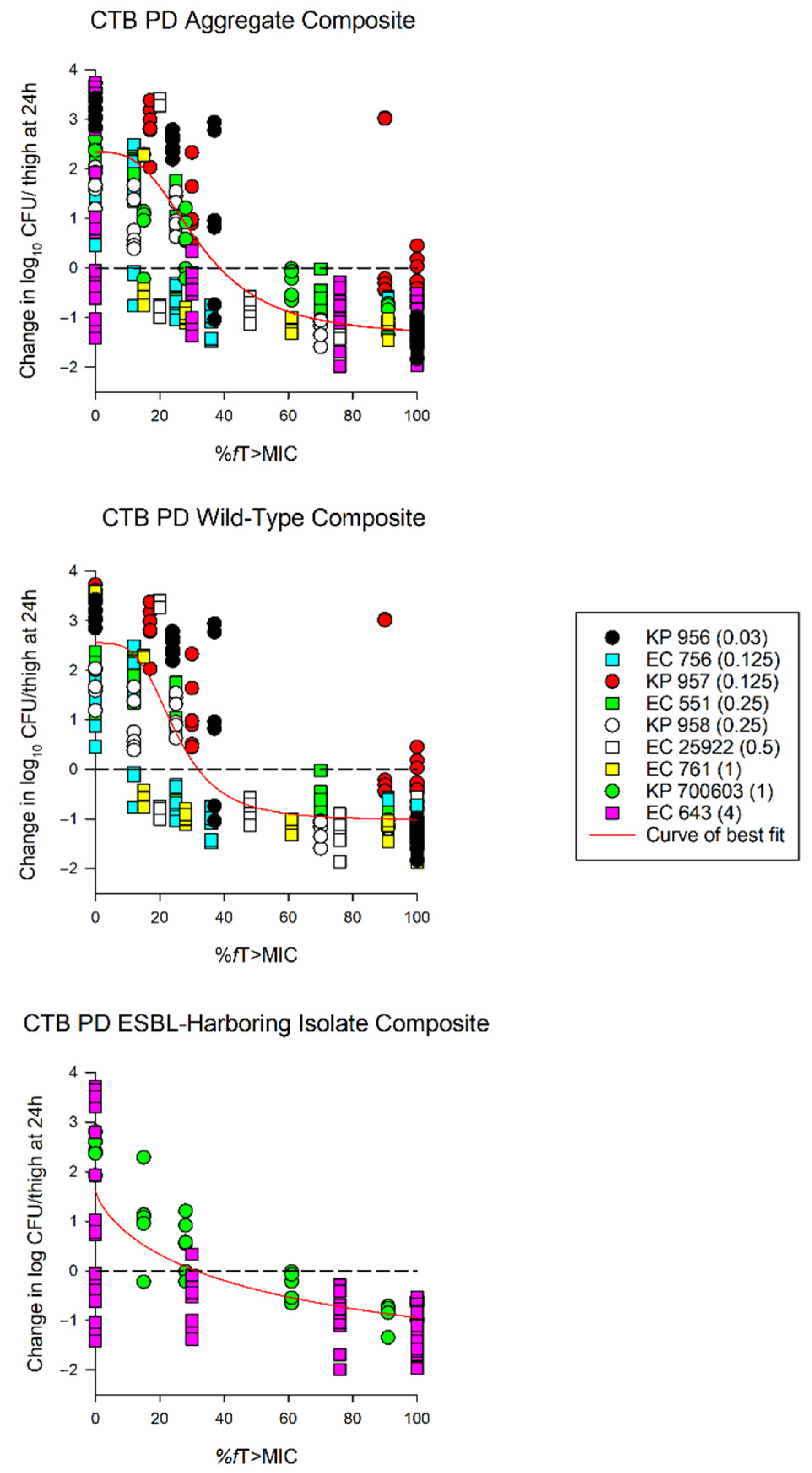
The average growth (± standard deviation) of the 0 h and 24 h control groups were 5.97 ± 0.37 log10 CFU/thigh and 8.51 ± 0.84 log10 CFU/thigh, respectively (Figure 2). The administration of ceftibuten HSR resulted in bacterial reductions in all isolates (range: -0.49 to 1.43 log10 CFU/thigh), and five of the nine isolates achieved a 1-log10 CFU/thigh reduction. The composite exposure–response relationship for ceftibuten against individual isolates is depicted in Table 3. Reflecting the strain variability among these clinical isolates, the exposure–response relationships for the isolates were also variable, based on the coefficient of determination (average R2 = 0.79, range: 0.39 to 0.92); however, the majority were relatively robust (R2 > 0.70). Using these sigmoidal fits, three of the nine isolates did not achieve a 1-log10 CFU/thigh reduction, while one isolate did not achieve stasis. The fT > MICs corresponding to the stasis and 1-log10 reduction for each individual isolate are provided in Table 3. On average, the fT > MIC required for the bacteriostasis and 1-log10 reduction against the five E. coli isolates evaluated was 34% and 61%, respectively. A higher fT > MIC threshold for the stasis (44%) and 1-log10 reduction (77%) was observed against the four K. pneumoniae isolates evaluated. The aggregate static targets for wild-type isolates were similar to the ESBL-harboring isolates (fT > MIC 32% vs. 31%). Based on the composite exposure–response data from all isolates (Figure 3), the ceftibuten fT > MIC values associated with the static and 1-log10 targets for these nine isolates were 39% and 67%, respectively.
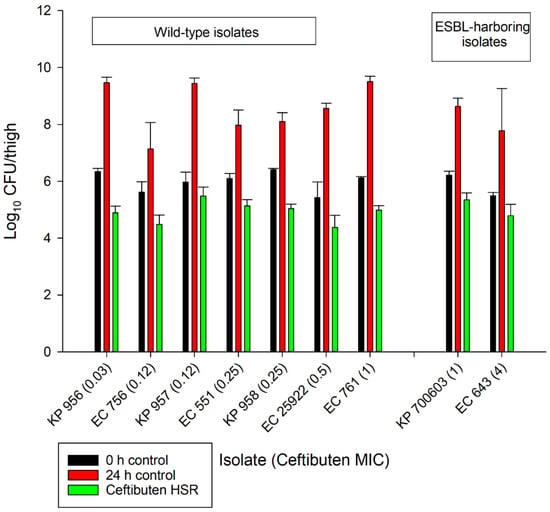
Figure 2.
In vivo antibacterial activity of the ceftibuten human-simulated regimen (300 mg taken orally every 8 h) compared to the 0 h and 24 h control groups.

Table 3.
%fT > MIC pharmacodynamic targets for ceftibuten against individual isolates and the aggregate composite.
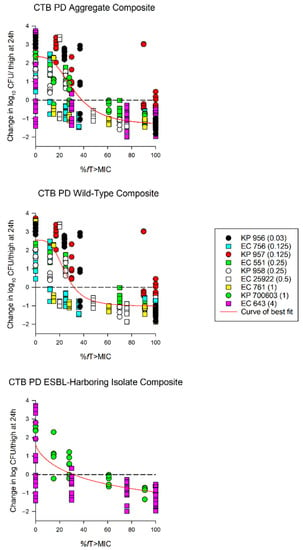
Figure 3.
Sigmoid Emax curves depicting %fT > MIC and change in log10 CFU/thigh for all isolates (aggregate composite), wild-type isolates, and extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-harboring isolates. Each dot represents the log10 CFU/thigh for each bacterial strain (ceftibuten MIC) per regimen. KP—Klebsiella pneumoniae; EC—Escherichia coli (EC). Aggregate composite: R2 = 0.79, EC50 = 32.46%, and Emax = 2.34 log10 CFU/thigh; wild-type composite: R2 = 0.83, EC50 = 24.92%, and Emax = 2.55 log10 CFU/thigh; ESBL composite: R2 = 0.64, EC50 = 58.87%, and Emax = 2.34 log10 CFU/thigh.
3. Discussion
The combination of novel BLIs with already-approved β-lactam agents continues to be a safe and attractive drug development strategy for combating the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance [6]. Although the majority of combination products in the pipeline are intravenous, a push towards the development of oral combination products to serve as a step-down option or to facilitate outpatient management is gaining momentum [7,16]. Characterizing the range of microbiological activity of β-lactam is imperative for understanding its potential activity against antibiotic resistant isolates when combined with a BLI. Therefore, this in vivo study sought to bridge the gap in ceftibuten pharmacodynamic knowledge and provide relevant exposure–response data against wild-type and ESBL-harboring isolates.
The ceftibuten dose-ranging experiments in this study demonstrated that a mean ceftibuten fT > MIC of 67% translated into a 1-log10 CFU/thigh reduction in bacterial burden. This data provide a ceftibuten-specific target, negating the extrapolation from ranges (40–70%) determined from other cephalosporin pharmacodynamic studies [10,11,12]. In addition, net stasis, an adopted microbiological surrogate for clinical efficacy in urinary tract infections (UTIs), [17] was observed at a ceftibuten fT > MIC of 39%.
Enzymatic mechanisms of resistance continue to be a major burden on public health, and ESBL-harboring isolates are no exception. ESBL-harboring Enterobaterales isolates continue to be a contributor to patient morbidity and mortality, with incidence increasing by 53% from 2012 to 2017 [18]. Unlike other forms of enzymatic resistance, ESBLs can commonly manifest in community and hospital-acquired infections [1]. The development of an appropriate oral BL/BLI against this infection entity is imperative. Ceftibuten is stable against narrow-spectrum ESBLs, but is readily hydrolyzed by broader spectrum variants [8,9]. In this study, the pharmacodynamic targets for ESBL-harboring isolates, albeit limited by the small sample size, were comparable to their wild-type counterpart, and were similar to previous findings [19]. In addition to classic dose-ranging studies, we also utilized a ceftibuten human-simulated regimen to evaluate the bactericidal activity of clinically-relevant ceftibuten exposure. Concordant with its clinical utility for UTIs, ceftibuten at an exposure equivalent to that of a human oral dose of 300 mg taken orally every 8 h resulted in bacterial stasis in all isolates and achieved a 1-log10 CFU/thigh reduction in five isolates. This regimen can be used in conjunction with a novel β-lactamase-inhibitor to optimize exposure profiles against ESBL- and carbapenemase-harboring isolates in vivo. Further studies evaluating the therapeutic potential of ceftibuten drug combinations are warranted.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antimicrobial Test Agents
Analytical grade ceftibuten (lot RCHX170002, Covalent Laboratories Private Limited, Hyderabad, India) was reconstituted and diluted to the desired dosing concentrations in a 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer. All doses were administered subcutaneously with a final volume of 0.2 mL.
4.2. Isolates
A total of nine clinical Enterobacterales isolates were obtained from the Centers for Disease Control and Food and Drug Administration Antimicrobial Resistance Isolate Bank (n = 1), the Antibacterial Research Leadership Group isolate bank (n = 5), the American Type Culture Collection (n = 2), and the Center for Anti-Infective Research and Development (CAIRD) isolate library (n=1). Escherichia coli (n = 5) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (n = 4) isolates were selected for their ESBL-harboring and wild-type genotypes. The ceftibuten broth microdilution MICs ranged from 0.03–4 mg/L. The individual isolate genotype and ceftibuten MICs are available in Table 4. Notably, one K. pneumoniae isolate (KP 956) was characterized as SHV-harboring, but displayed the phenotypic profile (ceftibuten MIC: 0.03 mg/L) of a wild-type isolate and thus was included in the wild-type isolate analysis. All of the isolates were stored frozen at −80 °C in skim milk. Prior to examination, each isolate was sub-cultured twice on trypticase soy agar with 5% sheep blood (Becton Dickinson and Co., Sparks, MD, USA) and incubated at 37 °C for 18–24 h.

Table 4.
Genotypic and phenotypic profiles of ceftibuten against the test isolates.
4.3. Animals
Specific-pathogen-free, female, CD-1 mice (20–22 g) were obtained from Charles River Laboratories, Inc. (Raleigh, NC, USA). All animals were allowed to acclimatize for 48 h prior to the study procedures, and were housed in groups of six animals at controlled room temperature in HEPA-filtered cages (Innovive, San Diego, CA, USA). The cages were supplemented with paper nesting material for enrichment purposes. Study rooms were maintained with diurnal cycles (12 h light/12 h dark), and food and water were provided ad libitum. Animals were monitored three times daily for signs of morbidity and were euthanized if found moribund; tissues were harvested subsequent to euthanasia.
4.4. Neutropenic Thigh Infection Model
Prior to both the pharmacokinetic and in vivo efficacy studies, the animals were prepared as follows: neutropenia was induced by administering 150 mg/kg of intraperitoneal (i.p.) cyclophosphamide on day 4 and 100 mg/kg on day 1. In addition, a predictable degree of renal impairment was produced using 5 mg/kg of uranyl nitrate administered i.p. on day 3 [20]. Bacterial suspensions of ~1 × 107 colony forming units (CFU)/mL in normal saline were used for the inoculation of both thighs (injection volume 0.1 mL) 2 h prior to the first antibacterial dose.
4.5. Murine Pharmacokinetic Studies
The ceftibuten pharmacokinetic parameters were derived from single dose pharmacokinetic studies. Briefly, six mice per time point were prepared for experimentation as described above, and were then subjected to a single dose of ceftibuten (0.5 mg/kg, 1.5 mg/kg, 6 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg, and 45 mg/kg). The mice were euthanized by CO2-asphyxiation and blood samples were obtained by cardiac puncture. Six time-points were assessed (0.25 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, and 8 h). Blood was collected in K2EDTA Tubes (Becton Dickinson and Co., Sparks, MD, USA) and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min at 8 °C. The separated plasma was stored at −80 °C until the total drug concentrations were determined using an ultra-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method. The pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated using the mean drug concentrations from each group of mice, while the AUC was estimated using the linear-up log-down trapezoidal rule. Using the pharmacokinetic parameter estimates derived from the single dose pharmacokinetic studies, concentration–time profiles over 24 h were simulated to obtain fT > MIC values for the respective doses administered. All pharmacokinetic analyses were performed in Phoenix WinNonlin (Pharsight Corp., Mountainview, CA, USA). The final weighting schemes were decided on by considering the Akaike information criterion and best visual fit. The averaged pharmacokinetic parameters were also used to develop a human-simulated regimen. Simulated-free ceftibuten concentrations were determined by considering the extent of murine protein binding (19.7%) [13].
4.6. Pharmacodynamic Studies
Eight ceftibuten regimens with doses ranging from 0.5 to 45 mg/kg over a frequency of once to every 3 h were developed to achieve various fT > MICs. In addition, a previously developed ceftibuten human-simulated dosing regimen (HSR) was administered to achieve plasma exposures similar to those achieved in humans following an oral dose of 300 mg of ceftibuten every 8 h [15,21]. During experimentation, 7 groups (2 control and 5 treatment groups) of 3 mice each were inoculated with the respective isolates. Two hours after thigh inoculation, one group was sacrificed at 0 h via CO2-asphxyation and cervical dislocation in order to determine the baseline bacterial burden. The remaining 6 groups received a subcutaneous injection of one of the following regimens for 24 h: ceftibuten HSR, a selected ceftibuten regimen to achieve a targeted fT > MIC, or an injection of 0.9% normal saline (NS) given at the same frequency as the ceftibuten HSR. After 24 h, all treatment groups were euthanized and the thighs (n = 6/group) were aseptically harvested and homogenized in NS. Each thigh was treated as an independent value. The homogenized thigh was serially diluted onto trypticase soy agar with 5% sheep blood (Becton Dickinson and Co., Sparks, MD, USA), and colonies were enumerated to determine the number of CFU per thigh after incubation overnight. The efficacy of each regimen was determined using the change in log10 CFU/thigh from the 0 h control. Log10 change in CFU/thigh was reported as mean ± SD for ceftibuten HSR. A uniform Emax model using the Hill equation was fitted to the fT > MIC vs. change in bacterial burden at 24 h using Phoenix WinNonlin for individual isolates. An aggregate composite model derived from the averaged Emax model parameters of all bacterial strain data was constructed. Similarly, composite profiles for all the wild-type, ESBL-harboring, E. coli, and K. pneumonia isolates were also constructed using their respective strain data. These models were used to calculate effective stasis and 1-log10 reduction pharmacodynamic targets for individual isolates and the aggregate composite.
5. Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study examining the pharmacodynamics of ceftibuten. In conjunction with the classic exposure–response profiles, the clinical exposure assessment using the human-simulated regimen provides a framework for the selection of ceftibuten as a partner agent in BL/BLI oral combinations against isolates frequently causing urinary tract infections. Additional studies evaluating these types of drug combinations are warranted.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed significantly to the completion of this paper in the following manner: conceptualization, D.P.N.; methodology, M.J.L., T.E.A., and D.P.N.; formal analysis, M.J.L., T.E.A., and D.P.N.; writing—original draft preparation, M.J.L.; writing—review and editing, M.J.L., T.E.A., and D.P.N.; funding acquisition, D.P.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was funded by Venatorx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Malvern, PA, USA), with federal funds from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institute of Health, and Department of Health and Human Services, under contract no. HHSN272201600029C. The funders provided financial support and did not exercise control over the conduct or reporting of the research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the National Research Council of the National Academy of Sciences standards. The study protocol (#HHC-2018-0052) was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Hartford Hospital (assurance #A3185-01).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon reasonable request to corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to recognize Alissa Padgett, Zach Fazzino, Deborah Santini, Janice Cunningham, Julio Rodriguez, Jennifer Tabor-Rennie, Rebecca Stewart, Nicole DeRosa, Ceara Wetteman, Lauren McLellan, Elizabeth Cyr, and Christian Gill from the Center for Anti-Infective Research and Development, and Lisa McLaughlin from Venatorx, for their assistance in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
D.P.N. has served as a consultant and speaker’s bureau member, and has received research funding from Allergan, Cepheid, Merck, Pfizer, Wockhardt, Shionogi, Tetraphase, and Venatorx. M.J.L. and T.E.A. have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Bush, K.; Bradford, P.A. Epidemiology of β-Lactamase-Producing Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guh, A.Y.; Bulens, S.N.; Mu, Y.; Jacob, J.T.; Reno, J.; Scott, J.; Wilson, L.E.; Vaeth, E.; Lynfield, R.; Shaw, K.M.; et al. Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in 7 US Communities, 2012–2013. JAMA 2015, 314, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDanel, J.; Schweizer, M.; Crabb, V.; Nelson, R.; Samore, M.; Khader, K.; Blevins, A.E.; Diekema, D.; Chiang, H.-Y.; Nair, R.; et al. Incidence of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella Infections in the United States: A Systematic Literature Review. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2017, 38, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meije, Y.; Pigrau, C.; Fernández-Hidalgo, N.; Clemente, M.; Ortega, L.; Sanz, X.; Loureiro-Amigo, J.; Sierra, M.; Ayestarán, A.; Morales-Cartagena, A.; et al. Non-intravenous carbapenem-sparing antibiotics for definitive treatment of bacteraemia due to Enterobacteriaceae producing extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) or AmpC β-lactamase: A propensity score study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Harrington, S.; Dihmess, A.; Woo, B.; Masoud, R.; Martis, P. Clinical epidemiology of carbapenem-intermediate or -resistant Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kotapati, S.; Kuti, J.L.; Nightingale, C.H.; Nicolau, D.P. Impact of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella species on clinical outcomes and hospital costs: A matched cohort study. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2006, 27, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp-Wallace, K.M. The latest advances in β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations for the treatment of Gram-negative bacterial infections. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2019, 20, 2169–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, R.C., Jr.; Nightingale, C.H.; Nicolau, D.P. Ceftibuten: An overview. Pharmacotherapy 1997, 17, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.G.; Harris, P.N.A.; Henderson, A.; Schembri, M.A.; Paterson, D.L. Oral cephalosporin and β-lactamase inhibitor combinations for ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae urinary tract infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 2384–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Society of Clincial Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Why Do EUCAST Have No Systemic Breakpoints for Enterobacterales with Oral Cephalosporins? Version 2. EUCAST. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Guidance_documents/Oral_ceph_breakpoints_v2_20200710.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Auckenthaler, R. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral beta-lactam antibiotics as a two-dimensional approach to their efficacy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50 (Suppl. 1), 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuti, J.L. Optimizing antimicrobial pharmacodynamics: A guide for your stewardship program. Rev. Med. Clin. Condes 2016, 27, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraouf, K.; Stainton, S.M.; Nicolau, D.P. In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Profile of Ceftibuten-Clavulanate Combination against Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in the Murine Thigh Infection Model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomovskaya, O.; Tsivkovski, R.; Nelson, K.; Rubio-Aparicio, D.; Sun, D.; Totrov, M.; Dudley, M.N. Spectrum of Beta-Lactamase Inhibition by the Cyclic Boronate QPX7728, an Ultrabroad-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Inhibitor of Serine and Metallo-Beta-Lactamases: Enhancement of Activity of Multiple Antibiotics against Isogenic Strains Expressing Single Beta-Lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Lim, J.; Radwanski, E.; Marco, A.; Affrime, M. Pharmacokinetics and dose proportionality of ceftibuten in men. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Target Product Profiles for Oral Therapy of Urinary Tract Infections; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Grayson, M.L.; Crowe, S.M.; McCarthy, J.S.; Mills, J.; Mouton, J.W.; Norrby, S.R.; Paterson, D.; Pfaller, M.A. Kucers’ the Use of Antibiotics Sixth Edition: A Clinical Review of Antibacterial, Antifungal and Antiviral Drugs; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jernigan, J.A.; Hatfield, K.M.; Wolford, H.; Nelson, R.E.; Olubajo, B.; Reddy, S.C.; McCarthy, N.; Paul, P.; McDonald, L.C.; Kallen, A.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Infections in U.S. Hospitalized Patients, 2012–2017. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andes, D.; Craig, W.A. Treatment of infections with ESBL-producing organisms: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolau, D.P.; Onyeji, C.O.; Zhong, M.; Tessier, P.R.; Banevicius, M.A.; Nightingale, C.H. Pharmacodynamic assessment of cefprozil against Streptococcus pneumoniae: Implications for breakpoint determinations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, L.M.; Abdelraouf, K.A.; Nicolau, D.P. Assesment of the In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Profile of Ceftibuten/VNRX-7145 Combination against Serine-Beta-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in the Neutropeneic Murine Thigh Infection Model. Presented at ASM Microbe, San Fransisco, CA, USA, 20–24 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).