Cross-Contamination of Enrofloxacin in Veterinary Medicinal and Nutritional Products in Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mund, M.D.; Khan, U.M.; Tahir, U.; Mustafa, B.-E.; Fayyaz, A. Antimicrobial drug residues in poultry products and implications on public health: A review. Int. J. Food. Prop. 2017, 20, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falowo, A.B.; Akimoladun, O.F. Veterinary Drug Residues in Meat and Meat Products: Occurrence, Detection and Implications. In Veterinary Medicine and Pharmaceuticals; Bekoe, S.O., Saravanan, M., Adosraku, R.K., Ramkumar, P.K., Eds.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. Residue Testing: National Residue Program. 2020. Washington, DC, USA. Available online: http://www.fsis.usda.gov/residue (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency. The Korean National Residue Program for- Veterinary Drugs and Contaminant Residues in Food of Animal Origin. 2008. Residue Chemistry & Toxicology Division, Korea. Available online: https://www.qia.go.kr/livestock/clean/listwebQiaCom.do?type=1_23clyfjy&clear=1 (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- National Residue Survey. Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment. Australian Government. Canberra, Australia. Available online: http://www.agriculture.gov.au/ag-farm-food/food/nrs (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Hao, H.; Sander, P.; Iqbal, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Yuan, Z. The risk of some veterinary antimicrobial agents on public health associated with antimicrobial resistance and their molecular basis. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratacós-Cubarsí, M.; García-Regueiro, J.A.; Castellari, M. Assessment of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin accumulation in pig and calf hair by HPLC and fluorimetric detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1991–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The United States Food and Drug Administration. Final Decision of the Commissioner Docket No. 2000N-1571: Withdrawal of Enrofloxacin for Poultry. 2017. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth/RecallsWithdrawals/ucm042004.htm (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Nelson, J.M.; Chiller, T.M.; Powers, J.H.; Angulo, F.J. Fluoroquinolone-resistant Campylobacter species and the withdrawal of fluoroquinolones from use in poultry: A public health success story. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Food and Agriculture Organization. Current Status of Knowledge on Veterinary Drug Carryover. Carryover in Feed and Transfer from Feed to Food of Unavoidable and Unintended Residues of Approved Veterinary Drugs. Joint FAO/WHO Expert Meeting. 2019. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ca6296en/ca6296en.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Cornejo, J.; Lapierre, L.; Iragüen, D.; Cornejo, S.; Cassus, G.; Richter, P.; San Martín, B. Study of enrofloxacin and flumequine residues depletion in eggs of laying hens after oral administration. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Therap. 2011, 35, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezenduka, E.V.; Oboegbulem, S.I.; Nwanta, J.A.; Onunkwo, J.I. Prevalence of antimicrobial residues in raw table eggs from farms and retail outlets in Enugu State, Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2011, 43, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, J.; Umoh, V.; Audu-Okoh, E.; Umoh, J.; Kwaga, J. Veterinary drug use in poultry farms and determination of antimicrobial drug residues in commercial eggs and slaughtered chicken in Kaduna State, Nigeria. Food Control 2004, 15, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, H.M.; Tavakoli, H.; Hashemi, G.; Mousavi, T.; Rostami, H.; Fesharaki, M.G.; Gholian, M. The occurrence of residues of furazolidone metabolite, 3-Amino-2-Oxazolidone, in eggs distributed in Mazandaran province, Iran. SCIMETR 2014, 2, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Moscoso, S.; De Los Santos, F.S.; Andino, A.; Diaz-Sanchez, S.; Hanning, I. Detection of quinolones in commercial eggs obtained from farms in the Espaíllat Province in the Dominican Republic. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eulambius, M. Pharmaceutical product cross-contamination: Industrial and clinical pharmacy practice. Dar. Es Sal. Med. Stud. J. 2012, 19, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cross-Contamination in Drug Manufacturing: The Regulatory Trends. FierceMarkets Custom Publishing, Washington, United States. 2014. Available online: https://www.vekamaf.cz/documents/99/Cross-contamination%20in%20drug%20manufacturing.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Fazio, T.T.; Singh, A.K.; Kedor-Hackmann, E.R.; Santoro, M.I. Quantitative determination and sampling of azathioprine residues for cleaning validation in production area. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 1495–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.W.; Hossain, M.A.; Park, H.C.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, K.J.; Park, S.W. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic integration of enrofloxacin against Salmonella Enteritidis after administering to broiler chicken by per-oral and intravenous routes. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 20, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
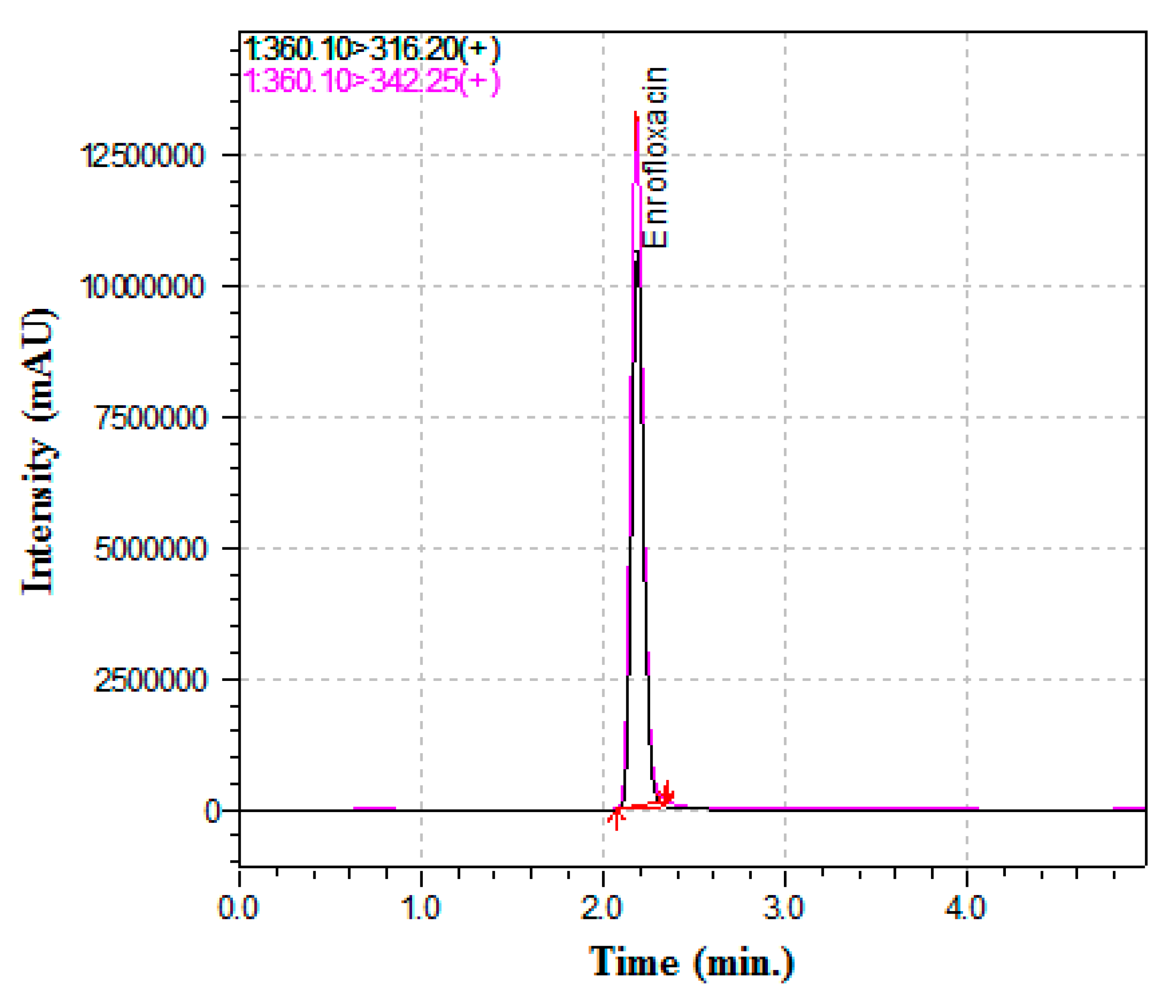
| Parameters of Method Validation | Units | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Retention time | min | 2.32 |
| Linearity (R2) | - | 0.99 |
| Average recovery | % | 99 |
| Coefficient of variation (CV) | % | 1.9 |
| Limit of detection (LOD) | ng/g | 0.1 |
| Limit of quantitation (LOQ) | ng/g | 0.3 |
| Lot Number | Concentration in ppm (mean ± SD) |
|---|---|
| 812901 | 4.57 ± 0.04 |
| 812902 | 179.08 ± 0.93 |
| 812903 | 9.71 ± 0.18 |
| Product Category | Number of Tested Product | Number of Contaminated Product | Label Claimed Active Ingredients | Concentration of Enrofloxacin Contaminant (mean ± SD) ppm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutritional Supplements | 19 | 0 | - | - |
| Penicillin antibiotics | 12 | 0 | - | - |
| Non-Penicillin antibiotics | 18 | 2 | Florfenicol | 3.00 ± 0.23 |
| Sulfatrimethoprim | 0.57 ± 0.11 | |||
| Other medicine (other than antibiotic) | 27 | 0 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.; Hossain, M.A.; Park, H.-c.; Jeong, O.m.; Park, S.-w.; Her, M. Cross-Contamination of Enrofloxacin in Veterinary Medicinal and Nutritional Products in Korea. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020128
Kang J, Hossain MA, Park H-c, Jeong Om, Park S-w, Her M. Cross-Contamination of Enrofloxacin in Veterinary Medicinal and Nutritional Products in Korea. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(2):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020128
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, JeongWoo, Md. Akil Hossain, Hae-chul Park, Ok me Jeong, Sung-won Park, and Moon Her. 2021. "Cross-Contamination of Enrofloxacin in Veterinary Medicinal and Nutritional Products in Korea" Antibiotics 10, no. 2: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020128
APA StyleKang, J., Hossain, M. A., Park, H.-c., Jeong, O. m., Park, S.-w., & Her, M. (2021). Cross-Contamination of Enrofloxacin in Veterinary Medicinal and Nutritional Products in Korea. Antibiotics, 10(2), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020128







