A Label-Free, Quantitative Fecal Hemoglobin Detection Platform for Colorectal Cancer Screening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
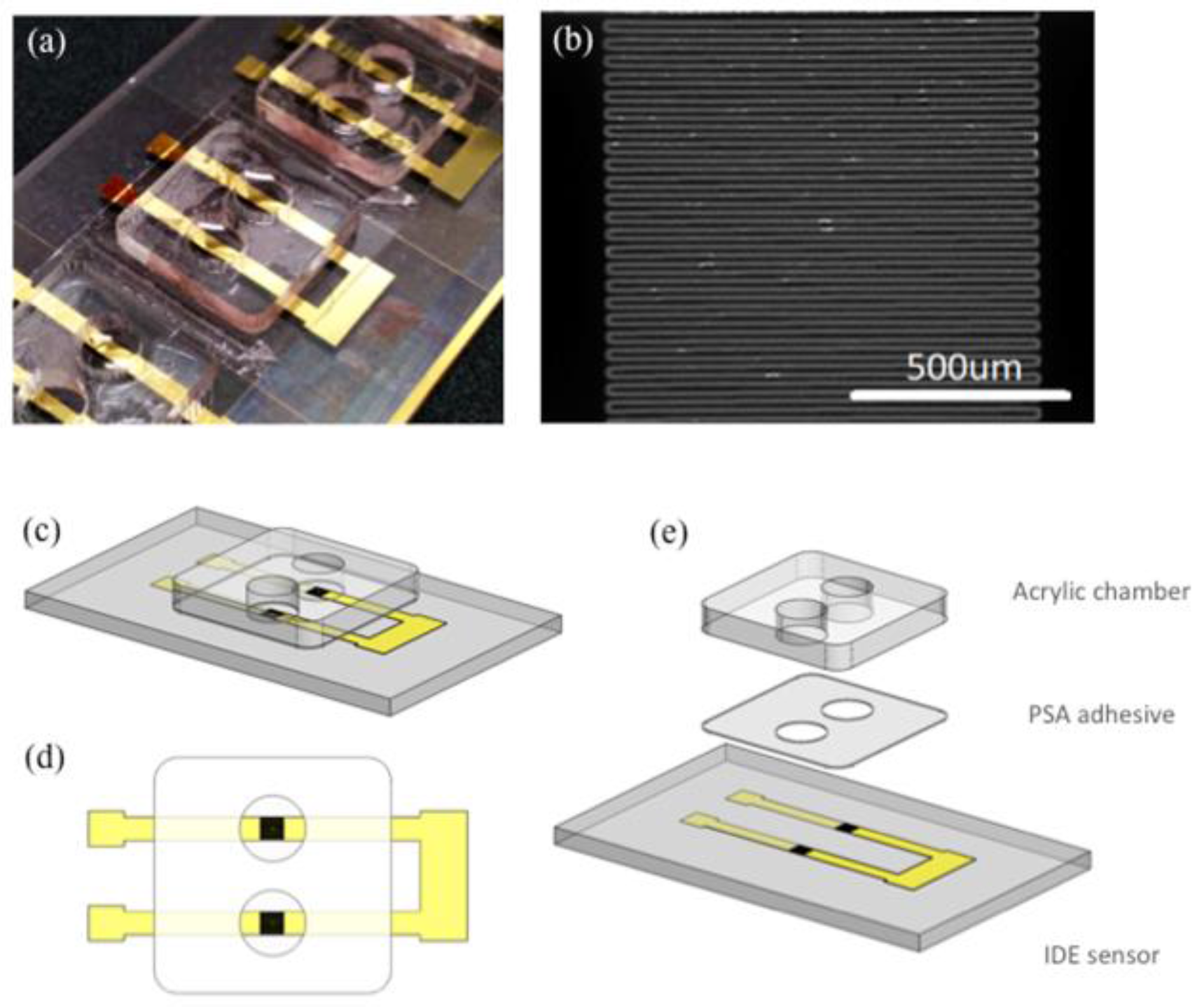
2.1. Sensor Fabrication
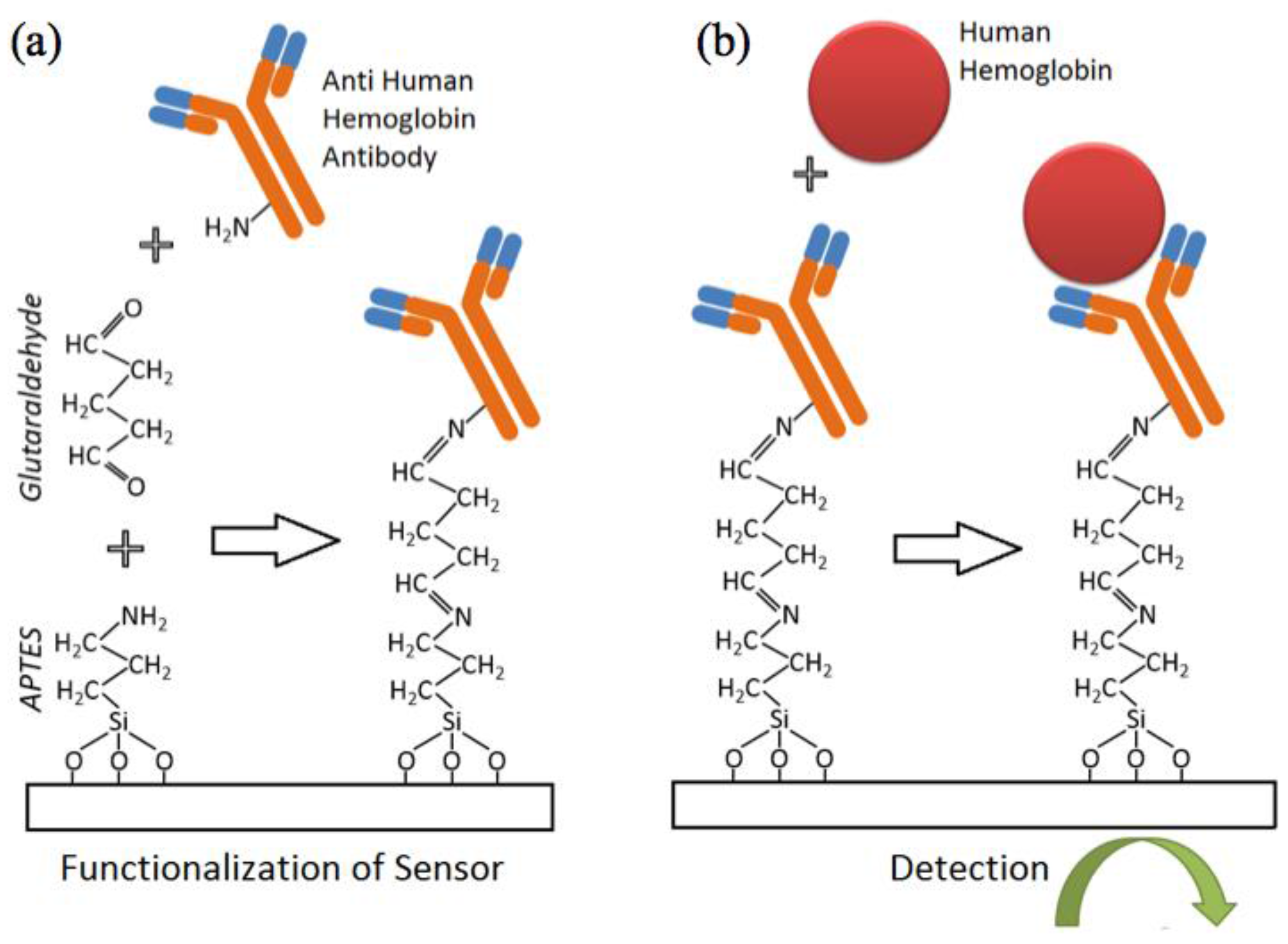
2.2. Sensor Functionalization, Sample Preparation and Measurement Workflow
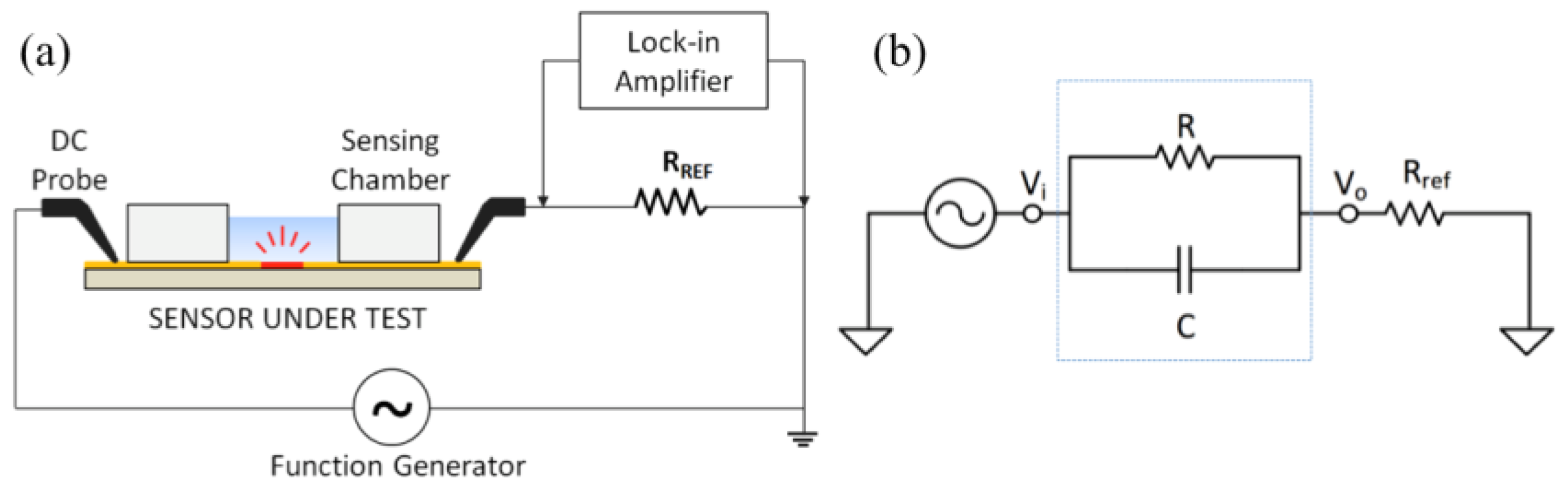
2.3. Electrical Measurement Setup and Circuit Modelling
2.4. Statistical Analysis
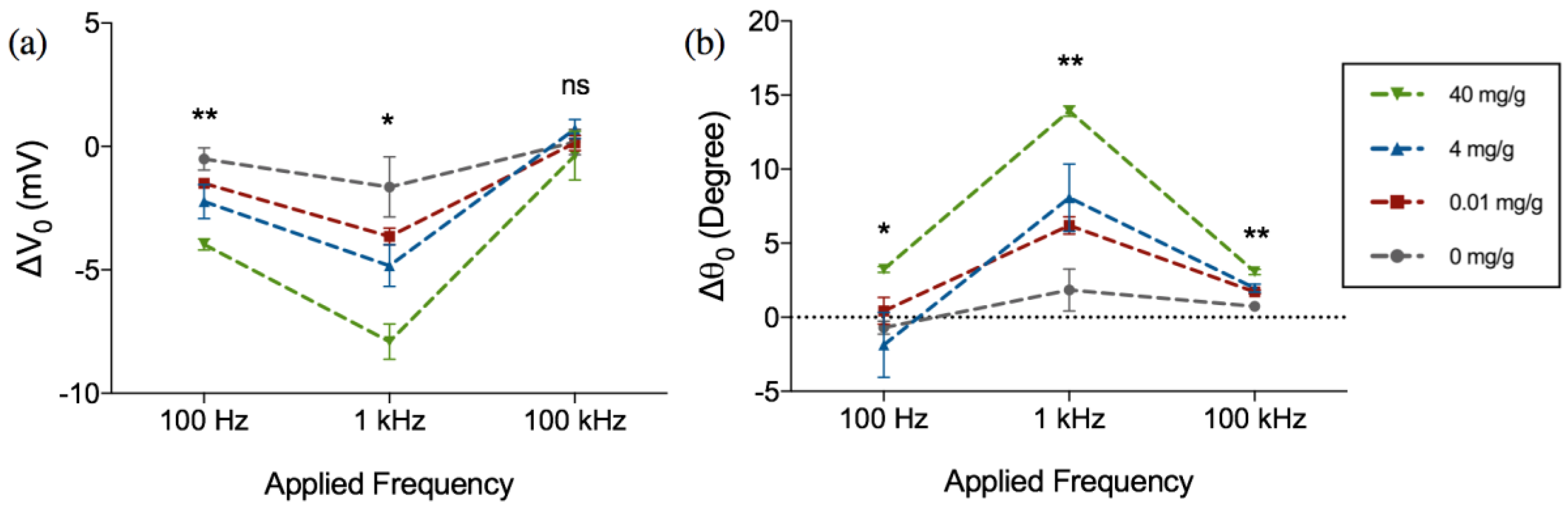
3. Results and Discussion
4. Future Research
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Ervik, M.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 [Internet]. International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2013; Available online: http://globocan.iarc.fr (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Karsa, L.V.; Lignini, T.A.; Patnick, J.; Lambert, R.; Sauvaget, C. The dimensions of the CRC problem. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 24, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center, M.M.; Jemalm, A.; Ward, E. International trends in colorectal cancer incidence rates. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 1688–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishehsari, F.; Mahdavinia, M.; Vacca, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Mariani-Costantini, R. Epidemiological transition of colorectal cancer in developing countries: Environmental factors, molecular pathways, and opportunities for prevention. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 6055–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Institute. SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Colon and Rectum Cancer. 2014. Available online: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/colorect.html (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Kekelidze, M.; D’Errico, L.; Pansini, M.; Tyndall, A.; Hohmann, J. Colorectal cancer: Current imaging methods and future perspectives for the diagnosis, staging and therapeutic response evaluation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 8502–8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmunzer, B.J.; Hayward, R.A.; Schoenfeld, P.S.; Saini, S.D.; Deshpande, A.; Waljee, A.K. Effect of flexible sigmoidoscopy-based screening on incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS Med. 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardcastle, J.D.; Chamberlain, J.O.; Robinson, M.H.; Moss, S.M.; Amar, S.S.; Balfour, T.W.; James, P.D.; Mangham, C.M. Randomised controlled trial of faecal-occult-blood screening for colorectal cancer. Lancet 1996, 348, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.; Sauvaget, C.; Sankaranarayanan, R. Mass screening for colorectal cancer is not justified in most developing countries. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashist, S.K.; Schleicher, E.; Luppa, P.; Luong, J.H.T. Glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) monitoring for diabetes diagnosis, management and therapy. In Point-of-Care Glucose Detection for Diabetic Monitoring and Management; Vashist, S.K., Luong, J.H., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2017; pp. 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, C.G.; Matthew, G.M.; Mowat, N.A.G.; Wilson, J.A.; Carey, F.A.; Steele, R.J.C. Immunochemical testing of individuals positive for guaiac faecal occult blood test in a screening programme for colorectal cancer: An observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloran, S.; Launoy, G.; Zappa, M. European guidelines for quality assurance in colorectal cancer screening and diagnosis. Endoscopy 2012, 10, 65–87. [Google Scholar]
- Young, G.P. Fecal immunochemical tests (FIT) vs. office-based guaiac fecal occult blood test (FOBT). Pract Gastroenterol 2004, 28, 49–50. [Google Scholar]
- Young, G.P.; Cole, S.R. Which fecal occult blood test is best to screen for colorectal cancer? Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, G.P.; Symonds, E.L.; Allison, J.E.; Cole, S.R.; Fraser, C.G.; Halloran, S.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Seaman, H.E. Advances in Fecal Occult Blood Tests: The FIT Revolution. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omata, F.; Shintani, A.; Isozaki, M.; Masuda, K.; Fujita, Y.; Fukui, T. Diagnostic performance of quantitative fecal immunochemical test and multivariate prediction model for colorectal neoplasms in asymptomatic individuals. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 23, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegeman, I.; de Wijkerslooth, T.R.; Stoop, E.M.; van Leerdam, M.E.; Dekker, E.; van Ballegooijen, M.; Kuipers, E.J.; Fockens, P.; Kraaijenhagen, R.A.; Bossuyt, P.M. Combining risk factors with faecal immunochemical test outcome for selecting CRC screenees for colonoscopy. Gut 2014, 63, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.I.; Ryu, S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, S-H.; Lee, C.K.; Eun, C.S.; Han, D.S. Comparison of guaiac-based and quantitative immunochemical fecal occult blood testing in a population at average risk undergoing colorectal cancer screening. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, H.; Tao, S. Superior diagnostic performance of faecal immunochemical tests for haemoglobin in a head-to-head comparison with guaiac based faecal occult blood test among 2235 participants of screening colonoscopy. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3049–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Government Department of Health. National Bowel Cancer Screening Program. Available online: https://www.bowelcanceraustralia.org/national-bowel-cancer-screening-program (accessed on 5 October 2016).
- Reagents, A.D.I.A. Hemotrust. Available online: http://www.alldiag.com/vus/produits/tdr/immunologie/hemotrust/index.html. (accessed on 1 June 2016).
- Eiken Chemical Co., LTD. OC-LIGHT ′Eiken′ Immunological Fecal Occult Blood Test. Available online: http://www.ilexmedical.com/files/Diagnostics%20%20Medtechnica/OCLIGHT.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2016).
- Evaluation of Quantitative Faecal Immunochemical Tests for Haemoglobin. Available online: http://194.97.148.137/assets/downloads/pdf/activities/fit_reports/gmec_fit_evaluation_report.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2016).
- Abeyrathne, C.D.; Halgamuge, M.N.; Farrell, P.M.; Skafidas, E. Performance analysis of on-chip coplanar waveguide for in vivo dielectric analysis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeyrathne, C.D.; Halgamuge, M.N.; Farrell, P.M.; Skafidas, E. On the Utility of Dielectric Spectroscopy Techniques to Identify Compounds and Estimate Concentrations of Binary Mixtures. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdat, D.; Marin, A.; Herrera, F.; Gijs, M.A.M. DNA biosensor using fluorescence microscopy and impedance spectroscopy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 118, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdat, D.; Rodríguez, A.C.M.; Herrera, F.; Gijs, M.A.M. Label-free detection of DNA with interdigitated micro-electrodes in a fluidic cell. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-S.; Banada, P.P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bhunia, A.K.; Bashir, R. Electrical characterization of DNA molecules in solution using impedance measurements. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 143902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.F.; Marenchic, I.G.; Spencer, R.H. Antibody-and receptor-based biosensors for detection and process control. Anal. Chim. Acta 1991, 249, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, O.; Heves, E.; Kaynak, M.; Basaga, H.; Gurbuz, Y. Label-free, capacitive immunosensor for protein detection. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE Conference on Sensors (IEEE sensors 2006), Daegu, Korea, 22–25 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.; Niazi, J.H.; Kallempudi, S.; Gurbuz, Y. Label-free capacitive biosensor for sensitive detection of multiple biomarkers using gold interdigitated capacitor arrays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2318–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, M.; Li, Y. Interdigitated array microelectrode based impedance biosensor coupled with magnetic nanoparticle–antibody conjugates for detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2408–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Erf, G.F. Interdigitated Array Microelectrode-Based Electrochemical Impedance Immunosensor for Detection of Escherichia c oli O157: H7. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, M.; Li, Y. Double interdigitated array microelectrode-based impedance biosensor for detection of viable Escherichia coli O157: H7 in growth medium. Talanta 2008, 74, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laczka, O.; Baldrich, E.; Muñoz, F.X.; del Campo, F.G. Detection of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium using interdigitated microelectrode capacitive immunosensors: The importance of transducer geometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 7239–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashist, S.; Lam, E.; Hrapovic, S.; Luong, J.H.T. Immobilization of antibodies and enzymes on 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane-functionalized bioanalytical platforms for biosensors and diagnostics. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11083–11130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, B.; Chana, G.; Lee, T.T.; Nguyen, T.; Abeyrathne, C.; D’Abaco, G.M.; Dottori, M.; Skafidas, E. Vertical Nanowire Electrode Arrays as Novel Electrochemical Label-Free Immunosensors. Small 2015, 24, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeyrathne, C.D.; Huynh, D.H.; Mcintire, T.W.; Nguyen, T.C.; Nasr, B.; Zantomio, D.; Chana, G.; Abbott, I.; Choong, P.; Catton, M.; et al. Lab on a Chip Sensor for Rapid Detection and Antibiotic Resistance Determination of Staphylococcus Aureus. Analyst 2016, 141, 1922–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
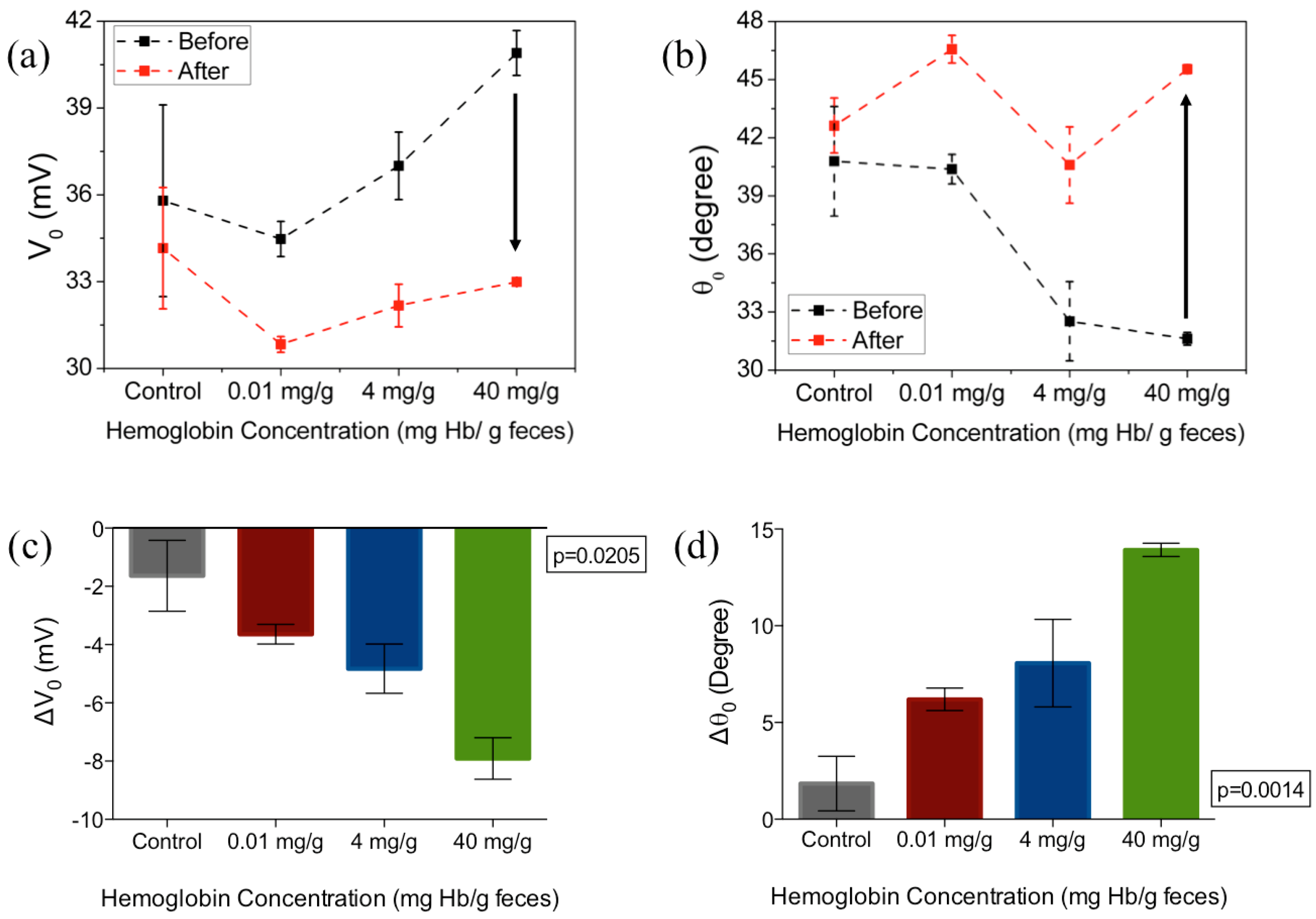
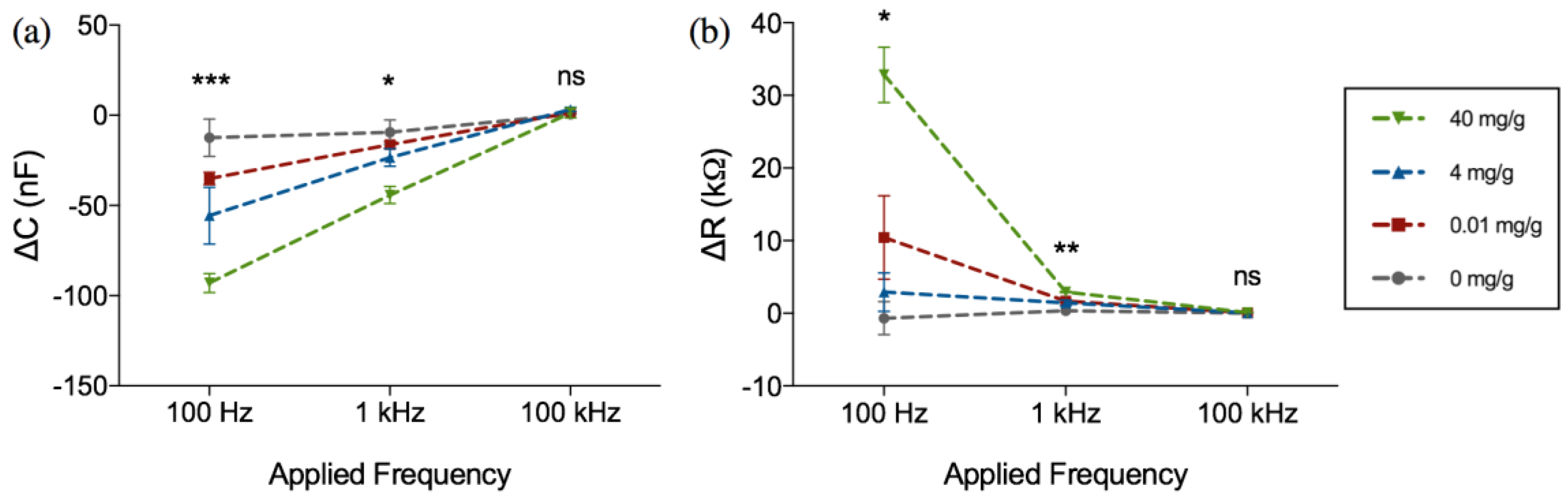
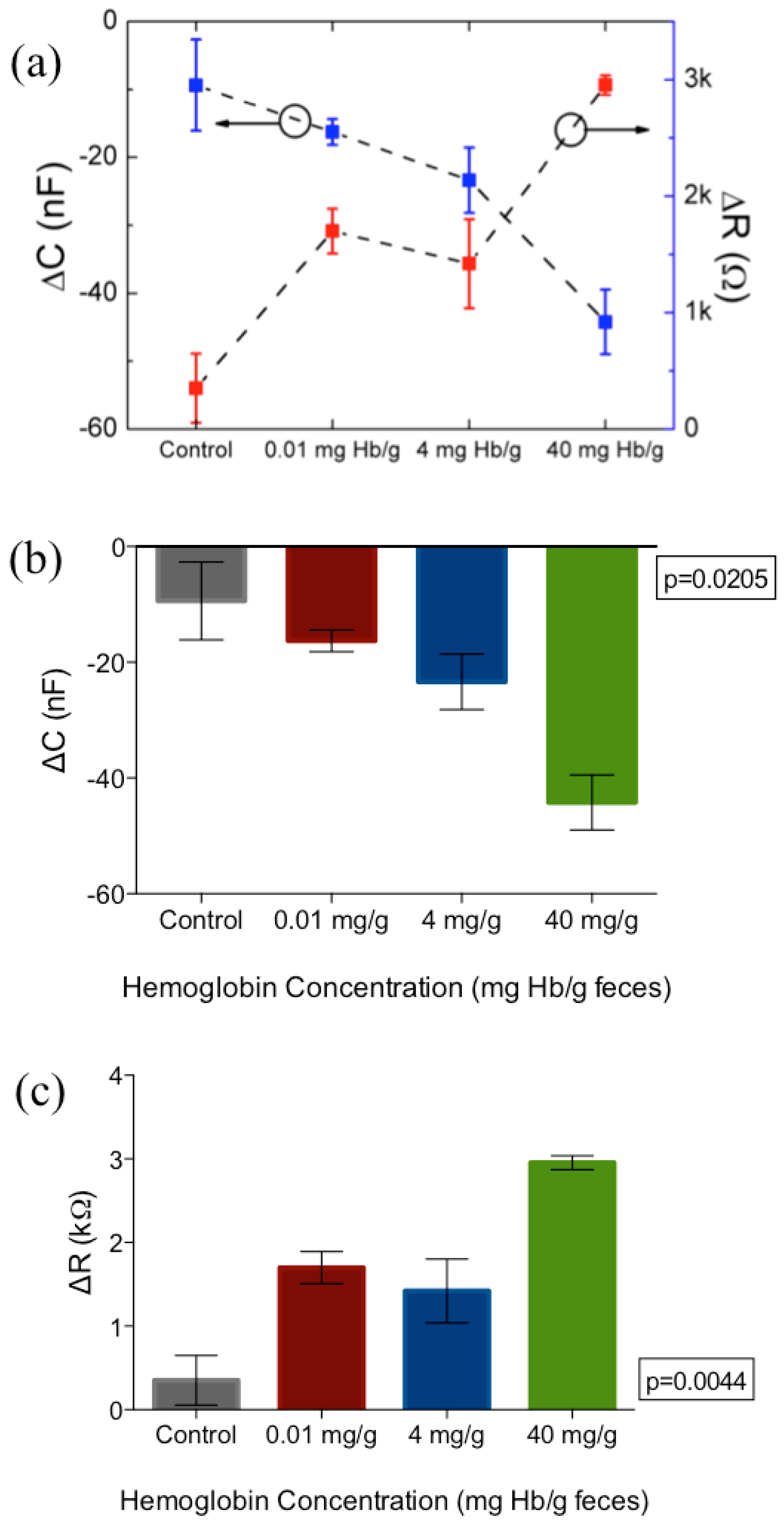
| Assay Platform | Physical Form | Clinical Cutoff | Quoted Lower Limit of Detection | Result Output | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative FIT | Lateral-flow immune-chromatography | Cassette form | Varying depending on manufacture | ALL-DIAG-Hemotrust®: 6 µg·Hb/g·Feces [21] | Positive or Negative based on manufacturer cutoff |
| Eiken OC Light®: 10 µg·Hb/g·Feces [22] | Subjective Interpretation | ||||
| Quantitative FIT | Immuno-turbidimetric | Laboratory based, bulky machinery | Varying depending on end-user | HM-Jackarc®: 7 µg·Hb/g·Feces [23] NS-PLUS C15®: 4 µg·Hb/g·Feces [23] | Positive or Negative based on end user’s cutoff |
| OC-SENSOR DIANA®: 10 µg·Hb/g·Feces [23] FOB Gold®: 2.55 µg·Hb/g·Feces [23] | Objective Interpretation |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soraya, G.V.; Nguyen, T.C.; Abeyrathne, C.D.; Huynh, D.H.; Chan, J.; Nguyen, P.D.; Nasr, B.; Chana, G.; Kwan, P.; Skafidas, E. A Label-Free, Quantitative Fecal Hemoglobin Detection Platform for Colorectal Cancer Screening. Biosensors 2017, 7, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7020019
Soraya GV, Nguyen TC, Abeyrathne CD, Huynh DH, Chan J, Nguyen PD, Nasr B, Chana G, Kwan P, Skafidas E. A Label-Free, Quantitative Fecal Hemoglobin Detection Platform for Colorectal Cancer Screening. Biosensors. 2017; 7(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoraya, Gita V., Thanh C. Nguyen, Chathurika D. Abeyrathne, Duc H. Huynh, Jianxiong Chan, Phuong D. Nguyen, Babak Nasr, Gursharan Chana, Patrick Kwan, and Efstratios Skafidas. 2017. "A Label-Free, Quantitative Fecal Hemoglobin Detection Platform for Colorectal Cancer Screening" Biosensors 7, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7020019
APA StyleSoraya, G. V., Nguyen, T. C., Abeyrathne, C. D., Huynh, D. H., Chan, J., Nguyen, P. D., Nasr, B., Chana, G., Kwan, P., & Skafidas, E. (2017). A Label-Free, Quantitative Fecal Hemoglobin Detection Platform for Colorectal Cancer Screening. Biosensors, 7(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7020019







