A Low-Cost, High-Performance System for Fluorescence Lateral Flow Assays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
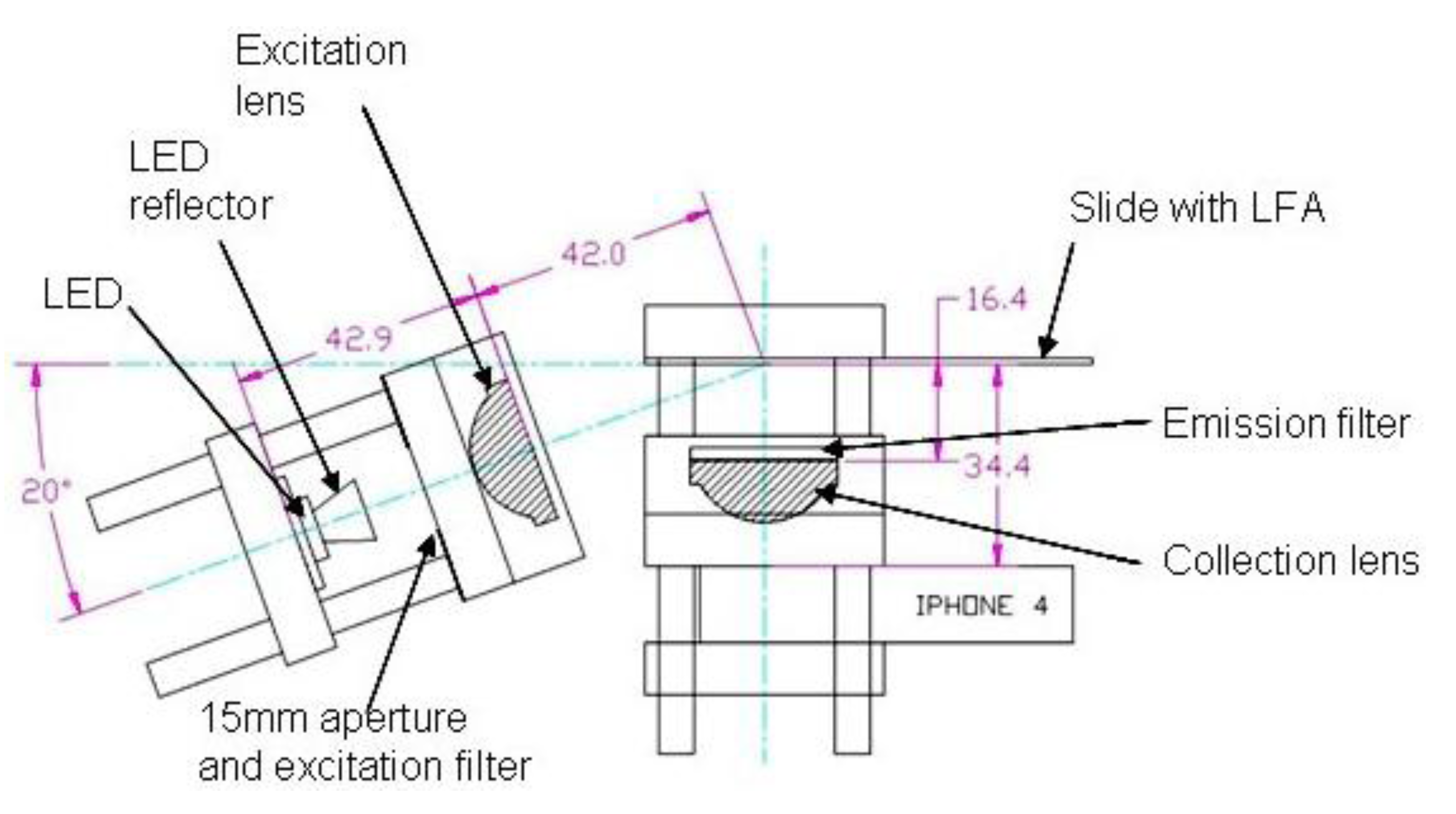
2.2. Optics Breadboard Design and Construction
| Dye | LED | Excitation Filter | Emission Filter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atto 430-LS | 447 nm, 910 mW at 700 mA, Luxeon® Star with 7° reflector | 2 mm thick Schott BG3 colored glass | Chroma 565/40 M interference filter after lens |
| Atto 465 | 447 nm, 910 mW at 700 mA, Luxeon® Star with Dialight 7° reflector | 2 mm thick Schott BG3 colored glass | Chroma 520/30 M interference filter after lens |
| Brilliant Violet 605 | 405 nm, 475 mW at 700 mA, Prolight with 10° Prolight reflector | 2.5 mm thick Hoya B-390 colored glass | 2 mm Schott OG570 colored glass before lens |
| Chromeo 494 | 505 nm, 122 lm at 700 mA, Luxeon® Star with Dialight 7° reflector | Chroma 520/30M interference filter after lens | Two 2 mm Schott OG570 colored glass filters after lens |
| Alexa Fluor 532 | 530 nm, 150lm at 700 mA, Luxeon® Star with Dialight 7° reflector | Chroma 520/30M interference filter after lens | Two 2 mm Schott OG570 colored glass filters after lens |
| R-Phycoerythrin | 505 nm, 122lm at 700 mA, Luxeon® Star with Dialight 7° reflector | Two 0.003″ thick plastic films (Supergel #69, brilliant blue) | One 0.003″ plastic film (Supergel #15 Deep Straw) and one 2 mm Schott OG570 colored glass filter before lens |
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Nonspecific Binding Measurement
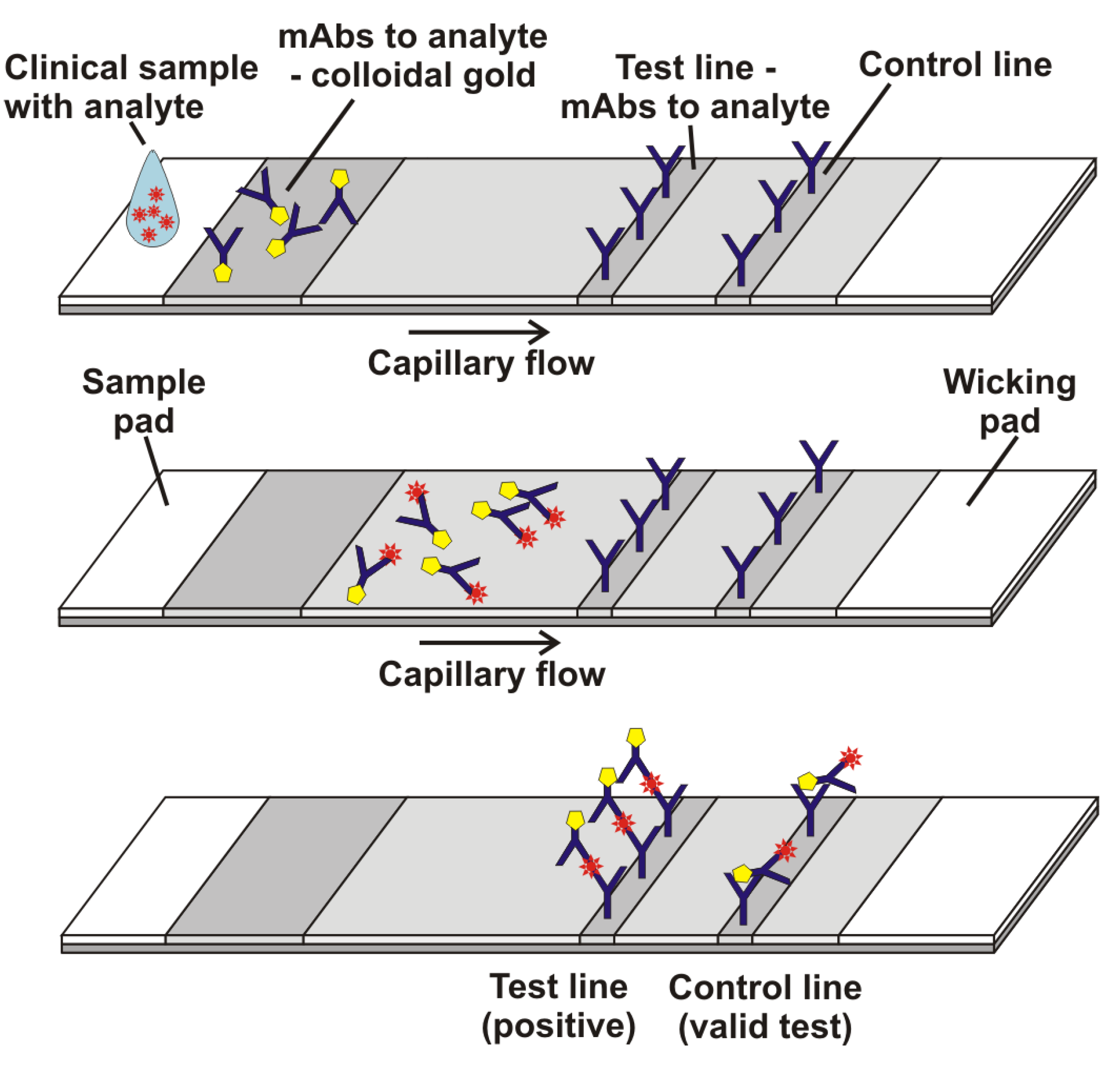
2.5. Lateral Flow with Streptavidin, Biotinylated BSA, and Either R-PE-Streptavidin or Gold-Streptavidin

2.6. Lateral Flow with Anti-hCG, β-hCG, and Either Biotinylated Anti-hCG + R-PE-Streptavidin or Biotinylated Anti-hCG + Gold-Streptavidin
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Survey of Fluorescent Reporters; Ratio of Signal to Nonspecific Binding
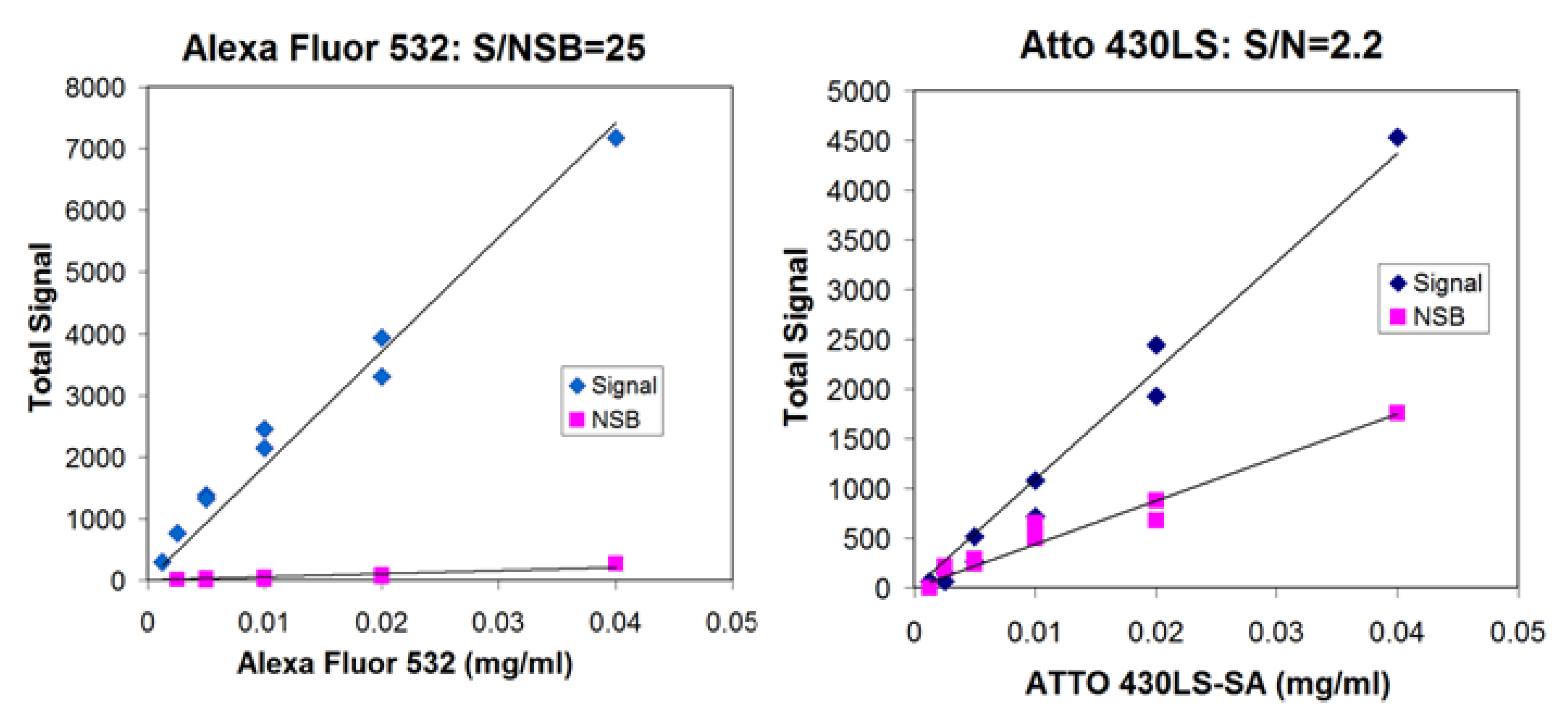
| Dye-labeled streptavidin | Signal/NSB |
|---|---|
| R-PE | 50 |
| Alexa Fluor 532 | 27 |
| Atto 430-LS | 2.2 |
| Atto 465 | 1.6 |
| Chromeo 494 | 1.4 |
| Brilliant Violet 605 | 0.15 |
3.2. Fluorescence Reader System
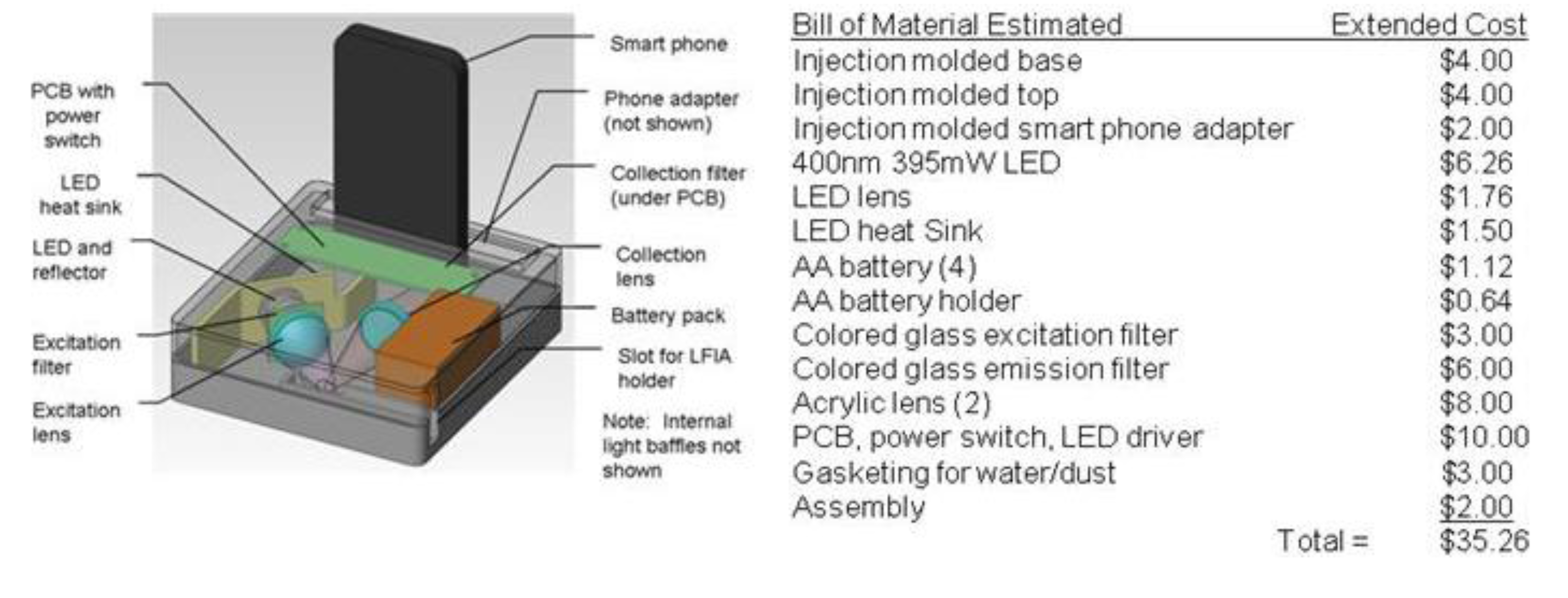
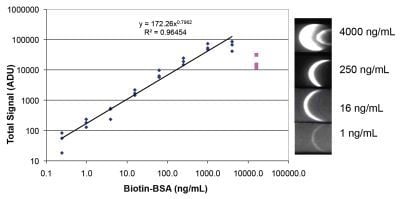
3.3. Lateral Flow with a Sandwich of Streptavidin, Biotinylated BSA, and Labeled Streptavidin
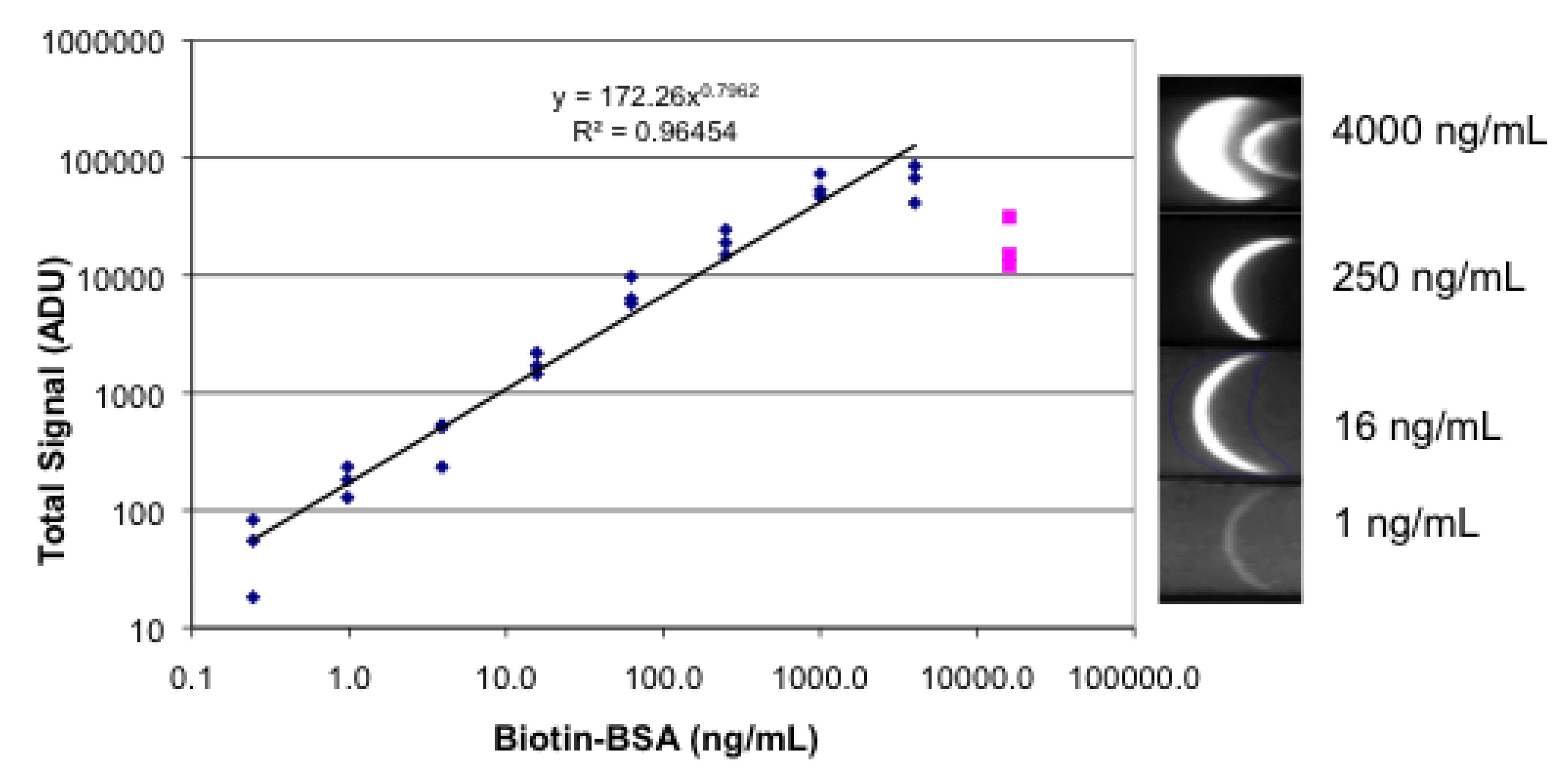

3.4. Lateral Flow Using a Sandwich of Polyclonal Anti-hCG, hCG, and Biotinylated Monoclonal Anti hCG/Labeled Streptavidin
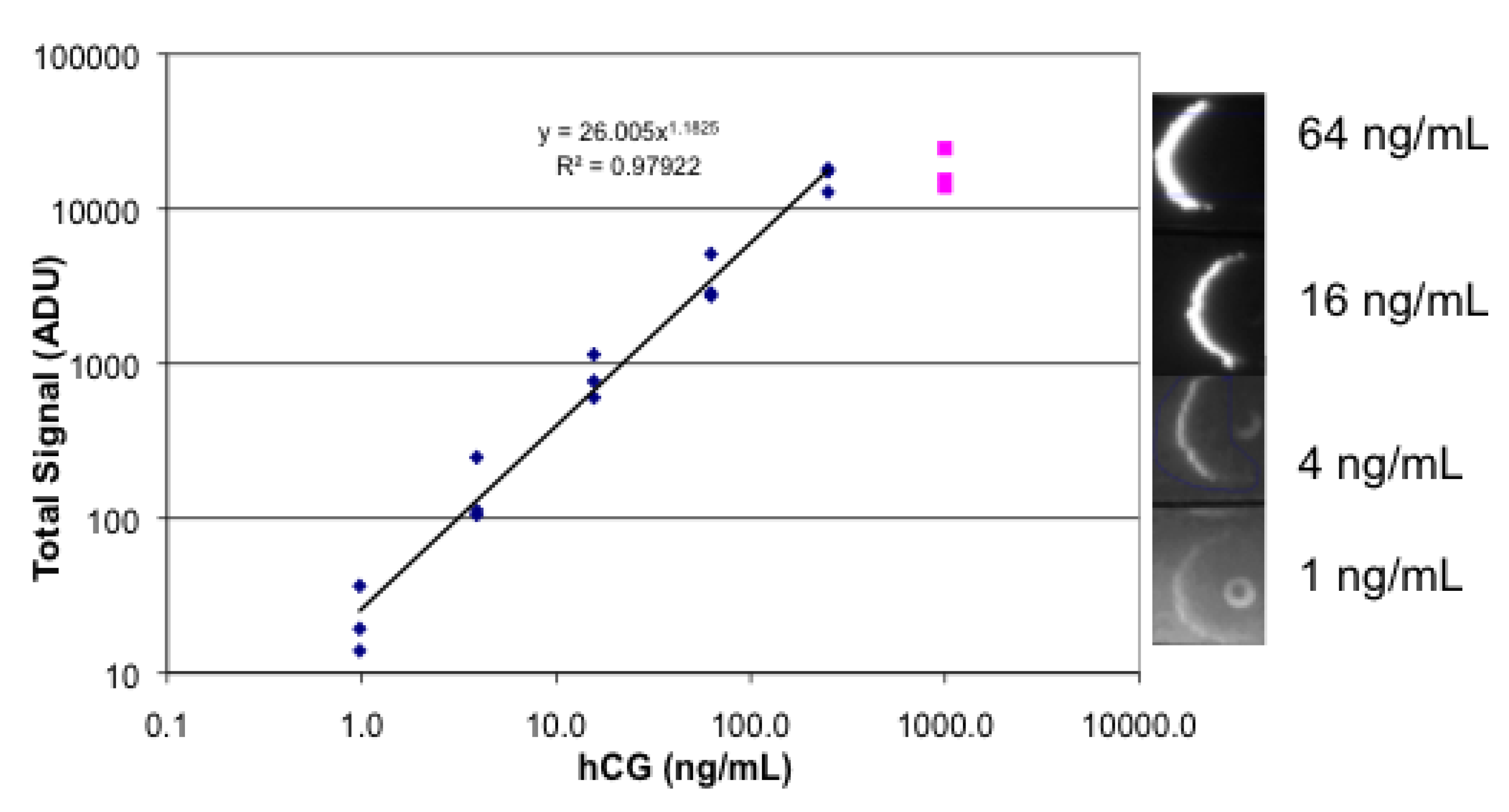
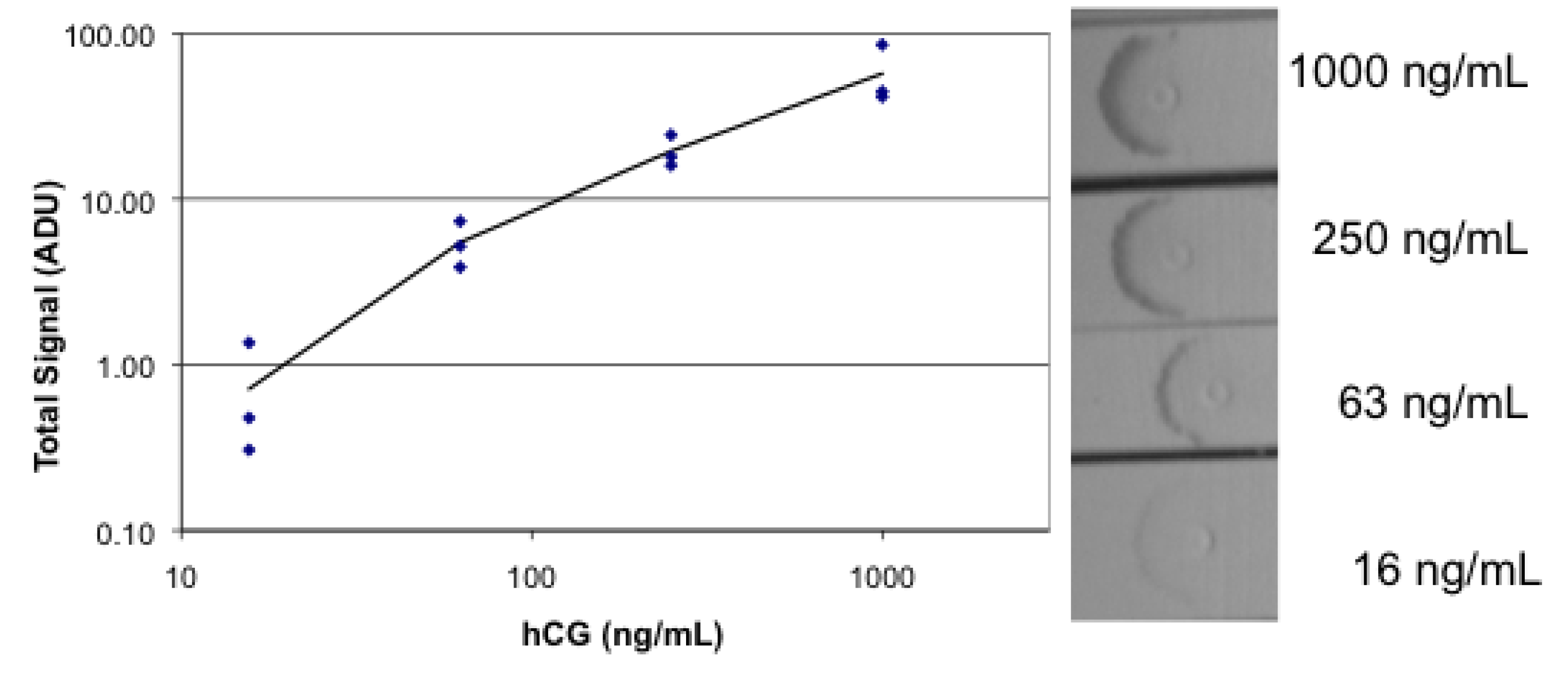
3.5. Photobleaching of Alexa Fluor 532 and R-PE
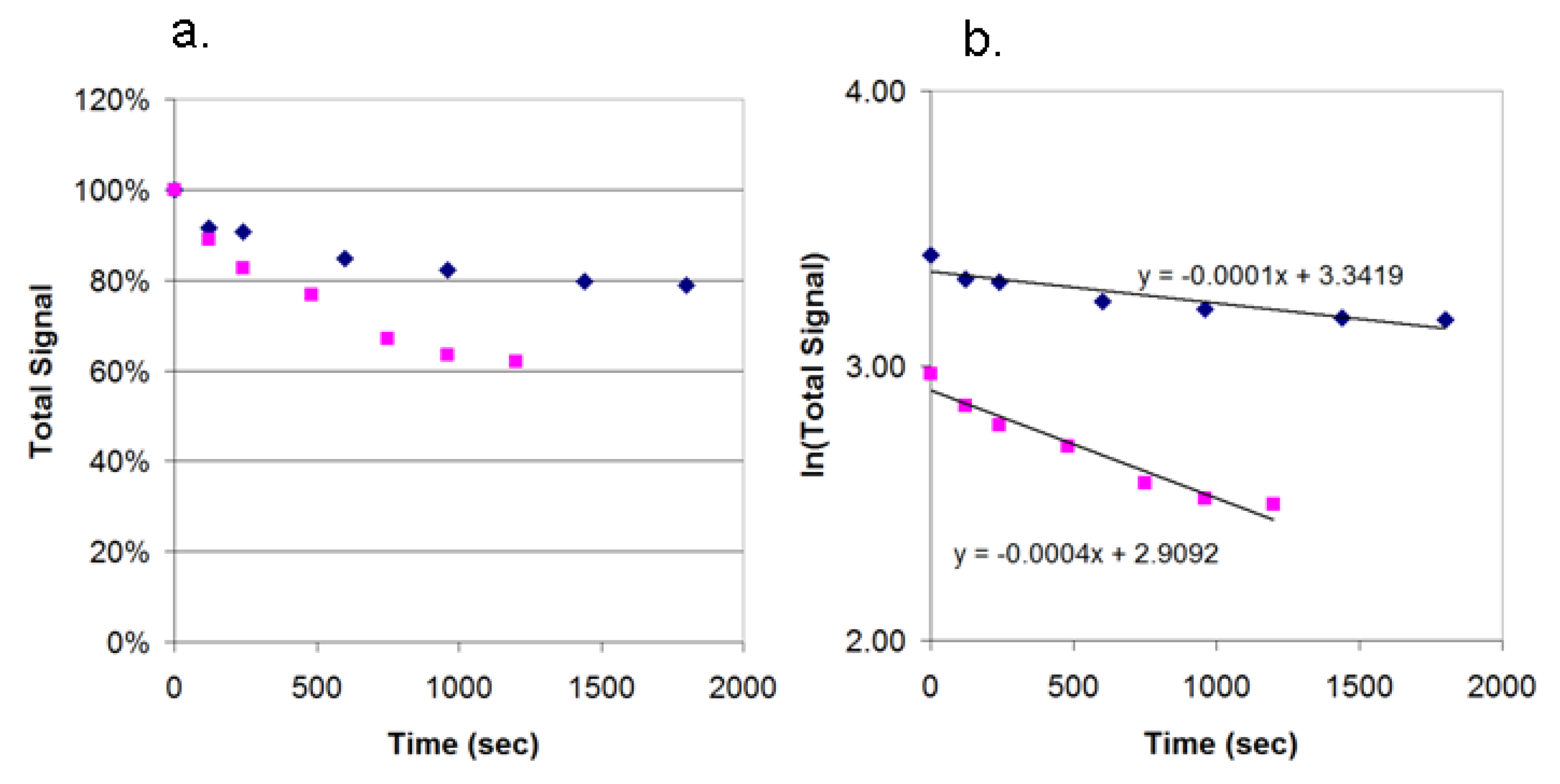
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Posthum-Trumpie, G.A.; Korf, J.; van Amerongen, A. Lateral flow (immuno) assay: Its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.K.; Bennett, J.W. Rapid diagnosis of malaria. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacksell, S.D. Commercial dengue rapid diagnostic tests for point-of-care application: Recent evaluations and future needs? J. Biomed. Biotech. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.F.; Ooi, E.E. Diagnosis of dengue: An update. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2012, 10, 895–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, D.R.; Maheshwari, M.; Arora, B. Rapid point-of-care testing for detection of HIV and clinical monitoring. ISRN AIDS 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choia, D.H.; Leec, S.K.; Oha, Y.K.; Baec, B.W.; Leec, S.D.; Kimd, S.; Shina, Y.-B.; Kima, M.-G. A dual gold nanoparticle conjugate-based lateral flow assay (LFA) method for the analysis of troponin I. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1999–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Miano, R.; Mele, G.O.; Germani, S.; Bove, P.; Sansalone, S.; Pugliese, P.F.; Micali, F. Evaluation of a new, rapid, qualitative, one-step PSA test for prostate cancer screening: The PSA RapidScreen test. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2005, 8, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Bau, H.H. A mathematical model of lateral flow bioreactions applied to sandwich assays. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 322, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Linares, E.M.; Kubota, L.T.; Michaelis, J.; Thalhammer, S. Enhancement of the detection limit for lateral flow immunoassays: Evaluation and comparison of bioconjugates. J. Immunol. Methods 2012, 375, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.; Du, D.; Wang, J.; Smith, J.N.; Timchalk, C.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y. Quantum dot-based immunochromatographic fluorescent biosensor for biomonitoring Trichloropyridinol, a biomarker of exposure to chlorpyrifos. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5125–5133. [Google Scholar]
- Khreich, N.; Lamourette, P.; Lagoutte, B.; Ronco, C.; Franck, X.; Créminon, C.; Volland, H. A fluorescent immunochromatographic test using immunoliposomes for detecting microcystins and nodularins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Pounds, J.G.; Lin, Y. Rapid and sensitive detection of protein biomarker using a portable fluorescence biosensor based on quantum dots and a lateral flow test strip. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7008–7014. [Google Scholar]
- Juntunen, E.; Myyryläinen, T.; Salminen, T.; Soukka, T.; Pettersson, K. Performance of fluorescent europium (III) nanoparticles and colloidal gold reporters in lateral flow bioaffinity assay. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 428, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gillet, P.; Mori, M.; van Esbroeck, M.; van den Ende, J.; Jacobs, J. Assessment of the prozone effect in malaria rapid diagnostic tests. Malaria J. 2009, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudanyali, O.; Dimitrov, S.S.; Sikora, U.; Padmanabhan, S.; Navruz, I.; Ozcan, A. Integrated rapid-diagnostic-test reader platform on a cellphone. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2678–2686. [Google Scholar]
- Coskun, A.F.; Nagi, R.; Sadeghi, K.; Phillips, S.; Ozcan, A. Albuin testing in urine using a smart-phone. Lab Chip 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Mavandadi, S.; Coskun, A.F.; Yaglidere, O.; Ozcan, A. Optofluidic fluorescent imaging cytometry on a cell-phone. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6641–6647. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, P.Y.; Sum, K.W.; Cheung, K.Y.; Glatz, J.F.C.; Sanderson, J.E.; Hempel, A.; Lehmann, M.; Renneberg, I.; Renneberg, R. Development of a quantitative lateral-flow away for rapid detection of fatty acid-binding protein. J. Immunol. Methods. 2003, 279, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngom, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Bi, D. Development and application of lateral flow test strip technology for detection of infectious agents and chemical contaminants: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1113–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbotosho, G.O.; Okuboyejo, T.M.; Happi, C.T.; Sowunmi, A. Recrudescent plasmodium falciparum infections in children in an endemic area following artemisinin-based combination treatments: Implications for disease control. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2011, 1, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Fu, Z.; Yan, F.; Ju, H. Biomedical and clinical applications of immunoassays and immunosensors for tumor markers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 679–688. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, L.G.; Nordman, E.S.; Johnson, M.D.; Oldham, M.F. A Low-Cost, High-Performance System for Fluorescence Lateral Flow Assays. Biosensors 2013, 3, 360-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3040360
Lee LG, Nordman ES, Johnson MD, Oldham MF. A Low-Cost, High-Performance System for Fluorescence Lateral Flow Assays. Biosensors. 2013; 3(4):360-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3040360
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Linda G., Eric S. Nordman, Martin D. Johnson, and Mark F. Oldham. 2013. "A Low-Cost, High-Performance System for Fluorescence Lateral Flow Assays" Biosensors 3, no. 4: 360-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3040360
APA StyleLee, L. G., Nordman, E. S., Johnson, M. D., & Oldham, M. F. (2013). A Low-Cost, High-Performance System for Fluorescence Lateral Flow Assays. Biosensors, 3(4), 360-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3040360