AI-Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing Systems: A Paradigm Shift for Intelligent Food Safety Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
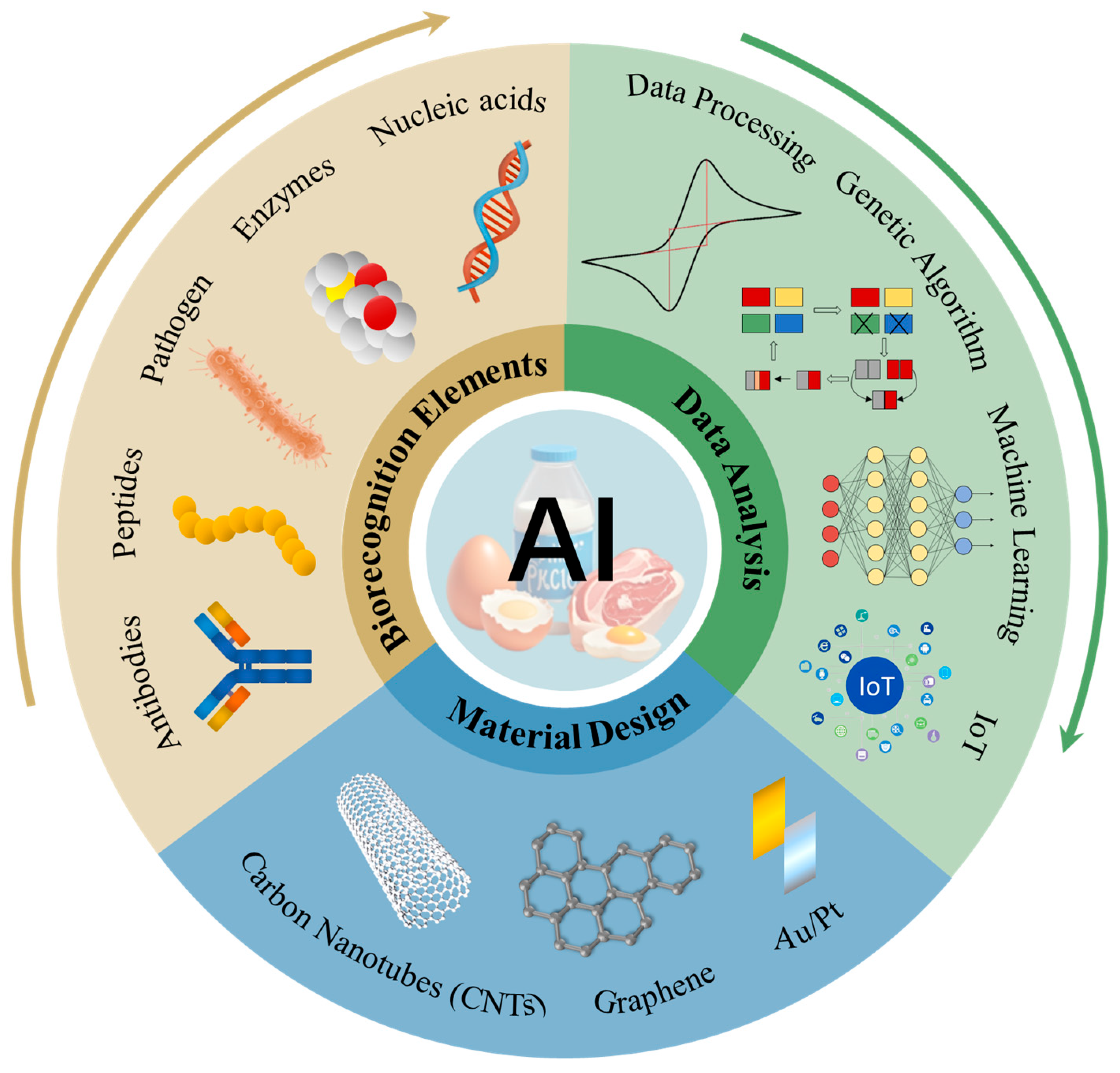
2. Adaptability of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Methodologies to Electrochemical Sensing
2.1. Mainstream AI Methodologies
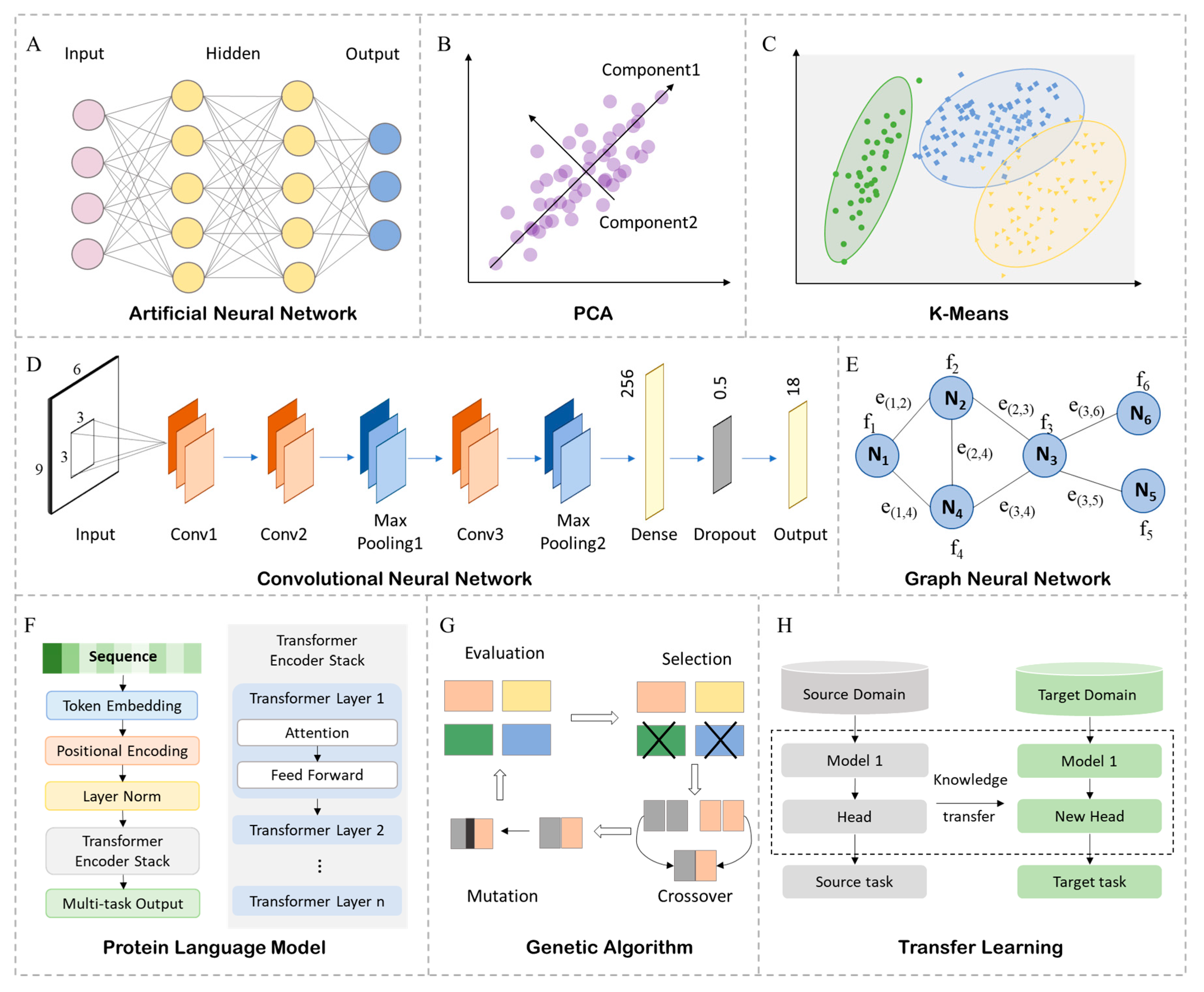
2.1.1. Supervised Learning
2.1.2. Unsupervised Learning
2.1.3. Deep Learning
2.1.4. Generative and Optimization Algorithms
2.1.5. Language Models and Graph Neural Networks
2.1.6. Few-Shot and Transfer Learning
2.2. Task-Specific Adaptation Analysis in Electrochemical Sensing
- Data Volume and Quality: In scenarios characterized by limited datasets or sparse labeling, strategies such as Few-Shot Learning, Transfer Learning, or lightweight model architectures are preferable to avoid overfitting and non-convergent training;
- Model Accuracy and Interpretability: In safety-critical domains such as foodborne pathogen detection, models must not only achieve high predictive accuracy but also provide transparent, traceable decision pathways to ensure regulatory compliance and operational trust;
- Computational Constraints and Deployment Platforms: For edge computing or field-deployable systems, models should exhibit fast inference speeds and low memory usage. Techniques such as model compression and knowledge distillation can be employed to reduce deployment barriers;
- Task Complexity and Environmental Dynamics: For systems dealing with multi-objective optimization or dynamically evolving environments, RL and adaptive control algorithms enhance robustness and generalizability across varying conditions;
- Model Update and Iteration Mechanisms: Long-term operational systems must support online model updates, incremental learning, and failure prediction to ensure sustained performance and reliability.
3. Construction of High-Performance Electrochemical Biosensing Systems
3.1. Intelligent Optimization of Biorecognition Molecules
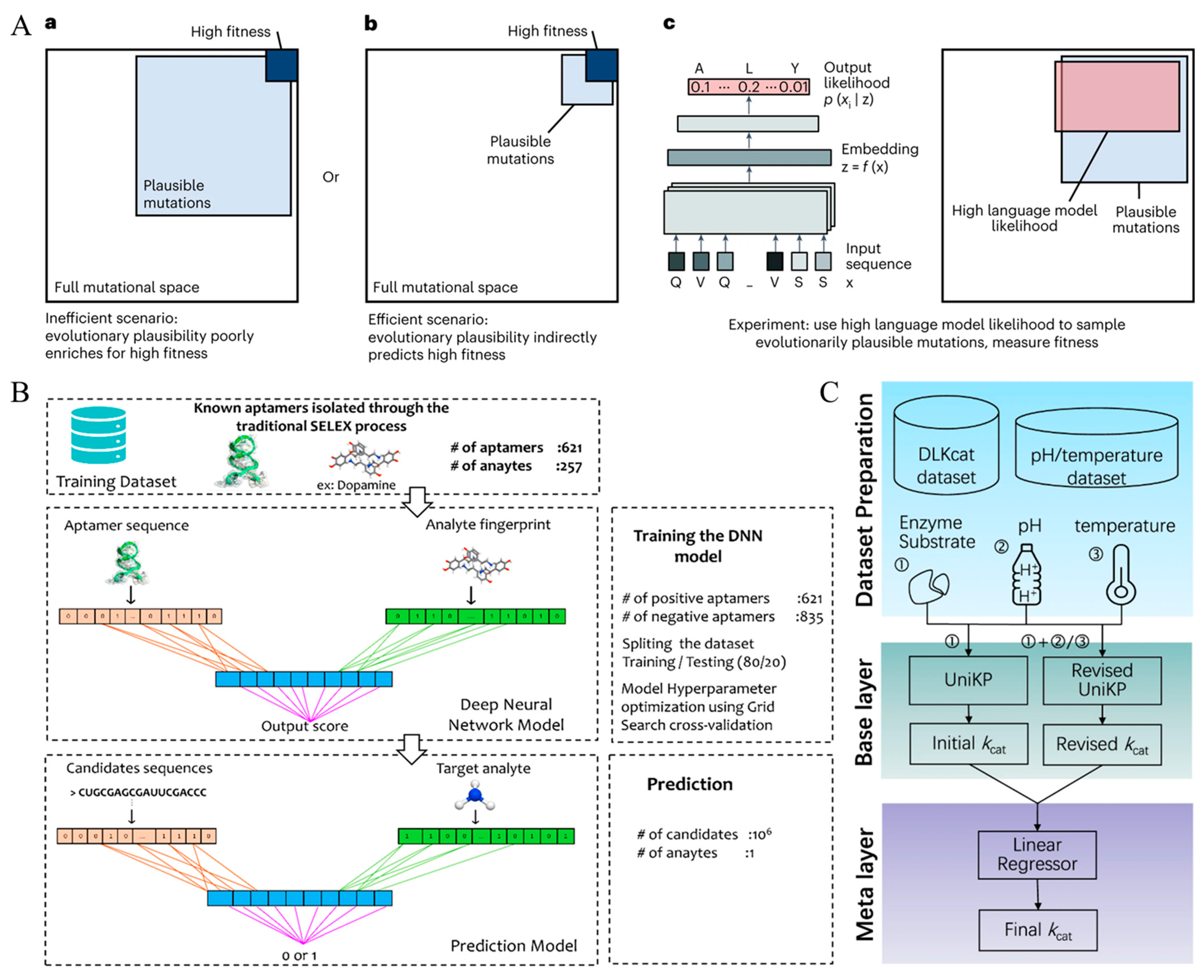
3.2. Algorithmic Regulation of Sensing Materials and Sensor Parameters
3.2.1. Algorithmic Optimization of Sensing Materials
3.2.2. Algorithmic Regulation of Sensor Parameters

3.3. AI-Driven Analysis and Optimization of Electrochemical Signals
3.3.1. High-Dimensional Signal Modeling
3.3.2. Signal Compensation and Calibration
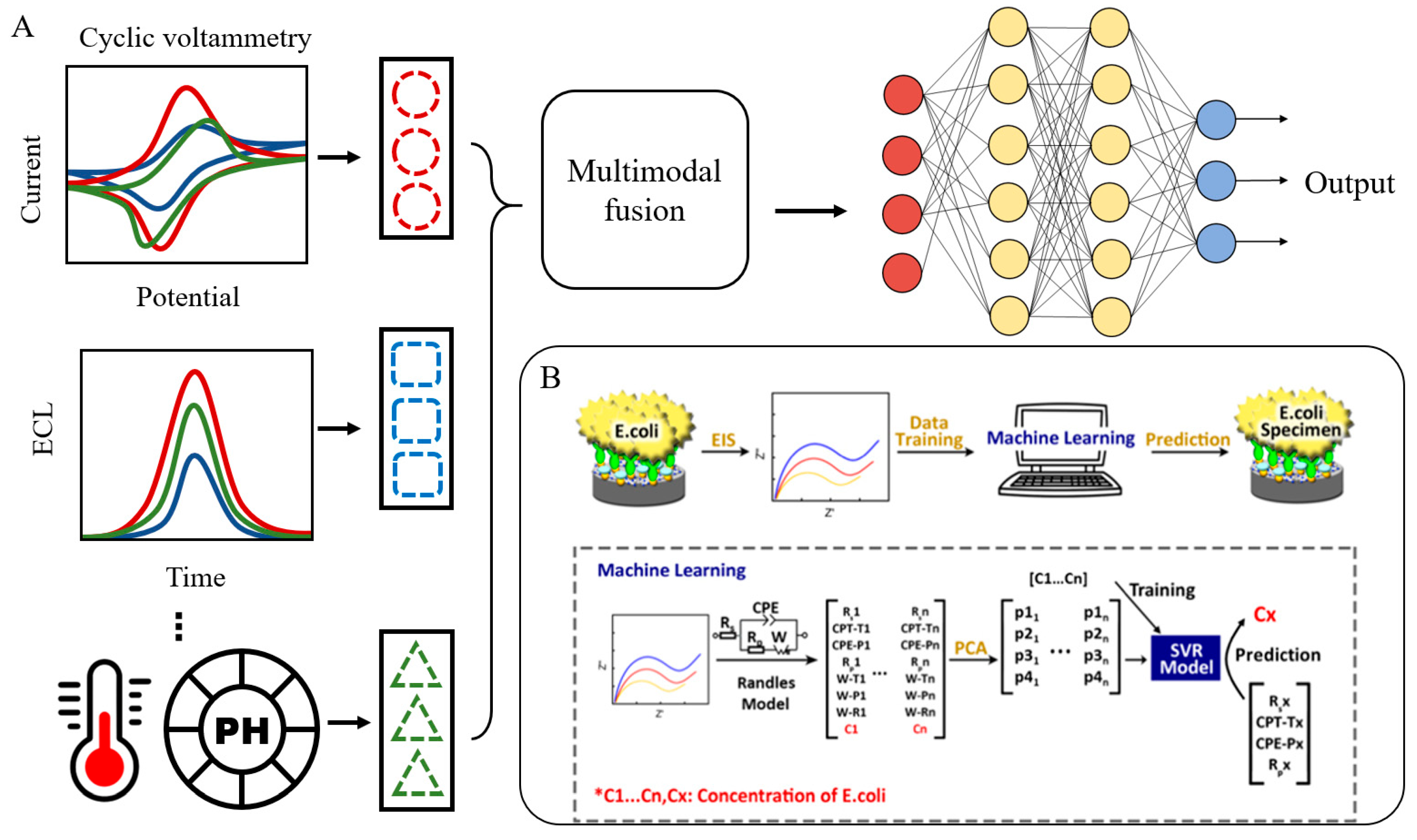
3.3.3. Multicomponent Detection
3.4. AI-Internet of Things (IoT) Integrated Sensing Platforms for On-Site Applications
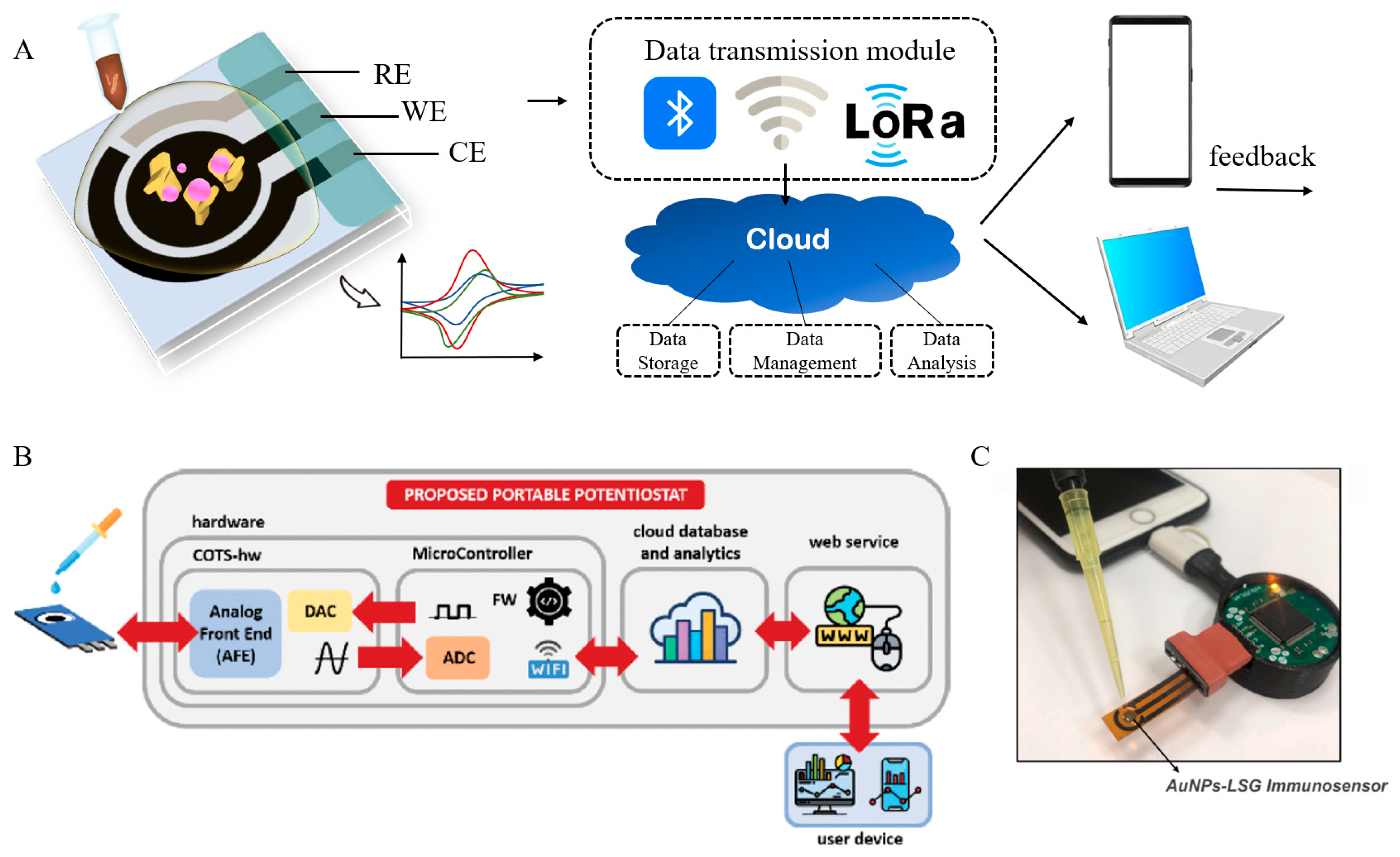
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foodborne Diseases Estimates. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/who-estimates-of-the-global-burden-of-foodborne-diseases (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Shen, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, Y. Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Salmonella in Food: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 149–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-M.; Chang, C.-L.; Hsu, M.-Y.; Lin, J.-Y.; Kuan, C.-M.; Wang, H.-K.; Huang, C.-T.; Chung, M.-C.; Huang, K.-C.; Hsu, C.-E.; et al. Paper-Based ELISA to Rapidly Detect Escherichia coli. Talanta 2015, 145, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, B.; Vicedo, B.; Aznar, R. PCR-based Procedures for Detection and Quantification of Staphylococcus Aureus and Their Application in Food. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintela, I.A.; Vasse, T.; Lin, C.-S.; Wu, V.C.H. Advances, Applications, and Limitations of Portable and Rapid Detection Technologies for Routinely Encountered Foodborne Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1054782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, L.M.; Schuh, D.A.; Reynolds, E.E.; Furst, A.L. Electrochemical Sensors to Detect Bacterial Foodborne Pathogens. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucherenko, I.S.; Soldatkin, O.O.; Dzyadevych, S.V.; Soldatkin, A.P. Electrochemical Biosensors Based on Multienzyme Systems: Main Groups, Advantages and Limitations—A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1111, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Ma, B.; Ju, H. Device Integration of Electrochemical Biosensors. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissel, M.; Schosland, M.; Töws, J.; Kalita, D.; Schneider, Y.; Kessler-Kühn, J.; Schröder, S.; Schubert, J.; Frankenberg, F.; Kwade, A. Quantifying the Impact of Cathode Composite Mixing Quality on Active Mass Utilization and Reproducibility of Solid-State Battery Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, 15, 2405405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainul, R.; Rafika, R.; Hasanudin, H.; Laghari, I.A.; Hamdani, D.M.H.; Mapanta, J.; Handayana, R.H.; Delson, D.; Mandeli, R.S.; Putra, H.; et al. Systematic Review of Electrochemical Stability and Performance Enhancement in Energy Storage and Analytical Applications. Asian J. Green Chem. 2024, 8, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Tan, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Geng, X.; Guttmann, P.; Hou, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. Revealing the Degradation Pathways of Layered Li-Rich Oxide Cathodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 19, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, R.A.; Aman, N.; Ullah, N.; Jamila, N.; Bibi, N. Recent Advancement for Enhanced E. Coli Detection in Electrochemical Biosensors. Microchem. J. 2024, 196, 109673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchu, M.S.; Ali, M.R.; Das, S.; Akter, S.; Sakamoto, H.; Suye, S.-I.; Rahman, M.M.; Campbell, K.; Khan, M.Z.H. A DNA Functionalized Advanced Electrochemical Biosensor for Identification of the Foodborne Pathogen Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi in Real Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1192, 339332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolti, O.; Suganthan, B.; Maynard, R.; Asadi, H.; Locklin, J.; Ramasamy, R.P. Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Listeria Monocytogenes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 067510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Z. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors for the Detection of Foodborne Pathogens: Current Perspective and Challenges. Foods 2023, 12, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veliscek, Z.; Perse, L.S.; Dominko, R.; Kelder, E.; Gaberscek, M. Preparation, Characterisation and Optimisation of Lithium Battery Anodes Consisting of Silicon Synthesised Using Laser Assisted Chemical Vapour Pyrolysis. J. Power Sources 2015, 273, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Song, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.-H.P. Protein Engineering for Electrochemical Biosensors. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 76, 102751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocan, A.; Siavash Moakhar, R.; del Real Mata, C.; Petkun, M.; De Iure-Grimmel, T.; Yedire, S.G.; Shieh, H.; Khorrami Jahromi, A.; Mahshid, S.S.; Mahshid, S. Machine-Learning-Aided Advanced Electrochemical Biosensors. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2417520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Filho, J.I.; Faleiros, M.C.; Ferreira, D.C.; Mani, V.; Salama, K.N. Empowering Electrochemical Biosensors with AI: Overcoming Interference for Precise Dopamine Detection in Complex Samples. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2300227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodkhe, G.A.; Kumar, V.; Li, X.; Pei, S.; Ma, L.; Kim, M. Biosensors in Microbial Ecology: Revolutionizing Food Safety and Quality. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.-H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S. Electrochemical Biosensors: Perspective on Functional Nanomaterials for on-Site Analysis. Biomater. Res. 2020, 24, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.F.D.; Magalhães, J.M.C.S.; Freire, C.; Delerue-Matos, C. Electrochemical Biosensors for Salmonella: State of the Art and Challenges in Food Safety Assessment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liang, T.; Xie, X.-Q.; Feng, Z.; Meng, L. A New Era of Antibody Discovery: An in-Depth Review of AI-Driven Approaches. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Jan, Z.; Ullah, I.; Alwabli, A.; Alharbi, F.; Habib, S.; Islam, M.; Shin, B.-J.; Lee, M.Y.; Koo, J. A Deep Dive into AI Integration and Advanced Nanobiosensor Technologies for Enhanced Bacterial Infection Monitoring. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2024, 13, 20240056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Gupta, D. Comparative Analysis of a Bioelectric Cell Biosensor Dataset Employing Machine Learning Classifiers for Reliable Listeria Monocytogenes Identification. In Proceedings of the 2024 15th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kamand, India, 24–28 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, Y.; Kaur, I.; Mishra, S. Foodborne Disease Symptoms, Diagnostics, and Predictions Using Artificial Intelligence-Based Learning Approaches: A Systematic Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2024, 31, 553–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskher, H.; Achi, F.; Ha, S.; Berregui, B.; Babanini, F.; Belkhalfa, H. Sensitive rGO/MOF Based Electrochemical Sensor for Penta-Chlorophenol Detection: A Novel Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Application. Sens. Diagn. 2022, 1, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Shin, H.; Cho, H.U.; Blaha, C.D.; Heien, M.L.; Oh, Y.; Lee, K.H.; Jang, D.P. Neurochemical Concentration Prediction Using Deep Learning vs Principal Component Regression in Fast Scan Cyclic Voltammetry: A Comparison Study. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 2288–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, N.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, M.; Xu, Y. Time-Lapse Electrochemical Impedance Detection of Bacteria Proliferation for Accurate Antibiotic Evaluation. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 5504–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Thoma, Y.; Rodino, F.; Carrara, S. Automatic Simulation of Electrochemical Sensors by Machine Learning for Drugs Quantification. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 491, 144304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-U.; Yu, S.I.; Bae, H.; Jang, A. Deep Learning-Enhanced Multi-Modal Modeling for Electrosorption Performance Prediction via Nyquist Plots. Environ. Res. 2025, 282, 122069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, F.; Cassie, E.; Nguyen, H.P.T.; Plank, N.O.; Unsworth, C.P.; Wang, A. Utilizing Deep Learning Algorithms for Signal Processing in Electrochemical Biosensors: From Data Augmentation to Detection and Quantification of Chemicals of Interest. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, A.; Sun, Q.; Peng, X. A Hybrid CNN-Transformer Model for Ozone Concentration Prediction. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Tünnermann, L.; Löfstedt, T.; Gratz, R. Transformer-Based Deep Learning for Predicting Protein Properties in the Life Sciences. eLife 2023, 12, e82819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Sharma, A.; Dhiman, G.; Shabaz, M. The Identification Nanoparticle Sensor Using Back Propagation Neural Network Optimized by Genetic Algorithm. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 7548329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakilian, K.A. Optimization Methods Can Increase the Durability of Smart Electrochemical Biosensors. In Proceedings of the 2022 8th Iranian Conference on Signal Processing and Intelligent Systems (ICSPIS), Shahrood, Iran, 28–29 December 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan, E.J. Bayesian Optimization Strategies for Electrochemical Technology Development. In Proceedings of the Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts PRiME2024, Honolulu, HI, USA, 6–11 October 2024; The Electrochemical Society, Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2024; p. 1921. [Google Scholar]
- Cheon, M.; Byun, H.; Lee, J.H. Non-Myopic Bayesian Optimization Using Model-Free Reinforcement Learning and Its Application to Optimization in Electrochemistry. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2024, 184, 108624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruz, N.; Höcker, B. Controllable Protein Design with Language Models. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayo-Alarcon, R.; Amstalden, M.K.; Zannoni, A.; Bajramovic, M.; Sharma, C.M.; Brochado, A.R.; Rezaei, M.; Müller, C.L. Pre-Trained Molecular Representations Enable Antimicrobial Discovery. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briceno-Mena, L.A.; Romagnoli, J.A.; Arges, C.G. PemNet: A Transfer Learning-Based Modeling Approach of High-Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Electrochemical Systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 3350–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J. The Application of Transfer Learning Models in the Construction of Microbial Intelligent Monitoring and Identification System. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Machine Intelligence and Digital Applications, Ningbo, China, 30–31 May 2024; pp. 802–807. [Google Scholar]
- Murugan, K.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Sakthivel, K.; Subramanian, S.; Li, I.-C.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Chiu, T.-W.; Chang-Chien, G.-P. Machine Learning-Driven Advances in Electrochemical Sensing: A Horizon Scan. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 097503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsch, F.; Umasankar, I.L.; Moreta, L.S.; Latawa, P.; Lange, D.B.; Wengel, J.; Konjen, H.; Code, C. AptaBERT: Predicting Aptamer Binding Interactions. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, R.; Lim, I.H.Y.; Lewis, J.C.; Lim, C.H.; Yap, M.K.K.; Tan, H.S. Selecting Antibacterial Aptamers against the BamA Protein in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa by Incorporating Genetic Algorithm to Optimise Computational Screening Method. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.S.; Roy, J.K.; Mandal, N. Conv-Random Forest-Based IoT: A Deep Learning Model Based on CNN and Random Forest for Classification and Analysis of Valvular Heart Diseases. IEEE Open J. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 2, 2500717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khozeimeh, F.; Sharifrazi, D.; Izadi, N.H.; Joloudari, J.H.; Shoeibi, A.; Alizadehsani, R.; Tartibi, M.; Hussain, S.; Sani, Z.A.; Khodatars, M. RF-CNN-F: Random Forest with Convolutional Neural Network Features for Coronary Artery Disease Diagnosis Based on Cardiac Magnetic Resonance. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment: RNA Ligands to Bacteriophage T4 DNA Polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, F.H. Directed Evolution: Bringing New Chemistry to Life. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2017, 57, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, D.; Bill, R.M.; Jawhari, A.; Rothnie, A.J. Overcoming Bottlenecks in the Membrane Protein Structural Biology Pipeline. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüthrich, K. NMR Studies of Structure and Function of Biological Macromolecules. Biosci. Rep. 2003, 23, 119–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.; Rao, R.; Verkuil, R.; Liu, J.; Sercu, T.; Rives, A. Language Models Enable Zero-Shot Prediction of the Effects of Mutations on Protein Function. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 29287–29303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hie, B.L.; Shanker, V.R.; Xu, D.; Bruun, T.U.; Weidenbacher, P.A.; Tang, S.; Wu, W.; Pak, J.E.; Kim, P.S. Efficient Evolution of Human Antibodies from General Protein Language Models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, V.R.; Bruun, T.U.J.; Hie, B.L.; Kim, P.S. Unsupervised Evolution of Protein and Antibody Complexes with a Structure-Informed Language Model. Science 2024, 385, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yang, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, D.; Zou, X. Advances of Nanobody-Based Immunosensors for Detecting Food Contaminants. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 156, 104871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Amorim, C.G.; Qatouseh, L.F.A.; Montenegro, M.C. Nanobody-Based Immunodiagnostics: A Systematic Review of Nanobody Integration in Diagnostics and Deep Insight into Electrochemical Immunoassays. Microchem. J. 2024, 196, 109628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon, A.; Ali, M.; Atkinson, M.; Saturnino, A.; Didi, K.; Visentin, C.; Ricagno, S.; Xu, X.; Greenig, M.; Sormanni, P. Assessing Antibody and Nanobody Nativeness for Hit Selection and Humanization with AbNatiV. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2024, 6, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Gu, M.; Zhang, P.; Dong, M.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M. Nanobody–Antigen Interaction Prediction with Ensemble Deep Learning and Prompt-Based Protein Language Models. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2024, 6, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaki, A.; Garoli, D.; Inam, A.K.M.S.; Angeli, M.A.C.; Cantarella, G.; Rocchia, W.; Wang, J.; Petti, L.; Lugli, P. Smart Approach for the Design of Highly Selective Aptamer-Based Biosensors. Biosensors 2022, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Cui, H.; Li, J.C.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zhao, H. Enzyme Function Prediction Using Contrastive Learning. Science 2023, 379, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuta-Navajas, G.H.; Roa-Prada, S.; Chalela-Alvarez, G. Kinetic Model Parameter Estimation Using Genetic Algorithms of the Oxidation of Phenol in Water Catalyzed by the Laccase Enzyme for the Design of a Biosensor. Bioremediat. J. 2022, 26, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachas, S.; Rakocevic, G.; Spencer, D.; Sastry, A.V.; Haile, R.; Sutton, J.M.; Kasun, G.; Stachyra, A.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Yassine, E.; et al. Antibody Optimization Enabled by Artificial Intelligence Predictions of Binding Affinity and Naturalness. bioRxiv 2022. bioRxiv:2022.08.16.504181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Huang, G.-H.; Cui, W.-R.; Zhang, N.; Cai, Y.-D. Prediction of Aptamer-Target Interacting Pairs with Pseudo-Amino Acid Composition. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Deng, H.; He, J.; Keasling, J.D.; Luo, X. UniKP: A Unified Framework for the Prediction of Enzyme Kinetic Parameters. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCuyer, K.A.; Crothers, D.M. Kinetics of an RNA Conformational Switch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3373–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umuhire Juru, A.; Patwardhan, N.N.; Hargrove, A.E. Understanding the Contributions of Conformational Changes, Thermodynamics, and Kinetics of RNA–Small Molecule Interactions. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 824–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Xie, L.; Tong, Y.; Xu, X. cRNAsp12 Web Server for the Prediction of Circular RNA Secondary Structures and Stabilities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soylu, N.N.; Sefer, E. Bert2ome: Prediction of 2′-O-Methylation Modifications from Rna Sequence by Transformer Architecture Based on Bert. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2023, 20, 2177–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Xie, C.; Lu, H. Advances in MXene-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Multiplexed Detection in Biofluids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, M.; Zhong, W. Multiplex Detection of Biomarkers Empowered by Nanomaterials. Precis. Chem. 2025, 3, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Mo, G. A Gold Nanoparticles and MXene Nanocomposite Based Electrochemical Sensor for Point-of-Care Monitoring of Serum Biomarkers. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 16980–16994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, P.; Abubakar Sadique, M.; Yadav, S.; Khan, R. An Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on Gold-Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites with Ionic Liquid for Detecting the Breast Cancer CD44 Biomarker. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 20802–20812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, P.; Bisetty, K.; Cai, Y.; Duan, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Rao, L.; Xu, Q.; Xu, J. An Emerging Machine Learning Strategy for Electrochemical Sensor and Supercapacitor Using Carbonized Metal–Organic Framework. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 920, 116634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavya, K.V.; Kumar, R.S.; Rajendra Kumar, R.T.; Ramesh, S.; Yang, W.; Kakani, V.; Haldorai, Y. Fabrication of 1D/2D Au Nanofiber/MIL-101(Cr)–NH2 Composite for Selective Electrochemical Detection of Caffeic Acid: Predicting Sensor Performance by Machine Learning and Investigating the Porosity Using AI and Computer Vision-Based Image Analysis. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhadali, A.; Bonakdar, G.A. Multivariate Optimization of Mebeverine Analysis Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Electrochemical Sensor Based on Silver Nanoparticles. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, A.; Hosseinpour, S.; Keyhani, A.; Azimzadeh, M. Modeling and Optimization of Oligonucleotide-Based Nanobiosensor Using Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm Based Procedure. Iran. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 51, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarahmadi, B.; Hashemianzadeh, S.M.; Milani Hosseini, S.M.-R. Machine-Learning-Based Predictions of Imprinting Quality Using Ensemble and Non-Linear Regression Algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, H.; Hui, X.; He, X.; Mu, X. Plasmonic Biosensor Augmented by a Genetic Algorithm for Ultra-Rapid, Label-Free, and Multi-Functional Detection of COVID-19. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 9437–9444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, D.; Zhai, T.; Liu, J.-M.; Wang, S. Machine Learning-Based Smart Technology Enables Precise and Efficient Detection of Food Safety Risks. Food Rev. Int. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.H.; Zhang, S.; He, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, X.; Huang, G.; Zhang, J. A Convolutional Neural Network Based Auto Features Extraction Method for Tea Classification with Electronic Tongue. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundry, L.; Guo, S.-X.; Kennedy, G.; Keith, J.; Robinson, M.; Gavaghan, D.; Bond, A.M.; Zhang, J. Recent Advances and Future Perspectives for Automated Parameterisation, Bayesian Inference and Machine Learning in Voltammetry. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 1855–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Jiang, K.; Chen, B.; Zheng, S. Data-Driven Design of Electrocatalysts: Principle, Progress, and Perspective. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 3849–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopic Detection of E. coli with Machine Learning. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 047508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ccopa Rivera, E.; Swerdlow, J.J.; Summerscales, R.L.; Uppala, P.P.T.; Maciel Filho, R.; Neto, M.R.C.; Kwon, H.J. Data-Driven Modeling of Smartphone-Based Electrochemiluminescence Sensor Data Using Artificial Intelligence. Sensors 2020, 20, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, B.L.; Siraj, S.; Wong, D.K.Y. Recent Strategies to Minimise Fouling in Electrochemical Detection Systems. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 35, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiassa, S.; Ny Hanitra, I.; Sandri, G.; Totu, T.; Grassi, F.; Criscuolo, F.; De Micheli, G.; Carrara, S.; Demarchi, D. Continuous Monitoring of Propofol in Human Serum with Fouling Compensation by Support Vector Classifier. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curulli, A. Nanomaterials in Electrochemical Sensing Area: Applications and Challenges in Food Analysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawaid, S.; Sharma, B.P.; Hussain Tumrani, S.; Abbas, Z.; Ali Soomro, R.; Karakuş, S.; Küçükdeniz, T.; Nafady, A. Enhanced Electrochemical Oxidation and Machine Learning-Assisted Sensing of Tetrabromobisphenol A Using Activated Carbon Facilitated CoWO4 Heterostructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2024, 308, 117546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.-C.; Chung, K.-J.; Chen, B.-W.; Dai, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-C. Electrochemical Detection Combined with Artificial Neural Networks for the Simultaneous Intelligent Sensing of Caffeine and Chlorogenic Acid. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 463, 142820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet-San-Emeterio, M.; González-Calabuig, A.; del Valle, M. Artificial Neural Networks for the Resolution of Dopamine and Serotonin Complex Mixtures Using a Graphene-Modified Carbon Electrode. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecilla, J.S.; Mena, M.L.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; García, J. A Neural Network Approach Based on Gold-Nanoparticle Enzyme Biosensor. J. Chemom. 2008, 22, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Ha, S.M.; Gurudatt, N.G.; Heo, W.; Hyun, K.-A.; Kim, J.; Jung, H.-I. Machine Learning-Powered Electrochemical Aptasensor for Simultaneous Monitoring of Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate and Bisphenol A in Variable pH Environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462, 132775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madakam, S.; Ramaswamy, R.; Tripathi, S. Internet of Things (IoT): A Literature Review. J. Comput. Commun. 2015, 3, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocu, R. Extended Review Concerning the Integration of Electrochemical Biosensors into Modern IoT and Wearable Devices. Biosensors 2024, 14, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çıtmacı, B.; Luo, J.; Jang, J.B.; Korambath, P.; Morales-Guio, C.G.; Davis, J.F.; Christofides, P.D. Digitalization of an Experimental Electrochemical Reactor via the Smart Manufacturing Innovation Platform. Digit. Chem. Eng. 2022, 5, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, D.; Coyle, S.; Scarmagnani, S.; Hayes, J. Wireless Sensor Networks and Chemo-/Biosensing. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 652–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyare, R.; Lee, S.R. Towards Internet of Things (IOTS): Integration of Wireless Sensor Network to Cloud Services for Data Collection and Sharing. Int. J. Comput. Netw. Commun. 2013, 5, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, E.M.; Sanaan Jabbar, H.; Mireya Romero-Parra, R.; Raheem Lateef Al-Awsi, G.; Setia Budi, H.; Altamimi, A.S.; Abdulfadhil Gatea, M.; Falih, K.T.; Singh, K.; Alkhuzai, K.A. Smartphone-Assisted Microfluidic Sensor as an Intelligent Device for on-Site Determination of Food Contaminants: Developments and Applications. Microchem. J. 2023, 190, 108692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, V.; Boni, A.; Bassoli, M.; Giannetto, M.; Fortunati, S.; Careri, M.; De Munari, I. IoT and Biosensors: A Smart Portable Potentiostat with Advanced Cloud-Enabled Features. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 141544–141554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.K.; Dhau, J.S.; Gohel, H.; Mishra, Y.K.; Kateb, B.; Kim, N.-Y.; Goswami, D.Y. Electrochemical SARS-CoV-2 Sensing at Point-of-Care and Artificial Intelligence for Intelligent COVID-19 Management. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 7306–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beduk, D.; Ilton de Oliveira Filho, J.; Beduk, T.; Harmanci, D.; Zihnioglu, F.; Cicek, C.; Sertoz, R.; Arda, B.; Goksel, T.; Turhan, K.; et al. “All In One” SARS-CoV-2 Variant Recognition Platform: Machine Learning-Enabled Point of Care Diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 10, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lee, M.H.; Zhou, A.; Khanthaphixay, B.; Hwang, D.S.; Yoon, J.-Y. eXtreme Gradient Boosting-Based Classification of Bacterial Mixtures in Water and Milk Using Wireless Microscopic Imaging of Quorum Sensing Peptide-Conjugated Particles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 227, 115144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sensing Module | AI Methodology | Distinctive Strengths | Concise Descriptions and Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biorecognition Molecule Design | Protein language models, GNNs | Cross-structural modeling, label-free learning | Design high-performance antibodies, aptamers, or enzymes by optimizing sequence-structure-function relationships (e.g., ESM models for antibody affinity or CNN-based “smart SELEX” for aptamer screening). |
| Material Structure and Parameter Tuning | GA, Bayesian Optimization, RL | Global search, multi-objective trade-off | Enhance conductivity/stability by tuning parameters like nanoporous gold porosity or MOFs synthesis temperature. |
| Electrochemical Signal Modeling and Noise Reduction | ANN, SVM, RF, CNN | Nonlinear modeling, automatic feature extraction | Improve accuracy via RF for baseline drift correction or CNN for impedance feature extraction. |
| Environmental Compensation and Auto-Calibration | Few-Shot Learning, Transfer Learning, RBF Kernels | Anomaly modeling, strong adaptability | Compensate temperature/pH interference with RBF kernels or transfer learning. |
| Multimodal Data Fusion and Feedback Control | Multimodal Neural Networks, Edge Deep Learning | Data integration, low-latency processing | Enable real-time control by fusing electrochemical/spectral data with edge AI. |
| Module Category | Optimization Subtask | AI Methodology | Technical Advantages | Representative Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Design | Sequence Function Annotation | Contrastive Learning, ESM | No structural input required; suitable for data-scarce conditions | [54,61] |
| Structure-Guided Optimization | AlphaFold + ESM-IF1, GNNs | Cross-target transferability; balanced binding affinity and stability | [55] | |
| Multi-Objective Property Tuning | GA, Bayesian Optimization | Simultaneous optimization of affinity and “nativeness” | [63] | |
| Non-Protein Molecule Design | CNN-SELEX, Feature Embedding | Sequence compression, cycle reduction, complex target adaptation | [60] | |
| Environmental Adaptation Modeling | Meta-Learning, Language Models + Knowledge Graphs | Integrates external conditions like pH and temperature | [65] | |
| Materials and Parameters | Electrode Material Property Prediction | ANN, CNN, SVM | Image + structure modeling; high-dimensional performance mapping | [74] |
| Conductive Material Structure Tuning | Bayesian Optimization, GNN | Material graph interpretation; inverse design | [75] | |
| Joint Optimization of Working Parameters | ANN + GA | Multi-parameter coupling; global optimization | [77] | |
| Plasmonic Structure Design | GA | Structure-signal co-modeling; detection limit enhancement | [79] | |
| Signal Processing | High-Dimensional Signal Modeling | SVM, RF, CNN, PCA | Nonlinear modeling; data compression; variable selection | [82,84] |
| Multimodal Data Fusion | Multimodal Deep Networks, Ensemble Learning | Joint modeling of image and current signals | [85] | |
| Signal Compensation/Correction | SVC, RBF Kernel, ANN | Nonlinear interference modeling; adaptive response tuning | [87] | |
| Matrix Effect Compensation | ANN, Few-Shot Learning | Environment adaptation without external standards | [89] | |
| Multicomponent Detection | ANN, Boosting Algorithms | Signal deconvolution; peak recognition; interference resolution | [90,91,92] | |
| System Integration | Real-Time Data Upload and Control | IoT + Edge AI | Automated sensing; remote transmission; feedback loop | [100] |
| Low-Power On-Site Deployment | Lightweight Neural Networks, Compressed Models | Extended monitoring; portable integration; resource efficiency | [101] | |
| Variant Recognition and Risk Forecasting | Deep Neural Networks | Multi-class classification; high-sensitivity screening | [102] |
| Optimization Module | Current AI Applications | Technical Bottlenecks |
|---|---|---|
| Recognition Molecule Design | Sequence modeling, functional prediction | Label scarcity |
| Electrode Material Optimization | Performance regression, structure generation | Insufficient experimental validation |
| Electrochemical Signal Analysis | Pattern recognition and classification | High feature interference |
| Response Parameter Prediction | Sensitivity/LOD modeling | Data imbalance |
| Multicomponent Detection | Signal deconvolution and discrimination | Peak overlap interference |
| Dynamic Adaptation | Noise modeling, self-calibration | Poor cross-scenario adaptability |
| Long-Term Stability Modeling | Degradation forecasting, fault monitoring | Lack of real-world condition data |
| Multi-Objective Optimization | Hyperparameter search, multi-task learning | Frequent performance trade-offs |
| System Integration | IoT connectivity and feedback control | Power/compute resource limitations |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Lian, C.; Jiang, Y.; Qu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. AI-Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing Systems: A Paradigm Shift for Intelligent Food Safety Monitoring. Biosensors 2025, 15, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090565
Zhao Y, Sun T, Zhang H, Li W, Lian C, Jiang Y, Qu M, Zhao Z, Wang Y, Sun Y, et al. AI-Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing Systems: A Paradigm Shift for Intelligent Food Safety Monitoring. Biosensors. 2025; 15(9):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090565
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yuliang, Tingting Sun, Huawei Zhang, Wenjing Li, Chao Lian, Yongqiang Jiang, Mingyue Qu, Zhongpeng Zhao, Yuhang Wang, Yang Sun, and et al. 2025. "AI-Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing Systems: A Paradigm Shift for Intelligent Food Safety Monitoring" Biosensors 15, no. 9: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090565
APA StyleZhao, Y., Sun, T., Zhang, H., Li, W., Lian, C., Jiang, Y., Qu, M., Zhao, Z., Wang, Y., Sun, Y., Duan, H., Ren, Y., Liu, P., Lang, X., & Chen, S. (2025). AI-Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing Systems: A Paradigm Shift for Intelligent Food Safety Monitoring. Biosensors, 15(9), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090565





