A Stretchable and Transparent Electrode for Visual Electrophysiological Acquisition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
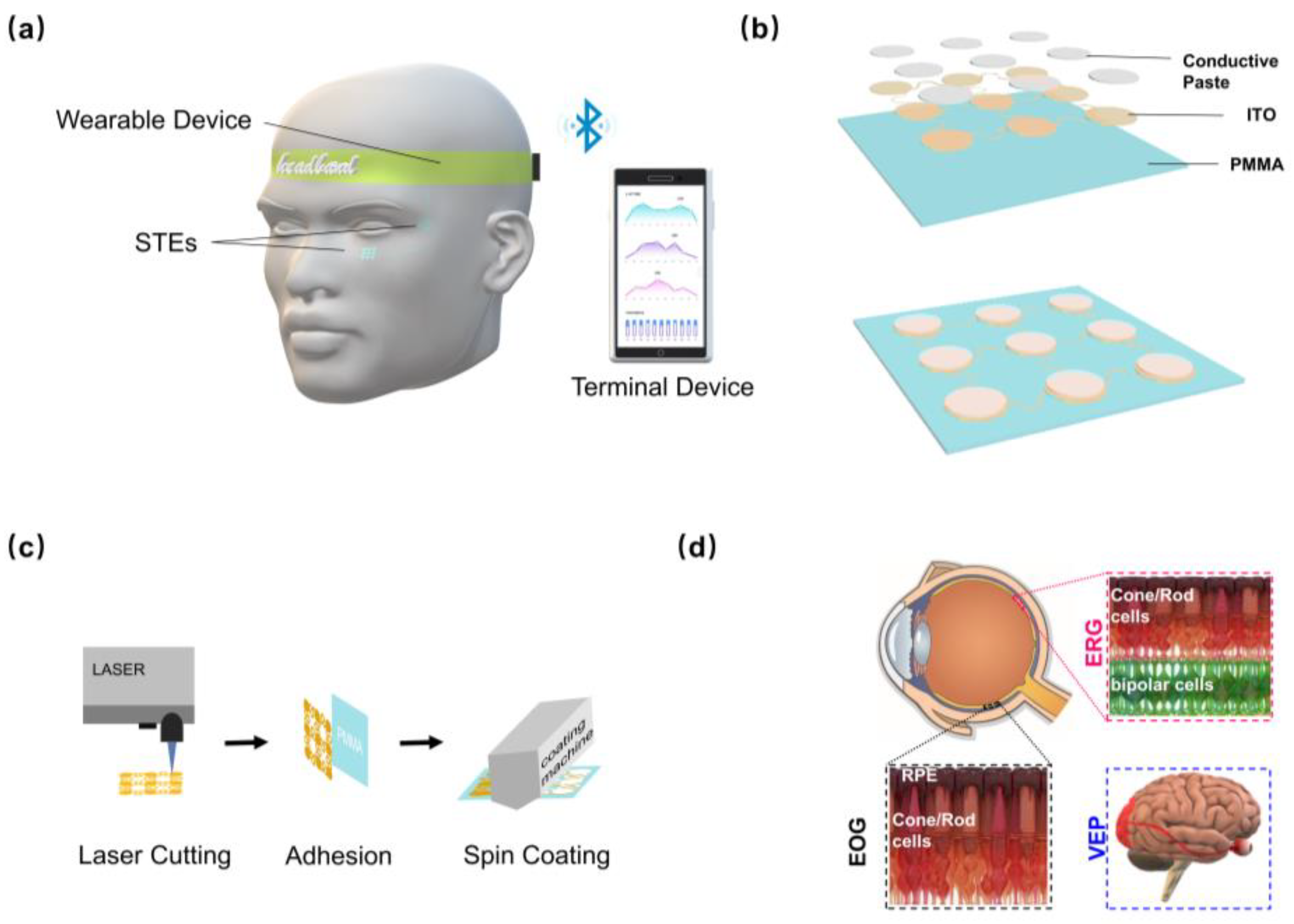
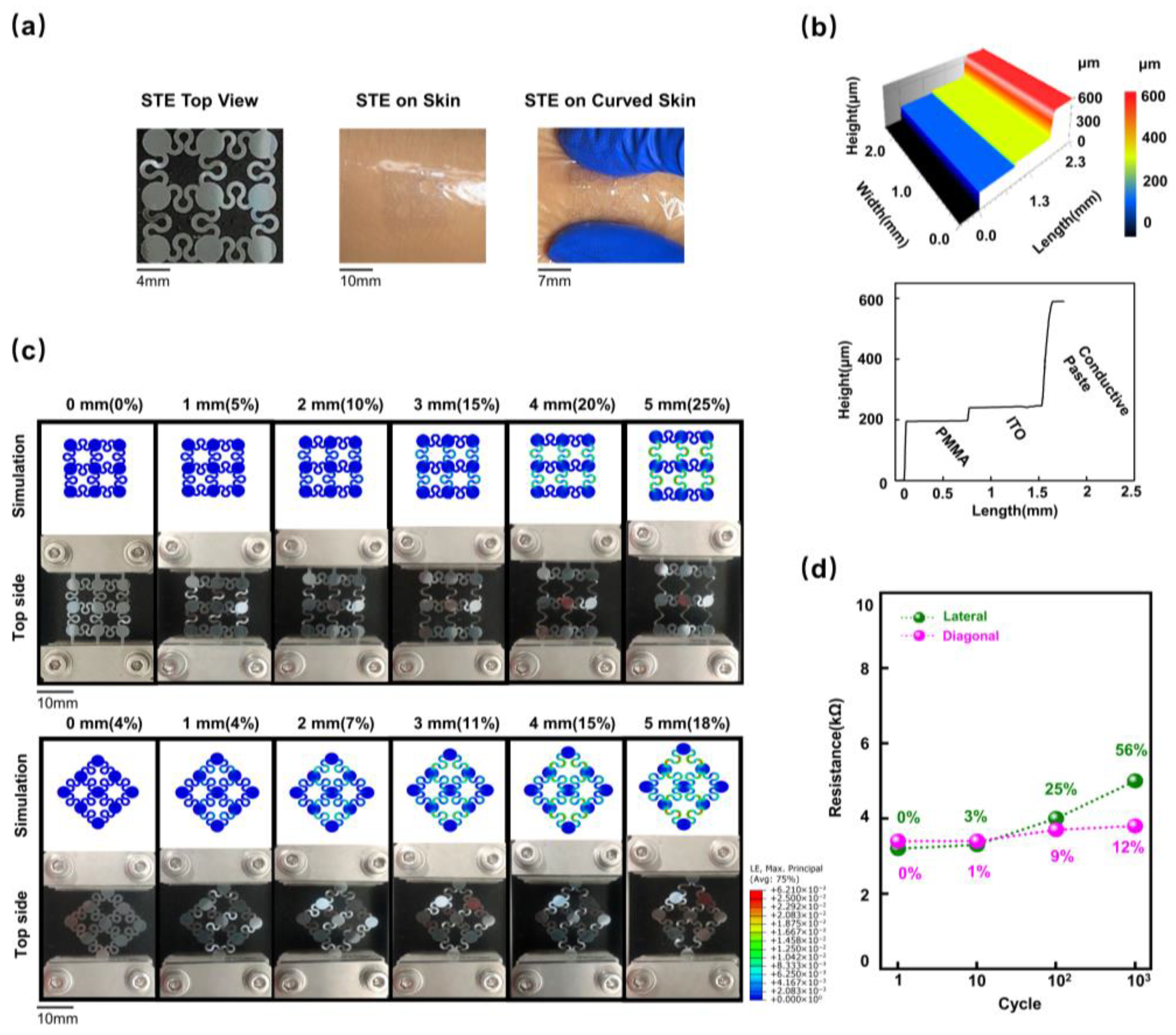
2.1. Fabrication and Characterization of the STE
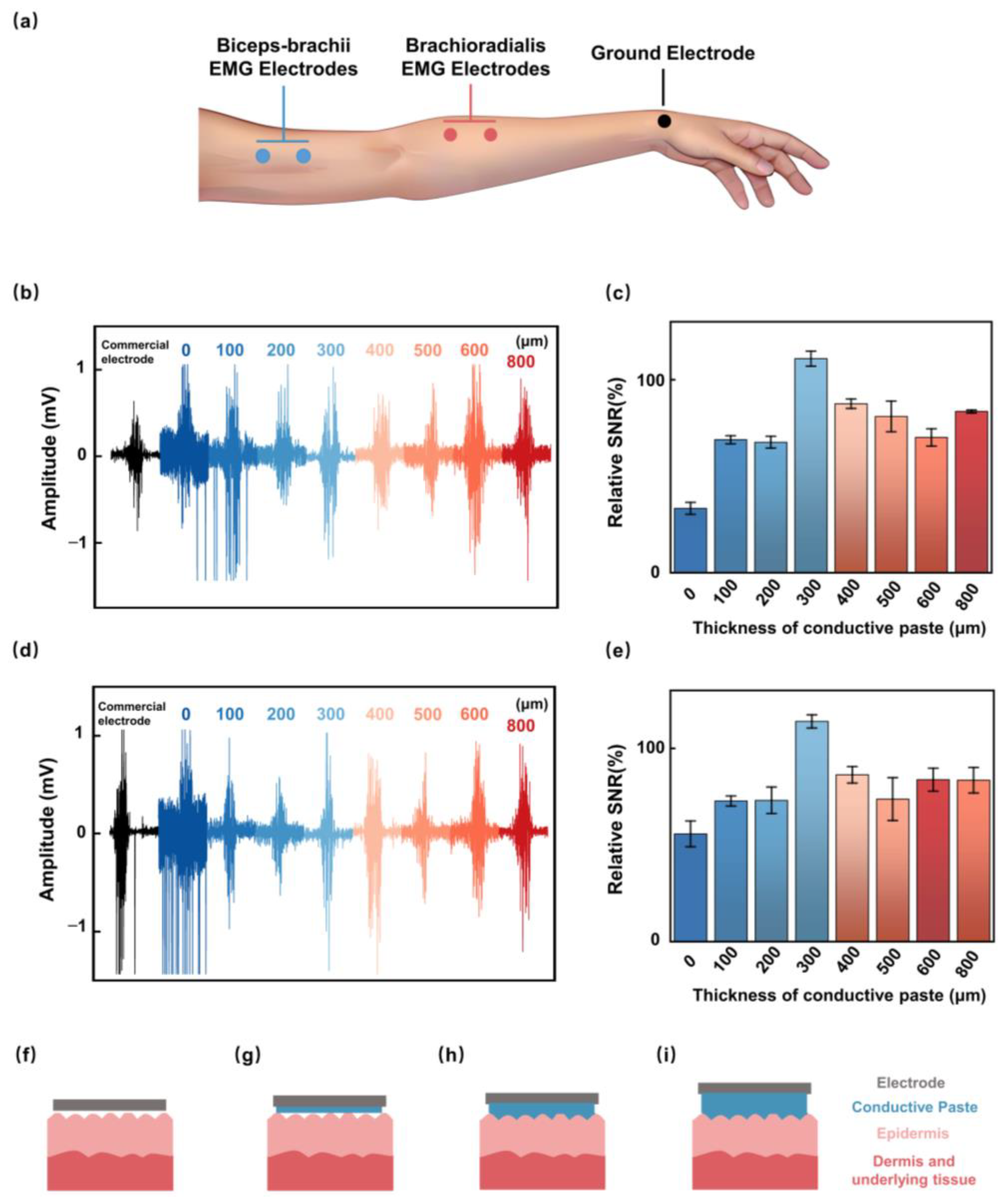
2.2. Conductive Paste Thickness Optimization
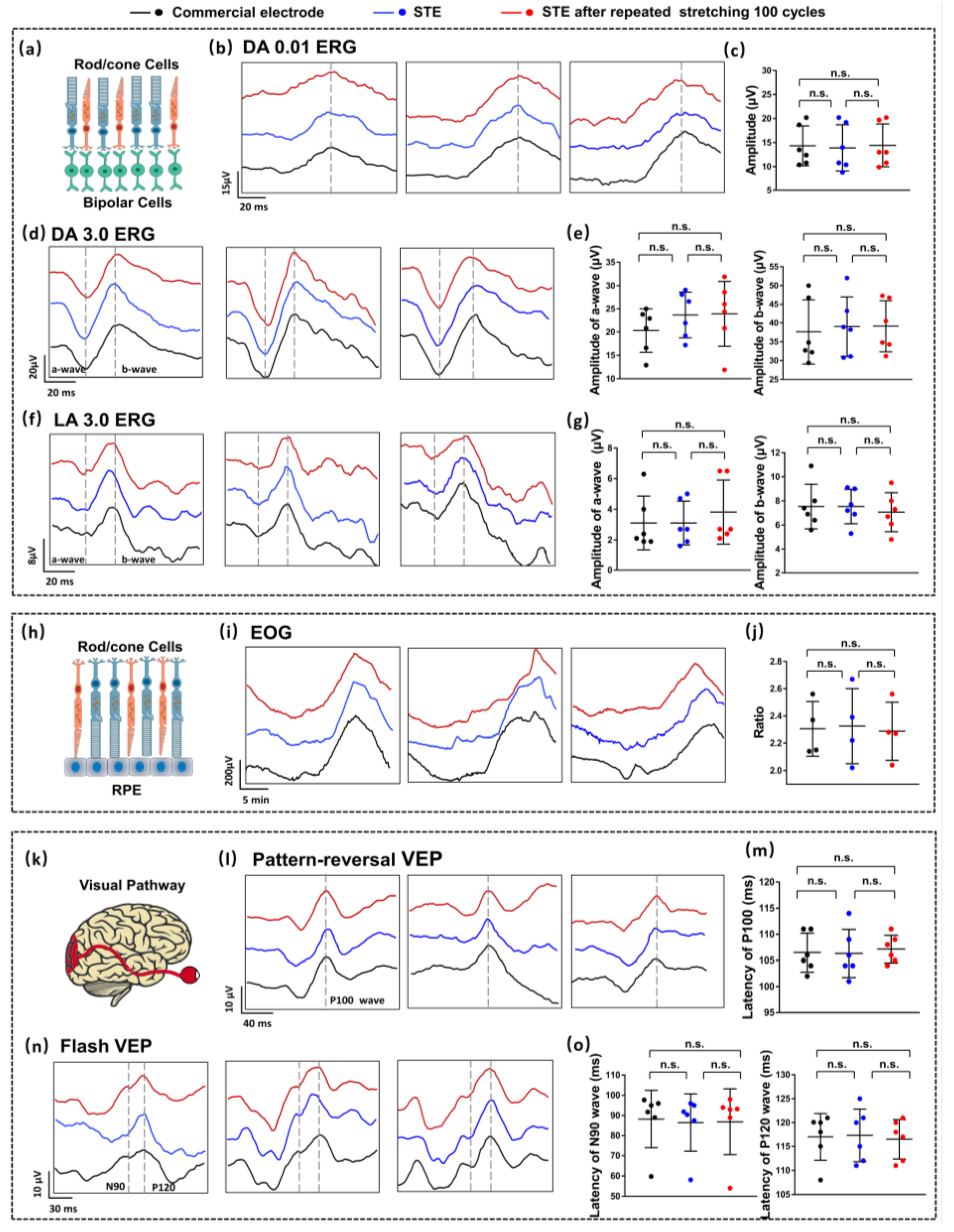
2.3. Clinical EP Examinations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design and Characterization of the STE
3.2. Effect of Conductive Paste Thickness on SNR
3.3. Clinical EP Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbara, W.; Harrington, L.; Kohler-Evans, P.; Sumpter, D. Coming to Our Senses: Incorporating Brain Research Findings into Classroom Instruction. Education 2008, 128, 659. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, B.A.; Mullins, R.F.; Stone, E.M. Stem Cells for Investigation and Treatment of Inherited Retinal Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2024, 23, R9–R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupert, B.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Flaxman, S.; Briant, P.S.; Taylor, H.R.; Resnikoff, S.; Casson, R.J.; Abdoli, A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Afshin, A.; et al. Trends in Prevalence of Blindness and Distance and near Vision Impairment over 30 Years: An Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 2, e130–e143. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.L.; Gao, M.L.; Lei, X.L.; Lv, J.N.; Zhao, H.; He, K.W.; Xia, X.X.; Li, L.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Li, Y.P.; et al. Gene Correction Reverses Ciliopathy and Photoreceptor Loss in Ipsc-Derived Retinal Organoids from Retinitis Pigmentosa Patients. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 4, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januleviciene, I.; Derkac, I.; Grybauskiene, L.; Paulauskaite, R.; Gromnickaite, R.; Kuzmiene, L. Effects of Preservative-Free Tafluprost on Tear Film Osmolarity, Tolerability, and Intraocular Pressure in Previously Treated Patients with Open-Angle Glaucoma. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2012, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, C.M.; Igboeli, O. A Review of the Inflammatory Chorioretinopathies: The White Dot Syndromes. ISRN Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 783190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.S.; Choi, K.Y.; Chan, H.H. Paediatric Norms for Photopic Electroretinogram Testing Based on a Large Cohort of Chinese Preschool Children. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2024, 9, e001393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Ding, J.; Yu, M.; Dong, Z.; Cruz, S.; Ding, N.; Aubinet, C.; Laureys, S.; Di, H.; Chen, Y. Exploring the Clinical Diagnostic Value of Linguistic Learning Ability in Patients with Disorders of Consciousness Using Electrooculography. Neuroimage 2024, 297, 120753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmoy, O.R. The Visual Evoked Potential. In Ophthalmic Diagnostics: Technology, Techniques, and Clinical Applications; Das, T., Satgunam, P.N., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 435–447. [Google Scholar]
- Guang, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, M.; Liao, F.; Lin, Y. Smart Contact Lenses: Catalysts for Science Fiction Becoming Reality. Innovation 2024, 6, 100710. [Google Scholar]
- Hunkyu, S.; Chung, W.G.; Kwon, Y.W.; Kim, S.; Hong, Y.-M.; Park, W.; Kim, E.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.; et al. Smart Contact Lenses as Wearable Ophthalmic Devices for Disease Monitoring and Health Management. Chem. Rev. 2023, 19, 11488–11558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xingyi, G.; Yao, G.; Li, C.; Mu, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhou, C.; Li, P.; Dong, Q.; Chen, K.; Zhao, K.; et al. Closed-Eye Intraocular Pressure and Eye Movement Monitoring Via a Stretchable Bimodal Contact Lens. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2025, 1, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Junshi, L.; Ma, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Hong, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Shi, X.; et al. High-Performance Flexible Microneedle Array as a Low-Impedance Surface Biopotential Dry Electrode for Wearable Electrophysiological Recording and Polysomnography. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 1, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Chenzheng, Z.; Yao, G.; Gan, X.; Chai, K.; Li, P.; Peng, J.; Pan, T.; Gao, M.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, B.; et al. Modulus-Adjustable and Mechanically Adaptive Dry Microneedle Electrodes for Personalized Electrophysiological Recording. npj Flex. Electron. 2025, 1, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhengjie, L.; Xu, X.; Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Liu, Z.; Yao, C.; He, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.-J.; Liu, J.; et al. Multichannel Microneedle Dry Electrode Patches for Minimally Invasive Transdermal Recording of Electrophysiological Signals. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2024, 1, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Gowda, A.; Healey, B.; Ezaldein, H.; Merati, M. A Systematic Review Examining the Potential Adverse Effects of Microneedling. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2021, 1, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Heo, U.; Jayashankar, D.K.; Agno, K.C.; Kim, Y.; Kim, C.Y.; Oh, Y.; Byun, S.H.; Choi, B.; et al. Skin Preparation-Free, Stretchable Microneedle Adhesive Patches for Reliable Electrophysiological Sensing and Exoskeleton Robot Control. Sci. Adv. 2024, 3, eadk5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiakang, Q.; Yu, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, G.; Zhao, Y.; Du, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; et al. A Bioinspired, Durable, and Nondisposable Transparent Graphene Skin Electrode for Electrophysiological Signal Detection. ACS Mater. Lett. 2020, 8, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.C.; Moon, J.H.; Baek, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, Y.Y.; Hong, J.S.; Lee, S.H. Cnt/Pdms Composite Flexible Dry Electrodesfor Long-Term Ecg Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 5, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Kim, E.; Choi, C.; Yeo, W.H. Advances in Soft and Dry Electrodes for Wearable Health Monitoring Devices. Micromachines 2022, 13, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyeonghee, L.; Seo, H.; Chung, W.G.; Song, H.; Oh, M.; Ryu, S.Y.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.-U. Material and Structural Considerations for High-Performance Electrodes for Wearable Skin Devices. Commun. Mater. 2024, 1, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Liangtao, Y.; Gan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J. Insight into the Contact Impedance between the Electrode and the Skin Surface for Electrophysical Recordings. ACS Omega 2022, 16, 13906–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, J.; Xie, Z.; Hong, W.; Jiang, C.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Liu, J. Stretchable Parylene-C Electrodes Enabled by Serpentine Structures on Arbitrary Elastomers by Silicone Rubber Adhesive. J. Mater. 2020, 2, 330–338. [Google Scholar]
- Shuangyuan, L.; Xu, X.; Jiang, J. Flexible Transparent Ito Thin Film with High Conductivity and High-Temperature Resistance. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 47649–47654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, S.; Hermens, H. European Recommendations for Surface Electromyography. Roessingh Res. Dev. 1999, 1, 13–54. [Google Scholar]
- Stanisław, S.; DeVita, P.; Rider, P.; Long, B.; Hortobágyi, T. Teager-Kaiser Operator Improves the Accuracy of Emg Onset Detection Independent of Signal-to-Noise Ratio. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2008, 2, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, G.Y.P. Circadian Regulation in the Retina: From Molecules to Network. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 1, 194–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapkovska, A.; Palmowski-Wolfe, A.M.; Todorova, M.G. Comparing Dtl Microfiber and Neuroline Skin Electrode in the Mini Ganzfeld Erg. BMC Ophthalmol. 2016, 16, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, A.G.; Frishman, L.J.; Grigg, J.; Hamilton, R.; Jeffrey, B.G.; Kondo, M.; Li, S.; McCulloch, D.L. Iscev Standard for Full-Field Clinical Electroretinography (2022 Update). Doc. Ophthalmol. 2022, 144, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, P.A.; Bach, M.; Frishman, L.J.; Jeffrey, B.G.; Robson, A.G.; International Society for Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision. Iscev Standard for Clinical Electro-Oculography (2017 Update). Doc. Ophthalmol. 2017, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odom, J.V.; Bach, M.; Brigell, M.; Holder, G.E.; McCulloch, D.L.; Mizota, A.; Tormene, A.P.; International Society for Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision. Iscev Standard for Clinical Visual Evoked Potentials: (2016 Update). Doc. Ophthalmol. 2016, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, A.G.; Nilsson, J.; Li, S.; Jalali, S.; Fulton, A.B.; Tormene, A.P.; Holder, G.E.; Brodie, S.E. Iscev Guide to Visual Electrodiagnostic Procedures. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2018, 1, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polachan, K.; Chatterjee, B.; Weigand, S.; Sen, S. Human Body-Electrode Interfaces for Wide-Frequency Sensing and Communication: A Review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxim, M.; Ruzgas, T.; Svedenhag, P.; Anderson, C.D.; Ollmar, S.; Engblom, J.; Björklund, S. Skin Hydration Dynamics Investigated by Electrical Impedance Techniques in Vivo and in Vitro. Sci. Rep. 2020, 1, 17218. [Google Scholar]
- Krittika, G.; Borkholder, D.A.; Day, S.W. Dependence of Skin-Electrode Contact Impedance on Material and Skin Hydration. Sensors 2022, 22, 8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, G.; Turovets, S.; Gunn, A.; Tucker, D.; Luu, P. Direct Current Conditioning to Reduce the Electrical Impedance of the Electrode to Skin Contact in Physiological Recording and Stimulation. 2017. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017arXiv171101059G (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Vidhya, C.M.; Maithani, Y.; Singh, J.P. Recent Advances and Challenges in Textile Electrodes for Wearable Biopotential Signal Monitoring: A Comprehensive Review. Biosensors 2023, 13, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, D.L.; Marmor, M.F.; Brigell, M.G.; Hamilton, R.; Holder, G.E.; Tzekov, R.; Bach, M. Iscev Standard for Full-Field Clinical Electroretinography (2015 Update). Doc. Ophthalmol. 2015, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Q.; Xie, M.; Yuan, M.; Lou, W.; Yao, G.; Lin, Y. A Stretchable and Transparent Electrode for Visual Electrophysiological Acquisition. Biosensors 2025, 15, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100701
Dong Q, Xie M, Yuan M, Lou W, Yao G, Lin Y. A Stretchable and Transparent Electrode for Visual Electrophysiological Acquisition. Biosensors. 2025; 15(10):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100701
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Qiwei, Maowen Xie, Mengyao Yuan, Wenhao Lou, Guang Yao, and Yuan Lin. 2025. "A Stretchable and Transparent Electrode for Visual Electrophysiological Acquisition" Biosensors 15, no. 10: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100701
APA StyleDong, Q., Xie, M., Yuan, M., Lou, W., Yao, G., & Lin, Y. (2025). A Stretchable and Transparent Electrode for Visual Electrophysiological Acquisition. Biosensors, 15(10), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100701



