Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Anti-Inflammatory and Antibiotic Drugs: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Progress and Challenges Associated with Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors for Drug Detection
1.2. Electrochemical Detection Modes in Sensor Applications
1.3. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Description, Common Agents, Therapeutic Uses, and Side Effects
1.3.1. Recognition Elements in Electrochemical Sensors
1.3.2. Electrochemical Detection of NSAIDs
1.3.3. Electrochemical Detection of Naproxen
2. Electrochemical Detection of Ibuprofen
2.1. Electrochemical Detection of Naproxen and Ibuprofen: Mechanistic Insights and Advancements in Sensor Platforms
| Target Drug | Electrode/Modification | Technique | LOD (µM) | Sample Matrix | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naproxen | GO/GCE (various dopings) | DPV | 1.900 | Pharmaceutical tablets | [12] |
| Naproxen | CdS-modified GCE | SWV | 0.00143 | Pharmaceuticals | [76] |
| Ibuprofen | Ag–zeolite/–MWCNT composite | CV / DPV | 0.00018 | Water samples, pharma | [77] |
| Naproxen and Ibuprofen | Al2O3-modified GCE | SWV | 0.012 | Biological, pharmaceuticals | [28] |
| DCF, Naproxen, Ibuprofen | CNF/GR-CNT paste electrode | SWV | 6.08 × 10−6–2.86 × 10−3 | Pharmaceuticals | [18] |
| Ibuprofen | Bare BDDE | CV / DPV | 0.410 | Pharmaceuticals, urine | [13] |
| Ibuprofen | Cu3TeO6/GCE | CV / DPV | 0.017 | Pharmaceuticals | [73] |
| Ibuprofen | TGA/CdTe QD aptasensor | SWV | 3.33 × 10−7 | Pharmaceutical samples | [72] |
| Ibuprofen | Apt/AuNPs@N-GQDs nanocomposite | SWV | 0.03333 | Pharmaceuticals | [72] |
| Naproxen | CPE/FeNi3/CuS/BiOCl | Chronoamperometry | 0.060 | Pharmaceutical samples | [78] |
| Naproxen | Ni-Fe LDH/Au electrode | CV / DPV | 0.001 | Pharmaceuticals | [79] |
2.2. Electrochemical Detection of Aspirin
2.3. Electrochemical Detection of Diclofenac: Mechanistic and Analytical Perspectives
2.4. Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Naproprex, Ibuprophen, and Diclofenac
3. Antibiotics Drugs (Antibacterial Drugs)
3.1. Description, Main Popularly Antibiotics Drugs, General Proposes, and Side Effects
3.2. Amoxicillin (Pinicillin Drugs): Description, Action Mechanism, and Electrochemical Detection
| Drug | Electrode Material | Method | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | GCE/quantum dots/PEDOT:PSS | SWV | 50 nM | [104] |
| Paper based electrode | DPV | 8 μM | [105] | |
| SPE/cobalt-doped titanium dioxide | SWV | 5.8 μM | [17] | |
| Ciprofloxacin | CPE/choline chloride | SWV | 0.036 nM | [106] |
| Gentamicin | graphene oxide–gadolinium oxide/SPCE | CV | 0.424 pM | [107] |
| Tetracycline | CPE/Magnetic nanoparticles–MIP | SWV | 0.15 μM | [108] |
| Doxycycline | SPCE/Ni.Gr | SWV | 0.0096 μM | [109] |
| Erythromycin | GCE /Arg-MIP | SWV | 2.01 nM | [110] |
| Rifampicin | GCE/Fe3O4NPs@MWCNT | DPV | 0.64 μM | [111] |
| Clarithromycin | GCE/molecularly imprinted polyarylene phthalide | DPV | 0.053 μM | [112] |
| Azithromycin | SPCE/4-aminobenzoic acid | DPV | 0.08 μM | [113] |
| Kanamycin | GCE/Co, Mo@CNFs | DPV | 2.56 pmol·L−1 | [114] |
| Chloramphenicol | GCE/poly (eriochrome black T) | DPV | 11 nmol L−1 | [115] |
| Levofloxacin | GCE/PEDOT/Chitosan | DPV | 0.4 nM | [116] |
| Streptomycin | GCE/molecularly imprinted composite | DPV | 0.25 pM | [117] |
| Metronidazole | GCE/f-Co@rGO | DPV | 0.015 nM | [118] |
| Cephalexin | GCE/MIP | DPV | 3.2 nM | [119] |
4. Ciprofloxacin
4.1. Cephalexin (a Cephalosporin Drug): Description, Mechanism of Action, and Electrochemical Detection
4.2. Azithromycin (Macrolide Drugs): Description, Action Mechanism and Electrochemical Detection
5. Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riffat, I.; Shah, A. Electrochemical and Optical Protocols for the Detection and Removal of an Antibiotic Drug Rifaximin from Wastewater. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 22867–22876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigoli, M.; Krupa, M.P.; Hooyberghs, G.; Lowdon, J.W.; Cleij, T.J.; Diliën, H.; Eersels, K.; van Grinsven, B. Electrochemical Sensors for Antibiotic Detection: A Focused Review with a Brief Overview of Commercial Technologies. Sensors 2024, 24, 5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ye, C.; Xiao, X.; Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Fu, L.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Chen, J.; Lin, C.-T. Graphene-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Antibiotics: Sensing Theories, Synthetic Methods, and on-Site Monitoring Applications. Mater. Horiz. 2025, 12, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepfumbada, C.; Mthombeni, N.H.; Sigwadi, R.; Ajayi, R.F.; Feleni, U.; Mamba, B.B. Functionalities of Electrochemical Fluoroquinolone Sensors and Biosensors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 31, 3394–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, S.R.; Miranda Ribeiro Júnior, E.J. Graphene-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Detection of Environmental Pollutants. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 29, 100381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, V.; C S, S.; Mondal, D.; Sundarabal, N.; Nag, P.; Sadani, K. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensing and Remediation Technologies for Ciprofloxacin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 2210–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Han, N.; Shen, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Cao, Y.; Si, W.; Wang, F.; Ni, B.-J.; Thakur, V.K. MXene-Based Electrochemical (Bio) Sensors for Sustainable Applications: Roadmap for Future Advanced Materials. Nano Mater. Sci. 2023, 5, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, N.; Alexander, P.S.; Pham, P.T.; Ramachandran, B.; Nivedha, D.R.; Shekar, N.; Muraleetharan, M.; Kiran, S.K.; Hwang, M.T. Exploring the Potential of MXenes for Biomedical and Environmental Applications—An Abridged Review. Luminescence 2025, 40, e70238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Kim, H. Recent Advances in MXene Gas Sensors: Synthesis, Composites, and Mechanisms. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2025, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, J.; Barse, B.; Gatto, G.; Broncova, G.; Kumar, A. Electrochemical Sensors and Their Applications: A Review. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Durairaj, S.; Prins, S.; Chen, A. Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors for the Detection of Pharmaceutical Compounds. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Thiruppathi, A.R.; Elmahdy, R.; van der Zalm, J.; Chen, A. Graphene-Oxide-Based Electrochemical Sensors for the Sensitive Detection of Pharmaceutical Drug Naproxen. Sensors 2020, 20, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Švorc, Ľ.; Strežová, I.; Kianičková, K.; Stanković, D.M.; Otřísal, P.; Samphao, A. An Advanced Approach for Electrochemical Sensing of Ibuprofen in Pharmaceuticals and Human Urine Samples Using a Bare Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 822, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj-Rossi, C.; Rezzonico Jost, T.; Cavallini, A.; Grassi, F.; De Micheli, G.; Carrara, S. Continuous Monitoring of Naproxen by a Cytochrome P450-Based Electrochemical Sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimuam, K.; Rodthongkum, N.; Ngamrojanavanich, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Ruecha, N. Single Step Preparation of Platinum Nanoflowers/Reduced Graphene Oxide Electrode as a Novel Platform for Diclofenac Sensor. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalauddin, M.; Akhter, S.; Basirun, W.J.; Bagheri, S.; Anuar, N.S.; Johan, M.R. Hybrid Nanocellulose/f-MWCNTs Nanocomposite for the Electrochemical Sensing of Diclofenac Sodium in Pharmaceutical Drugs and Biological Fluids. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 304, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.K.A.; Silva-Neto, H.A.; Rocha, D.S.; de Abreu, F.C.; Silva, A.C.A.; Dantas, N.O.; Coltro, W.K.T.; Garcia, P.T. Disposable Sensor Based on Carbon Electrodes Modified with Cobalt-Doped Titanium Dioxide Nanocrystals for Electrochemical Detection of Amoxicillin. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 942, 117587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoc, S.; Manea, F.; Baciu, A.; Orha, C.; Pop, A. Electrochemical Method for Ease Determination of Sodium Diclofenac Trace Levels in Water Using Graphene—Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Paste Electrode. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, O.; Elik, M. Potentiometric Determination of Anti-Inflammatory Drug Etodolac in Pharmaceutical Samples and Its Greenness Assessment. Chem. Pap. 2025, 79, 5765–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagarsamy, S.; Mariappan, K.; Chen, S.-M.; Ramachandran, R.; Devanesan, S.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Arunachalam, P.; Sivaganesh, D.; Vinoth Kumar, J.; Chuang, H.-Y. 2D/2D Cobalt Vanadate Nanoplatelets/S-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanosheets Composite for the Detection of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug: Acetaminophen. FlatChem 2023, 42, 100563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Lira, G.Y.; López-Barriguete, J.E.; Hernandez, P.; Álvarez-Romero, G.A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Simultaneous Voltammetric Determination of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Using a Modified Carbon Paste Electrode and Chemometrics. Sensors 2022, 23, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroco, P.B.; Rocha-Filho, R.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O. A New and Simple Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Amoxicillin and Nimesulide Using Carbon Black within a Dihexadecylphosphate Film as Electrochemical Sensor. Talanta 2018, 179, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushotham, M.; Gupta, P.; Goyal, R.N. Graphene Modified Glassy Carbon Sensor for the Determination of Aspirin Metabolites in Human Biological Samples. Talanta 2015, 143, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, R.C.; Betts, A.J.; Cassidy, J.F. Diclofenac Determination Using CeO2 Nanoparticle Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes—A Study of Background Correction. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, G.Z.d.M.G.; Silva, F.W.L.; Lopes, C.S.C.; Braz, B.F.; Santelli, R.E.; Cincotto, F.H. Development of a New Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor to Piroxicam Anti-Inflammatory Determination Using a Disposable Screen-Printed Electrode. Ion. (Kiel) 2024, 30, 2793–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxib and Traditional NSAID Trialists’ (CNT) Collaboration. Vascular and Upper Gastrointestinal Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Meta-Analyses of Individual Participant Data from Randomised Trials. Lancet 2013, 382, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, M. Toxicity of the Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Acetylsalicylic Acid, Paracetamol, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen and Naproxen towards Freshwater Invertebrates: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.P.; Nunes, G.L.; Franco, R.G.; Mariano-Neto, R.; Oliveira, G.S.; Richter, E.M.; Nossol, E.; Munoz, R.A.A. Al2O3 Microparticles Immobilized on Glassy-carbon Electrode as Catalytic Sites for the Electrochemical Oxidation and High Detectability of Naproxen: Experimental and Simulation Insights. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 882, 114988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, E.; Babington, R.; Broto, M.; Petanas, S.; Galve, R.; Marco, M.-P. Application of Bioassays/Biosensors for the Analysis of Pharmaceuticals in Environmental Samples. In Analysis, Fate and Removal of Pharmaceuticals in the Water Cycle; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 195–229. [Google Scholar]
- Alagumalai, K.; Musuvadhi Babulal, S.; Chen, S.-M.; Shanmugam, R.; Yesuraj, J. Electrochemical Evaluation of Naproxen through Au@f-CNT/GO Nanocomposite in Environmental Water and Biological Samples. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 104, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ding, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; He, Y. Low Oxidation Potential Electrochemiluminescence from Novel Iridium(III) Complexes Comprising N-Heterocyclic Carbene Main Ligands Containing Dibenzothiophene Motif. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 895, 115534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.M.; Lee, S.; Ban, C. Aptamers and Their Biological Applications. Sensors 2012, 12, 612–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, I.; Hepel, M.; Kurzątkowska-Adaszyńska, K. Advances in Design Strategies of Multiplex Electrochemical Aptasensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.; Yan, S.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Song, Z. Recent Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Antibiotic Analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-J.; Shin, J.-H.; Jung, S.-H.; Oh, B.-K. Recent Advances in Biosensors Using Enzyme-Stabilized Gold Nanoclusters. Biosensors 2024, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, M.; Liu, Y. Recent Advances in Enzyme Immobilization: The Role of Artificial Intelligence, Novel Nanomaterials, and Dynamic Carrier Systems. Catalysts 2025, 15, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, S.R.; de Souza Nascimento, T.; Roque, C.R.; de Andrade, G.M.; Oriá, R.B. Recent Advances in the Development of Immunosensors for Infectious Diseases. In Biosensors for Emerging and Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 19–72. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, S.R.; Júnior, E.J.M.R.; de Andrade, G.M.; Oriá, R.B. Metal-Organic Framework–Based Electrochemical Immunosensors for Virus Detection. In Advanced Functional Metal-Organic Frameworks; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 269–288. [Google Scholar]
- Maduraiveeran, G.; Sasidharan, M.; Ganesan, V. Electrochemical Sensor and Biosensor Platforms Based on Advanced Nanomaterials for Biological and Biomedical Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 103, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadurmus, L.; Sahin, I.F.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Ozkan, S.A. Electrochemical Determination of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2019, 15, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalambate, P.K.; Noiphung, J.; Rodthongkum, N.; Larpant, N.; Thirabowonkitphithan, P.; Rojanarata, T.; Hasan, M.; Huang, Y.; Laiwattanapaisal, W. Nanomaterials-Based Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors for the Detection of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, V.; Selvakumar, P.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Satheeskumar, V.; Godwin Vijaysunder, M.; Hariharan, S.; Antony, K. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensor Developments for Detecting Emerging Pollutant in Water Environment. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Gupta, R.; Bansal, D.; Bhateria, R.; Sharma, M. A Review on Recent Trends and Future Developments in Electrochemical Sensing. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 7336–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyszczuk-Rotko, K.; Kozak, J.; Czech, B. Screen-Printed Voltammetric Sensors—Tools for Environmental Water Monitoring of Painkillers. Sensors 2022, 22, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, S.; de Lima, F.; Nascimento, V.; de Andrade, G.; Oriá, R. Advancement in Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensing and Emerging Diagnostic Methods. Biosensors 2023, 13, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, J.N.; Vij, V.; Kemp, K.C.; Kim, K.S. Engineered Carbon-Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Biomolecules. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 46–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roushani, M.; Shahdost-fard, F. Fabrication of an Ultrasensitive Ibuprofen Nanoaptasensor Based on Covalent Attachment of Aptamer to Electrochemically Deposited Gold-Nanoparticles on Glassy Carbon Electrode. Talanta 2015, 144, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetti, N.P.; Malode, S.J.; Nayak, D.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Reddy, K.R. Nanostructured Silver Doped TiO2/CNTs Hybrid as an Efficient Electrochemical Sensor for Detection of Anti-Inflammatory Drug, Cetirizine. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, E.; Reza Khaleghi, M.; Asghari, A. Development of ZnO-Pd/Bi2O3 Nanocomposite Modified Carbon Paste Electrode as a Sensor for the Simultaneous Determination of Piroxicam and Naproxen. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, F.; Rounaghi, G.H.; Ashraf, N.; Deiminiat, B. A New Electrochemical Sensing Platform for Quantitative Determination of Diclofenac Based on Gold Nanoparticles Decorated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Film. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Toppo, A.E.; Garima; Mehta, S.K.; Sharma, S. Synthesis of Polypyrrole (PPY) Functionalized Halloysite Nanotubes (HNTs): An Electrochemical Sensor for Ibuprofen. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 652, 159280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.L.C.; de Andrade Rodrigues, G.; Magalhães, J.L.; de Sousa Luz, R.A.; da Silva, E.T.S.G.; Cantanhêde, W. Effect of Ibuprofen on the Electrochemical Properties of Prussian Blue/Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Nanocomposite Modified Electrode. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 25, 101276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumya, W.; Taoufik, N.; Achak, M.; Bessbousse, H.; Elhalil, A.; Barka, N. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors for the Determination of Diclofenac in Pharmaceutical, Biological and Water Samples. Talanta Open 2021, 3, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, H.; Parrilla, M.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Montiel, N.F.; Barfidokht, A.; Van Echelpoel, R.; De Wael, K.; Wang, J. Wearable Electrochemical Sensors for the Monitoring and Screening of Drugs. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2679–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagarsamy, P.; Settu, R.; Chen, S.-M.; Chen, T.-W.; Hong, I.-S.; Rao, M.M. Amperometric Determination of Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) Using Graphene Oxide Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 7930–7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashkhourian, J.; Hemmateenejad, B.; Beigizadeh, H.; Hosseini-Sarvari, M.; Razmi, Z. ZnO Nanoparticles and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Modified Carbon Paste Electrode for Determination of Naproxen Using Electrochemical Techniques. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 714–715, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, X.; Fan, S.; Zhong, M.; Zhou, B. Construction of a Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on MIP-ZrMOFs/RGO for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Ketoprofen. Microchem. J. 2025, 213, 113903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, G.A.; Berrio Velasco, L.F.; Silbestri, G.F.; Molina, P.G.; Moyano, F. Gold Nanoparticles Stabilized by Sulfonated Imidazolium Salt for the Manufacture of Modified Electrodes in Order to Electrochemical Detection of Indomethacin. Microchem. J. 2022, 183, 107992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, A. Development of a Porous Polycitric Acid-Branch Coated Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Infused with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Advanced Electrochemical Sensing of Piroxicam in Authentic and Pharmaceutical Samples. Microchem. J. 2025, 214, 114078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu, M.E.; Bayraktepe, D.E.; Polat, K.; Yazan, Z. Electro-Oxidation Mechanism of Meloxicam and Electrochemical Sensing Platform Based on Graphene Nanoparticles for Its Sensing Pharmaceutical Sample. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 15, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsaee, Z.; Karachi, N.; Abrishamifar, S.M.; Kahkha, M.R.R.; Razavi, R. Silver-Choline Chloride Modified Graphene Oxide: Novel Nano-Bioelectrochemical Sensor for Celecoxib Detection and CCD-RSM Model. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 45, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarahomi, S.; Rounaghi, G.H.; Daneshvar, L. A Novel Disposable Sensor Based on Gold Digital Versatile Disc Chip Modified with Graphene Oxide Decorated with Ag Nanoparticles/β-Cyclodextrin for Voltammetric Measurement of Naproxen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 286, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, R.H.O.; Lima, A.P.; Cunha, R.R.; Guedes, T.J.; dos Santos, W.T.P.; Nossol, E.; Richter, E.M.; Munoz, R.A.A. Size Effects of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on the Electrochemical Oxidation of Propionic Acid Derivative Drugs: Ibuprofen and Naproxen. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 775, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoum, A.; Hamimed, S.; Slimi, H.; Othmani, A.; Abdel-Haleem, F.M.; Bechelany, M. Modern Designs of Electrochemical Sensor Platforms for Environmental Analyses: Principles, Nanofabrication Opportunities, and Challenges. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 38, e00199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.; Hossain, M.R.; Ferdous, T. The Recent Advancement of Low-Dimensional Nanostructured Materials for Drug Delivery and Drug Sensing Application: A Brief Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 320, 114427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, R.N.; Bishnoi, S.; Agrawal, B. Electrochemical Sensor for the Simultaneous Determination of Caffeine and Aspirin in Human Urine Samples. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 655, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdost-fard, F.; Roushani, M. An Impedimetric Aptasensor Based on Water Soluble Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) Quantum Dots (QDs) for Detection of Ibuprofen. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 763, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M.; Sakthivel, M.; Chen, S.-M.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Pandi, K. One-Step Synthesis of Porous Copper Oxide for Electrochemical Sensing of Acetylsalicylic Acid in the Real Sample. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 501, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, S.; Cavallini, A.; Erokhin, V.; De Micheli, G. Multi-Panel Drugs Detection in Human Serum for Personalized Therapy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3914–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoc, S.; Remes, A.; Pop, A.; Manea, F.; Schoonman, J. Electrochemical Detection and Degradation of Ibuprofen from Water on Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes-Epoxy Composite Electrode. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushani, M.; Shahdost-fard, F. Applicability of AuNPs@N-GQDs Nanocomposite in the Modeling of the Amplified Electrochemical Ibuprofen Aptasensing Assay by Monitoring of Riboflavin. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 126, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutharani, B.; Rajakumaran, R.; Chen, S.-M.; Ranganathan, P.; Chen, T.-W.; Al Farraj, D.A.; Ajmal Ali, M.; Al-Hemaid, F.M.A. Facile Synthesis of 3D Stone-like Copper Tellurate (Cu3TeO6) as a New Platform for Anti-Inflammatory Drug Ibuprofen Sensor in Human Blood Serum and Urine Samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, M.; Jahromi, Z.; Nekooie, R. Sensitive Voltammetric Method for the Determination of Naproxen at the Surface of Carbon Nanofiber/Gold/Polyaniline Nanocomposite Modified Carbon Ionic Liquid Electrode. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenik, J.; Nieszporek, J. Construction of a Glassy Carbon Ibuprofen Electrode Modified with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Cyclodextrins. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quddus, F.; Shah, A.; Ullah, N.; Shah, I. Metal-Based Nanomaterials for the Sensing of NSAIDS. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoc, S.; Manea, F.; Baciu, A.; Vasilie, S.; Pop, A. Highly Sensitive and Simultaneous Electrochemical Determinations of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Water Using Nanostructured Carbon-Based Paste Electrodes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh Jahani, P.; Akbari Javar, H.; Mahmoudi-Moghaddam, H. Development of a Novel Electrochemical Sensor Using the FeNi3/CuS/BiOCl Nanocomposite for Determination of Naproxen. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 14022–14034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandam, G.; Srinivasan, S.; Nesakumar, N.; Hariharan, G.; Gunasekaran, B.M. Electrochemical Investigation on Naproxen Sensing and Steady-State Diffusion Analysis Using Ni-Fe Layered Double Hydroxide Modified Gold Electrode. Measurement 2023, 220, 113389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruanetr, S.; Prabhu, R.; Pollard, P.; Fernandez, C. Pharmaceutical Electrochemistry: The Electrochemical Detection of Aspirin Utilising Screen Printed Graphene Electrodes as Sensors Platforms. Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem. 2015, 51, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusankar, G.; Sasikumar, R.; Chen, S.-M.; Gopu, G.; Sengottuvelan, N.; Rwei, S.-P. Electrochemical Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots Decorated Copper Oxide for the Sensitive and Selective Detection of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug in Berries. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 523, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Xue, Z.; Wu, B.; Lu, X. Acetylsalicylic Acid Electrochemical Sensor Based on PATP–AuNPs Modified Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Film. Talanta 2011, 85, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiğit, A.; Yardım, Y.; Çelebi, M.; Levent, A.; Şentürk, Z. Graphene/Nafion Composite Film Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol, Aspirin and Caffeine in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Talanta 2016, 158, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lin, J. Electrochemically Reduced Graphene Oxide Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Sensitive Determination of Acetylsalicylic Acid. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 10177–10186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diouf, A.; Moufid, M.; Bouyahya, D.; Österlund, L.; El Bari, N.; Bouchikhi, B. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on Chitosan Capped with Gold Nanoparticles Combined with a Voltammetric Electronic Tongue for Quantitative Aspirin Detection in Human Physiological Fluids and Tablets. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassa, A.; Bitew, Z.; Abebe, A. A Non-Toxic Poly(Resorcinol) Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Highly Selective Square Wave Voltammetry Determination of Aspirin in Tablet Formulations and Human Urine Samples. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2023, 39, 100554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Güney, S.; Kuźniarska-Biernacka, I.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Neves, I.C.; Fonseca, A.M.; Parpot, P. Electrochemical Oxidation of Diclofenac on CNT and M/CNT Modified Electrodes. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 12622–12633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Lira, G.Y.; Álvarez-Romero, G.A.; Zamora-Suárez, A.; Palomar-Pardavé, M.; Rojas-Hernández, A.; Rodríguez-Ávila, J.A.; Páez-Hernández, M.E. New Insights on Diclofenac Electrochemistry Using Graphite as Working Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 794, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Măghinici, A.-R.; Bounegru, A.-V.; Apetrei, C. Electrochemical Detection of Diclofenac Using a Screen-Printed Electrode Modified with Graphene Oxide and Phenanthroline. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postolović, K.; Stanić, Z. Chitosan/TiO2 Nanoparticles Modified Carbon Paste Electrode as a Sensitive Voltammetric Sensor for the Determination of Diclofenac Sodium as an Anti-Inflammatory Drug. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 37, 107416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalauddin, M.; Akhter, S.; Bagheri, S.; Abd Karim, M.S.; Adib Kadri, N.; Basirun, W.J. Immobilized Copper Ions on MWCNTS-Chitosan Thin Film: Enhanced Amperometric Sensor for Electrochemical Determination of Diclofenac Sodium in Aqueous Solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 19951–19960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghali, R.A.; Ahmed, R.A.; Alharthi, A.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Electrochemical Sensor Based on Polymeric /TiO2Nanocomposite Modified with Imidizolium Ionic Liquid for Determination of Diclofenac. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 10390–10414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Bahiraei, A.; Madrakian, T. Gold Nanoparticle/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode as a Sensitive Voltammetric Sensor for the Determination of Diclofenac Sodium. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yan, Y.; Yang, X.; Chang, J.; Song, Y.; Jia, Y.; Pan, P.; Mi, W.; et al. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on Plasma-Treated Zinc Oxide Nanoflowers for the Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Diclofenac Sodium. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanichelli, V.; Sharland, M.; Cappello, B.; Moja, L.; Getahun, H.; Pessoa-Silva, C.; Sati, H.; van Weezenbeek, C.; Balkhy, H.; Simão, M.; et al. The WHO AWaRe (Access, Watch, Reserve) Antibiotic Book and Prevention of Antimicrobial Resistance. Bull. World Health Organ. 2023, 101, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muteeb, G.; Rehman, M.T.; Shahwan, M.; Aatif, M. Origin of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance, and Their Impacts on Drug Development: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llor, C.; Bjerrum, L. Antimicrobial Resistance: Risk Associated with Antibiotic Overuse and Initiatives to Reduce the Problem. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2014, 5, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrioua, A.; Loudiki, A.; Farahi, A.; Bakasse, M.; Lahrich, S.; Saqrane, S.; El Mhammedi, M.A.A. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors for Amoxicillin Detection in Biological and Environmental Samples. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 137, 107687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertonha, A.F.; Silva, C.C.L.; Shirakawa, K.T.; Trindade, D.M.; Dessen, A. Penicillin-Binding Protein (PBP) Inhibitor Development: A 10-Year Chemical Perspective. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2023, 248, 1657–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.P.; Bergamini, M.F.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Voltammetric Sensor for Amoxicillin Determination in Human Urine Using Polyglutamic Acid/Glutaraldehyde Film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 133, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Bevilacqua, M.; Busson, B.; Corva, M.; Tadjeddine, A.; Vizza, F.; Vesselli, E.; Bozzini, B. An in Situ IR-Vis Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy Study of Cyanide Adsorption during Zinc Electrodeposition. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 855, 113641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Tian, D.-H.; Yan, S.; Li, X.-C.; Dai, F.; Zhou, B. Developing a Styrylpyridinium-Based Fluorescent Probe with Excellent Sensitivity for Visualizing Basal H2S Levels in Mitochondria. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 327, 128937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, K.; Wei, X.; Ye, B. Sensitive Determination of Methotrexate at Nano-Au Self-Assembled Monolayer Modified Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 674, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Santos, A.M.; Cincotto, F.H.; Moraes, F.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. A New Electrochemical Platform Based on Low Cost Nanomaterials for Sensitive Detection of the Amoxicillin Antibiotic in Different Matrices. Talanta 2020, 206, 120252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, C.C.; Lisboa, T.P.; de Oliveira, W.B.V.; Abarza Muñoz, R.A.; Costa Matos, M.A.; Matos, R.C. Simple Strategy for the Detection of the Amoxicillin Antibiotic in Different Matrices Using a Low-Cost Paper Electrode. Talanta 2023, 253, 124050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adane, W.D.; Chandravanshi, B.S.; Tessema, M. A Simple, Ultrasensitive and Cost-Effective Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Various Types of Samples. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2023, 39, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanshu, J.K.; Lakshmi, G.B.V.S.; Singh, A.K.; Solanki, P.R. Reduced Graphene Oxide-Gadolinium Oxide-Functionalized Paper Based Immunosensor for Electrochemical Detection of Gentamicin. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2024, 17, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, S.; Wong, A.; Khan, S.; Hussain, S.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. Using Magnetic Nanoparticles/MIP-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Quantification of Tetracycline in Milk Samples. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 900, 115713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asran, A.M.; Mohamed, M.A.; Abd El-Rahman, M.K.; Mousavi, M.P.S. Green Ecofriendly Electrochemical Sensing Platform for the Sensitive Determination of Doxycycline. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.; Shu, H.; Tian, X.; Ren, J.; Cui, X.; Bai, H.; Xiao, X.C.; Wang, Y.D. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Poly-Arginine for Highly Sensitive and Selective Erythromycin Determination. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Asrami, P.N.; Altuner, E.E.; Gulbagca, F.; Tiri, R.N.E.; Aygun, A.; Kaynak, İ.; Sen, F.; Cheraghi, S. An Ultra-Sensitive Rifampicin Electrochemical Sensor Based on Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Anchored Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarkaeva, Y.A.; Nazyrov, M.I.; Dymova, D.A.; Maistrenko, V.N. A Voltammetric Sensor Based on a Chitosan, Graphitized Carbon Black, and Molecularly Imprinted Polyarylene Phthalide Composite for Clarithromycin Detection. J. Anal. Chem. 2024, 79, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, P.; Pacheco, J.G.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S.; Melo, A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Azithromycin Electrochemical Detection Using a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Prepared on a Disposable Screen-Printed Electrode. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xing, Y.; Lv, C.; Luo, L.; Chen, F. Boronate Affinity Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on Electrospun Carbon Nanofibres for Selective Kanamycin Detection. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 111743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewnu, K.; Promsuwan, K.; Kanatharana, P.; Thavarungkul, P.; Limbut, W. A Simple and Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor for Chloramphenicol Detection in Pharmaceutical Samples. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 087506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Abdiryim, T.; Jamal, R.; Liu, X.; Xue, C.; Xie, S.; Tang, X.; Wei, J. A Novel Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor from Poly (3, 4-Ethylenedioxythiophene)/Chitosan for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Levofloxacin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, K.; Ghorbani, M. Fabrication of a New Ultrasensitive AuNPs-MIC-Based Sensor for Electrochemical Determination of Streptomycin. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 299, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Lin, J.; Lin, J.; Zhu, F.; Lai, G.; Li, Y. Ultrasensitive Determination of Metronidazole Using Flower-like Cobalt Anchored on Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Electrochemical Sensor. Microchem. J. 2023, 188, 108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feier, B.; Blidar, A.; Pusta, A.; Carciuc, P.; Cristea, C. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for the Detection of Cefalexin. Biosensors 2019, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smajdor, J.; Paczosa-Bator, B.; Piech, R. Electrochemical Sensor Based on the Hierarchical Carbon Nanocomposite for Highly Sensitive Ciprofloxacin Determination. Membranes 2023, 13, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, R.; Deep, A.; Mizaikoff, B.; Singh, S. Copper Based Organic Framework Modified Electrosensor for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Ciprofloxacin. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.A.S.; Singh, S.; Nate, Z.; Pawar, C.; Chauhan, R.; Thapliyal, N.B.; Karpoormath, R.; Patel, R. One-Pot Synthesis of β-Cyclodextrin Modified Silver Nanoparticles for Highly Sensitive Detection of Ciprofloxacin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 203, 114219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, J.M.P.J.; Melle-Franco, M.; Strutyński, K.; Borges, F.; Brett, C.M.A.; Garrido, E.M.P.J. β–Cyclodextrin Carbon Nanotube-Enhanced Sensor for Ciprofloxacin Detection. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2017, 52, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayen, P.; Chaplin, B.P. Selective Electrochemical Detection of Ciprofloxacin with a Porous Nafion/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Composite Film Electrode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, L.; Pereira, J.; Azevedo, G.; Matos, M.; Munoz, R.; Matos, R. Square-Wave Voltammetry Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Pharmaceutical Formulations and Milk Using a Reduced Graphene Oxide Sensor. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, S.; Beitollahi, H.; Zaeimbashi, R.; Sheikhshoaei, M.; Askari, M.B.; Salarizadeh, P. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on V2O5 Nanoparticles for the Detection of Ciprofloxacin. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 17558–17567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.N.; de Oliveira Cândido, T.C.; Pereira, A.C. Simple and Disposable Device Based on Gold Nanoparticles Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Detection of Ciprofloxacin. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2025, 29, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burç, M.; Güngör, Ö.; Titretir Duran, S. High-Sensitivity Electrochemical Sensor Using No Nanomaterials for the Detection of Ciprofloxacin with Poly 2-(Hydroxymethyl)Thiophene-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 6283–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissawong, N.; Srijaranai, S.; Boonchiangma, S.; Uppachai, P.; Seehamart, K.; Jantrasee, S.; Moore, E.; Mukdasai, S. An Electrochemical Sensor for Voltammetric Detection of Ciprofloxacin Using a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Activated Carbon, Gold Nanoparticles and Supramolecular Solvent. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, S.B.; Veve, M.P.; Wagner, J.L. Cephalosporins: A Focus on Side Chains and β-Lactam Cross-Reactivity. Pharmacy 2019, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassa, A.; Amare, M.; Benor, A.; Tigineh, G.T.; Beyene, Y.; Tefera, M.; Abebe, A. Potentiodynamic Poly(Resorcinol)-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode as a Voltammetric Sensor for Determining Cephalexin and Cefadroxil Simultaneously in Pharmaceutical Formulation and Biological Fluid Samples. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 34599–34607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feier, B.; Gui, A.; Cristea, C.; Săndulescu, R. Electrochemical Determination of Cephalosporins Using a Bare Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 976, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Xu, H. Recent Progress and Novel Perspectives of Electrochemical Sensor for Cephalosporins Detection. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 8639–8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Allafchian, A.R.; Rezaei, B. A Sensitive and Selective Voltammetric Sensor Based on Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Decorated with MgCr2O4 for the Determination of Azithromycin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Lu, L.; Wen, Y.; Xu, J.; Duan, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.; Nie, T. Facile Synthesis of the Necklace-like Graphene Oxide-Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Nanohybrid and Its Application in Electrochemical Sensing of Azithromycin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 787, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, S.; Dehghani, M.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Azimzadeh, M. An Azithromycin Electrochemical Sensor Based on an Aniline MIP Film Electropolymerized on a Gold Nano Urchins/Graphene Oxide Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 829, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopaj, F.; Loshaj, F.; Contini, A.; Mehmeti, E.; Veseli, A. Preparation of an Efficient and Selective Voltammetric Sensor Based on Screen Printed Carbon Ink Electrode Modified with TiO2 Nanoparticles for Azithromycin Quantification. Results Chem. 2023, 6, 101123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidary, M.; Ebrahimi Samangani, A.; Kargari, A.; Kiani Nejad, A.; Yashmi, I.; Motahar, M.; Taki, E.; Khoshnood, S. Mechanism of Action, Resistance, Synergism, and Clinical Implications of Azithromycin. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogăcean, F.; Varodi, C.; Măgeruşan, L.; Stefan-van Staden, R.-I.; Pruneanu, S. Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Azithromycin with Graphene-Modified Electrode. Sensors 2022, 22, 6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiwanti, P.K.; Insani, S.A.; Sari, A.P.; Wafiroh, S. A New Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Azithromycin Using Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode Modified with Boron-Doped Diamond Nanoparticles and Reduced-Graphene Oxide. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202400520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, E.M.; Cestarolli, D.T. Azithromycin Electrochemical Detection Using a VO2 Thin Film. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 885, 160997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamdouh, S.; Shehata, M.; Fekry, A.M.; Ameer, M.A. Graphite-Based Sensor Amended with Fumed Silica for Electrodetection of Azithromycin. Can. J. Chem. 2022, 100, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamdouh, S.; Shehata, M.; Fekry, A.M.; Ameer, M.A. Electro-Polymerization of Modified Carbon Paste Sensor for Detecting Azithromycin. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.Y.; Hou, C.T.; Liu, X.X.; Li, H.B.; Hu, X.Y. Electrochemical Behavior of Azithromycin at Graphene and Ionic Liquid Composite Film Modified Electrode. Talanta 2011, 86, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoian, I.-A.; Iacob, B.-C.; Dudaș, C.-L.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Bogdan, D.; Marian, I.O.; Bodoki, E.; Oprean, R. Biomimetic Electrochemical Sensor for the Highly Selective Detection of Azithromycin in Biological Samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 155, 112098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafazadeh, R.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ghaffarinejad, A.; Tajabadi, F.; Hamidian, Y. Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor Based on Carbon Paste Electrode Modified with Graphene Nanoribbon–CoFe2O4@NiO and Ionic Liquid for Azithromycin Antibiotic Monitoring in Biological and Pharmaceutical Samples. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 5829–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyitanga, T.; Khan, M.Q.; Ahmad, K.; Khan, R.A. Fabrication of an Azithromycin Sensor. Biosensors 2023, 13, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Tao, Y.; Jin, H.; Song, B.; Jing, T.; Luo, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lee, Y.-I.; Mei, S. Fabrication of a Selective and Sensitive Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer/Acetylene Black for the Determination of Azithromycin in Pharmaceuticals and Biological Samples. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
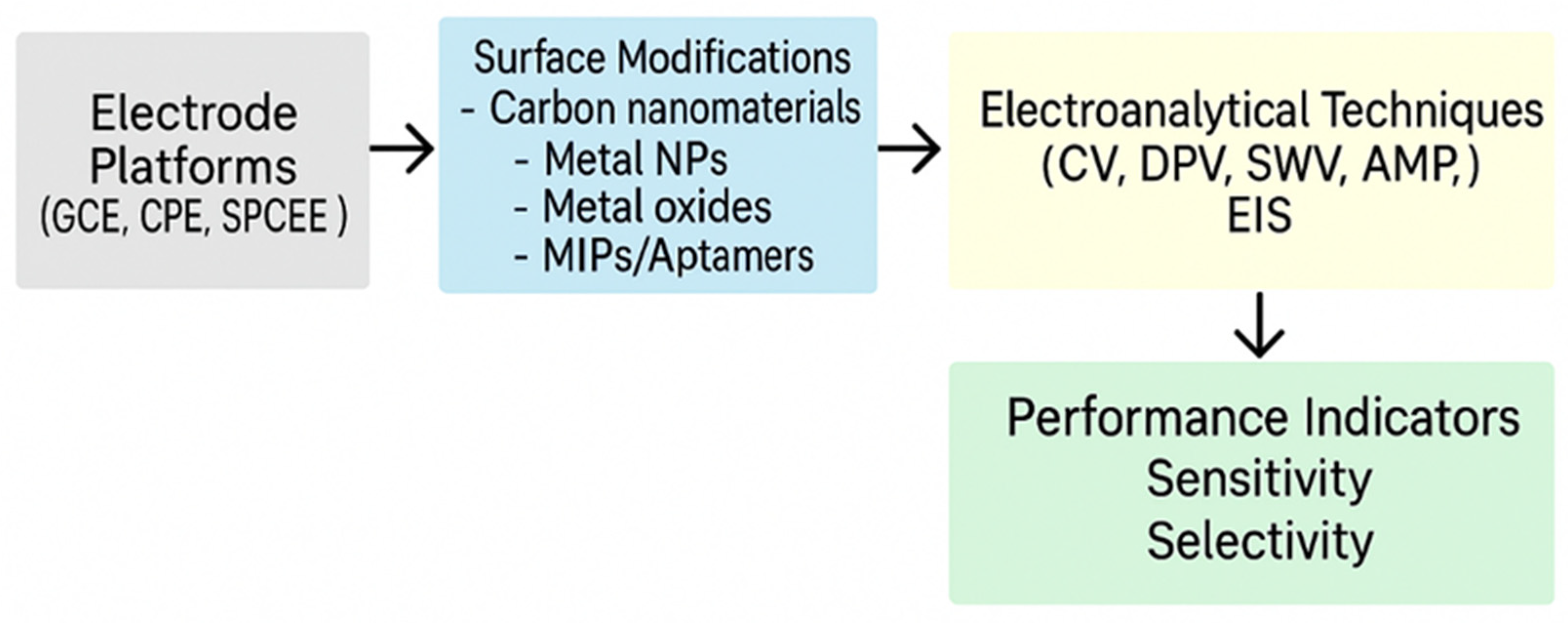
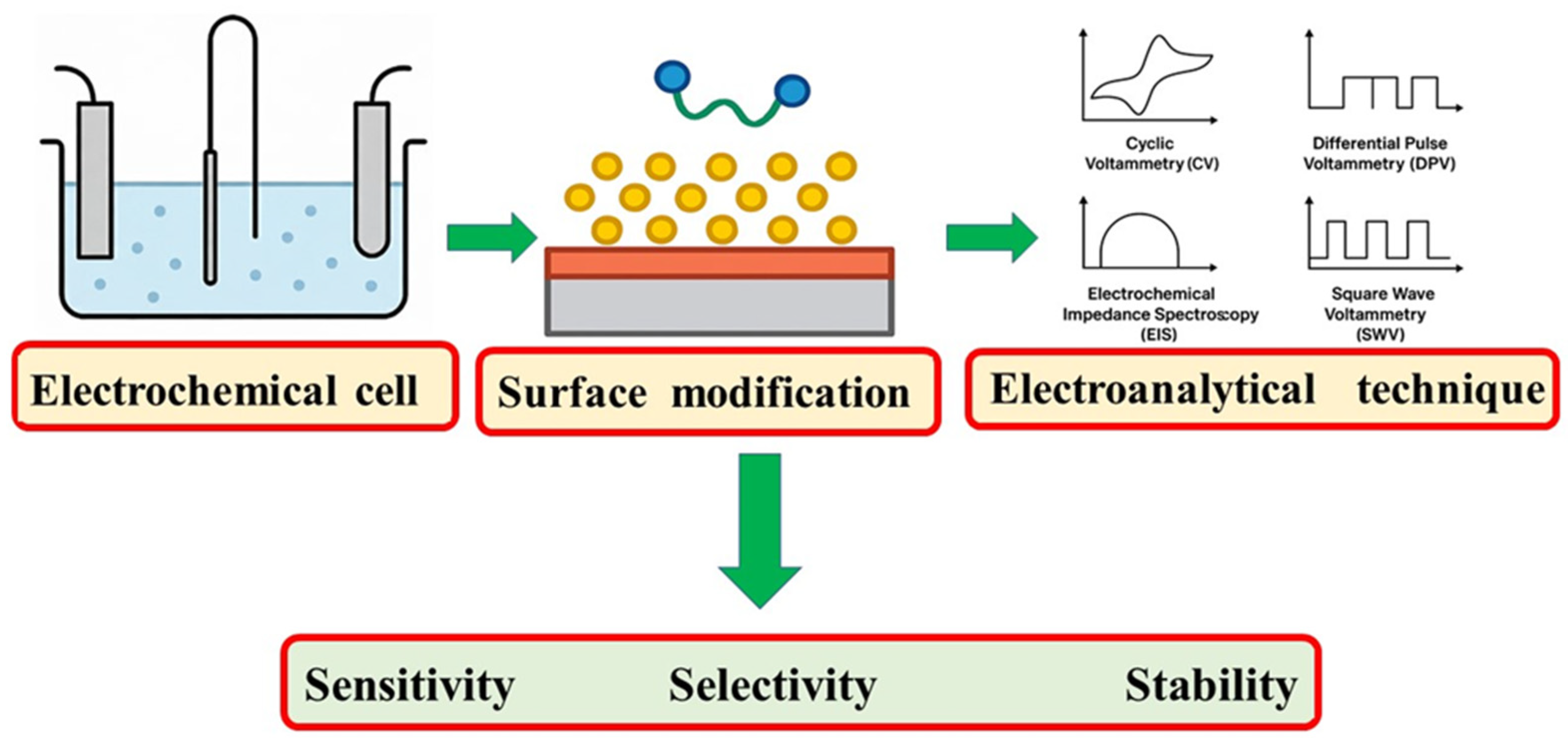
| Technique | Electrode Configuration | Cell Setup | Analyte Type | Advantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) | GCE, CPE, BDDE, SPCE | 3-electrode system | NSAIDs, antibiotics | Redox mechanism insights, surface studies | [12,13] |
| Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) | GCE, SPCE, MIP-modified electrodes | 3-electrode system | Ibuprofen, aspirin, diclofenac | High sensitivity, low background current | [14,15,16] |
| Square Wave Voltammetry (SWV) | GCE, CNT-modified, QD based | 3-electrode system | Naproxen, azithromycin | Fast scanning, excellent sensitivity | [17,18] |
| Amperometry (CA/MPA) | Modified SPEs, enzyme based | 2- or 3-electrode system | Real-time detection of NSAIDs | Real-time monitoring, simple instrumentation | [19,20] |
| Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) | Au, MIP-functionalized, SPCE | 3-electrode system | Label-free antibiotic sensors | Interface characterization, high specificity | [21,22] |
| Recognition Element | Advantages | Limitations | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aptamers | High specificity and affinity; easily synthesized and modified; good stability and reusability | Costly selection process; sometimes reduced performance in complex matrices | Detection of drugs in serum, plasma, and other biological fluids [32,33]. |
| Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) | Robust, low-cost, chemically stable; resistant to harsh conditions; easy to prepare | Template removal may be incomplete; nonspecific binding possible | Environmental monitoring (wastewater, surface water), pharmaceutical formulations [34,35]. |
| Enzymes | High specificity; catalytic signal amplification; well established in biosensors | Limited stability; sensitive to pH and temperature; short shelf life | Biosensing of drugs and metabolites, therapeutic monitoring [36,37]. |
| Antibodies | Strong antigen–antibody selectivity; clinically validated | Expensive; sensitive to storage conditions; limited reusability | Immunosensors for pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, and food safety [2,38]. |
| Nanomaterials (pseudo-recognition) | Large surface area; enhance adsorption and electron transfer; tunable catalytic activity | Lack intrinsic molecular specificity; potential reproducibility issues | General sensing, particularly for nonbiological matrices and trace-level detection [39,40]. |
| Drug | Electrode Material | Technique | LOD (mM) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | GCE/aptamer to gold-nanoparticles | DPV | 0.0000005 | [48] |
| Aspirin | GCE/GO | SWV | 0.021 | [56] |
| Naproxen | ZnO–MWCNT | SWV | 0.010 | [57] |
| Diclofenac | GCE/Pt nanoflowers + rGO | DPV, CV | 0.003 | [15] |
| Ketoprofen | GCE/MIP-ZrMOFs/RGO | DPV | 0.00022 | [58] |
| Indomethacin | CPE/Gold NPs | SWV | 0.00068 | [59] |
| Piroxicam | Fe3O4-GO-PCA | DPV | 0.056 | [60] |
| Meloxicam | GR/GCE | SWV | 0.066 | [61] |
| Celecoxib | CPE/Ag-NPs-Ch-GO | CV | 0.00251 | [62] |
| Etodolac | Poly vinyl chloride | DPV | 4.66 | [19] |
| Electrode/Modification | Technique(s) | Linear Range | LOD | Matrix/Application | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWCNTs nanocomposite decorated with MgCr2O4 spinel | DPV | 0.25–4.0 and 4.0–10.0 μm | 0.07 µM | Pharmaceutical, plasma, urine | Hydrophobic and electrostatic interaction enhanced adsorption | [134] |
| Aniline-MIP/GCE | Not specified | 0.3–920.0 nM | 0.1 nM | Pharmaceutical | High electron transfer rate | [136] |
| EGr/GCE | Amperometry | 0.01–10 µM | 3.03 nM | Pharmaceutical drugs | High selectivity and reusability | [139] |
| Fumed silica/CPE | DPV | 44.0–1000.0 µM | 11 mM | Pharmaceutical, plasma, urine | Sensor showed high sensitivity and stability | [142] |
| Poly-threonine carbon paste electrode (PTCPE) | SWV | 8.88–1000.0 µM | 0.32 µM | Pharmaceutical formulations | High sensitivity and stability | [143] |
| Gr/IL/GCE | DPV | 0.65–38 µM | 0.25 µM | Pharmaceutical formulations | Enhanced electron transfer | [144] |
| Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) | CV, EIS | 13.33 nM–66.67 μM | 0.85 nM | Biological fluids | Rapid mass transfer and high surface area for binding | [145] |
| Graphene nanoribbon + ionic liquid/CPE | SWV | 10 µM–2 mM | 0.66 µM | Pharmaceutical and Biological Samples | Ionic liquid enhances conductivity | [146] |
| Molybdenum disulfide/titanium aluminum carbide/ GCE | LSV | 0.05–25 µM | 0.009 µM | Pharmaceutical and Biological Samples | 2D nanocomposite improves electron transfer and structural stability | [147] |
| MIP/acetylene black/CPE | DPV | 0.2–20 µM | 2.3 µM | Pharmaceutical and Biological Samples | Superior current response and high selectivity | [148] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mello, G.A.B.; Benjamin, S.R.; de Lima, F.; Dutra, R.F. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Anti-Inflammatory and Antibiotic Drugs: A Comprehensive Review. Biosensors 2025, 15, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100676
Mello GAB, Benjamin SR, de Lima F, Dutra RF. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Anti-Inflammatory and Antibiotic Drugs: A Comprehensive Review. Biosensors. 2025; 15(10):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100676
Chicago/Turabian StyleMello, Gisele Afonso Bento, Stephen Rathinaraj Benjamin, Fábio de Lima, and Rosa F. Dutra. 2025. "Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Anti-Inflammatory and Antibiotic Drugs: A Comprehensive Review" Biosensors 15, no. 10: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100676
APA StyleMello, G. A. B., Benjamin, S. R., de Lima, F., & Dutra, R. F. (2025). Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Anti-Inflammatory and Antibiotic Drugs: A Comprehensive Review. Biosensors, 15(10), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100676







