Duplex EIS Sensor for Salmonella Typhi and Aflatoxin B1 Detection in Soil Runoff
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Electrode Surface Modification and Testing Process
2.3. Sensor Design
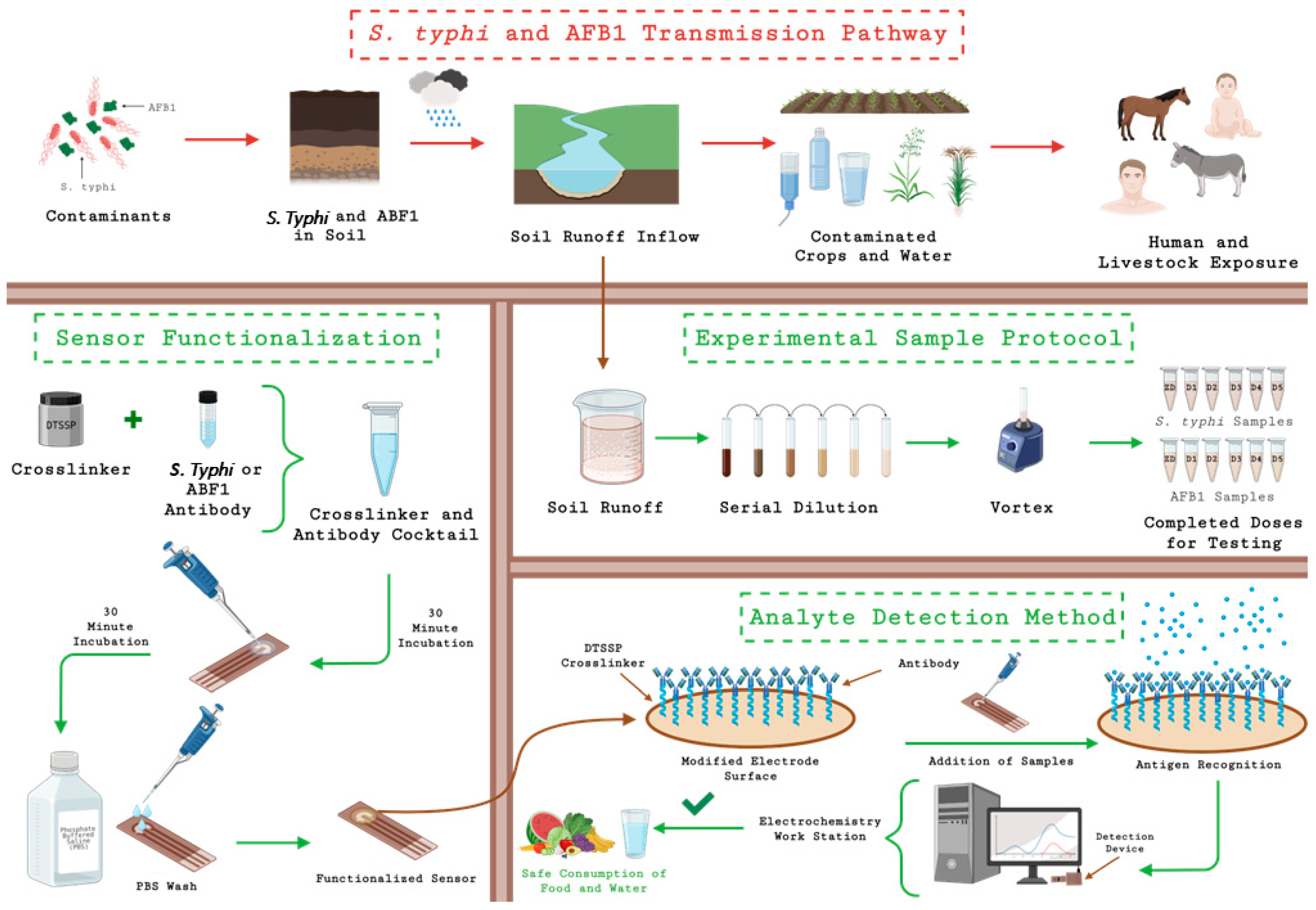
2.4. Sample Preparation and Duplex Sensor Design
3. Results and Discussion
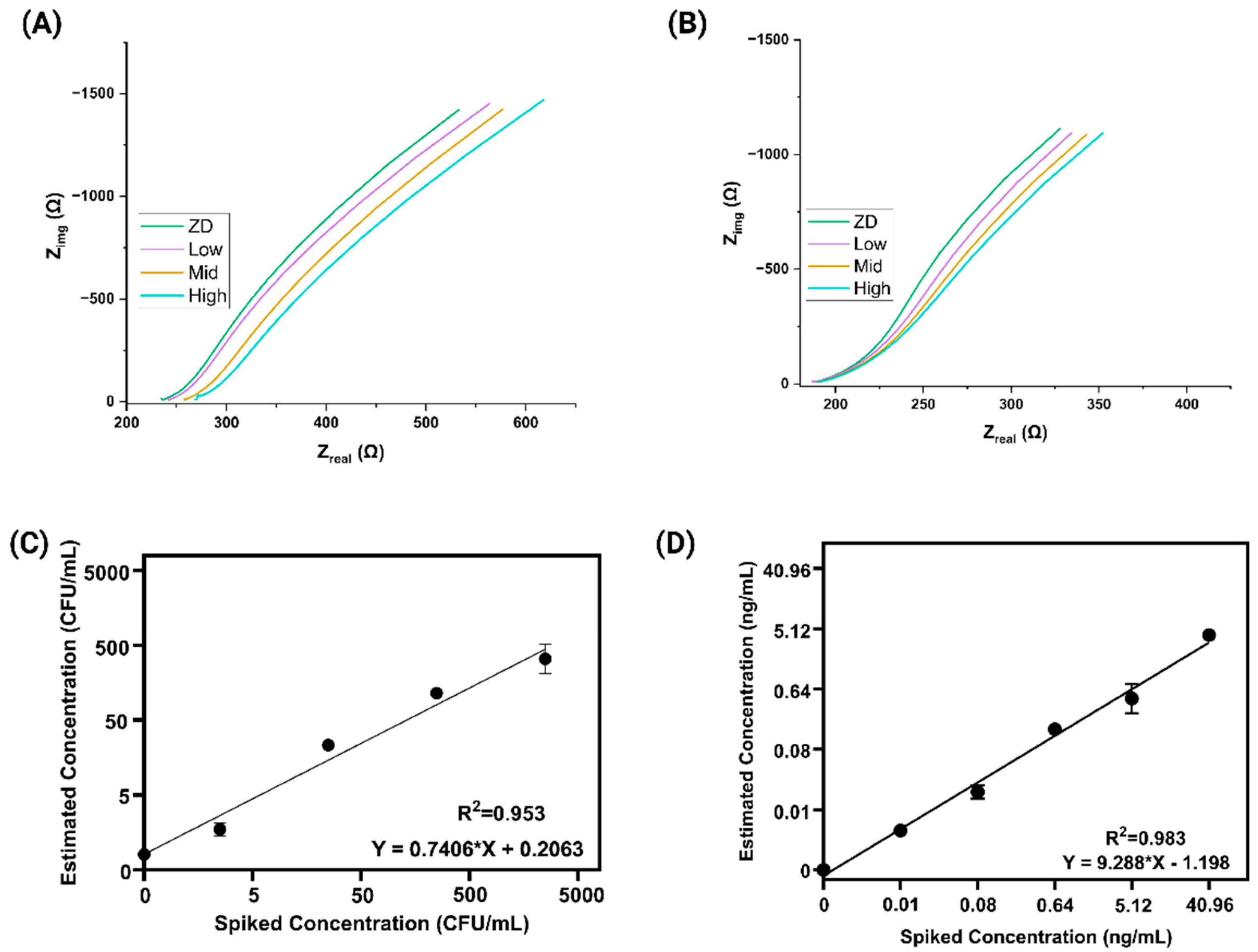
3.1. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) Analysis and Spike and Recovery Assessment
3.2. Correlation Study Between the Benchtop and Portable Device
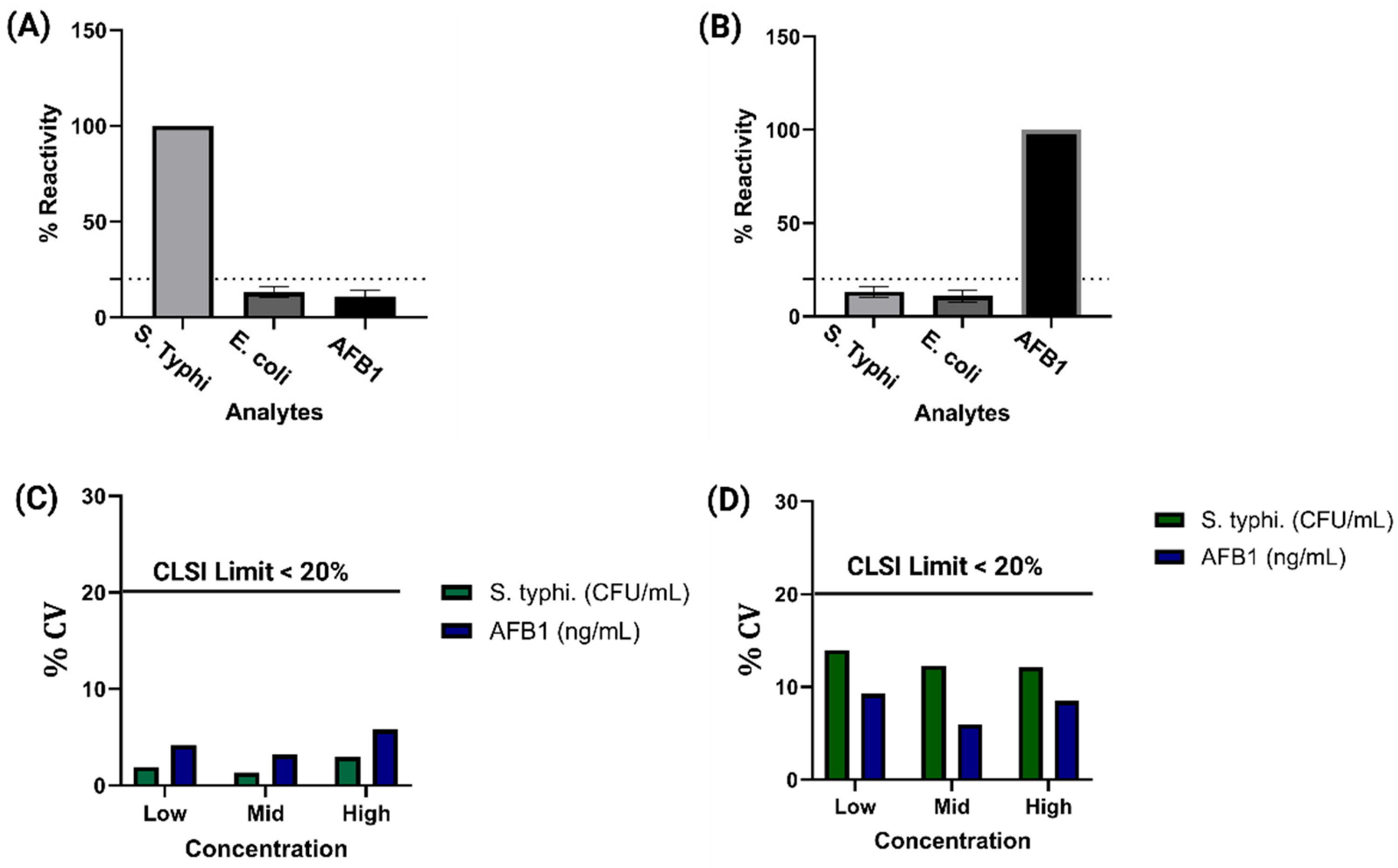
3.3. Cross Reactivity Repeatability and Reproducibility
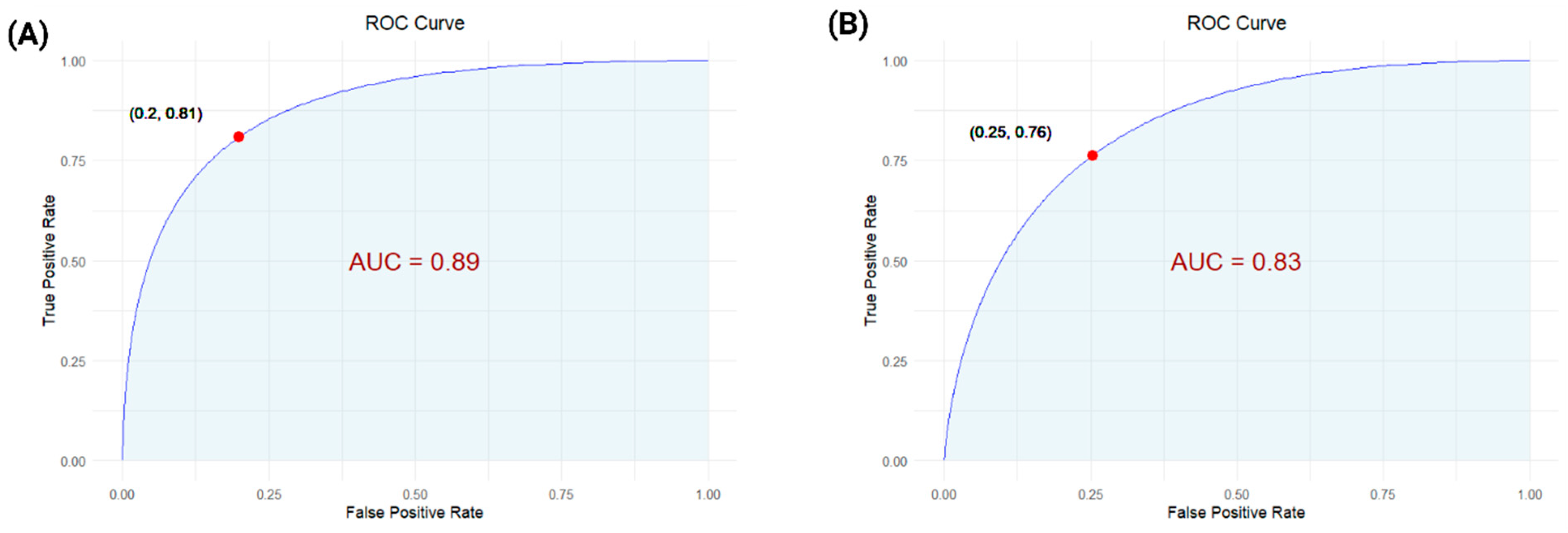
3.4. Classifier Model Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galán, J.E. Salmonella Typhimurium and inflammation: A pathogen-centric affair. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, K.E.; Roth, J.R. Linkage Map of Salmonella Typhimurium, Edition VII. Microbiol. Rev. 1988, 52, 485–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushing, B.R.; Selim, M.I. Aflatoxin B1: A review on metabolism, toxicity, occurrence in food, occupational exposure, and detoxification methods. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guengerich, F.; Johnson, W.W.; Shimada, T.; Ueng, Y.-F.; Yamazaki, H.; Langouët, S. Activation and detoxication of aflatoxin B1. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1998, 402, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, S.; Kim, J.E.; Coulombe, R. Aflatoxin B1 in poultry: Toxicology, metabolism and prevention. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 89, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciobanu, D.; Hosu-Stancioiu, O.; Melinte, G.; Ognean, F.; Simon, I.; Cristea, C. Recent Progress of Electrochemical Aptasensors toward AFB1 Detection (2018–2023). Biosensors 2024, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-M.; Chen, S.-C. A probabilistic modeling approach to assess human inhalation exposure risks to airborne aflatoxin B1 (AFB1). Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6481–6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.R.; Yu, A.T.; Saha, S.; Shakya, J.; Aiemjoy, K.; Horng, L.; Qamar, F.; Garrett, D.; Baker, S.; Saha, S.; et al. Environmental Surveillance as a Tool for Identifying High-risk Settings for Typhoid Transmission. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, S71–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsley, R.A.; Bäumler, A.J. Host adaptation and the emergence of infectious disease: The Salmonella paradigm. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coburn, B.; A Grassl, G.; Finlay, B.B. Salmonella, the host and disease: A brief review. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2006, 85, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, J.A.; Heyderman, R.S. A Perspective on Invasive Salmonella Disease in Africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, S235–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsougeni, K.; Papadakis, G.; Gianneli, M.; Grammoustianou, A.; Constantoudis, V.; Dupuy, B.; Petrou, P.S.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Tserepi, A.; Gizeli, E.; et al. Plasma nanotextured polymeric lab-on-a-chip for highly efficient bacteria capture and lysis. Lab Chip 2015, 16, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awang, M.S.; Bustami, Y.; Hamzah, H.H.; Zambry, N.S.; Najib, M.A.; Khalid, M.F.; Aziah, I.; Manaf, A.A. Advancement in Salmonella Detection Methods: From Conventional to Electrochemical-Based Sensing Detection. Biosensors 2021, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, K.G.; Falkenhorst, G.; Ceper, T.H.; Dalby, T.; Ethelberg, S.; Mølbak, K.; Krogfelt, K.A. Detecting Non-Typhoid Sal-monella in Humans by ELISAs: A Literature Review. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, B.; von Müffling, T.; Chaunchom, S.; Hartung, J. Salmonella contamination in pigs at slaughter and on the farm: A field study using an antibody ELISA test and a PCR technique. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 115, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, A.; Mancini, M.; Gioia, V.; Cinti, S. Office Paper-Based Electrochemical Strips for Organophosphorus Pesticide Monitoring in Agricultural Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8859–8865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, X.; Gai, P.; Liu, X.; Li, F. Degradable metal-organic framework/methylene blue composites-based homogeneous electrochemical strategy for pesticide assay. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 323, 128701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, F. Portable electrochemical biosensor based on laser-induced graphene and MnO2 switch-bridged DNA signal amplification for sensitive detection of pesticide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 199, 113906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Yu, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lu, C.; Jiang, X. Application Status and Prospect of Impedance Spectroscopy in Agricultural Product Quality Detection. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Wu, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, C.; Jia, N. Highly sensitive electrochemical impedance spectroscopy immunosensor for the detection of AFB1 in olive oil. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, M.; Riccò, B. Electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for biological analysis and food characterization: A review. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2017, 6, 303–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.K.; Dhamu, V.N.; Kokala, A.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Advancing food Safety: Two-plex electrochemical biosensor for mycotoxin detection in food matrices. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2025, 25, 100626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huo, X.; Qi, W.; Xia, Z.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella Typhimurium using nickel nanowire bridge for electrochemical impedance amplification. Talanta 2020, 211, 120715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, V.; La Belle, J.T.; Reed, J.; Shah, M.; Cochran, D.; Joshi, L.; Alford, T. A methodology for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium using label-free electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, K.K.; Dhamu, V.N.; Jophy, C.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Electroanalytical Platform for Rapid E. coli O157:H7 Detection in Water Samples. Biosensors 2024, 14, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.K.; Dhamu, V.N.; Poudyal, D.C.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. PathoSense: A rapid electroanalytical device platform for screening Salmonella in water samples. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ruan, C.; Li, Y. Detection of viable Salmonella typhimurium by impedance measurement of electrode capacitance and medium resistance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 19, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Tellez, J.; Sanchez-Ortega, I.; Hornung-Leoni, C.T.; Santos, E.M.; Miranda, J.M.; Rodriguez, J.A. Impedimetric Biosensor Based on a Hechtia argentea Lectin for the Detection of Salmonella spp. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambry, N.S.; Awang, M.S.; Hamzah, H.H.; Mohamad, A.N.; Khalid, M.F.; Khim, B.K.; Bustami, Y.; Jamaluddin, N.F.; Ibrahim, F.; Aziah, I.; et al. A portable label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella Typhi. Anal. Methods 2024, 16, 5254–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvano, F.; Pilloton, R.; Albanese, D. A novel impedimetric biosensor based on the antimicrobial activity of the peptide nisin for the detection of Salmonella spp. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Chee, G.; Yamada, K.; Jun, S. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopic technique with a functionalized microwire sensor for rapid detection of foodbornepathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owino, J.H.O.; Ignaszak, A.; Al-Ahmed, A.; Baker, P.G.L.; Alemu, H.; Ngila, J.C.; Iwuoha, E.I. Modelling of the impedimetric responses of an aflatoxin B1 immunosensor prepared on an electrosynthetic polyaniline platform. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, J.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. A label-free electrochemical impedance immunosensor for the sensitive detection of aflatoxin B1. Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 2354–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Shen, Y. Fabricating electrochemical aptasensors for detecting aflatoxin B1 via layer-by-layer self-assembly. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 870, 114247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaerd, A.; Banks, C.E.; Bergamini, M.F.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H. Nanomodified Screen-Printed Electrode for direct determination of Aflatoxin B1 in malted barley samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 307, 127547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiro, J.C.K.; Mishra, K.K.; Dhamu, V.N.; Bhatia, A.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Development of a porElectrochemi electrochemical sensing platform for impedance spectroscopy-based biosensing using an ARM-based microcontroller. Sens. Diagn. 2024, 3, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanak, A.S.; Jagannath, B.; Tamrakar, Y.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Non-faradaic electrochemical impedimetric profiling of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as a dual marker biosensor for early sepsis detection. Anal. Chim. Acta: X 2019, 3, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, J.S.; Pourmand, N. Label-Free Impedance Biosensors: Opportunities and Challenges. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 1239–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminiaris, M.D.; Mavrikou, S.; Georgiadou, M.; Paivana, G.; Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Kintzios, S. An Impedance Based Electrochemical Immunosensor For Aflatoxin B1 Monitoring in Pistachio Matrices. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Petrou, P.; Misiakos, K.; Raptis, I.; Kakabakos, S. Simultaneous Detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Drinking Water and Milk with Mach–Zehnder Interferometers Monolithically Integrated on Silicon Chips. Biosensors 2022, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curulli, A. Electrochemical Biosensors in Food Safety: Challenges and Perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.; Neves, M.M.P.S.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Electrochemical Immunosensor for the Simultaneous Determination of Two Main Peanut Allergenic Proteins (Ara h 1 and Ara h 6) in Food Matrices. Foods 2021, 10, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Braiek, M.; Florea, A.; Chrouda, A.; Farre, C.; Bonhomme, A.; Bessueille, F.; Vocanson, F.; Zhang, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Aflatoxin B1 Detection Using a Highly-Sensitive Molecularly-Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on an Electropolymerized Metal Organic Framework. Toxins 2015, 7, 3540–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Evaluation of Precision of Quantitative Measurement Procedures; Approved Guideline. CLSI Document EP05-A3; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Wayne (PA). Available online: https://webstore.ansi.org/preview-pages/CLSI/preview_CLSI+EP05-A3.pdf?srsltid=AfmBOormwSYKgjARaNMMeixA3GWxnTnjfL3VgFIl7W9UKVf4yls_LBcP (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Mishra, K.K.; Dhamu, V.N.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Quick and Sensitive Two-Plex Electrochemical Platform for Pathogen Detection in Water. Nano Sel. 2025, e70017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkowski, C.M. Sensitivity, specificity, receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves and likelihood ratios: Communicating the performance of diagnostic tests. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2008, 29, S83–S87. [Google Scholar]
- Tieu, M.-V.; Choi, S.H.; Le, H.T.N.; Cho, S. Electrochemical impedance-based biosensor for label-free determination of plasma P-tau181 levels for clinically accurate diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1273, 341535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, T. An Introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.K.; Thakkar, K.M.; Dhamu, V.N.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Electrochemical Sensor Platform for Rapid Detection of Foodborne Toxins. Biosensors 2025, 15, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohlman, E. Mycotoxin Hazards and Regulations; U.S Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Paniel, N.; Radoi, A.; Marty, J.-L. Development of an Electrochemical Biosensor for the Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Sensors 2010, 10, 9439–9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, W.-B.; Kim, M.J.; Mun, H.; Kim, M.-G. An Aptamer-Based Dipstick Assay for the Rapid and Simple Detection of Aflatoxin B1. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeyeva, T.; Yarynka, D.; Piletska, E.; Linnik, R.; Zaporozhets, O.; Brovko, O.; Piletsky, S.; El’skaya, A. Development of a Smartphone-Based Biomimetic Sensor for Aflatoxin B1 Detection Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Membranes. Talanta 2019, 201, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, L.; Zhao, Q. Aptamer Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor for Aflatoxin B1. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, C.-R.; Wang, W.-C.; Xue, J.; Huang, Y.-L.; Yang, X.-X.; Tan, B.; Zhou, X.-P.; Shao, C.; Ding, S.-J.; et al. A Novel Electrochemical Immunosensor for Highly Sensitive Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Corn Using Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes/Chitosan. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Ma, L.; Guo, T.; Zhou, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, H.; Yu, Y. A Novel Fluorescence Aptasensor Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Aflatoxin B1. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1068, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Rapid Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium in Foods Using an Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on Screen-Printed Interdigitated Microelectrode and Immunomagnetic Separation. Talanta 2016, 148, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, D.; Chen, F.C.; Bridgman, R.C. Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in Romaine Lettuce Using a Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor. Biosensors 2019, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokken, G.C.A.M.; Corbee, R.J.; Van Knapen, F.; Bergwerff, A.A. Immunochemical Detection of Salmonella Group B, D and E Using an Optical Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 222, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Yi, S.Y.; Woubit, A.; Kim, M. A Portable Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium. Appl. Sci. Converg. Technol. 2016, 25, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; An, H.; Duan, Y. ω-Shaped Fiber-Optic Probe-Based Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Real-Time Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13640–13646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, K.H.; Brackett, R.E.; Hartman, N.F.; Campbell, D.P. Development of a Rapid Response Biosensor for Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.D.; RoyChaudhuri, C.; Maji, S.; Das, S.; Saha, H. Macroporous Silicon Based Simple and Efficient Trapping Platform for Electrical Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium Pathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3215–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farka, Z.; Juřík, T.; Pastucha, M.; Kovář, D.; Lacina, K.; Skládal, P. Rapid Immunosensing of Salmonella Typhimurium Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy: The Effect of Sample Treatment. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; Pandey, A.; Tiwari, U.K.; Sinha, R.K. A Label-Free Fiber Optic Biosensor for Salmonella Typhimurium Detection. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2018, 46, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Bie, S.; Suo, T.; Jia, G.; Liu, B.; Ye, R.; Li, Z. Development of an Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid and Effective Detection of Pathogenic Escherichia coli in Licorice Extract. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housaindokht, M.R.; Sheikhzadeh, E.; Pordeli, P.; Rouhbakhsh Zaeri, Z.; Janati-Fard, F.; Nosrati, M. Mashreghi, M.; Nakhaeipour, A.; A. Esmaeili, A.; Solimani, S. A Sensitive Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Single Wall Carbon Nanotube Modified Screen Printed Electrode for Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2018, 9, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Cui, M.; Huang, J. Electrochemical Immunosensor Assay (EIA) for Sensitive Detection of E. coli O157:H7 with Signal Amplification on a SG-PEDOT-AuNPs Electrode Interface. Analyst 2015, 140, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mishra, K.K.; Thakkar, K.M.; Karmakar, S.; Dhamu, V.N.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Duplex EIS Sensor for Salmonella Typhi and Aflatoxin B1 Detection in Soil Runoff. Biosensors 2025, 15, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100654
Mishra KK, Thakkar KM, Karmakar S, Dhamu VN, Muthukumar S, Prasad S. Duplex EIS Sensor for Salmonella Typhi and Aflatoxin B1 Detection in Soil Runoff. Biosensors. 2025; 15(10):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100654
Chicago/Turabian StyleMishra, Kundan Kumar, Krupa M Thakkar, Sumana Karmakar, Vikram Narayanan Dhamu, Sriram Muthukumar, and Shalini Prasad. 2025. "Duplex EIS Sensor for Salmonella Typhi and Aflatoxin B1 Detection in Soil Runoff" Biosensors 15, no. 10: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100654
APA StyleMishra, K. K., Thakkar, K. M., Karmakar, S., Dhamu, V. N., Muthukumar, S., & Prasad, S. (2025). Duplex EIS Sensor for Salmonella Typhi and Aflatoxin B1 Detection in Soil Runoff. Biosensors, 15(10), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100654





