Single Nucleotide Recognition and Mutation Site Sequencing Based on a Barcode Assay and Rolling Circle Amplification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentations and Materials
2.2. Optimizing Conditions for RCA Loop Formation and Amplification
2.3. Fabrication of the CdSe/PS Nanocomposite
2.4. Validation of the CdSe/PS Nanocomposite for Single Base Resolution Performance
2.5. Statistics Section
3. Results and Discussion
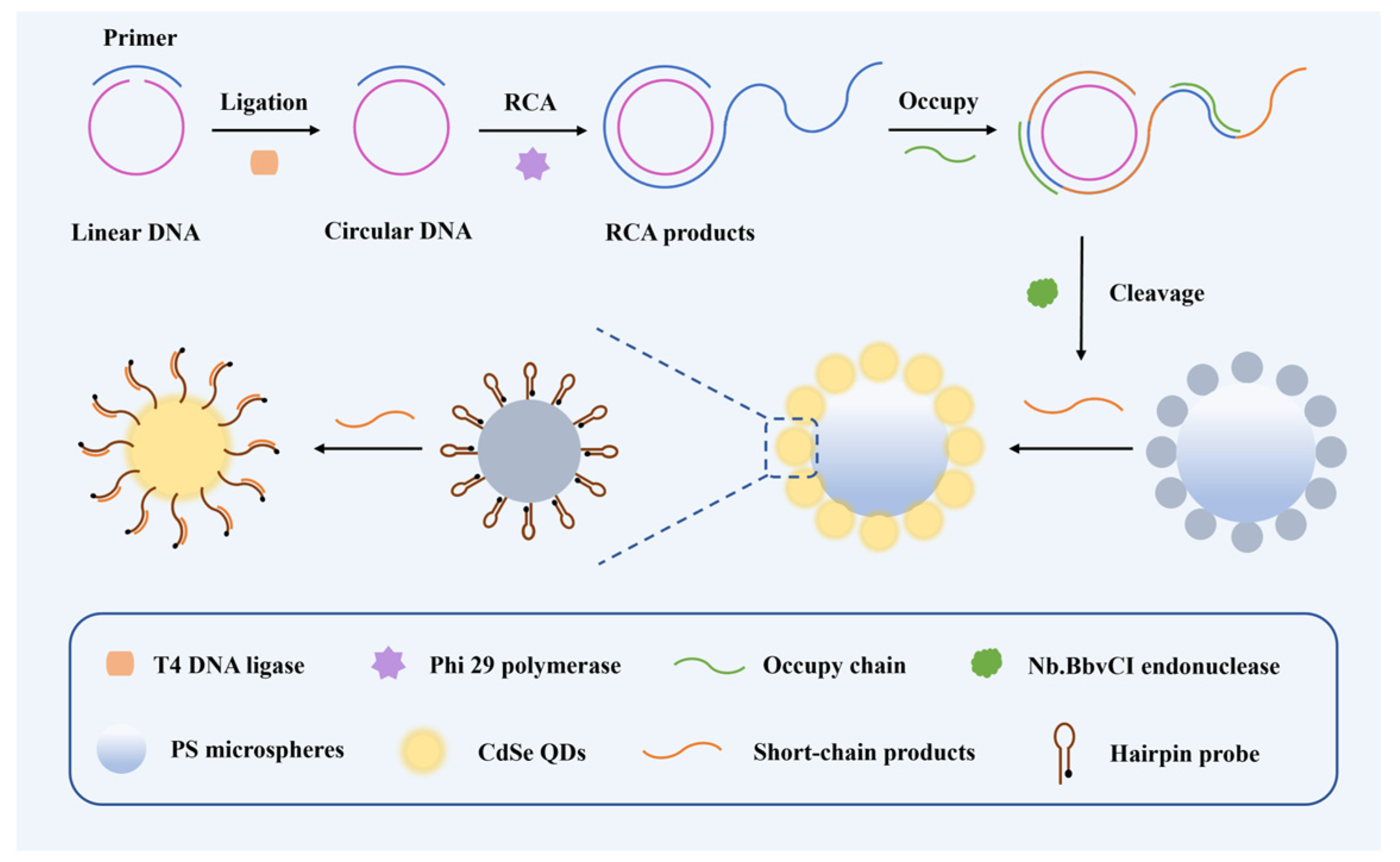
3.1. The Principle of the Barcode-Based Single Base Mutation Sequencing
3.2. Single Nucleotide Recognition and RCA Amplification of Target Nucleic Acids
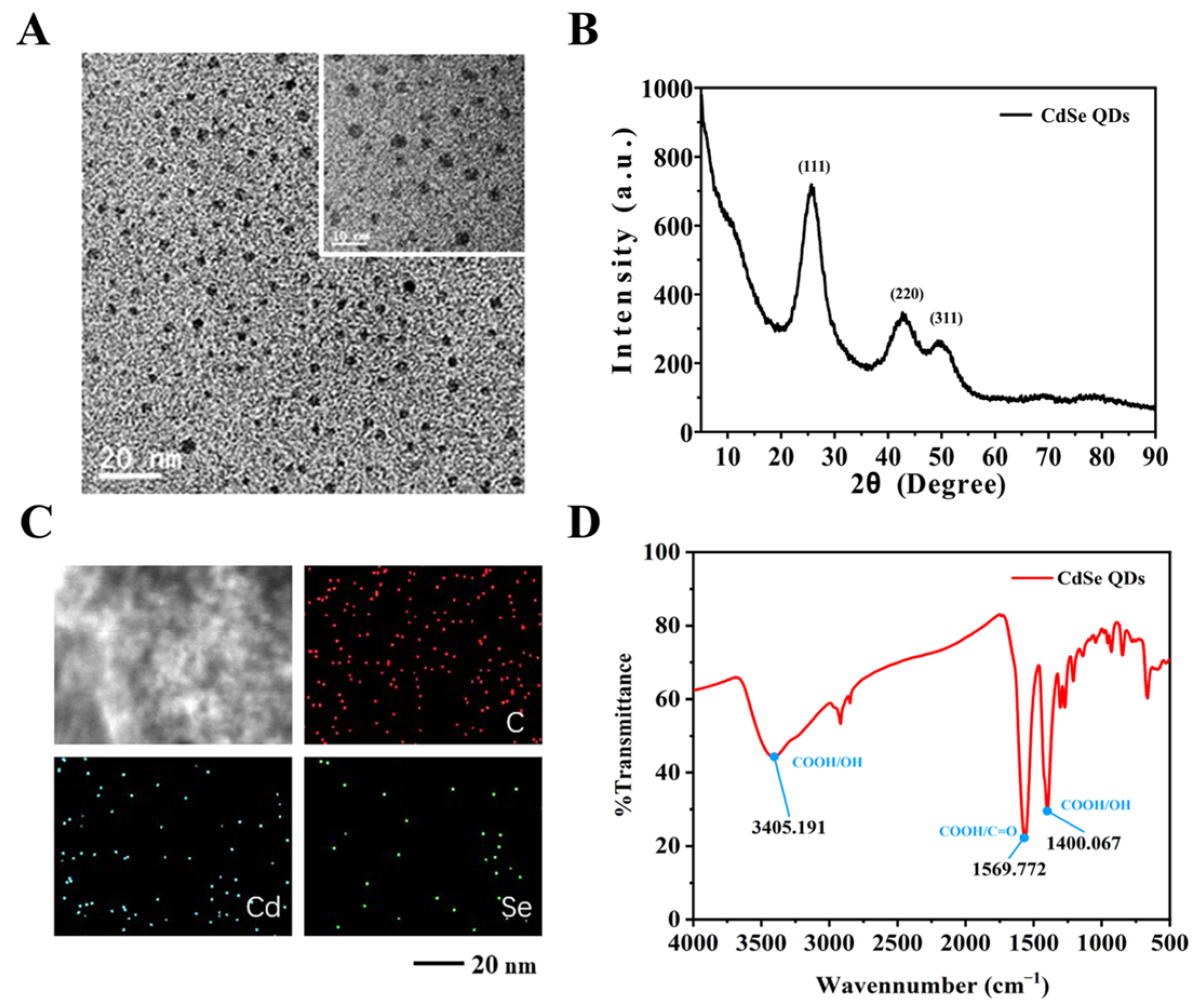
3.3. Construction of the CdSe/PS Nanocomposite and Fluorescence Signal Readout System
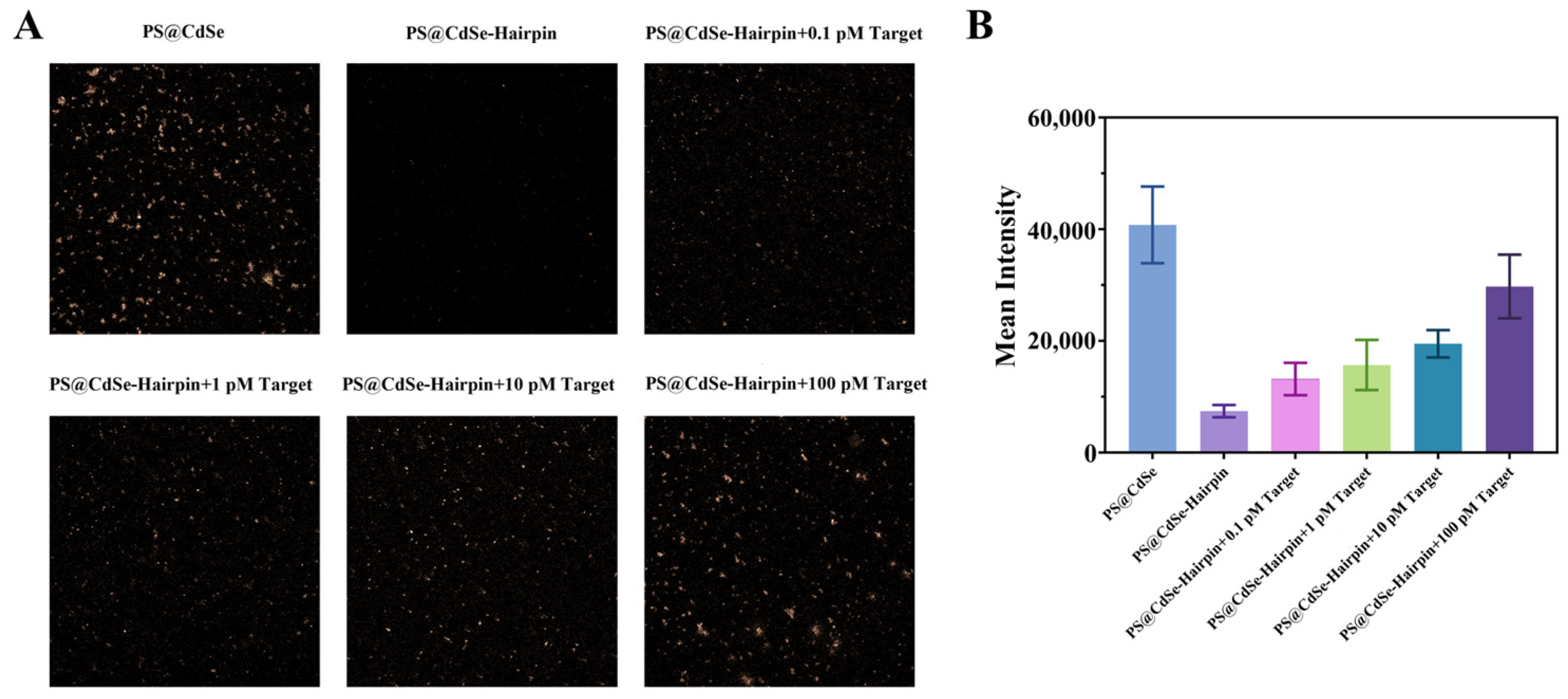
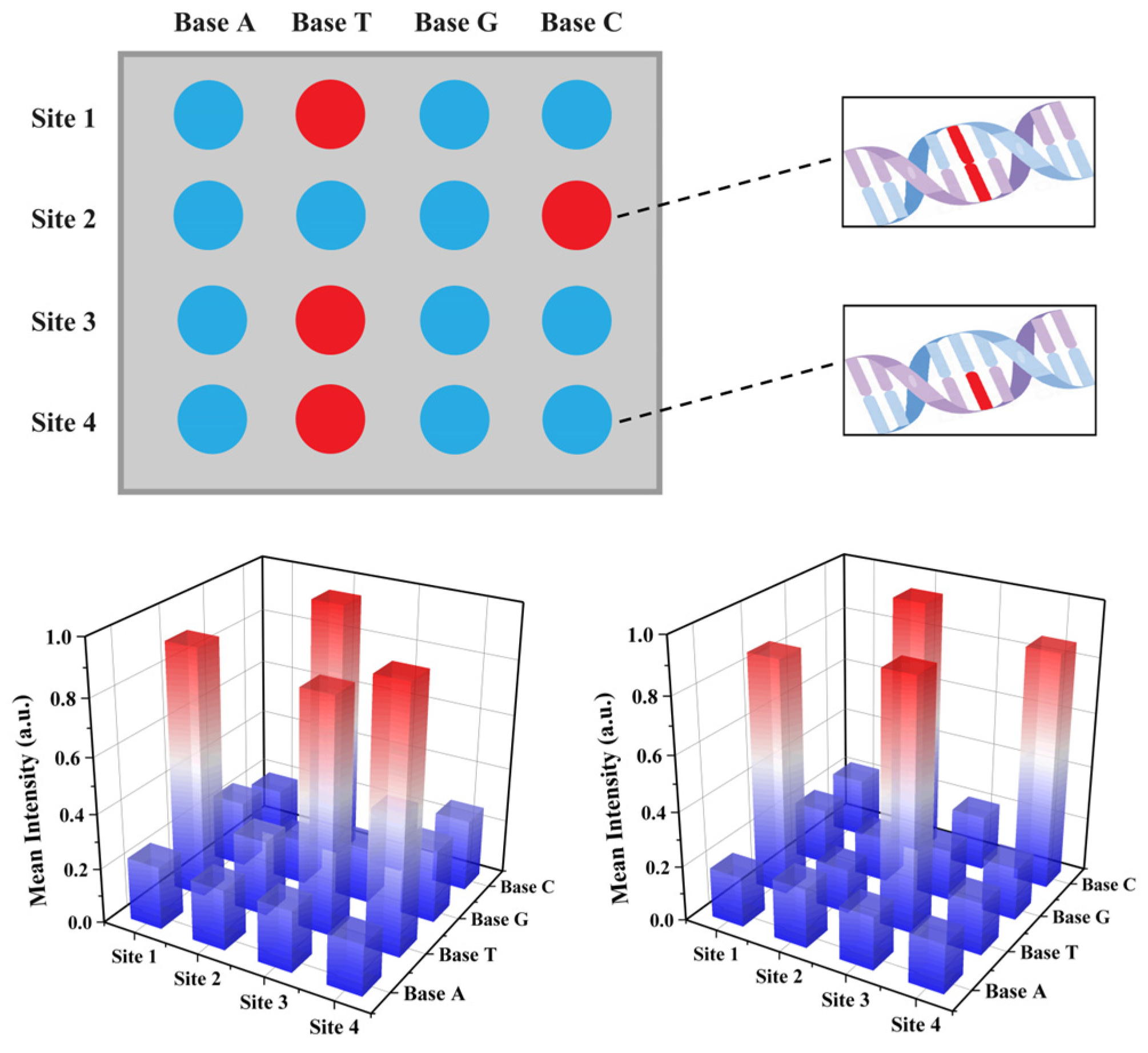
3.4. CdSe/PS Nanocomposite Detection Performance Evaluation and Applications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gruber, A.J.; Zavolan, M. Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makova, K.D.; Hardison, R.C. The effects of chromatin organization on variation in mutation rates in the genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, V.; Harismendy, O.; Tewhey, R.; Murray, S.S.; Schork, N.J.; Topol, E.J.; Frazer, K.A. Accurate detection and genotyping of SNPs utilizing population sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nimse, S.B.; Song, K.S.; Warkad, S.D.; Kim, T. A Novel Method That Allows SNP Discrimination with 160:1 Ratio for Biosensors Based on DNA-DNA Hybridization. Biosensors 2021, 11, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Niu, K.; Du, H.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Lu, X. Sensitive Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid Screening of Tumor Biomarker TP53 Gene Mutation Hotspot. Biosensors 2022, 12, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.F.; Guo, Y.C.; Chen, H.J.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, G.M. A comprehensive system for detecting rare single nucleotide variants based on competitive DNA probe and duplex-specific nuclease. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1166, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Wang, L.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, X.Y.; Dong, J.H.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zhang, X.X. Ultrasensitive Multiplex Detection of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Based on Short-Chain Hybridization Combined with Online Preconcentration of Capillary Electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10620–10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dang, H.; Yang, S.; Zuo, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Xie, G. Tuning the specificity of DNA probes using bulge-loops for low-abundance SNV detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 154, 112092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bu, S.; Xu, S.; Huang, T.; Yang, F.; Tan, Q.; Deng, M.; Xie, W.; Cai, B.; Chen, J. Double base mismatches mediated catalytic hairpin assembly for enzyme-free single-base mutation detection: Integrating signal recognition and amplification in one. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Kong, F.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chao, L.; Nie, L.; Huang, Z. Recent Progress in Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Biosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Cheng, Y.; Shang, L.R.; Wang, J.; Xie, Z.Y.; Gu, Z.Z. Microfluidic Synthesis of Barcode Particles for Multiplex Assays. Small 2015, 11, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, K.; Susaki, E.A.; Endo, M.; Asanuma, H.; Kashida, H. Color-Changing Fluorescent Barcode Based on Strand Displacement Reaction Enables Simple Multiplexed Labeling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Huang, W.; Zhou, B.; Liu, C.; Mow, W.H. PiCode: A New Picture-Embedding 2D Barcode. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 3444–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, J.; Xie, P.; Lin, Z.; Javanmard, M. Electronic classification of barcoded particles for multiplexed detection using supervised machine learning analysis. Talanta 2020, 215, 120791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Gao, Q.; Li, S.; Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Fischer, P.; Stavrakis, S.; deMello, A.J. Laminar Flow-Based Fiber Fabrication and Encoding via Two-Photon Lithography. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 54068–54074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Gu, Y.; Lu, H.; Dong, H.; Zhang, K.; Dai, W.; Meng, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X. Highly-sensitive microRNA detection based on bio-bar-code assay and catalytic hairpin assembly two-stage amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1004, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Pan, B.; Long, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, D.; Luan, X.; He, B.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y. Metal Organic Framework-Based Bio-Barcode CRISPR/Cas12a Assay for Ultrasensitive Detection of MicroRNAs. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 9714–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Pan, Y.; Luan, X.; He, B.; Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y. Metal-Organic Framework-DNA Bio-Barcodes Amplified CRISPR/Cas12a Assay for Ultrasensitive Detection of Protein Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhou, G.; Huang, L.L. PCR-free MDR1 polymorphism identification by gold nanoparticle probes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, C.; Chen, M.; Hu, Z.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Wu, L.; Liang, D. A protospacer adjacent motif-free, multiplexed, and quantitative nucleic acid detection platform with barcode-based Cas12a activity. MedComm 2023, 4, e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, L.; Rout, S.R.; Varma, R.S.; Otyepka, M.; Jayaramulu, K.; Dandela, R. Recent advancements in metal–organic frameworks integrating quantum dots (QDs@MOF) and their potential applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 1947–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, A.A.H.; Younis, M.A.; Alsharidah, M.; Al Rugaie, O.; Tawfeek, H.M. Biomedical Applications of Quantum Dots: Overview, Challenges, and Clinical Potential. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 1951–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.C.; Hu, J.; Luo, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, C.Y. Development of a Single Quantum Dot-Mediated FRET Nanosensor for Sensitive Detection of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism in Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 14568–14576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Deng, T.; Chu, X.; Yang, R.; Jiang, J.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Rolling circle amplification combined with gold nanoparticle aggregates for highly sensitive identification of single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2811–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Nie, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Yu, R. A universal fluorescence biosensor based on rolling circle amplification and locking probe for DNA detection. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-M.; Seo, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Jeong, W.; Hwang, S.-H.; Kim, D.-E. Fluorometric detection of single-nucleotide mutations using tandem gene amplification. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2020, 314, 128071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; You, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, W.; Jang, K.; Park, J.; Na, S. Enhanced selective discrimination of point-mutated viral RNA through false amplification regulatory direct insertion in rolling circle amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 252, 116145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.; Roy, S.; Ganguly, S.; Qian, X.; Caruthers, M.H.; Nilsson, M. Formation of Silver Nanostructures by Rolling Circle Amplification Using Boranephosphonate-Modified Nucleotides. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6660–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Salmi-Mani, H.; Roger, P.; Chang, S.M. A microgel of CdSe quantum dots for fluorescent bisphenol A detection. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, H.; Zhong, X.; Yi, S.; Jia, Z.; Chen, L.; Hu, S. A CRISPR/Cas12a-assisted array for Helicobacter pylori DNA analysis in saliva. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1239, 340736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Initial Concentration (pM) | Fortified Concentration (pM) | Total Concentration (pM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (n = 3, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saliva | 0.0 | 10.0 | 10.3 | 104.1% | 2.43% |
| Saliva | 0.0 | 25.0 | 25.5 | 101.7% | 1.55% |
| Saliva | 0.0 | 50.0 | 48.7 | 97.7% | 3.20% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, L.; Chen, H.; Cao, S.; Hu, S. Single Nucleotide Recognition and Mutation Site Sequencing Based on a Barcode Assay and Rolling Circle Amplification. Biosensors 2024, 14, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14110521
Zhong L, Chen H, Cao S, Hu S. Single Nucleotide Recognition and Mutation Site Sequencing Based on a Barcode Assay and Rolling Circle Amplification. Biosensors. 2024; 14(11):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14110521
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Linmin, Huiping Chen, Shuang Cao, and Shanwen Hu. 2024. "Single Nucleotide Recognition and Mutation Site Sequencing Based on a Barcode Assay and Rolling Circle Amplification" Biosensors 14, no. 11: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14110521
APA StyleZhong, L., Chen, H., Cao, S., & Hu, S. (2024). Single Nucleotide Recognition and Mutation Site Sequencing Based on a Barcode Assay and Rolling Circle Amplification. Biosensors, 14(11), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14110521






