Development of a Dual Mode UCNPs-MB Biosensor in Combination with PCR for Sensitive Detection of Salmonella
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Synthesis and Modification of UCNPs
2.4. Bacterial Culture and DNA Extraction
2.5. PCR Amplification Process
2.6. Dual-Mode Colorimetric-Fluorescence Assays of Salmonella PCR Products Using UCNPs-MB Biosensors
2.7. Specificity of UCNPs-MB PCR Biosensor for Salmonella
2.8. Preparation and Detection of Actual Food Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of OA@UCNPs and AEP@UCNPs
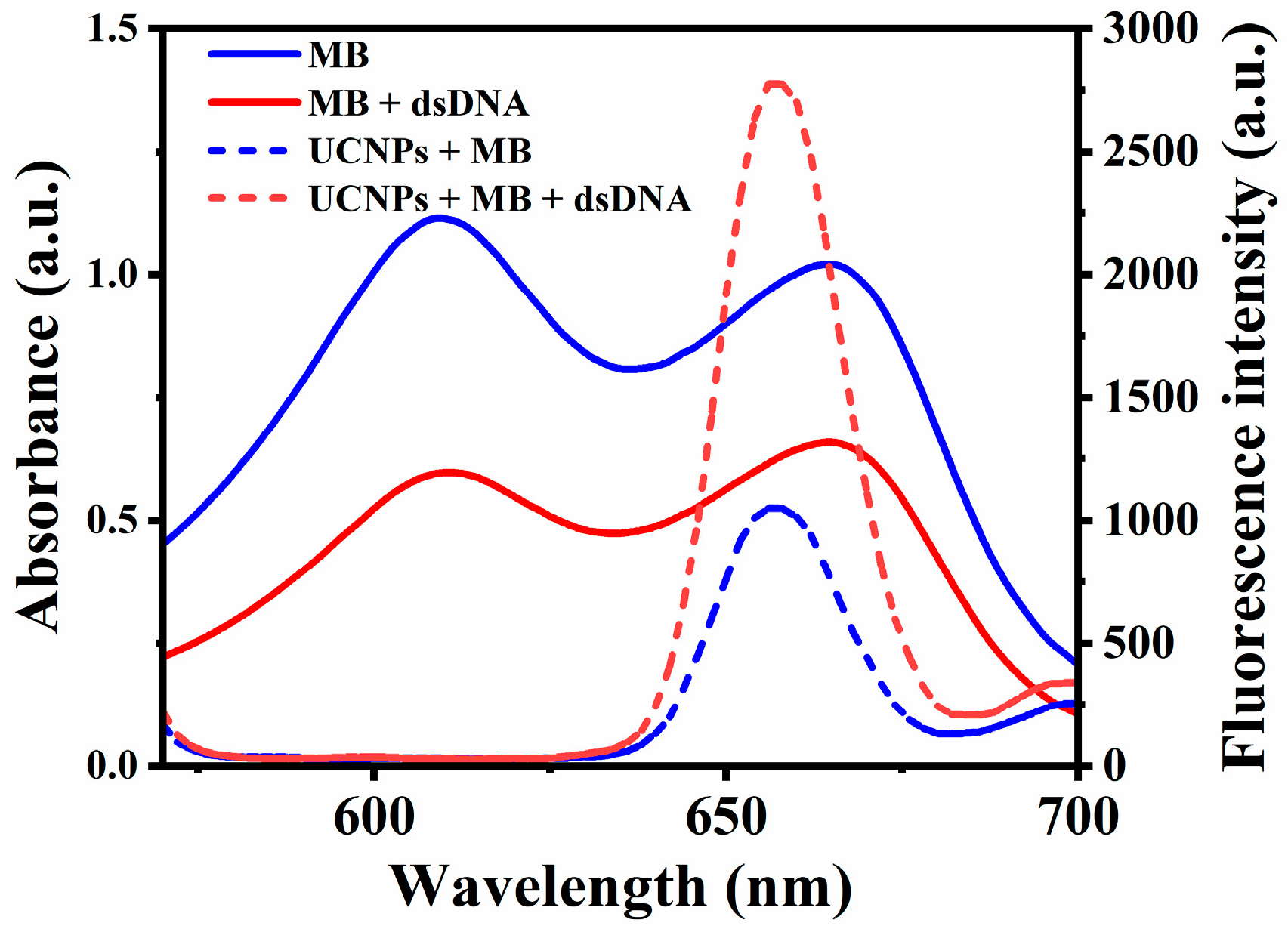
3.2. Mechanism of the Dual Mode UCNPs-MB PCR Biosensor for Salmonella Detection
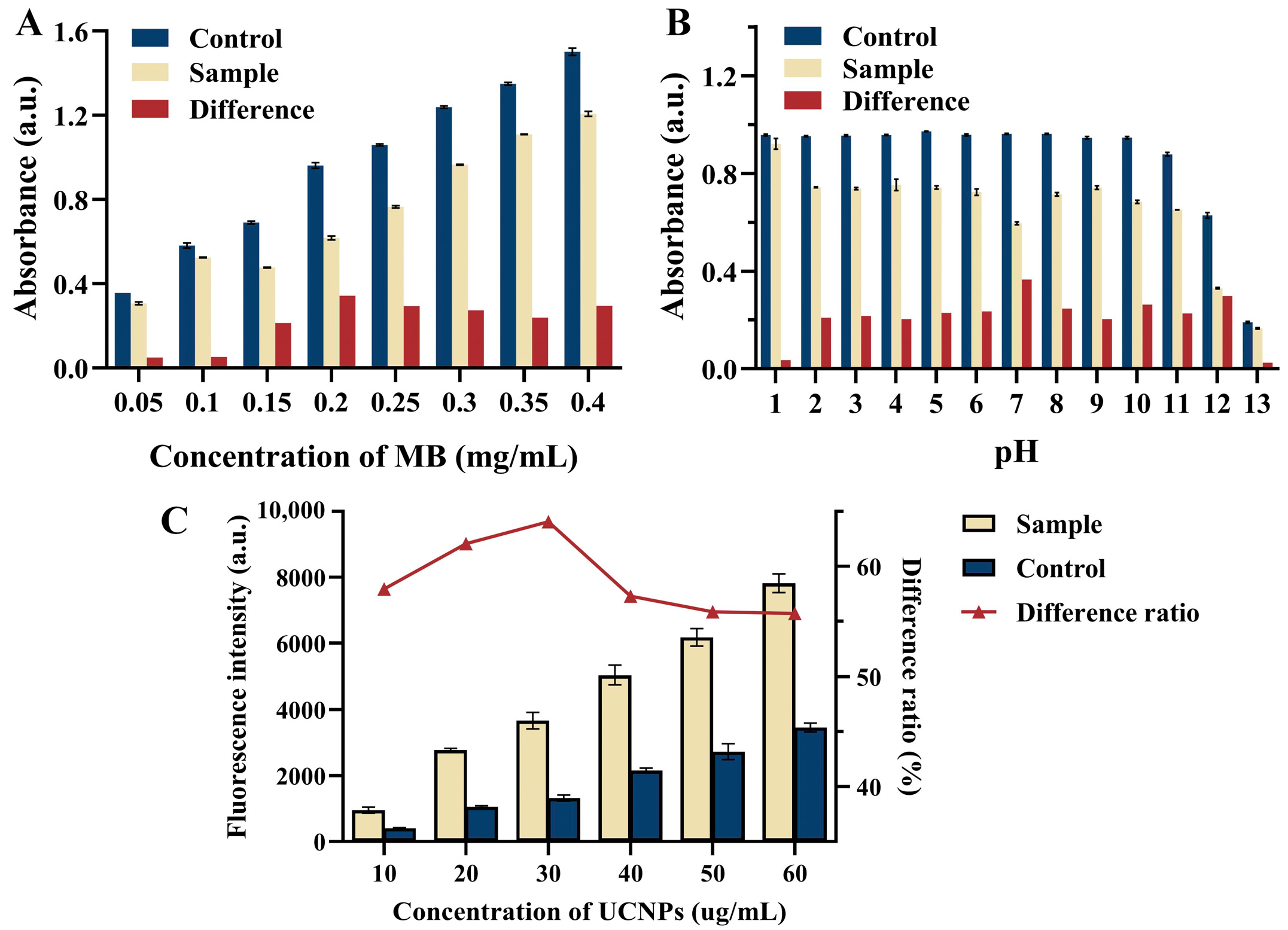
3.3. Optimization of Detection Parameters
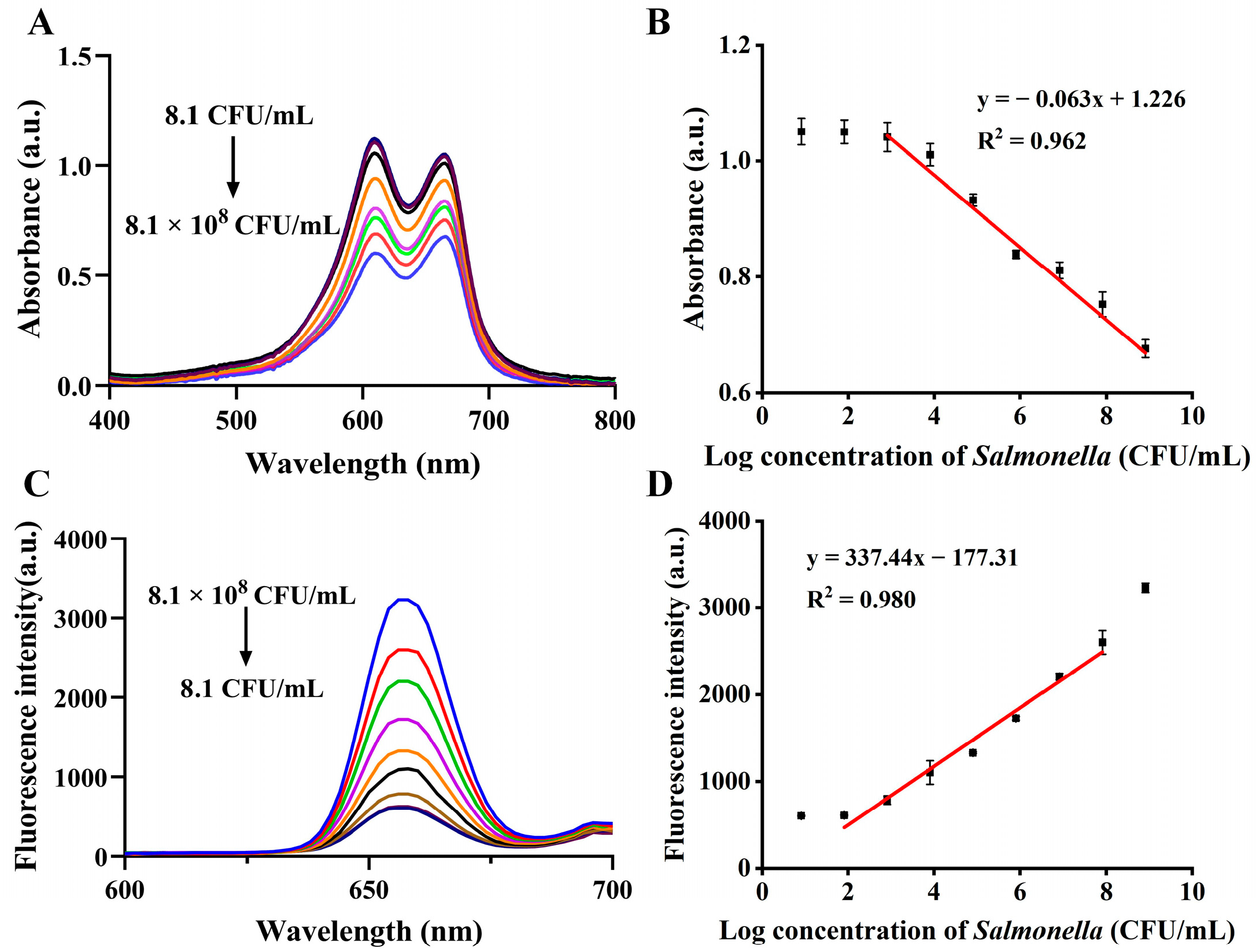
3.4. Analytical Performance Using UCNPs-MB PCR Biosensor for Salmonella
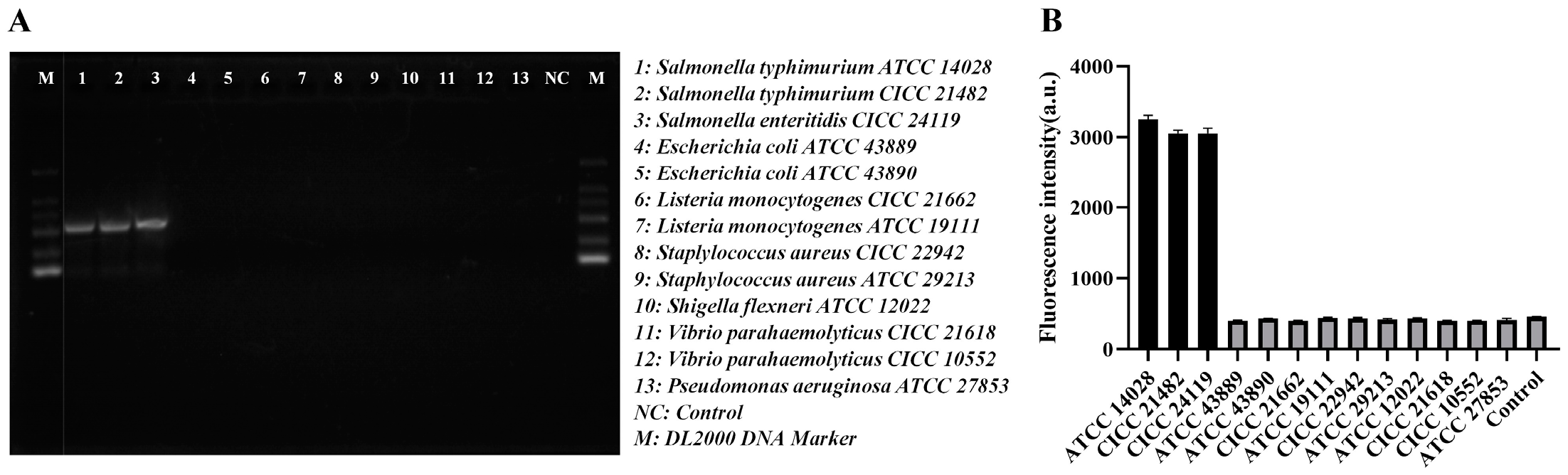
3.5. Selectivity for Salmonella Detection
3.6. Determination Performance for Salmonella in Food
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suo, Y.; Yin, W.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, W.; Cao, W.; Mu, Y. A Specific and Sensitive Aptamer-Based Digital PCR Chip for Salmonella Typhimurium Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, D.; Yin, X.; Lu, Z.; Lv, F.; Zhao, H.; Bie, X. Occurrence, Drug Resistance, and Virulence Genes of Salmonella Isolated from Chicken and Eggs. Food Control 2020, 113, 107109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chousalkar, K.; Gast, R.; Martelli, F.; Pande, V. Review of Egg-Related Salmonellosis and Reduction Strategies in United States, Australia, United Kingdom and New Zealand. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymans, R.; Vila, A.; van Heerwaarden, C.A.; Jansen, C.C.; Castelijn, G.A.; van der Voort, M.; Biesta-Peters, E.G. Rapid Detection and Differentiation of Salmonella Species, Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis by Multiplex Quantitative PCR. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Explains Zoonotic Diseases: Salmonella; Lund University Press: Lund, Sweden, 2014.
- Dehghani, Z.; Nguyen, T.; Golabi, M.; Hosseini, M.; Rezayan, A.H.; Mohammadnejad, J.; Wolff, A.; Vinayaka, A.C. Magnetic Beads Modified with Pt/Pd Nanoparticle and Aptamer as a Catalytic Nano-Bioprobe in Combination with Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification for the on-Site Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in Food and Fecal Samples. Food Control 2021, 121, 107664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhou, D.; Xie, G.; Liu, J.; Xiong, Q.; Xu, H. A Novel Photoreactive DNA-Binding Dye for Detecting Viable Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Powdered Infant Formula. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 4895–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liao, T.; Zhou, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, P.; Yang, X.; Chen, X. Colorimetric Method for Salmonella Spp. Detection Based on Peroxidase-like Activity of Cu(II)-RGO Nanoparticles and PCR. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 615, 114068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Q.; Huang, X.H.; Guo, L.Q.; Shen, Z.C.; Lv, L.X.; Li, F.X.; Zhou, Z.H.; Zhang, D.F. Rapid and Visual Detection of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus in Aquatic Foods Using BlaCARB-17 Gene-Based Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Lateral Flow Dipstick (LAMP-LFD). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 1672–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Hu, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X. Improving the Detection Limit of Salmonella Colorimetry Using Long SsDNA of Asymmetric-PCR and Non-Functionalized AuNPs. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 626, 114229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Tian, J.; Li, K.; Du, Z.; Xu, W. Universal Linker Polymerase Chain Reaction-Triggered Strand Displacement Amplification Visual Biosensor for Ultra-Sensitive Detection of Salmonella. Talanta 2021, 222, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Bu, T.; Jia, P.; He, K.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, L. Polydopamine Nanospheres-Assisted Direct PCR for Rapid Detection of Escherichia Coli O157:H7. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 654, 114797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.G.; Choi, W.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S.G.; Lee, M.Y.; Jung, H.S. PCR-Coupled Paper-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Respiratory Bacterial DNA. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, X.; Fu, S.; Qin, X.; Yang, T.; Man, C.; Jiang, Y. A Novel AuNPs Colorimetric Sensor for Sensitively Detecting Viable Salmonella Typhimurium Based on Dual Aptamers. Food Control 2020, 115, 107281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhan, Z.; Liang, T.; Xie, G.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Xu, H. Dual-Signal Amplification Strategy: Universal Asymmetric Tailing-PCR Triggered Rolling Circle Amplification Assay for Fluorescent Detection of Cronobacter spp. in Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3055–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Chu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Lyu, S.; Xu, W. MSN/NA-Doped Nanoflower Enhancing Isothermal Fluorescent Sensor with a Portable PCR Tube Fluorescence Reader for the on-Site Detection of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1200, 339448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Gao, R.; Jia, L. Enhancement of the Peroxidase-like Activity of Aptamers Modified Gold Nanoclusters by Bacteria for Colorimetric Detection Of. Talanta 2021, 221, 121476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Sui, N.; Liu, M.; Yu, W.W. A Colorimetric Assay for Hg(II) Based on the Use of a Magnetic Aptamer and a Hybridization Chain Reaction. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2855–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Huang, G.; Bai, C.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Tang, C.; Kong, J.; Huang, J.; Li, Z. A Versatile Platform for Colorimetric, Fluorescence and Photothermal Multi-Mode Glyphosate Sensing by Carbon Dots Anchoring Ferrocene Metal-Organic Framework Nanosheet. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Ye, Y.; Wu, Y. Polydopamine-Based Nanozyme with Dual-Recognition Strategy-Driven Fluorescence-Colorimetric Dual-Mode Platform for Listeria Monocytogenes Detection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Gao, H.; Gu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhu, L.; et al. Combination of Colorimetry, Inner Filter Effect-Induced Fluorometry and Smartphone-based Digital Image Analysis: A Versatile and Reliable Strategy for Multi-Mode Visualization of Food Dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Kundu, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Patra, A. A Hybrid Upconversion Nanoprobe for Ratiometric Detection of Aliphatic Biogenic Amines in Aqueous Medium. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 3232–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.H.; Im, S.G.; Sung, H.; Hah, S.S.; Cong, V.T.; Lee, D.H.; Son, S.J.; Oh, H.B. Upconversion Nanoparticle-Based Förster Resonance Energy Transfer for Detecting the IS6110 Sequence of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex in Sputum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Chen, Q.; Li, H.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhao, J. Fabricating a Novel Label-Free Aptasensor for Acetamiprid by Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer between NH2-NaYF4: Yb, Ho@SiO2 and Au Nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Song, Y.; Han, L.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Pan, L.; Tu, K. An Ultrasensitive Upconversion Fluorescence Aptasensor Based on Graphene Oxide Release and Magnetic Separation for Staphylococcus Aureus Detection. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 2791–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Kutsanedzie, F.Y.H.; Cheng, W.; Agyekum, A.A.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. A Nanosystem Composed of Upconversion Nanoparticles and N, N-Diethyl-p-Phenylenediamine for Fluorimetric Determination of Ferric Ion. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ahmad, W.; Chen, Q.; Ouyang, Q. Development of a Dual-Mode Upconversion Nanoparticles-3-Aminophenol Nanosystem Based on Inner Filter Effect for Sensitive Detection of Nitrite and Its Application on Test Strips. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 374, 132740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, T.; Li, Z.; Xue, C.; Xu, J. Ratiometric Fluorescent Nanosystem Based on Upconversion Nanoparticles for Histamine Determination in Seafood. Food Chem. 2022, 390, 133194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Distinction of Single Base Mismatches in Duplex DNA Using Methylene Blue as Optical Indicator. Analyst 2010, 135, 2960–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardevanyan, P.O.; Antonyan, A.P.; Parsadanyan, M.A.; Shahinyan, M.A.; Petrosyan, N.H. Study of Interaction of Methylene Blue with DNA and Albumin. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Xu, J.G.; He, X.W. Characterization of the Binding of Methylene Blue to DNA by Spectroscopic Methods. Anal. Lett. 2000, 33, 2453–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Pan, L.; Tu, K. A Fluorescence Biosensor for Salmonella Typhimurium Detection in Food Based on the Nano-Self-Assembly of Alendronic Acid Modified Upconversion and Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 2415–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Chao, Z.; Liu, C.; Ma, H.; Liu, Y.; Ju, H. Boosting Luminance Energy Transfer Efficiency in Upconversion Nanoparticles with an Energy-Concentrating Zone. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 12245–12250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Zhou, S.; Fauconnier, M.L.; Gao, F.; Fan, B.; Lin, J.; Wang, F.; Zheng, J. Sensitive and Simultaneous Detection of Different Pathogens by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Based on Aptamer and Raman Reporter Co-Mediated Gold Tags. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 317, 128182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Tao, Y.; Qiao, S. Effects of Surface Modification of Upconversion Nanoparticles on Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2016, 32, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Dong, W.; Wang, T.; Shi, W.; Fu, C.; Wu, Y. Aptasensor Based on MoS 2 Quantum Dots with Upconversion Fluorescence for Microcystin-LR Detection via the Inner Filter Effect. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 10939–10946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Gao, X.; Li, H.; Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Rapid and Simultaneous Detection of Salmonella Spp., Escherichia Coli O157:H7, and Listeria Monocytogenes in Meat Using Multiplex Immunomagnetic Separation and Multiplex Real-Time PCR. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Guo, R.; Xue, L.; Cai, G.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Liao, M.; Wang, M.; Lin, J. An Acid-Responsive Microfluidic Salmonella Biosensor Using Curcumin as Signal Reporter and ZnO-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Signal Amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 312, 127958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Tang, F.; Wang, L.; Tang, M.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Liu, C. Nanozyme Sensor Based-on Platinum-Decorated Polymer Nanosphere for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium with the Naked Eye. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 346, 130560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, S.; Duan, H.; Liu, Y. A Fluorescent Biosensor for Sensitive Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium Using Low-Gradient Magnetic Field and Deep Learning via Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network. Biosensors 2021, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Jia, F.; Sun, Y.; Fang, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Fu, Y. An Electrochemical Sensing Method Based on CRISPR/Cas12a System and Hairpin DNA Probe for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 369, 132301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, T.; Yang, T.; Liang, X.; Wu, B.; Zou, D.; Hu, L.; Huang, G.; Zhang, J. NMR Rapid Detection of Salmonella in Milk Based on Ultra-Small Iron Oxide Nanobiosensor. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 110, 104807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | Linear Range (CFU/mL) | LOD (CFU/mL) | Detection Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qPCR | 1.2 × 102–1.2 × 108 | 120 | <3 h | [37] |
| Acid-responsive microfluidic biosensor | 102–107 | 63 | <1.5 h | [38] |
| Nanozyme optical biosensor | 104–106 | 3 × 102 | <50 min | [39] |
| Fluorescent biosensor | 6.9 × 101–1.1 × 103 | 55 | <2.5 h | [40] |
| PCR-based E-CRISPR biosensor | 6.7 × 101–6.7 × 105 | 55 | <2.5 h | [41] |
| Ultra-small iron oxide nanobiosensor | 2.3 × 101–2.3 × 106 | 2.3 × 103 | <2.5 h | [42] |
| UCNPs-MB dual mode PCR biosensor | 8.1 × 101–8.1 × 107 | 21.8 | <1.5 h | This work |
| Sample | Spiked Levels (CFU/mL) | Measured (Mean a ± SD b) (CFU/mL) | Accuracy (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorimetric Sensor | Fluorescent Sensor | qPCR | Colorimetric Sensor | Fluorescence Sensor | qPCR | ||
| Chicken | 1.0 × 103 | (0.995 ± 0.120) × 103 | (1.003 ± 0.090) × 103 | (1.009 ± 0.237) × 103 | 99.5 | 100.3 | 100.9 |
| 1.0 × 105 | (1.061 ± 0.039) × 105 | (1.006 ± 0.035) × 105 | (0.983 ± 0.043) × 105 | 106.1 | 100.6 | 98.3 | |
| 1.0 × 107 | (1.036 ± 0.140) × 107 | (1.018 ± 0.060) × 107 | (1.024 ± 0.073) × 107 | 103.6 | 101.8 | 102.4 | |
| Egg | 1.0 × 103 | (1.020 ± 0.124) × 103 | (0.942 ± 0.018) × 103 | (1.006 ± 0.294) × 103 | 102.0 | 94.2 | 100.6 |
| 1.0 × 105 | (1.050 ± 0.081) × 105 | (0.989 ± 0.049) × 105 | (1.031 ± 0.057) × 105 | 105.0 | 98.9 | 103.1 | |
| 1.0 × 107 | (1.077 ± 0.164) × 107 | (0.982 ± 0.075) × 107 | (0.940 ± 0.023) × 107 | 107.7 | 98.2 | 94.0 | |
| Fish | 1.0 × 103 | (1.004 ± 0.078) × 103 | (1.014 ± 0.049) × 103 | (1.010 ± 0.769) × 103 | 100.4 | 101.4 | 101.0 |
| 1.0 × 105 | (1.039 ± 0.114) × 105 | (0.990 ± 0.067) × 105 | (0.967 ± 0.060) × 105 | 103.9 | 99.0 | 96.7 | |
| 1.0 × 107 | (1.048 ± 0.136) × 107 | (0.964 ± 0.082) × 107 | (1.061 ± 0.126) × 107 | 104.8 | 96.4 | 106.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, L.; Chen, M.; Song, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, D.; Pan, L.; Tu, K. Development of a Dual Mode UCNPs-MB Biosensor in Combination with PCR for Sensitive Detection of Salmonella. Biosensors 2023, 13, 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13040475
Han L, Chen M, Song Y, Yan Z, Zhou D, Pan L, Tu K. Development of a Dual Mode UCNPs-MB Biosensor in Combination with PCR for Sensitive Detection of Salmonella. Biosensors. 2023; 13(4):475. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13040475
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Lu, Min Chen, Yaqi Song, Zhongyu Yan, Dandan Zhou, Leiqing Pan, and Kang Tu. 2023. "Development of a Dual Mode UCNPs-MB Biosensor in Combination with PCR for Sensitive Detection of Salmonella" Biosensors 13, no. 4: 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13040475
APA StyleHan, L., Chen, M., Song, Y., Yan, Z., Zhou, D., Pan, L., & Tu, K. (2023). Development of a Dual Mode UCNPs-MB Biosensor in Combination with PCR for Sensitive Detection of Salmonella. Biosensors, 13(4), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13040475






