Combined Use of Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems and Microfluidic Devices for the Detection of Prostate-Specific Antigen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
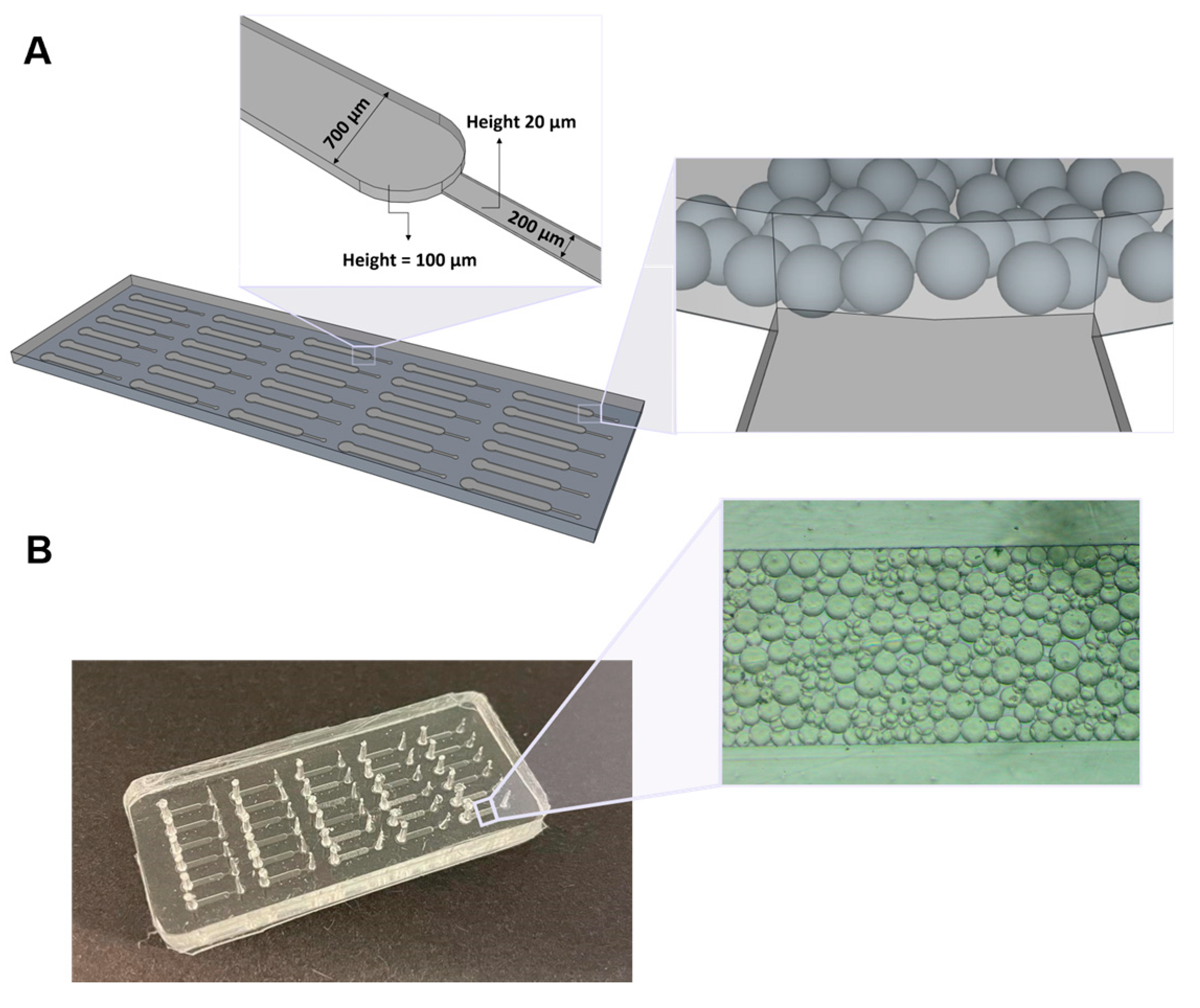
2.1. Fabrication of PDMS Microchannel Structures
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Microfluidic Handling
2.4. Microfluidic Immunoassay for the Detection of Spiked Solutions of PSA in PBS, Human Serum and Aqueous Solutions of ABS Components
2.5. Aqueous Biphasic System Preparation
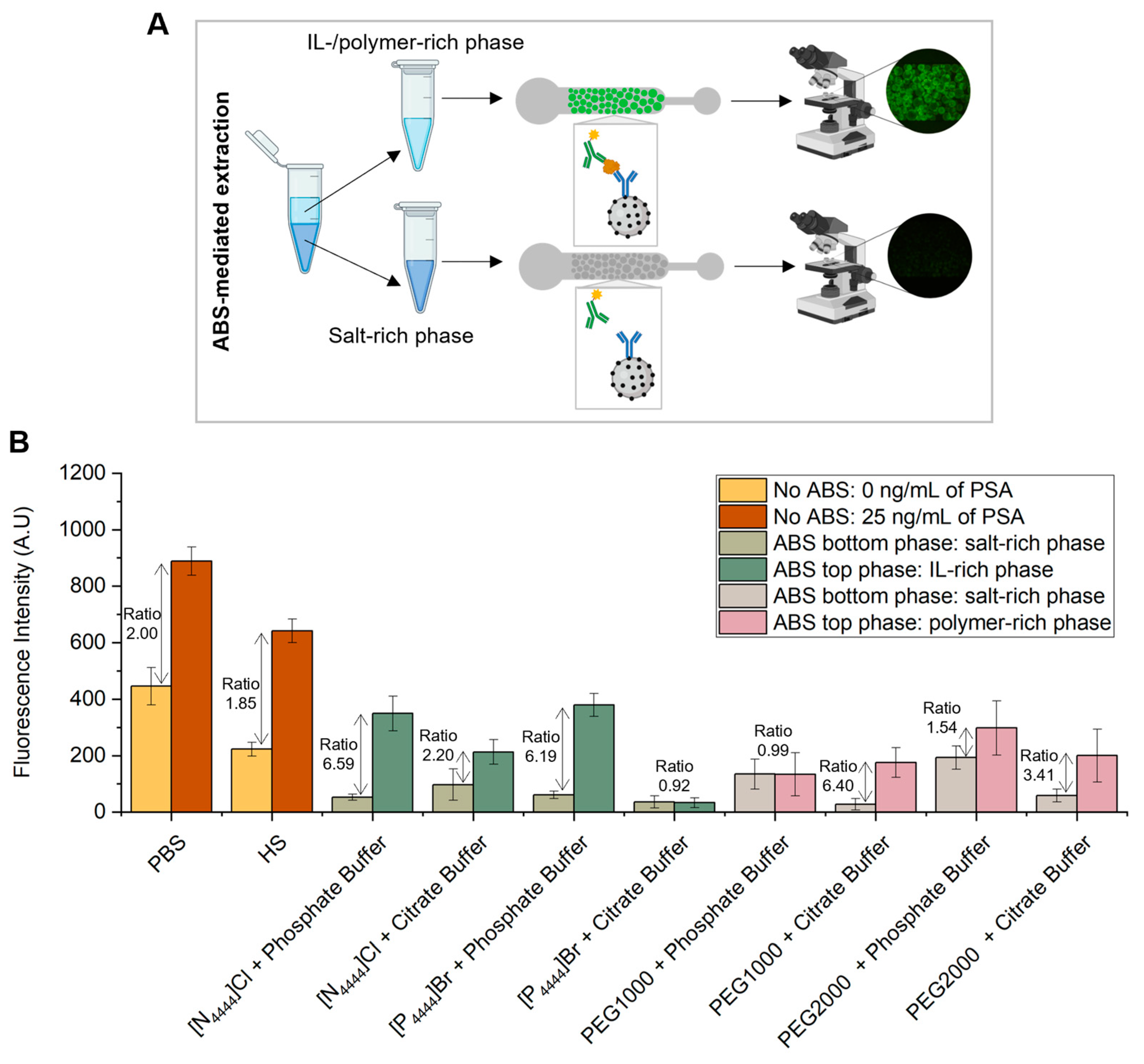
2.6. On-Chip Microfluidic Immunoassays Following ABS-Mediated Extraction
2.7. Image Acquisition and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
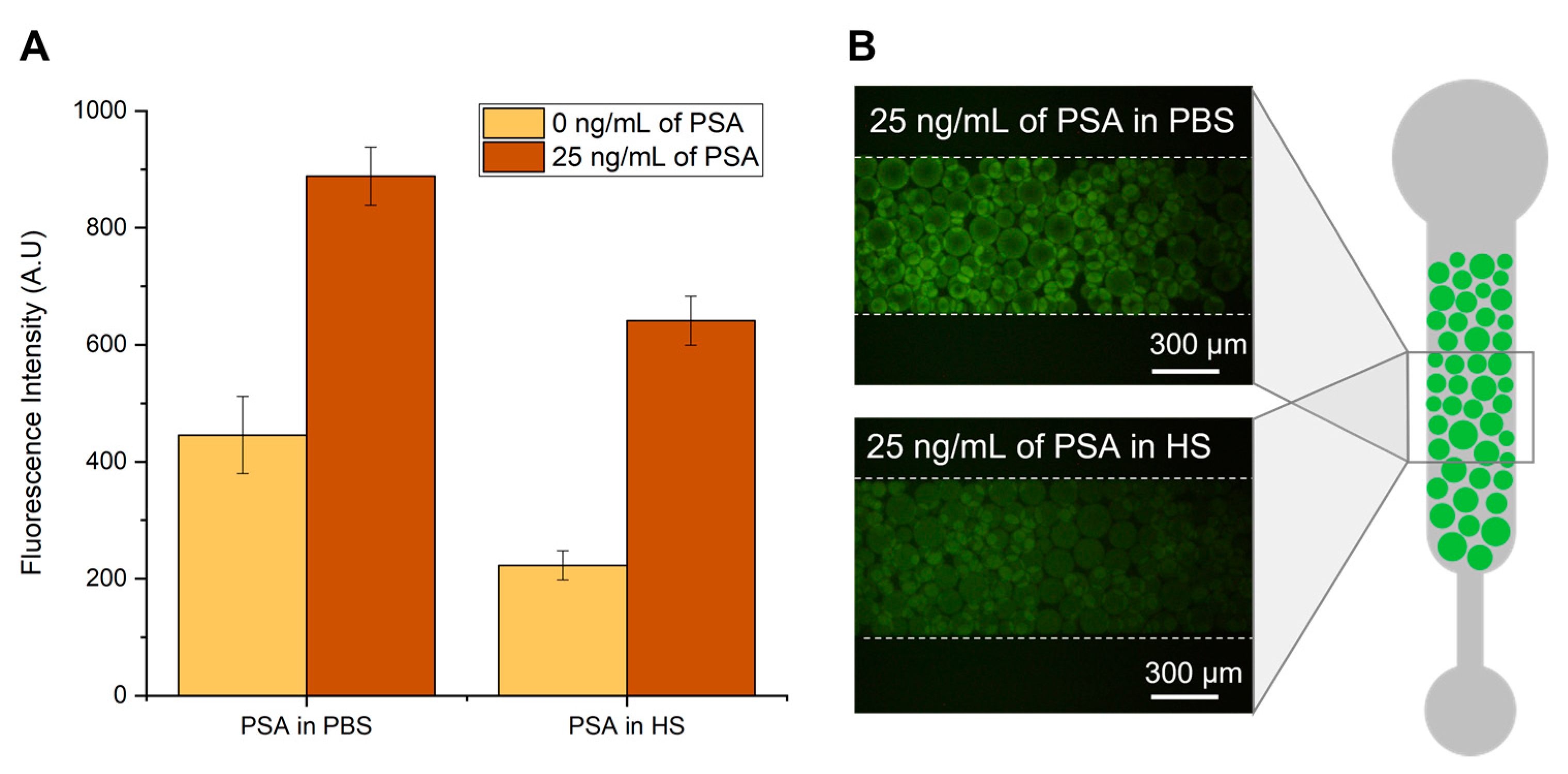
3.1. PSA Detection in Microfluidics
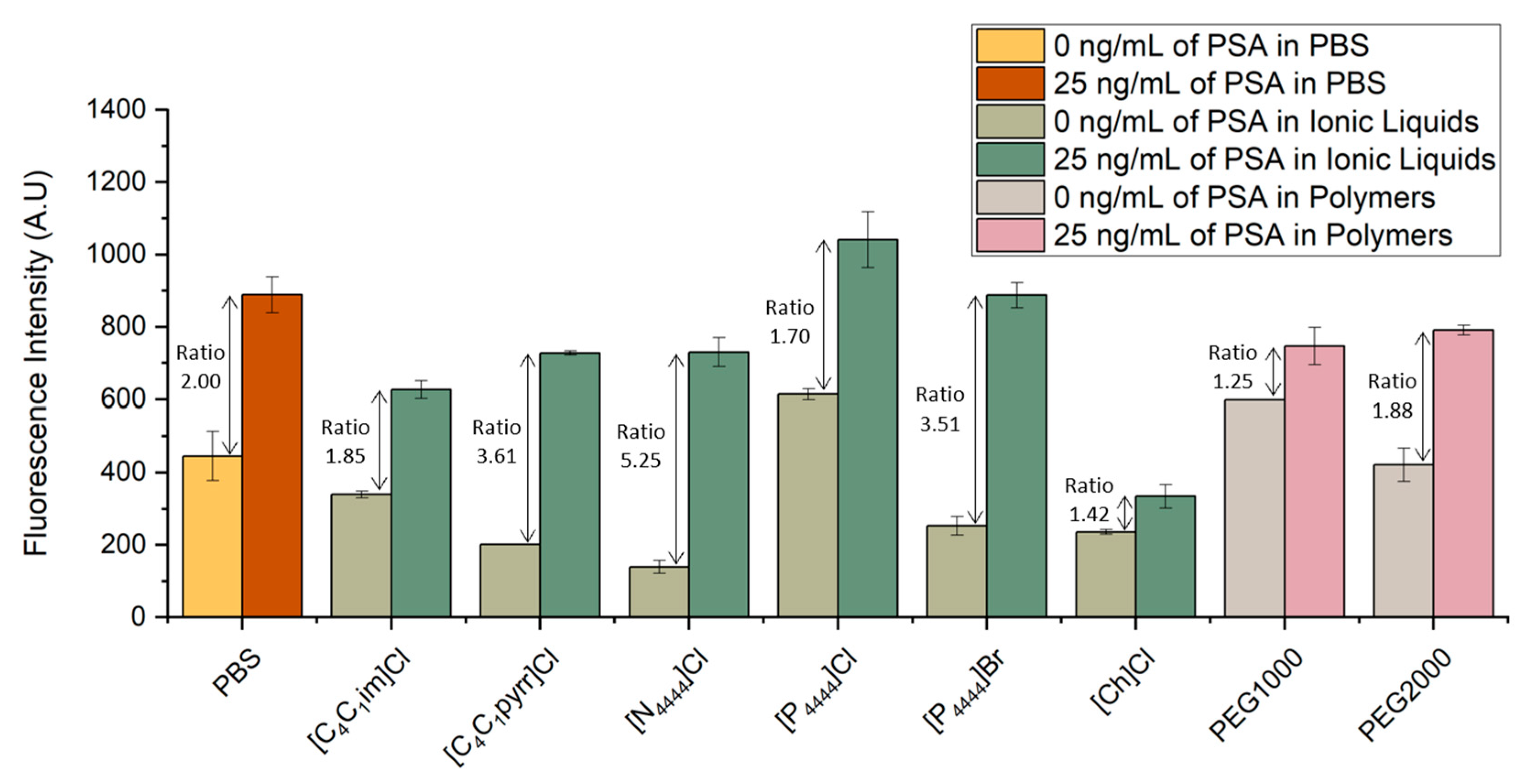
3.2. PSA Detection in Aqueous Solutions of ABS Components
3.3. Off-Chip ABS with Subsequent On-Chip Microscale PSA Detection
3.4. Sensitivity of Sandwich Immunoassay for Detection of PSA Following ABS-Mediated Extraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mordente, A.; Meucci, E.; Martorana, G.E.; Silvestrini, A.; Mordente, A.; Meucci, E.; Martorana, G.E.; Silvestrini, A. Cancer Biomarkers Discovery and Validation: State of the Art, Problems and Future Perspectives. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 867, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velonas, V.M.; Woo, H.H.; dos Remedios, C.G.; Assinder, S.J. Current Status of Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 11034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.; Huang, C.; Song, G.; Xiong, G.; Fang, D.; Wang, H.; Hao, H.; Cai, L.; He, Q.; He, Z.; et al. Are the Pathological Characteristics of Prostate Cancer More Aggressive or More Indolent Depending upon the Patient Age? Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.K. Kallikreins as Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balk, S.P.; Ko, Y.J.; Bubley, G.J. Biology of prostate-specific antigen. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, L.; Corradi, R.; Eastham, J.A. Prostatic specific antigen for Prostate Cancer detection. Int. Braz J Urol 2009, 35, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, P.; Damborsky, P.; Madaboosi, N.; Soares, R.R.G.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P.; Katrlik, J.; Estrela, P. DNA aptamer-based sandwich microfluidic assays for dual quantification and multi-glycan profiling of cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.K.; Leslie, S.W. Prostate Specific Antigen. Aust. Prescr. 2022, 34, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaboosi, N.; Soares, R.R.G.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. A microfluidic immunoassay platform for the detection of free prostate specific antigen: A systematic and quantitative approach. Analyst 2015, 140, 4423–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Putalun, W.; Vimolmangkang, S.; Phoolcharoen, W.; Shoyama, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Morimoto, S. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative/qualitative analysis of plant secondary metabolites. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 72, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Wang, J.H.; Wu, H.W.; Lee, G.B. Microfluidic Immunoassays. JALA J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 2010, 15, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.L.; Anderson, N.G. The human plasma proteome: History, character, and diagnostic prospects. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2002, 1, 845–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazayeri, M.H.; Pourfathollah, A.A.; Rasaee, M.J.; Porpak, Z.; Jafari, M.E. The concentration of total serum IgG and IgM in sera of healthy individuals varies at different age intervals. Biomed. Aging Pathol. 2013, 3, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsson, P.Å. Partition of Proteins in Liquid Polymer–Polymer Two-Phase Systems. Nature 1958, 182, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.F.B.; Lima, Á.S.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic liquids as adjuvants for the tailored extraction of biomolecules in aqueous biphasic systems. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Marrucho, I.M.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Aqueous biphasic systems: A boost brought about by using ionic liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4966–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutowski, K.E.; Broker, G.A.; Willauer, H.D.; Huddleston, J.G.; Swatloski, R.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Controlling the aqueous miscibility of ionic liquids: Aqueous biphasic systems of water-miscible ionic liquids and water-structuring salts for recycle, metathesis, and separations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6632–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.F.B.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Rogers, R.D.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Combining ionic liquids and polyethylene glycols to boost the hydrophobic-hydrophilic range of aqueous biphasic systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 19580–19583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Pei, Y.; Wang, J.; He, M. Design of environmentally friendly ionic liquid aqueous two-phase systems for the efficient and high activity extraction of proteins. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2941–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Ding, X.; Chen, J. Extraction and separation of proteins by ionic liquid aqueous two-phase system. Analyst 2013, 138, 6445–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonova, K.; Svinyarov, I.; Bogdanov, M. Ionic Liquids—Based Biphasic Systems for Enzyme Extraction: Preliminary Data From Ionic Liquids ’ Screening. Mater. J. Int. Sci. Publ. 2015, 9, 442–451. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, D.; Sharma, M.; Quental, M.V.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Prasad, K.; Freire, M.G. Suitability of bio-based ionic liquids for the extraction and purification of IgG antibodies. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 6071–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, M.; Almeida, M.R.; Silva, F.A.E.; Domingues, P.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Novel biocompatible and self-buffering ionic liquids for biopharmaceutical applications. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 4781–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Cheng, D.H.; Chen, X.W.; Du, Z.; Fang, Z.L. Direct extraction of double-stranded DNA into ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate and its quantification. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.M.; Brito, L.L.R.; de Miranda, R.d.C.M.; de Souza, R.L.; Soares, C.M.F.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G.; Lima, Á.S. Pre-treatment strategies based on aqueous two-phase systems comprising ionic liquids to improve the adrenal cancer diagnosis. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.; Calixto, J.D.; Sousa, A.C.A.; Pereira, B.J.; Lima, Á.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Towards the differential diagnosis of prostate cancer by the pre-treatment of human urine using ionic liquids. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, I.F.; Caneira, C.R.F.; Soares, R.R.G.; Madaboosi, N.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Conde, J.P.; Azevedo, A.M.; Chu, V. The application of microbeads to microfluidic systems for enhanced detection and purification of biomolecules. Methods 2017, 116, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Castanheira, A.P.; Edwards, A.D.; Reis, N.M. A lab-in-a-briefcase for rapid prostate specific antigen (PSA) screening from whole blood Lab on a Chip A lab-in-a-briefcase for rapid prostate specific antigen (PSA) screening from whole blood. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2869–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, K.; Xuan, X.; Lu, X. Ionic liquid-based aqueous two-phase extraction of selected proteins. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 64, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, K. Design of functional guanidinium ionic liquid aqueous two-phase systems for the efficient purification of protein. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 815, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.K.; Streefland, M.; Wijffels, R.H.; Eppink, M.H.M. Extraction and stability of selected proteins in ionic liquid based aqueous two phase systems. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; Sousa, S.G.; Freire, M.G.; Serafim, L.S.; Lima, Á.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Design of ionic liquids for lipase purification. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 2679–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louros, C.L.S.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Neves, C.M.S.S.; Freire, M.G.; Marrucho, I.M.; Pauly, J.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Extraction of Biomolecules Using Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids + K3PO4 Aqueous Biphasic Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belchior, D.C.V.; Quental, M.V.; Pereira, M.M.; Mendonça, C.M.N.; Duarte, I.F.; Freire, M.G. Performance of tetraalkylammonium-based ionic liquids as constituents of aqueous biphasic systems in the extraction of ovalbumin and lysozyme. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 233, 116019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Feng, Z.; Liu, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Ji, G. Extraction and purification of wheat-esterase using aqueous two-phase systems of ionic liquid and salt. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 2878–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Shinji, F.; Tahara, Y. Extraction of Proteins with Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Formed by Protic Ionic Liquids and Inorganic Salts. Solvent Extr. Res. Dev. Jpn. 2021, 28, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Quental, M.V.; Correia, I.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Extraction and stability of bovine serum albumin (BSA) using cholinium-based Good’s buffers ionic liquids. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.; Pedro, S.N.; Quental, M.V.; Lima, Á.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Enhanced extraction of bovine serum albumin with aqueous biphasic systems of phosphonium- and ammonium-based ionic liquids. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 206, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capela, E.V.; Santiago, A.E.; Rufino, A.F.C.S.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Pereira, M.M.; Mohamadou, A.; Raquel Aires-Barros, M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Azevedo, A.M.; Freire, M.G. Sustainable strategies based on glycine-betaine analogue ionic liquids for the recovery of monoclonal antibodies from cell culture supernatants †. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 5671–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.A.E.; Sintra, T.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Recovery of paracetamol from pharmaceutical wastes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintra, T.E.; Cruz, R.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Phase diagrams of ionic liquids-based aqueous biphasic systems as a platform for extraction processes. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2014, 77, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belchior, D.C.V.; Freire, M.G. Simultaneous separation of egg white proteins using aqueous three-phase partitioning systems. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Faustino, V.F.M.; Mondal, D.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Improving the extraction and purification of immunoglobulin G by the use of ionic liquids as adjuvants in aqueous biphasic systems. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 236, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolduc, S.; Lacombe, L.; Naud, A.; Grégoire, M.; Fradet, Y.; Tremblay, R.R. Urinary PSA: A potential useful marker when serum PSA is between 2.5 ng/mL and 10 ng/mL. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2013, 1, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novo, P.; Moulas, G.; Prazeres, D.M.F.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. Detection of ochratoxin A in wine and beer by chemiluminescence-based ELISA in microfluidics with integrated photodiodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 176, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, I.F.; Santos, D.R.; Soares, R.R.G.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Chu, V.; Azevedo, A.M.; Conde, J.P. A regenerable microfluidic device with integrated valves and thin-film photodiodes for rapid optimization of chromatography conditions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 3636–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneira, C.R.F.; Santos, D.R.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. Regenerable bead-based microfluidic device with integrated thin-film photodiodes for real-time monitoring of DNA detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 359, 131607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of ABS Component | Abbreviation | Name | Supplier | Purity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salts | Citrate Buffer | Potassium citrate tribasic monohydrate Citric acid 1-hydrate for analysis, ACS, ISO | Acros Organics, Geel, Belgium and Panreac, Chicago, IL, USA | 99 99.5–102.0 |
| Phosphate Buffer | Di-potassium hydrogen phosphate trihydrate Potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate | Scharlau, Barcelona, Spain and Fisher Chemical, Waltham, MA, USA | 98–102 99.95 | |
| Polymers | PEG1000 | Polyethylene glycol (1000) | Alfa Aesar, Haverhill, MA, USA | - |
| PEG2000 | Polyethylene glycol (2000) | Alfa Aesar, Haverhill, MA, USA | - | |
| Ionic Liquids | [C4C1im] Cl | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride | Iolitec, Heilbronn, Germany | 99 |
| [C4C1pyrr] Cl | 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium chloride | Iolitec, Heilbronn, Germany | 99 | |
| [N4444] Cl | Tetrabutylammonium chloride | Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA | ≥97 | |
| [P4444] Cl | Tetrabutylphosphonium chloride | Iolitec, Heilbronn, Germany | >95 | |
| [Ch]Cl | Cholinium chloride | Acros Organics, Geel, Belgium | 99 | |
| [P4444] Br | Tetrabutylphosphonium bromide | Iolitec, Heilbronn, Germany | >95 |
| Solution | Q (uL/min) | t (min) |
|---|---|---|
| Protein G microbeads | 5 | ~2 |
| PBS | 5 | 2 |
| Anti-PSA capture Ab | 0.5 | 10 |
| PSA | 0.5 | 10 |
| BSA 4% (w/v) | 0.5 | 10 |
| Anti-PSA detector Ab–A430 | 0.5 | 10 |
| PBS (intermittent washing) | 5 | 1 |
| Total assay time | ~48 min | |
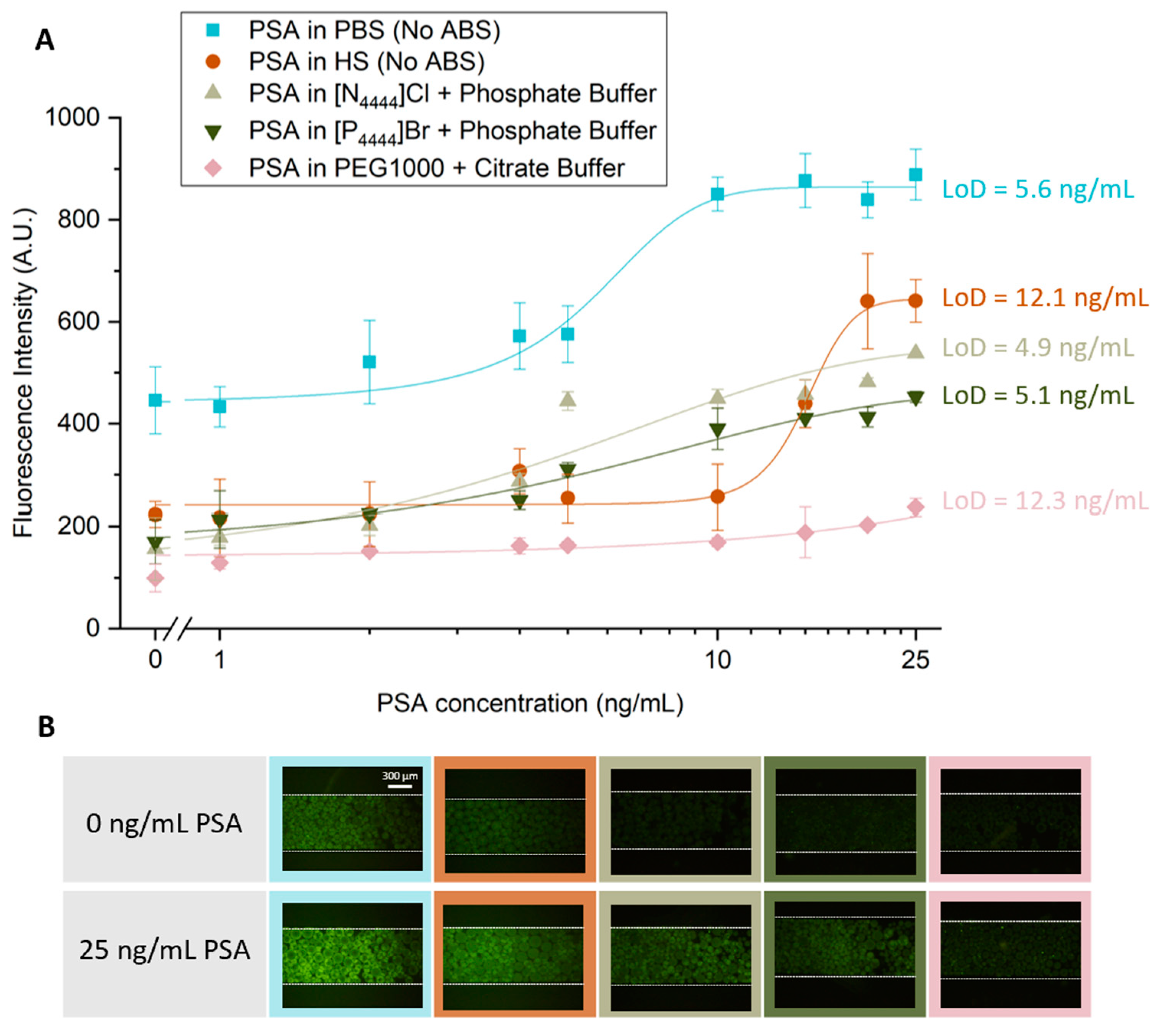
| System | Minimum Concentration of PSA Tested (ng/mL) | Data Correlation (R2) w/ Dose Response Fitting | LoD |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | 1 | 0.9855 | 5.6 |
| HS | 0.9699 | 12.1 | |
| [N4444]Cl + phosphate buffer | 0.9568 | 4.9 | |
| [P4444]Br + phosphate buffer | 0.9944 | 5.1 | |
| PEG1000 + citrate buffer | 0.9457 | 12.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flora, F.C.; Relvas, S.B.; Silva, F.A.e.; Freire, M.G.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. Combined Use of Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems and Microfluidic Devices for the Detection of Prostate-Specific Antigen. Biosensors 2023, 13, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030334
Flora FC, Relvas SB, Silva FAe, Freire MG, Chu V, Conde JP. Combined Use of Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems and Microfluidic Devices for the Detection of Prostate-Specific Antigen. Biosensors. 2023; 13(3):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030334
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlora, Filipa C., Sofia B. Relvas, Francisca A. e Silva, Mara G. Freire, Virginia Chu, and João Pedro Conde. 2023. "Combined Use of Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems and Microfluidic Devices for the Detection of Prostate-Specific Antigen" Biosensors 13, no. 3: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030334
APA StyleFlora, F. C., Relvas, S. B., Silva, F. A. e., Freire, M. G., Chu, V., & Conde, J. P. (2023). Combined Use of Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems and Microfluidic Devices for the Detection of Prostate-Specific Antigen. Biosensors, 13(3), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030334






