Electrochemical Sensing of Urinary Chloride Ion Concentration for Near Real-Time Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Test Solution Preparation
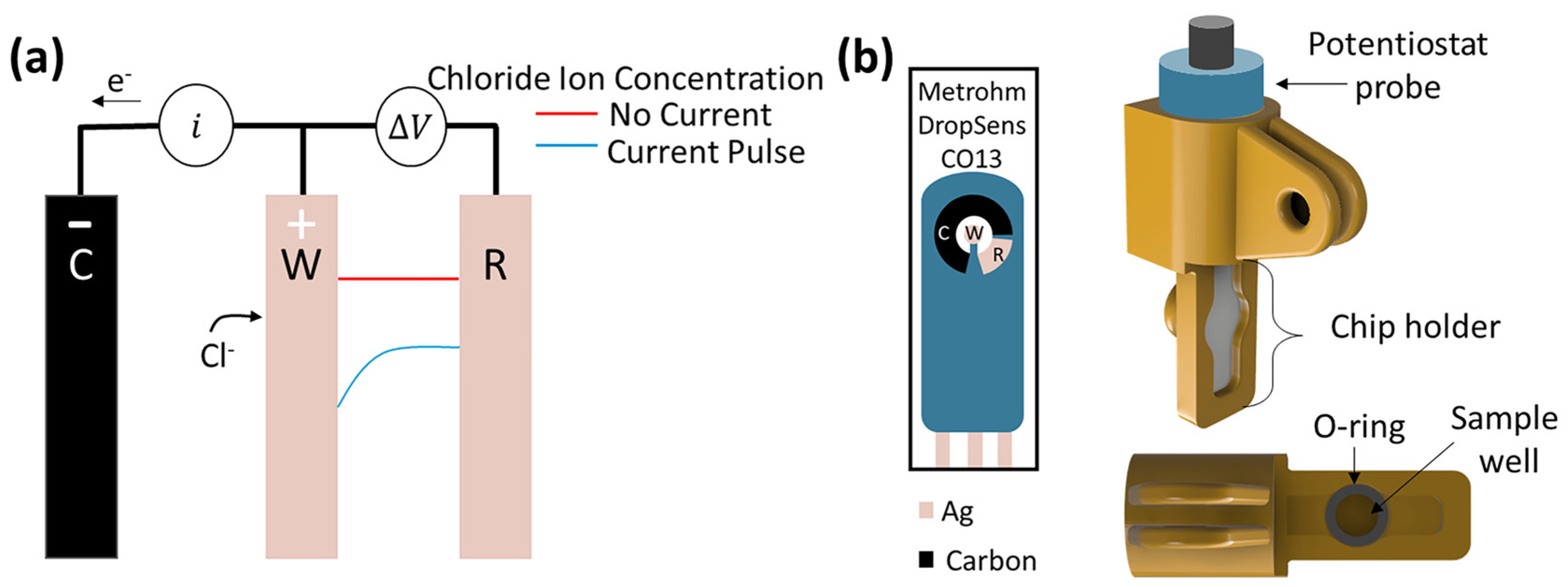
3.2. Sensors and Experimental Setup
3.3. Measurement and Data Analysis
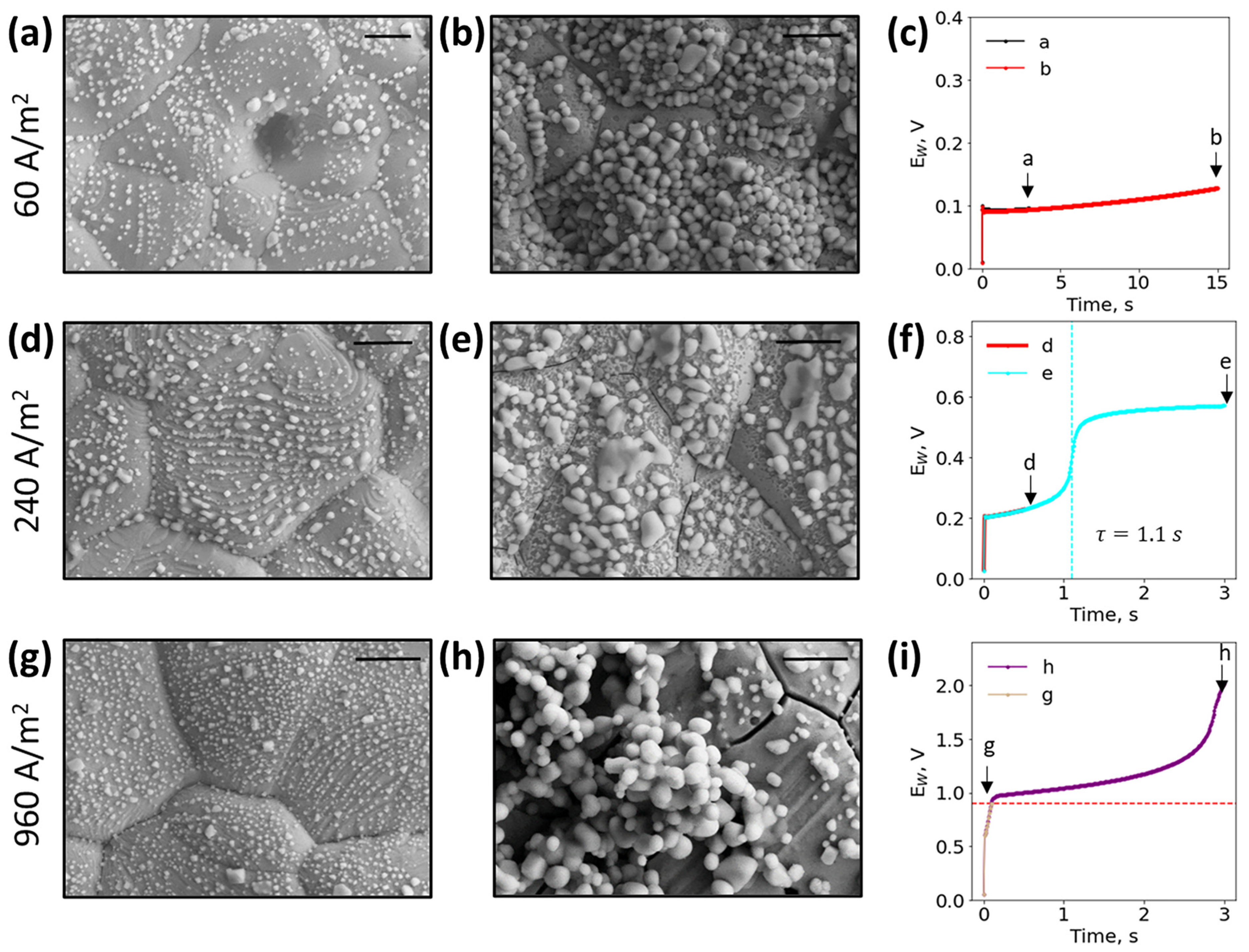
3.4. Electrode Surface Characterization
4. Results and Discussion
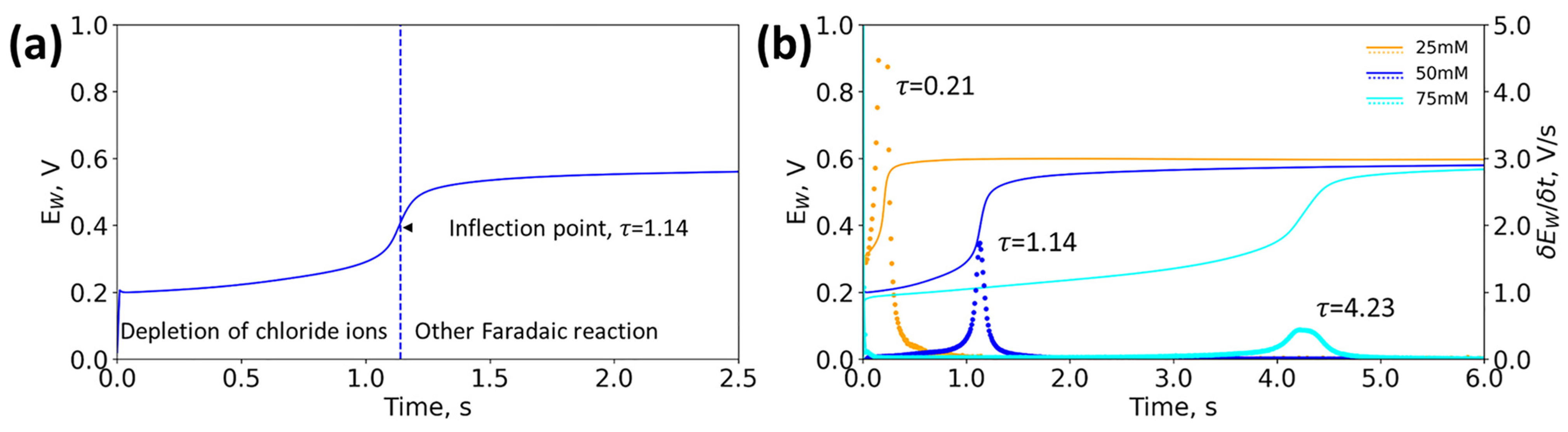
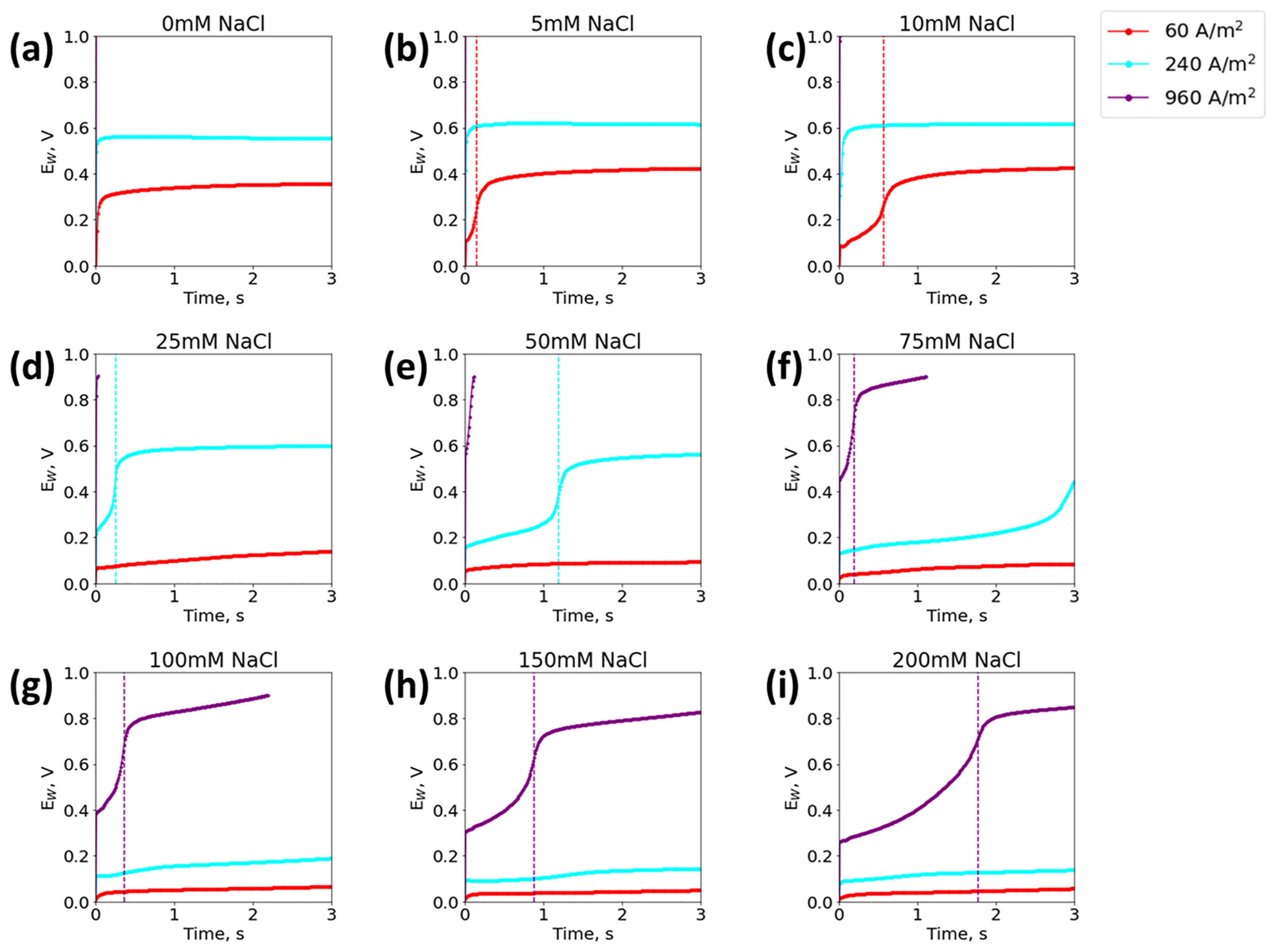
4.1. Detection of Chloride ion Concentration Using Chronopotentiometry
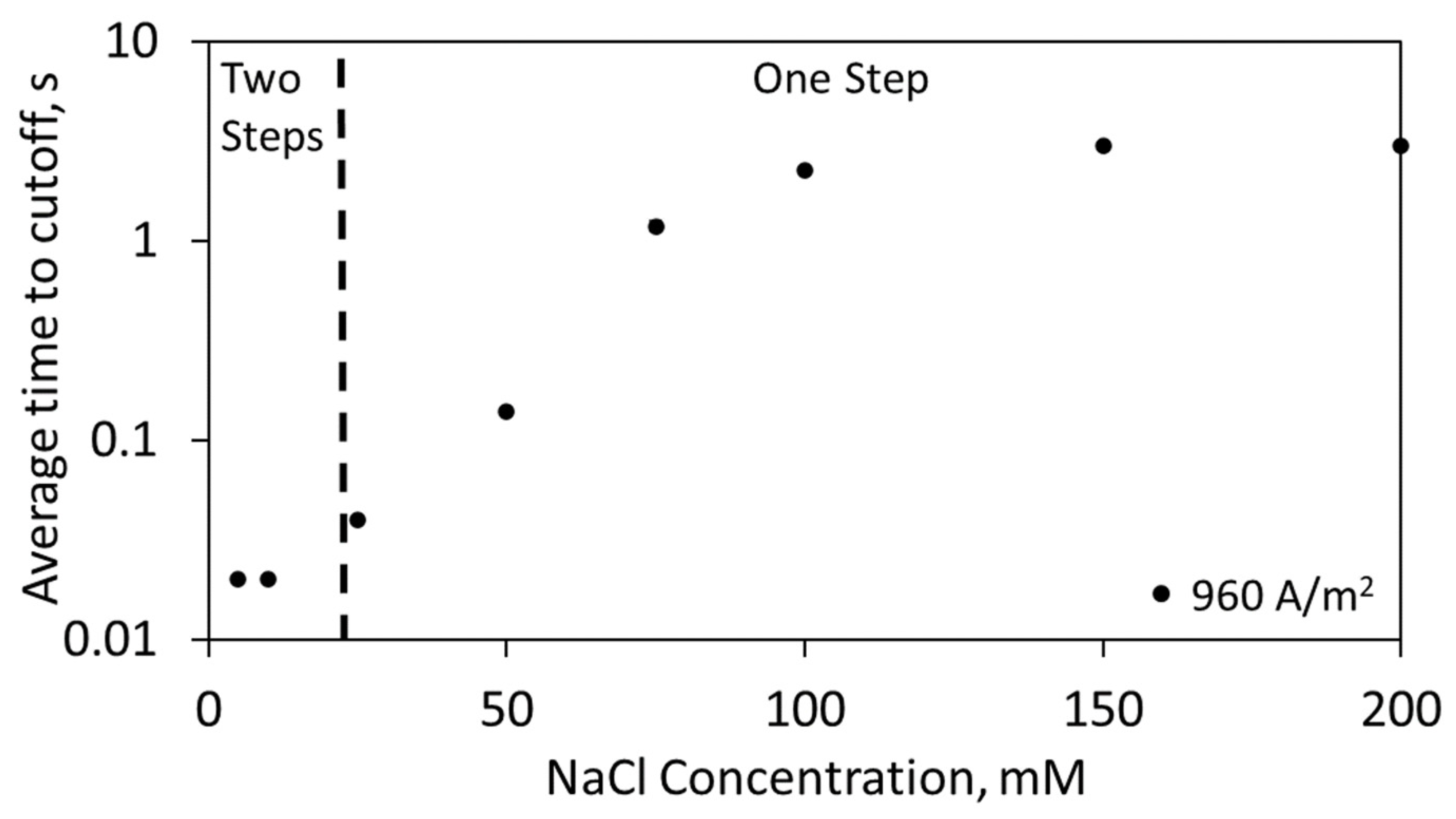
4.2. Current Density Optimization for Detection of Biologically Relevant Chloride Concentration
4.3. Detection of Chloride ion Concentration Using Swept Current Densities
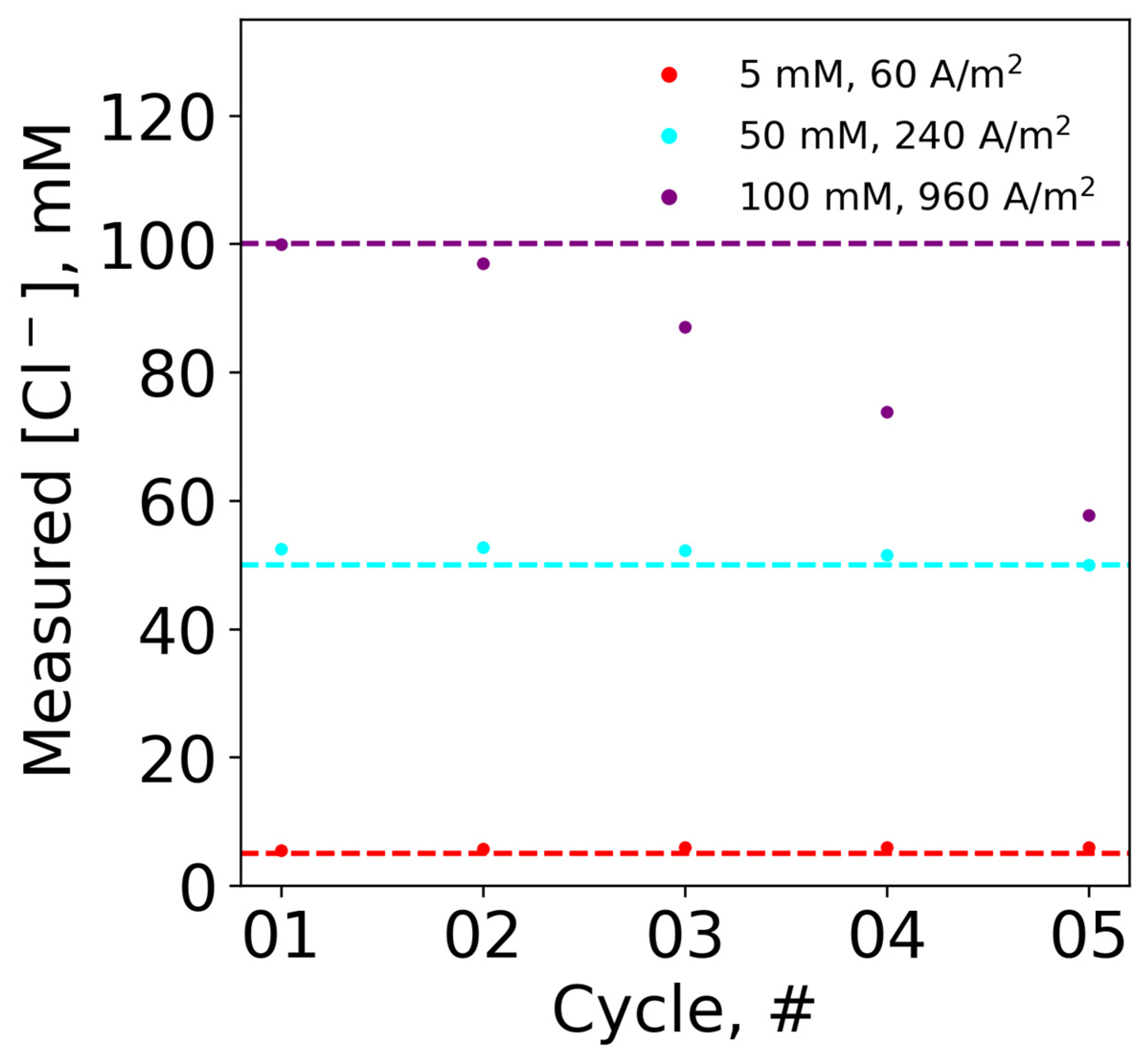
4.4. Sensor Reusability
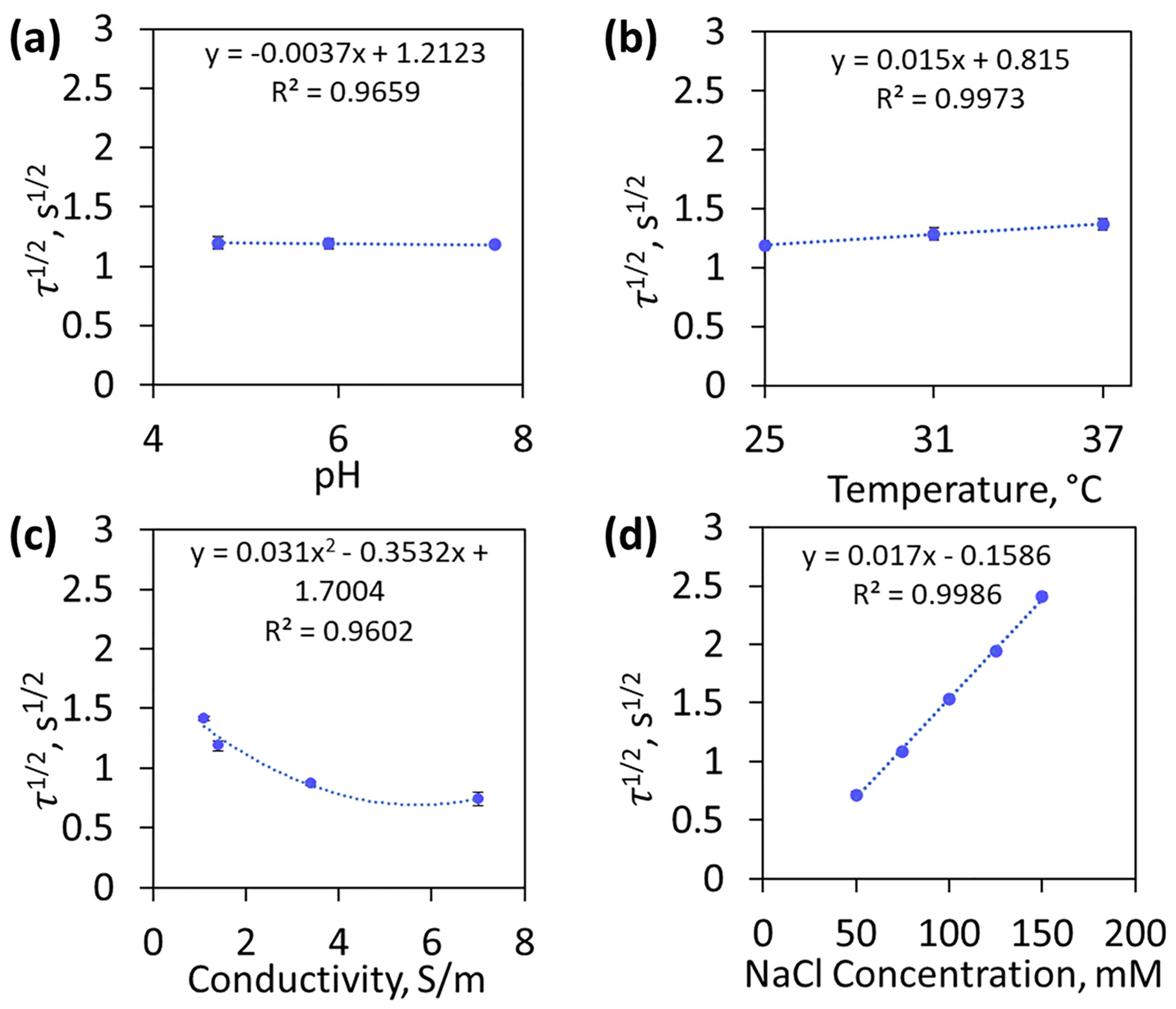
4.5. Effect of Relevant Clinical Parameters on Transition Time
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rein, J.L.; Coca, S.G. “I don’t get no respect”: The role of chloride in acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2019, 316, F587–F605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berend, K.; van Hulsteijn, L.H.; Gans, R.O. Chloride: The queen of electrolytes? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 23, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandak, G.; Kashani, K.B. Chloride in intensive care units: A key electrolyte. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaru, Y.; Doi, K.; Matsuura, R.; Yoshida, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yoshimoto, K.; Nangaku, M. Urinary chloride concentration as a prognostic marker in critically ill patients. Nephrology 2020, 25, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H. Clinical Significance of Spot Urinary Chloride Concentration Measurements in Patients with Acute. Cardio. Open 2021, 6, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Yunos, N.M.; Bellomo, R.; Story, D.; Kellum, J. Bench-to-bedside review: Chloride in critical illness. Crit. Care 2010, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasumathi, R.; Neelamegam, P. Development of Bio-analyzer for the Determination of Urinary Chloride. Sens. Transducers 2010, 119, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Cogswell, M.E.; Loria, C.M.; Chen, T.-C.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Swanson, C.A.; Caldwell, K.L.; Perrine, C.G.; Carriquiry, A.L.; Liu, K.; et al. Urinary Excretion of Sodium, Potassium, and Chloride, but Not Iodine, Varies by Timing of Collection in a 24-Hour Calibration Study. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. The Use of Selected Urine Chemistries in the Diagnosis of Kidney Disorders. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, R.A.; Eisinger, R.P. The use (and misuse) of urinary sodium and chloride measurements. JAMA 1982, 247, 3121–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Leeuw, J.; de Borst, M.H.; Kieneker, L.M.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Rookmaaker, M.B. Separating the effects of 24-hour urinary chloride and sodium excretion on blood pressure and risk of hypertension: Results from PREVEND. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuccio, V.; Pizzini, P.; Parlongo, G.; Caridi, G.; Tripepi, R.; Mafrica, A.; Cutrupi, S.; D’Arrigo, G.; Porto, G.; Garofalo, C.; et al. Urine chloride self-measurement to monitor sodium chloride intake in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeney, N.; Lee, R.; Hockin, B.; Clarke, D.; Sanatani, S.; Armstrong, K.; Sedlak, T.; Claydon, V. At-home determination of 24-h urine sodium excretion: Validation of chloride test strips and multiple spot samples. Auton. Neurosci. 2021, 233, 102797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüngel, M.; Kluthe, R.; Fürst, P. Evaluation of Various Rapid Chloride Tests for Assessing Urinary NaCl Excretion. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2001, 45, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H. Chloride in Heart Failure Syndrome: Its Pathophysiologic Role and Therapeutic Implication. Cardiol. Ther. 2021, 10, 407–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderinezhad, F.; Koydemir, H.C.; Tseng, D.; Karinca, D.; Liang, K.; Ozcan, A.; Tasoglu, S. Sensing of electrolytes in urine using a miniaturized paper-based device. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.S.F.; Diehl, L.O.; Duarte, F.; Santos, M.F.P.; Guimarães, R.C.L.; Dressler, V.L.; Flores, E. Chloride determination by ion chromatography in petroleum coke after digestion by microwave-induced combustion. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1213, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X. Micro-fabricated electrochemical chloride ion sensors: From the present to the future. Talanta 2020, 211, 120734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Cheng, C.; Yuan, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Cui, Z.; et al. Smartphone-based battery-free and flexible electrochemical patch for calcium and chloride ions detections in biofluids. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroshenko, I.; Kirsanov, D.; Kartsova, L.; Sidorova, A.; Borisova, I.; Legin, A. Determination of urine ionic composition with potentiometric multisensor system. Talanta 2015, 131, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attari, A.; Ashton-Miller, J.A.; Delancey, J.O.; Burns, M.A.; Kirkbride, T.M.; Carlin, E.P.; Ramachandran, A.J.; Day, C.A. Uroflowmetry Systems Having Wearable Uroflowmeters, and Methods of Operating the Same. U.S. Patent US20210121112A1, 29 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Jung, M.; Lee, H.; Han, M.S. Development of a fluorescent chemosensor for chloride ion detection in sweat using Ag+-benzimidazole complexes. Dye. Pigment. 2020, 177, 108291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šídlo, M.; Lubal, P.; Anzenbacher, P. Colorimetric Chemosensor Array for Determination of Halides. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujes-Garrido, J.; Arcos-Martínez, M. Development of a wearable electrochemical sensor for voltammetric determination of chloride ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujes-Garrido, J.; Bote, D.I.; Heras, A.; Colina, A.; Arcos-Martínez, M. Determination of halides using Ag nanoparticles-modified disposable electrodes. A first approach to a wearable sensor for quantification of chloride ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1012, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, Y.; Olthuis, W.; van den Berg, A. A chronopotentiometric approach for measuring chloride ion concentration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.; de Graaf, D.B.; Olthuis, W.; van den Berg, A. No more conventional reference electrode: Transition time for determining chloride ion concentration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 821, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, D.B.; Abbas, Y.; Bomer, J.G.; Olthuis, W.; Berg, A.V.D. Sensor–actuator system for dynamic chloride ion determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 888, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Prasad, S. Passively Addressable Ultra-Low Volume Sweat Chloride Sensor. Sensors 2019, 19, 4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Huang, C.-H.; Pai, P.-C.; Seo, J.; Lei, K.F. A Review on Microfluidics-Based Impedance Biosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoh, A.; Rattanarat, P.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O. Simple and selective paper-based colorimetric sensor for determination of chloride ion in environmental samples using label-free silver nanoprisms. Talanta 2018, 178, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheen, H.-J.; Panigrahi, B.; Kuo, T.-R.; Hsu, W.-C.; Chung, P.-S.; Xie, Q.-Z.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-T.; Fan, Y.-J. Electrochemical biosensor with electrokinetics-assisted molecular trapping for enhancing C-reactive protein detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Nguyen, U.T.N.; Hsieh, H.-Y.; Tahara, H.; Chang, Y.-S.; Wang, B.-Y.; Gu, B.-C.; Dai, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Tsai, I.-J.; et al. Peptide-based electrochemical sensor with nanogold enhancement for detecting rheumatoid arthritis. Talanta 2022, 236, 122886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.-J.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Gu, B.-C.; Wu, C.-C. Voltammetric measurement of Escherichia coli concentration through p-APG hydrolysis by endogenous β-galactosidase. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.-H.; Cheng, W.-L.; Muthuraman, G.; Hsu, C.-T.; Chung, H.-H.; Zen, J.-M. A disposable screen-printed silver strip sensor for single drop analysis of halide in biological samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3008–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, A.; Rice, P.; Lin, K.-C.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. A Combinatorial Electrochemical Biosensor for Sweat Biomarker Benchmarking. SLAS Technol. Transl. Life Sci. Innov. 2020, 25, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Cai, H.; Fang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Wearable and flexible electrochemical sensors for sweat analysis: A review. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Lv, Z.; He, Y.; Cheng, L.; Qiu, Y.; Huang, X.; Ding, C.; Wu, H.; Liu, A. In-situ admittance sensing of sweat rate and chloride level in sweat using wearable skin-interfaced microfluidic patch. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergveld, P.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; Olthuis, W. Detection of protein concentrations with chronopotentiometry. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1997, 12, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R.; White, H.S. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Adamson, A. A Textbook of Physical Chemistry; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, J.; Thomas-Alyea, K.E. Electrochemical Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Marickar, Y.M.F. Electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids in urine. Urol. Res. 2010, 38, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-C.; Burns, M.A. Low-power micro-fabricated liquid flow-rate sensor. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 3981–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-C.; Brondum, K.; Monroe, C.W.; Burns, M.A. Multifunctional Water Sensors for pH, ORP, and Conductivity Using Only Microfabricated Platinum Electrodes. Sensors 2017, 17, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delange, F.; Benoist, B.d.; Bürgi, H. Determining median urinary iodine concentration that indicates adequate iodine intake at population level. Bull. World Health Organ. 2002, 80, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nelson, A.M.; Habibi, S.; DeLancey, J.O.L.; Ashton-Miller, J.A.; Burns, M.A. Electrochemical Sensing of Urinary Chloride Ion Concentration for Near Real-Time Monitoring. Biosensors 2023, 13, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030331
Nelson AM, Habibi S, DeLancey JOL, Ashton-Miller JA, Burns MA. Electrochemical Sensing of Urinary Chloride Ion Concentration for Near Real-Time Monitoring. Biosensors. 2023; 13(3):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030331
Chicago/Turabian StyleNelson, Anna M., Sanaz Habibi, John O. L. DeLancey, James A. Ashton-Miller, and Mark A. Burns. 2023. "Electrochemical Sensing of Urinary Chloride Ion Concentration for Near Real-Time Monitoring" Biosensors 13, no. 3: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030331
APA StyleNelson, A. M., Habibi, S., DeLancey, J. O. L., Ashton-Miller, J. A., & Burns, M. A. (2023). Electrochemical Sensing of Urinary Chloride Ion Concentration for Near Real-Time Monitoring. Biosensors, 13(3), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030331






