Fabrication of an Azithromycin Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
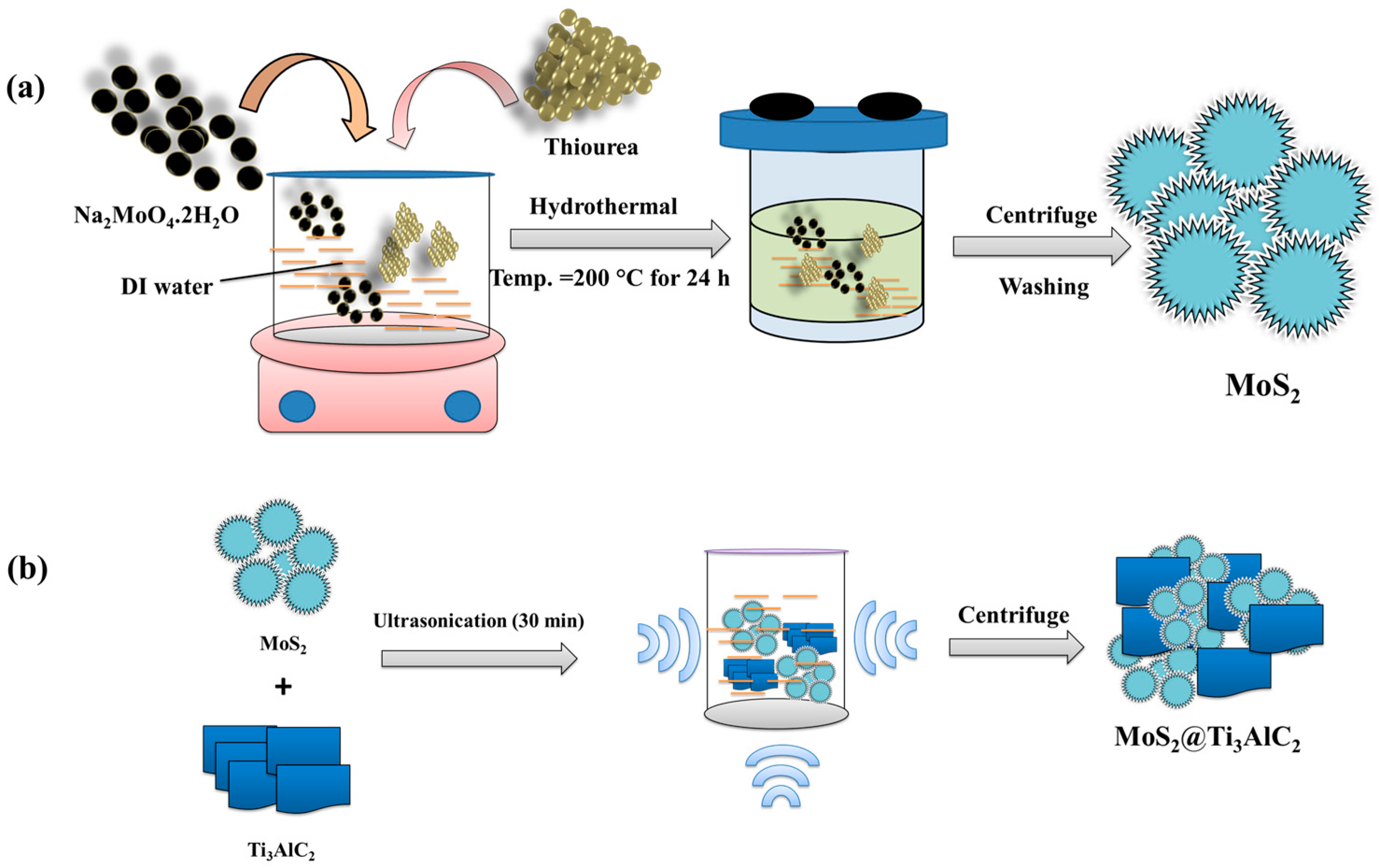
2.1. Synthesis of MoS2@Ti3AlC2
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Materials
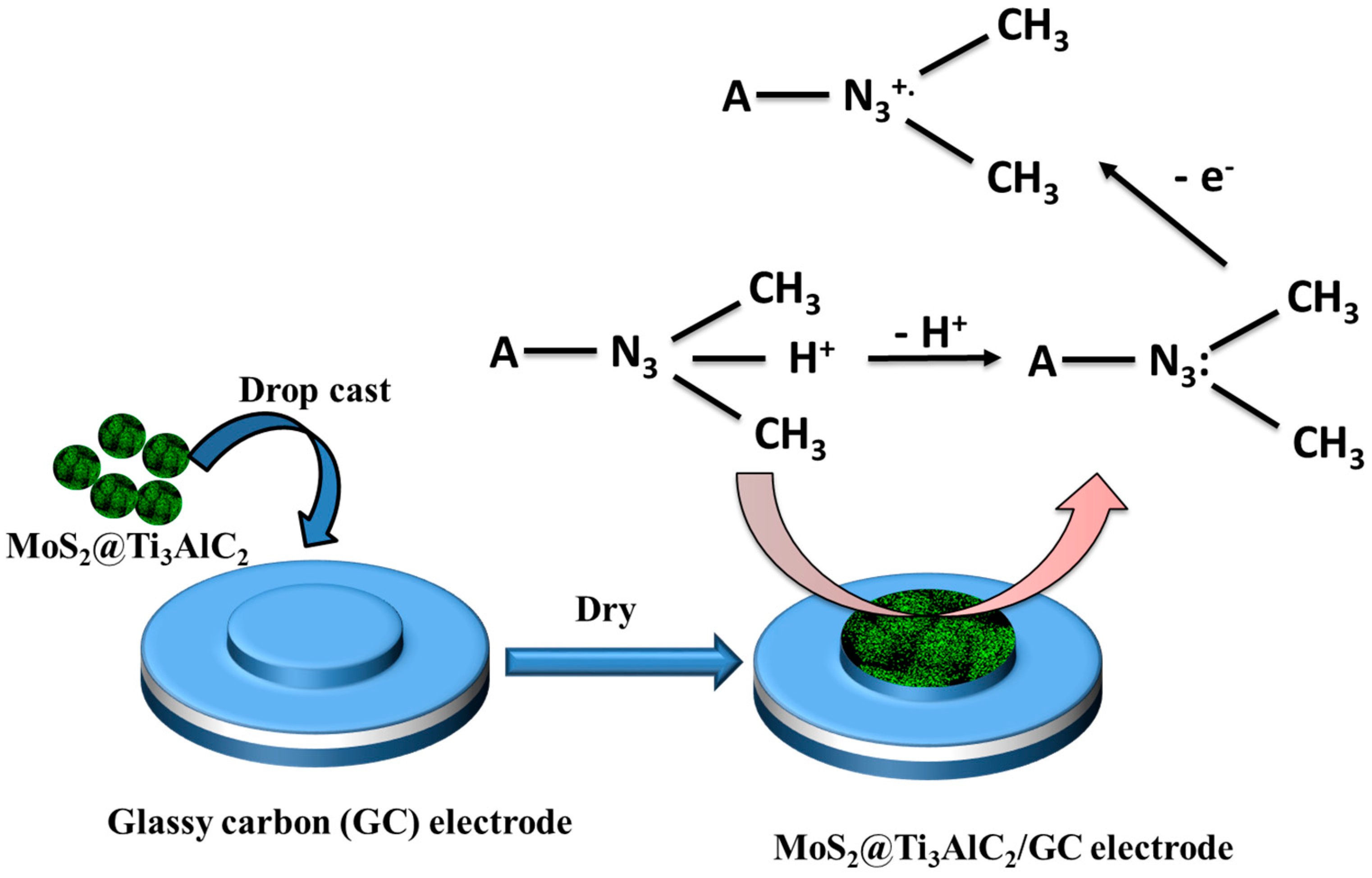
2.4. Fabrication of the Sensor
3. Results and Discussion
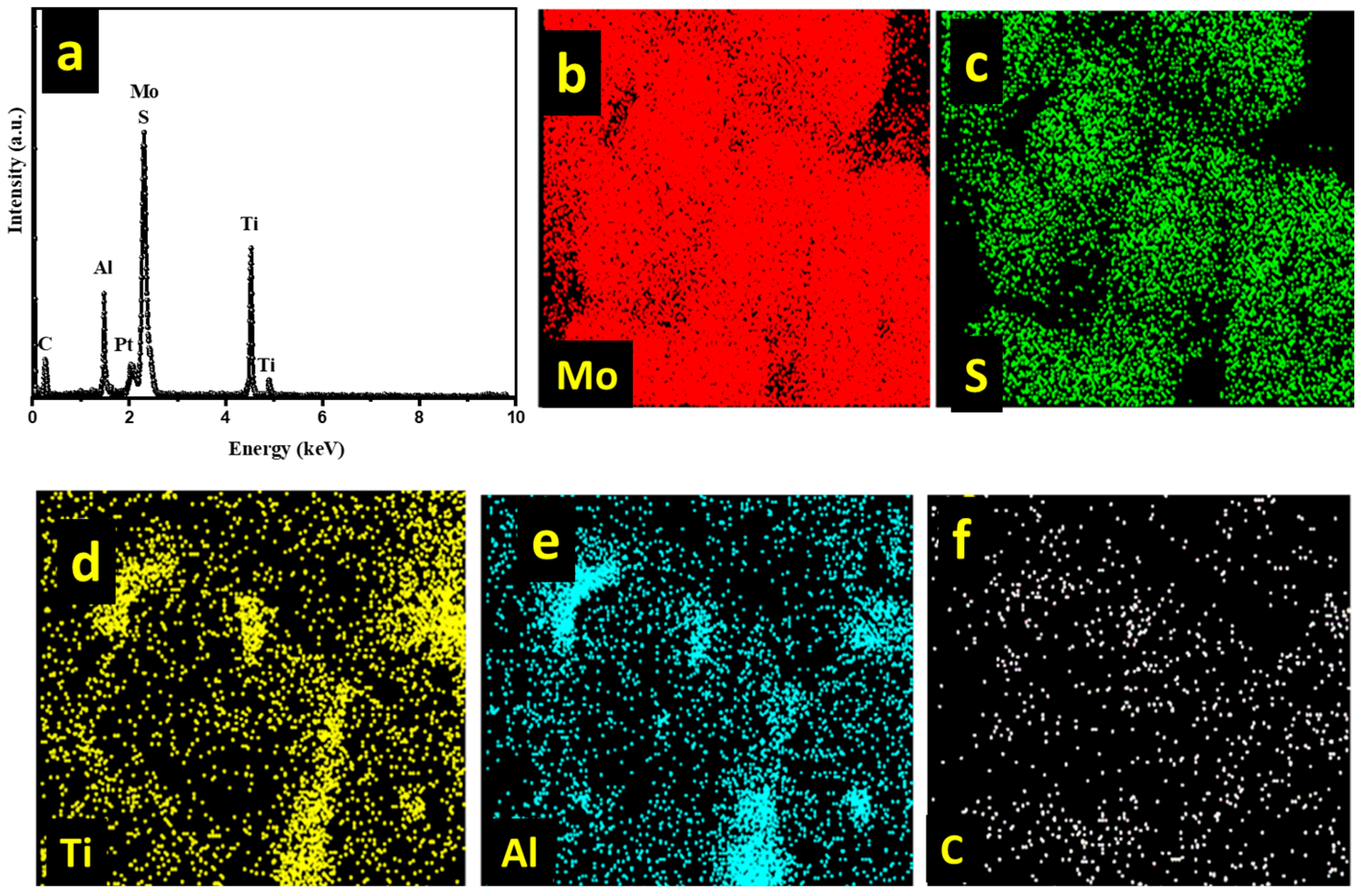
3.1. Material Characterization
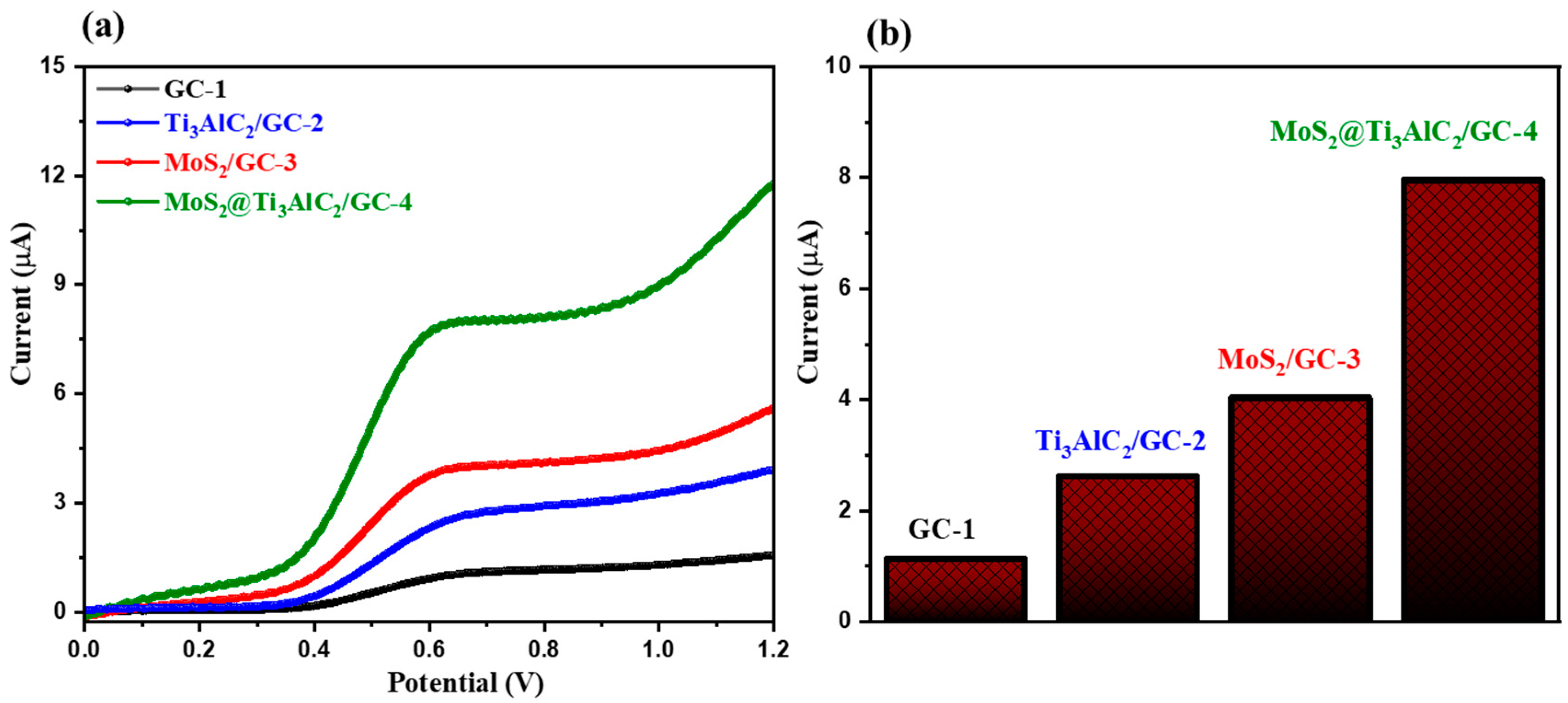
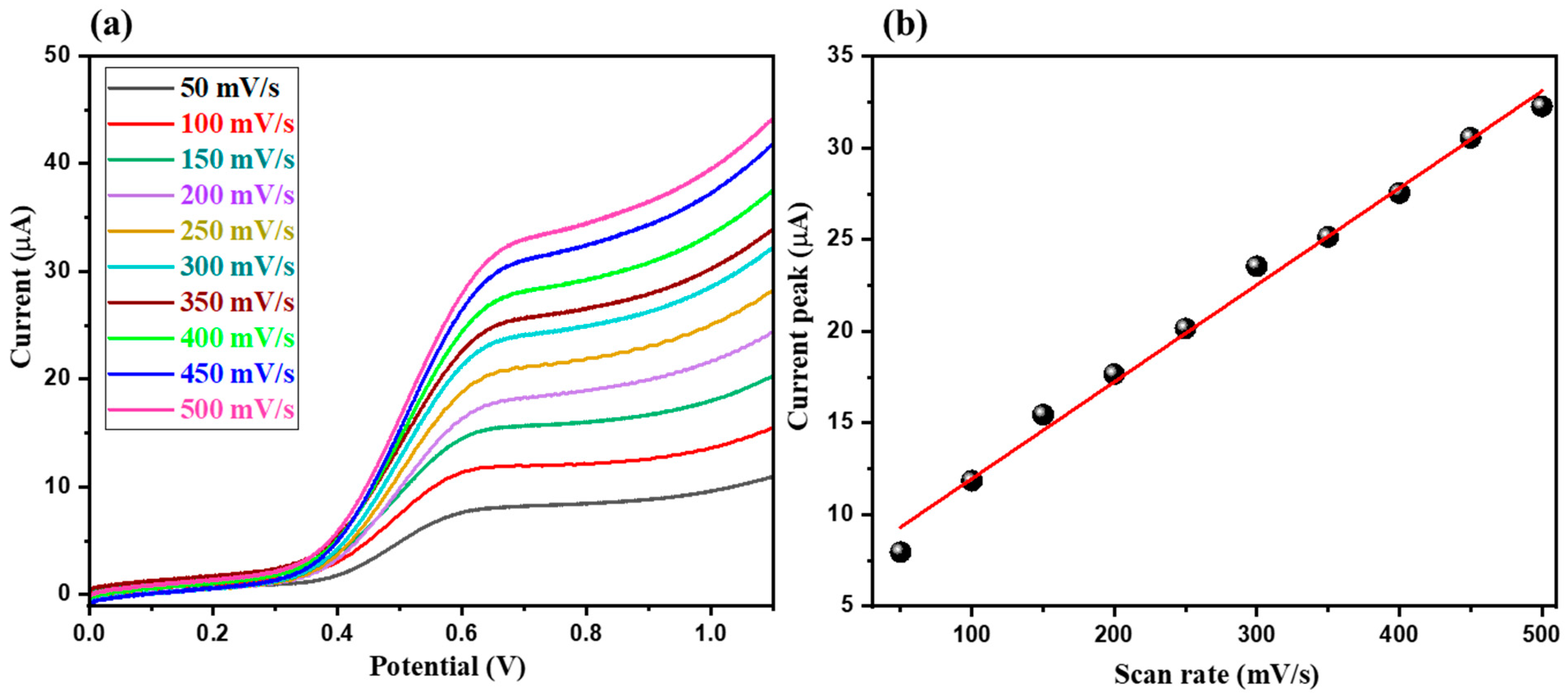
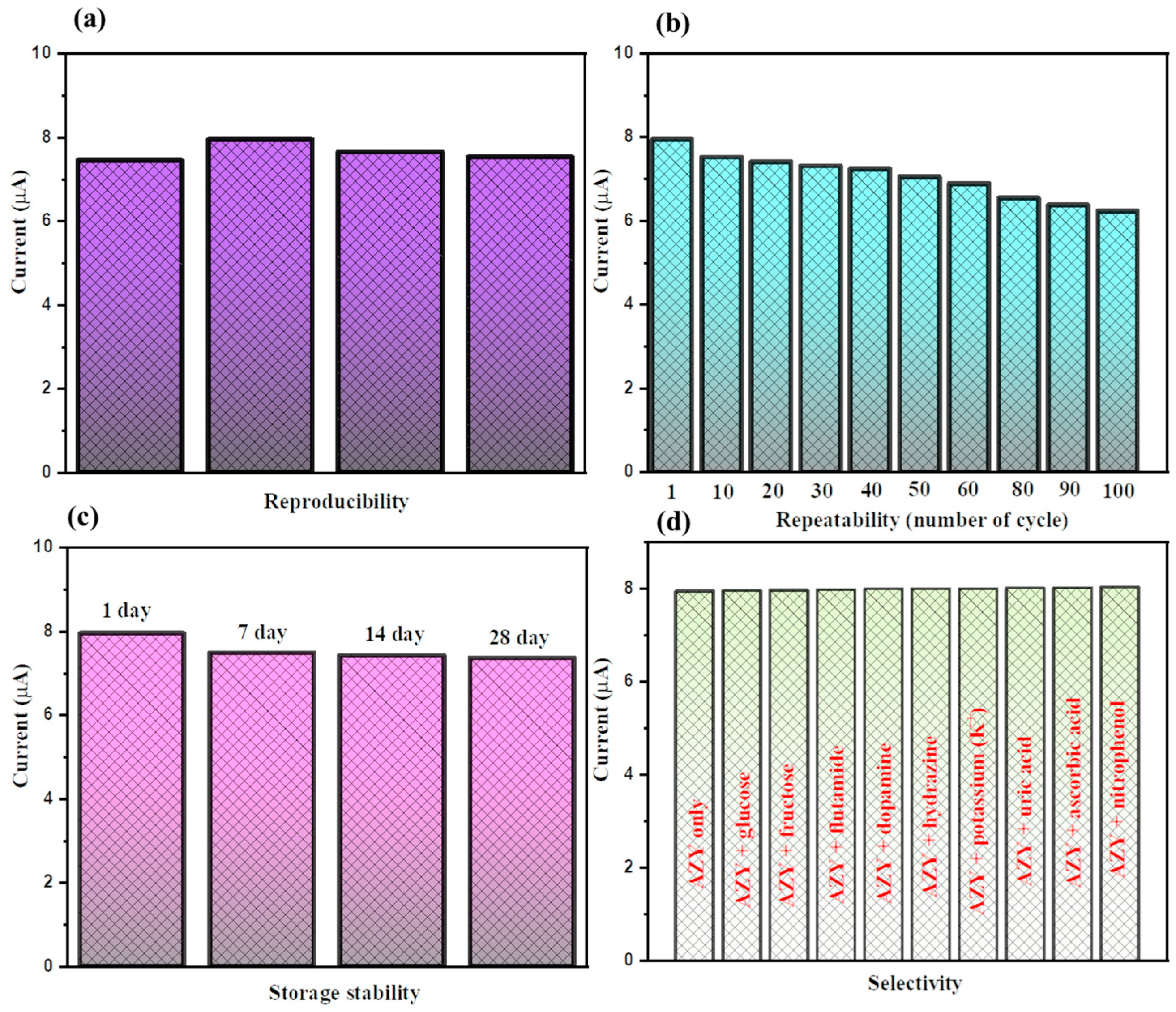
3.2. Electrochemical Sensing Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, W.A.; Murray, K.T.; Hall, K.; Arbogast, P.G.; Stein, C.M. Azithromycin and the Risk of Cardiovascular Death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, N.-T.; Tran, C.-S.; Nguyen, T.-L.; Hoang, T.; Trinh, T.-D.; Nguyen, T.-N. Formulation and biopharmaceutical evaluation of bitter taste masking microparticles containing azithromycin loaded in dispersible tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 126, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanstrom, H.; Pasternak, B.; Hviid, A. Use of azithromycin and death from cardiovascular causes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnham, M.J.; Haber, V.E.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Perletti, G.; Verleden, G.M.; Vos, R. Azithromycin: Mechanisms of action and their relevance for clinical applications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 143, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ji, X.; Hu, S. Studies on electrochemical oxidation of azithromycin and its interaction with bovine serum albumin. Bioelectrochemistry 2004, 64, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenez, J.-P.; Van Bambeke, F.; Piret, J.; Schanck, A.; Brasseur, R.; Tulkens, P.M.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.-P. Interaction of the macrolide azithromycin with phospholipids. II. Biophysical and computer-aided conformational studies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 314, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, V.; Johnston, S.L.; Edwards, M.R. Azithromycin induces anti-viral responses in bronchial epithelial cells. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorin, E.; Dai, M.; Shulman, E.; Wadhwani, L.; Bar-Cohen, R.; Barbhaiya, C.; Aizer, A.; Holmes, D.; Bernstein, S.; Spinelli, M.; et al. The QT interval in patients with COVID-19 treated with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 808–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.; Jayaram, L.; Karalus, N.; Eaton, T.; Tong, C.; Hockey, H.; Milne, D.; Fergusson, W.; Tuffery, C.; Sexton, P.; et al. Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (EMBRACE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauriola, M.; Pani, A.; Ippoliti, G.; Mortara, A.; Milighetti, S.; Mazen, M.; Perseghin, G.; Pastori, D.; Grosso, P.; Scaglione, F. Effect of combination therapy of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on mortality in COVID-19 patients. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, S.; Kilgore, P.; Chaudhry, Z.S.; Jacobsen, G.; Wang, D.D.; Huitsing, K.; Brar, I.; Alangaden, G.J.; Ramesh, M.S.; McKinnon, J.E.; et al. Treatment with hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, and combination in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 97, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Saleh, M.; Gabriels, J.; Ismail, H.; Goldner, B.; Willner, J.; Beldner, S.; Mitra, R.; John, R.; Epstein, L.M. Inpatient Use of Ambulatory Telemetry Monitors for COVID-19 Patients Treated with Hydroxychloroquine and/or Azithromycin. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2992–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paula, C.E.R.; Almeida, V.G.K.; Cassella, R.J. Novel spectrophotometric method for the determination of azithromycin in pharmaceutical formulations based on its charge transfer reaction with quinalizarin. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 21, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrer, J.; Cova, F. “Quick and dirty”: Intuitive cognitive style predicts trust in Didier Raoult and his hydroxychloroquine-based treatment against COVID-19. Judgm. Decis. Mak. 2020, 15, 889–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Mohammad, A.; Rajak, R.; Mobin, S.M. Construction of TiO2nanosheets modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE/TiO2) for the detection of hydrazine. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 074005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Khan, M.Q.; Khan, R.A.; Kim, H. Benign approach for the synthesis of ZnO hexagonal plates for electrochemical sensing of l-tryptophan. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 287, 126297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Kim, H. Synthesis of MoS2/WO3 hybrid composite for hydrazine sensing applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 148, 106803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Q.; Ahmad, K.; Alsalme, A.; Kim, H. Hydrothermal synthesis of nanostructured NiO for hydrazine sensing application. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 289, 126463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, W.; Ahmad, K.; Kim, H. Nitrogen-doped graphene as an efficient metal-free catalyst for ammonia and non-enzymatic glucose sensing. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 160, 110359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Guo, H.; Fan, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Guan, Q.; Wu, N.; Cao, Y.; Yang, W. MoS2/Ni(OH)2 composites derived from in situ grown Ni-MOF coating MoS2 as electrode materials for supercapacitor and electrochemical sensor. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 615, 126178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, P.; Ge, Y.; Wu, R.; Xue, T.; Sheng, Y.; Ai, S.; Tang, K.; Wen, Y. MoS2/MWCNTs porous nanohybrid network with oxidase-like characteristic as electrochemical nanozyme sensor coupled with machine learning for intelligent analysis of carbendazim. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 862, 113940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cai, H.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Ma, D.; Gao, Q. Hierarchical Mo2C@MoS2 nanorods as electrochemical sensors for highly sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide and cancer cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 311, 127863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xing, Y.; Fei, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T. The synergistic effects of MoS2 and reduced graphene oxide on sensing performances for electrochemical chloramphenicol sensor. FlatChem 2022, 33, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megalamani, M.B.; Patil, Y.N.; Nandibewoor, S.T. Electrochemical sensing of carcinogenic p-dimethylamino antipyrine using sensor comprised of eco-friendly MoS2 nanosheets encapsulated by PVA capped Mn doped ZnS nanoparticle. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 151, 110617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütfi Yola, M. Carbendazim imprinted electrochemical sensor based on CdMoO4/gC3N4 nanocomposite: Application to fruit juice samples. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehru, R.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. In-situ growth of MoS2 nanosheets on g-C3N4 nanotube: A novel electrochemical sensing platform for vanillin determination in food samples. Carbon 2023, 208, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. Construction of MoS2-nitrogen-deficient graphitic carbon nitride anode toward high performance sodium-ions batteries. Mater. Lett. 2020, 273, 127890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Treifeldt, J.E.; Firestein, K.L.; Fernando, J.F.; Zhang, C.; Siriwardena, D.P.; Lewis, C.-E.M.; Golberg, D.V. The effect of Ti3AlC2 MAX phase synthetic history on the structure and electrochemical properties of resultant Ti3C2 MXenes. Mater. Des. 2021, 199, 109403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, G.; Hai, A.; Rambabu, K.; Pazhanivel, T.; Hasan, S.W.; Banat, F. Designed assembly of Ni/MAX (Ti3AlC2) and porous graphene-based asymmetric electrodes for capacitive deionization of multivalent ions. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 129048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, M.W.; Radovic, M. Elastic and Mechanical Properties of the MAX Phases. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2011, 41, 195–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zou, X.; Hu, Y.; Lu, X.; Xiong, X.; Xu, Q.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, Z. Electrochemical Reduction of TiO2/Al2O3/C to Ti3AlC2 and Its Derived Two-Dimensional (2D) Carbides. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, E97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, H.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Qi, F.; Ouyang, X.; Zhao, N. Microstructure, mechanical and electrochemical properties of Ti3AlC2 coatings prepared by filtered cathode vacuum arc technology. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 2073–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, D.; Yang, M.; Tian, J.; Tao, R.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Wang, R. Cathode catalyst selection for enhancing oxygen reduction reactions of microbial fuel cells: COF-300@ NiAl-LDH/GO and Ti3AlC2/NiCoAl-LDH. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 16179–16188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwaran, S.; Balaji, R.; Chen, S.-M.; Liao, Y.-C.; Chandrasekar, N.; Ethiraj, S.; Samuel, M.S. Fabrication of 2D–0D Ti3AlC2@SmVO4 heterojunction nanocomposites for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of sulfathiazole in environmental samples. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Tao, Y.; Jin, H.; Song, B.; Jing, T.; Luo, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lee, Y.-I.; Mei, S.; et al. Fabrication of a selective and sensitive sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer/acetylene black for the determination of azithromycin in pharmaceuticals and biological samples. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Zhou, T.; Feng, J.; Jin, H.; Tao, Y.; Luo, D.; Mei, S.; Lee, Y.-I. A rapid and sensitive molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence sensor for azithromycin determination in biological samples. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 813, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Dehghani, M.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Azimzadeh, M. An azithromycin electrochemical sensor based on an aniline MIP film electropolymerized on a gold nano urchins/graphene oxide modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 829, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoian, I.-A.; Iacob, B.-C.; Duda, C.-L.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Bogdan, D.; Marian, I.O.; Bodoki, E.; Oprean, R. Biomimetic electrochemical sensor for the highly selective detection of azithromycin in biological samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 155, 112098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lu, L.; Wen, Y.; Xu, J.; Duan, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.; Nie, T. Facile synthesis of the necklace-like graphene oxide-multi-walled carbon nanotube nanohybrid and its application in electrochemical sensing of Azithromycin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 787, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Techniques | LOD (µM) | Sensitivity (µA/µM.cm2) | Linear Range (µM) | Detection Process | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoS2@Ti3AlC2 | LSV | 0.009 | 6.77 | 0.05–25 | oxidation | This study |
| MIP/acetylene black | DPV | 0.07 | - | 0.1–20 | oxidation | [35] |
| MIP/CPE | electrochemiluminescence | 2.3 | - | 1–100 | oxidation | [36] |
| gold nano-urchin/GO | DPV | 0.1 | - | 0.3–920 | oxidation | [37] |
| MIP/2,2‘-bithiophene/3-thienyl boronic acid | EIS | 0.85 | - | 13.33–66.67 | oxidation | [38] |
| GO/MWCNT | LSV | 0.07 | - | 0.1–10 | oxidation | [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niyitanga, T.; Khan, M.Q.; Ahmad, K.; Khan, R.A. Fabrication of an Azithromycin Sensor. Biosensors 2023, 13, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110986
Niyitanga T, Khan MQ, Ahmad K, Khan RA. Fabrication of an Azithromycin Sensor. Biosensors. 2023; 13(11):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110986
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiyitanga, Theophile, Mohd Quasim Khan, Khursheed Ahmad, and Rais Ahmad Khan. 2023. "Fabrication of an Azithromycin Sensor" Biosensors 13, no. 11: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110986
APA StyleNiyitanga, T., Khan, M. Q., Ahmad, K., & Khan, R. A. (2023). Fabrication of an Azithromycin Sensor. Biosensors, 13(11), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110986





