Implementation of an Integrated Dielectrophoretic and Magnetophoretic Microfluidic Chip for CTC Isolation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
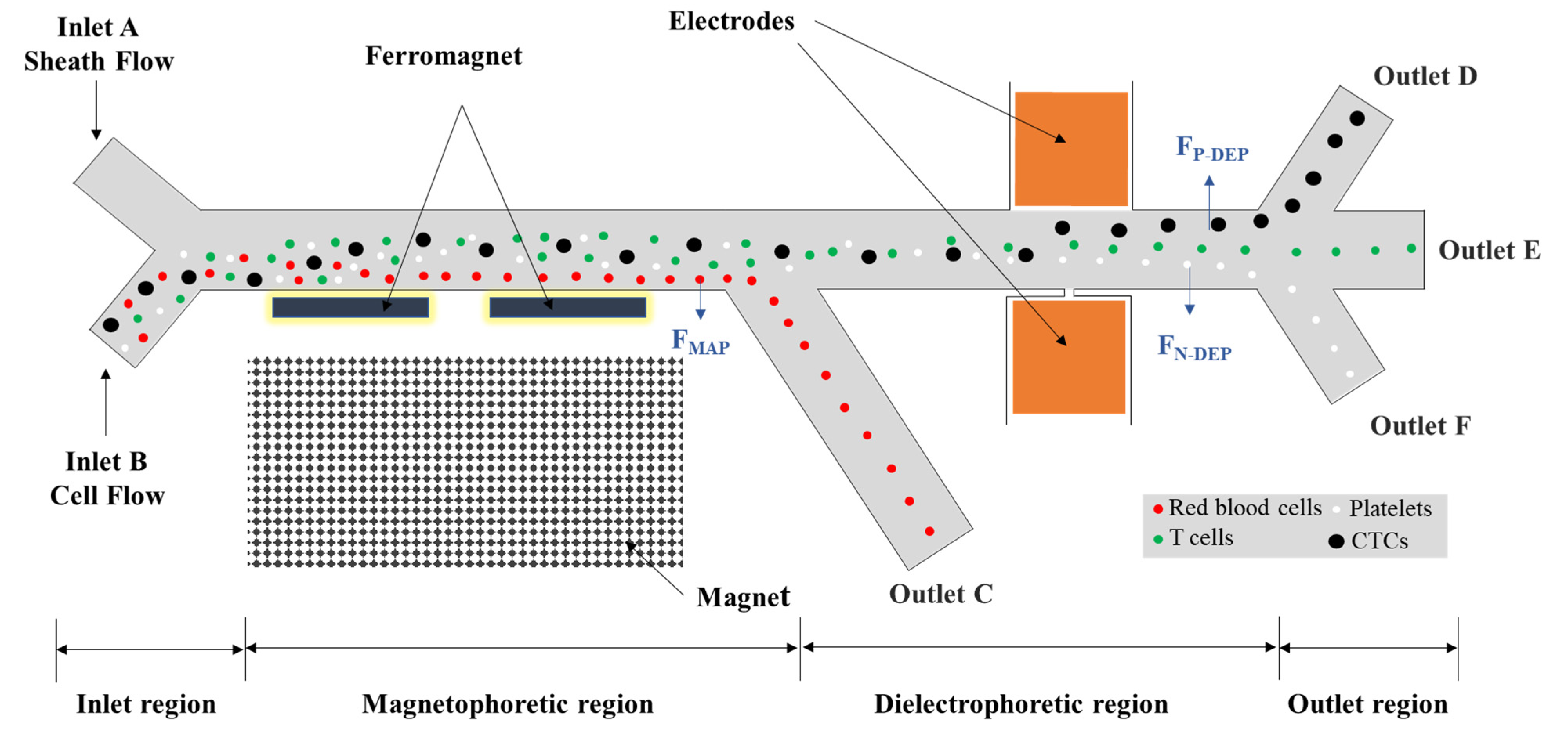
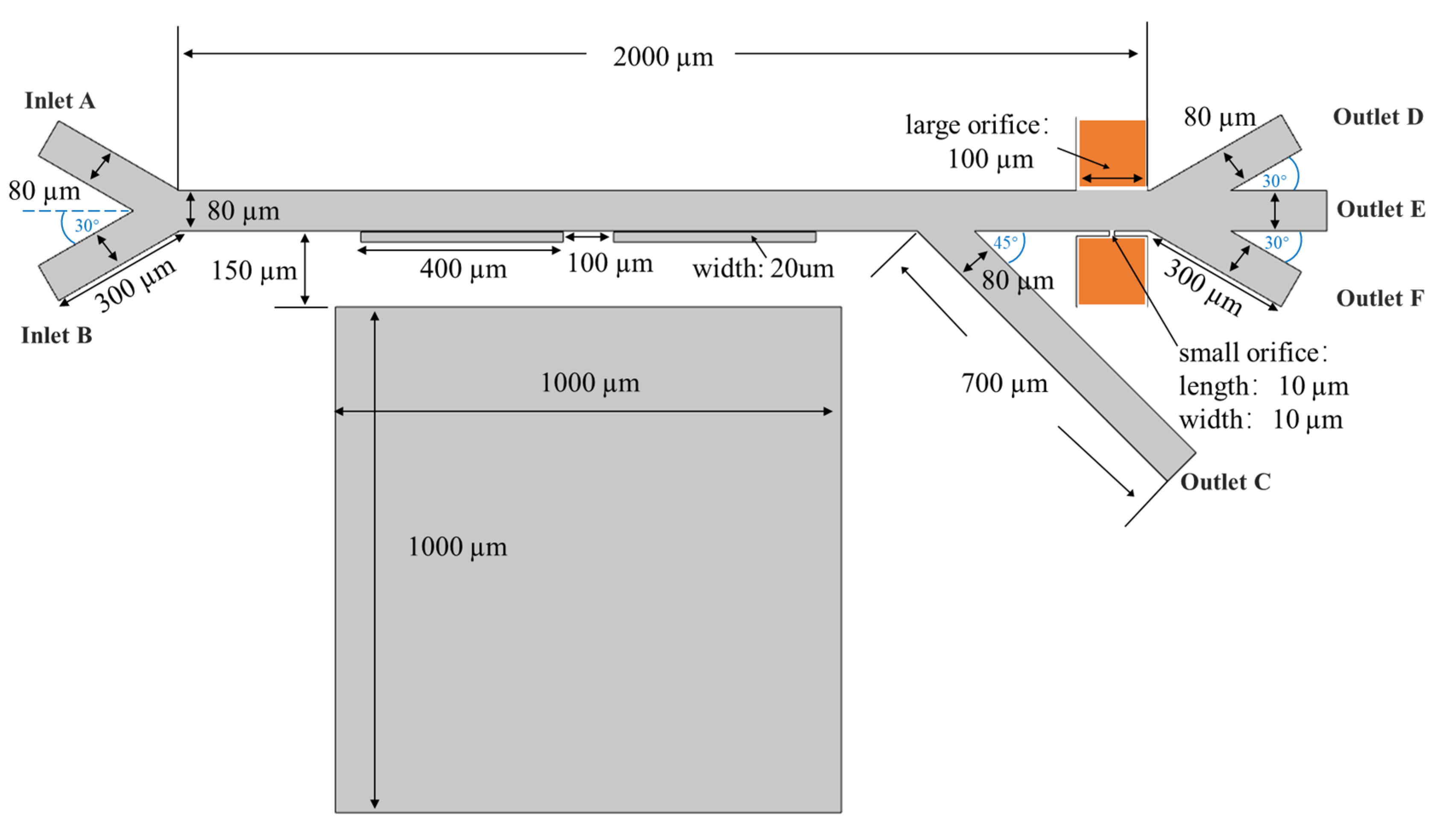
2.1. Separation Mechanism
2.2. Physical and Mathematical Models
2.2.1. The Flow Field
2.2.2. The Magnetic Field
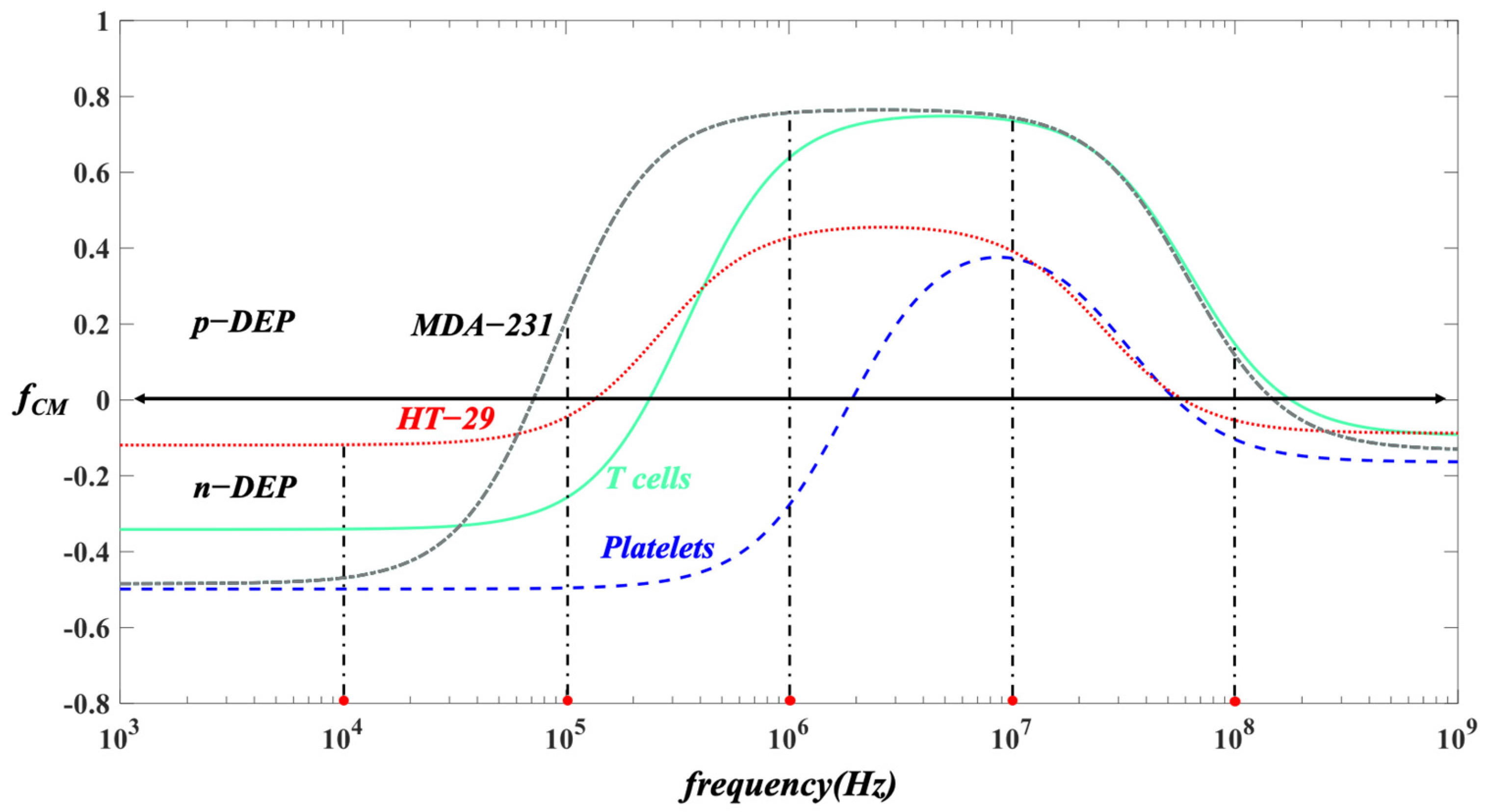
2.2.3. The Electric Field
2.2.4. Particle Tracing
2.3. Numerical Simulation
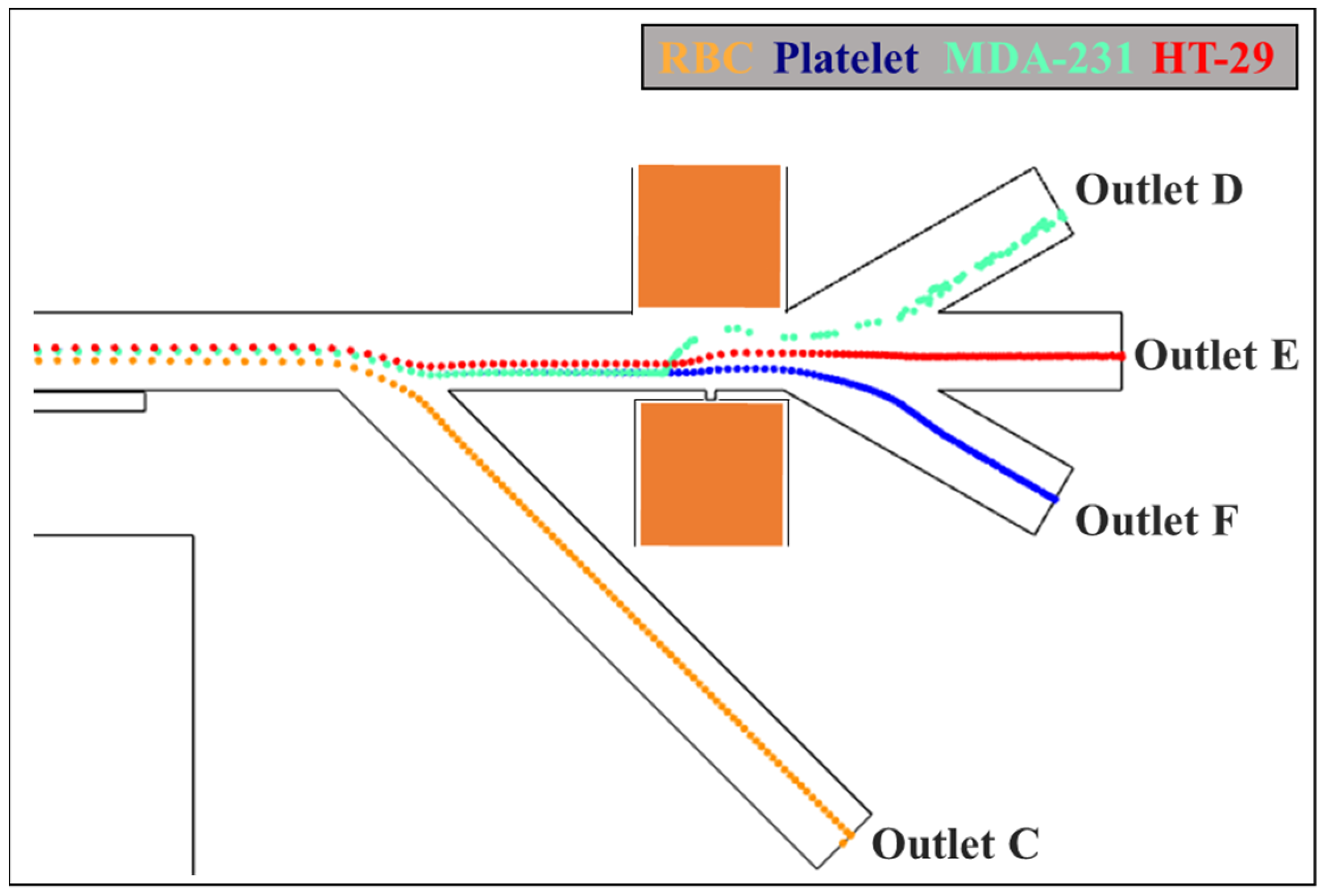
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of the Ferromagnet Structure on the Magnetic Field
3.2. The Effect of the Flow Rate
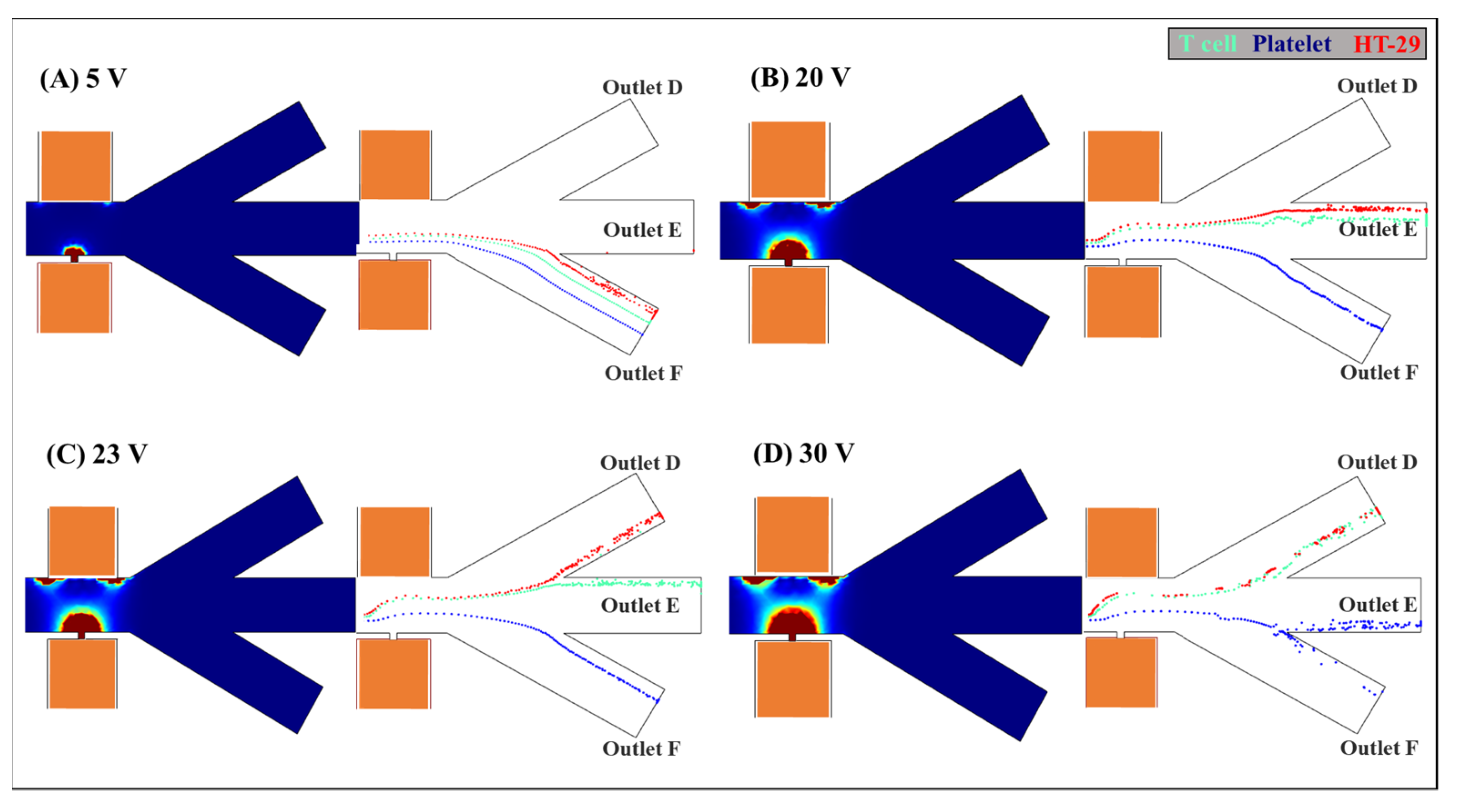
3.3. The Effect of the Applied Voltage
3.4. Isolation of CTCs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Zheng, X.L.; Hu, N.; Yang, J.; Luo, H.Y.; Jiang, F.; Liao, Y.J. Research Progress on Microfluidic Chip of Cell Separation Based on Dielectrophoresis. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 43, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt Shields Iv, C.; Reyes, C.D.; López, G.P. Microfluidic Cell Sorting: A Review of the Advances in the Separation of Cells from Debulking to Rare Cell Isolation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1230–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, S.H.; Edd, J.; Stoddard, A.E.; Wong, K.H.K.; Fachin, F.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A.; Stott, S.L.; Kapur, R.; Toner, M. Microfluidic Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters by Size and Asymmetry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Guan, G.; Luan, K.B.; Lee, W.C.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Kant Chaudhuri, P.; Tan, D.S.W.; Lim, W.T.; Lee, S.C.; Chen, P.C.Y.; et al. Slanted Spiral Microfluidics for the Ultra-Fast, Label-Free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Relationship of Circulating Tumor Cells to Tumor Response, Progression-Free Survival, and Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, R.; Shamloo, A.; Akbari, J.; Tebon, P.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Ahadian, S. Design and Simulation of an Integrated Centrifugal Microfluidic Device for CTCs Separation and Cell Lysis. Micromachines 2020, 11, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzenberg, L.A.; Parks, D.; Sahaf, B.; Perez, O.; Roederer, M.; Herzenberg, L.A. The History and Future of the Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorter and Flow Cytometry: A View from Stanford. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.; Pavlath, G.K.; Parks, D.R.; Walsh, F.S.; Blau, H.M. Isolation of Human Myoblasts with the Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorter. Exp. Cell Res. 1988, 174, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Han, L.; Yang, L.; Xu, T.; He, J.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yu, X.; Jia, L. Natural Fish Trap-Like Nanocage for Label-Free Capture of Circulating Tumor Cells. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2002259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Weng, S.; Zhang, F.; Allen, S.; Li, X.; Bao, L.; Lam, R.H.W.; MacOska, J.A.; Merajver, S.D.; Fu, J. Nanoroughened Surfaces for Efficient Capture of Circulating Tumor Cells without Using Capture Antibodies. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Sun, H.; Jiang, W.; Xu, T.; Song, B.; Peng, R.; Han, L.; Jia, L. A Chemical Method for Specific Capture of Circulating Tumor Cells Using Label-Free Polyphenol-Functionalized Films. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 4372–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossett, D.R.; Weaver, W.M.; MacH, A.J.; Hur, S.C.; Tse, H.T.K.; Lee, W.; Amini, H.; Di Carlo, D. Label-Free Cell Separation and Sorting in Microfluidic Systems. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 3249–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Larasati; Duncker, B.P.; Li, D. Continuous Cell Characterization and Separation by Microfluidic Alternating Current Dielectrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6304–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nivedita, N.; Papautsky, I. Continuous Separation of Blood Cells in Spiral Microfluidic Devices. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 054101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoodi, E.; Sarikhani, E.; Montazerian, H.; Ahadian, S.; Costantini, M.; Swieszkowski, W.; Willerth, S.M.; Walus, K.; Mofidfar, M.; Toyserkani, E.; et al. Extrusion and Microfluidic-Based Bioprinting to Fabricate Biomimetic Tissues and Organs. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1901044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommer, M.S.; Zhang, Y.; Keerthi, N.; Chen, D.; Thomson, J.A.; Meinhart, C.D.; Soh, H.T. Dielectrophoretic Separation of Platelets from Diluted Whole Blood in Microfluidic Channels. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasukawa, T.; Yamada, J.; Shiku, H.; Matsue, T.; Suzuki, M. Microfluidic Separation of Blood Cells Based on the Negative Dielectrophoresis Operated by Three Dimensional Microband Electrodes. Micromachines 2020, 11, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, N.; Mernier, G.; Tornay, R.; Renaud, P. Separation of Platelets from Other Blood Cells in Continuous-Flow by Dielectrophoresis Field-Flow-Fractionation. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 034122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siani, O.Z.; Sojoodi, M.; Targhi, M.Z.; Movahedin, M. Blood Particle Separation Using Dielectrophoresis in a Novel Microchannel: A Numerical Study. Cell J. 2019, 22, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.R.; Cox, E.C.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. Continuous Particle Separation Through Deterministic Lateral Displacement. Science 2004, 304, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaee, F.; Movahed, S.; Fatouraee, N.; Daneshmand, F. Numerical Simulation of Separation of Circulating Tumor Cells from Blood Stream in Deterministic Lateral Displacement (DLD) Microfluidic Channel. J. Mech. 2016, 32, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Kamei, D.T.; Ho, C.M. On-Chip Continuous Blood Cell Subtype Separation by Deterministic Lateral Displacement. In Proceedings of the 2007 2nd IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, Bangkok, Thailand, 16–19 January 2007; pp. 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.; Whyte, G.; Bailey, J.; Vergara-Irigaray, N.; Ekpenyong, A.; Guck, J.; Duke, T. Separation of Blood Cells with Differing Deformability Using Deterministic Lateral Displacement. Interface Focus 2014, 4, 20140011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geislinger, T.M.; Eggart, B.; Braunmüller, S.; Schmid, L.; Franke, T. Separation of Blood Cells Using Hydrodynamic Lift. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 183701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiriny, A.; Bayareh, M. On Magnetophoretic Separation of Blood Cells Using Halbach Array of Magnets. Meccanica 2020, 55, 1903–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamloo, A.; Parast, F.Y. Simulation of Blood Particle Separation in a Trapezoidal Microfluidic Device by Acoustic Force. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2019, 66, 1495–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.C.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Duan, W. Lab-on-a-Chip: A Component View. Microsyst. Technol. 2010, 16, 1995–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Simone, G.; Salieb-Beugelaar, G.B.; Kim, J.T.; Manz, A. Latest Developments in Micro Total Analysis Systems. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4830–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamloo, A.; Yazdani, A.; Saghafifar, F. Investigation of a Two-Step Device Implementing Magnetophoresis and Dielectrophoresis for Separation of Circulating Tumor Cells from Blood Cells. Eng. Life Sci. 2020, 20, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Li, D.; Kalams, S.A.; Eid, J.E. DC-Dielectrophoretic Separation of Biological Cells by Size. Biomed. Microdevices 2008, 10, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.F.; Du, H.; Li, W.H. Bioparticle Separation and Manipulation Using Dielectrophoresis. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 133, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, D. Manipulation and Separation of Oil Droplets by Using Asymmetric Nano-Orifice Induced DC Dielectrophoretic Method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 512, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Li, D. Tunable Droplet Manipulation and Characterization by Ac-DEP. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 36572–36581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascoyne, P.R.C.; Vykoukal, J. Particle Separation by Dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, D. Continuous Separation of Nanoparticles by Type via Localized DC-Dielectrophoresis Using Asymmetric Nano-Orifice in Pressure-Driven Flow. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 250, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeesh, P.; Sen, A.K. Particle Separation and Sorting in Microfluidic Devices: A Review. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 17, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Peng, R.; Li, D. Separation of Nanoparticles by a Nano-Orifice Based DC-Dielectrophoresis Method in a Pressure-Driven Flow. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 18945–18955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Mohanty, S. Dielectrophoretic Separation of Micron and Sub-Micron Particles: A Review. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 2656–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshmanesh, K.; Zhang, C.; Nahavandi, S.; Tovar-Lopez, F.J.; Baratchi, S.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Size Based Separation of Microparticles Using a Dielectrophoretic Activated System. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 034904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wei, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, J. Separation and Characterization of Microplastic and Nanoplastic Particles in Marine Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 297, 118773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bashir, R. Dielectrophoretic Orientation, Manipulation and Separation of Live and Heat-Treated Cells Of Listeria on Microfabricated Devices with Interdigitated Electrodes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; Volume 729, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gascoyne, P.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, M.; Satayavivad, J.; Watcharasit, P.; Becker, F.F. Microsample Preparation by Dielectrophoresis: Isolation of Malaria. Lab Chip 2002, 2, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.S.; Kwon, K.; Kim, S.I.; Han, H.; Sohn, J.; Lee, S.; Jung, H.I. Continuous Separation of Breast Cancer Cells from Blood Samples Using Multi-Orifice Flow Fractionation (MOFF) and Dielectrophoresis (DEP). Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Rosano, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Garson, C.J.; Prabhakarpandian, B.; Pant, K.; Klarmann, G.J.; Perantoni, A.; Alvarez, L.M.; Lai, E. Continuous-Flow Sorting of Stem Cells and Differentiation Products Based on Dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, W. Dielectrophoretic Separation of Microalgae Cells in Ballast Water in a Microfluidic Chip. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahey, M.D.; Voldman, J. An Equilibrium Method for Continuous-Flow Cell Sorting Using Dielectrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3135–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, S.; Chen, X.; Bai, F.; Song, S.; Fu, J. Dielectrophoresis-Based Protein Enrichment for a Highly Sensitive Immunoassay Using Ag/SiO2 Nanorod Arrays. Small 2018, 14, 1703265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, Y.C.; Huang, K.W.; Chong, W.; Chiou, P.Y. Tunnel Dielectrophoresis for Tunable, Single-Stream Cell Focusing in Physiological Buffers in High-Speed Microfluidic Flows. Small 2016, 12, 4343–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voldman, J. Electrical Forces for Microscale Cell Manipulation. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 8, 425–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Fattah, A.R.; Ghosh, S.; Puri, I.K. High Gradient Magnetic Field Microstructures for Magnetophoretic Cell Separation. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1027, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamme, N.; Wilhelm, C. Continuous Sorting of Magnetic Cells via On-Chip Free-Flow Magnetophoresis. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Hahn, Y.K.; Oh, S.; Kwon, S.; Um, E.; Choi, S.; Kang, J.H. Advection Flows-Enhanced Magnetic Separation for High-Throughput Bacteria Separation from Undiluted Whole Blood. Small 2018, 14, 1801731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karle, M.; Miwa, J.; Czilwik, G.; Auwärter, V.; Roth, G.; Zengerle, R.; Von Stetten, F. Continuous Microfluidic DNA Extraction Using Phase-Transfer Magnetophoresis. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3284–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.H.; Bruno Frazier, A. A Microfluidic System for Continuous Magnetophoretic Separation of Suspended Cells Using Their Native Magnetic Properties. Proc. Nanotechnol. 2005, 1, 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Cheng, R.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Mao, L. Combining Positive and Negative Magnetophoreses to Separate Particles of Different Magnetic Properties. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 17, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.B.Y. Marcos Sorting Spermatozoa by Morphology Using Magnetophoresis. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2017, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaz, A.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Nguyen, N.T. Recent Advances and Current Challenges in Magnetophoresis Based Micro Magnetofluidics. Biomicrofluidics 2018, 12, 031501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlani, E.P. Analysis of Particle Transport in a Magnetophoretic Microsystem. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 024912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. AC Electrokinetics: Colloids and Nanoparticles; Research Studies Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; ISBN 0863802559. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Holzel, R.; Pethig, R.; Wang, X.B. Differences in the AC Electrodynamics of Viable and Non-Viable Yeast Cells Determined through Combined Dielectrophoresis and Electrorotation Studies. Phys. Med. Biol. 1992, 37, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.Z.; Ho, C.T.; Liu, C.H.; Chang, H.Y. Dielectrophoresis Based-Cell Patterning for Tissue Engineering. Biotechnol. J. 2006, 1, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Lanry Yung, L.Y.; Lim, K.M. Dielectrophoretic Capture Voltage Spectrum for Measurement of Dielectric Properties and Separation of Cancer Cells. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 014113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahavandi, M. Continuous-Flow Separation of Malaria-Infected Human Erythrocytes Using DC Dielectrophoresis: An Electrokinetic Modeling and Simulation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 5484–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Biswas, K.; Das, S. A Microfluidic Device for Continuous Manipulation of Biological Cells Using Dielectrophoresis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Li, D. Numerical Studies of Manipulation and Separation of Janus Particles in Nano-Orifice Based DC-Dielectrophoretic Microfluidic Chips. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 095007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Donath, E. Electrorotation Measurements of Diamide-Induced Platelet Activation Changes. Biophys. J. 1995, 68, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascoyne, P.; Satayavivad, J.; Ruchirawat, M. Microfluidic Approaches to Malaria Detection. Acta Trop. 2004, 89, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermolina, I.; Polevaya, Y.; Feldman, Y.; Ginzburg, B.Z.; Schlesinger, M. Study of Normal and Malignant White Blood Cells by Time Domain Dielectric Spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2001, 8, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polevaya, Y.; Ermolina, I.; Schlesinger, M.; Ginzburg, B.Z.; Feldman, Y. Time Domain Dielectric Spectroscopy Study of Human Cells II. Normal and Malignant White Blood Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 1999, 1419, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirmohammadli, V.; Manavizadeh, N. Numerical Modeling of Cell Trajectory Inside a Dielectrophoresis Microdevice Designed for Breast Cancer Cell Screening. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 8215–8222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| 80 | |
| (F m−1) | 8.85 × 10−12 |
| (N A−2) | 4π × 10−7 |
| (kg m−3) | 1000 |
| (Pa·s) | 1 × 10−3 |
| Electrical conductivity of buffer (mS m−1) | 55 |
| (kg m−3) | 1050 |
| (kg m3) | −9 × 10−6 |
| (T) | 1 |
| Length of main channel (μm) | 2000 |
| Length of microchannel A, B, D, E and F (μm) | 300 |
| Length of microchannel C (μm) | 700 |
| Width of the whole microchannel (μm) | 80 |
| Property | RBC | T cells | Title 2 | Title 3 | Title 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| interior conductivity (S/m) | 0.31 | 0.65 | 0.203 | 0.62 | 0.25 |
| membrane conductivity (S/m) | 1 × 10−6 | 27.4 × 10−6 | 34.82 × 10−6 | 0.9 × 10−6 | 1 × 10−6 |
| interior dielectric constant | 59 | 60 | 61.14 | 52 | 50 |
| membrane dielectric constant | 4.4 | 11.1 | 6.01 | 14.69 | 6 |
| magnetic susceptibility (m3/kg) | −3.9 × 10−6 | −9.9 × 10−6 | −9.5 × 10−6 | −9.5 × 10−6 | −9.2 × 10−6 |
| radius (μm) | 3 | 3.4 | 6.6 | 9 | 0.9 |
| membrane thickness (nm) | 9 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, K.; Zhao, P.; Dong, J.; Wei, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, J. Implementation of an Integrated Dielectrophoretic and Magnetophoretic Microfluidic Chip for CTC Isolation. Biosensors 2022, 12, 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090757
Zhao K, Zhao P, Dong J, Wei Y, Chen B, Wang Y, Pan X, Wang J. Implementation of an Integrated Dielectrophoretic and Magnetophoretic Microfluidic Chip for CTC Isolation. Biosensors. 2022; 12(9):757. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090757
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Kai, Penglu Zhao, Jianhong Dong, Yunman Wei, Bin Chen, Yanjuan Wang, Xinxiang Pan, and Junsheng Wang. 2022. "Implementation of an Integrated Dielectrophoretic and Magnetophoretic Microfluidic Chip for CTC Isolation" Biosensors 12, no. 9: 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090757
APA StyleZhao, K., Zhao, P., Dong, J., Wei, Y., Chen, B., Wang, Y., Pan, X., & Wang, J. (2022). Implementation of an Integrated Dielectrophoretic and Magnetophoretic Microfluidic Chip for CTC Isolation. Biosensors, 12(9), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090757








