Recent Advances of NIR-II Emissive Semiconducting Polymer Dots for In Vivo Tumor Fluorescence Imaging and Theranostics
Abstract
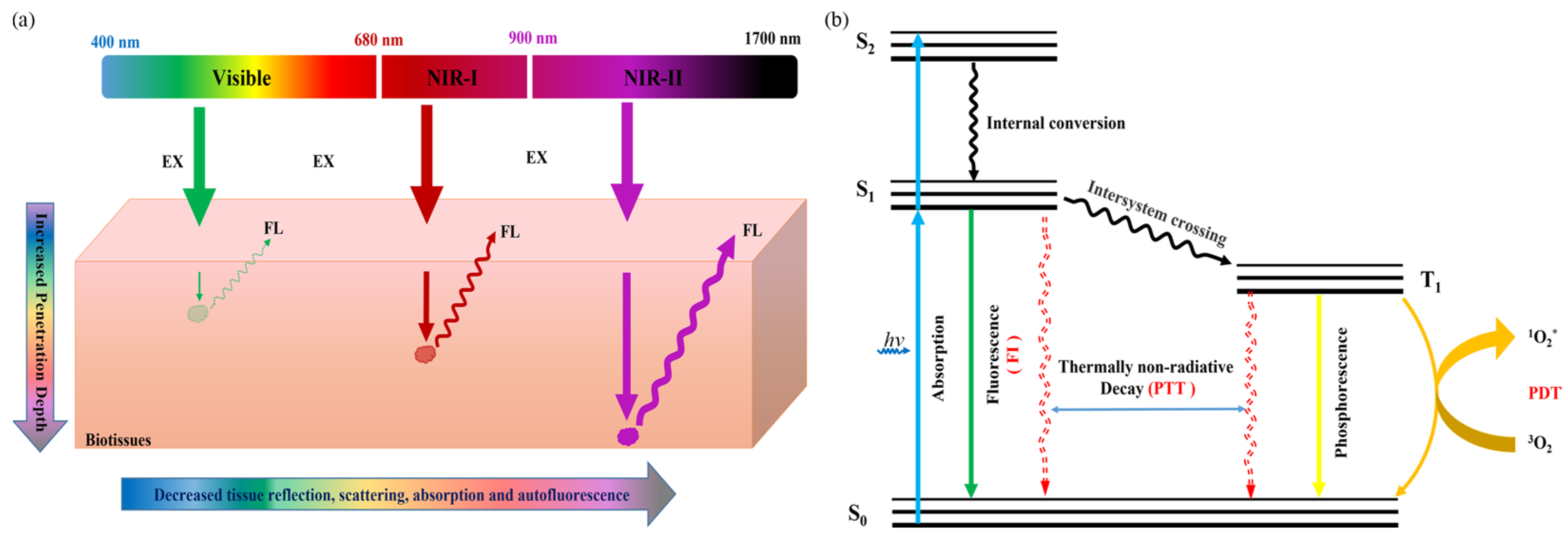
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Engineering of Efficient NIR-II Pdots for In Vivo Tumor FI
3. Active-Tumor-Targeting NIR-II Pdots for In Vivo Tumor FI
4. NIR-II Pdots as Tumor Theranostic Platforms
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Bhattarai, P.; Dai, Z.; Chen, X. Photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging via nanotheranostics in fighting cancer. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2053–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Zhu, R.; Song, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, X. Photoacoustic imaging: Contrast agents and their biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1805875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, X.; Pu, K.; Jiang, X. Photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles: Signal amplification and second near-infrared construction. Small 2021, 17, e2004723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ren, W.X.; Hou, J.T.; Won, M.; An, J.; Chen, X.; Shu, J.; Kim, J.S. Fluorescence imaging of pathophysiological microenvironments. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8887–8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Schnitzer, M.J. Fluorescence imaging of large-scale neural ensemble dynamics. Cell 2022, 185, 9–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Younis, M.H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Cai, W.; Ni, D. Spectral computed tomography with inorganic nanomaterials: State-of-the-art. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 189, 114524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, W.M.; Elsinga, P.H.; Gasca-Salas, C.; Versluis, M.; Martínez-Fernández, R.; Dierckx, R.; Borra, R.J.H.; Luurtsema, G. Focused ultrasound for opening blood-brain barrier and drug delivery monitored with positron emission tomography. J. Control. Release 2020, 324, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floresta, G.; Abbate, V. Recent progress in the imaging of c-Met aberrant cancers with positron emission tomography. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 1588–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verger, A.; Grimaldi, S.; Ribeiro, M.J.; Frismand, S.; Guedj, E. Single photon emission computed tomography/positron emission tomography molecular imaging for parkinsonism: A fast-developing field. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 90, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Tian, R.; Antaris, A.L.; Chen, X.; Dai, H. Near-infrared-II molecular dyes for cancer imaging and surgery. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1900321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Fan, C.; Ge, Z. Responsive optical probes for deep-tissue imaging: Photoacoustics and second near-infrared fluorescence. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 173, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, J.; Sun, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, C.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Nanoaggregate probe for breast cancer metastasis through multispectral optoacoustic tomography and aggregation-induced NIR-I/II fluorescence imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10111–10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, P.; Li, Z.; Qu, L.; Guo, W. Natural flavylium-inspired far-red to NIR-II dyes and their applications as fluorescent probes for biomedical sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 7170–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y. NIR-II bioimaging of small organic molecule. Biomaterials 2021, 271, 120717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wu, L.; Yu, J.; Kuo, C.T.; Jian, T.; Wu, I.C.; Rong, Y.; Chiu, D.T. Highly photostable wide-dynamic-range pH sensitive semiconducting polymer dots enabled by dendronizing the near-IR emitters. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 7236–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Younis, N.K.; Ghoubaira, J.A.; Bassil, E.P.; Tantawi, H.N.; Eid, A.H. Metal-based nanoparticles: Promising tools for the management of cardiovascular diseases. Nanomedicine 2021, 36, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, S.; Ding, B.; Qu, C.; Chen, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lan, X.; Cheng, Z. Synergistic strategy of rare-earth doped nanoparticles for NIR-II biomedical imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 9116–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, W.; Xie, L.; Sang, W.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Tian, H.; Yan, J.; Tian, Y.; et al. A metal-polyphenolic nanosystem with NIR-II fluorescence-guided combined photothermal therapy and radiotherapy. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 11473–11476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, S.; Ma, D. Recent advances of near infrared inorganic fluorescent probes for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 7856–7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Koo, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Du, M.; Lu, S.; et al. Versatile types of inorganic/organic NIR-IIa/IIb fluorophores: From strategic design toward molecular imaging and theranostics. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 209–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Tang, C.; Wei, Z.; Song, C.; Zou, H.; Zhang, G.; Ran, J.; Han, W. Fused-ring small-molecule-based bathochromic nano-agents for tumor NIR-II fluorescence imaging-guided photothermal/photodynamic therapy. ACS. Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, F.; Yin, S. NIR-II phototherapy agents with aggregation-induced emission characteristics for tumor imaging and therapy. Biomaterials 2022, 285, 121535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Wang, D.; Tang, B.Z. NIR-II AIEgens: A win-win integration towards bioapplications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 7476–7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J. Semiconducting polymer dots as fluorescent probes for in vitro biosensing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6248–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wei, Q.; Xian, C.; Dai, C.; He, X.; Wu, C.; Sun, G.; Chen, L. Highly efficient and non-doped red conjugated polymer dot for photostable cell imaging. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022; 107867, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, D.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; DuFort, C.C.; Hingorani, S.R.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Chiu, D.T. A BODIPY-based donor/donor-acceptor system: Towards highly efficient long-wavelength-excitable near-IR polymer dots with narrow and strong absorption features. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7008–7012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Zhu, C.; Yuan, H.; Liu, L.; Lv, F.; Wang, S. Conjugated polymer nanoparticles: Preparation, properties, functionalization and biological applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6620–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, L.R.; Shaikh, H.; Garcia-Hernandez, J.D.; Vespa, M.; Fukui, T.; Manners, I. Functional nanoparticles through π-conjugated polymer self-assembly. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fang, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; He, S.; Zheng, J.; Yang, B.; Qin, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Semiconducting polymer dots with dual-enhanced NIR-IIa fluorescence for through-skull mouse-brain imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3691–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, J.; Metternich, J.T.; Herbertz, S.; Kruss, S. Biosensing with fluorescent carbon nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wei, R.; Sun, L. Lanthanide nanoparticles with efficient near-infrared-II emission for biological applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10257–10270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Pan, J.; Chu, C.; Liu, G. Organic sonosensitizers for sonodynamic therapy: From small molecules and nanoparticles toward clinical development. Small 2021, 17, e2101976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, K.; Chattopadhyay, N.; Rao, J. Recent advances of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles in in vivo molecular imaging. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Son, J.; Yi, G.; Yoo, J.; Park, C.; Koo, H.; Choi, H.S. Light-responsive nanomedicine for biophotonic imaging and targeted therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 138, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, S.K.; Singh, E.; Singh, P.; Meyyappan, M.; Nalwa, H.S. A review on graphene-based nanocomposites for electrochemical and fluorescent biosensors. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8778–8881. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.T.; Wu, I.C.; Chen, L.; Yu, J.; Wu, L.; Chiu, D.T. Improving the photostability of semiconducting polymer dots using buffers. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11785–11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimov, I.B.; Moser, M.; Malliaras, G.G.; McCulloch, I. Semiconducting polymers for neural applications. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 4356–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, J.; Men, X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, C.; Chiu, D.T. Reversible ratiometric NADH sensing using semiconducting polymer dots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12007–12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Chiu, D.T.; McNeill, J. Dual-mode superresolution imaging using charge transfer dynamics in semiconducting polymer dots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 16173–16180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upputuri, P.K.; Pramanik, M. Recent advances in photoacoustic contrast agents for in vivo imaging. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Ilyas, I.; He, S.; Xing, Y.; Jin, Z.; Huang, C. Ratiometric pH sensing and imaging in living cells with dual-emission semiconductor polymer dots. Molecules 2019, 24, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Hou, W.; Qin, W.; Wu, C. Recent advances in semiconducting polymer dots as optical probes for biosensing. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, W.; Qin, W.; Meng, Z.; Wu, C. In vivo dynamic cell tracking with long-wavelength excitable and near-infrared fluorescent polymer dots. Biomaterials 2020, 254, 120139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Guo, L.; Li, Q. Peptide-coated semiconductor polymer dots for stem cells labeling and tracking. Chemistry 2017, 23, 6836–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Q.; Yang, L.; Gao, F. Simultaneous inhibition of planktonic and biofilm bacteria by self-adapting semiconducting polymer dots. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6658–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, G.; Sun, H.; Yin, S. Recent advances in the development and applications of conjugated polymer dots. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2995–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Liu, Y.; Hu, D.; Qi, Q.; Gao, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.; Sheng, Z.; et al. Highly stable conjugated polymer dots as multifunctional agents for photoacoustic imaging-guided photothermal therapy. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7012–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeken, Y.; Cheruku, S.; Ethirajan, A.; Maes, W. Conjugated polymer nanoparticles for bioimaging. Materials 2017, 10, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, S. Conjugated polymer nanoparticles for imaging, cell activity regulation, and therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.Y.; Hu, D.H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.J.; Yuan, Z.; Sheng, Z.H.; Zheng, H.R. Recent advances in conjugated polymer nanoparticles for NIR-II imaging and therapy. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hussain, S.; Abbas, A.; Hao, Y.; Malik, A.H.; Tian, X.; Song, H.; Gao, R. Conjugated polymer nanoparticles and their nanohybrids as smart photoluminescent and photoresponsive material for biosensing, imaging, and theranostics. Mikrochim. Acta 2022, 189, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Rao, J.H.; Pu, K.Y. Recent progress on semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for molecular imaging and cancer phototherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 155, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, G.; Zou, Y.; Antaris, A.L.; Diao, S.; Wu, D.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, B.; He, Y.; et al. Ultrafast fluorescence imaging in vivo with conjugated polymer fluorophores in the second near-infrared window. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Qi, W.; Ye, Z.; He, S.; et al. Fluorination enhances NIR-II fluorescence of polymer dots for quantitative brain tumor imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 21049–21057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Su, S.P.; Yang, C.H.; Liu, M.H.; Lo, P.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsu, C.P.; Lee, Y.J.; Chiang, H.K.; Chan, Y.H. Molecular design of ultrabright semiconducting polymer dots with high NIR-II fluorescence for 3D tumor mapping. Adv. Health Mater. 2021, 10, e2100993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.; Geng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Du, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, G.; Wu, C.; Yuan, Z. Biomimetic semiconducting polymer dots for highly specific NIR-II fluorescence imaging of glioma. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 16, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, W.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Feng, W.; Xu, C.; Li, F. Ultrabright NIR-II emissive polymer dots for metastatic ovarian cancer detection. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2000441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Nuernisha, A.; Xue, D.; He, C.; Qian, J.; Hu, Q.; Chen, H.; et al. Semiconducting polymer nanoparticles as theranostic system for near-infrared-II fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy under safe laser fluence. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2509–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Jiang, X.; Sun, B.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Fan, Q.; Huang, W. Electron-acceptor density adjustments for preparation conjugated polymers with NIR-II absorption and brighter NIR-II fluorescence and 1064 nm active photothermal/gas therapy. Biomaterials 2022, 280, 121319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Xue, D.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Qian, J.; Huang, W. Simultaneous enhancement of the long-wavelength NIR-II brightness and photothermal performance of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 8705–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y.; Yin, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, W.; Fan, Q. Capsaicin-decorated semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for light-controlled calcium-overload/photodynamic combination therapy. Small 2022, 18, e2200152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.F.; Li, Y.Y.; Lu, X.M.; Hu, X.M.; Zhao, H.; Hu, W.B.; Lu, F.; Fan, Q.L.; Huang, W. Bio-erasable intermolecular donor-acceptor interaction of organic semiconducting nanoprobes for activatable NIR-II fluorescence imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.B.; Miao, Y.W.; Zhu, Y.W.; Zou, W.T.; Yu, B.; Shen, Y.Q.; Cong, H.L. A design strategy for D-A conjugated polymers for NIR-II fluorescence imaging. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 4707–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.K.; Wang, C.I.; Liao, C.H.; Yao, C.N.; Kuo, T.J.; Liu, M.H.; Hsu, C.P.; Lin, S.Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Pyle, J.R.; et al. Molecular design of near-infrared fluorescent Pdots for tumor targeting: Aggregation-induced emission versus anti-aggregation-caused quenching. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Gan, Q.; Cao, Y.; Yuan, H.; Hua, D. Donor-acceptor-type conjugated polymer-based multicolored drug carriers with tunable aggregation-induced emission behavior for self-illuminating cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 41853–41861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Fang, Y.; Miao, Q.; Qi, X.; Ding, D.; Chen, P.; Pu, K. Regulating near-infrared photodynamic properties of semiconducting polymer nanotheranostics for optimized cancer therapy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 8998–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.X.; Liu, X.R.; Zhu, D.C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.F.; Qiu, N.S.; Chen, X.S.; Shen, Y.Q. Nonviral cancer gene therapy: Delivery cascade and vector nanoproperty integration. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 115, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Fu, L.H.; Li, C.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Conquering the hypoxia limitation for photodynamic therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2103978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shao, C.; Liu, T.; Chao, Z.; Chen, H.; Xiao, F.; He, H.; Wei, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. An NIR-II-emissive photosensitizer for hypoxia-tolerant photodynamic theranostics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2003471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, C.; Li, Q.; Kong, D.; Sun, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Tian, G.; et al. NIR-II fluorescence imaging-guided oxygen self-sufficient nano-platform for precise enhanced photodynamic therapy. Small 2022, 3, e2205647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Pdots | λabs (nm) | λem (nm) | λex (nm) | Φf (%) | ε/Weight (g L−1 cm−1) | Tumor Model | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m-PBTQ4F | 946 | 1123 | 808 | 3.2 | n.a. | Mouse medulloblastoma tumor | FI | [54] |
| IR-Pttc | 706 | 1008 | 793 | 4.9 | n.a. | 4T1 breast tumor | 3D FI | [55] |
| IR-TPA | 670 | 950 | 793 | 6.7 | n.a. | 4T1 breast tumor | 3D FI | [55] |
| IR-TPE | 702 | 1010 | 793 | 14 | n.a. | 4T1 breast tumor | 3D FI | [55] |
| Pdots-C6 | 745 | 1055 | 808 | 0.6 | n.a. | C6-glioma tumor | FI | [56] |
| Pdots-GnRH | 710 | 1020 | 730 | 5.5 | 15.3 | A2780-metastatic ovarian tumor | FI | [57] |
| L1057 | 980 | 1057 | 980 | 1.25 | 18 | 4T1 breast tumor | FI + PTT | [58] |
| TTQ-MnCO | 808 | 1115 | 808 | n.a. | n.a. | MCF-7 breast tumor | FI + PTT + Gas | [59] |
| PBQ45 | 1064 | ~1200 | 1064 | 0.048 | 27.5 | Peritoneal carcinomatosis/4T1 tumor | FI/PTT | [60] |
| CSPN | 700 | 893 | 835 | 1.76 | n.a. | U373 glioma tumor | FI + PDT | [61] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Q.; Xu, D.; Li, T.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L. Recent Advances of NIR-II Emissive Semiconducting Polymer Dots for In Vivo Tumor Fluorescence Imaging and Theranostics. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121126
Wei Q, Xu D, Li T, He X, Wang J, Zhao Y, Chen L. Recent Advances of NIR-II Emissive Semiconducting Polymer Dots for In Vivo Tumor Fluorescence Imaging and Theranostics. Biosensors. 2022; 12(12):1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121126
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Qidong, Dingshi Xu, Tianyu Li, Xuehan He, Jiasi Wang, Yi Zhao, and Lei Chen. 2022. "Recent Advances of NIR-II Emissive Semiconducting Polymer Dots for In Vivo Tumor Fluorescence Imaging and Theranostics" Biosensors 12, no. 12: 1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121126
APA StyleWei, Q., Xu, D., Li, T., He, X., Wang, J., Zhao, Y., & Chen, L. (2022). Recent Advances of NIR-II Emissive Semiconducting Polymer Dots for In Vivo Tumor Fluorescence Imaging and Theranostics. Biosensors, 12(12), 1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121126






