Paper-Based Airborne Bacteria Collection and DNA Extraction Kit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
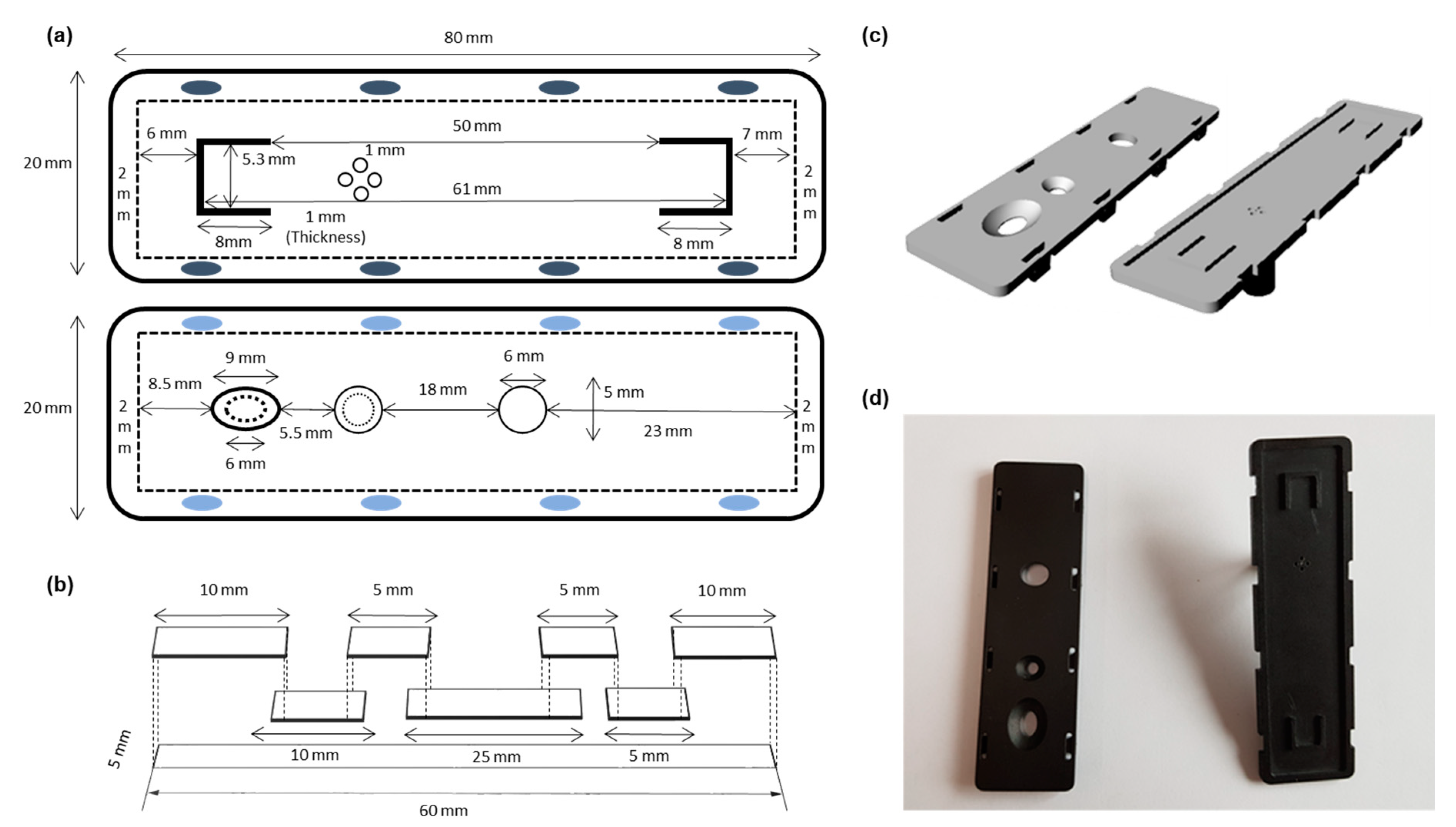
2.2. 3D Printing
2.3. Paper Kit Assembly
2.4. Operation of Paper Kit
2.5. Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteria Culture
2.6. Quantification of S. aureus by Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.7. Closed Cabinet System
2.7.1. Fabrication of Closed Cabinet System
2.7.2. Pressure, Temperature, and Humidity Control
2.7.3. Production of S. aureus Aerosol
2.7.4. Ultraviolet Exposure Remediation
2.8. Operation of Impactor Sampler
3. Results and Discussion
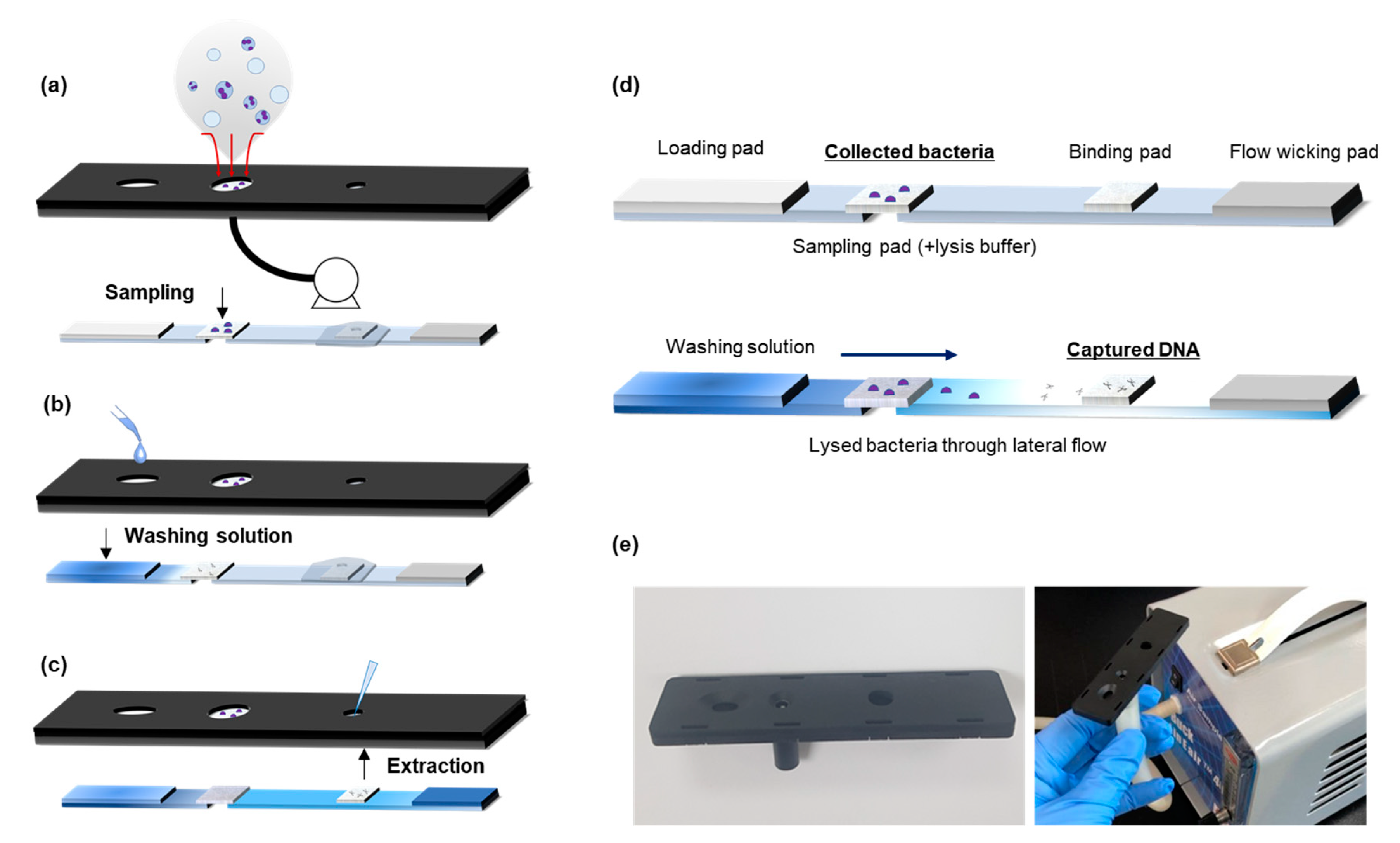
3.1. Airborne Bacteria Collection and DNA Extraction
3.2. Assembly of Paper-Based Airborne Bacteria Monitoring Kit
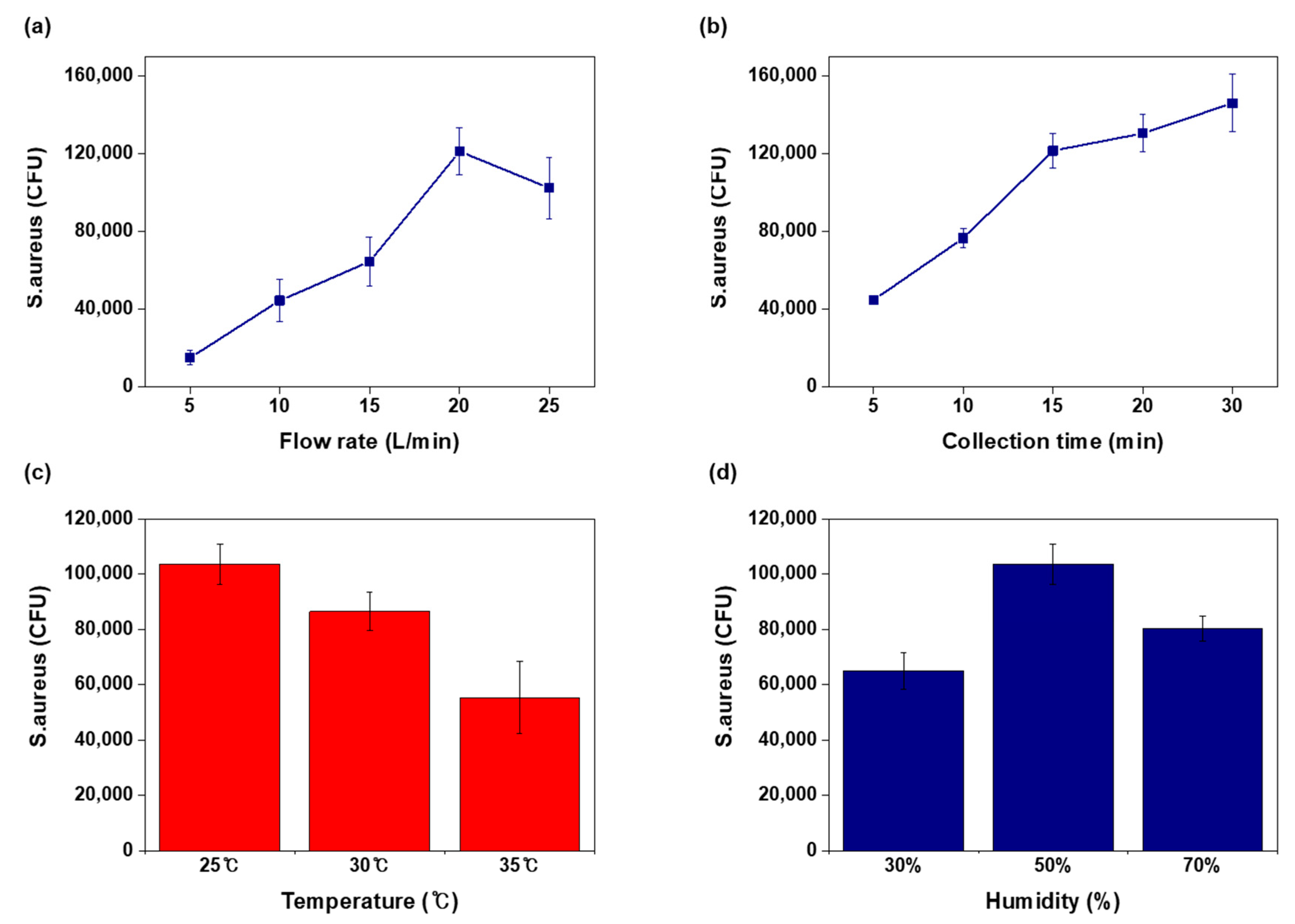
3.3. Operation Factors of Air Sampling
3.4. Results of Airborne Bacteria Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Guidelines for the Global Surveillance of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS): Updated Recommendations, October 2004; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Human infection with new influenza A (H1N1) virus: Clinical observations from Mexico and other affected countries, May 2009. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. Relev. Épidémiologique Hebd. 2009, 84, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Killerby, M.E.; Biggs, H.M.; Midgley, C.M.; Gerber, S.I.; Watson, J.T. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus transmission. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Udugama, B.; Kadhiresan, P.; Kozlowski, H.N.; Malekjahani, A.; Osborne, M.; Li, V.Y.C.; Chen, H.; Mubareka, S.; Gubbay, J.B.; Chan, W.C.W. Diagnosing COVID-19: The Disease and Tools for Detection. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3822–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broughton, J.P.; Deng, X.; Yu, G.; Fasching, C.L.; Servellita, V.; Singh, J.; Miao, X.; Streithorst, J.A.; Granados, A.; Sotomayor-Gonzalez, A.; et al. CRISPR-Cas12-based detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Leavey, A.; Wang, Y.; O’Neil, C.; Wallace, M.A.; Burnham, C.-A.D.; Boon, A.C.M.; Babcock, H.; Biswas, P. Comparing the performance of 3 bioaerosol samplers for influenza virus. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 115, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Kim, H.R.; Ko, H.S.; Jeong, S.B.; Chan Kim, B.; Jung, J.H. Continuous Surveillance of Bioaerosols On-Site Using an Automated Bioaerosol-Monitoring System. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronczek, C.F.; Yoon, J.Y. Biosensors for Monitoring Airborne Pathogens. J. Lab Autom. 2015, 20, 390–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haig, C.W.; Mackay, W.G.; Walker, J.T.; Williams, C. Bioaerosol sampling: Sampling mechanisms, bioefficiency and field studies. J. Hosp. Infect. 2016, 93, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Tan, M.; Wang, Z.; Yao, M.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Zhu, T. Integrating silicon nanowire field effect transistor, microfluidics and air sampling techniques for real-time monitoring biological aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7473–7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, V.; Clark, C.; Bjornson, H.; Samuels, S.; Holland, J. A comparison of two-stage and six-stage Andersen impactors for viable aerosols. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1981, 42, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennelly, K.P.; Tribby, M.D.; Wu, C.Y.; Weil, G.; Radonovich, L.J.; Loeb, J.C.; Lednicky, J.A. Collection and measurement of aerosols of viable influenza virus in liquid media in an Andersen cascade impactor. Virus Adapt Treat 2015, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.W.; Park, C.W.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, J. Fast monitoring of indoor bioaerosol concentrations with ATP bioluminescence assay using an electrostatic rod-type sampler. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Park, J.-w.; Kim, H.S.; Yong, D.; Hwang, J. Comparison of lab-made electrostatic rod-type sampler with single stage viable impactor for identification of indoor airborne bacteria. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 115, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, J.Y.; Kuznetsova, M.R.; Jahns, C.J.; Kemp, P.F. The sea surface microlayer as a source of viral and bacterial enrichment in marine aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.W.; Park, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, J. Real-time monitoring of bioaerosols via cell-lysis by air ion and ATP bioluminescence detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Huh, H.J.; Park, E.; Chung, D.-R.; Kang, M. Multiplex Molecular Point-of-Care Test for Syndromic Infectious Diseases. Biochip J. 2021, 15, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, J.; Gallegos-Graves, V.; Gans, J.; Morse, S.A.; Pillai, S.; Anderson, K.; Hodge, D.R. Evaluation of DNA extraction methods to detect bacterial targets in aerosol samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 153, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, H.; Han, T.; Fennell, D.E.; Mainelis, G. Release of free DNA by membrane-impaired bacterial aerosols due to aerosolization and air sampling. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7780–7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jing, W.; Zhao, W.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Tsai, C.T.; Fan, X.; Wu, W.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Sui, G. Microfluidic device for efficient airborne bacteria capture and enrichment. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5255–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, Y.; Batule, B.S.; Kim, M.-G. Lab-on-paper for all-in-one molecular diagnostics (LAMDA) of zika, dengue, and chikungunya virus from human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozer, T.; McMahon, C.; Henry, C.S. Advances in Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 13, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dincer, C.; Bruch, R.; Kling, A.; Dittrich, P.S.; Urban, G.A. Multiplexed Point-of-Care Testing-xPOCT. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.G.; Joung, H.A.; Noh, H.; Song, M.B.; Kim, M.G.; Jung, H. One-touch-activated blood multidiagnostic system using a minimally invasive hollow microneedle integrated with a paper-based sensor. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3286–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauglitz, G. Point-of-care platforms. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 7, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Seok, Y.; Jung, H.; Yang, B.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Pyo, H.; Song, C.S.; Choi, W.; Kim, M.G.; et al. Integrated Bioaerosol Sampling/Monitoring Platform: Field-Deployable and Rapid Detection of Airborne Viruses. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3915–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhrbrand, K.; Koponen, I.K.; Schultz, A.C.; Madsen, A.M. Evaluation of air samplers and filter materials for collection and recovery of airborne norovirus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Pande, T.; van de Ven, T.G. Qualitative and quantitative detection of T7 bacteriophages using paper based sandwich ELISA. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 132, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, Y.; Jang, H.; Oh, J.; Joung, H.-A.; Kim, M.-G. A handheld lateral flow strip for rapid DNA extraction from staphylococcus aureus cell spiked in various samples. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2019, 5, 035035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.E.; Rodriguez, R.A.; Hawkins, M.A.; Hargy, T.M.; Larason, T.C.; Linden, K.G. Comparison of UV-induced inactivation and RNA damage in MS2 phage across the germicidal UV spectrum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batule, B.S.; Seok, Y.; Kim, M.-G. An innovative paper-based device for DNA extraction from processed meat products. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrnes, S.A.; Bishop, J.D.; Yager, P. Enabling lateral transport of genomic DNA through porous membranes for point-of-care applications. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 3450–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.-H.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Wu, C.-Y.; Heimbuch, B.; Wander, J. Method for contamination of filtering facepiece respirators by deposition of MS2 viral aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 2010, 41, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Day 1 (Spring) | Day 2 (Summer) | Day 3 (Autumn) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | 2019.05.15 | 2019.09.04 | 2019.11.13 | |
| Outdoor | Temperature | 27 °C | 27 °C | 13 °C |
| Humidity | 48% | 90% | 65% | |
| Indoor | Temperature | 22 °C | 24 °C | 22 °C |
| Humidity | 55% | 62% | 55% | |
| Paper kit collection | 150 CFU | 192 CFU | 56 CFU | |
| S. aureusin the air | Paper kit | 500 CFU/m3 | 640 CFU/m3 | 187 CFU/m3 |
| Colony counting | 36 CFU/m3 | 50 CFU/m3 | 20 CFU/m3 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seok, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, M.-G. Paper-Based Airborne Bacteria Collection and DNA Extraction Kit. Biosensors 2021, 11, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100375
Seok Y, Lee J, Kim M-G. Paper-Based Airborne Bacteria Collection and DNA Extraction Kit. Biosensors. 2021; 11(10):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100375
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeok, Youngung, Joonseok Lee, and Min-Gon Kim. 2021. "Paper-Based Airborne Bacteria Collection and DNA Extraction Kit" Biosensors 11, no. 10: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100375
APA StyleSeok, Y., Lee, J., & Kim, M.-G. (2021). Paper-Based Airborne Bacteria Collection and DNA Extraction Kit. Biosensors, 11(10), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100375





