Sintering Copper Nanoparticles with Photonic Additive for Printed Conductive Patterns by Intense Pulsed Light
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles
2.2. Ink and Conductive Patterns Preparation
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
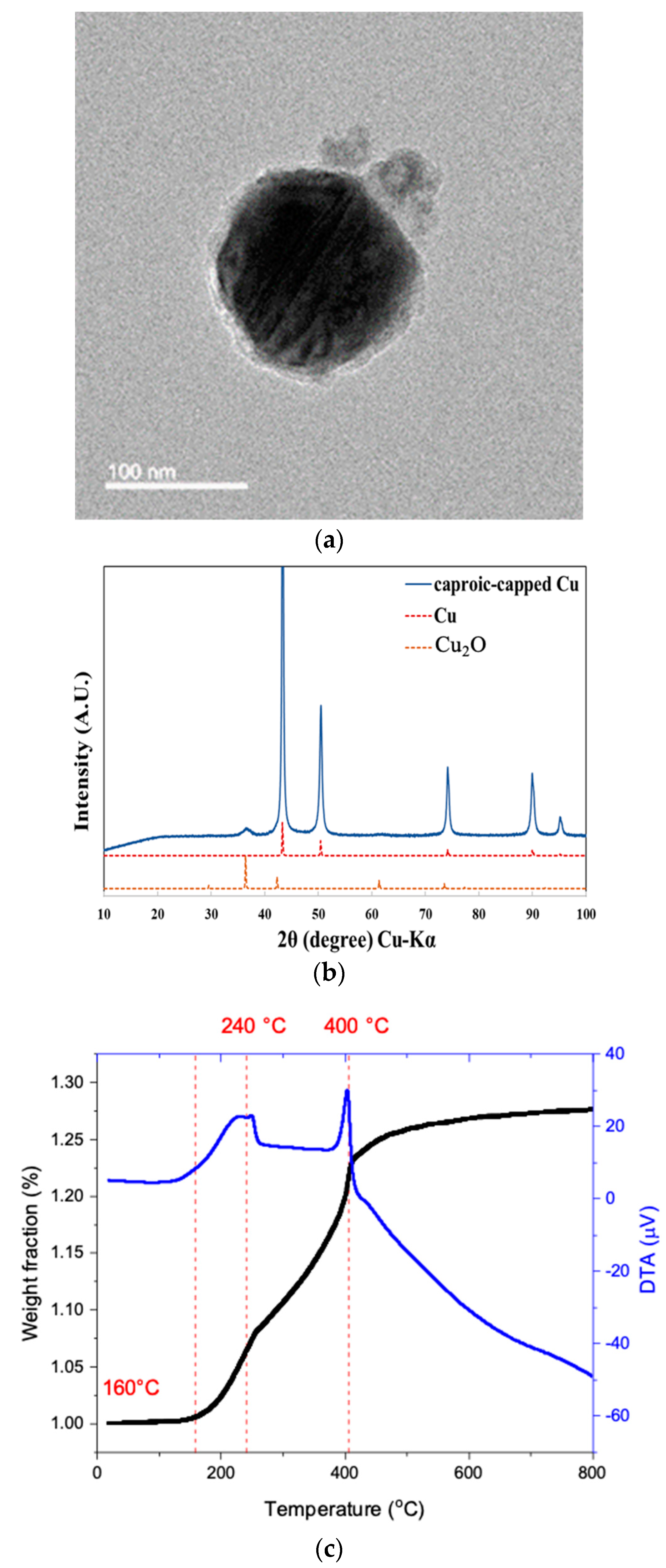
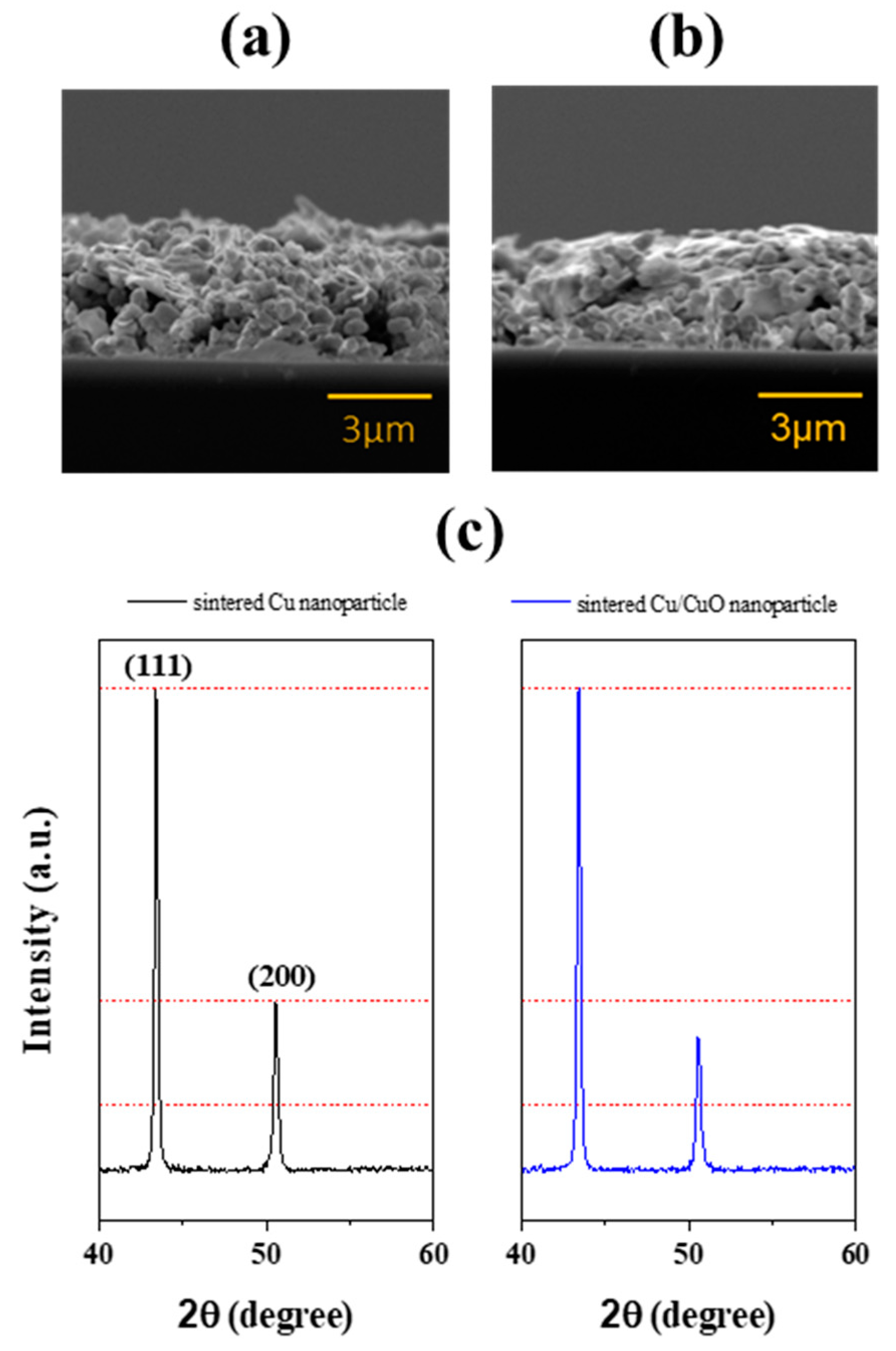
3.1. Characterization of Core-Shell Copper Nanoparticles
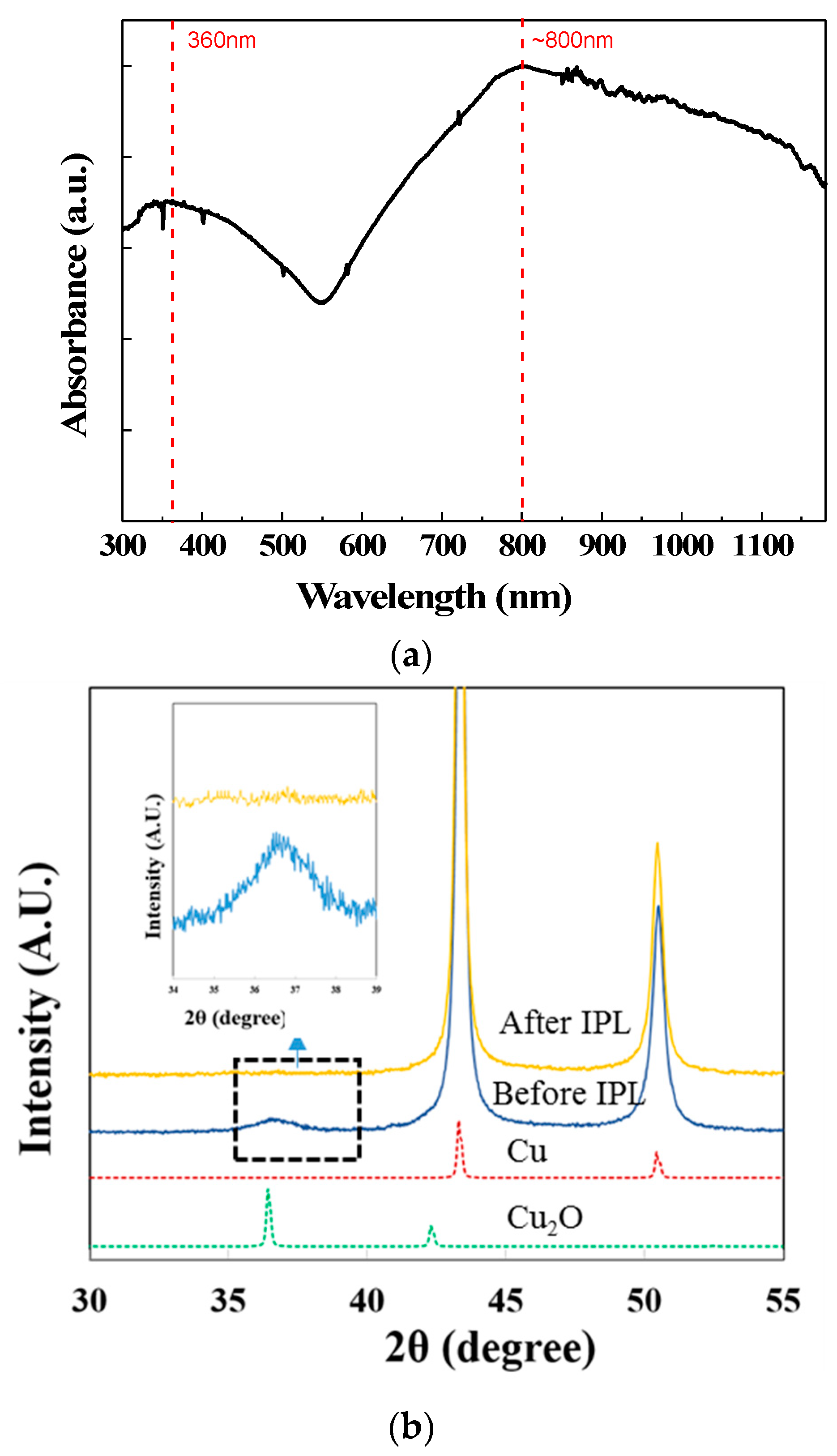
3.2. IPL Sintering for CuNPs
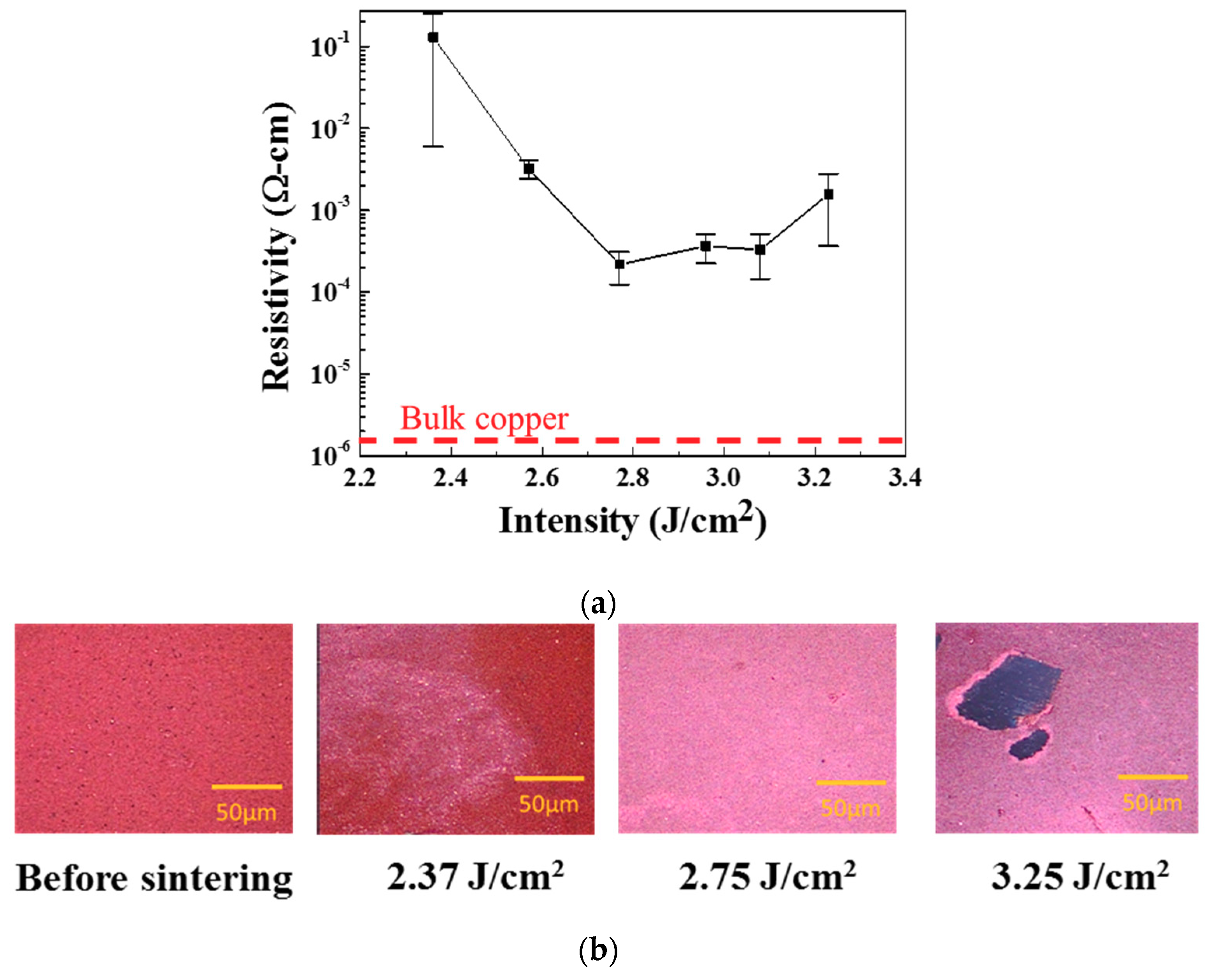
3.3. Effects of IPL Energy Intensity on Film Conductivity
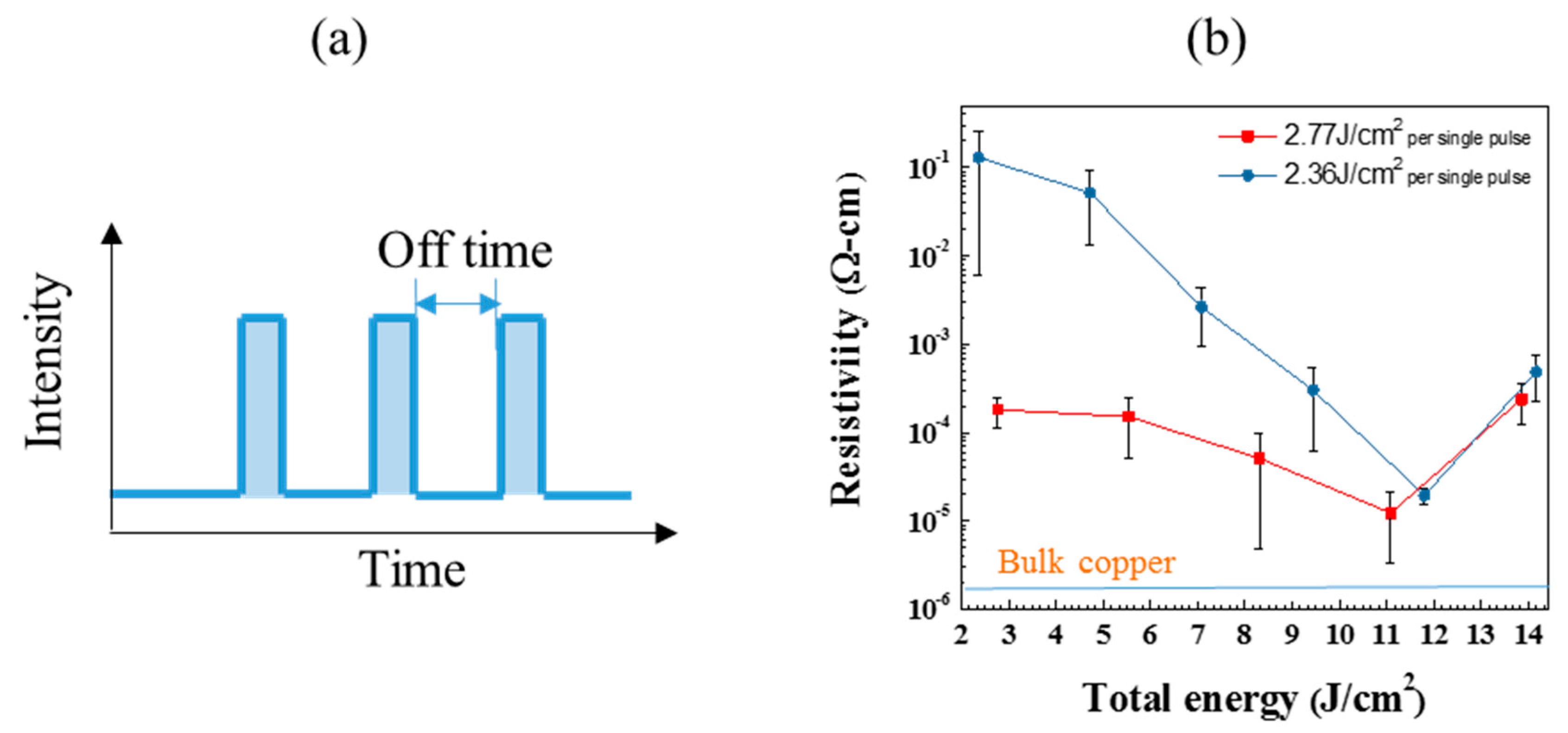
3.4. Multi-Pulse IPL Sintering
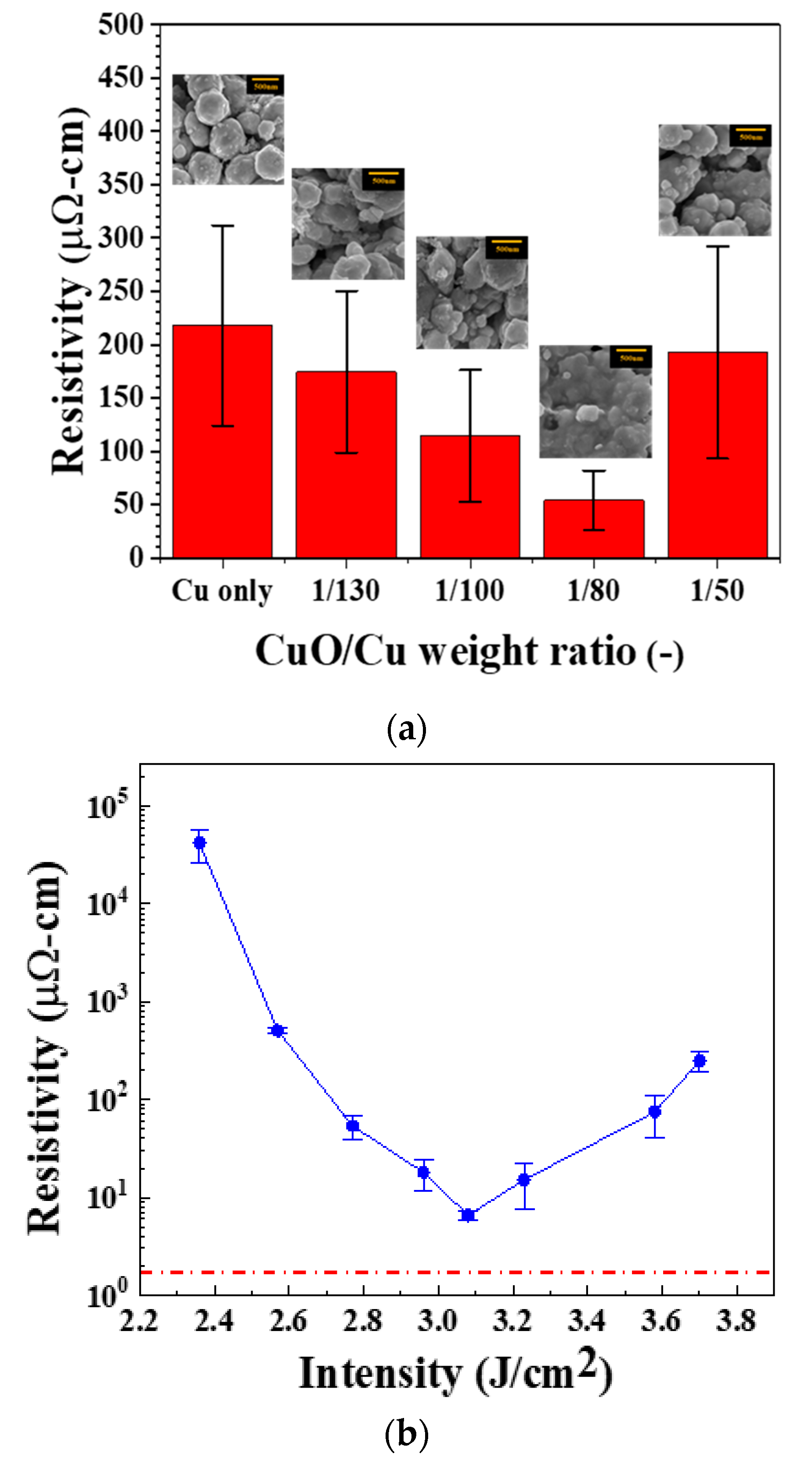
3.5. Addition of Cupric Oxide (CuO) Nanoparticles
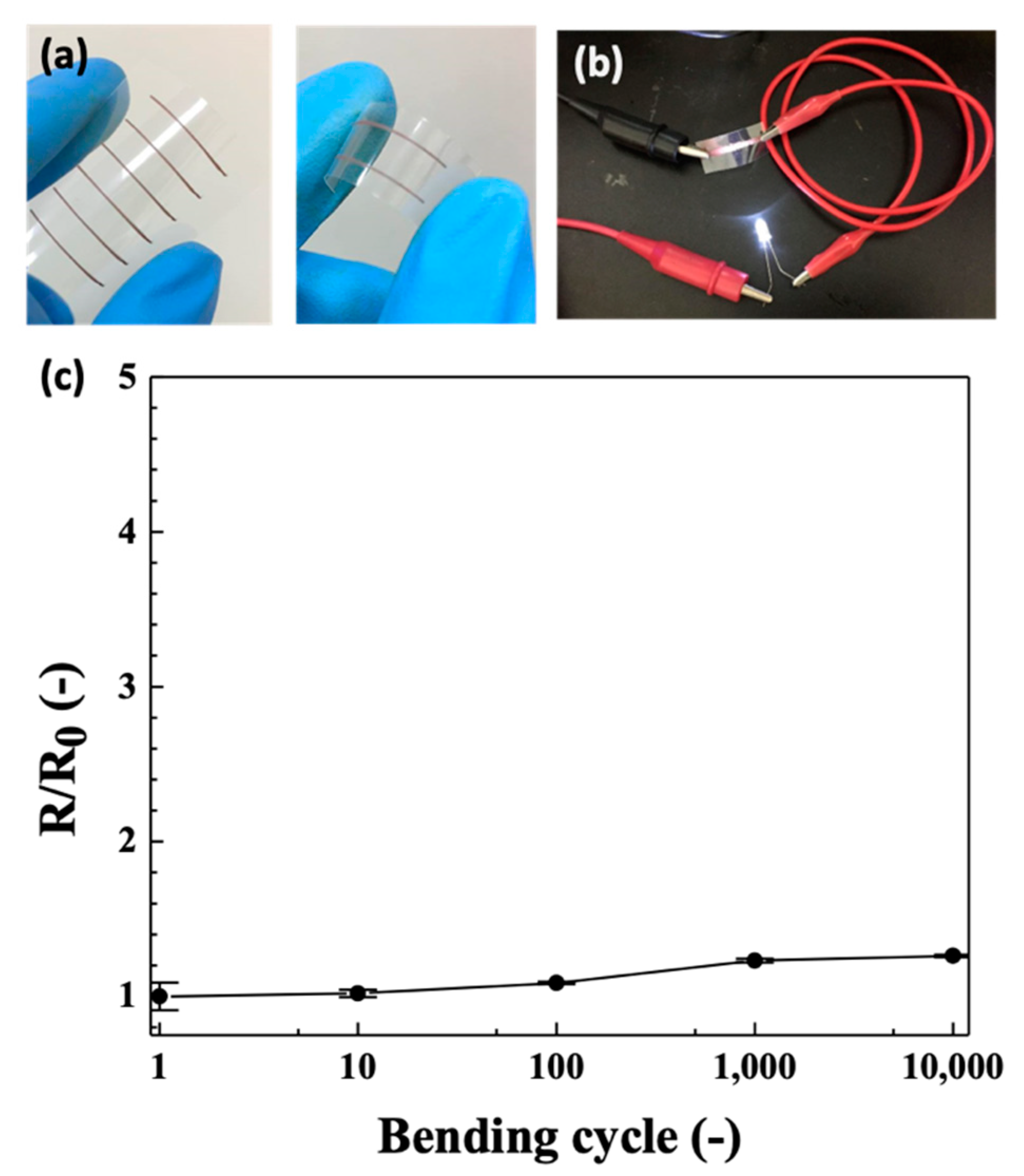
3.6. Conductive Patterns Preparation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.-P.; Chiu, H.-L.; Wang, P.-H.; Liao, Y.-C. Inkjet printed conductive tracks for printed electronics. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, P3026–P3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, F.; Dahl, G.T.; Besztejan, S.; Schroer, M.A.; Lehmkuhler, F.; Grubel, G.; Vossmeyer, T.; Lange, H. Ligand layer engineering to control stability and interfacial properties of nanoparticles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 7897–7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, F.; Friedrich, W.; Hoppe, K.; Vossmeyer, T.; Weller, H.; Lange, H. Effective pegylation of gold nanorods. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7296–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, A.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Abdellah, A.; Lugli, P.; Salmerón, J.F. Inkjet printing and photonic sintering of silver and copper oxide nanoparticles for ultra-low-cost conductive patterns. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 3546–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdassi, S.; Grouchko, M.; Berezin, O.; Kamyshny, A. Triggering the sintering of silver nanoparticles at room temperature. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdassi, S.; Grouchko, M.; Kamyshny, A. Copper nanoparticles for printed electronics: Routes towards achieving oxidation stability. Materials 2010, 3, 4626–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Kim, Y.; Woo, K.; Ryu, E.-H.; Yon, K.-Y.; Cao, G.; Moon, J. Synthesis of oxidation-resistant core–shell copper nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 15169–15177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, T.; Nishida, N.; Hyono, A. One-pot preparation of antioxidized copper fine particles with a unique structure by chemical reduction at room temperature. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 548–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Q.; Song, W. Preparation of solid silver nanoparticles for inkjet printed flexible electronics with high conductivity. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marqués-Hueso, J.; Abargues, R.; Canet-Ferrer, J.; Agouram, S.D.; Valdés, J.L.S.; Martínez-Pastor, J.P. Au-pva nanocomposite negative resist for one-step three-dimensional e-beam lithography. Langmuir 2009, 26, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Hueso, J.; Abargues, R.; Canet-Ferrer, J.; Valdes, J.; Martinez-Pastor, J. Resist-based silver nanocomposites synthesized by lithographic methods. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhlund, T.; Schuppert, A.K.; Hummelgard, M.; Bäckström, J.; Nilsson, H.-E.; Olin, H.k. Inkjet fabrication of copper patterns for flexible electronics: Using paper with active precoatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18273–18282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Sowade, E.; Baumann, R.R. Photonic Sintering of Inkjet Printed Copper Oxide Layer. NIP Digit. Fabr. Conf. 2013, 2013, 494–497. [Google Scholar]
- Krcmar, P.; Kuritka, I.; Maslik, J.; Urbanek, P.; Bazant, P.; Machovsky, M.; Suly, P.; Merka, P. Fully inkjet-printed cuo sensor on flexible polymer substrate for alcohol vapours and humidity sensing at room temperature. Sensors 2019, 19, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, G.L.; Dharmadasa, R.; Staats, M.E.; Lavery, B.W.; Druffel, T. Fabrication of elemental copper by intense pulsed light processing of a copper nitrate hydroxide ink. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16478–16485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Sowade, E.; Baumann, R.R. Direct intense pulsed light sintering of inkjet-printed copper oxide layers within six milliseconds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 1682–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, M.; Yonezawa, T.; Tsukamoto, H. Effect of glass transition temperature of stabilizing polymer of air-stable gelatin-stabilized copper fine particles during redox two-step low-temperature sintering process. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 88, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Kim, H.-S.; Hahn, H.T. Reactive sintering of copper nanoparticles using intense pulsed light for printed electronics. J. Electron. Mater. 2011, 40, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-J.; Oh, K.-H.; Kim, H.-S. All-photonic drying and sintering process via flash white light combined with deep-uv and near-infrared irradiation for highly conductive copper nano-ink. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.H.; Joo, S.J.; Kim, H.S. Multi-pulse flash light sintering of bimodal cu nanoparticle-ink for highly conductive printed cu electrodes. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 205205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-P.; Kao, Z.-K.; Lin, J.-L.; Liao, Y.-C. Silver conductive features on flexible substrates from a thermally accelerated chain reaction at low sintering temperatures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 7064–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-H.; Hong, S.-H. Effect of the amine concentration on phase evolution and densification in printed films using cu (ii) complex ink. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8101–8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farraj, Y.; Grouchko, M.; Magdassi, S. Self-reduction of a copper complex mod ink for inkjet printing conductive patterns on plastics. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farraj, Y.; Smooha, A.; Kamyshny, A.; Magdassi, S. Plasma-induced decomposition of copper complex ink for the formation of highly conductive copper tracks on heat-sensitive substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 8766–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-M.; Tsukamoto, H.; Yong, Y.; Chiu, H.-L.; Nguyen, M.T.; Yonezawa, T.; Liao, Y.-C. Stabilization of the thermal decomposition process of self-reducible copper ion ink for direct printed conductive patterns. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 25095–25100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.-T.; Chung, W.-H.; Jang, Y.-R.; Kim, H.-S. Intensive plasmonic flash light sintering of copper nanoinks using a band-pass light filter for highly electrically conductive electrodes in printed electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8591–8599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, T.; Tsukamoto, H.; Matsubara, M. Low-temperature nanoredox two-step sintering of gelatin nanoskin-stabilized submicrometer-sized copper fine particles for preparing highly conductive layers. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 61290–61297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y.; Yonezawa, T.; Matsubara, M.; Tsukamoto, H. The mechanism of alkylamine-stabilized copper fine particles towards improving the electrical conductivity of copper films at low sintering temperature. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5890–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y.; Nguyen, M.T.; Yonezawa, T.; Asano, T.; Matsubara, M.; Tsukamoto, H.; Liao, Y.-C.; Zhang, T.; Isobe, S.; Nakagawa, Y. Use of decomposable polymer-coated submicron cu particles with effective additive for production of highly conductive cu films at low sintering temperature. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillán, J.; Videla, F.; Fernández van Raap, M.; Schinca, D.; Scaffardi, L. Analysis of the structure, configuration, and sizing of cu and cu oxide nanoparticles generated by fs laser ablation of solid target in liquids. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 134305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Dhage, S.R.; Shim, D.-E.; Hahn, H.T. Intense pulsed light sintering of copper nanoink for printed electronics. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2009, 97, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yang, C.; Gao, Y. Investigations of cuprous oxide and cupric oxide thin films by controlling the deposition atmosphere in the reactive sputtering method. Sens. Mater. 2016, 28, 817–824. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, S.-J.; Hwang, H.-J.; Kim, H.-S. Highly conductive copper nano/microparticles ink via flash light sintering for printed electronics. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 265601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.-B.; Joo, S.-J.; Ahn, H.; Kim, H.-S. Two-step flash light sintering process for enhanced adhesion between copper complex ion/silane ink and a flexible substrate. Thin Solid Film. 2016, 603, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchena, M.; Song, Z.; Senaratne, W.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Baker, D.; Ferrer, J.C.; Mazumder, P.; Soni, K.; Lee, R. Direct growth of 2d and 3d graphene nano-structures over large glass substrates by tuning a sacrificial cu-template layer. 2D Mater. 2017, 4, 025088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference | Particle Composition | Sintering Methods | Substrate | Resistivity (μΩ·cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. [10] | CuO | 7.48 J/cm2 | Poly(ethylene terephthalate) films (PET) | 5.5 |
| Ref. [13] | CuNPs (20–50 nm) | 12.5 J/cm2 + deep UV (30 mW) | PI (Kapton polymide) | 7.6 |
| Ref. [20] | Cu nanoparticles (<100 nm) | 8 J/cm2, 1 ms duration 30 pulses + 4 J/cm2 | PI | 6.9 |
| Ref. [33] | Cu nanoparticle (20 ~ 50 nm) + microparticle (2 µm) | 12.5 J/cm2 | PI | 72.8 |
| Ref. [34] | Cu(NO3)2 + CuNPs | 35 pulses, 30 ms duration. 7 J/cm2 + 1 pulse, 9 J/cm2 | PI | 7.6 |
| Ref. [35] | Graphene + catalytic copper particle | @1100 °C under Ar/H2 environment | Glass | 149.6 |
| This work | Cu/Cu2O core-shell NPs (100 nm/20 nm) + CuO NPs (<50 nm) | 3.08 J/cm2 | PET | 6.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, W.-Y.; Lai, Y.-C.; Yonezawa, T.; Liao, Y.-C. Sintering Copper Nanoparticles with Photonic Additive for Printed Conductive Patterns by Intense Pulsed Light. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081071
Chung W-Y, Lai Y-C, Yonezawa T, Liao Y-C. Sintering Copper Nanoparticles with Photonic Additive for Printed Conductive Patterns by Intense Pulsed Light. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(8):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081071
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Wan-Yu, Yi-Chin Lai, Tetsu Yonezawa, and Ying-Chih Liao. 2019. "Sintering Copper Nanoparticles with Photonic Additive for Printed Conductive Patterns by Intense Pulsed Light" Nanomaterials 9, no. 8: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081071
APA StyleChung, W.-Y., Lai, Y.-C., Yonezawa, T., & Liao, Y.-C. (2019). Sintering Copper Nanoparticles with Photonic Additive for Printed Conductive Patterns by Intense Pulsed Light. Nanomaterials, 9(8), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081071






