Current Conjugation Methods for Immunosensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Selection of Antigen Binding Molecules
3. Immunosensor Types and Common Material Selection
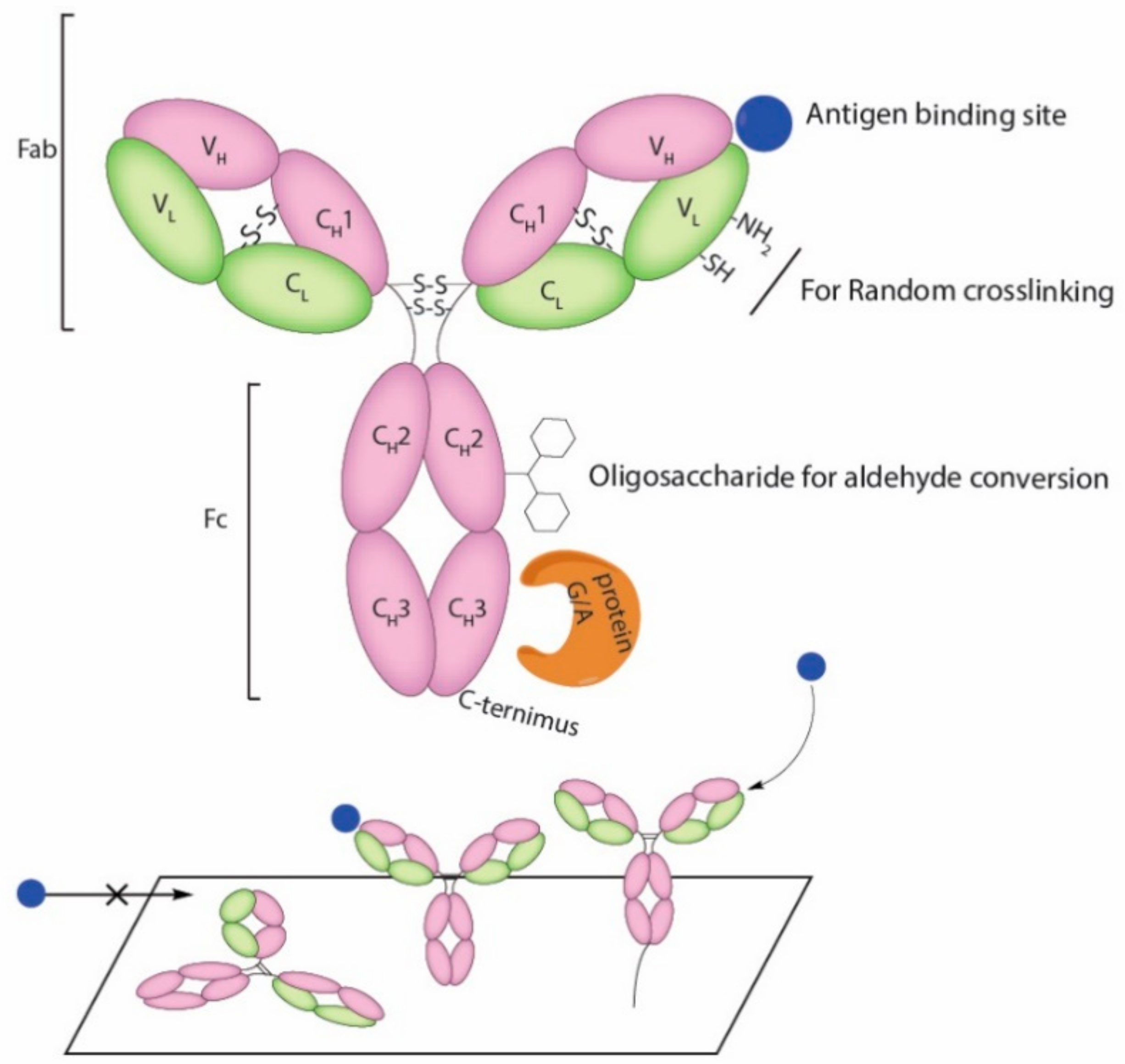
4. Current Conjugation Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heineman, W.R.; Jensen, W.B. Leland C. Clark Jr. (1918–2005). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1403–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, K.R.; Chou, R.C. Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and derivatives: Historical perspectives and future directions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliger, P.; Hudson, P.J. Engineered antibody fragments and the rise of single domains. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies: Natural single-domain antibodies. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binz, H.K.; Amstutz, P.; Kohl, A.; Stumpp, M.T.; Briand, C.; Forrer, P.; Grutter, M.G.; Pluckthun, A. High-affinity binders selected from designed ankyrin repeat protein libraries. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nord, K.; Gunneriusson, E.; Ringdahl, J.; Stahl, S.; Uhlen, M.; Nygren, P.A. Binding proteins selected from combinatorial libraries of an alpha-helical bacterial receptor domain. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Battig, M.R.; Wang, Y. Aptamer-based molecular recognition for biosensor development. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidarsson, G.; Dekkers, G.; Rispens, T. IgG subclasses and allotypes: From structure to effector functions. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipman, N.S.; Jackson, L.R.; Trudel, L.J.; Weis-Garcia, F. Monoclonal versus polyclonal antibodies: Distinguishing characteristics, applications, and information resources. ILAR J. 2005, 46, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, N.; Dwiwedi, P.; Charan, J.; Kaur, R.; Sidhu, P.; Chugh, V.K. Monoclonal antibodies: A review. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banker, D.D. Monoclonal antibodies. A review. Indian J. Med. Sci. 2001, 55, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vira, S.; Mekhedov, E.; Humphrey, G.; Blank, P.S. Fluorescent-labeled antibodies: Balancing functionality and degree of labeling. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 402, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werthen, M.; Nygren, H. Effect of antibody affinity on the isotherm of antibody binding to surface-immobilized antigen. J. Immunol. Methods 1988, 115, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trilling, A.K.; Beekwilder, J.; Zuilhof, H. Antibody orientation on biosensor surfaces: A minireview. Analyst 2013, 138, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bever, C.S.; Dong, J.X.; Vasylieva, N.; Barnych, B.; Cui, Y.; Xu, Z.L.; Hammock, B.D.; Gee, S.J. Vhh antibodies: Emerging reagents for the analysis of environmental chemicals. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 5985–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, A. Biotechnological applications of recombinant single-domain antibody fragments. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, P.; White, R.R. Aptamers for targeted drug delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 1761–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, L.J.; Larson, S.B.; Hasel, K.W.; McPherson, A. Refined structure of an intact IgG2a monoclonal antibody. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubala, M.H.; Kovtun, O.; Alexandrov, K.; Collins, B.M. Structural and thermodynamic analysis of the GFP: GFP-nanobody complex. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 2389–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecqueur, L.; Duellberg, C.; Dreier, B.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, C.; Pluckthun, A.; Surrey, T.; Gigant, B.; Knossow, M. An Anti-Tubulin Darpin Caps the Microtubule Plus-End. Available online: http://www.rcsb.org/structure/4DUI (accessed on 15 February 2013).
- Midelfort, K.S.; Hernandez, H.H.; Lippow, S.M.; Tidor, B.; Drennan, C.L.; Wittrup, K.D. Substantial energetic improvement with minimal structural perturbation in a high affinity mutant antibody. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigenbrot, C.; Ultsch, M.; Dubnovitsky, A.; Abrahmsen, L.; Hard, T. Structural basis for high-affinity HER2 receptor binding by an engineered protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15039–15044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, E.B.; Polaski, J.T.; Morck, M.M.; Batey, R.T. Recurrent RNA motifs as scaffolds for genetically encodable small-molecule biosensors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbany, S.Y.; Donner, B.L.; Ligler, F.S. Optical immunosensors. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1994, 22, 307–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felix, F.S.; Angnes, L. Electrochemical immunosensors—A powerful tool for analytical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, W.; Yan, X.; Zhu, C.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Recent advances in electrochemical immunosensors. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, Q.M. High-temperature piezoelectric crystals for acoustic wave sensor applications. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2016, 63, 486–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrazza, G. Piezoelectric biosensors for organophosphate and carbamate pesticides: A review. Biosensors 2014, 4, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkoyun, A.; Bilitewski, U. Optimisation of glass surfaces for optical immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederoder, M.S.; Kendall, E.L.; Han, J.H.; Ulrich, R.G.; DeVoe, D.L. Flow-through microfluidic immunosensors with refractive index-matched silica monoliths as volumetric optical detection elements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, G.A. Optical immunosensors. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1991, 19, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Lin, Y. Nanomaterial labels in electrochemical immunosensors and immunoassays. Talanta 2007, 74, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munge, B.S.; Krause, C.E.; Malhotra, R.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Electrochemical immunosensors for interleukin-6. Comparison of carbon nanotube forest and gold nanoparticle platforms. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Malhotra, R.; Peczuh, M.W.; Rusling, J.F. Electrochemical immunosensors for antibodies to peanut allergen ara h2 using gold nanoparticle-peptide films. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5865–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piro, B.; Reisberg, S. Recent advances in electrochemical immunosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hees, J.; Heidrich, N.; Pletschen, W.; Sah, R.E.; Wolfer, M.; Williams, O.A.; Lebedev, V.; Nebel, C.E.; Ambacher, O. Piezoelectric actuated micro-resonators based on the growth of diamond on aluminum nitride thin films. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 025601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiseman, M.E.; Frank, C.W. Antibody adsorption and orientation on hydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, X.; Grant, C.; Lu, J.R.; Williams, D.E.; Penfold, J. Orientation of a monoclonal antibody adsorbed at the solid/solution interface: A combined study using atomic force microscopy and neutron reflectivity. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6313–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zourob, M. Recognition Receptors in Biosensors; Springer: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2010; p. xvi. 863p. [Google Scholar]
- Ligler, F.S.; Taitt, C.A.R. Optical Biosensors: Present and Future, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. viii. 607p. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, V.C.-M.; Ngo, T.T. Biosensors and Their Applications; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. xviii. 360p. [Google Scholar]
- Rasooly, A.; Herold, K.E. Biosensors and Biodetection: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Elsevier/AP: London, UK; Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; p. xvii. 1146p. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R.R.; Preedy, V.R. Genetically Modified Organisms in Food: Production, Safety, Regulation and Public Health; Elsevier Science/Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Nertherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2016; p. xxi. 494p. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, W.; Durgannavar, T.A.; Chung, S.J. Fc-binding ligands of immunoglobulin G: An overview of high affinity proteins and peptides. Materials 2016, 9, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spicer, C.D.; Davis, B.G. Selective chemical protein modification. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, G.C.; Bethell, D.R. Basic Methods in Antibody Production and Characterization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; p. 271. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.T.W.; Maruani, A.; Richards, D.A.; Baker, J.R.; Caddick, S.; Chudasama, V. Enabling the controlled assembly of antibody conjugates with a loading of two modules without antibody engineering. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 2056–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
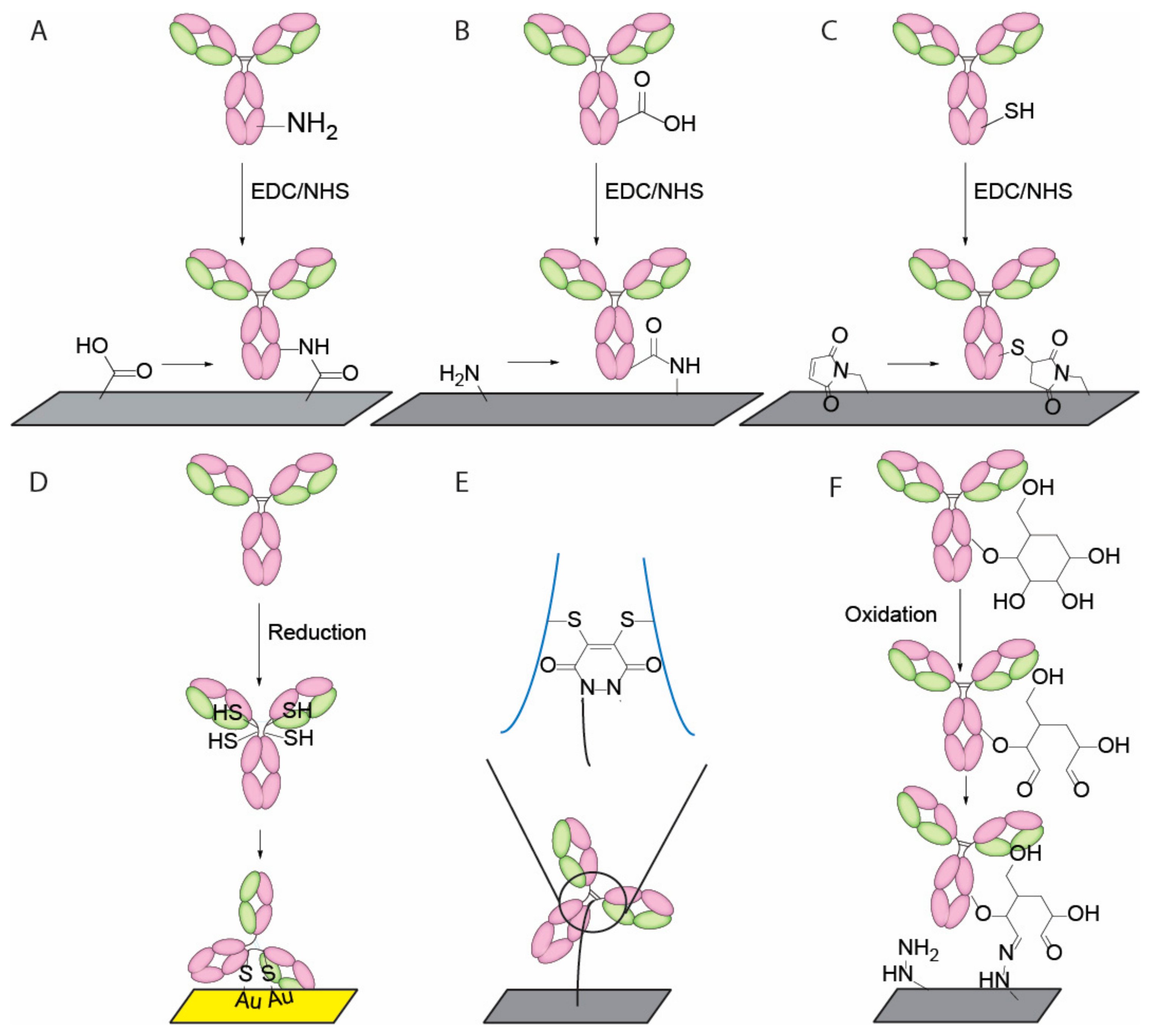
- Kang, J.H.; Choi, H.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Han, S.H.; Jeon, J.Y.; Lee, E.K. Improving immunobinding using oriented immobilization of an oxidized antibody. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1161, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makaraviciute, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. Site-directed antibody immobilization techniques for immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, N.J.; Champion, M.M.; Stefanick, J.F.; Handlogten, M.W.; Moustakas, D.T.; Shi, Y.; Shaw, B.F.; Navari, R.M.; Kiziltepe, T.; Bilgicer, B. Selective photocrosslinking of functional ligands to antibodies via the conserved nucleotide binding site. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5700–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boozer, C.; Ladd, J.; Chen, S.; Yu, Q.; Homola, J.; Jiang, S. DNA directed protein immobilization on mixed ssdna/oligo(ethylene glycol) self-assembled monolayers for sensitive biosensors. Anal. Chem 2004, 76, 6967–6972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
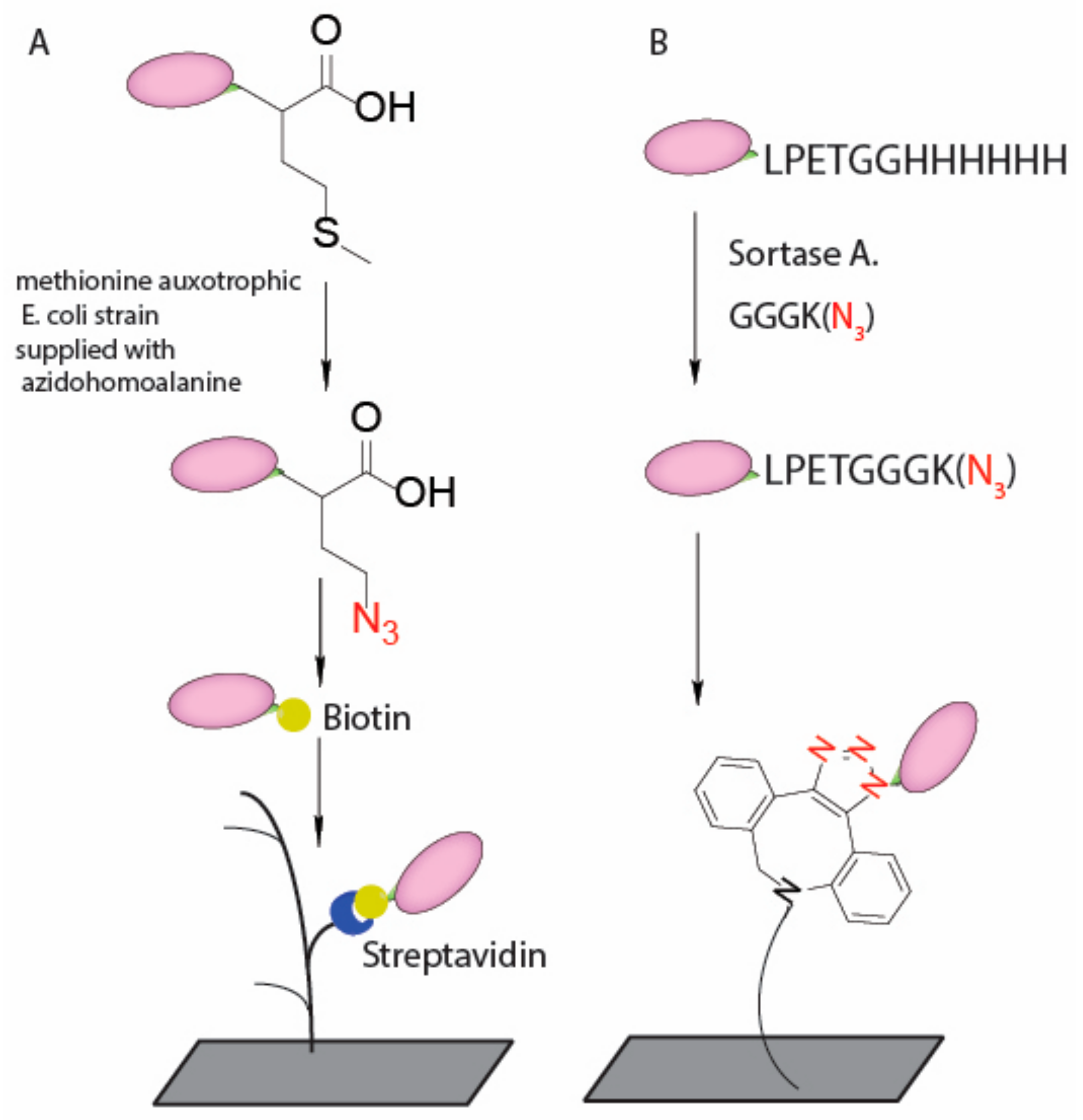
- Trilling, A.K.; Harmsen, M.M.; Ruigrok, V.J.; Zuilhof, H.; Beekwilder, J. The effect of uniform capture molecule orientation on biosensor sensitivity: Dependence on analyte properties. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, J.S.; Bertozzi, C.R. New aldehyde tag sequences identified by screening formylglycine generating enzymes in vitro and in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12240–12241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Y.; Li, Z.; Theile, C.S.; Bardhan, N.M.; Kumar, P.V.; Duarte, J.N.; Maruyama, T.; Rashidfarrokh, A.; Belcher, A.M.; Ploegh, H.L. Graphene oxide nanosheets modified with single-domain antibodies for rapid and efficient capture of cells. Chemistry 2015, 21, 17178–17183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Y.; Li, Z.; Duarte, J.N.; Esteban, A.; Cheloha, R.W.; Theile, C.S.; Fink, G.R.; Ploegh, H.L. Rapid capture and labeling of cells on single domain antibodies-functionalized flow cell. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shen, Z.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mernaugh, R.L.; Zeng, X. Engineering peptide linkers for scFv immunosensors. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Mernaugh, R.L.; Yan, H.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X. Engineered recombinant single-chain fragment variable antibody for immunosensors. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6834–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falco, C.N.; Dykstra, K.M.; Yates, B.P.; Berget, P.B. Scfv-based fluorogen activating proteins and variable domain inhibitors as fluorescent biosensor platforms. Biotechnol. J. 2009, 4, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, F.-L.; Lan, K.-C.; Chang, C.-Y.; Hsu, C.-H.; Ho, T.-Y.; Hsieh, M.-H.; Kuo, T.-H.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Lin, R.-H.; Hsu, W.-H.; et al. E.Cotector: The fluorescent E. coli with surface displayed anti-cancer marker scFv to detect specific cancer markers. PLoS Collect. 2016. Available online: http://blogs.plos.org/blog/2016/10/15/igem-research-article-e-cotector-the-fluorescent-e-coli-with-surface-displayed-anti-cancer-marker-scfv-to-detect-specific-cancer-markers/ (accessed on 15 March 2018).
- Deyev, S.; Proshkina, G.; Ryabova, A.; Tavanti, F.; Menziani, M.C.; Eidelshtein, G.; Avishai, G.; Kotlyar, A. Synthesis, characterization, and selective delivery of darpin-gold nanoparticle conjugates to cancer cells. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 2569–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, C.; Pluckthun, A. Engineered proteins with desired specificity: Darpins, other alternative scaffolds and bispecific igGs. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2014, 27, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Su, X. Label-free aptamer biosensor for selective detection of thrombin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 899, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa, S.; Zourob, M. Aptamer- based label-free electrochemical biosensor array for the detection of total and glycated hemoglobin in human whole blood. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farokhzad, O.C.; Karp, J.M.; Langer, R. Nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for cancer targeting. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- York, D.; Baker, J.; Holder, P.G.; Jones, L.C.; Drake, P.M.; Barfield, R.M.; Bleck, G.T.; Rabuka, D. Generating aldehyde-tagged antibodies with high titers and high formylglycine yields by supplementing culture media with copper(ii). BMC Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyer, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Depicker, A. Nanobody-based products as research and diagnostic tools. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardhan, N.M.; Kumar, P.V.; Li, Z.; Ploegh, H.L.; Grossman, J.C.; Belcher, A.M.; Chen, G.Y. Enhanced cell capture on functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets through oxygen clustering. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1548–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.; Duarte, J.N.; Ling, J.; Li, Z.; Guzman, J.S.; Ploegh, H.L. Structurally defined alphaMHC-ii nanobody-drug conjugates: A therapeutic and imaging system for B-cell lymphoma. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 2416–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Theile, C.S.; Chen, G.Y.; Bilate, A.M.; Duarte, J.N.; Avalos, A.M.; Fang, T.; Barberena, R.; Sato, S.; Ploegh, H.L. Fluorophore-conjugated holliday junctions for generating super-bright antibodies and antibody fragments. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 11706–11710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
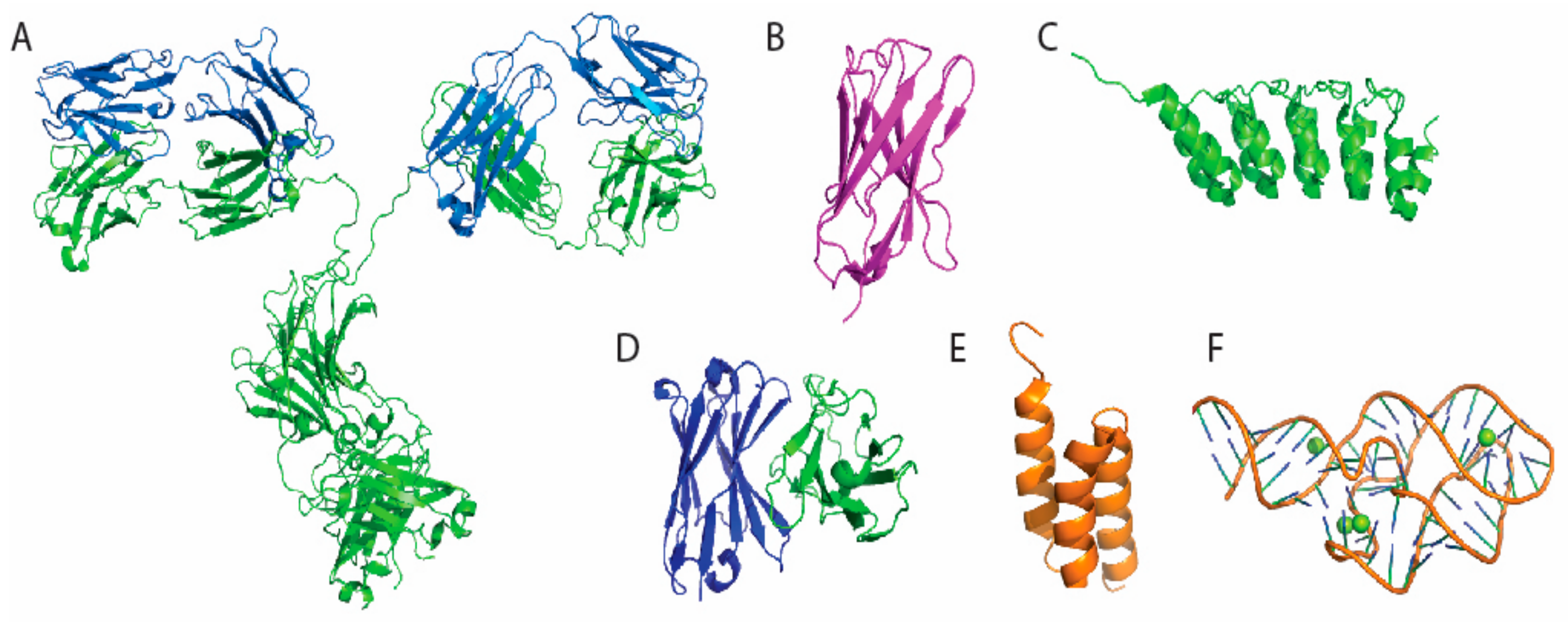
| Immunosensor Type | Common Materials | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optical | Evanescent wave | Quartz, glass, graphene oxide (GO) sheets, hydrogels | [24,29,30,31] |
| Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) | Silver, gold, copper, aluminum | ||
| Electrochemical | Conductive | Carbon, indium tin oxide, carbon nanotube, hydrogels, polythiophene | [32,33,34,35] |
| Amperometric | Graphite, Lipid, Platinum, Gold, Nickel | ||
| Piezoelectric | Bulk acoustic wave | Aluminium phosphate, aluminium nitride, zinc oxide, crystalized topaz, crystalized tourmaline, barium titanate, gallium orthophosphate, lead titanate | [27,28,36] |
| Surface acoustic wave | |||
| Type of Antigen Binding Molecules | Types of Immobilization | Functional Group | Orientation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Adsorption | Various | Random | [39,40,41,42] |
| Affinity | Antigen-antibody reaction | Partially oriented | [42,43,44] | |
| Protein A or G (non-covalent) binding | Partially oriented | [41,45] | ||
| Radom crosslinking | Amine/carboxylic acid | Random | [43,44,46,47] | |
| Thiol group | Random | [44,46,48] | ||
| Sugar chain on CH2 | Partially Oriented | [49,50] | ||
| DNA-directed | Nucleotide Binding Site ssDNA hybridization | Uniformly oriented | [51,52] | |
| C terminus | Enzyme mediated biotinylation | Uniformly oriented | [49] | |
| VHH | C terminus | non-natural amino-acid | Uniformly oriented | [53,54] |
| C terminus | Enzyme mediated transpeptidation | Uniformly oriented | [55,56] | |
| scFv | Tag mediated | Cysteine or Histidine containing linker | Partially Oriented | [57,58,59] |
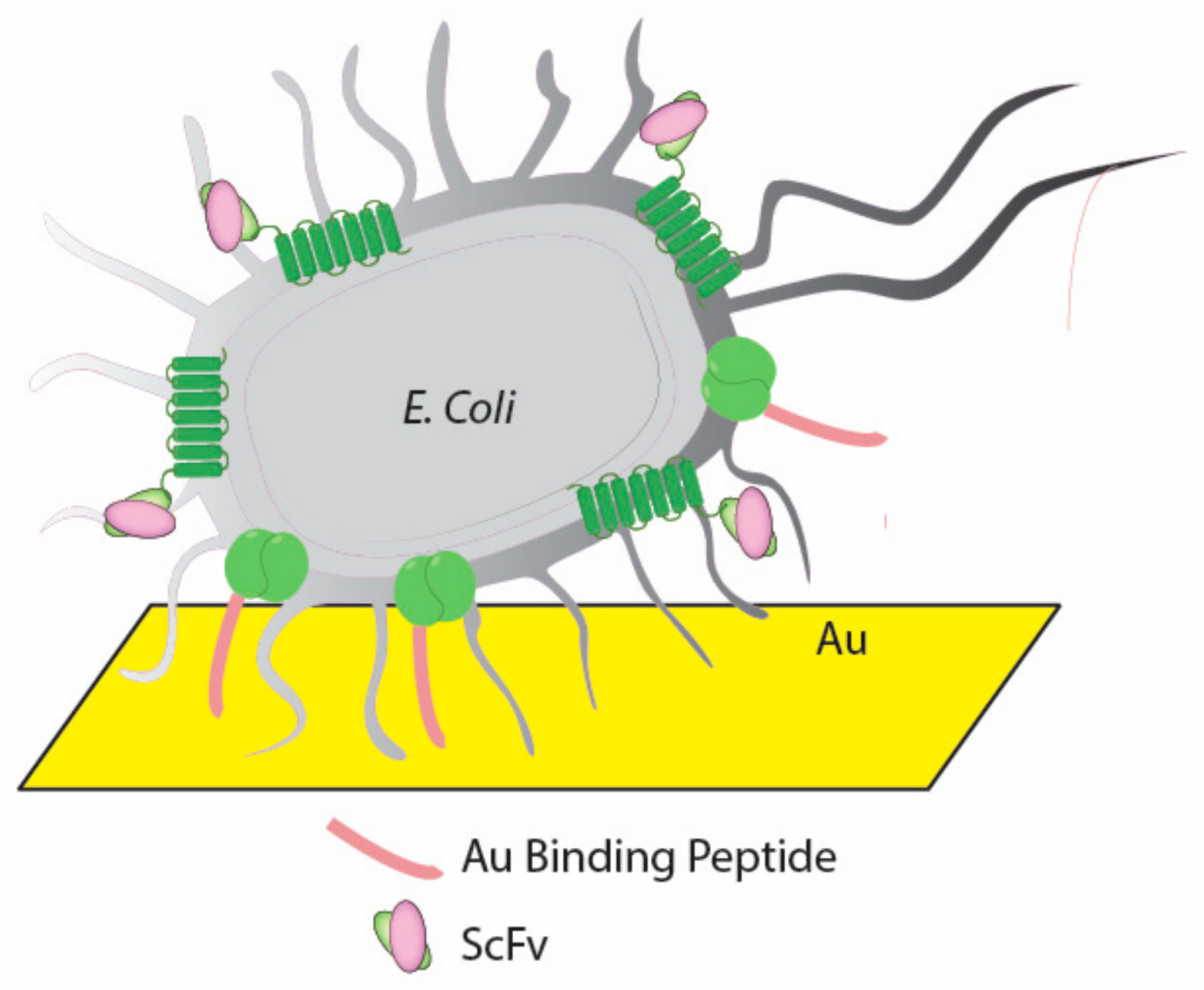
| E. coli surface displayed | Genetic fusion | Uniformly oriented | [60] | |
| DARPins | Radom crosslinking | Amine group | Random | [61,62] |
| Aptamer | Terminal modification | Thiol | Uniformly oriented | [63,64,65] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Chen, G.-Y. Current Conjugation Methods for Immunosensors. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050278
Li Z, Chen G-Y. Current Conjugation Methods for Immunosensors. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(5):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050278
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zeyang, and Guan-Yu Chen. 2018. "Current Conjugation Methods for Immunosensors" Nanomaterials 8, no. 5: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050278
APA StyleLi, Z., & Chen, G.-Y. (2018). Current Conjugation Methods for Immunosensors. Nanomaterials, 8(5), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050278





