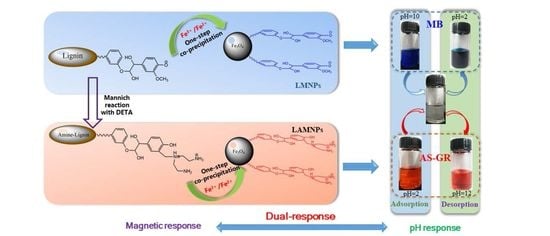
One-Step Fabrication of Dual Responsive Lignin Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Cationic and Anionic Dyes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
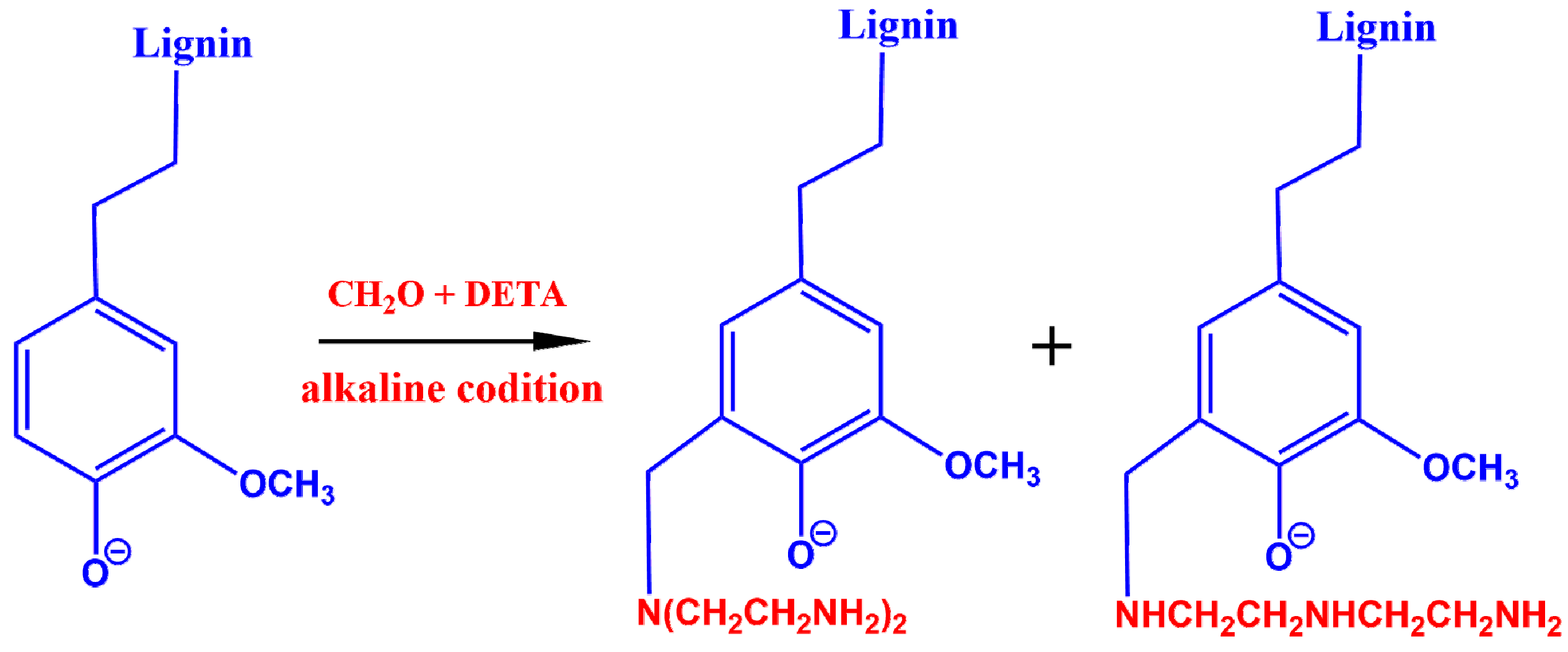
2.2. Preparation of Lignin Amine (LA)
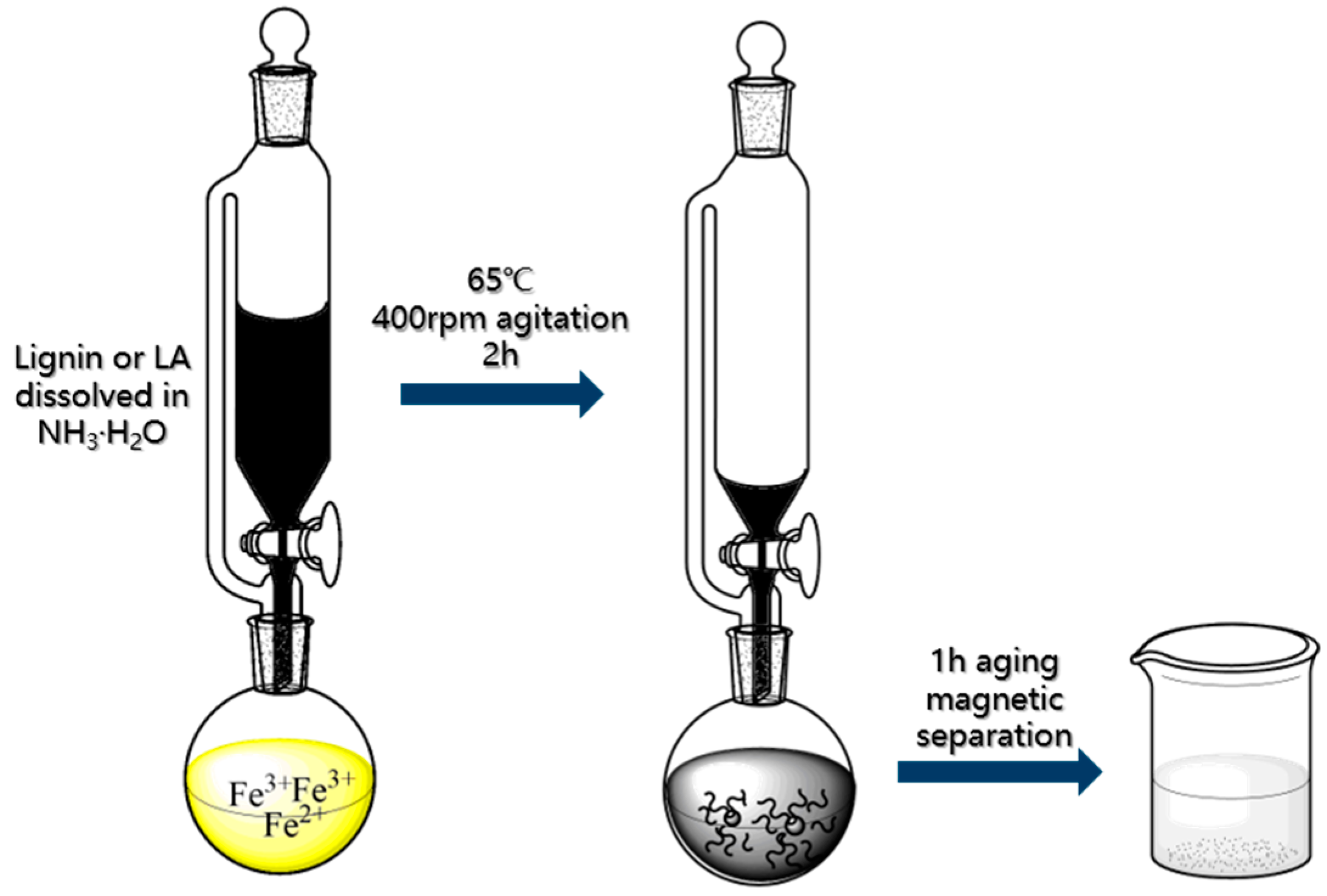
2.3. Preparation of Lignin and Lignin Amine Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
2.4. Adsorption and Desorption of Different Dyes
2.5. Instrumental Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Lignin Amine
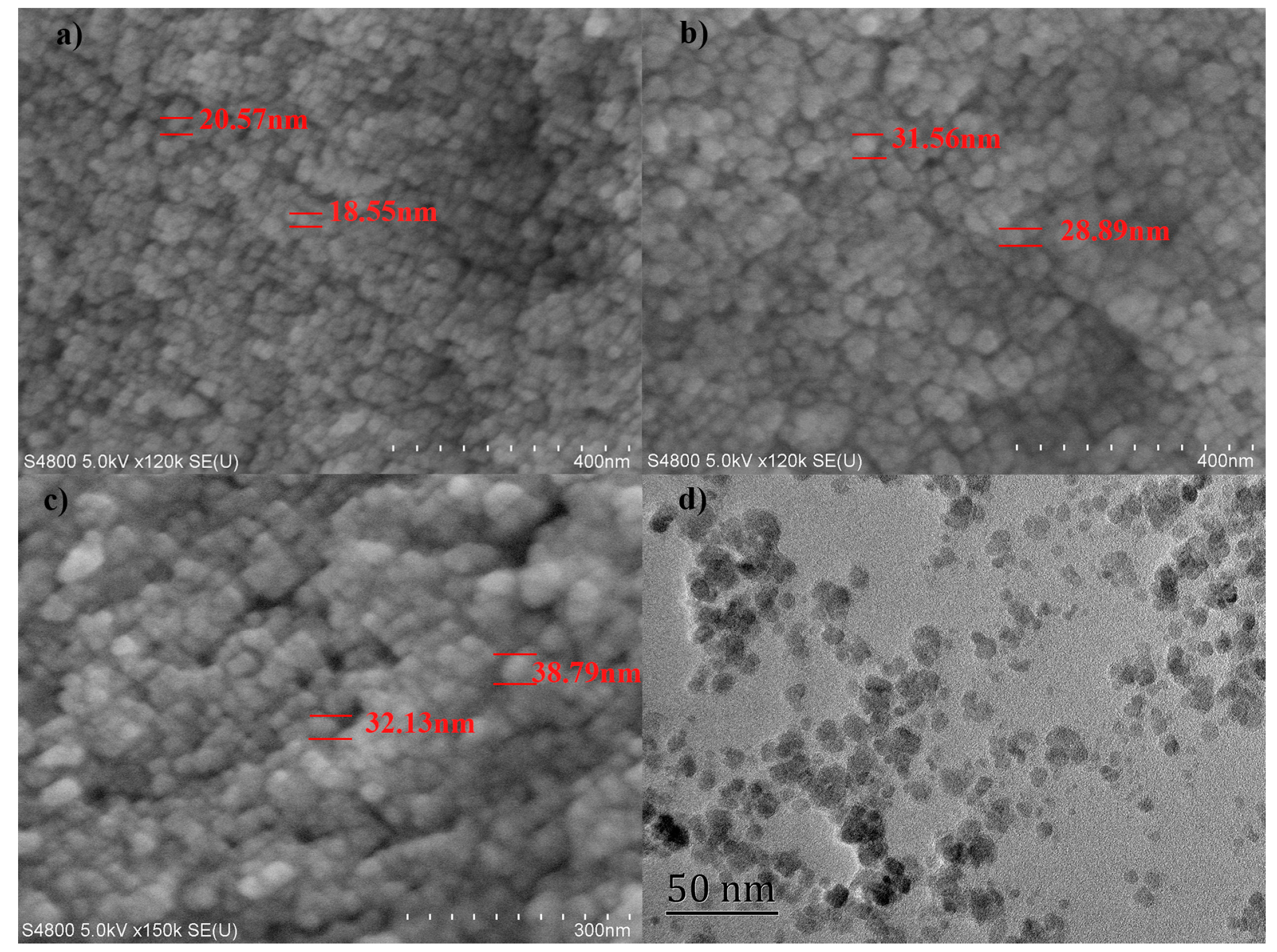
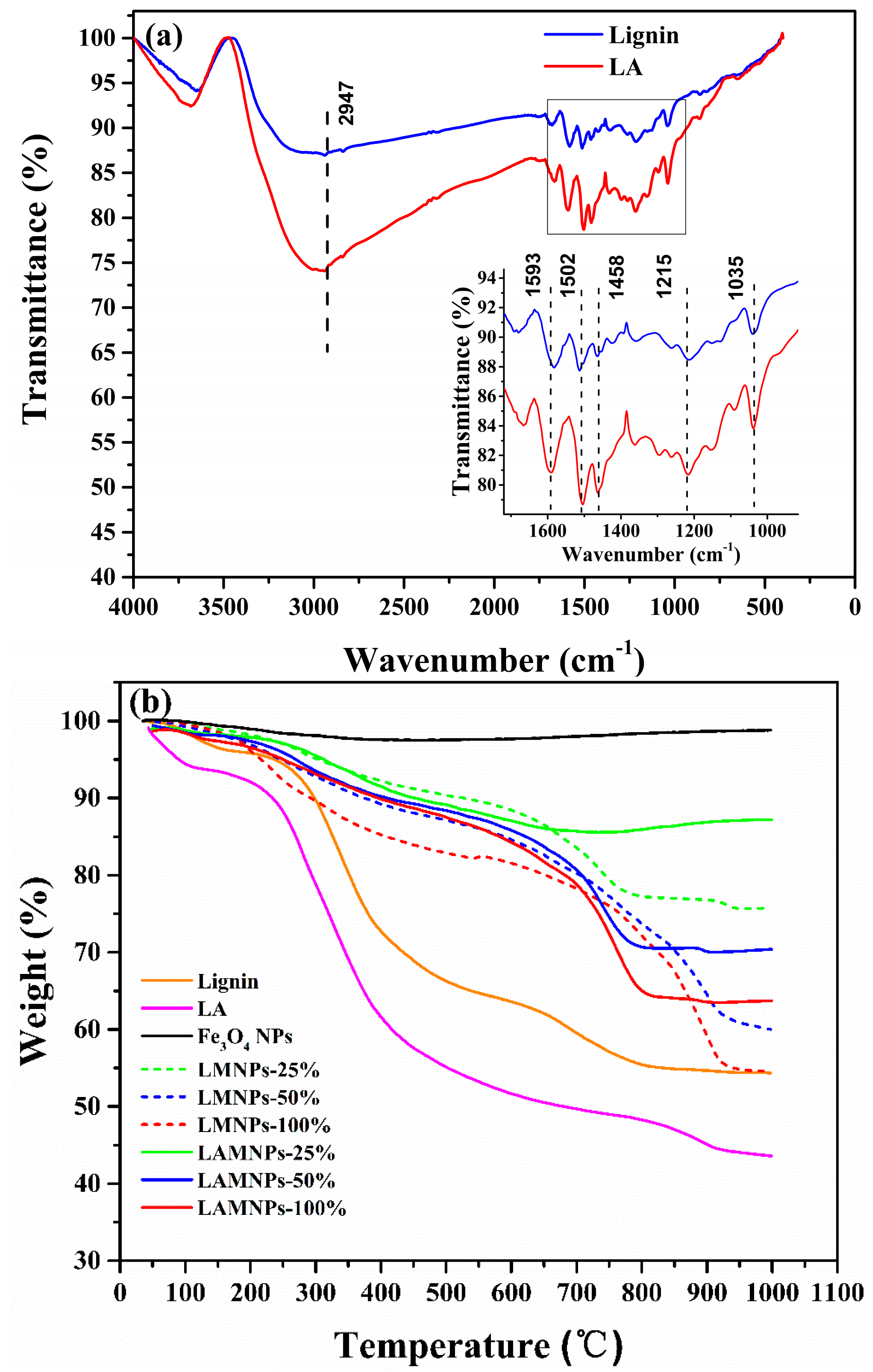
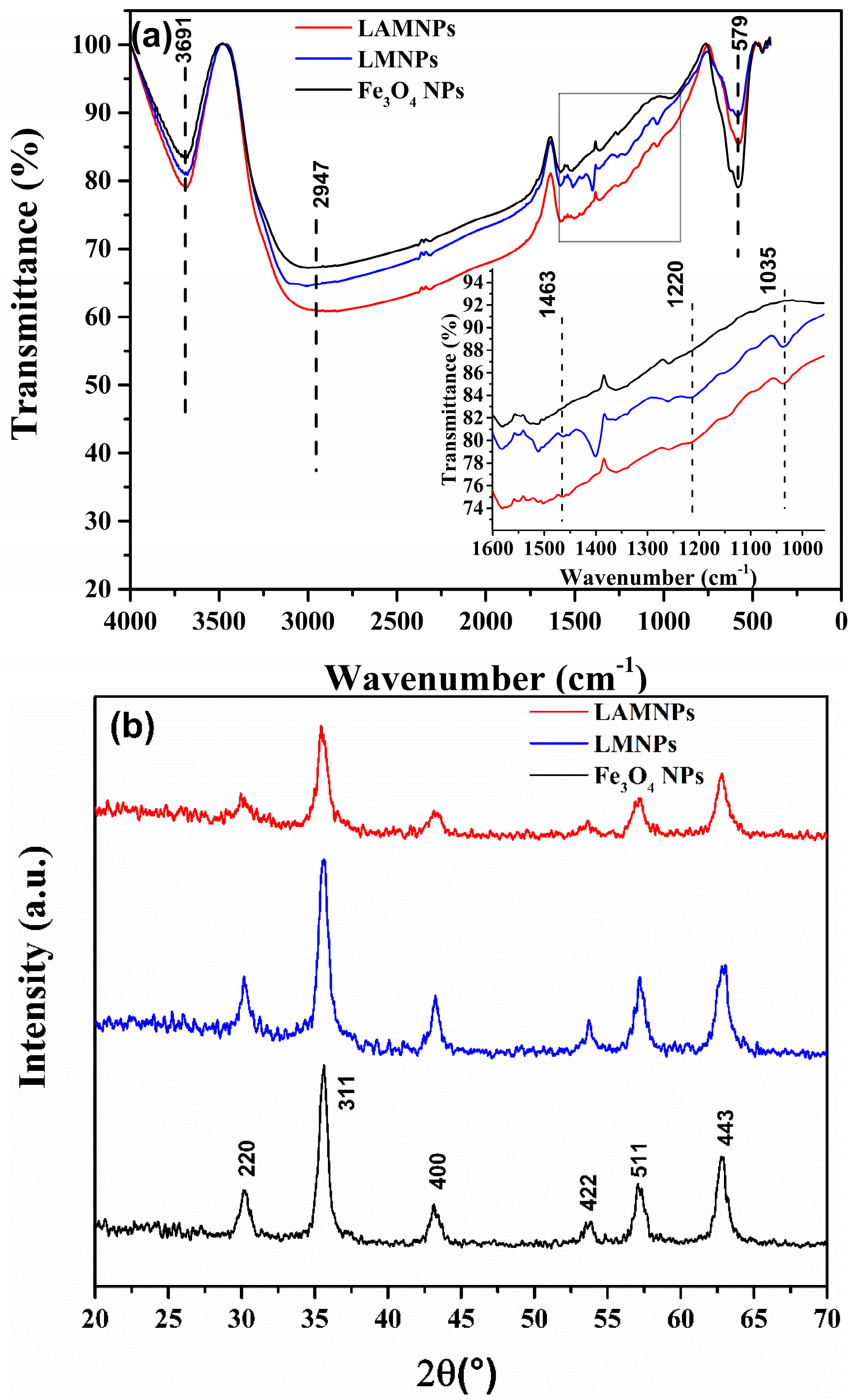
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of LMNPs and LAMNPs
3.3. Adsorption of Dyes on LMNPs and LAMNPs
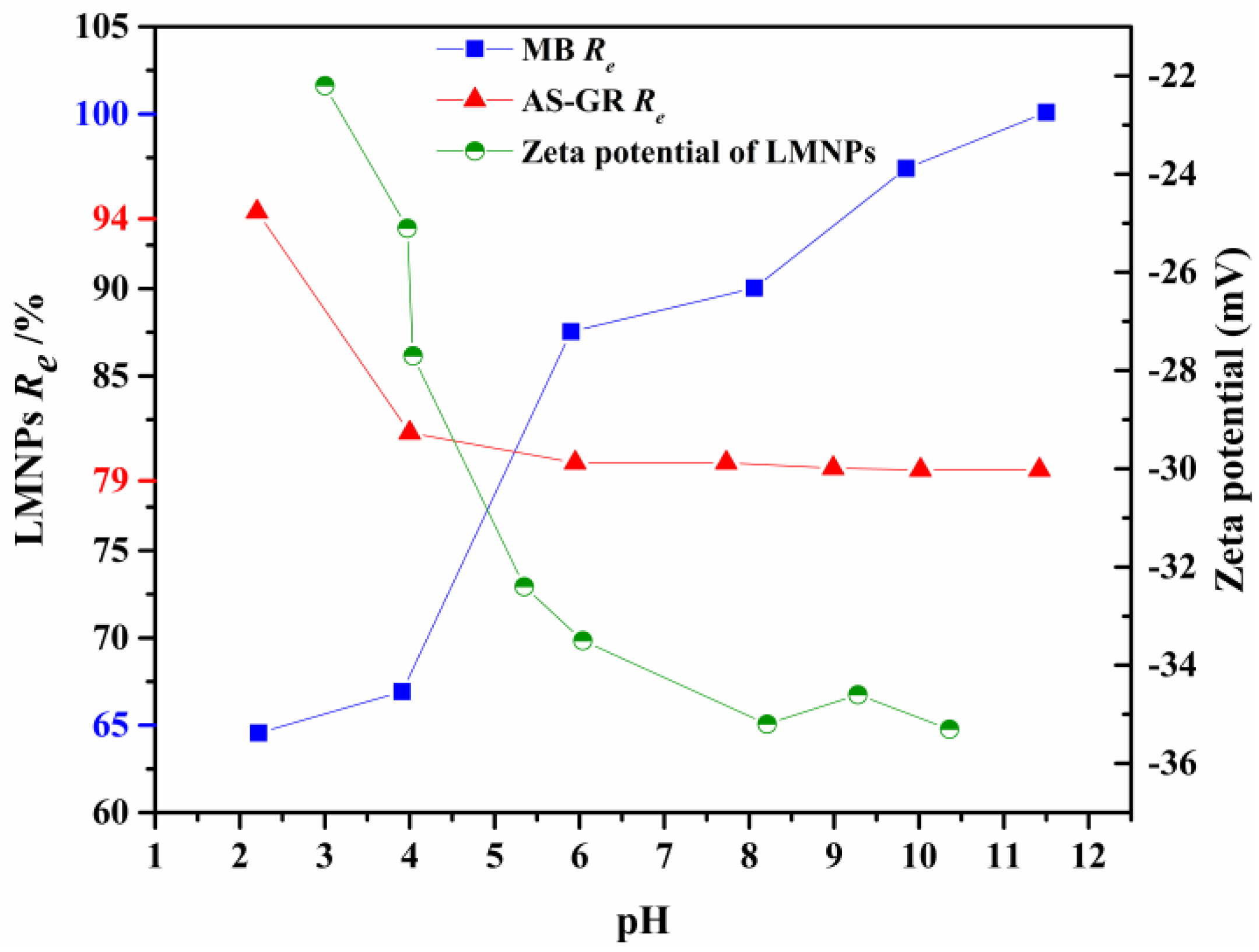
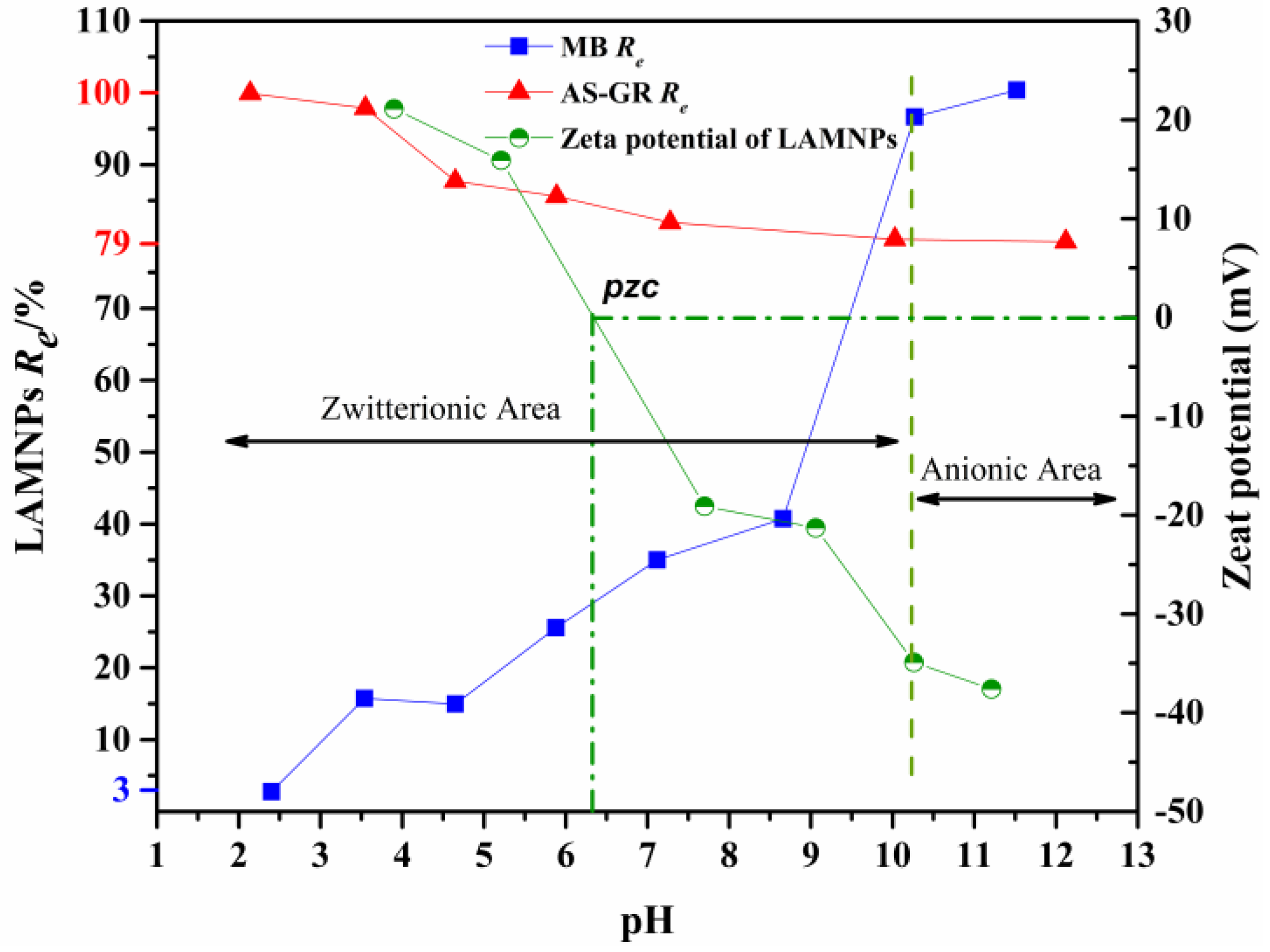
3.3.1. Effects of pH
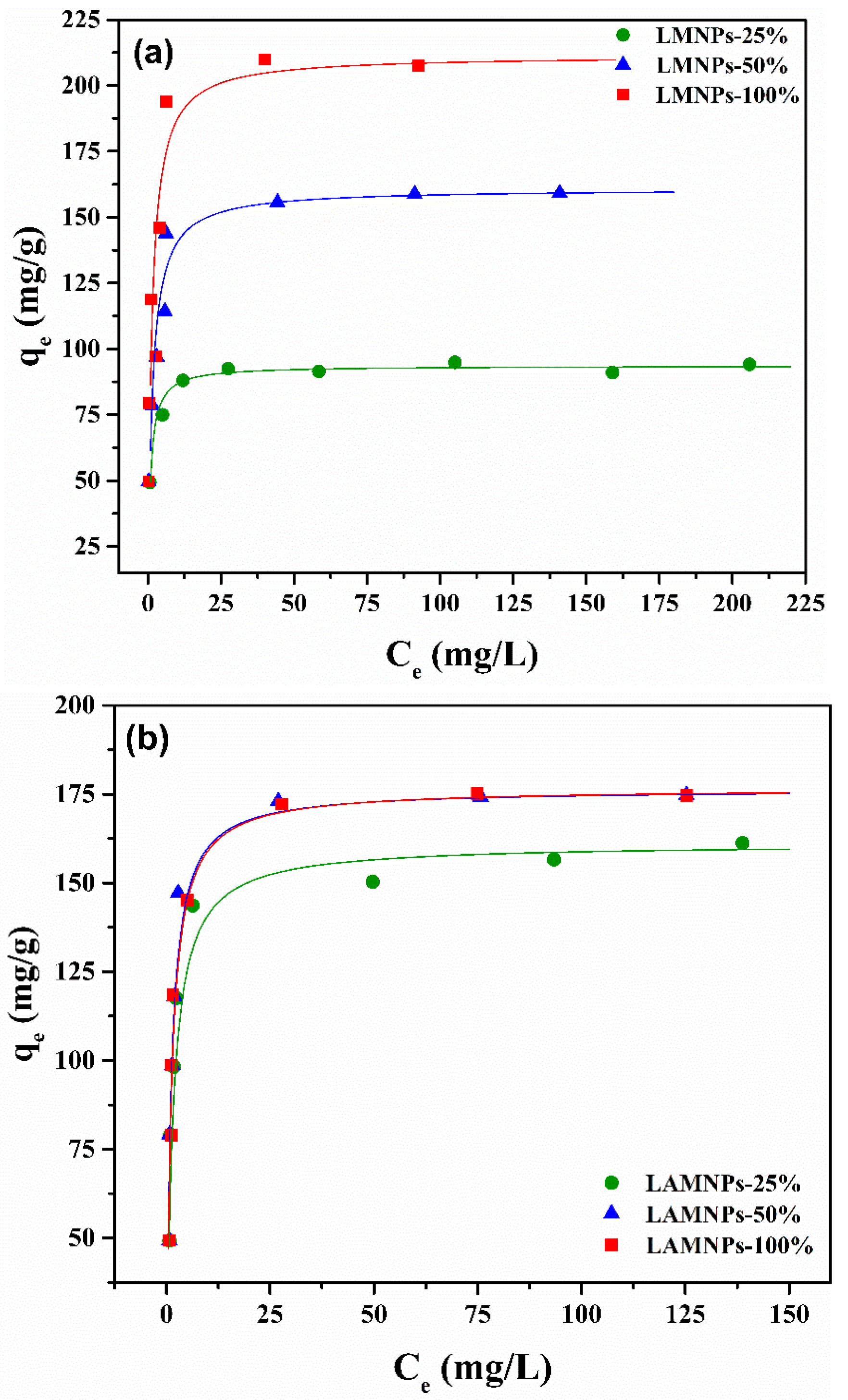
3.3.2. Equilibrium Studies
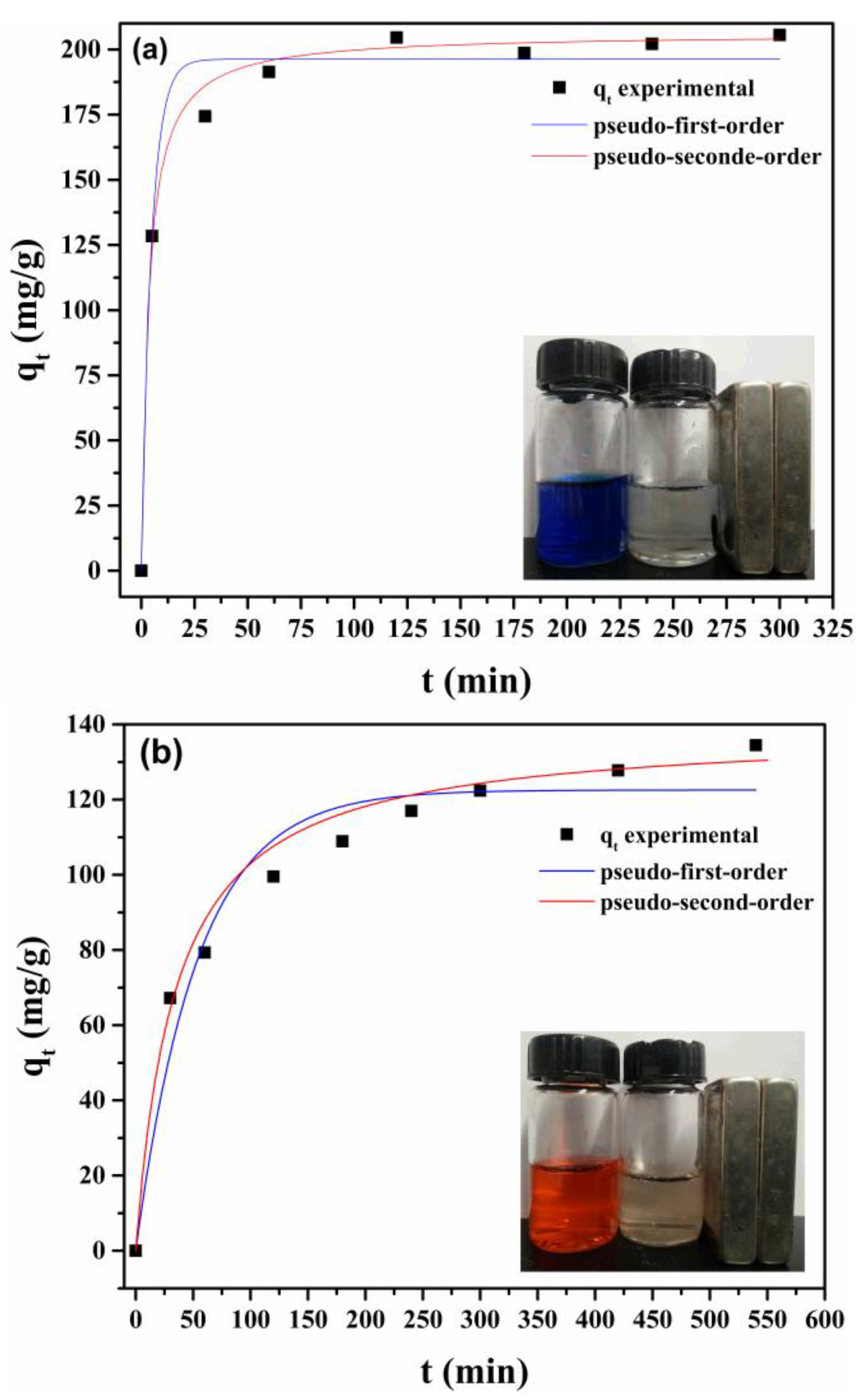
3.3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
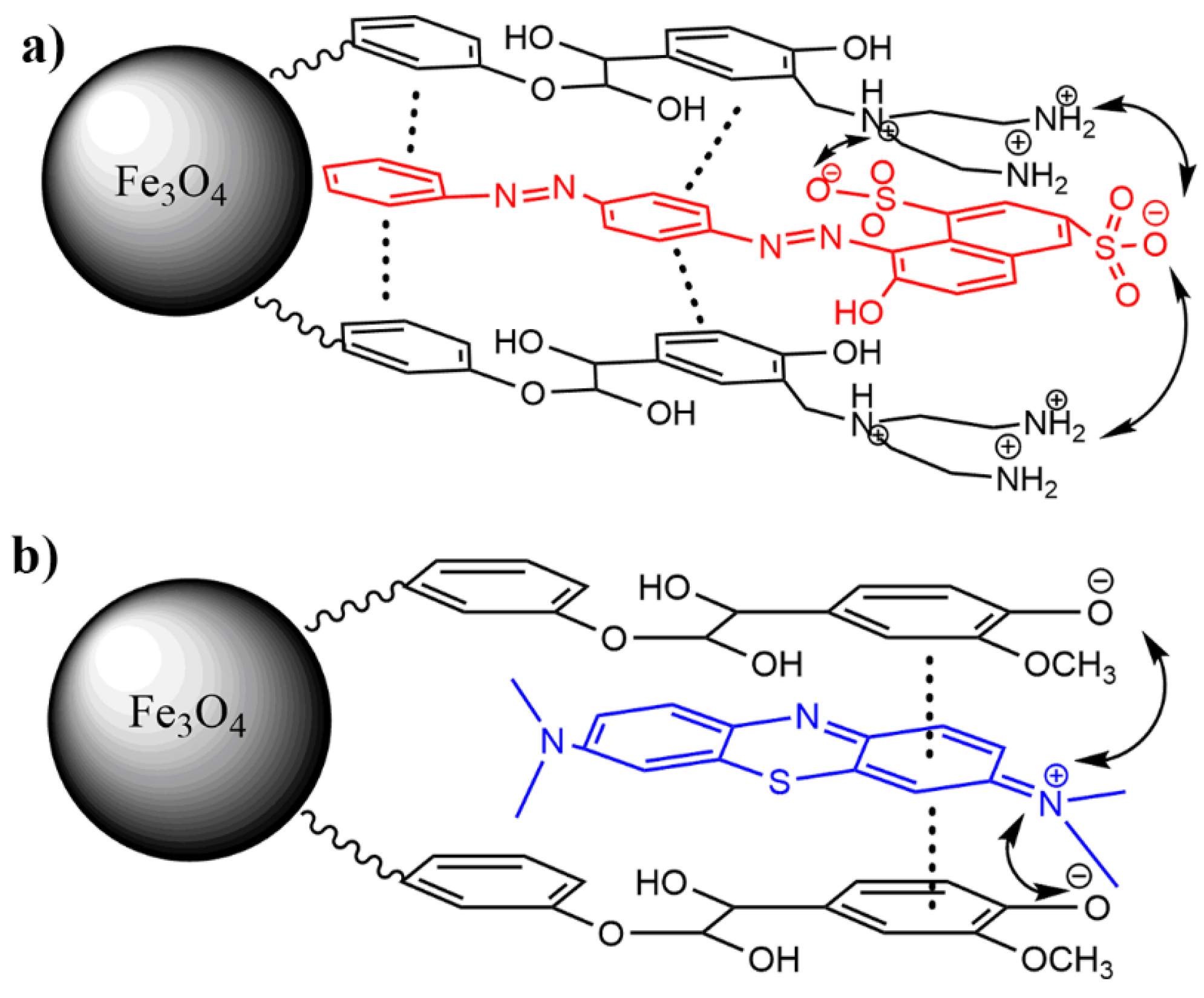
3.4. Mechanism of Adsorption
3.5. Desorption
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, T.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P. Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: A critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhao, E.; Kim, T.; Wang, J.; Hableel, G.; Reardon, P.J.T.; Ananthakrishna, S.J.; Wang, T.; Arconada-Alvarez, S.; Knowles, J.C.; et al. Organosilica nanoparticles with an intrinsic secondary amine: An efficient and reusable adsorbent for dyes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15566–15576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kuringen, H.P.C.; Eikelboom, G.M.; Shishmanova, I.K.; Broer, D.J.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Responsive nanoporous smectic liquid crystal polymer networks as efficient and selective adsorbents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5045–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chung, S.; Oh, G.; Seo, T.S. Three-dimensional graphene oxide nanostructure for fast and efficient water-soluble dye removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakzeski, J.; Bruijnincx, P.C.A.; Jongerius, A.L.; Weckhuysen, B.M. The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3552–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.; Cheng, X.; Xu, X. Synthesis of lignin-base cationic flocculant and its application in removing anionic azo-dyes from simulated wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7323–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, C.; Dai, X.; Zhou, Z.; Si, N. Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of aminated lignin by a mannich reaction and its decolorizing properties for anionic azo-dyes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 28156–28164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadarin, A.B.; Collins, M.N.; Naushad, M.; Shirazian, S.; Walker, G.; Mangwandi, C. Activated lignin-chitosan extruded blends for efficient adsorption of methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.G.; Ruggiero, R.; Gontijo, P.D.M.; Pinto, R.B.; Royer, B.; Lima, E.C.; Fernandes, T.H.M.; Calvete, T. Adsorption of brilliant red 2BE dye from water solutions by a chemically modified sugarcane bagasse lignin. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, M.A.; Prola, L.D.; Lima, E.C.; Puchana-Rosero, M.J.; Cataluna, R.; Saucier, C.; Umpierres, C.S.; Vaghetti, J.C.; da Silva, L.G.; Ruggiero, R. Adsorption of procion blue MX-R dye from aqueous solutions by lignin chemically modified with aluminium and manganese. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of magnetic lignin-based hollow microspheres: A highly adsorptive and reusable adsorbent derived from renewable resources. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5523–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievonen, M.; Valle-Delgado, J.J.; Mattinen, M.-L.; Hult, E.-L.; Lintinen, K.; Kostiainen, M.A.; Paananen, A.; Szilvay, G.R.; Setälä, H.; Österberg, M. A simple process for lignin nanoparticle preparation. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Deng, Y.; Liu, B.; Ren, Y.; Liang, J.; Qian, Y.; Qiu, X.; Li, C.; Zheng, D. Preparation of nanocapsules via the self-assembly of kraft lignin: A totally green process with renewable resources. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Deng, Y.; Qiu, X.; Li, H.; Yang, D. Formation of uniform colloidal spheres from lignin, a renewable resource recovered from pulping spent liquor. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2156–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.P.; Bharti, B.; Armstrong, H.B.; Brown, J.S.; Plemmons, D.; Paunov, V.N.; Stoyanov, S.D.; Velev, O.D. Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable lignin nanoparticles with tunable surface properties. Langmuir 2016, 32, 6468–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortora, M.; Cavalieri, F.; Mosesso, P.; Ciaffardini, F.; Melone, F.; Crestini, C. Ultrasound driven assembly of lignin into microcapsules for storage and delivery of hydrophobic molecules. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten, E.; Ling, C.; Wang, Y.; Srivastava, A.; Dempere, L.A.; Vermerris, W. Lignin nanotubes as vehicles for gene delivery into human cells. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, S.S.; Sharma, S.; Pu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Pan, S.; Zhu, J.Y.; Deng, Y.; Ragauskas, A.J. High shear homogenization of lignin to nanolignin and thermal stability of nanolignin-polyvinyl alcohol blends. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 3513–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Simmons, B.; Singh, S.; Ragauskas, A.; Cheng, G. From lignin association to nano-/micro-particle preparation: Extracting higher value of lignin. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5693–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Chen, R.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, H. Adsorption of phenols by magnetic polysulfone microcapsules containing tributyl phosphate. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Han, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Hou, Y.; Gai, L.; Li, D.; Lu, X.; Fu, T. Superparamagnetic core–shell structured microspheres carrying carboxyl groups as adsorbents for purification of genomic DNA. Colloids Surf. A 2012, 401, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Chen, D.H. Preparation and adsorption properties of monodisperse chitosan-bound Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for removal of Cu(II) ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 283, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolatkhah, A.; Wilson, L.D. Magnetite/polymer brush nanocomposites with switchable uptake behavior toward methylene blue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5595–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Liao, J.; He, B.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, F.; Huang, X.; Zhou, L. One-step fabrication of graphene oxide enhanced magnetic composite gel for highly efficient dye adsorption and catalysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnacca, G.; Allera, A.; Montoneri, E.; Celi, L.; Benito, D.E.; Gagliardi, L.G.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Mártire, D.O.; Carlos, L. Novel magnetite nanoparticles coated with waste-sourced biobased substances as sustainable and renewable adsorbing materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Song, Q.; Li, Z. A mannich base biosorbent derived from alkaline lignin for lead removal from aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 23, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Li, Z.; Kong, Y.; Song, Q.; Wang, K. Heavy metal ions retention by bi-functionalized lignin: Synthesis, applications, and adsorption mechanisms. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 4429–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, J.; Lindström, M.E. Modification of industrial softwood kraft lignin using mannich reaction with and without phenolation pretreatment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 52, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; He, B.; Zhang, F. Facile one-pot synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles cross-linked magnetic poly(vinyl alcohol) gel beads for drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Qiao, X.; Binks, B.P.; Sun, K.; Bai, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Magnetic pickering emulsions stabilized by Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 3308–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passauer, L.; Struch, M.; Schuldt, S.; Appelt, J.; Schneider, Y.; Jaros, D.; Rohm, H. Dynamic moisture sorption characteristics of xerogels from water-swellable oligo(oxyethylene) lignin derivatives. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5852–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.X.; Liu, T.; Thurnauer, M.C.; Csencsits, R.; Rajh, T. Fe2O3 nanoparticle structures investigated by X-ray absorption near-edge structure, surface modifications, and model calculations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 8539–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, M.D.; Reveles, J.U.; Khanna, S.N.; Carpenter, E.E. Reactive nature of dopamine as a surface functionalization agent in iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2482–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, C.; Chen, D.; Ma, Y.; Yang, W. Ammonium-functionalized hollow polymer particles as a pH-responsive adsorbent for selective removal of acid dye. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 16690–16698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alswieleh, A.M.; Cheng, N.; Canton, I.; Ustbas, B.; Xue, X.; Ladmiral, V.; Xia, S.; Ducker, R.E.; El Zubir, O.; Cartron, M.L.; et al. Zwitterionic poly(amino acid methacrylate) brushes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 9404–9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragan, E.S.; Mayr, J.; Haring, M.; Cocarta, A.I.; Diaz, D.D. Spectroscopic characterization of azo dyes aggregation induced by dabco-based ionene polymers and dye removal efficiency as a function of ionene structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 30908–30919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Cheng, H.; Chen, F.; Zhou, X.; Wang, P.; Xie, Y. Investigation of cationic dye adsorption from water onto acetic acid lignin. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2015, 36, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.H.; Cheng, H.L.; Li, J.L.; Wang, P.; Xie, Y.M. Adsorption behavior of basic dye from aqueous solution onto alkali extracted lignin. Bioresources 2014, 9, 3602–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A.W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suteu, D.; Malutan, T.; Bilba, D. Removal of reactive dye brilliant red HE-3B from aqueous solutions by industrial lignin: Equilibrium and kinetics modeling. Desalination 2010, 255, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dye Molecule | Structure | λmax/nm |
|---|---|---|
| MB | 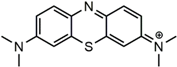 | 622 |
| AS-GR | 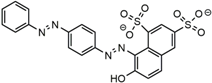 | 508 |
| Samples | Element Content wt % | Mole Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N% | C% | H% | C/H | |
| Lignin | 0.51 | 48.37 | 4.718 | 0.85 |
| LA | 6.58 | 43.59 | 6.174 | 0.59 |
| Sample | LMNPs | LAMNPs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fwt | 25% | 50% | 100% | 25% | 50% | 100% | |
| Langmuir | qmax (mg/g) | 93.63 | 160.77 | 211.42 | 161.03 | 176.37 | 176.49 |
| KL (L/mg) | 1.2404 | 0.6858 | 0.7666 | 0.7017 | 0.9742 | 0.9027 | |
| r2 | 0.9995 | 0.9999 | 0.9991 | 0.9995 | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | |
| Tempkin | b (J/mol) | 345.06 | 135.14 | 86.99 | 142.91 | 119.31 | 115.79 |
| A | 4443.83 | 79.87 | 32.74 | 129.49 | 77.61 | 60.35 | |
| r2 | 0.8239 | 0.8942 | 0.8585 | 0.8245 | 0.8019 | 0.8435 | |
| Freundlich | KF | 59.4764 | 76.0066 | 90.8346 | 80.2623 | 85.2757 | 83.2293 |
| 1/n | 0.1017 | 0.1804 | 0.2315 | 0.1640 | 0.1808 | 0.1873 | |
| r2 | 0.7918 | 0.8558 | 0.8044 | 0.7117 | 0.6783 | 0.7268 | |
| Absorbent | Dyes | qmax (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic lignin hollow microspheres | Methylene blue | 31.23 | [12] |
| Rhodamine B | 17.62 | ||
| Lignin-chitosan extruded pellets | Methylene blue | 36.25 | [9] |
| Acetic acid lignin | Methylene blue | 63.3 | [38] |
| Alkali extracted lignin | Methylene blue | 121.20 | [39] |
| LMNPs | Methylene blue | 211.42 | This work |
| LAMNPs | AS-GR | 176.49 | This work |
| Sample | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fwt | qe (mg/g) | k1 (min−1) | r2 | qe (mg/g) | k2 (min−1) | r2 | |
| LMNPs | 100 | 196.26 | 0.2105 | 0.9805 | 205.76 | 0.0015 | 0.9995 |
| LAMNPs | 100 | 122.54 | 0.0186 | 0.9574 | 138.70 | 0.0002 | 0.9922 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; He, Y.; Sui, H.; He, L. One-Step Fabrication of Dual Responsive Lignin Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Cationic and Anionic Dyes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030162
Li X, He Y, Sui H, He L. One-Step Fabrication of Dual Responsive Lignin Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Cationic and Anionic Dyes. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(3):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030162
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xingang, Youyi He, Hong Sui, and Lin He. 2018. "One-Step Fabrication of Dual Responsive Lignin Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Cationic and Anionic Dyes" Nanomaterials 8, no. 3: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030162
APA StyleLi, X., He, Y., Sui, H., & He, L. (2018). One-Step Fabrication of Dual Responsive Lignin Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Cationic and Anionic Dyes. Nanomaterials, 8(3), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030162