A Comparison of the Effects of Packaging Containing Nano ZnO or Polylysine on the Microbial Purity and Texture of Cod (Gadus morhua) Fillets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coatings Preparation
- (1)
- Two grams of Methocel™ were introduced into 96 mL of water. The mixture was mixed for 1 h using a magnetic stirrer (Ika) at 1500 rpm. Next, 2 g of polylysine were introduced into 98 g of mixture. The mixture was then mixed for 1 h using a magnetic stirrer (Ika) at 1500 rpm. The mixture was used to cover the cellulose boxes to obtain 2% polylysine coatings as active substance.
- (2)
- Exactly 0.082 g of ZnO nanoparticles were introduced into 50 mL of water. Initially, the mixture was mixed for 1 h using a magnetic stirrer (450 rpm). Next, the mixture was sonicated (sonication parameters: cycle: 0.5; amplitude: 20%; time: 10 min), while, at the same time, a second mixture (4 g of MHPC into 50 mL) was prepared as described above. The ZnO nanoparticles solution was introduced into the MHPC mixture and sonicated (sonication parameters: cycle: 0.5; amplitude: 20%; time: 10 min).
2.2. Packaging and Storage
2.3. Mechanical Analysis
2.4. Microbiological Purity
2.5. Dry Mass Tests
2.6. L* a* b* Tests
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
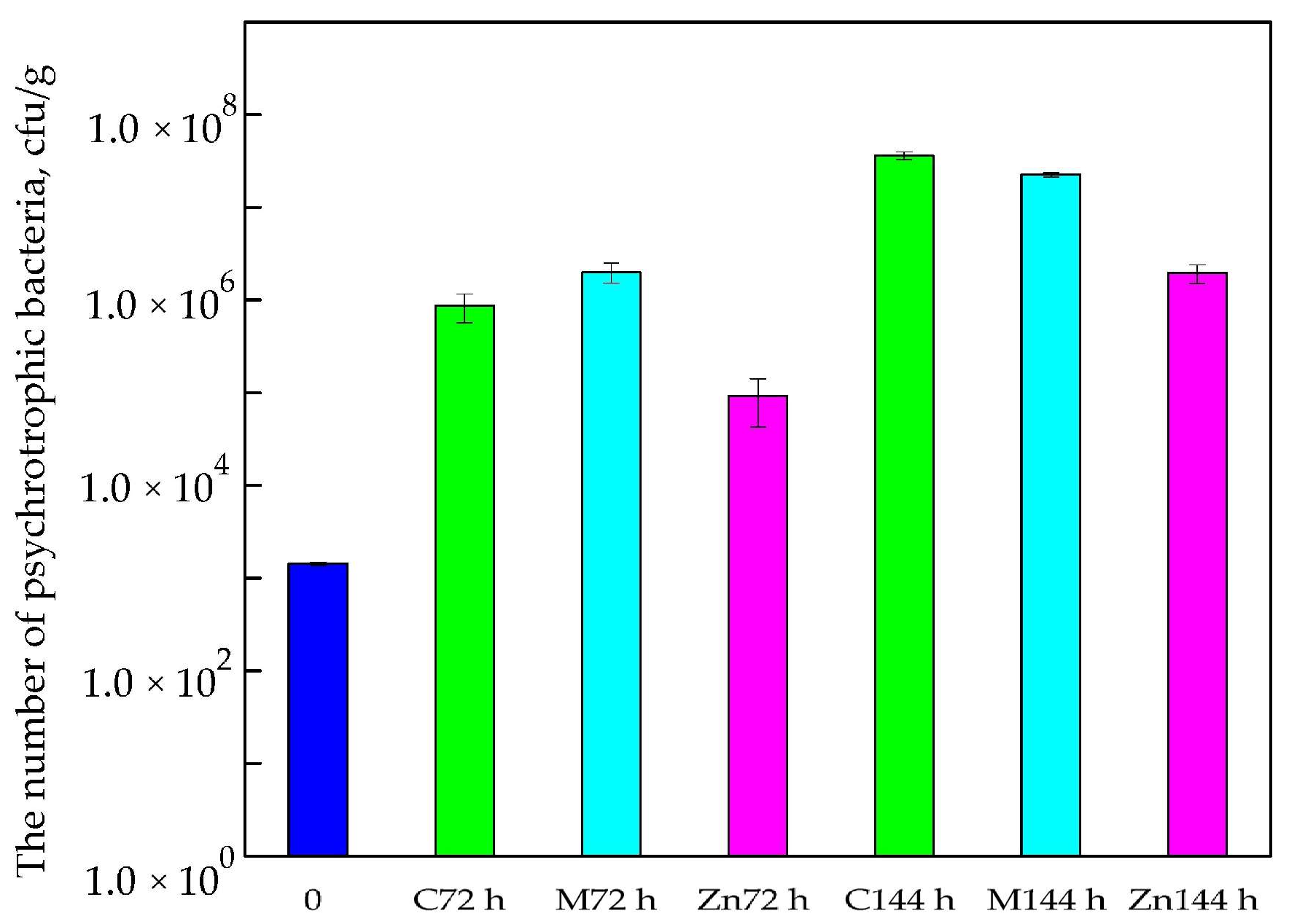
3.1. Microbial Purity Analysis
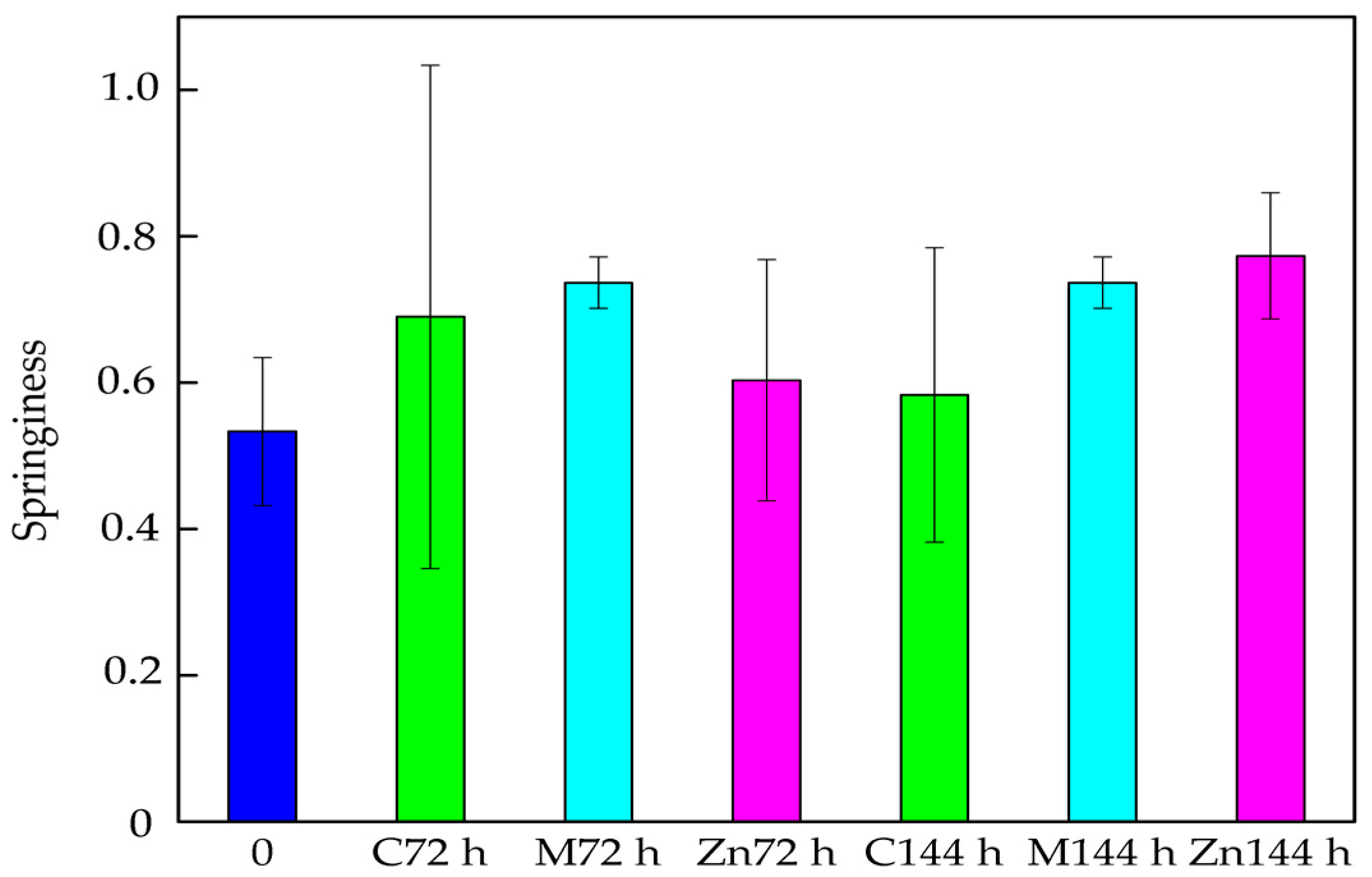
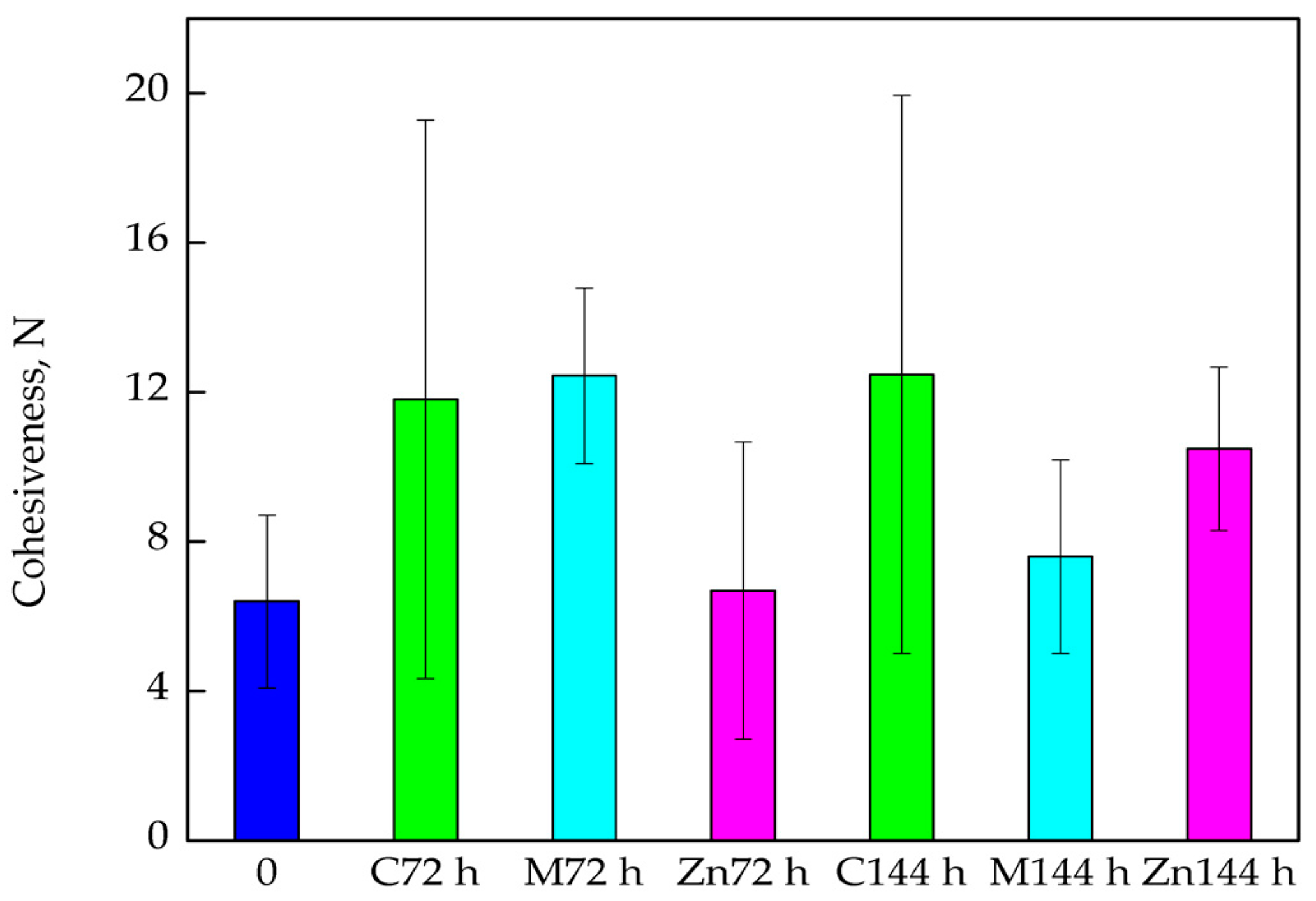
3.2. Mechanical Analysis
3.3. Dry Mass Analysis
3.4. L* a* b* Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, S.; Lee, M.; Gaikwad, K.K.; Lee, Y.S. Antibacterial and amine scavenging properties of silver-silica composite for post-harvest storage of fresh fish. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 107, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuuliala, L.; Hage, Y.A.; Ioannidis, A.-G.; Sader, M.; Kerckhof, F.-M.; Vanderroost, M.; Boon, N.; De Baets, B.; De Meulenaer, B.; Ragaert, P.; et al. Microbiological, chemical and sensory spoilage analysis of raw Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) stored under modified atmospheres. Food Microbiol. 2018, 70, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mireles DeWitt, C.A.; Oliveira, A.C.M. Modified Atmosphere Systems and Shelf Life Extension of Fish and Fishery Products. Foods 2016, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivertsvik, M. The optimized modified atmosphere for packaging of pre-rigor filleted farmed cod (Gadus morhua) is 63 mL/100 mL oxygen and 37 mL/100 mL carbon dioxide. LWT 2007, 40, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampola, V.G.; Keller, C.L. Shelf Life Extension of Drawn Whole Atlantic Cod, Gadus morhua, and Cod Fillets by Treatment with Potassium Sorbate. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1985, 47, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, S.; Röcker, B.; Pettersen, M.K.; Nilsen-Nygaard, J.; Ayhan, Z.; Rutkaite, R.; Radusin, T.; Suminska, P.; Marcos, B.; Coma, V. Active Packaging Applications for Food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowiak, A.; Mizielińska, M.; Sumińska, P.; Romanowska-Osuch, A.; Lisiecki, S. Innovations in food packaging materials. In Emerging and Traditional Technologies for Safe, Healthy and Quality Food; Nedovic, V., Raspor, P., Lević, J., Tumbas, V., Barbosa-Canovas, G.V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Sveinsdóttir, K.; Magnússon, H. Martinsdóttir, Combined Application of Modified Atmosphere Packaging and Superchilled Storage to Extend the Shelf Life of Fresh Cod (Gadus morhua) Loins. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, A.; Anal, A.K. Zinc oxide nanoparticles loaded active packaging, a challenge study against Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus in readyto-eat poultry meat. Food Control 2014, 38, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.; Rollo, G.; Cimmino, S.; Silvestre, C. Assessment on the Effects of ZnO and Coated ZnO Particles on iPP and PLA Properties for Application in Food Packaging. Coatings 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizielińska, M.; Łopusiewicz, Ł.; Mężyńska, M.; Bartkowiak, A. The influence of accelerated UV-A and Q-SUN irradiation on the antimicrobial properties of coatings containing ZnO nanoparticles. Molecules 2017, 22, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, S.; Ahmad, M.B.; Hussein, M.Z.; Ibrahim, N.A. Synthesis, Antibacterial and Thermal Studies of Cellulose Nanocrystal Stabilized ZnO-Ag Heterostructure Nanoparticles. Molecules 2013, 18, 6269–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizielińska, M.; Lisiecki, S.; Jotko, M.; Chodzyńska, I.; Bartkowiak, A. The antimicrobial properties of polylactide films covered with ZnO nanoparticles-containing layers. Przem. Chem. 2015, 94, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Noshirvani, N.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Mokarram, R.R.; Hashemi, M. Novel active packaging based on carboxymethyl cellulose-chitosan-ZnO NPs nanocomposite for increasing the shelf life of bread. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2017, 11, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, A.E.; Pandel, L.M.; Dumitrescu, A.M.; Andronescu, E.; Grumezescu, V.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Mogoantă, L.; Bălşeanu, T.-A.; Mogoşanu, G.D.; Socol, G.; et al. Bioactive ZnO Coatings Deposited by MAPLE—An Appropriate Strategy to Produce Efficient Anti-Biofilm Surfaces. Molecules 2016, 21, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, C.; Duraccio, D.; Marra, A.; Strongone, V.; Cimmino, S. Development of antimicrobial composite films based on isotactic polypropylene and coated ZnO particles for active food packaging. Coatings 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Mayorgaa, J.L.; Fabraa, M.J.; Pourrahimib, A.M.; Olssonb, R.T.; Lagarona, J.M. The impact of zinc oxide particle morphology as anantimicrobial and when incorporated inpoly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)films for food packaging and food contact surfacesapplications. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 101, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, P.M.; Mujeeb, V.M.A.; Muraleedharan, K. Flexible chitosan-nano ZnO antimicrobial pouches as a new material for extending the shelf life of raw meat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emamifar, A.; Kadivar, M.; Shahedi, M.; Soleimanianzad, S. Evaluation of nanocomposite packaging containing Ag and ZnO on shelf life of fresh orange juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, W.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yun, J.; Yao, T.; Zhang, P. Effect of nano-ZnO-coated active packaging on quality of fresh-cut ‘Fuji’ apple. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1947–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Chi, H.; Li, L.; Lan, T.; Han, P.; Chen, H.; Qin, Y. Development of Antimicrobial Packaging Film Made from Poly(Lactic Acid) Incorporating Titanium Dioxide and Silver Nanoparticles. Molecules 2017, 22, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, M.; Qin, Y. Evaluation of PLA nanocomposite films on physicochemical and microbiological properties of refrigerated cottage cheese. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoviadou, K.G.; Koutsoumanis, K.P.; Biliaderis, C.G. Physical and thermo-mechanical properties of whey protein isolate films containing antimicrobials, and their effect against spoilage flora of fresh beef. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünalan, I.U.; Uçar, K.D.A.U.; Arcan, I.; Korel, F.; Yemeni̇ci̇oğlu, A. Antimicrobial Potential of Polylysine in Edible Films. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2011, 17, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-ISO 11036:1999 Standard. Available online: http://sklep.pkn.pl/pn-iso-11036-1999p.html (accessed on 10 March 2018).
- PN-EN ISO 4833-2:2013-12. Available online: http://sklep.pkn.pl/pn-en-iso-4833-2-2013-12p.html (accessed on 10 March 2018).
- PN-ISO 17410:2004. Available online: http://sklep.pkn.pl/pn-iso-17410-2004p.html (accessed on 10 March 2018).
- PN-EN ISO 6887-3:2017-05. Available online: http://sklep.pkn.pl/pn-en-iso-6887-3-2017-05e.html (accessed on 10 March 2018).
- Tokarczyk, G.; Bienkiewicz, G.; Suryn, J. Comparative analysis of the quality parameters and the fatty acid composition of two economically important batlic fish: cod, Gadus Morhua and Flounder, Platichthys flesus (Actinopterygii) subjected to iced storage. Acta Ichtiol. Piscat. 2017, 47, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Sun, D.W.; Han, Z.; Zeng, X.A. Texture and Structure Measurements and Analyses for Evaluation of Fish and Fillet Freshness Quality: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.M.L.; Mendes, R.; Nunes, M.L. Instrumental Texture and Sensory Characteristics of Cod Frankfurter Sausages. Int. J. Food Prop. 2009, 12, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavand, F.; Rouhi, M.; Razavi, S.H.; Cacciotti, I. Improving the integrity of natural biopolymer films used in food packaging by crosslinking approach: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 687–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalczyk, M.; Surówka, K. Microstructure and instrumentally measured textural changes of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) gravads during production and storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahuaud, D.; Gaarder, M.; Veiseth-Kent, E.; Thomassen, M. Fillet texture and protease activities in different families of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2010, 310, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, M.D.; Santaella, M.; Martínez, C.; Periago, M.J.; Alfonso Blanco, A.; Vázquez, J.M.; Albors, O.L. Muscle tissue structure and flesh texture in gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata L., fillets preserved by refrigeration and by vacuum packaging. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Time (h) | Dry Mass (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | C | M | Zn | |
| 0 | 17.64 | - | - | - |
| 72 | - | 20.00 | 22.58 | 19.18 |
| 144 | - | 23.06 | 24.96 | 18.90 |
| Time (h) | C | M | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 72 | ∆Elab | 5.45 ± 3.00 | 3.70 ± 1.10 | 18.23 ± 0.26 |
| ∆L | 0.4 ± 6.15 | −0.42 ± 0.83 | 17.91 ± 0.44 | |
| 144 | ∆Elab | 12.57 ± 0.70 | 54.03 ± 18.40 | 21.05 ± 5.10 |
| ∆L | 11.51 ± 0.74 | 0.49 ± 1.98 | 20.84 ± 5.04 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mizielińska, M.; Kowalska, U.; Jarosz, M.; Sumińska, P. A Comparison of the Effects of Packaging Containing Nano ZnO or Polylysine on the Microbial Purity and Texture of Cod (Gadus morhua) Fillets. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030158
Mizielińska M, Kowalska U, Jarosz M, Sumińska P. A Comparison of the Effects of Packaging Containing Nano ZnO or Polylysine on the Microbial Purity and Texture of Cod (Gadus morhua) Fillets. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(3):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030158
Chicago/Turabian StyleMizielińska, Małgorzata, Urszula Kowalska, Michał Jarosz, and Patrycja Sumińska. 2018. "A Comparison of the Effects of Packaging Containing Nano ZnO or Polylysine on the Microbial Purity and Texture of Cod (Gadus morhua) Fillets" Nanomaterials 8, no. 3: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030158
APA StyleMizielińska, M., Kowalska, U., Jarosz, M., & Sumińska, P. (2018). A Comparison of the Effects of Packaging Containing Nano ZnO or Polylysine on the Microbial Purity and Texture of Cod (Gadus morhua) Fillets. Nanomaterials, 8(3), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030158