A Computational Approach for Understanding the Interactions between Graphene Oxide and Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase with Implications for Heart Failure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
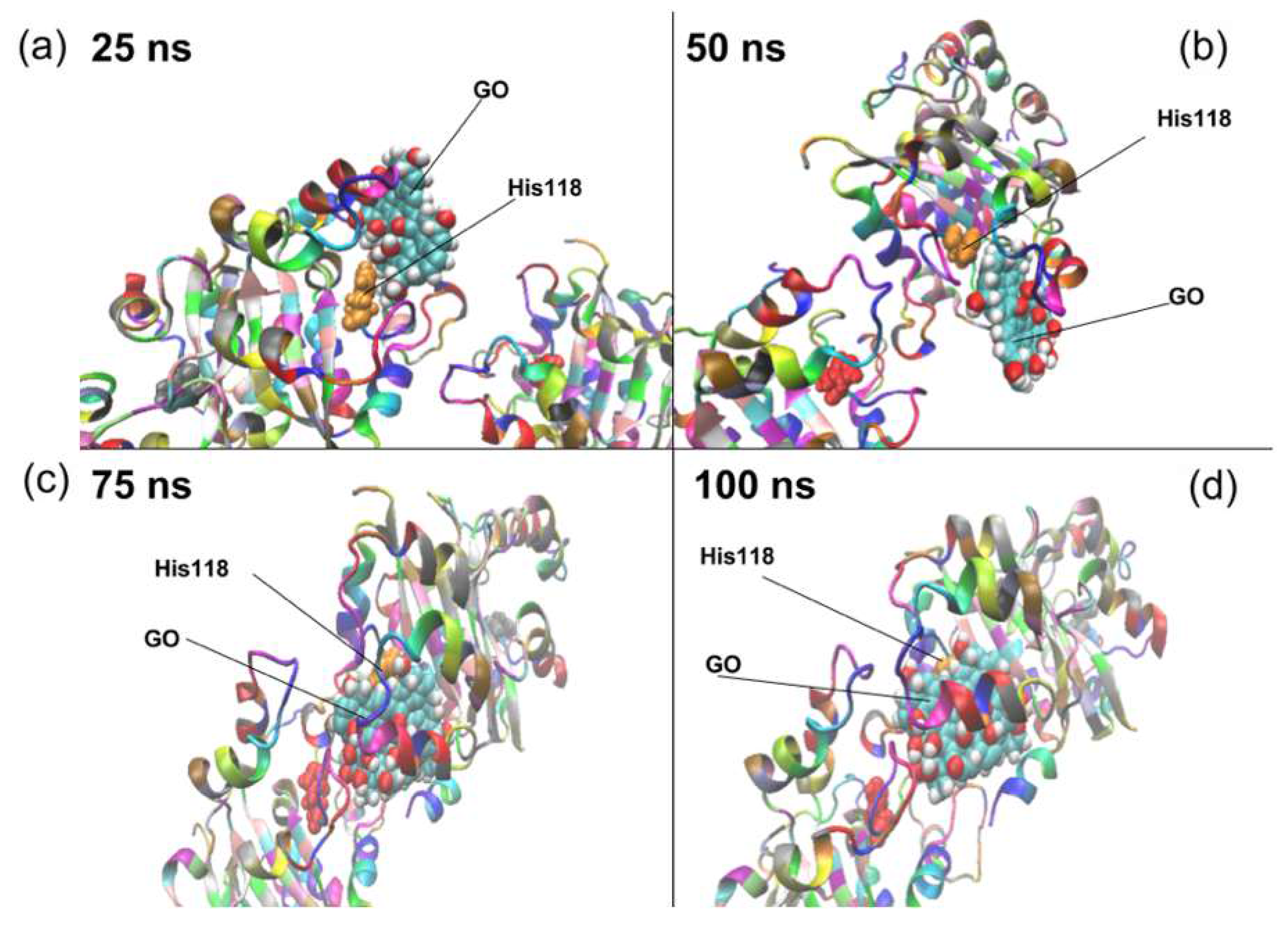
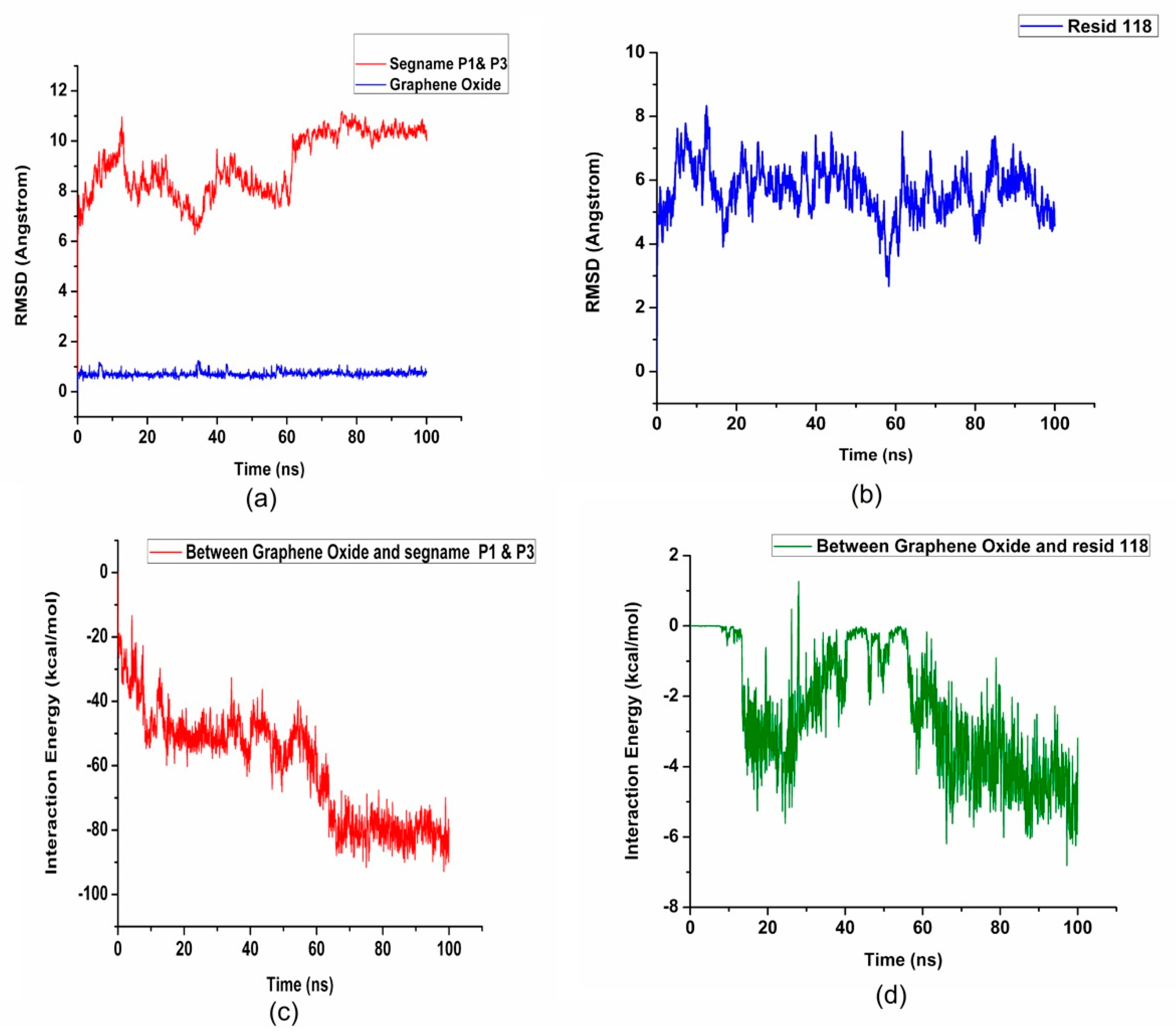
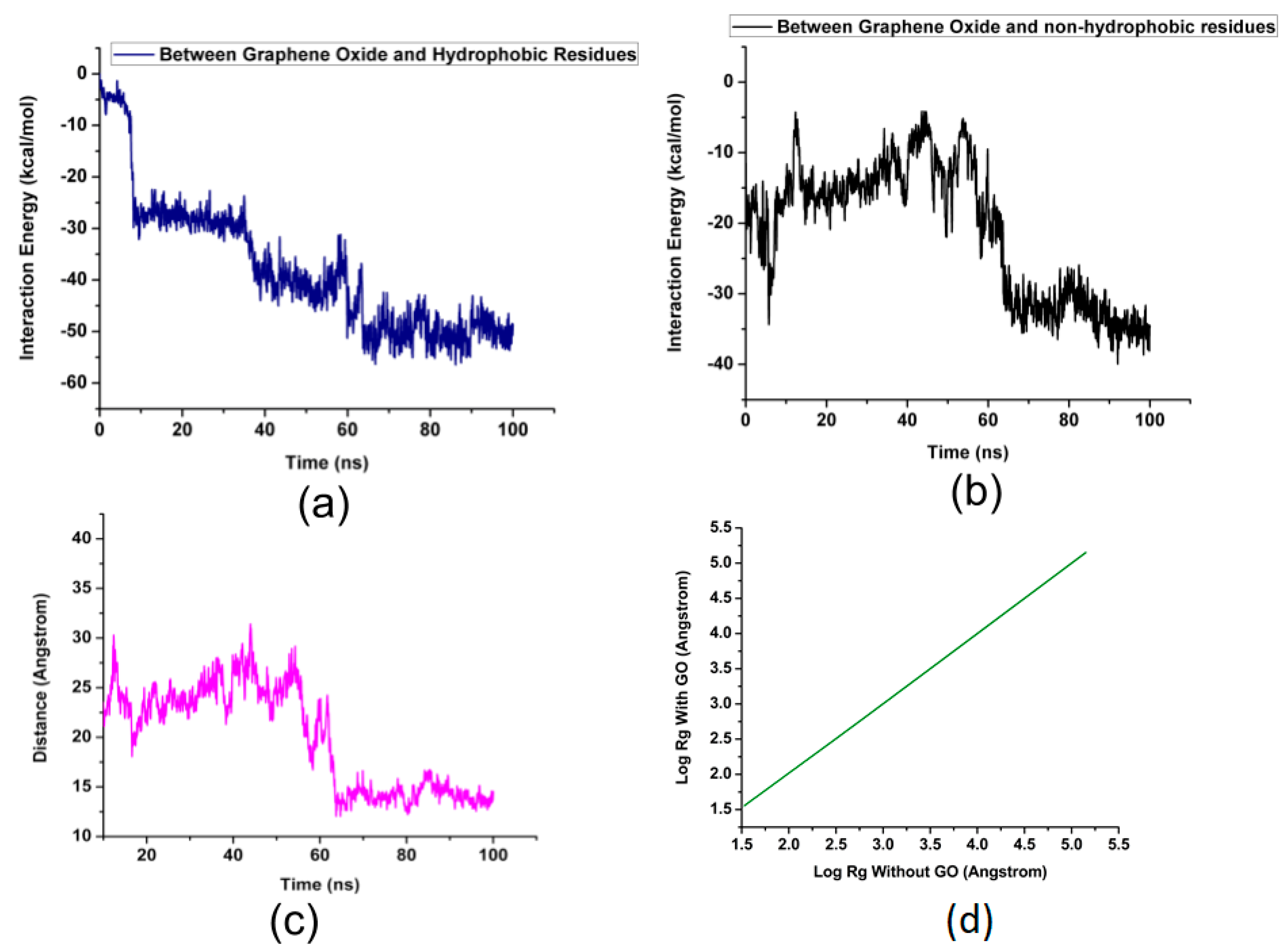
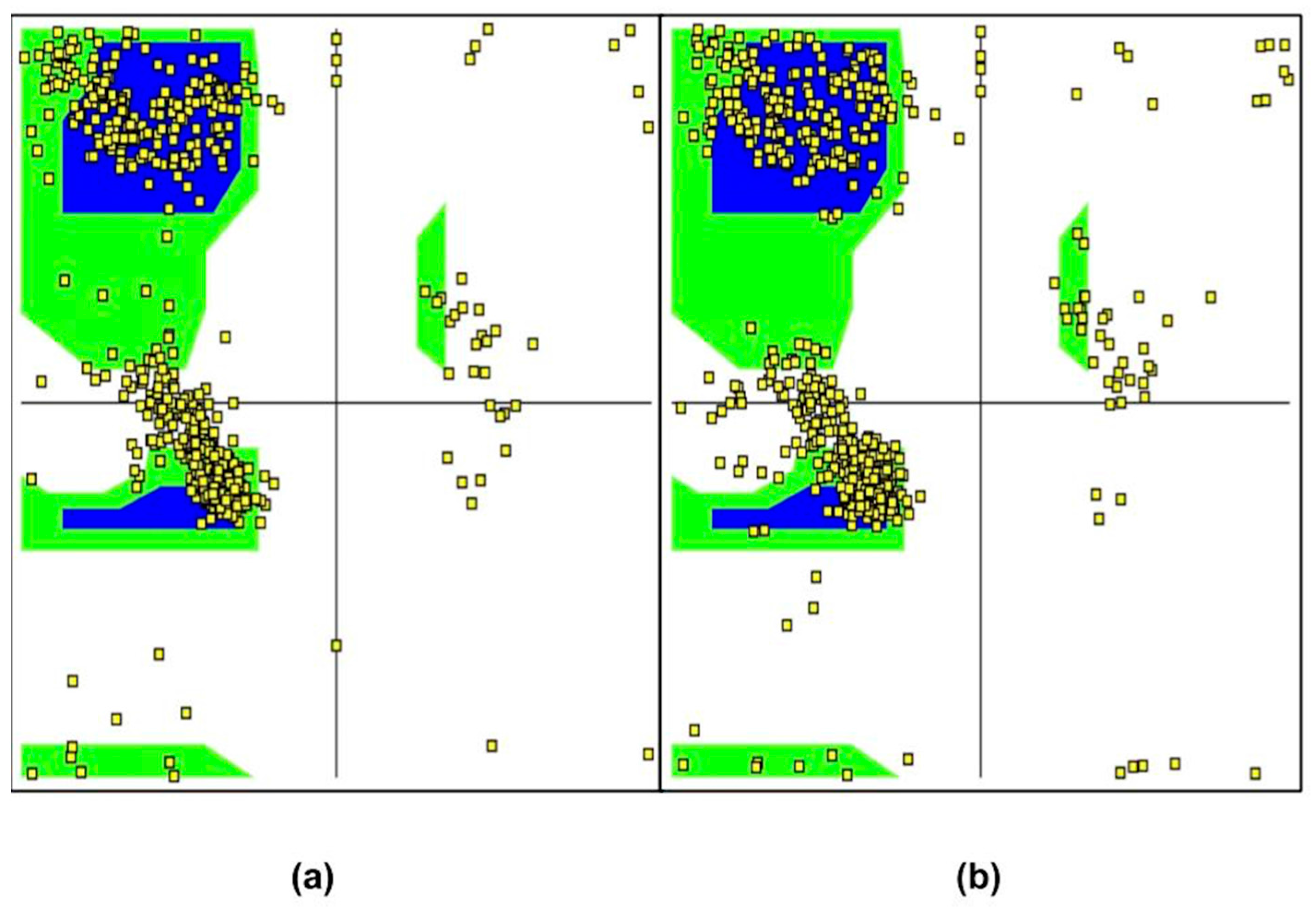
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccolo, M. cAMP signal transduction in the heart: Understanding spatial control for the development of novel therapeutic strategies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Anderson, M.E. Mechanisms of Altered Ca2+ Handling in Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 690–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takács-Vellai, K.; Vellai, T.; Farkas, Z.; Mehta, A. Nucleoside diphosphate kinases (NDPKs) in animal development. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1447–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Randazzo, P.A.; Northup, J.K.; Kahn, R.A. Regulatory GTP-binding proteins (ADP-ribosylation factor, Gt, and RAS) are not activated directly by nucleoside diphosphate kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 18182–18189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.-Y.; Artman, M. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase: A new player in heart failure? Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 49, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippe, H.-J.; Luedde, M.; Lutz, S.; Koehler, H.; Eschenhagen, T.; Frey, N.; Katus, H.A.; Wieland, T.; Niroomand, F. Regulation of Cardiac cAMP Synthesis and Contractility by Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase B/G Protein βγ Dimer Complexes. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, N. Role of Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase in G-Protein Action; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 485–498. [Google Scholar]
- Pronin, A.N.; Gautam, N. Interaction between G-protein 13 and y subunit types is selective (signal transduction/subunit families). Biochem. Commun. Melvin 1992, 89, 6220–6224. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Erlichman, B.; Weinstein, L.S. The Stimulatory G Protein α-Subunit Gsα Is Imprinted in Human Thyroid Glands: Implications for Thyroid Function in Pseudohypoparathyroidism Types 1A and 1B. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4336–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Taha, I.H.; Heijman, J.; Feng, Y.; Vettel, C.; Dobrev, D.; Wieland, T. Regulation of heterotrimeric G-protein signaling by NDPK/NME proteins and caveolins: An update. Lab. Investig. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, J.; Scholz, H.; Döring, V.; Schmitz, W.; Von Meyerinck, L.; Kalmárb, P. Increase in myocardial Gi-proteins in heart failure. Lancet 1988, 332, 936–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Taha, I.H.; Heijman, J.; Hippe, H.-J.; Wolf, N.M.; El-Armouche, A.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Schäfer, M.; Würtz, C.M.; Neef, S.; Voigt, N.; et al. Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase-C Suppresses cAMP Formation in Human Heart FailureClinical Perspective. Circulation 2017, 135, 881–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, S.; Mura, R.; Baltus, D.; Movsesian, M.; Kübler, W.; Niroomand, F. Increased activity of membrane-associated nucleoside diphosphate kinase and inhibition of cAMP synthesis in failing human myocardium. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 49, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroomand, F.; Mura, R.; Jakobs, K.H.; Rauch, B.; Kübler, W. Receptor-Independent Activation of Cardiac Adenylyl Cyclase by GDP and Membrane-Associated Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase. A New Cardiotonic Mechanism? J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1997, 29, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anciaux, K.; Van Dommelen, K.; Willems, R.; Roymans, D.; Slegers, H. Inhibition of nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK/nm23) by cAMP analogues. FEBS Lett. 1997, 400, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldinucci, A.; Turco, A.; Biagioli, T.; Toma, F.M.; Bani, D.; Guasti, D.; Manuelli, C.; Rizzetto, L.; Cavalieri, D.; Massacesi, L.; et al. Carbon Nanotube Scaffolds Instruct Human Dendritic Cells: Modulating Immune Responses by Contacts at the Nanoscale. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 6098–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, A.; Kostarelos, K.; Prato, M. Applications of carbon nanotubes in drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2005, 9, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiriba, S.-E.; Frey, H.; Haag, R. Dendritic polymers in biomedical applications: From potential to clinical use in diagnostics and therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2002, 41, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Welsher, K.; Robinson, J.T.; Goodwin, A.; Zaric, S.; Dai, H. Nano-graphene oxide for cellular imaging and drug delivery. Nano Res. 2008, 1, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Mahendra, S.; Lyon, D.Y.; Brunet, L.; Liga, M.V.; Li, D.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: Potential applications and implications. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4591–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Y. Functionalized carbon nanotubes and nanofibers for biosensing applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Feng, Z.; Hou, T.; Li, Y. Mechanism of Graphene Oxide as an Enzyme Inhibitor from Molecular Dynamics Simulations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7153–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Aphale, A.N.; Macwan, I.G.; Patra, P.K.; Gonzalez, W.G.; Miksovska, J.; Leblanc, R.M. Graphene Oxide as a Quencher for Fluorescent Assay of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 7069–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Cote, L.J.; Kim, F.; Yuan, W.; Shull, K.R.; Huang, J. Graphene Oxide Sheets at Interfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8180–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Huang, C.; Zheng, G.; Bohm, E.; Bhatele, A.; Phillips, J.C.; Yu, H.; Kale, L.V. Scalable Molecular Dynamics with NAMD on the IBM Blue Gene/L system. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2008, 52, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Lu, J.; Cui, F. Molecular Dynamics Study of the Aggregation Process of Graphene Oxide in Water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 26712–26718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKerell, A.D., Jr.; Bashford, D.; Bellott, M.; Dunbrack, R.L., Jr.; Evanseck, J.D.; Field, M.J.; Fischer, S.; Gao, J.; Guo, H.; Ha, S.; et al. All-Atom Empirical Potential for Molecular Modeling and Dynamics Studies of Proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 3586–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towns, J.; Cockerill, T.; Dahan, M.; Foster, I.; Gaither, K.; Grimshaw, A.; Hazlewood, V.; Lathrop, S.; Lifka, D.; Peterson, G.D.; et al. XSEDE: Accelerating Scientific Discovery. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2014, 16, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Residue Name | Residue ID | Residue Type |
|---|---|---|
| Histidine | 122, 118 | Basic, positively charged |
| Aspartic Acid | 57, 124, 148, 14, 121 | Acidic, negatively charged |
| Glutamic Acid | 123, 125 | Acidic, negatively charged |
| Tryptophan | 144, 151 | Aromatic, hydrophobic |
| Leucine | 152, 64, 112 | Aliphatic, hydrophobic |
| Tyrosine | 153, 52 | Aromatic, hydrophobic |
| Methionine | 10 | Sulfur-containing, hydrophobic |
| Lysine | 12, 58 | Basic, positively charged |
| Glycine | 126, 63, 71, 113, 119 | Aliphatic, hydrophobic |
| Proline | 13, 59, 72 | Aliphatic |
| Glutamine | 42 | Amidic, polar uncharged |
| Isoleucine | 43, 68 | Aliphatic, hydrophobic |
| Threonine | 69 | Hydrophilic, polar uncharged |
| Valine | 73 | Aliphatic, hydrophobic |
| Asparagine | 115 | Amidic, polar uncharged |
| Phenylalanine | 60, 67 | Aromatic, hydrophobic |
| Solvent Accessible Surface Area (SASA) (nm2) | Presence of GO | Absence of GO |
|---|---|---|
| Segment P1 | 96.71 (68, 109.61) | 89.40 (22.54, 66.85) |
| Segment P2 | 97.80 (66.7, 111) | 83.65 (22.83, 60.81) |
| Segment P3 | 104.70 (68.58, 116.52) | 87.35 (21.76, 65.6) |
| Segment P4 | 97.70 (65.95, 110.9) | 84.25 (21.52, 62.72) |
| NDPK (whole) | 328.80 | 286.19 |
| Hydrophobic region of NDPK | 243.80 | 65.13 |
| Hydrophilic region of NDPK | 426.95 | 221.06 |
| GO Flake | Active Site Location | Approximate Distance from Active Site (Angstroms) |
|---|---|---|
| GO1 | P4 | 35.94 |
| GO2 | P4 | 31.61 |
| GO3 | P2 | 34.24 |
| GO4 | P2 | 28.85 |
| GO5 | P3 | 32.83 |
| GO6 | P1 | 29.98 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ray, A.; Macwan, I.; Singh, S.; Silwal, S.; Patra, P. A Computational Approach for Understanding the Interactions between Graphene Oxide and Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase with Implications for Heart Failure. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020057
Ray A, Macwan I, Singh S, Silwal S, Patra P. A Computational Approach for Understanding the Interactions between Graphene Oxide and Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase with Implications for Heart Failure. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(2):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020057
Chicago/Turabian StyleRay, Anushka, Isaac Macwan, Shrishti Singh, Sushila Silwal, and Prabir Patra. 2018. "A Computational Approach for Understanding the Interactions between Graphene Oxide and Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase with Implications for Heart Failure" Nanomaterials 8, no. 2: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020057
APA StyleRay, A., Macwan, I., Singh, S., Silwal, S., & Patra, P. (2018). A Computational Approach for Understanding the Interactions between Graphene Oxide and Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase with Implications for Heart Failure. Nanomaterials, 8(2), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020057






