Investigating Exchange Bias and Coercivity in Fe3O4–γ-Fe2O3 Core–Shell Nanoparticles of Fixed Core Diameter and Variable Shell Thicknesses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
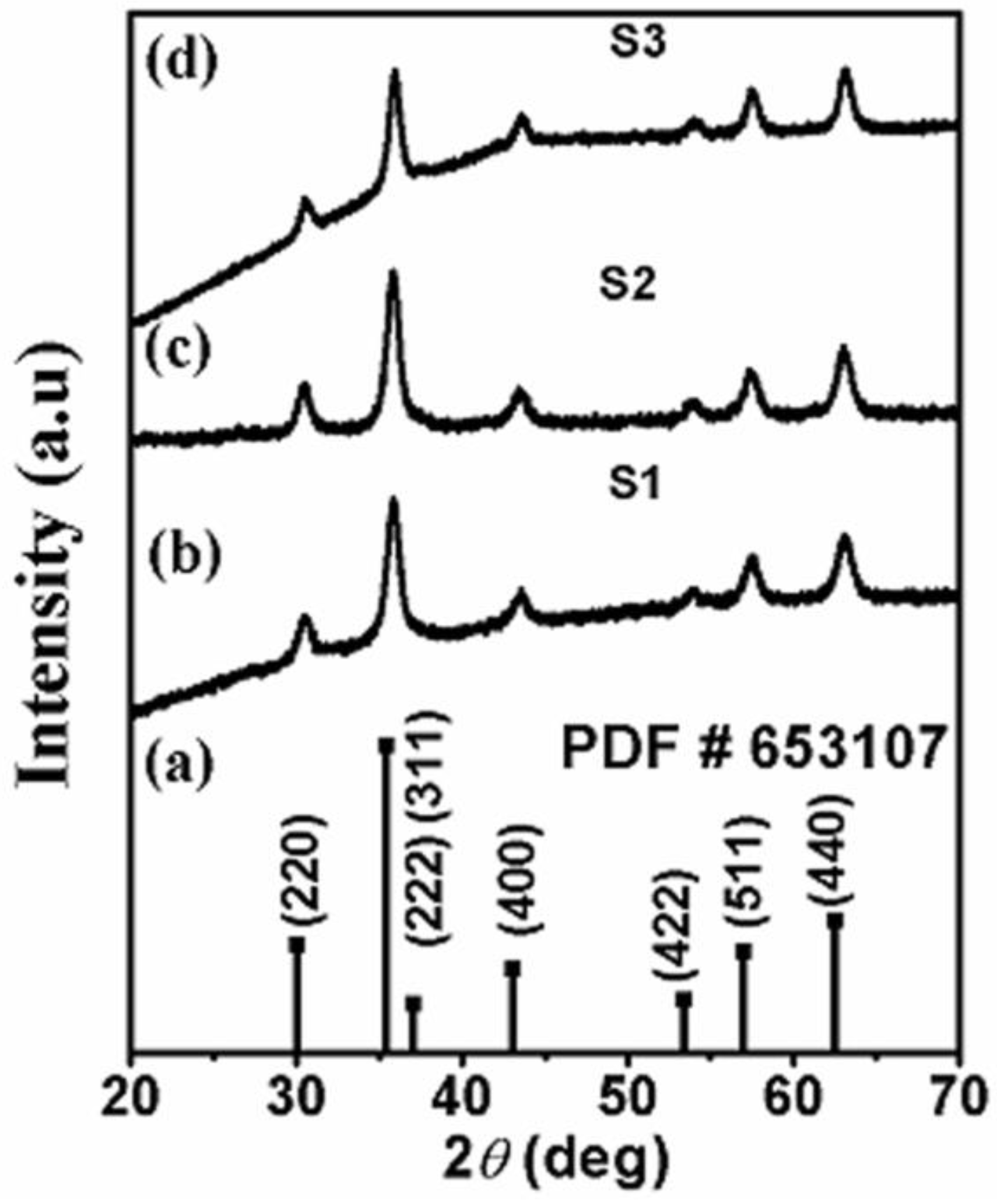
2.1. Structural and Phase Analysis
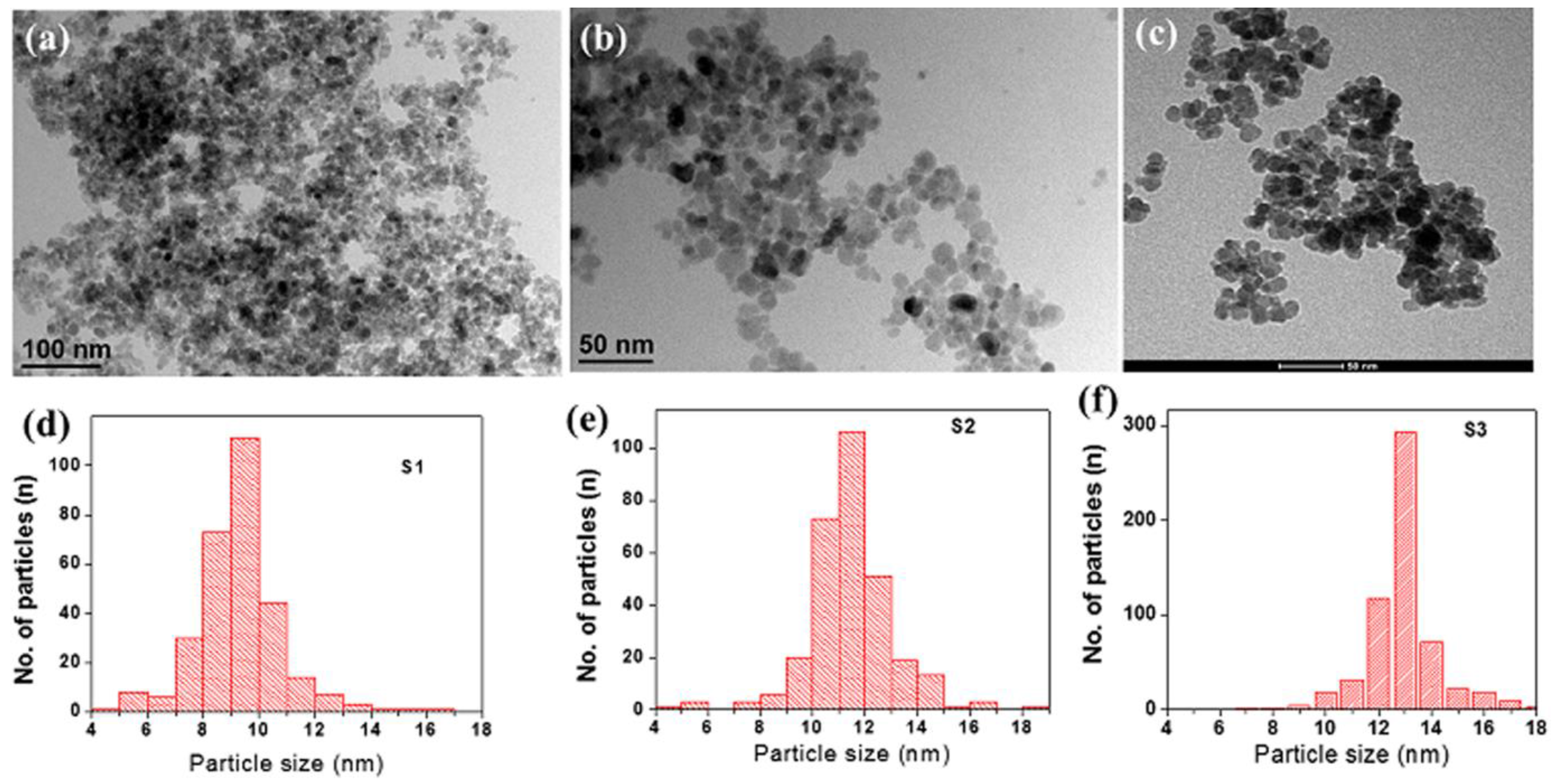
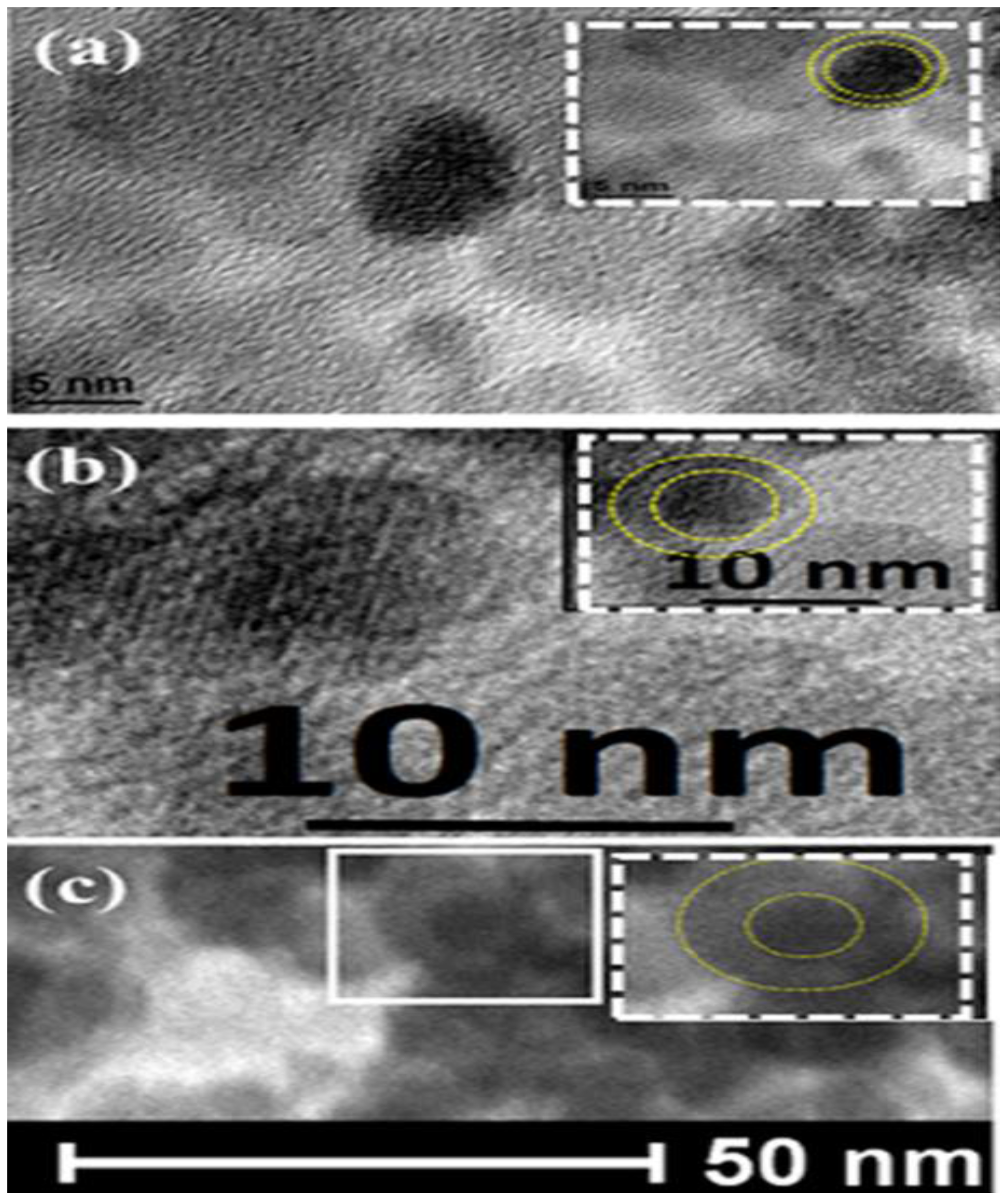
2.2. Morphological Analysis
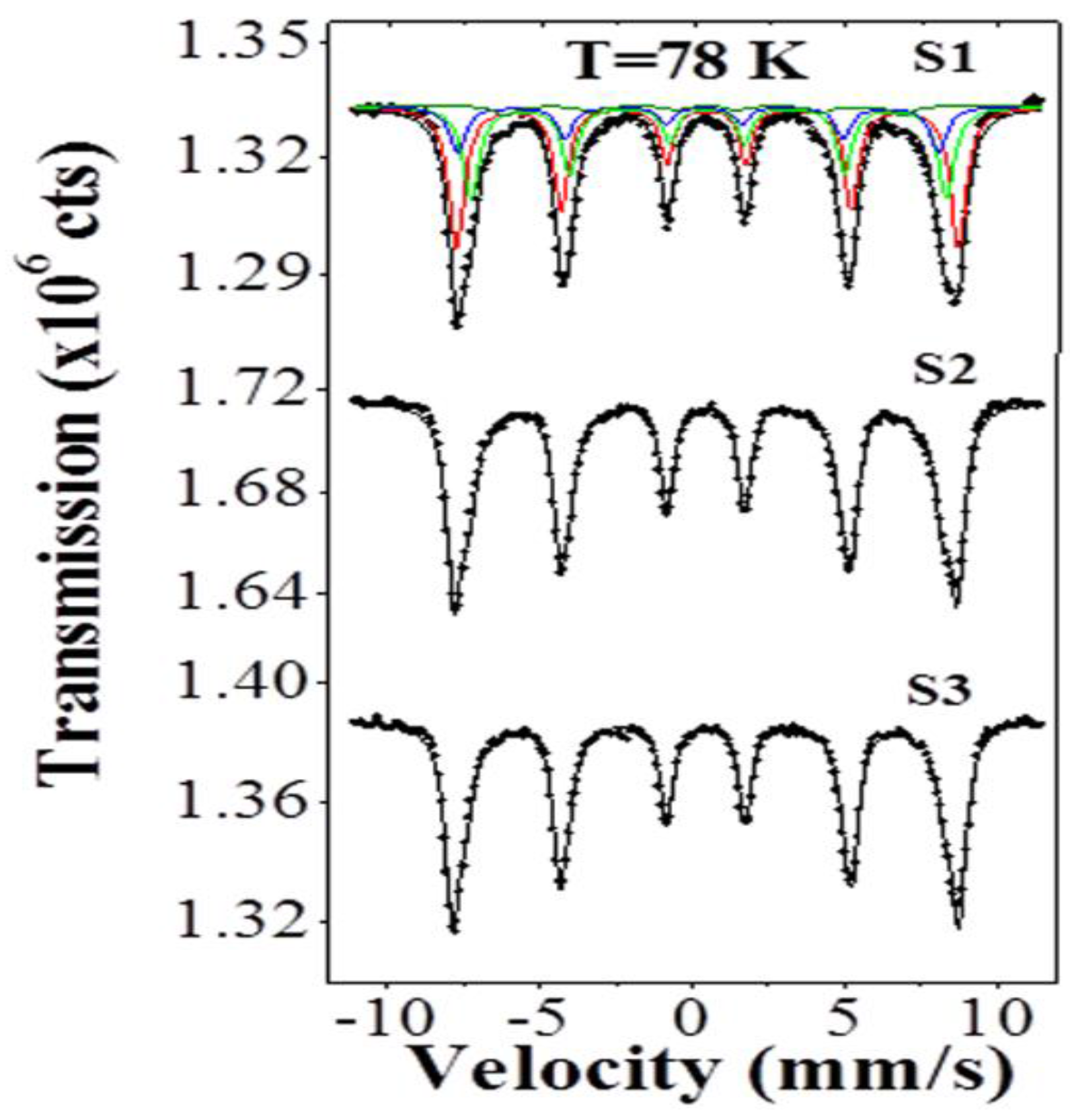
2.3. Mössbauer Analysis
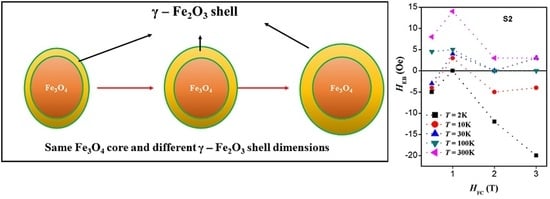
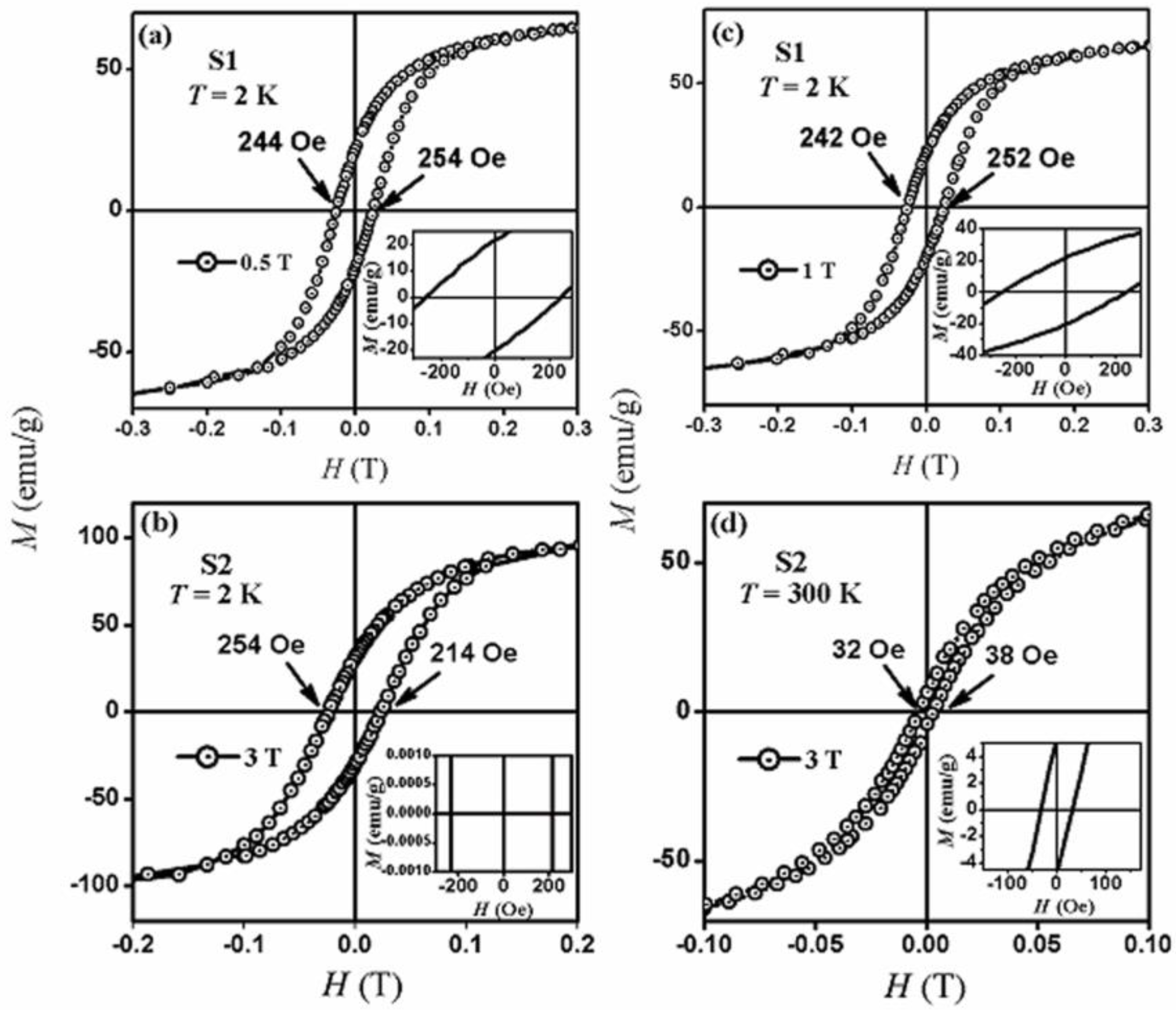
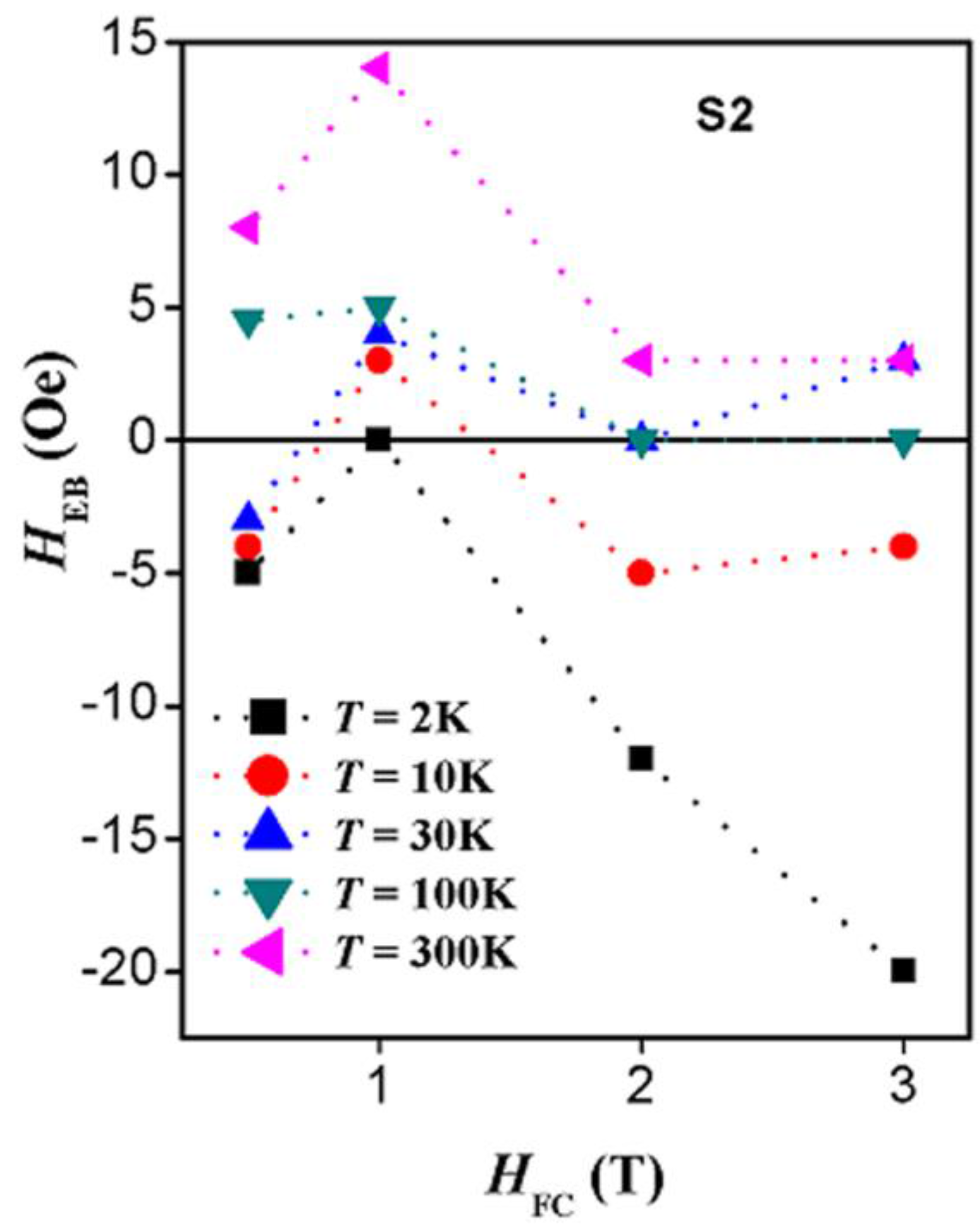
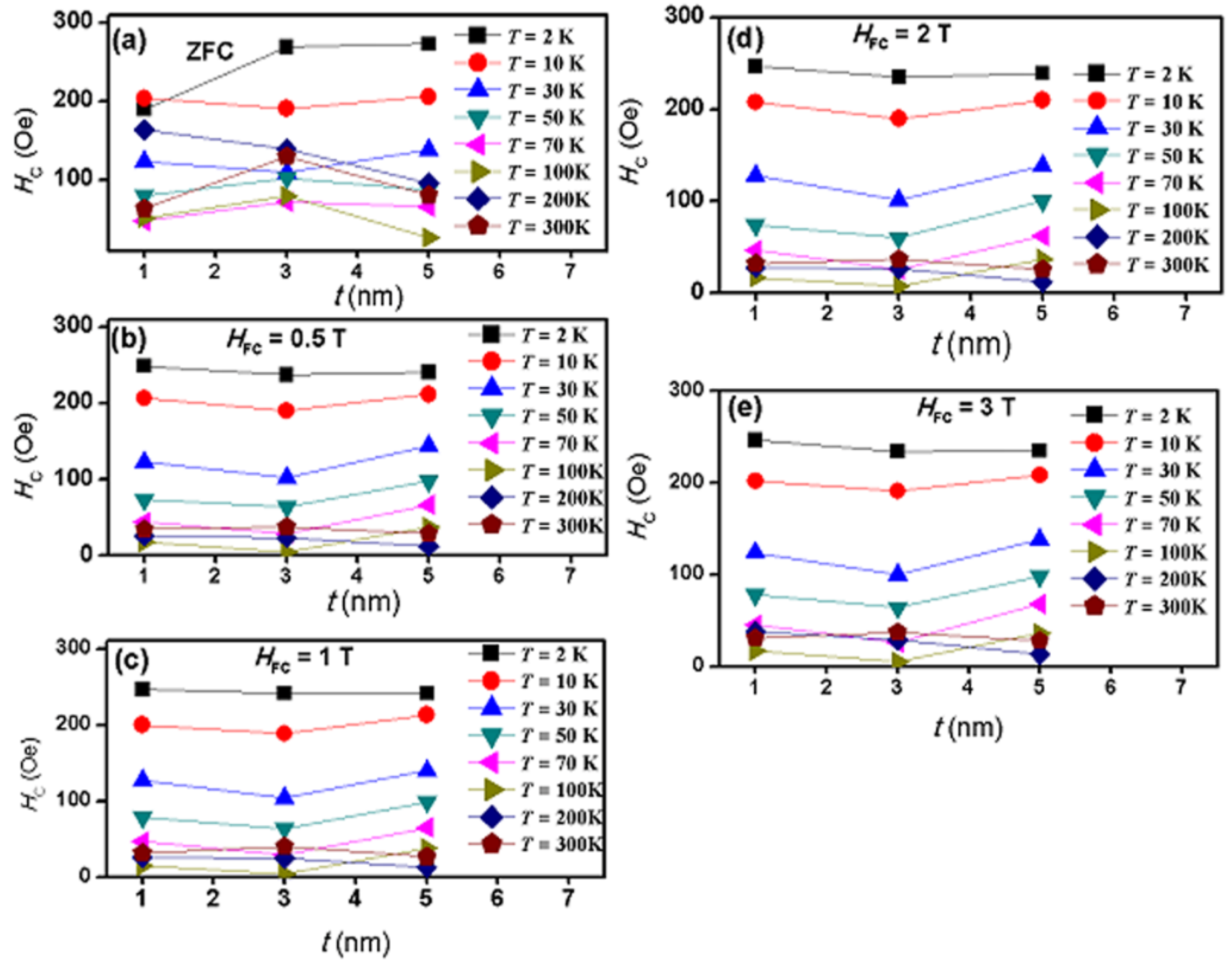
2.4. Magnetic Properties
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nogues, J.; Sort, J.; Langlais, V.; Skumryev, V.; Surinach, S.; Munoz, J.S.; Baro, M.D. Exchange bias in nanostructures. Phys. Rep. 2015, 422, 65–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ortega, A.; Estrader, M.; Salazar-Alvarez, G.; Rocad, A.G.; Nogués, J. Applications of exchange coupled bi-magnetic hard/soft and soft/hard magnetic core/shell nanoparticles. Phys. Rep. 2015, 553, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skumryev, V.; Stoyanov, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hadjipanayis, G.; Givord, D.; Nogués, J. Beating the superparamagnetic limit with exchange bias. Nature 2003, 423, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, D.K. FeRh-FePt Core Shell Nanostructure for Ultra-High Density Storage Media. U.S. Patent 7,964,013, 21 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.S.; Gu, B.X.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, H.Y.; Du, Y.W. Ferromagnetic/antiferromagnetic exchange coupling in SrFe12O19/CoO composites. Appl. Phys. A 2003, 77, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groza, I.; Morel, R.; Brenac, A.; Beigne, C.; Notin, L. Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Co/CoO Core–Shell Clusters. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 3355–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamnejadi, A.; Venkatesan, M.; Alaria, J.; Boese, M.; Kameli, P.; Salamati, H.; Coey, J.M.D. Conventional and inverse magnetocaloric effects in La0.45Sr0.55MnO3 Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 043905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbic, M.; Scherer, A. Magnetic nanostructures as amplifiers of transverse fields in magnetic resonance. Sol. State Nucl. Magn. Res. 2005, 28, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.L.; Chae, M.K.; Jang, E.J.; Lee, C. Cleaved Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as T2 Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 4217–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sort, J.; Nogues, J.; Surinach, S.; Munoz, J.S.; Baro, M.D.; Chappel, E.; Dupont, F.; Chouteau, G. Coercivity and squareness enhancement in ball-milled hard magnetic–antiferromagnetic composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 1142–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangopadhyay, S.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Sorensen, C.M.; Klabunde, K.J. Magnetic properties of ultrafine Co particles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1992, 28, 3174–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meikleohn, W.H.; Bean, C.P. New Magnetic Anisotropy. Phys. Rev. 1956, 102, 1413–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, A.E.; Takano, K. Exchange anisotropy—A review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 552–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Nogues, J.; Leighton, C.; Masuda, H.; Nishio, K.; Roshchin, I.V.; Schuller, I.K. Fabrication and thermal stability of arrays of Fe nanodots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 4434–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.-K.; Sun, Y.; Heng, Z.-H. Cooling field dependence of exchange bias in phase-separated La0.88Sr0.12CoO3. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 023914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binek, C.; He, X.; Polisetty, S. Temperature dependence of the training effect in a Co/CoO exchange-bias layer. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 054408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.B.; Ding, J. Exchange coupling in CoO–Co bilayer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 303, e160–e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Alvarez, G.; Sort, J.; Surinach, S.; Baro, M.D.; Nogues, J. Synthesis and Size-Dependent Exchange Bias in Inverted Core−Shell MnO|Mn3O4 Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9102–9108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavich, D.W.; Dickerson, J.H.; Mahajan, S.V.; Hasan, S.A.; Park, J.H. Exchange bias of singly inverted FeO/Fe3O4 core-shell nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 174414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, P.; Basu, S.; Dutta, S.; Brahma, P.; Chakravorty, D. Exchange bias in ferrimagnetic–antiferromagnetic nanocomposite produced by mechanical attrition. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 2269–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorani, D.; Del Bianco, L.; Testa, A.M. Glassy dynamics in an exchange bias nanogranular system: Fe/FeOx. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 300, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desautels, R.D.; Skoropata, E.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Ouyang, H.; Freeland, J.W.; Lierop, J.V. Tuning the surface magnetism of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with a Cu shell. App. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 262501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, X.; Labarta, A. Finite-size effects in fine particles: Magnetic and transport properties. J. Phys. D 2002, 35, R15–R42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-H.; Lai, C.-H. Size-dependent magnetic properties of PtMn nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 3069–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrynin, A.N.; Levlev, D.N.; Temst, K.; Lievens, P.; Margueritat, J.; Gonzalo, V.; Afonso, C.N.; Zhou, S.Q.; Vantomme, A.; Piscopiello, E.; et al. Critical size for exchange bias in ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic particles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 87, 012501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Huls, N.F.; Sigdel, A.; Sun, S. Tuning exchange bias in core/shell FeO/Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriadis, V.; Kechrakos, D.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O.; Tsiantos, V. Shape-dependent exchange bias effect in magnetic nanoparticles with core-shell morphology. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 064420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Reethu, K.; Thanveer, T.; Myint, M.T.Z.; Al-Harthi, S.H. Effect of shell thickness on the exchange bias blocking temperature and coercivity in Co-CoO core-shell nanoparticles. J. App. Phys. 2017, 122, 063902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bellouard, C.; Mirebeau, I.; Hennion, M. Magnetic correlations of fine ferromagnetic particles studied by small-angle neutron scattering. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, 5570–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, M.-H.; Alonso, J.; Khurshid, H.; Lampen-Kelley, P.; Chandra, S.; Repa, K.S.; Nemati, Z.; Das, R.; Iglesias, O.; Srikanth, H. Exchange Bias Effects in Iron Oxide-Based Nanoparticle Systems. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.; Angappane, S.; Park, J.; An, K.; Hyeon, T.; Park, J.-G. Exchange bias behavior of monodisperse Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3 core/shell nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Boubeta, C.; Simeonidis, K.; Angelakeris, M.; Pazos-Pérez, N.; Giersig, M.; Delimitis, A.; Nalbandian, L.; Alexandrakis, V.; Niarchos, D. Critical radius for exchange bias in naturally oxidized Fe nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 054430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakaki, M.; Trohidou, K.N.; Nogués, J. Enhanced Magnetic Properties in Antiferromagnetic-Core/Ferrimagnetic-Shell Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilakaki, M.; Trohidou, K.N. Numerical study of the exchange-bias effect in nanoparticles with ferromagnetic core/ferrimagnetic disordered shell morphology. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 144402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häggström, L.; Kamali, S.; Ericsson, T.; Nordblad, P.; Ahniyaz, A.; Bergström, L. Mössbauer and magnetization studies of iron oxide nanocrystals. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on the Applications of the Mössbauer Effect (ICAME 2007), Kanpur, India, 14–19 October 2007; pp. 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberghe, R.E.; de Grave, E. Mössbauer effect studies of oxidic spinels. In Mössbauer Spectroscopy Applied to Inorganic Chemistry; Long, G.J., Grandjean, F., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; Volume 3, pp. 59–182. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, E.; Brandl, A.L.; Arelaro, A.D.; Goya, G.F. Spin disorder and magnetic anisotropy in Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 083908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronc, E.; Ezzir, A.; Cherkaoui, R.; Chanéac, C.; Noguès, M.; Kachkachi, H.; Fiorani, D.; Testa, A.M.; Grenèche, J.M.; Jolivet, J.P. Surface-related properties of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 2000, 221, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brice-Profeta, S.; Arrio, M.-A.; Tronc, E.; Menguy, N.; Letard, I.; Cartier dit Moulin, C.; Noguès, M.; Chanéac, C.; Jolivet, J.-P.; Sainctavit, P. Magnetic order in γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: A XMCD study. J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 2005, 288, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbasov, R.R.; Cherepanov, V.M.; Chuev, M.A.; Polikarpov, M.A.; Panchenko, V.Y. Size effect of Mossbauer parameters in iron oxide Nanoparticles. Hyperfine Interact. 2014, 226, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.; Hussain, N.; Shafi, M. Identification of Iron Oxides Qualitatively/Quantitatively Formed during the High Temperature Oxidation of Superalloys in Air and Steam Environments. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2009, 25, 479–482. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, W.B.; Hu, Y.; Du, A.; You1, B.; Xiao, M.W.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, S.M.; Du, J. Cooling field and temperature dependent exchange bias in spin glass/ferromagnet bilayers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan Ali, S.; Bilal Janjua, M.; Fecioru-Morariu, M.; Lott, D.; Smits, C.J.P.; Güntherodt, G. Role of interface alloying in the exchange bias of Fe/Cr bilayers. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 020402(R). [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Adie, P.; Marrows, C.H.; Greig, D.; Hickey, B.J.; Stamps, R.L. Exchange bias using a spin glass. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolle, D.; Goering, E.; Tietze, T.; Schütz, G.; Figuerola, A.; Manna, L. Structural and magnetic deconvolution of FePt/FeOx-nanoparticles using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 033034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.; Li, J.; Jenkins, C.A.; Arenholz, E.; Scholl, A.; Hwang, C.; Qiu, Z.Q. Exchange bias in epitaxially grown CoO/MgO/Fe/Ag(001). Phys. Rev. B. 2012, 86, 064406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.M.; Imhoff, D.; Yu-Zhang, K.; Leprince-Wang, Y. Effect of field cooling on magnetic properties of ultrafine CoO/Co particles. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process 2015, 81, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, C.; Ilyn, M.; Vega, V.; Prida, V.M.; González, J.; Mendoza-Reśendez, R. Size Distribution and Frustrated Antiferromagnetic Coupling Effects on the Magnetic Behavior of Ultrafine Akaganéite (β-FeOOH) Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 21128–21139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-K.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, Z.-H. Exchange bias associated with phase separation in the perovskite cobaltite La1−xSrxCoO3. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 174419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosvenor, A.P.; Kobe, B.A.; McIntyre, N.S. Examination of the oxidation of iron by oxygen using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and QUASES TM. Surf. Sci. 2004, 565, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Bhf (T) γ-Fe2O3 | δ (mm/s) γ-Fe2O3 | W (mm/s) γ-Fe2O3 | A (%) γ-Fe2O3 | Bhf (T) Fe3O4 | δ (mm/s) Fe3O4 | W (mm/s) Fe3O4 | A (%) of the 2-Sites Fe3O4 | Total A (%) Fe3O4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 51.2 | 0.44 | 0.54 | 48.4 | 48.4 49.0 | 0.47 0.24 | 0.54 0.54 | 32.2 16.1 | 48.3 |
| S2 | 51.1 | 0.44 | 0.48 | 80.1 | 48.4 49.0 | 0.47 0.24 | 0.48 0.48 | 11.2 5.6 | 16.8 |
| S3 | 51.0 | 0.44 | 0.48 | 89.0 | 48.4 49.0 | 0.47 0.24 | 0.48 0.48 | 5.7 2.8 | 8.5 |
| Sample | Core Diameter (nm) Fe3O4 | Shell Thickness (nm) γ-Fe2O3 | Core Volume (nm3) Fe3O4 | Shell Volume (nm3)γ-Fe2O3 | Total A (%) Fe3O4 | A (%) γ-Fe2O3 | Shell Volume/Core Volume | [A (%) γ-Fe2O3/Total A (%) Fe3O4] × 0.981 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 8±0.9 | 1±0.06 | 268.1 | 255.5 | 48.3 | 48.4 | 0.953 | 0.983 |
| S2 | 8±0.9 | 3±0.05 | 268.1 | 1169 | 16.8 | 80.1 | 4.360 | 4.678 |
| S3 | 8±0.9 | 5±0.06 | 268.1 | 2786 | 8.5 | 89.0 | 10.392 | 10.272 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obaidat, I.M.; Nayek, C.; Manna, K.; Bhattacharjee, G.; Al-Omari, I.A.; Gismelseed, A. Investigating Exchange Bias and Coercivity in Fe3O4–γ-Fe2O3 Core–Shell Nanoparticles of Fixed Core Diameter and Variable Shell Thicknesses. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120415
Obaidat IM, Nayek C, Manna K, Bhattacharjee G, Al-Omari IA, Gismelseed A. Investigating Exchange Bias and Coercivity in Fe3O4–γ-Fe2O3 Core–Shell Nanoparticles of Fixed Core Diameter and Variable Shell Thicknesses. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(12):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120415
Chicago/Turabian StyleObaidat, Ihab M., Chiranjib Nayek, Kaustuv Manna, Gourab Bhattacharjee, Imaddin A. Al-Omari, and Abbasher Gismelseed. 2017. "Investigating Exchange Bias and Coercivity in Fe3O4–γ-Fe2O3 Core–Shell Nanoparticles of Fixed Core Diameter and Variable Shell Thicknesses" Nanomaterials 7, no. 12: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120415
APA StyleObaidat, I. M., Nayek, C., Manna, K., Bhattacharjee, G., Al-Omari, I. A., & Gismelseed, A. (2017). Investigating Exchange Bias and Coercivity in Fe3O4–γ-Fe2O3 Core–Shell Nanoparticles of Fixed Core Diameter and Variable Shell Thicknesses. Nanomaterials, 7(12), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120415