Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Properties of Ti-Ni-Si-O Nanostructures on Ti-Ni-Si Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
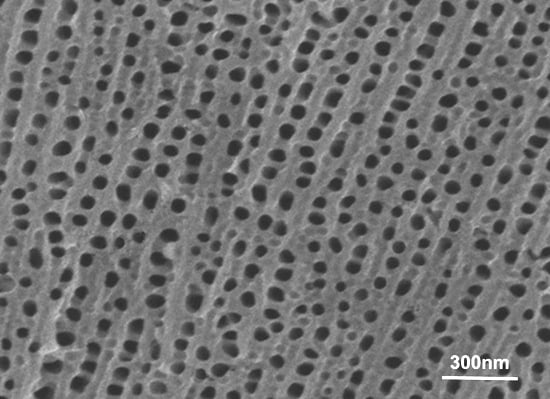
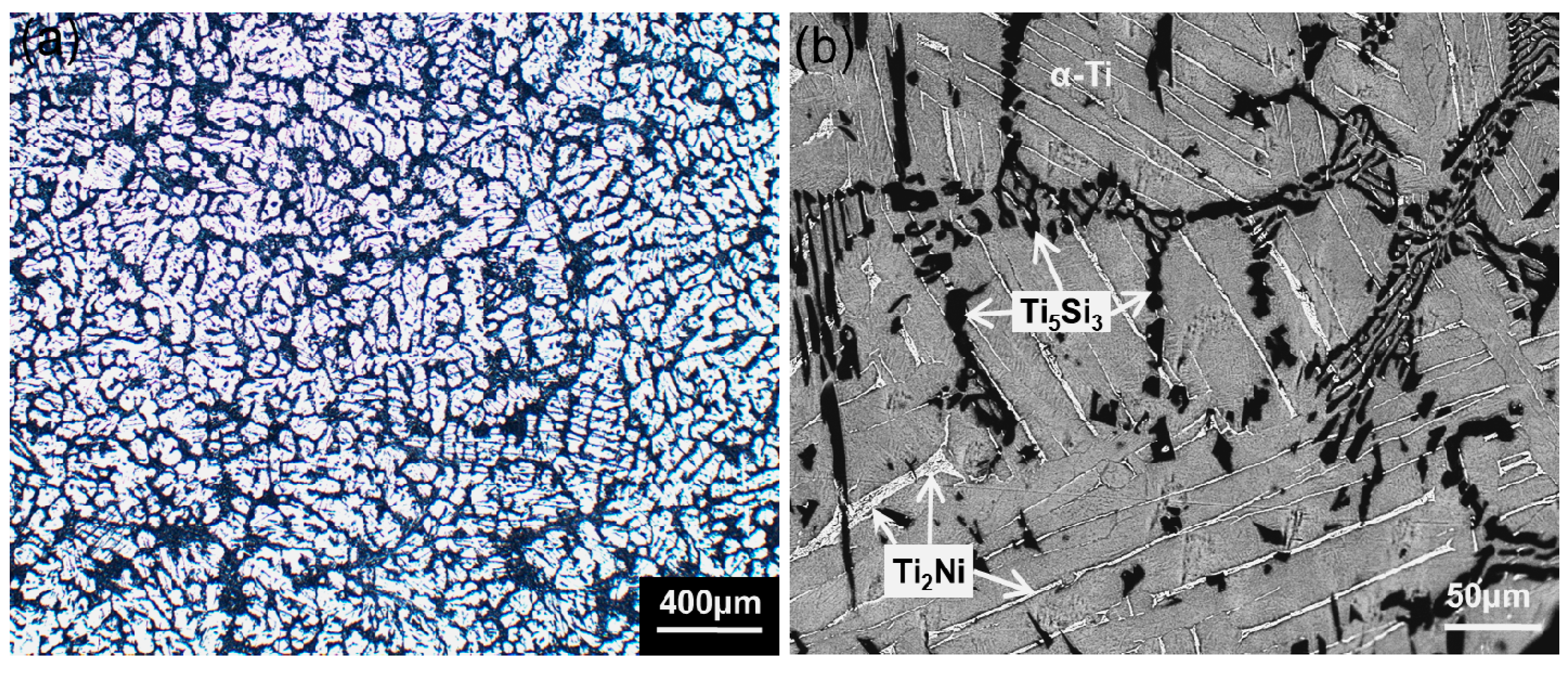
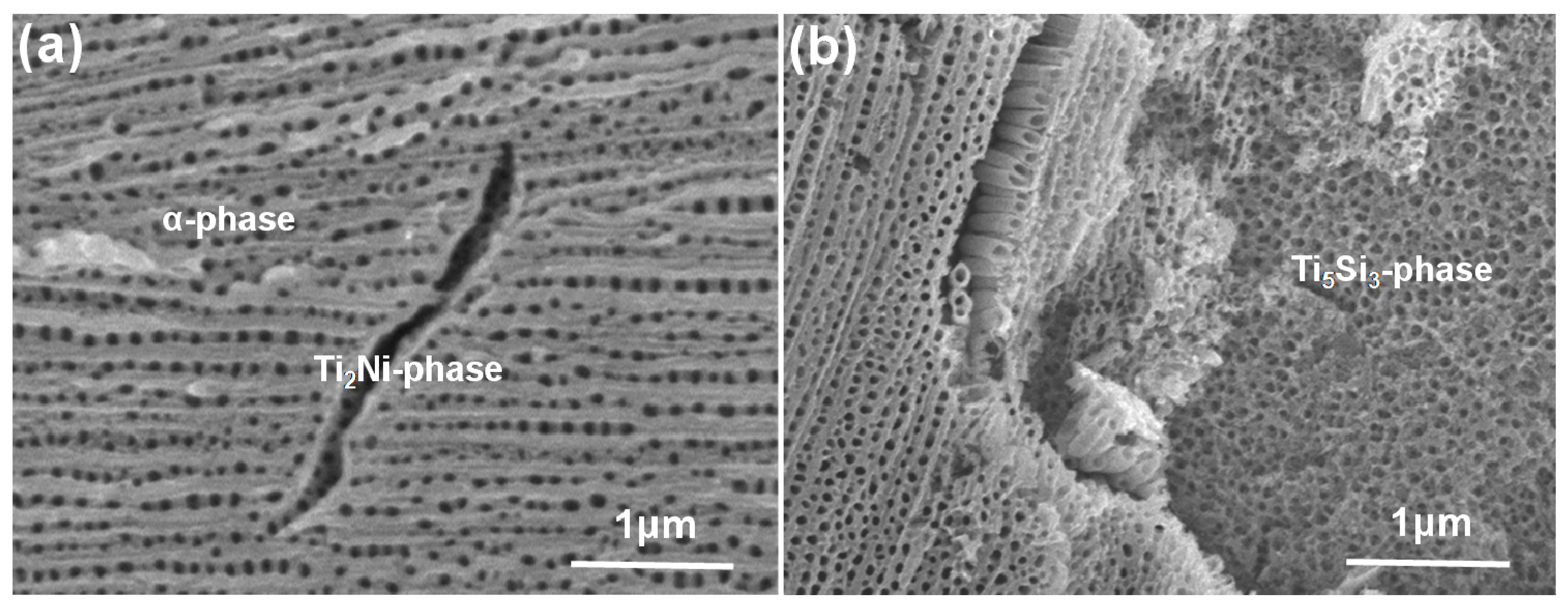
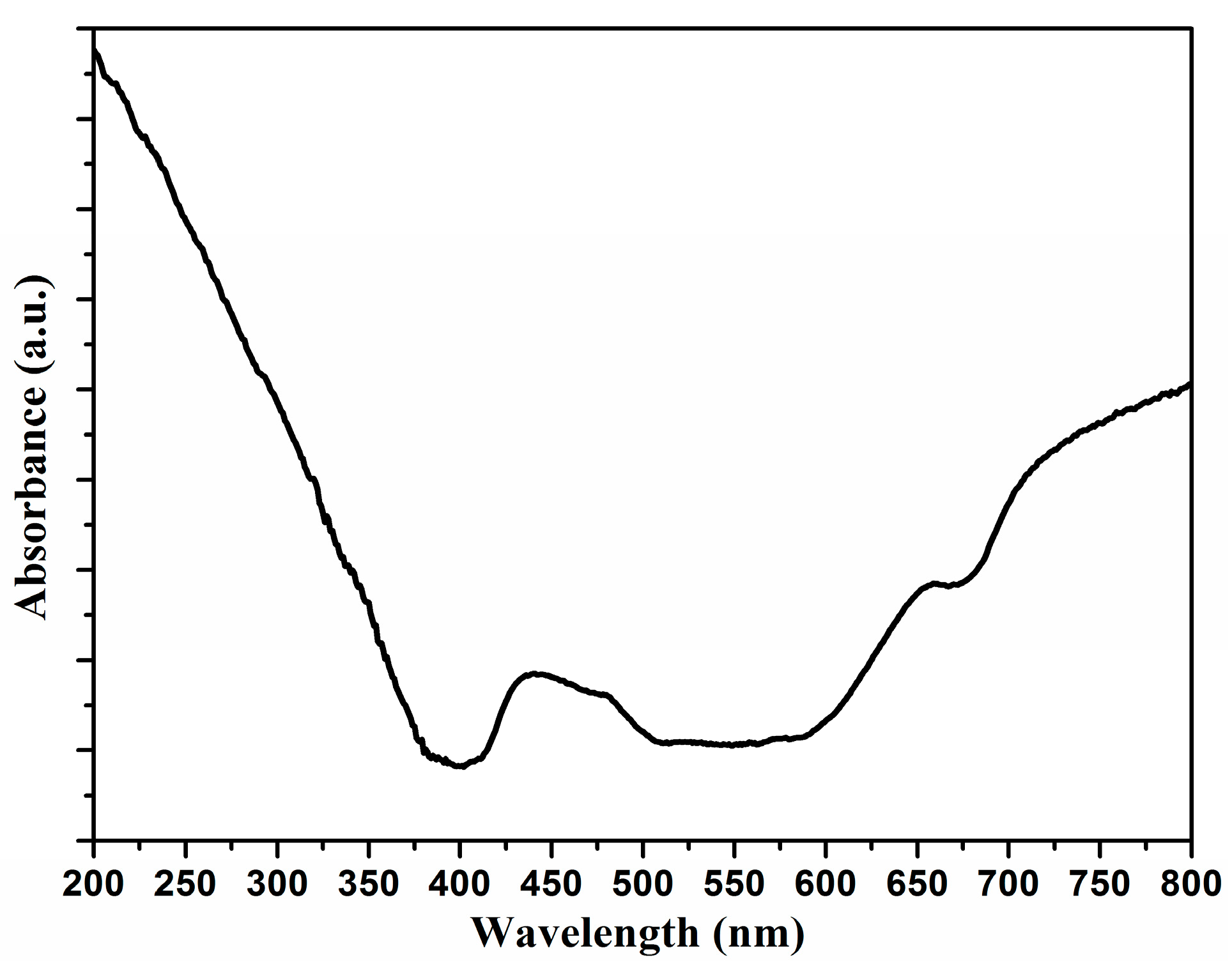
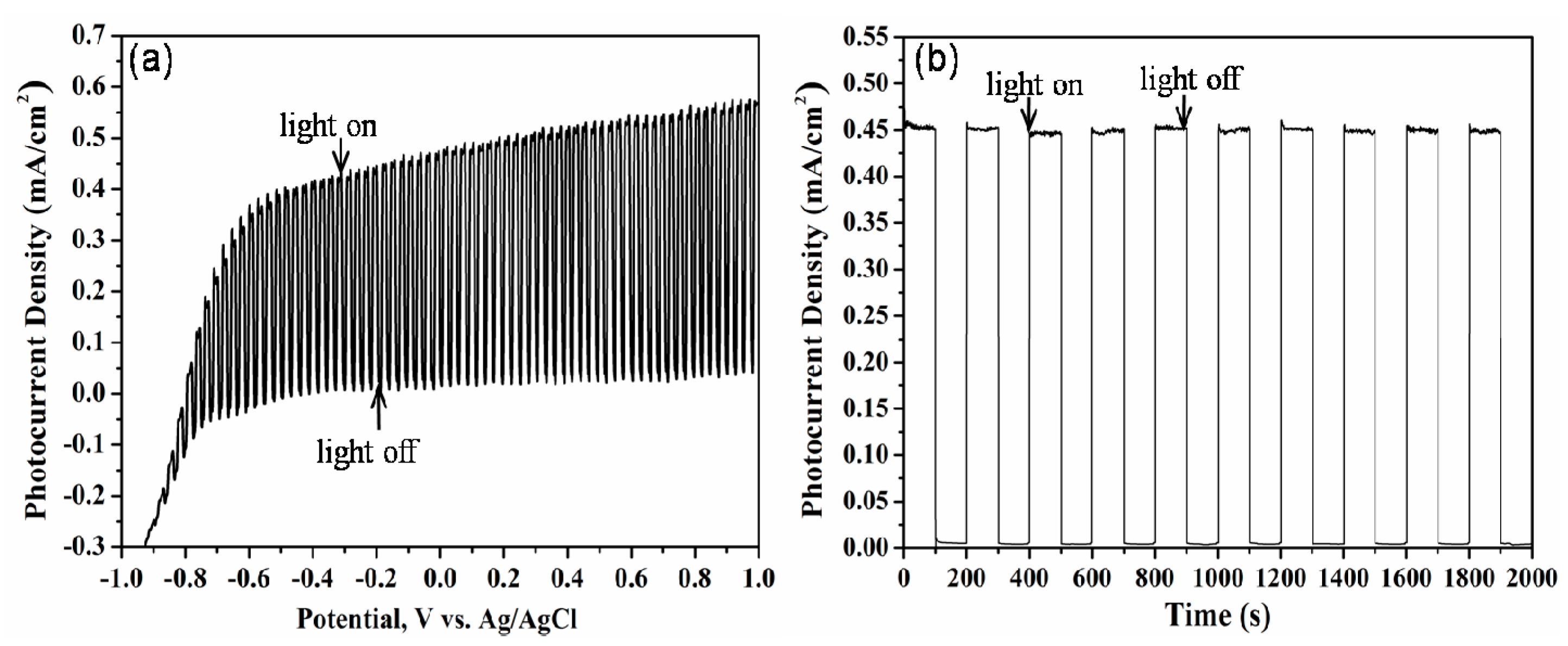
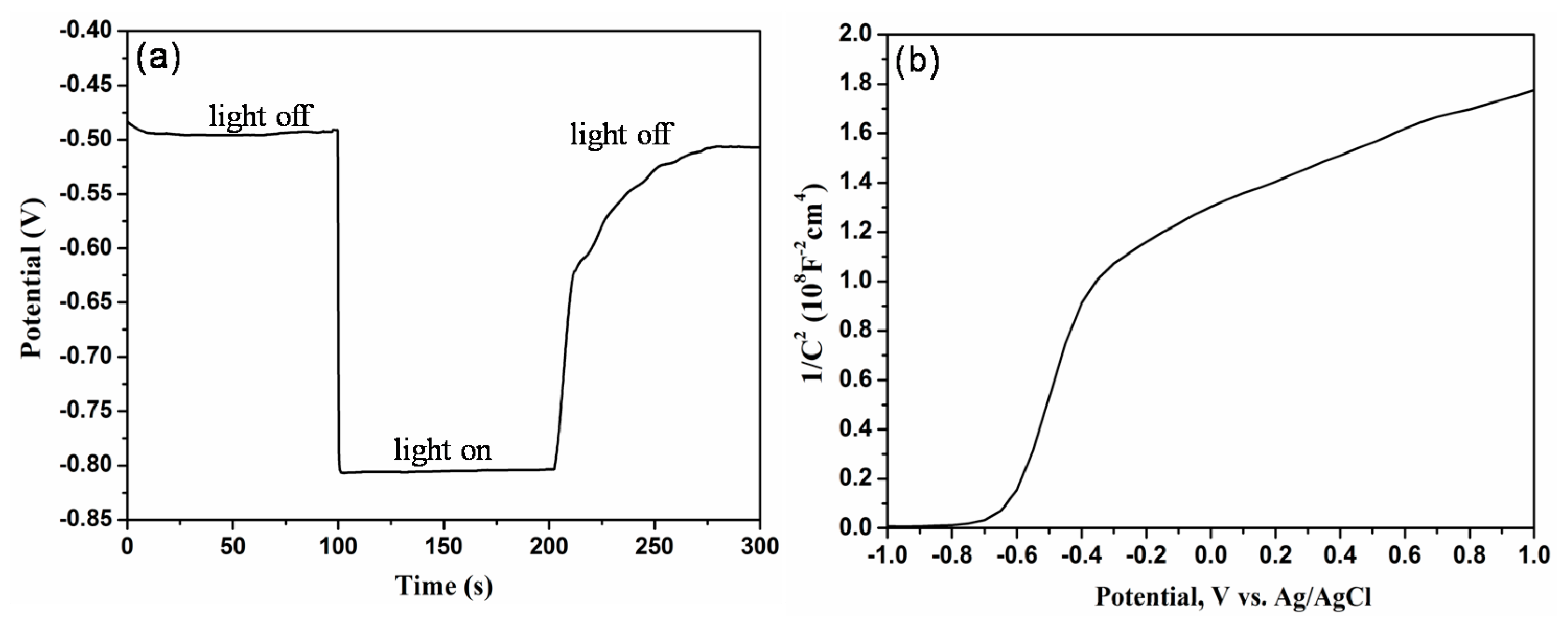
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.; Mazare, A.; Schmuki, P. One-dimensional titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Nanotubes. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9385–9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, A.; Miseki, Y. Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Lai, Y.; Lin, C. Electrochemically multi-anodized TiO2 nanotube arrays for enhancing hydrogen generation by photoelectrocatalytic water splitting. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 4776–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreethawong, T.; Junbua, C.; Chavadej, S. Photocatalytic H2 production from water splitting under visible light irradiation using Eosin Y-sensitized mesoporous-assembled Pt/TiO2 nanocrystal photocatalyst. J. Power Sources 2009, 190, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Z. Freestanding TiO2 nanotube arrays with ultrahigh aspect ratio via electrochemical anodization. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Lin, V.S.Y.; Lin, Z. Formation of various TiO2 nanostructures from electrochemically anodized titanium. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3682–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Xin, X.; Lin, C.; Lin, Z. High efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells based on hierarchically structured nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3214–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Wang, J.; Han, W.; Ye, M.; Lin, Z. Dye-sensitized solar cells based on a nanoparticle/nanotube bilayer structure and their equivalent circuit analysis. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Ding, D.Y.; Ning, C.Q.; Wang, X.W. α-Fe2O3/Ti-Nb-Zr-O composite photoanode for enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2015, 196, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.E.R.; Rohani, S. Modified TiO2 nanotube arrays (TNTAS): Progressive strategies towards visible light responsive photoanode, a review. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.P.; Yu, W.Y.; Ku, M.C.; Liou, Y.C.; Chien, S.H. Pt/titania-nanotube: A potential catalyst for CO2 adsorption and hydrogenation. Appl. Catal. B 2008, 84, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Jia, J.B.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, B.L.; Dong, S.J. Pt modified TiO2 nanotubes electrode: Preparation and electrocatalytic application for methanol oxidation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 12169–12173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.D.; Qu, Y.F.; Zhou, X.M.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.Y.; Schmuki, P. Pt-decorated g-C3N4/ TiO2 nanotube arrays with enhanced visible–light photocatalytic activity for H2 evolution. Chem. Open 2016, 5, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kang, S.H.; Min, S.K.; Sung, Y.E.; Han, S.H. Co-sensitization of vertically aligned TiO2 nanotubes with two different sizes of cdse quantum dots for broad spectrum. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.R.; Kamat, P.V. Photosensitization of TiO2 nanostructures with CdS quantum dots: Particulate versus tubular support architectures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.Y.; Ning, C.Q.; Huang, L.; Jin, F.C.; Hao, Y.Q.; Bai, S.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Mao, D.L. Anodic fabrication and bioactivity of Nb-doped TiO2 nanotubes. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 305103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, R.; Ding, D.Y.; Ning, C.Q.; Liu, H.G.; Zhu, B.S.; Li, M.; Mao, D.L. Ni-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays on shape memory alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 6308–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, K.A.; Naduvath, J.; Mallick, S.; Pledger, J.W.; Remillard, S.K.; DeYoung, P.A.; Thankamoniamma, M.; Shripathi, T.; Philip, R.R. Electrochemical synthesis of novel Zn-doped TiO2 nanotube/ZnO nanoflake heterostructure with enhanced DSSC efficiency. Nano-Micro Lett. 2016, 8, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, M.; Lee, K.; Killian, M.S.; Selli, E.; Schmuki, P. Ta–doped TiO2 nanotubes for enhanced solar-light photoelectrochemical water splitting. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 5841–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.I.; Monllor-Satoca, D.; Kim, W.; Choi, W. N-doped TiO2 nanotubes coated with a thin TaOxNy layer for photoelectrochemical water splitting: Dual bulk and surface modification of photoanodes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A. Ferromagnetism in Cr-, Fe- and Ni-doped TiO2 samples. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 442, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ding, D.Y.; Ning, C.Q.; Wang, X.W. Reduced N/Ni-doped TiO2 nanotubes photoanodes for photoelectrochemical water splitting. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 95478–95487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.A.; Khan, M.M.; Ansari, M.O.; Cho, M.H. Nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide (N-doped TiO2) for visible light photocatalysis. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 3000–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, K.A.; Sreekantan, S.; Lai, C.W. Fabrication and photocatalysis of nanotubular C-doped TiO2 arrays: Impact of annealing atmosphere on the degradation efficiency of methyl orange. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyeremateng, N.A.; Hornebecq, V.; Martinez, H.; Knauth, P.; Djenizian, T. Electrochemical fabrication and properties of highly ordered Fe-doped TiO2 nanotubes. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 3707–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Ma, N.; Hua, X.; Wang, H. Si doping effects on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanotubes film prepared by an anodization process. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.C.; Wang, Y.L.; Xu, J. Revisiting the glass-forming ability of Ti-Ni-Si ternary alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 475, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.Y.; Yang, L.X.; Yu, Y. Investigations on the self–organized growth of TiO2 nanotube arrays by anodic oxidization. Thin Solid Film 2006, 515, 1802–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Kamarudin, S.K. Titanium dioxide nanotubes (TNT) in energy and environmental applications: An overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Berger, S.; Schmuki, P. TiO2 nanotubes: Synthesis and applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2904–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ding, D.Y.; Ning, C.Q.; Bai, S.; Huang, L.; Li, M.; Mao, D.L. Thermal stability and in vitro bioactivity of Ti-Al-V-O nanostructures fabricated on Ti6Al4V alloy. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 065708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, G.X.; Yan, K.P. TiO2 nanotubes for hydrogen generation by photocatalytic water splitting in a two-compartment photoelectrochemical cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 15502–15508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pesic, B.; Raja, K.S.; Rangaraju, R.R.; Misra, M. Hydrogen generation under sunlight by self-ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 3250–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunadian, I.; Lipka, S.M.; Swartz, C.R.; Qian, D.; Andrews, R. Determination of carrier densities of boron–and nitrogen-doped multiwalled carbon nanotubes using Mott–Schottky plots. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, K110–K115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmas, S.; Polcaro, A.M.; Ruiz, J.R.; Da Pozzo, A.; Mascia, M.; Vacca, A. TiO2 photoanodes for electrically enhanced water splitting. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 6561–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Jung, H.S.; No, J.H.; Kim, J.R.; Hong, K.S. Influence of anatase–rutile phase transformation on dielectric properties of sol–gel derived TiO2 thin films. J. Electroceram. 2006, 16, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, S.; Hidalgo, D.; Sacco, A.; Chiodoni, A.; Lamberti, A.; Cauda, V.; Tresso, E.; Saracco, G. Comparison of photocatalytic and transport properties of TiO2 and ZnO nanostructures for solar-driven water splitting. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 17, 7775–7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| EDS Testing Areas | Elements (wt %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | Ni | Si | |
| α-Ti phase | 98.81 | 0.12 | 1.07 |
| Ti2Ni phase | 88.02 | 11.89 | 0.09 |
| Ti5Si3 phase | 76.42 | 0.10 | 23.48 |
| EDS Testing Areas | Elements (wt %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | Ni | Si | O | |
| α-Ti phase region | 56.48 | – | 1.06 | 42.46 |
| Ti2Ni phase region | 66.77 | 1.94 | 0.82 | 30.47 |
| Ti5Si3 phase region | 60.35 | – | 9.74 | 29.91 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Ding, D.; Dong, Z.; Ning, C. Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Properties of Ti-Ni-Si-O Nanostructures on Ti-Ni-Si Alloy. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110359
Li T, Ding D, Dong Z, Ning C. Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Properties of Ti-Ni-Si-O Nanostructures on Ti-Ni-Si Alloy. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(11):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110359
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ting, Dongyan Ding, Zhenbiao Dong, and Congqin Ning. 2017. "Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Properties of Ti-Ni-Si-O Nanostructures on Ti-Ni-Si Alloy" Nanomaterials 7, no. 11: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110359
APA StyleLi, T., Ding, D., Dong, Z., & Ning, C. (2017). Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Properties of Ti-Ni-Si-O Nanostructures on Ti-Ni-Si Alloy. Nanomaterials, 7(11), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110359