Determination of Verapamil HCl in Pharmaceutical Preparations by a Fluorescent Nano Probe Based on CdTe/CdS/ZnS Quantum Dots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
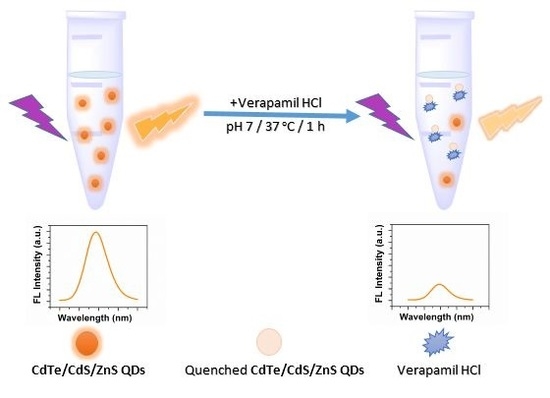
2.1. Schematic Illustration of the Method Designed
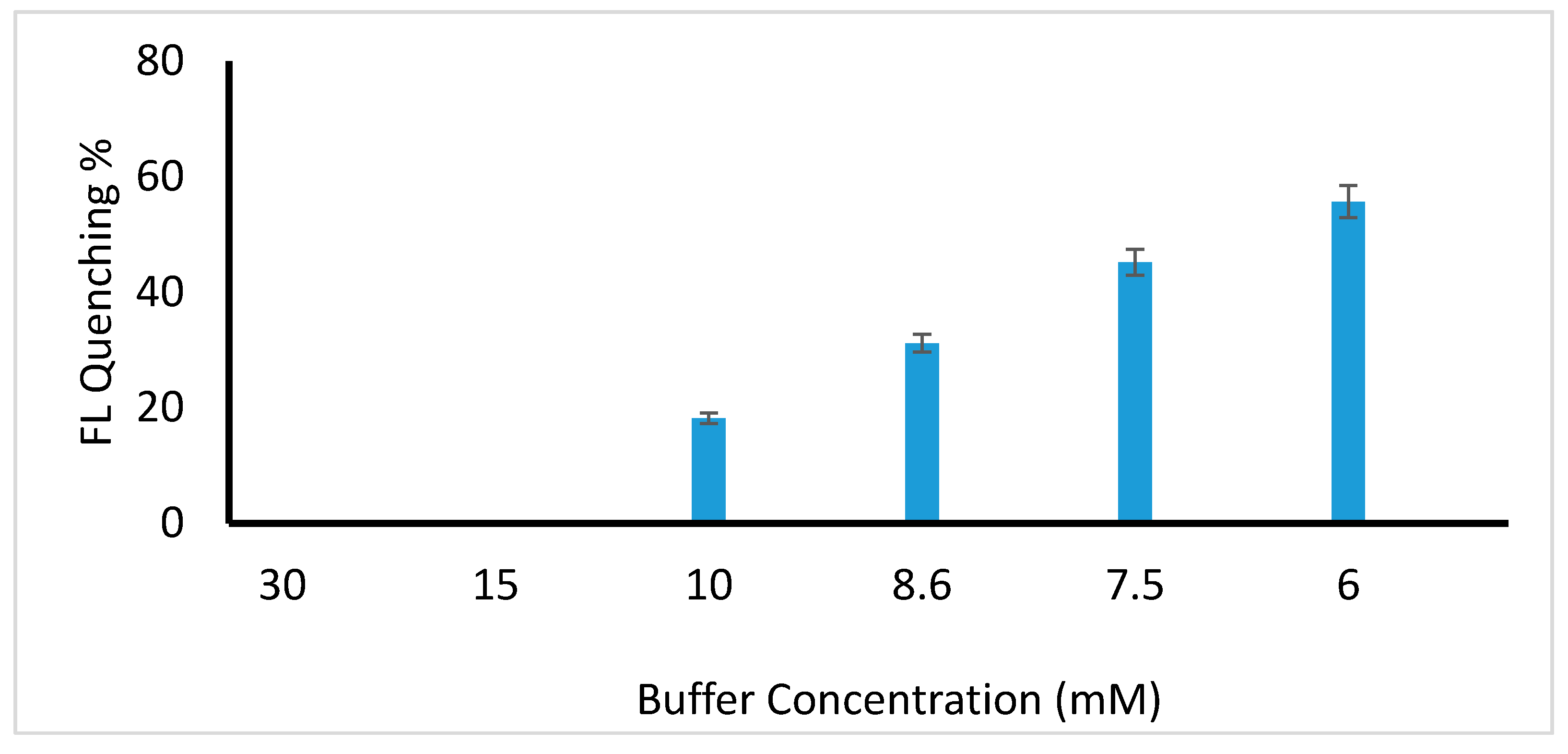
Optimization of Reaction Parameters
2.2. Selection of QDs Concentration
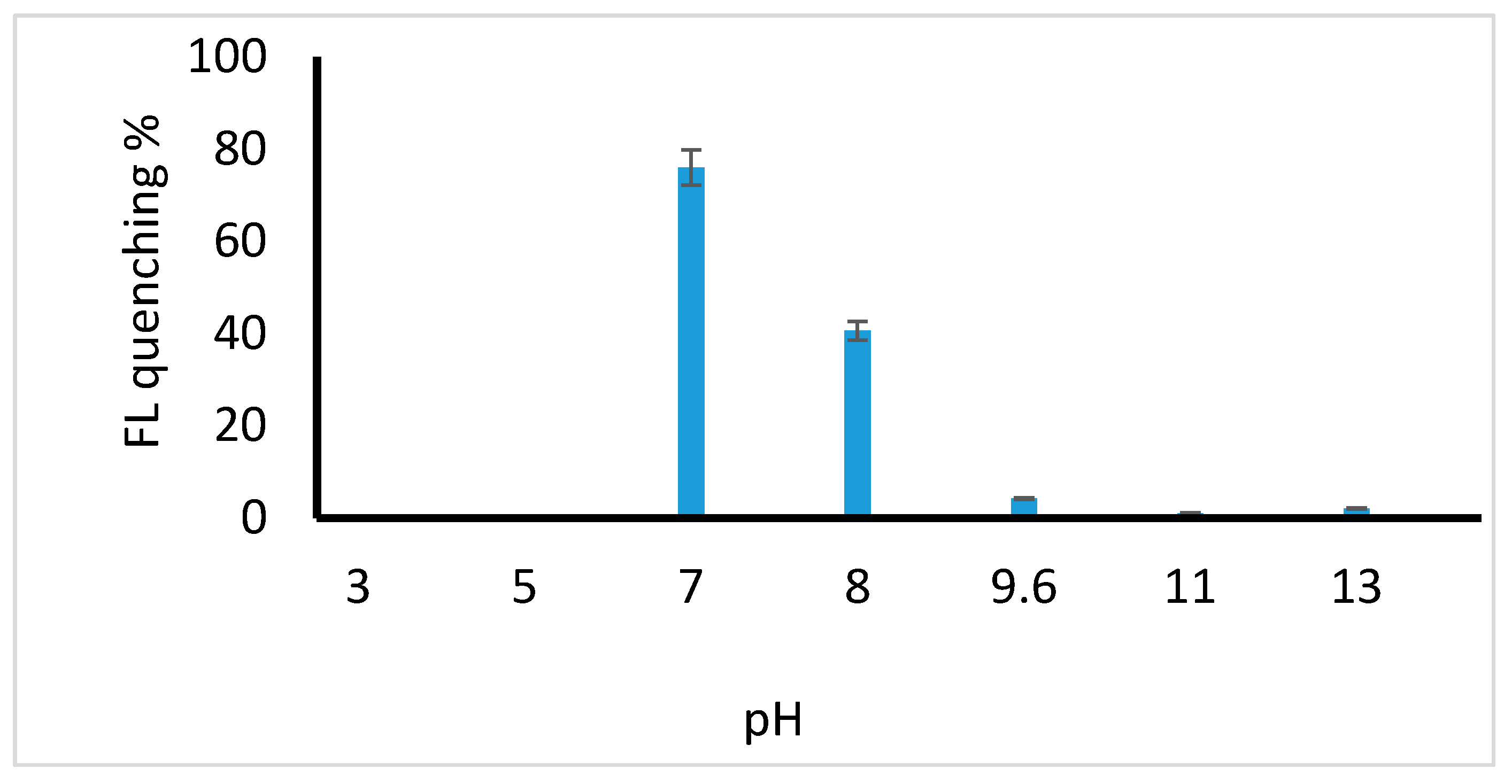
2.2.1. Effect of pH on the Reaction System
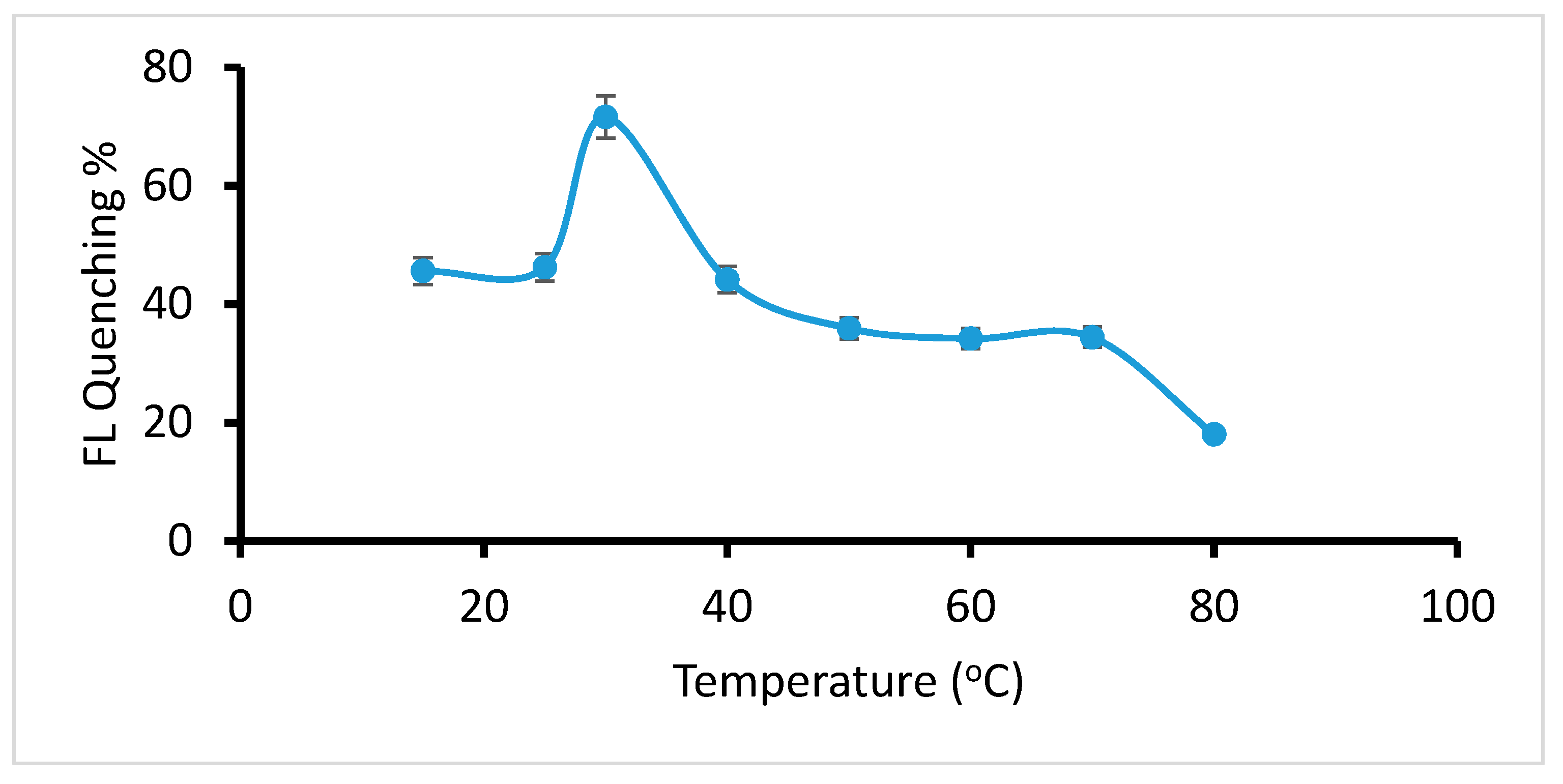
2.2.2. Optimization of Temperature
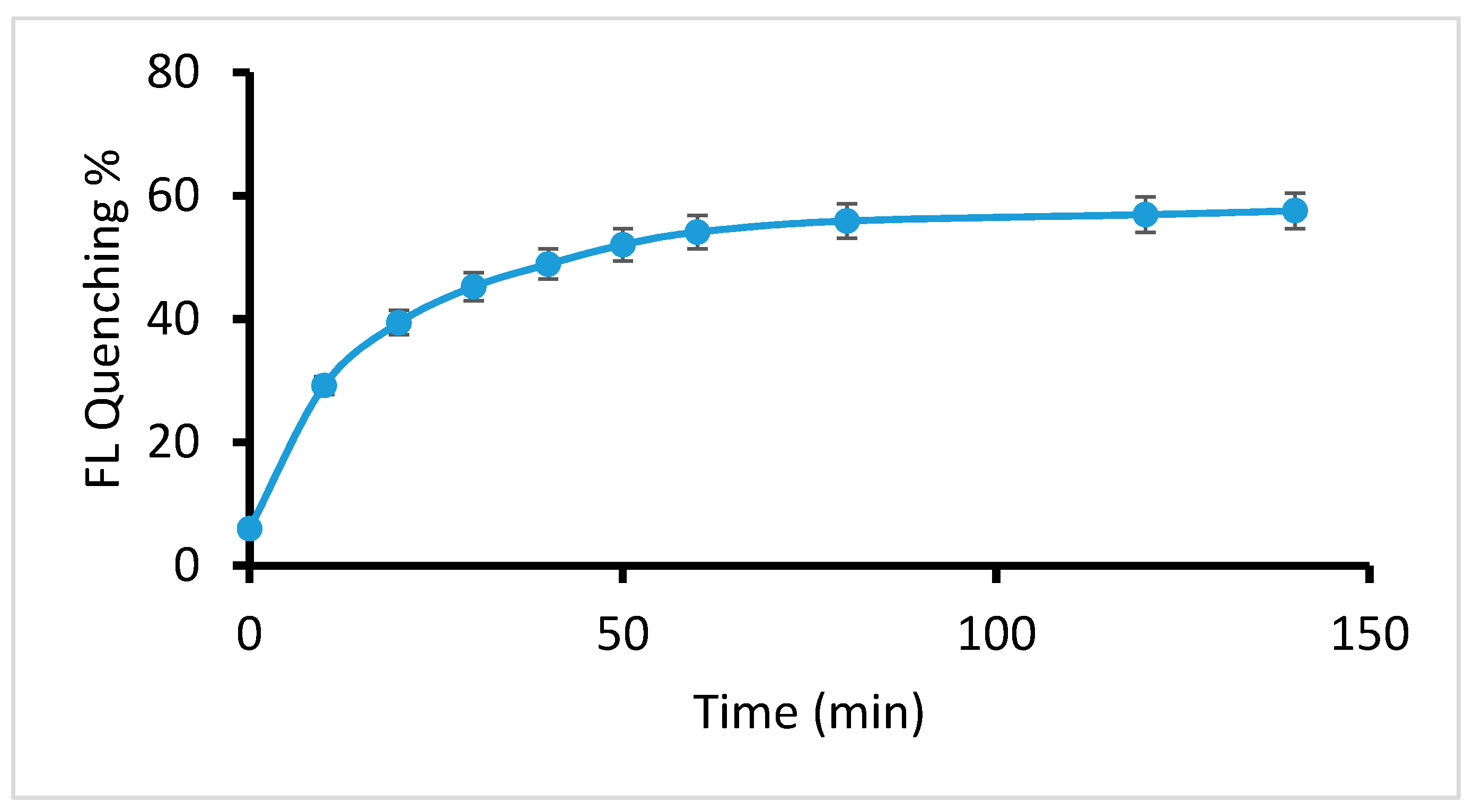
2.2.3. Effect of Reaction Time
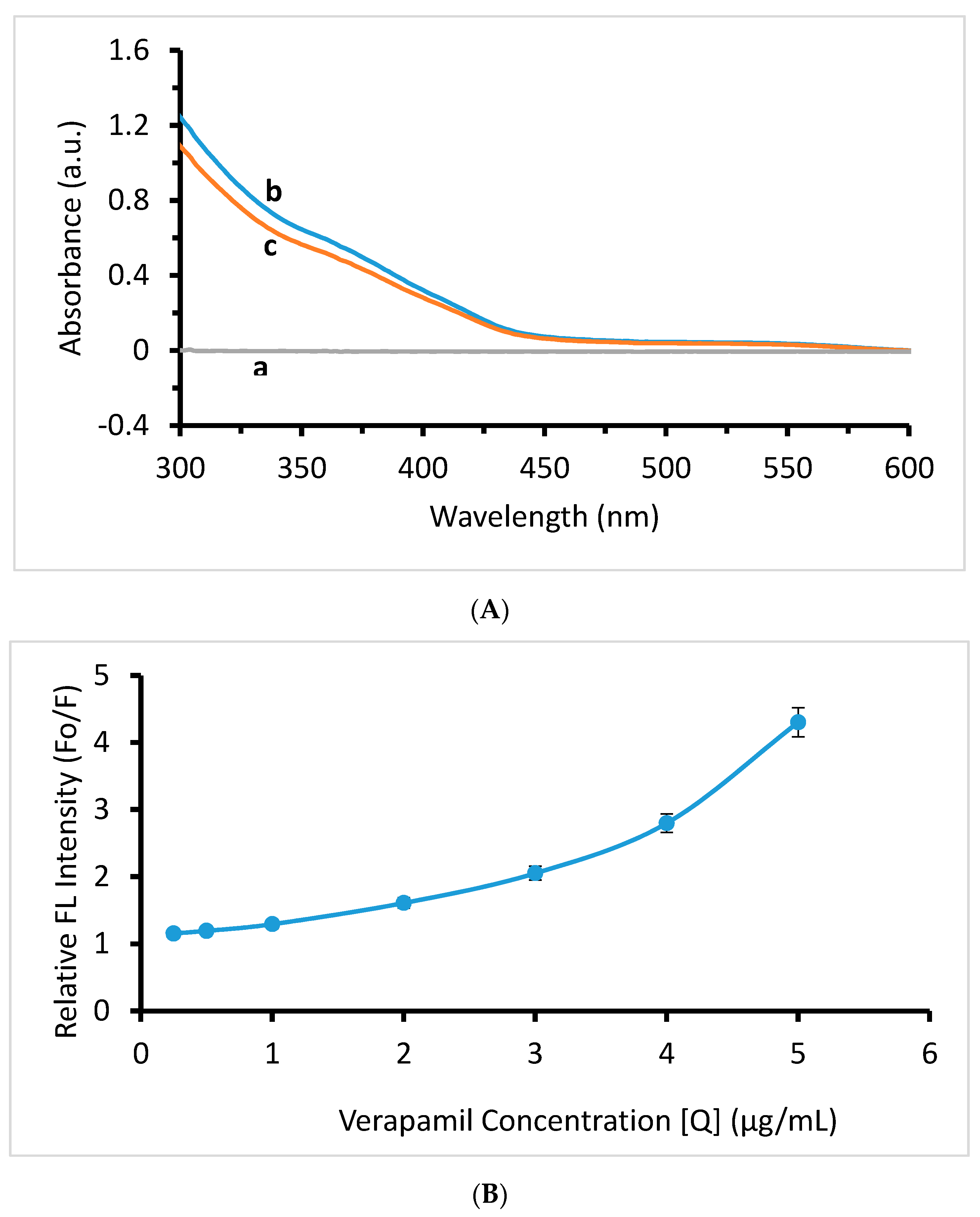
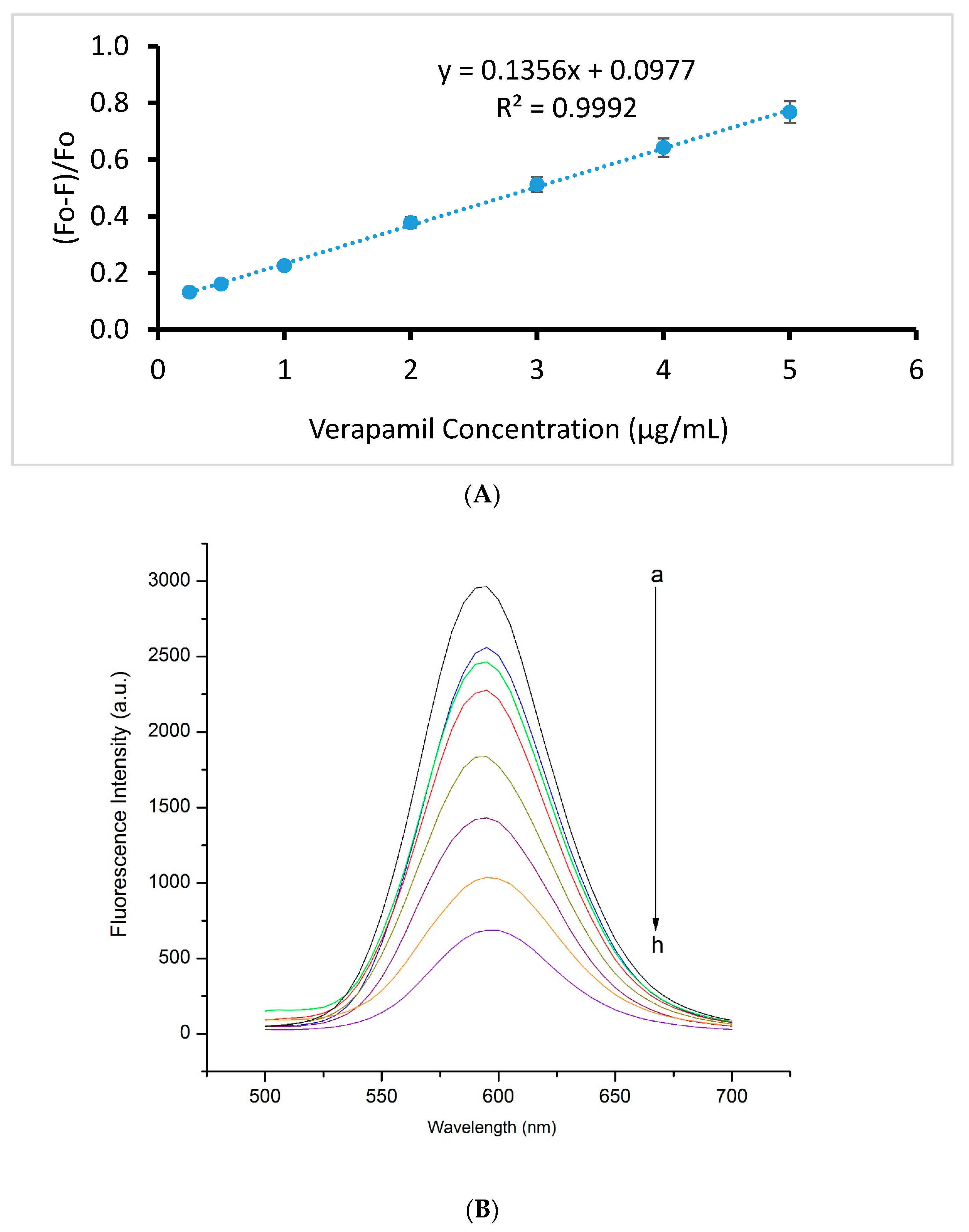
2.3. Mechanism of Quenching
2.4. Method Validation
Selectivity Experiment
2.5. Analytical Application
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Hypothesis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Synthesis of CdTe/CdS/ZnS QDs
3.4. Preparation of Verapamil Standard Solution and Sample
3.5. Procedure for Measurement of Verapamil HCl in Dosage Forms
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Hu, X. Study on the interaction between verapamil hydrochloride and eosin y by absorption, fluorescence and resonance rayleigh scattering spectra and their analytical applications. J. Fluoresc. 2011, 21, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Q.; Peng, S. Medicinal Chemistry; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, S.; Kelzieh, A. Determination of verapamil in pharmaceutical formulations using atomic emission spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 27, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenović, D.M.; Milošević, S.P.; Đurić, S.L.; Nasković, D.Č.; Mitić, S.S. Development and validation of an HPLC method for the determination of verapamil residues in supports of cleaning procedure. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 68, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinan Kaynak, M.; Akgeyik, E.; Ates, M.; Celebier, M.; Sahin, S. Development of HPLC Methods for Individual Determination of 20 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients for Ussing-Chamber Studies. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2017, 13, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegelhalder, B.; Eichelbaum, M. Determination of verapamil in human plasma by mass fragmentography using stable isotope-labelled verapamil as internal standard. Arzneimittel-Forschung 1976, 27, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Salh, D. Spectrophotometric Determination of Isoptin (Verapamil Hydrochloride) in Pharmaceutical Preparations. Ibn AL-Haitham J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2017, 23, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Farcaş, E.; Pochet, L.; Crommena, J.; Servaisa, A.; Fillet, M. Capillary electrophoresis in the context of drug discovery. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 144, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walash, M.; Belal, F.; El-Enany, N.; Abdelsalam, A. Spectrofluorometric determination of verapamil hydrochloride in pharmaceutical preparations and human plasma using organized media: Application to stability studies. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rambla-Alegre, M.; Gil-Agustí, M.T.; Capella-Peiró, M.E.; Carda-Broch, S.; Esteve-Romero, J.S. Direct determination of verapamil in urine and serum samples by micellar liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 839, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorskaya, O.; Krokhin, I.; Kataev, S. Experience in the Use of Solid-Phase Extraction in the Screening of Pharmaceuticals and Narcotics in the Blood by Gas. Chromatography with Mass Spectrometric Detection. Pharm. Chem. J. 2017, 51, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Molock, M.M.R.; Roy, I.; Basu, S.; Rana, D.; Gauri, S.S.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Chakraborty, M. In situ fluorescence of lac dye stabilized gold nanoparticles; DNA binding assay and toxicity study. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 7121–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, P.R.; Frigebrio, C.; Silvestre, C.I.C.; Santosb, J.L.M.; Lima, J.L.F.C.; Zagatto, E.A.G. Cadmium telluride nanocrystals as luminescent sensitizers in flow analysis. Talanta 2011, 84, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ma, P.; Wang, A.; Yu, C.; Qian, T.; Wu, S.; Shen, J. Dopamine fluorescent sensors based on polypyrrole/graphene quantum dots core/shell hybrids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.-G.; Ai, X.-P.; He, Z.-K.; Pang, D.-W. Functionalized CdSe quantum dots as selective silver ion chemodosimeter. Analyst 2004, 129, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koneswaran, M.; Narayanaswamy, R. L-Cysteine-capped ZnS quantum dots based fluorescence sensor for Cu 2+ ion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 139, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Yu, H.; Wei, F.; Xu, G.; Yang, J.; Cai, Z.; Hu, Q. Citrate-capped Mn-modified CdSe/CdS quantum dots as luminescent probes for levodopa detection in aqueous solution. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 91, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R. (Ed.) Quenching of Fluorescence. In Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 277–330. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhou, P.; Hu, Q. Synthesis of highly luminescent CdTe/CdS/ZnS quantum dots by a one-pot capping method. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Concentration of Verapamil HCl (µg/mL) | Interday | Intraday | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Recovery (%) ± SEM | RSD (%) | Mean Recovery (%) ± SEM | RSD (%) | |
| 0.75 | 99 ± 1.3 | 5.8 | 104 ± 1.4 | 5.4 |
| 2.5 | 97 ± 1.8 | 4.4 | 101 ± 0.7 | 3.2 |
| 4 | 94 ± 1.5 | 3 | 96 ± 2.1 | 4 |
| Metal Ion | Metal Ion: Verapamil HCl | Change in Quenching (%) | Excipient | Excipient: Verapamil HCl | Change in Quenching (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | 20 | 3.8 | Hydroxypropyl cellulose | 20 | −2.5 |
| Na+ | 20 | −0.2 | Corn starch | 10 | −2.5 |
| Ca2+ | 20 | −2.4 | A-Cellulose | 10 | −4.1 |
| Mg2+ | 20 | −5.0 | PEG | 10 | 0.4 |
| Al3+ | 1 | −0.1 | HPMC | 10 | 1.1 |
| Ag2+ | 0.25 | 1.7 | CMC | 20 | 0.6 |
| Fe2+ | 2 | −3.5 | Titanium dioxide | 5 | −0.4 |
| Fe3+ | 5 | −4.2 | Talc | 5 | 1.5 |
| Cu2+ | 0.17 | −4.2 | Mg-Stearate | 5 | −4.9 |
| Mn2+ | 5 | 4.4 | |||
| Cd2+ | 0.25 | 2.7 | |||
| Zn2+ | 2 | −4.6 |
| Test Number | Percentage of Drug in Standard Powder | Percentage of Drug in Tablet | Percentage of Drug in Injection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 99.5 | 95.5 | 103.1 |
| 2 | 98.6 | 97.2 | 102.3 |
| 3 | 98.7 | 93.4 | 102.3 |
| Mean ± SEM | 98.9 ± 0.3 | 95.4 ± 1.1 | 102.5 ± 0.3 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muhammad, S.; Xu, G.; Wei, F.; Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Song, Y.; Shi, M.; Xu, X.; Cen, Y.; Hu, Q. Determination of Verapamil HCl in Pharmaceutical Preparations by a Fluorescent Nano Probe Based on CdTe/CdS/ZnS Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110358
Muhammad S, Xu G, Wei F, Ma Y, Ma Y, Song Y, Shi M, Xu X, Cen Y, Hu Q. Determination of Verapamil HCl in Pharmaceutical Preparations by a Fluorescent Nano Probe Based on CdTe/CdS/ZnS Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(11):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110358
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuhammad, Sohail, Guanhong Xu, Fangdi Wei, Yujie Ma, Yunsu Ma, Yueyue Song, Menglan Shi, Xiaoman Xu, Yao Cen, and Qin Hu. 2017. "Determination of Verapamil HCl in Pharmaceutical Preparations by a Fluorescent Nano Probe Based on CdTe/CdS/ZnS Quantum Dots" Nanomaterials 7, no. 11: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110358
APA StyleMuhammad, S., Xu, G., Wei, F., Ma, Y., Ma, Y., Song, Y., Shi, M., Xu, X., Cen, Y., & Hu, Q. (2017). Determination of Verapamil HCl in Pharmaceutical Preparations by a Fluorescent Nano Probe Based on CdTe/CdS/ZnS Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials, 7(11), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110358