Effects of Thickness and Amount of Carbon Nanofiber Coated Carbon Fiber on Improving the Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphology of CNF

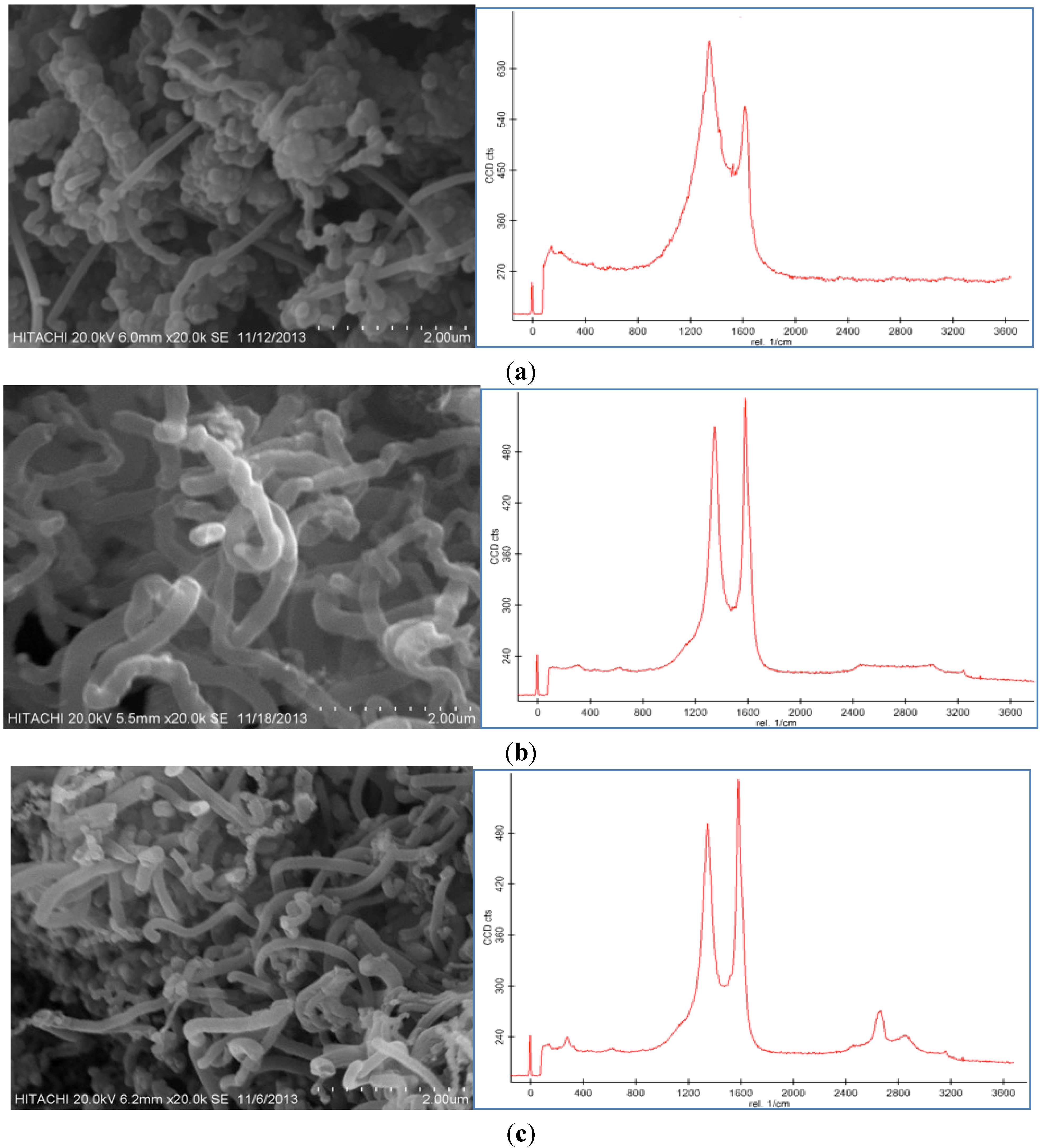
2.2. Effect of Catalyst Concentration

| Catalyst Conc. (mM) | Surface Area (m2/g) | Thickness of Carbon Nanofiber (CNF) (nm) | Yield (%) | Catalyst Activity (g/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1.36 | 1500 | 7 | 0.65 |
| 100 | 2.31 | 4000 | 24 | 1.6 |
| 150 | 2.52 | 4500 | 30 | 1.81 |
2.3. Effect of Reaction Temperature
| Temperature (°C) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Thickness of CNF (nm) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 450 | 1.88 | 3500 | 13.4 |
| 550 | 2.31 | 4000 | 24 |
| 650 | 3.16 | 4700 | 32.8 |
2.4. Effect of Reaction Time
| Time (min) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Thickness of CNF (nm) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1.42 | 2100 | 11.6 |
| 30 | 2.31 | 4000 | 24 |
| 50 | 2.61 | 4100 | 26.2 |
2.5. Effect of Hydrocarbon Flow Rate
| Flow Rate (sccm) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Thickness of CNF (nm) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 1.37 | 1800 | 18.6 |
| 50 | 2.31 | 4000 | 24 |
| 100 | 2.12 | 3800 | 28.8 |

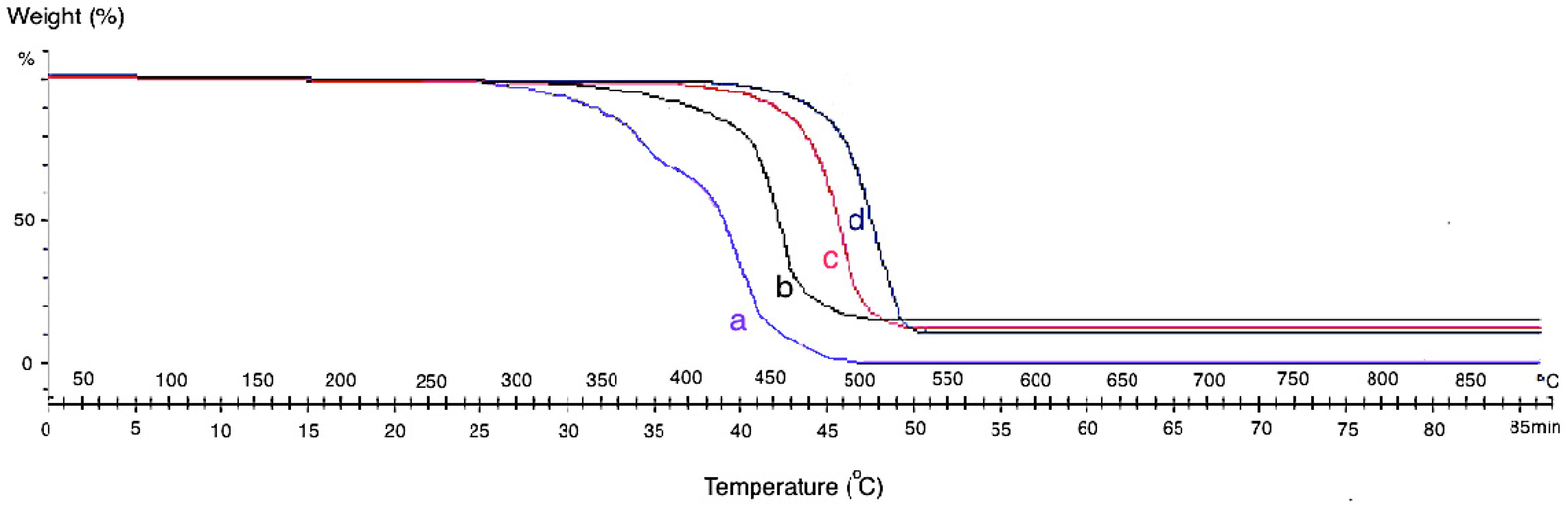
2.6. Mechanical Properties
| Sample No. | Thickness (nm) | Surface Area (m2/g) | Tensile Stress (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF-CNFL/PP | 1500–2100 | 1.36–1.42 | 21.9–22.2 | 0.65–0.68 |
| CF-CNFM/PP | 3500–4000 | 1.88–2.31 | 22.7–23.1 | 0.70–0.73 |
| CF-CNFH/PP | 4100–4700 | 2.61–3.16 | 23.9– 24.8 | 0.75–0.79 |

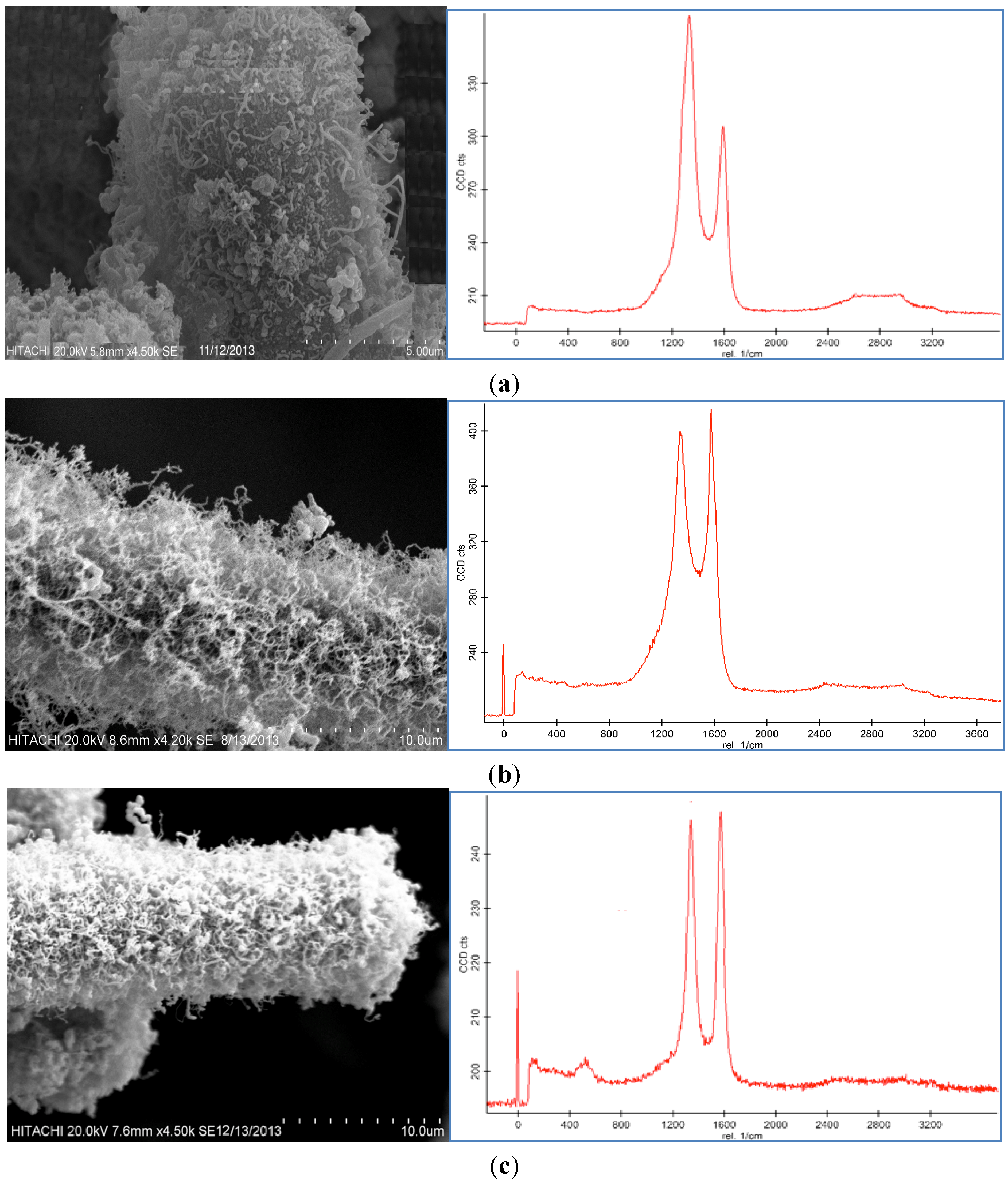
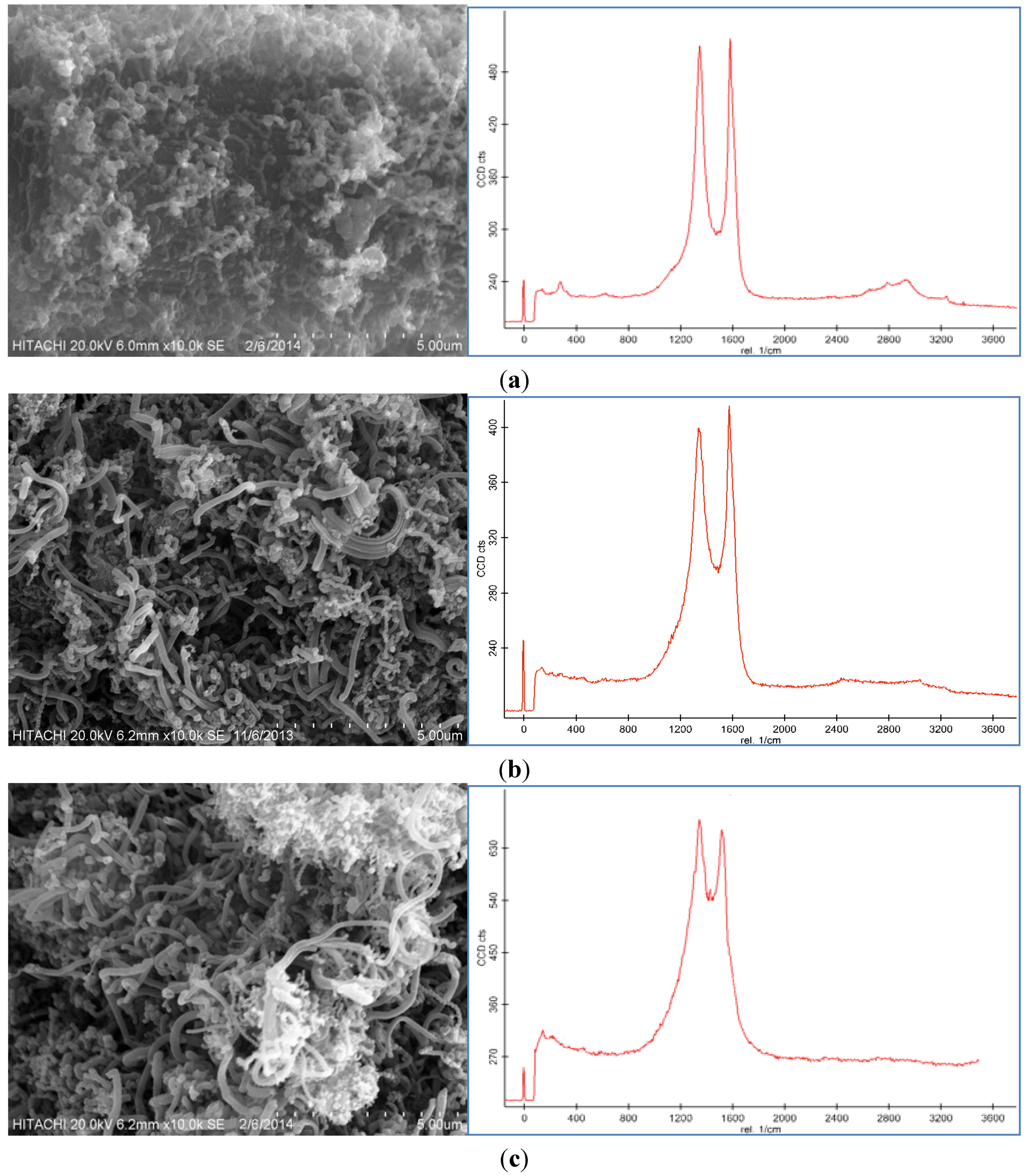
2.7. Morphology of Composites
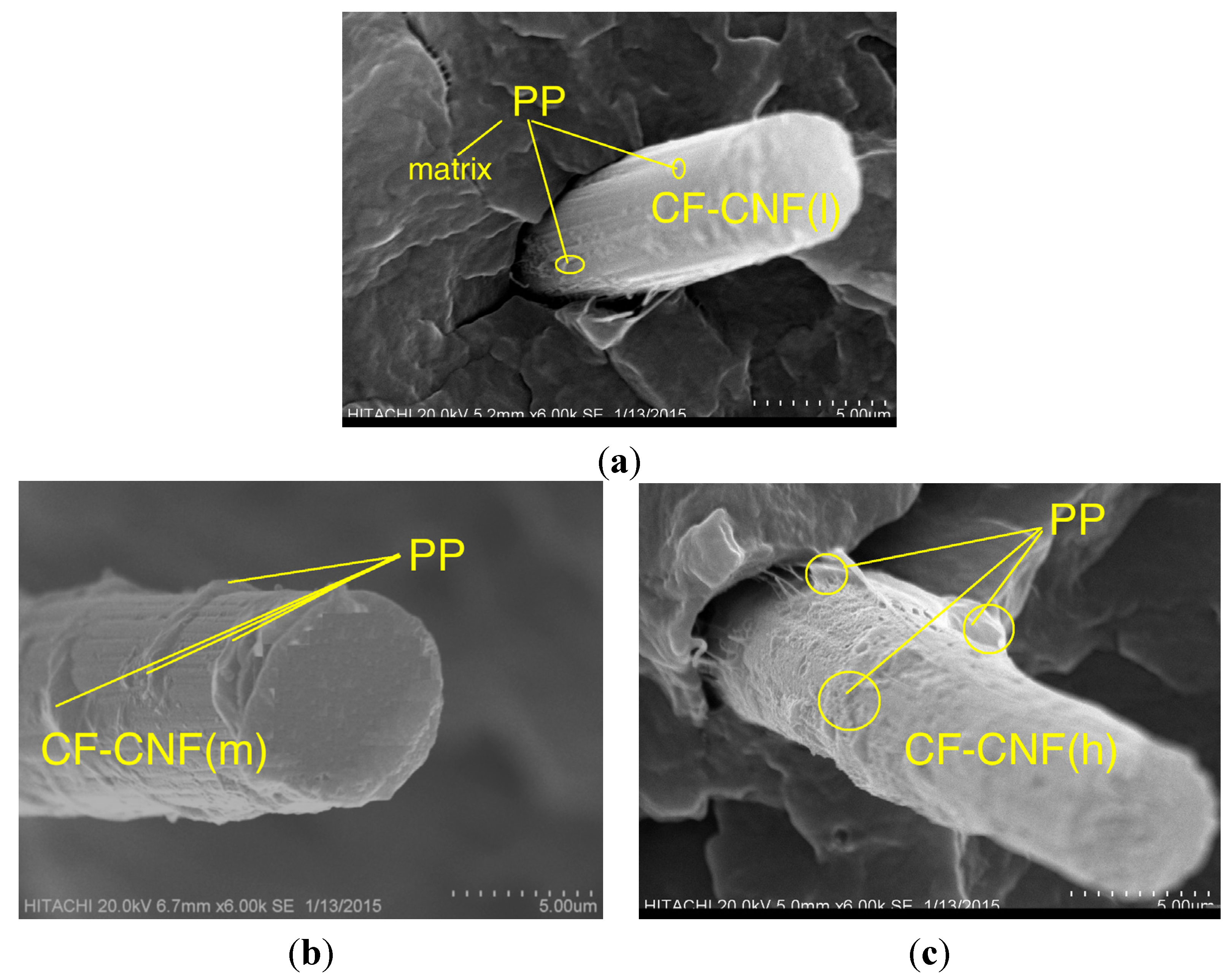
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of CNFs on CF
| Step | Fixed Parameters | Variable Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| Catalyst Concentration: |
| 50 mM | ||
| 100 mM | ||
| 150 mM | ||
| 2 |
| Temperature: |
| 450 °C | ||
| 550 °C | ||
| 650 °C | ||
| 3 |
| Time: |
| 10 min | ||
| 30 min | ||
| 50 min | ||
| 4 |
| Flow rate of C2H2: |
| 25 sccm | ||
| 50 sccm | ||
| 100 sccm |
3.3. Carbon Deposition Efficiency (Yield)
3.4. Catalyst Activity Calculations
3.5. Composites Preparation
3.6. Composite Characterization
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Sager, R.; Dai, L.; Baur, J. Hierarchical composites of carbon nanotubes on carbon fiber: Influence of growth condition on fiber tensile properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfuz, H.; Adnan, A.; Rangari, V.K.; Jeelani, S.; Jang, B.Z. Carbon nanoparticles/whiskers reinforced composites and their tensile response. Compos. A 2004, 35, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, F.; Yunus, R.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Rashid, S.A.; Ahmadian, A.; Lim, H.N. Effects of the surface modification of carbon fiber by growing different types of carbon nanomaterials on the mechanical and thermal properties of polypropylene. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 28822–28831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafraz-Yazdi, A.; Ghaemi, F.; Amiri, A. Comparative study of the sol–gel based solid phase microextraction fibers in extraction of naphthalene, fluorene, anthracene and phenanthrene from saffron samples extractants. Microchim. Acta 2012, 176, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, F.; Yunus, R.; Ahmadian, A.; Ismail, F.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Rashid, S.A. Few-and multi-layer graphene on carbon fibers: Synthesis and application. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 81266–81274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafraz-Yazdi, A.; Mosadegh, M.; Amiri, A. Determination of volatile organic compounds in environmental water samples using three solid-phase microextraction fibers based on sol–gel technique with gas chromatography–flame ionization detector. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafraz-Yazdi, A.; Rokhian, T.; Amiri, A.; Ghaemi, F. Carbon nanofibers decorated with magnetic nanoparticles as a new sorbent for the magnetic solid phase extraction of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 5621–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M.; Vittoria, V.; Vertuccio, L.; Lafdi, K.; De Vivo, B.; Tucci, V. The role of carbon nanofiber defects on the electrical and mechanical properties of CNF-based resins. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 305704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaemi, F.; Amiri, A.; Yunus, R. Methods for coating solid-phase microextraction fibers with carbon nanotubes. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 59, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafraz-Yazdi, A.; Abbasian, M.; Amiri, A. Determination of furan in food samples using two solid phase microextraction fibers based on sol–gel technique with gas chromatography–flame ionisation detector. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, R.L.; Gupta, N. Electrical properties of carbon nanofiber reinforced multiscale polymer composites. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saleh, M.H.; Gelves, G.A.; Sundararaj, U. Carbon nanofiber/polyethylene nanocomposite: Processing behavior, microstructure and electrical properties. Mater. Des. 2013, 52, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishkaee, M.S.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Yunus, R.; Biak, D.R.A.; Danafar, F.; Mirjalili, F. Effect of short carbon fiber surface treatment on composite properties. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaemi, F.; Ahmadian, A.; Yunus, R.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Senu, N. Effect of growing graphene flakes on branched carbon nanofibers based on carbon fiber on mechanical and thermal properties of polypropylene. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 9925–9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Bijwe, J.; Panier, S. Enhancing the adhesive wear performance of polyetherimide composites through nano-particle treatment of the carbon fabric. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 2891–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Bijwe, J.; Panier, S. Role of nano-YbF3-treated carbon fabric on improving abrasive wear performance of polyetherimide composites. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 42, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Saha, M.C.; Altan, M.C. Effect of carbon nanofibers on thermal conductivity of carbon fiber reinforced composites. Procedia Eng. 2013, 56, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, N.; Oshima, A.; Sakurai, S.; Yamada, T.; Yumura, M.; Hata, K.; Futaba, D.N. The Application of Gas Dwell Time Control for Rapid Single Wall Carbon Nanotube Forest Synthesis to Acetylene Feedstock. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Yang, H.S.; Yu, W.R. Fabrication of double-tubular carbon nanofibers using quadruple coaxial electrospinning. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 465602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.H.; Zhao, S.C. Effect of Carbon-Coating Morphologies on the Electrochemical Performance of Natural Graphite Spheres. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 875, 1590–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, Z.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tian, S.; Xing, M. Identification of a nuclear localization motif in the serine/arginine protein kinase PSRPK of physarum polycephalum. BMC Biochem. 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thostenson, E.T.; Li, W.Z.; Wang, D.Z.; Ren, Z.F.; Chou, T.W. Carbon nanotube/carbon fiber hybrid multiscale composites. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 6034–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Fan, Z.; Wu, C.; Chen, J. Catalytic graphitization of furan resin carbon by yttrium. Carbon 2008, 46, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Su, C.H.; Lehoczky, S.L.; Muntele, I.; Ila, D. Carbon nanotube growth on carbon fibers. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 1825–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.G.; Ci, L.J.; Cheng, H.M.; Bai, J.B. The growth of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with different morphologies on carbon fibers. Carbon 2005, 43, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, F.; Yunus, R.; Mohd Salleh, M.A.; Lim, H.N.; Rashid, S.A. Bulk production of high-purity carbon nanosphere by combination of chemical vapor deposition methods. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanost. 2015, 23, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpin, J.C.; Kardos, J.L. The Halpin-Tsai equations: A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1976, 16, 344–352. [Google Scholar]
- Cesano, F.; Scarano, D.; Bertarione, S.; Bonino, F.; Damin, A.; Bordiga, S.; Zecchina, A. Synthesis of ZnO–carbon composites and imprinted carbon by the pyrolysis of ZnCl2-catalyzed furfuryl alcohol polymers. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2008, 196, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, A.R.; Saurakhiya, N.; Deva, D.; Sharma, A.; Verma, N. Development of bimetal-grown multi-scale carbon micro-nanofibers as an immobilizing matrix for enzymes in biosensor applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 33, 4313–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmanian, S.; Thean, K.S.; Suraya, A.R.; Shazed, M.A.; Salleh, M.M.; Yusoff, H.M. Carbon and glass hierarchical fibers: Influence of carbon nanotubes on tensile, flexural and impact properties of short fiber reinforced composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 43, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.; Sarkar, B.K. Characterization of alkali-treated jute fibers for physical and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, I.; Abdin, Y.F. Modeling of strength and stiffness of short randomly oriented glass fiber—Polypropylene composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 1805–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, R.J.; Klein, P.J.; Lagoudas, D.C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Dai, L.; Baur, J.W. Effect of carbon nanotubes on the interfacial shear strength of T650 carbon fiber in an epoxy matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shazed, M.A.; Suraya, A.R.; Rahmanian, S.; Salleh, M.M. Effect of fibre coating and geometry on the tensile properties of hybrid carbon nanotube coated carbon fibre reinforced composite. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Yunus, R.; Ibrahim, N.A. Effect of fiber length on thermomechanical properties of short carbon fiber reinforced polypropylene composites. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics; ASTM: Filadelfia, PA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.Y.; Lauke, B.; Mader, E.; Yue, C.Y.; Hu, X. Tensile properties of short-glass-fiber-and short-carbon-fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites. Compos. A 2000, 31, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghaemi, F.; Ahmadian, A.; Yunus, R.; Ismail, F.; Rahmanian, S. Effects of Thickness and Amount of Carbon Nanofiber Coated Carbon Fiber on Improving the Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6010006
Ghaemi F, Ahmadian A, Yunus R, Ismail F, Rahmanian S. Effects of Thickness and Amount of Carbon Nanofiber Coated Carbon Fiber on Improving the Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhaemi, Ferial, Ali Ahmadian, Robiah Yunus, Fudziah Ismail, and Saeed Rahmanian. 2016. "Effects of Thickness and Amount of Carbon Nanofiber Coated Carbon Fiber on Improving the Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposites" Nanomaterials 6, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6010006
APA StyleGhaemi, F., Ahmadian, A., Yunus, R., Ismail, F., & Rahmanian, S. (2016). Effects of Thickness and Amount of Carbon Nanofiber Coated Carbon Fiber on Improving the Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials, 6(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6010006






