Theory of Carbon Nanotube (CNT)-Based Electron Field Emitters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Emission Properties of an Individual Nanotube
2.1. Electron Field Emission and the Fowler-Nordheim Equation


 .
.
2.2. Electric Field Enhancement
2.2.1. The Field Enhancement Effect and the Aspect Ratio of CNTs





2.2.2. Field Enhancement at Short Interelectrode Spacings




2.2.3. Field Enhancement in the Case of Tilted Nanotubes

| d (nm) | 1.4 | 3 | 6 | 10 |
| β0 | 795 | 393 | 209 | 132 |
| k | 0.466 | 0.466 | 0.466 | 0.463 |
2.3. Thermal Effects
2.3.1. Heat Conduction Equation


2.3.2. Transport Coefficients






2.3.3. Thermal Instability of a CNT-Based Emitter

2.4. Electrical Field Induced Alignment of CNTs
2.4.1. Growth of an Elongated Structure under the Action of the Electrical Field











 , z' is the coordinate along the cylinder axis) results in the following expression:
, z' is the coordinate along the cylinder axis) results in the following expression:


 is the distance from the spherical particle to the cylinder tip. Equation (32) is valid in the region z > l. This equation yields the formula connecting the electric field strength and the force exerted by the conducting cylindrical tube on the spherical particle in the field:
is the distance from the spherical particle to the cylinder tip. Equation (32) is valid in the region z > l. This equation yields the formula connecting the electric field strength and the force exerted by the conducting cylindrical tube on the spherical particle in the field:







2.4.2. Alignment of CNTs under the Action of the Electrical Field









 = 5 nm,
= 5 nm,  = 20 nm, and L = 5 μm of multilayer CNTs, we can estimate the value of the electric field strength required to ensure the vertical alignment of CNTs:
= 20 nm, and L = 5 μm of multilayer CNTs, we can estimate the value of the electric field strength required to ensure the vertical alignment of CNTs:  V/μm and
V/μm and  V/μm. For a single-layer CNT of the same length (Y = 1000 GPa and DSWNT = 1 nm), estimate Equation (47) yields ESWNT ≈ 0.3 V/μm. Thus, the above estimates show the possibility of the CNT vertical alignment as a result of application of the external electric field. In this case, the extent to which the CNT alignment is affected by the electric field is determined by the aspect ratio of the nanotube, as well as by its mechanical characteristics, which are determined by the value of the Young modulus.
V/μm. For a single-layer CNT of the same length (Y = 1000 GPa and DSWNT = 1 nm), estimate Equation (47) yields ESWNT ≈ 0.3 V/μm. Thus, the above estimates show the possibility of the CNT vertical alignment as a result of application of the external electric field. In this case, the extent to which the CNT alignment is affected by the electric field is determined by the aspect ratio of the nanotube, as well as by its mechanical characteristics, which are determined by the value of the Young modulus.| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (nm) | 49.3 | 45.8 | 46.8 | 27.9 | 38.7 | 19.5 | 22.2 | 27.1 | 10.4 | 15.5 | 42.7 |
| θ (°) | 66.3 | 59.1 | 60.2 | 53.6 | 71.1 | 61.4 | 57.1 | 66.3 | 57.4 | 63.6 | 57.4 |
| Y (GPa) | 36.9 | 45.2 | 18.9 | 34.7 | 19.8 | 44.2 | 47.4 | 30.5 | 49.7 | 43.0 | 25.6 |
| L (μm) (0.1–0.3) | 0.183 | 0.286 | 0.252 | 0.214 | 0.214 | 0.109 | 0.237 | 0.216 | 0.153 | 0.206 | 0.210 |
| L (μm) (0.5–0.8) | 0.754 | 0.695 | 0.730 | 0.573 | 0.524 | 0.602 | 0.674 | 0.633 | 0.732 | 0.524 | 0.702 |
| L (μm) (1–5) | 1.88 | 2.76 | 2.80 | 2.57 | 2.072 | 3.66 | 1.62 | 1.98 | 1.87 | 3.70 | 1.79 |

2.5. Degradation of a CNT-Based Emitter
2.5.1. The Trajectory of Ions
 . Here v ~ (2T/M)1/2 ~ 5 × 104 cm/s is the characteristic thermal velocity of the residual gas molecules; τi ~ (ML/2eE)1/2 is the characteristic time for which an ion formed within the inter-electrode space and moving towards the cathode surface under the action of the electrical field reaches this surface; L is the inter-electrode distance; М is the mass of a residual gas molecule. Inserting М ≈ 5 × 10−23 g (for air molecules); L = 10−2 cm; Е = 104 V/cm, one obtain the estimation τi ~ 0.4 × 10−8 s. Therefore the characteristic displacement of an ion in respect to the position of the CNT, from which the relevant electron was emitted even for very short inter-electrode gaps L = 10−2 cm accounts
. Here v ~ (2T/M)1/2 ~ 5 × 104 cm/s is the characteristic thermal velocity of the residual gas molecules; τi ~ (ML/2eE)1/2 is the characteristic time for which an ion formed within the inter-electrode space and moving towards the cathode surface under the action of the electrical field reaches this surface; L is the inter-electrode distance; М is the mass of a residual gas molecule. Inserting М ≈ 5 × 10−23 g (for air molecules); L = 10−2 cm; Е = 104 V/cm, one obtain the estimation τi ~ 0.4 × 10−8 s. Therefore the characteristic displacement of an ion in respect to the position of the CNT, from which the relevant electron was emitted even for very short inter-electrode gaps L = 10−2 cm accounts  ~ 10−4 cm, which exceeds the characteristic radius of a nanotube R ~ 10−6–10−5 cm as much as an order of magnitude. This estimation demonstrates that a main fraction of ions reaching the cathode surface does not fall onto the nanotube and therefore does not promote its degradation. This determines the necessity of the establishing the task on the degradation of a CNT as a result of the ion sputtering with taking into account the initial thermal motion of the residual gas molecules.
~ 10−4 cm, which exceeds the characteristic radius of a nanotube R ~ 10−6–10−5 cm as much as an order of magnitude. This estimation demonstrates that a main fraction of ions reaching the cathode surface does not fall onto the nanotube and therefore does not promote its degradation. This determines the necessity of the establishing the task on the degradation of a CNT as a result of the ion sputtering with taking into account the initial thermal motion of the residual gas molecules.
 ~ 10−10 s shows that the latter is more than an order of magnitude lesser than the above-estimated value of τi. This means that taking into account the initial longitudinal motion of molecules results in a minor (within several percent) changing the time of reaching the cathode surface and therefore the displacement of the ion Δρ. Neglecting this longitudinal component the distribution of the ion over the cathode surface is represented as follows:
~ 10−10 s shows that the latter is more than an order of magnitude lesser than the above-estimated value of τi. This means that taking into account the initial longitudinal motion of molecules results in a minor (within several percent) changing the time of reaching the cathode surface and therefore the displacement of the ion Δρ. Neglecting this longitudinal component the distribution of the ion over the cathode surface is represented as follows:

 is the equilibrium (maxwellian) distribution function of the residual gas molecules over the radial velocities, А = M/kT is the normalization constant, e, m is the electron charge and mass, correspondingly, М is the mass of the residual gas molecule, Т is the temperature. The Equation (48) is simplified by the use of a natural equation Ie = jeS (Ie is the emission current) which is valid for homogeneous distribution of the electron number density over the cross section of the beam. Violation of this assumption does not change the qualitative results of the present research. Note that the Equation (48) presents the number of ions bombarding per second the surface (ρ, ρ + dρ), so that the dimensionality of J is cm−1s−1.
is the equilibrium (maxwellian) distribution function of the residual gas molecules over the radial velocities, А = M/kT is the normalization constant, e, m is the electron charge and mass, correspondingly, М is the mass of the residual gas molecule, Т is the temperature. The Equation (48) is simplified by the use of a natural equation Ie = jeS (Ie is the emission current) which is valid for homogeneous distribution of the electron number density over the cross section of the beam. Violation of this assumption does not change the qualitative results of the present research. Note that the Equation (48) presents the number of ions bombarding per second the surface (ρ, ρ + dρ), so that the dimensionality of J is cm−1s−1.


2.5.2. The Degradation Rate and the Effective Lifetime of an Emitter





2.6. CNT-Based Emitters of Alternative Structure
3. Emission Properties of a CNT Array
3.1. Screening Effects

3.2. Statistical Spread of CNT Parameters







| The type of CNTs | Diameter (nm) | Emitters density (cm−2) | Inter-electrode gap (mm) | Δ β/β | Voltage range (kV) | Current range (μA) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SW * | 5 | 105 | 5–20 | 0.24 | 5–15 | 10−4–102 | [88] |
| SW | 1–2 | 105 | 0.006 | 0.16 | 0.01–0.02 | 10−4–102 | [89] |
| Unknown | 105 | 0.002 | 0.105 | 0.02–0.07 | 0.1–5 | [90] | |
| SW | 1.2 | 0.25 | 0.103 | 0.2–0.4 | 10−6–1 | [91] | |
| MW | 25 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.4–0.7 | 10−6–0.1 | [91] | |
| MW | 20 | 1 | 0.18 | 0.02–0.04 | 0.1–5 | [92] | |
| SW | 1–1.5 | 0.5 | 0.304 | 0.1–9 | 10−2–102 | [31] |





3.3. Field-Induced Alignment and Current-Voltage Characteristics

| No. | D (nm) | θ (°) | Y (GPa) | L (μm) (0.1–0.3) | L (μm) (0.5–0.8) | L (μm) (1–5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 49.3 | 66.3 | 36.9 | 0.183 | 0.754 | 1.88 |
| 2 | 45.8 | 59.1 | 45.2 | 0.286 | 0.695 | 2.76 |
| 3 | 46.8 | 60.2 | 18.9 | 0.252 | 0.730 | 2.80 |
| 4 | 27.9 | 53.6 | 34.7 | 0.214 | 0.573 | 2.57 |
| 5 | 38.7 | 71.1 | 19.8 | 0.214 | 0.524 | 2.07 |
| 6 | 19.5 | 61.4 | 44.2 | 0.109 | 0.602 | 3.66 |
| 7 | 22.2 | 57.1 | 47.4 | 0.237 | 0.674 | 1.62 |
| 8 | 27.1 | 66.3 | 30.5 | 0.216 | 0.633 | 1.98 |
| 9 | 10.4 | 57.4 | 49.7 | 0.153 | 0.732 | 1.87 |
| 10 | 15.5 | 63.6 | 43.0 | 0.206 | 0.524 | 3.70 |
| 11 | 42.7 | 57.4 | 25.6 | 0.21 | 0.702 | 1.79 |
3.4. Self Electric Field of Nanotubes



3.5. Optimization of Parameters of a CNT–Based Field Emission Cathode
- (1)
- Emission current I is specified for a nanotube of certain geometry.
- (2)
- A heat conduction Equation (10) is solved for a nanotube of length h at specified emission current I, following the approach described in Section 2.3.
- (3)
- The relationship between critical emission current Ic and local electric field strength E at a CNT tip is described by the Fowler-Nordheim Equation (1) containing the tip temperature as a parameter.
- (4)
- At a fixed average electric field strength Eo and local electric field E determined by Equation (66), we find the electric field enhancement factor β with taking into consideration the screening effect,where d is the nanotube’s diameter.E = в(S, h, d)Eo
- (5)
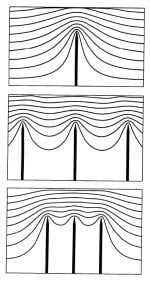
- We take into account the dependence of the electrical field enhancement factor on the nanotube geometry and inter-tube spacing S found earlier from the solution to a Laplace equation (Figure 15a) and determine optimum distance So corresponding to the given nanotube geometry (d, h). Obviously, the maximum emission current density is:



| h (μm) | a1 (V−1) | a2 (μm−1) | a3 (Aּμm2/cm2ּV2) | a4 (Aּμm/Vּcm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.012 | 0.085 | 0.146 | 1.608 |
| 20 | 0.013 | 0.040 | 0.090 | 0.463 |
| 40 | 0.015 | 0.019 | 0.057 | 0.135 |

 ) α = 1, lp = 480 nm; (■) α = 1.5, lf = 480 nm.
) α = 1, lp = 480 nm; (■) α = 1.5, lf = 480 nm.
 ) α = 1, lp = 480 nm; (■) α = 1.5, lf = 480 nm.
) α = 1, lp = 480 nm; (■) α = 1.5, lf = 480 nm.
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest
References
- Chernozatonskii, L.A.; Gulyaev, Y.V.; Kosakovskaja, Z.J.; Sinitsyn, N.I.; Torgashov, G.V.; Zakharchenko, Yu, F.; Fedorov, E.A.; Val’chuk, V.P. Electron field emission from nanofilament carbon films. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1995, 233, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Heer, W.A.; Chatelain, A.; Ugarte, D. A carbon nanotube field-emission electron source. Science 1995, 270, 1179–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Rinzler, A.G.; Hafner, J.H.; Nikolaev, P.; Nordlander, P.; Colbert, D.T.; Smalley, R.E.; Lou, L.; Kim, S.G. Unraveling nanotubes: Field emission from an atomic wire. Science 1995, 269, 1550–1553. [Google Scholar]
- Eletskii, A.V. Carbon nanotubes and their emission properties. Phys. Usp. 2002, 45, 369–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletskii, A.V. Carbon nanotube-based electron field emitters. Phys. Usp. 2010, 53, 863–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.I.; Lee, S.; Song, Y.H.; Choi, S.-Y.; Cho, K.-I.; Namet, K.-S. Patterned selective growth of carbon nanotubes and large field emission from vertically well-aligned carbon nanotube field emitter arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 901–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Yan, M.; Chang, R.P.H. Flat panel display prototype using gated carbon nanotube field emitters. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 1294–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauger, M.; Vu, T.V. Vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays for giant field emission displays. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2006, 24, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Mimura, H. Point X-ray source using graphite nanofibers and its application to X-ray radiography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 1637–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.Z.; Qiu, Q.; Gao, B.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shimoda, H.; Chang, S.; Lu, J.P.; Zhou, O. Generation of continuous and pulsed diagnostic imaging X-ray radiation using a carbon-nanotube-based field-emission cathode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, G.; Strumban, E.; Sozontov, E.; Jenrow, K. X-ray scalpel—A new device for targeted X-ray brachytherapy and stereotactic radiosurgery. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 1757–1770. [Google Scholar]
- Dickler, A. Xoft Axxent electronic brachytherapy—A new device for delivering brachytherapy to the breast. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Fuchs, H.; Steil, F.L.V.; Ziglio, F.; Kraus-Tiefenbacher, U.; Lohr, F.; Wenzet, F. A novel device for intravaginal electronic brachytherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 74, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivard, M.J.; Davis, S.D.; De Werd, L.A.; Rusch Thomas, W.; Axelrod, S. Calculated and measured brachytherapy dosimetry parameters in water for the Xoft Axxent X-Ray Source: An electronic brachytherapy source. Med. Phys. 2006, 33, 4020–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Ha, J.M.; Heo, S.H.; Choy, S.O. Small-sized flat-tip CNT emitters for miniaturized X-ray tubes. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Lee, Y.Z.; Lu, J.P.; Zhou, O. Multiplexing radiography using a carbon nanotube based X-ray source. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, K.; Hata, K.; Sato, H.; Saito, Y. Development of microfocused X-ray source by using carbon nanotube field emitter. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2006, 24, 950–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Uemura, S.; Hamaguchi, K. Cathode ray tube lighting elements with carbon nanotube field emitters. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 37, L346–L348. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, Y.; Uemura, S. Field emission from carbon nanotubes and its application to electron sources. Carbon 2000, 38, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obraztsov, A.N.; Kleshch, V.I. Cold and laser stimulated electron emission from nanocarbons. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2009, 4, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croci, M.; Arfaoui, I.; Stöckli, T.; Chatelain, A.; Bonard, J.-M. A fully sealed luminescent tube based on carbon nanotube field emission. Microelectron. J. 2004, 35, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, J.; Qiang, Y. Cathodoluminescence from a device of carbon nanotube-field emission display with ZnO nanocluster phosphor. Nanotechnology 2007, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonard, J.; Stöckli, T.; Noury, O.; Châtelain, A. Field emission from cylindrical carbon nanotube cathodes: Possibilities for luminescent tubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 2775–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, K.V.K.; Minoux, E.; Hudanski, L.; Peauger, F.; Schnell, J.-P.; Gangloff, L.; Legagneux, P.; Dieumegard, D.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; Milneet, W.I. Microwave devices: Carbon nanotubes as cold cathodes. Nature 2005, 437, 968–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, W.I.; Teo, K.B.K.; Minoux, E.; Groening, O.; Gangloff, L.; Hudanski, L.; Schnell, J.-P.; Dieumegard, D.; Peauger, F.; Bu, I.Y.Y.; et al. Aligned carbon nanotubes/fibers for applications in vacuum microwave amplifiers. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2006, 24, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, R.H.; Nordheim, L. Electron emission in intense electric fields. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1928, 119, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomer, R. Field Emission and Field Ionization, 2nd ed.; American Institute of Physics: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, L.; Groening, O.; Emmenegger, C.; Kuettel, O.; Schaller, E.; Schlapbach, L.; Kind, H.; Bonard, J.-M.; Kern, K. Scanning field emission from patterned carbon nanotube films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 2071–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharov, G.S.; Eletskii, A.V. Effect of screening on the emissivity of field electron emitters based on carbon nanotubes. Tech. Phys. 2005, 50, 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsky, M.; Bocharov, G.; Eletskii, A.; Sommerer, T. Field amplification in carbon nanotube’s based field emission cathodes. Tech. Phys. 2010, 55, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharov, G.S.; Eletskii, A.V.; Korshakov, A.V. Emission characteristics of carbon nanotube-based cathodes. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2003, 5, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, R.; Hu, J.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z. Carbon nanotubes as field emitter. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 7876–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, R.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M. Physical Properties of Carbon Nanotubes; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G.; Avouris, P. Carbon Nanotubes: Synthesis, Structure, Properties and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dobretsov, L.N.; Gomoyunova, M.V. Emission Electronics; Nauka Publishing House: Moscow, Russia, 1966; [in Russian]. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Peng, L.M.; Xue, Z.Q.; Wu, J.L. End potential barriers of single-walled carbon nanotubes and their role in field emission. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 155407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Ihm, J. First-principles study of field emission of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 2002, 241402(R). [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, L.; Wang, C.; Qu, C.; Zeng, Y.; Yu, S.S.; Hu, X.Y.; Zheng, W.T.; Jiang, Q. First-principles investigation on the field emission properties of B-doped carbon nanotubes. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2009, 18, 657–661. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Xu, N. Quantum-mechanical investigation of field-emission mechanism of a micrometer-long single-walled carbon nanotube. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 106803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoobi, P.; Walus, K.; Nojeh, A. First-principles study of quantum tunneling from nanostructures: Current in a single-walled carbon nanotube electron source. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 115422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulashevich, K.A.; Rotkin, V.V. Nanotube-based devices: Microscopic model. JETP Lett. 2002, 75, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, E.G.; Raikh, M. Electrostatics of straight and bent single-walled carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 155410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.B.; Wang, W.L. Analytic solution of charge density of single wall carbon nanotube under conditions of field electron emission. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2006, 23, 1616–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedrakyan, T.A.; Mishchenko, E.G.; Raikh, M.E. Penetration of external field into regular and random arrays of nanotubes: Implications for field emission. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 245325. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, O.; Qin, L.-C.; Tang, J. Fabrication and characterization of single carbon nanotube emitters as point electron sources. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.G.; Zettle, A. Unique characteristics of cold cathode carbon-nanotube-matrix field emitters. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 55, 9391–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, O. Electron field emission from carbon nanotubes. C. R. Phys. 2003, 4, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkorakis, G.; Modinos, A.; Xanthakis, J.P. Local electric field at the emitting surface of a carbon nanotube. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 4580–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletskii, A.V.; Bocharov, G.S. Emission properties of carbon nanotubes and cathodes on their basis. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2009, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Berríos, A.; Piazza, F.; Morell, G. Numerical study of the electrostatic field gradients present in various planar emitter field emission configurations relevant to experimental research. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2005, 23, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Bai, X.D.; Wang, E.G.; Wang, Z.L. Field emission of individual carbon nanotube with in situ tip image and real work function. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 163106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgcombe, C.J.; Valdrè, U. Microscopy and computational modelling to elucidate the enhancement factor for field electron emitters. J. Microsc. 2001, 203, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgcombe, C.J.; Valdrè, U. Experimental and computational study of field emission characteristics from amorphous carbon single nanotips grown by carbon contamination. I. Experiments and computation. Philos. Mag. B 2002, 82, 987–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Bai, X.D.; Wang, E.G. Geometrical enhancement of field emission of individual nanotubes studied by in situ transmission electron microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 133107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinson, T.; Malov, Y.I. Differential Equations of Mathematical Physics; N.E. Bauman MGTU: Moscow, Russia, 2002; [in Russian]. [Google Scholar]
- Vlasova, E.; Zarubin, V.; Kuvyrkin, G. Approximate Methods of Mathematical Physics; N.E. Bauman MGTU: Moscow, Russia, 2001; [in Russian]. [Google Scholar]
- Bocharov, G.S.; Eletskii, A.V. Thermal instability of field emission from carbon nanotubes. Tech. Phys. 2007, 52, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, P.; Purcell, S.T.; Journet, C.; Binh, V.T. Modelization of resistive heating of carbon nanotubes during field emission. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 075406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletskii, A.V. Transport properties of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Usp. 2009, 52, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Shi, L.; Majumdar, A.; McEuen, P.L. Thermal transport measurements of individual multiwalled nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 215502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Lu, L.; Zhang, D.-L.; Pan, Z.W.; Xie, S.S. Linear specific heat of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B. 1999, 59, R9015–R9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Komnik, A.; Egger, R.; Glattli, D.C.; Bachtold, A. Evidence for Luttinher-Liquid Behavior in Crossed Metallic Single-Wall Nanotubes. In Proceeding of the NT'05: 6th International Conference on the Science and Application of Nanotubes, Gothenburg, Sweden, 26 June–1 July 2005; p. 307.
- Sveningsson, M.; Hansen, K.; Svensson, K.; Olsson, E.; Campbell, E.E.B. Quantifying temperature-enhanced electron field emission from individual carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 085429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; She, J.C.; Chen, J.; Deng, S.Z.; Xu, N.S.; Bishop, H.; Huq, S.E.; Wang, L.; Zhong, D.Y.; Wang, E.G.; et al. Mechanism responsible for initiating carbon nanotube vacuum breakdown. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 075501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonard, J.M.; Maier, F.; Stöckli, T.; Châtelain, A.; de Heer, W.A.; Salvetat, J.-P.; Forró, L. Field emission properties of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Ultramicroscopy 1998, 73, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonard, J.M.; Klinke, C.; Dean, K.A.; Coll, B.F. Degradation and failure of carbon nanotube field emitters. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 115406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liang, S.D.; Deng, S.Z.; Xu, N.S. Comparison of field and thermionic emissions from carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. D 2006, 39, 5280–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharov, G.S.; Knizhnik, A.A.; Eletskii, A.V.; Sommerer, T.J. Influence of the electric field on the alignment of carbon nanotubes during their growth and emission. Tech. Phys. 2012, 57, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletskii, A.V. Growth of Elongated Structures in a Longitudinal Electrical Field. In Electronic Properties of Novel Materials—Molecular Nanostructures; Kuzmany, H., Fink, J., Mehring, M., Roth, S., Eds.; American Institute of Physics: Melville, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 544, p. 250. [Google Scholar]
- Merkulov, V.I.; Melechko, A.V.; Guillorn, M.A.; Simpson, M.L.; Lowndes, D.H.; Whealton, J.H.; Raridon, R.J. Controlled alignment of carbon nanofibers in a large-scale synthesis process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 4816–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkulov, V.I.; Melechko, A.V.; Guillorn, M.A.; Lowndes, D.H.; Simpson, M.L. Alignment mechanism of carbon nanofibers produced by plasma-enhanced chemical-vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 2970–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhowalla, M.; Teo, K.B.K.; Ducati, C.; Rupesinghe, N.L.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; Ferrari, A.C.; Roy, D.; Robertson, J.; Milne, W.I. Growth process conditions of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes using plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 5308–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao-Jie, M.A.; Guo, W.L. Mechanism of carbon nanotubes aligning along applied electric field. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2008, 25, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharov, G.S.; Eletskii, A.V. Degradation of a CNT-based field emission cathode due to ion sputtering. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2012, 20, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharov, G.S.; Eletskii, A.V. Degradation of a carbon nanotube-based field-emission cathode during ion sputtering. Tech. Phys. 2012, 57, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itikawa, Y.I. Cross sections for electron collisions with nitrogen molecules. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2006, 35, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itikawa, Y.I. Cross sections for electron collisions with oxygen molecules. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2009, 38, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, W. Atomic and Plasma-Material Interaction Data for Fusion; International Atomic Enegy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2001; pp. 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.M.; Song, K.Y.; Chu, C.N.; Kim, H. Better than 10 mA Field emission from an isolated structure emitter of a metal oxide/CNT composite. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmotti, V.V.; Tamburri, E.; Orlanducci, S.; Terranova, M.L.; Rossi, M.; Notarianni, M.; Fairchild, S.B.; Maruyama, B.; Behabtu, N.; Young, C.C.; et al. Macroscopic self-standing SWCNT fibres as efficient electron emitters with very high emission current for robust cold cathodes. Carbon 2013, 52, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navitski, A.; Serbun, P.; Müller, G.; Joshi, R.K.; Engstler, J.; Schneider, J.J. Role of height and contact interface of CNT microstructures on Si for high current field emission cathodes. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 59. Article Number 11302. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.S.; Chuang, F.C.; Cho, T.H.; Leung, T.C. The screening effect on field enhancement factor of the finite-length small radius single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 014301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.C.; Silva, S.R.P. Interpretation of the field enhancement factor for electron emission from carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 014314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharov, G.S.; Eletskii, A.V.; Sommerer, T.J. Optimization of the Parameters of a Carbon Nanotube-Based Field Emission Cathode. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on the Science and Application of Nanotubes, Montreal, Canada, 26 June–2 July 2010.
- Obraztsov, A.; Volkov, A.; Zakhidov, A.; Petrushenko, Y.V.; Satanovskaya, O.P. Fundamental aspects and applications of low field electron emission from nanocarbons. Surf. Eng. 2003, 19, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharov, G.S.; Eletskii, A.V.; Pal, A.F.; Pernbaum, A.G.; Pichugin, V.V. Emission Characteristics of CNT-Based Cathodes. In Electronic Properties of Synthetic Nanostructures; Kuzmany, H., Fink, J., Mehring, M., Roth, S., Eds.; American Institute of Physics: Melville, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 723, pp. 528–531. [Google Scholar]
- Bezmelnitsyn, V.N.; Domantovskii, A.G.; Eletskii, A.V.; Obraszova, E.D.; Pal, A.F.; Pernbaum, A.G.; Pichugin, V.V.; Prichod’ko, K.E.; Suetin, N.V.; Terekhov, S.V. Production of single walled nanotubes with Ni/Cr as catalyst. Phys. Solid State 2002, 44, 656–661. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Iwata, T.; Minesawa, R.; Matsumoto, K. Emission properties from carbon nanotube field emitter arrays (FEAs) grown on si emitters. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 40, L983–L985. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, K.; Kinosita, S.; Gotoh, Y.; Uchiyama, T.; Manalis, S.; Quate, C. Ultralow biased field emitter using single-wall carbon nanotube directly grown onto silicon tip by thermal chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.T.; Kim, H.J.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, N.; Jang, J.E.; Kim, J.W.; Jung, J.E.; Kim, J.M. Fabrication and characterization of gated field emitter arrays with self-aligned carbon nanotubes grown by chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 2070–2072. [Google Scholar]
- Wadhawan, A.; Stallcup, R.E.; Stephens, K.F.; Perez, J.M.; Akwani, I.A. Effects of O2, Ar, and H2 gases on the field-emission properties of single-walled and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 1867–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillorn, M.A.; Hale, M.D.; Merkulov, V.I.; Simpson, M.L.; Eres, G.Y.; Cui, H.; Puretzky, A.A.; Geohegan, D.B. Integrally gated carbon nanotube field emission cathodes produced by standard microfabrication techniques. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2003, 21, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xiao, C.; Chen, W.; Singh, A.K.; Asai, T.; Hirose, A. Growth mechanism and orientation control of well-aligned carbon nanotubes. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharov, G.S.; Eletskii, A.V.; Sommerer, T.J. Optimization of the parameters of a carbon nanotube-based field emission cathode. Tech. Phys. 2011, 56, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bocharov, G.S.; Eletskii, A.V. Theory of Carbon Nanotube (CNT)-Based Electron Field Emitters. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 393-442. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3030393
Bocharov GS, Eletskii AV. Theory of Carbon Nanotube (CNT)-Based Electron Field Emitters. Nanomaterials. 2013; 3(3):393-442. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3030393
Chicago/Turabian StyleBocharov, Grigory S., and Alexander V. Eletskii. 2013. "Theory of Carbon Nanotube (CNT)-Based Electron Field Emitters" Nanomaterials 3, no. 3: 393-442. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3030393
APA StyleBocharov, G. S., & Eletskii, A. V. (2013). Theory of Carbon Nanotube (CNT)-Based Electron Field Emitters. Nanomaterials, 3(3), 393-442. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3030393