Hydrothermal Synthesis and Characterization of Ni-Al Montmorillonite-Like Phyllosilicates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. X-Ray Diffraction
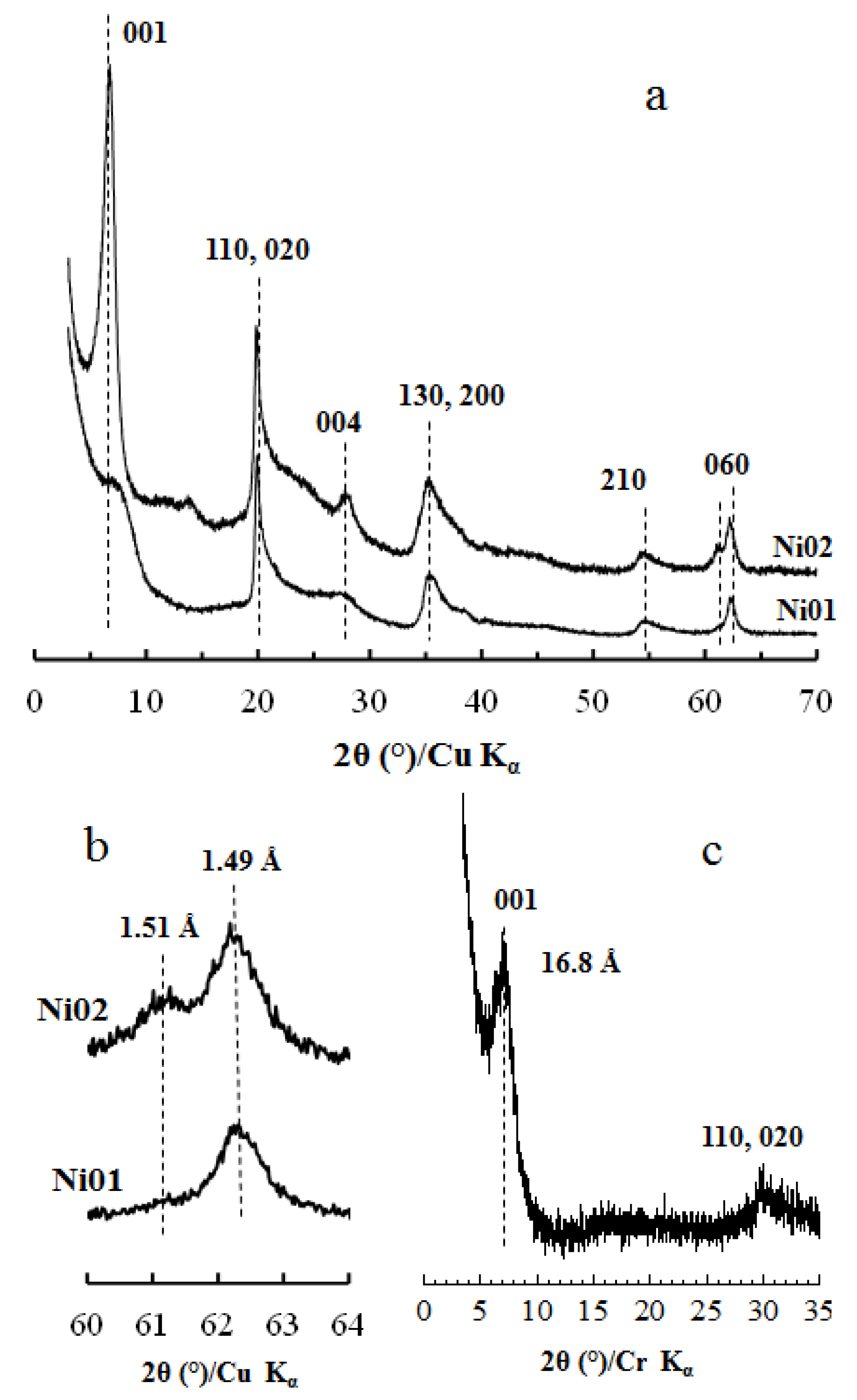
2.2. Chemical Analysis
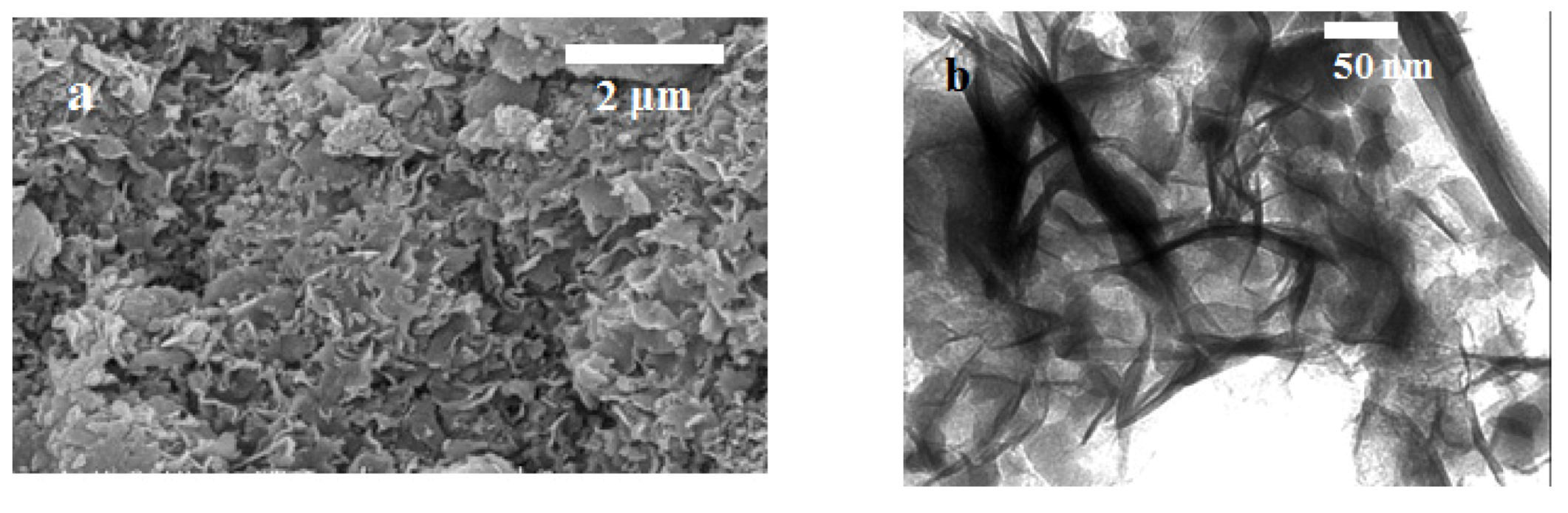
2.3. Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.4. Thermal Analyses

2.5. N2 Adsorption
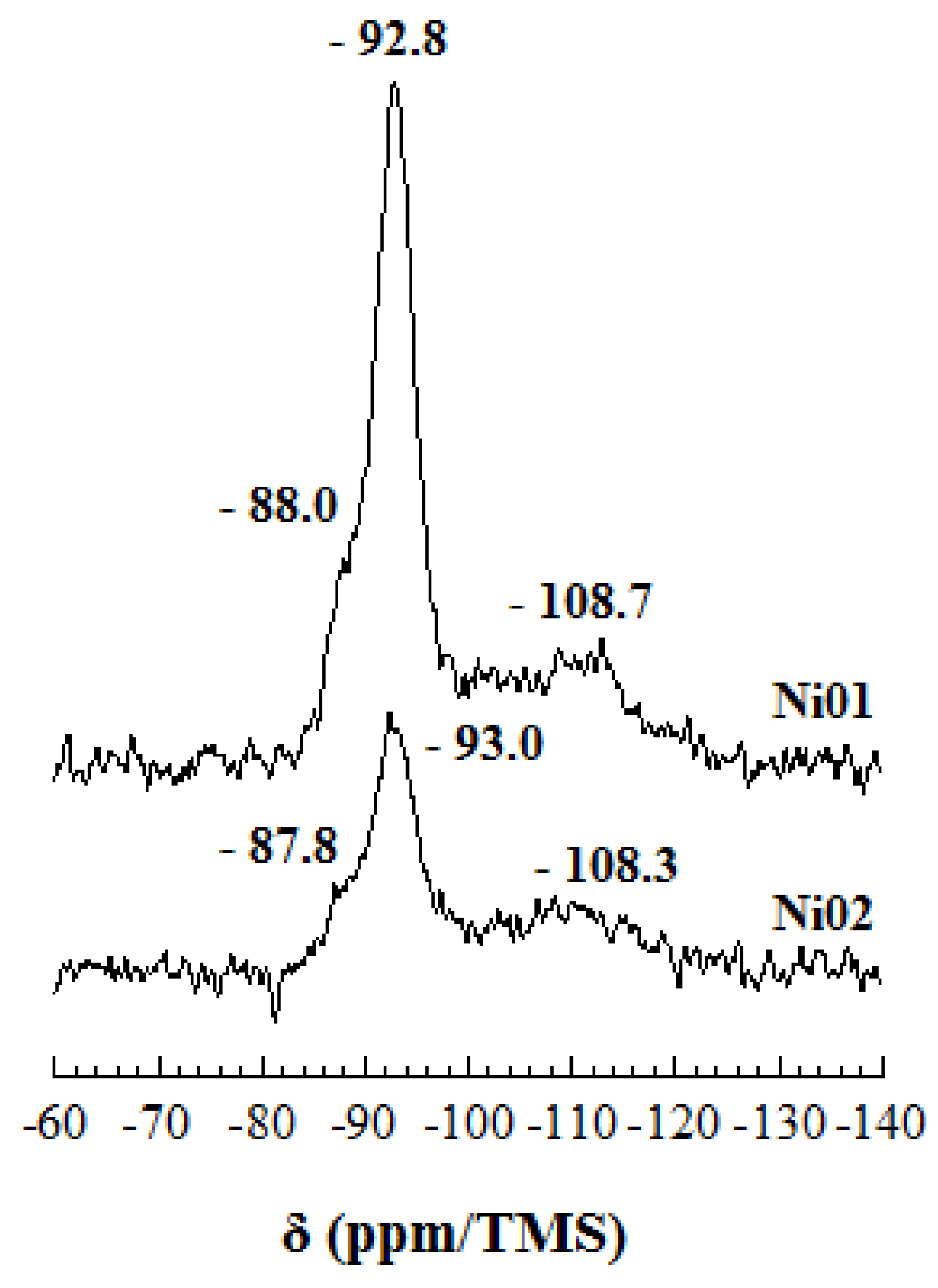
2.6. Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance

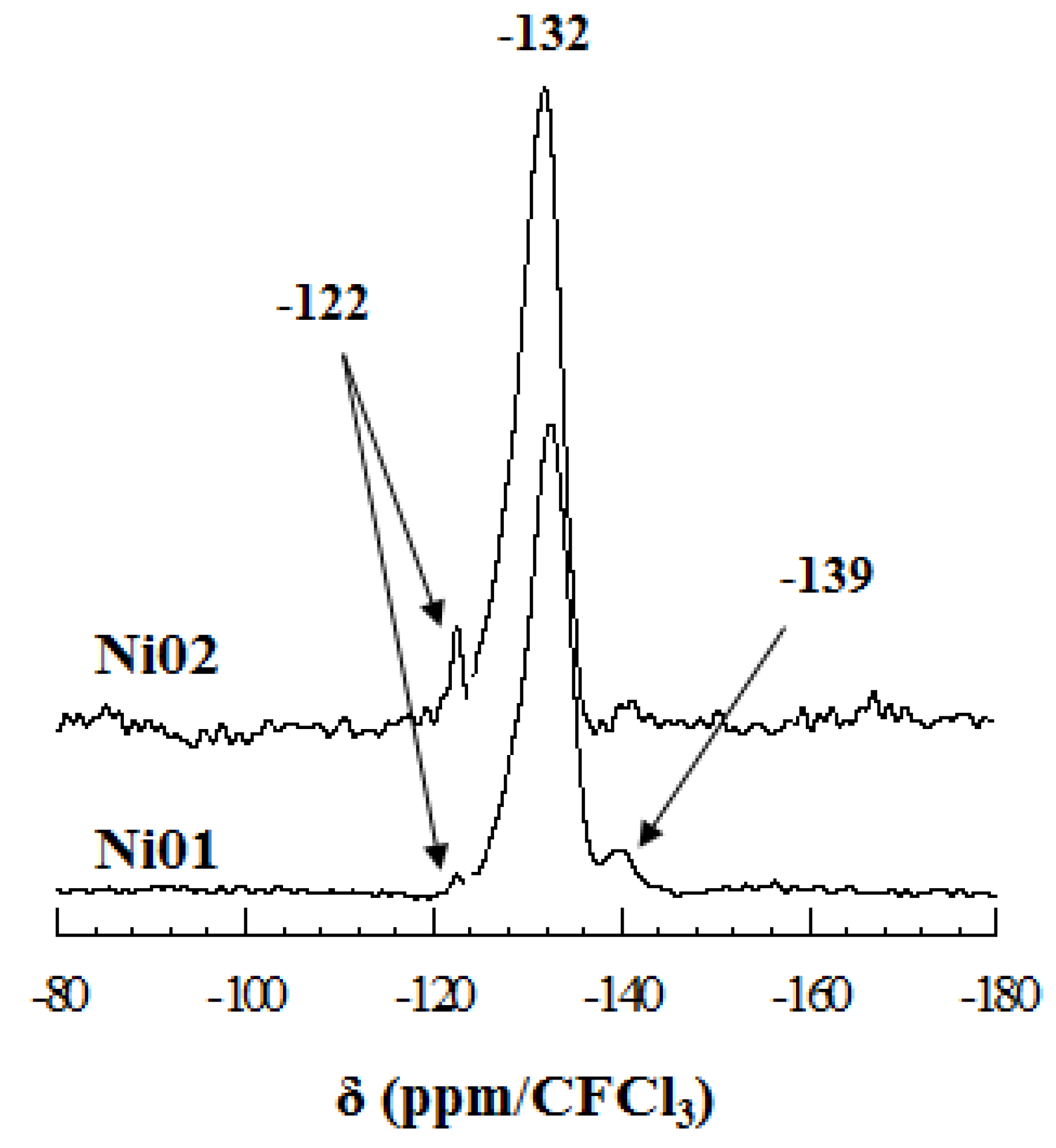
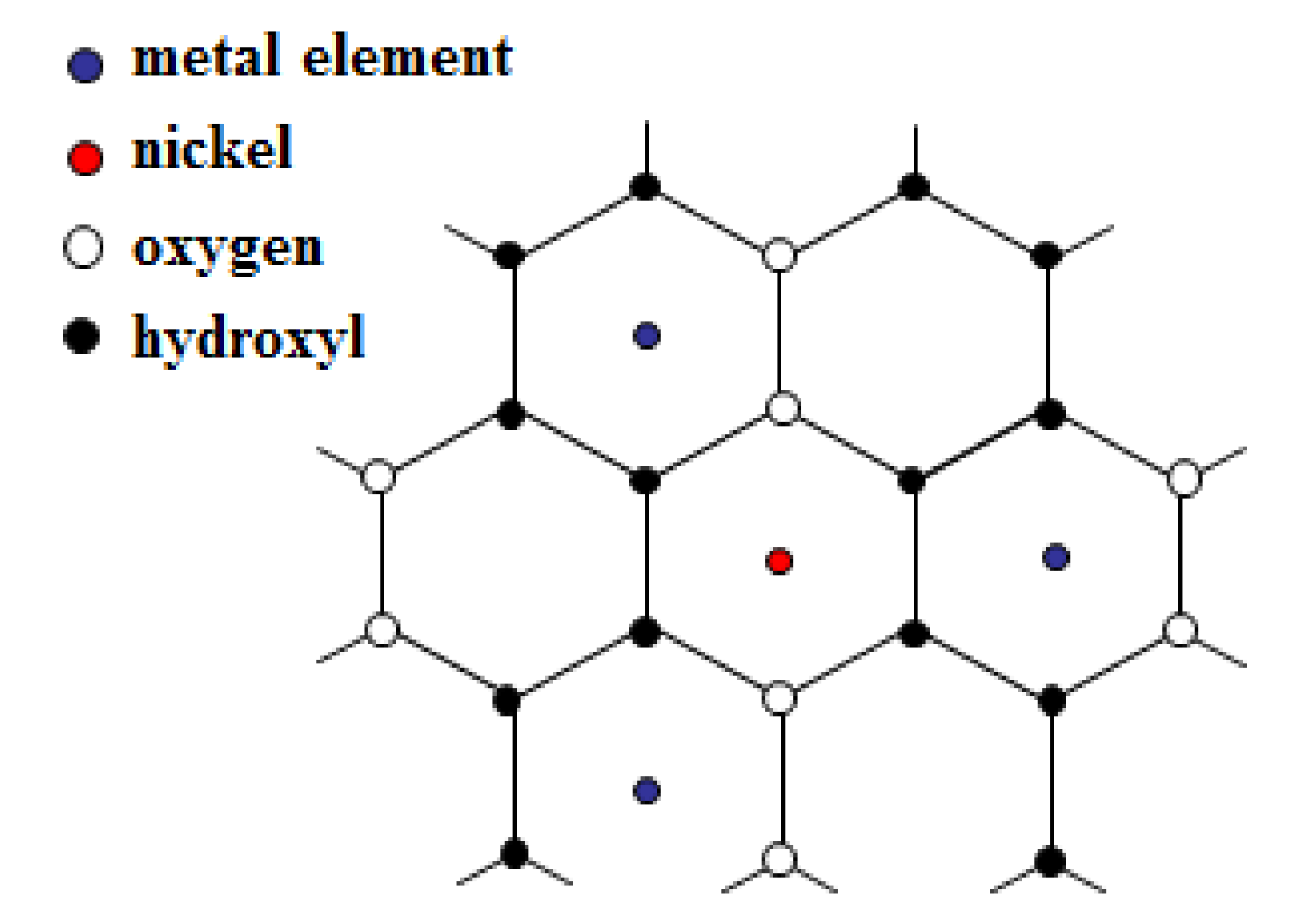
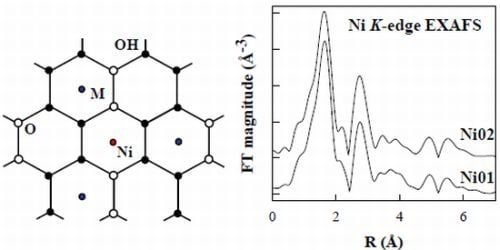
2.7. Ni K-Edge Extended X-Ray Absorption Fine Structure

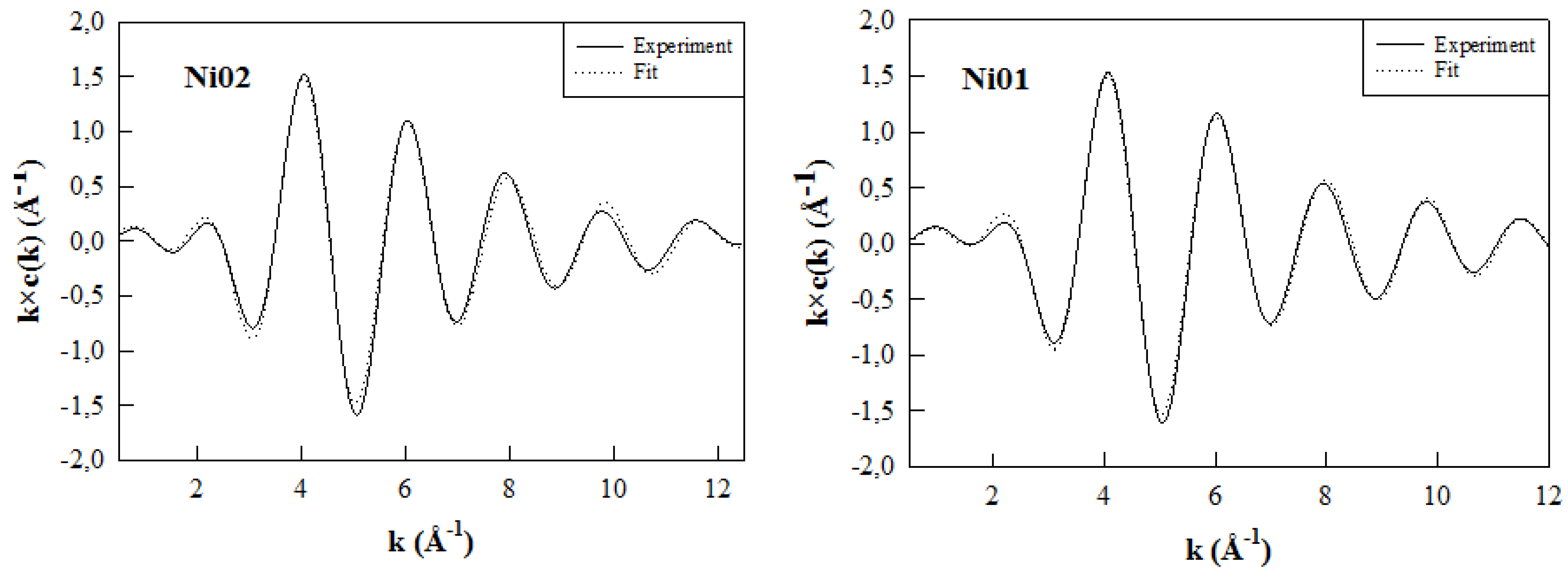
| Sample | Shell | N | D (Å) | σ2 (Å) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NN shell | Ni01 | Ni-O | 6.0 a | 2.05 ± 0.02 | 0.005 |
| Ni02 | Ni-O | 6.0 a | 2.05 ± 0.02 | 0.005 | |
| Zn01 | Zn-O | 5.9 | 2.08 ± 0.02 | 0.004 | |
| Zn02 | Zn-O | 5.9 | 2.07 ± 0.02 | 0.004 | |
| Al-O | 6.0 a | 1.92 ± 0.02 | 0.008 | ||
| Mg01 | Mg-O | 6.0 a | 2.12 ± 0.02 | 0.006 | |
| Mg02 | Mg-O | 6.0 a | 2.13 ± 0.02 | 0.007 | |
| Al-O | 6.0 a | 1.93 ± 0.02 | 0.006 | ||
| NNN shell | Ni01 | Ni-Ni | 1.2 b | 3.00 ± 0.01 | 0.003 |
| Ni-Al | 2.8 b | 3.02 ± 0.01 | 0.004 | ||
| Ni-Si | 4.0 a | 3.20 ± 0.04 | 0.002 | ||
| Ni02 | Ni-Ni | 2.1 b | 3.03 ± 0.01 | 0.004 | |
| Ni-Al | 1.9 b | 3.05 ± 0.01 | 0.006 | ||
| Ni-Si | 4.0 a | 3.21 ± 0.04 | 0.004 | ||
| Zn01 | Zn-Zn | 2.0 b | 3.11 ± 0.04 | 0.005 | |
| Zn-Al | 2.0 b | 2.98 ± 0.04 | 0.007 | ||
| Zn-Si | 4.0 a | 3.17 ± 0.04 | 0.005 | ||
| Zn02 | Zn-Zn | 2.3 b | 3.11 ± 0.04 | 0.006 | |
| Zn-Al | 1.7 b | 2.97 ± 0.04 | 0.006 | ||
| Zn-Si | 4.0 a | 3.25 ± 0.04 | 0.005 |

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Analytical Methods
3.2.1. X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)
3.2.2. Chemical Analysis
3.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.2.5. Thermogravimetric and Differential Thermal Analysis (TGA-DTA)
3.2.6. Nitrogen Adsorption-Desorption Manometry Experiments (BET)
3.2.7. Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (MAS-NMR)
3.2.8. Ni K-Edge Extended X-Ray Absorption Fine Structure (Ni K-EXAFS)
4. Conclusions
References
- Vaccari, A. Clays and catalysis: A promising future. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 14, 161–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, M.I.; Lagaly, G. Clays and health: An introduction. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 36, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, C.-H.; Lin, C.-X.; Tong, D.-S.; Yu, W.-H. Synthesis of clay minerals. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konta, J. Clay and man: Clay raw materials in the service of man. Appl. Clay Sci. 1995, 10, 275–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, H.H. Traditional and new applications for kaolin, smectite, and palygorskite: A general overview. Appl. Clay Sci. 2000, 17, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Frost, R.L.; Lu, G.Q.; Zhu, H.Y. Porous clays and pillared clays-based catalysts. Part 2: A review of the catalytic and molecular sieve applications. J. Porous Mater. 2001, 8, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, M.I. Clay minerals and their beneficial effects upon human health. A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2002, 21, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, J.-H.; Choi, S.-J.; Oh, J.-M.; Park, T. Clay minerals and layered double hydroxides for novel biological applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 36, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.T.; Bailey, S.W.; Eberl, D.D.; Fanning, D.S.; Guggenheim, S.; Kodama, H.; Pevear, D.R.; Srodon, J.; Wicks, F.J. Report of the clay minerals society nomenclature committee; revised classification of clay materials. Clays Clay Miner. 1991, 39, 333–335. [Google Scholar]
- Caillère, S.; Hénin, S.; Rautureau, M. Minéralogie des argiles, Tome 1: Structure et propriétés physico-chimiques, 2nd ed; Masson: Paris, France, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.H. An overview on strategies towards clay-based designer catalysts for green and sustainable catalysis. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 53, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinholdt, M.; Miehé-Brendlé, J.; Delmotte, L.; Tuilier, M.-H.; Le Dred, R.; Cortès, R.; Flank, A.-M. Fluorine route synthesis of montmorillonites containing Mg or Zn and characterization by XRD, thermal analysis, MAS NMR, and EXAFS spectroscopy. Eur. J. Inor. Chem. 2001, 11, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar]
- Reinholdt, M.; Miehé-Brendlé, J.; Delmotte, L.; Tuilier, M.-H.; Le Dred, R. Synthesis and characterization of montmorillonite-type phyllosilicates in a fluoride medium. Clay Miner. 2005, 40, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantenois, S.; Champallier, R.; Bény, J.-M.; Muller, F. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of dioctahedral smectites: A montmorillonites series. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 38, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Forestier, L.; Muller, F.; Villieras, F.; Pelletier, M. Textural and hydration properties of a synthetic montmorillonite compared with a natural Na-exchanged clay analogue. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsubo, Y.; Kato, C. Hydrothermal synthesis of montmorillonite-type silicates III. J. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1954, 75, 456–459. [Google Scholar]
- Nagase, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Ebina, T.; Hayashi, H.; Onodera, Y.; Chandra-Dutta, N. Hydrothermal synthesis of Fe-montmorillonite in Si-Fe-Mg system. Chem. Lett. 1999, 4, 303–304. [Google Scholar]
- Centi, G.; Perathoner, S. Catalysis by layered materials: A review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 107, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Trujillano, R.; Vicente, M.A.; Rives, V.; Korili, S.A.; Gil, A.; Ciuffi, K.J.; Nassar, E.J. Preparation, alumina-pillaring and oxidation catalytic performances of synthetic Ni-saponite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaiah, M.V.; Petit, S.; Barrault, J.; Batiot-Dupeyrat, C.; Valange, S. CO2 reforming of CH4 over Ni-containing phyllosilicates as catalyst precursors. Catal. Today 2010, 157, 397–403. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaiah, M.V.; Petit, S.; Beaufort, M.F.; Eyidi, D.; Barrault, J.; Batiot-Dupeyrat, C.; Valange, S. Nickel based catalysts derived from hydrothermally synthesized 1:1 and 2:1 phyllosilicates as precursors for carbon dioxide reforming of methane. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 140, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Sato, T. Expansion characteristics of montmorillonite and saponite under various relative humidity conditions. Clay Sci. 1988, 7, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, H.; Nakazawa, H.; Hashizume, H.; Shimomura, S.; Watanabe, T. Hydration behavior of Na-smectite crystals synthesized at high pressure and high temperature. Clays Clay Miner. 1994, 42, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Boeck, E.S.; Coveney, P.V.; Skipper, N.T. Monte Carlo molecular modeling studies of hydrated Li-, Na- and K-smectites: Understanding the role of potassium as a clay swelling inhibitor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 12608–12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonczek, J.L.; Harris, W.G.; Nkedi-Kizza, P. Monolayer to bilayer transitional arrangements of hexadecyltrimethylammonium cations on Na-Montmorillonite. Clays Clay Miner. 2002, 50, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Frost, R.L.; Bostrom, T.; Yuan, P.; Duong, L.; Yang, D.; Xi, Y.; Kloprogge, J.T. Changes in the morphology of organoclays with HDTMA+ surfactant loading. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 31, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapides, I.; Borosiver, M.; Yariv, S. Thermal analysis of hexadecyltrimethylammonium-montmorillonites Part 2. Thermo-XRD-spectroscopy-analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 105, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapides, I.; Borosiver, M.; Yariv, S. Thermal analysis of hexadecyltrimethylammonium-montmorillonites Part 1. Thermogravimetry, carbon and hydrogen analysis and thermo-IR spectroscopy analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 105, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Pierre, A.C. Colloidal behaviour of montmorillonite in the presence of Fe3+ ions. Colloid Surf. A 1999, 155, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravero, F.; Keith, K.S.; Murray, H.H.; Toth, T. A white bentonite from San Juan Province, Argentina—Geology and potential industrial applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2000, 16, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Christidis, G.E. Formation and growth of smectites in bentonites: A case study from Kimolos Island, Aegean, Greece. Clays Clay Miner. 2001, 49, 204–215. [Google Scholar]
- B. Bauluz, B.; Peacor, D.R.; Ylagan, R.F. Transmission electron microscopy study of smectite illitization during hydrothermal alteration of a rhyolitic Hyaloclastite from Ponza, Italy. Clays Clay Miner. 2002, 50, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadros, J.; Delgado, A.; Cardenete, A.; Reyes, E.; Linares, J. Kaolinite/montmorillonite resembles beidellite. Clays Clay Miner. 1994, 42, 643–651. [Google Scholar]
- Drits, V.A.; Lindgreen, H.; Salyn, A.L.; Ylagan, R.; McCarty, D.K. Semiquantitative determination of trans-vacant and cis-vacant 2:1 layers in illites and illite-smectites by thermal analysis and X-ray diffraction. Am. Miner. 1998, 83, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Emmerich, K.; Madsen, F.T.; Kahr, G. Dehydroxylation behavior of heat-treated and steam-treated homoionic cis-vacant montmorillonites. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 591–604. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, R.L.; Ruan, H.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Gates, W.P. Dehydration and dehydroxylation of nontronites and ferruginous smectite. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 346, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, A.U.; Dogan, M.; Onal, M.; Sarikaya, Y.; Aburub, A.; Wurster, D.E. Baseline studies of the clay minerals society source clays: Specific surface area by the Brunauer Emmett Teller (BET) method. Clays Clay Miner. 2006, 54, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Salles, F.; Douillard, J.-M.; Denoyel, R.; Bildstein, O.; Jullien, M.; Beurroies, I.; van Damme, H. Hydration sequence of swelling clays: Evolutions of specific surface area and hydration energy. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2009, 333, 510–522. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaiah, M.V.; Petit, S.; Brendlé, J.; Patrier, P. Rapid synthesis of aluminium polycations by microwave assisted hydrolysis of aluminium via decomposition of urea and preparation of Al-pillared montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, M.; Muller, F.; Le Forestier, L.; Beny, J.-M.; Guegan, R. NH4-smectite: Characterization, hydration properties and hydro mechanical behavior. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 49, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougeon, R.D.; Soulard, M.; Reinholdt, M; Miehé-Brendlé, J.; Chézeau, J.-M.; Le Dred, R.; Marchal, R.; Jeandet, P. Polypeptide adsorption on a synthetic montmorillonite: A combined solid-state NMR spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, thermal analysis and N2 adsorption study. Eur. J. Inor. Chem. 2003, 7, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Marty, N.C.M.; Cama, J.; Sato, T.; Chino, D.; Villiéras, F.; Razafitianamaharavo, A.; Brendlé, J.; Giffaut, E.; Soler, J.M.; Gaucher, E.C.; et al. Dissolution kinetics of synthetic Na-smectite. An integrated experimental approach. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 5849–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J.; Serratosa, J.M. 29Si and 27Al high-resolution MAS-NMR spectra of phyllosilicates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 4790–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, N.; Oldfield, E. Prediction of silicon-29 nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shifts using a group electronegativity approach: Applications to silicate and aluminosilicate structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 6769–6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, C.A.; Altaner, S.P.; Kirkpatrick, R.J. High-resolution silicon-29 spectroscopy of 2:1 layer silicates: Corellations among chemical shift, structural distortions and chemical variations. Am. Miner. 1987, 72, 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, W.P.; Komadel, P.; Madejová, J.; Bujdak, J.; Stucki, J.W.; Kirkpatrick, R.J. Electronic and structural properties of reduced-charge Montmorillonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2000, 16, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, B.A.; Stucki, J.W. The use of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) for the determination of tetrahedral aluminium in montmorillonite. Clay Miner. 1984, 19, 663–667. [Google Scholar]
- Drachman, S.R.; Roch, G.E.; Smith, M.E. Solid state NMR characterization of the thermal transformation of Fuller’s Earth. Solid State Nucl. Magn. 1997, 9, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huve, L. Synthèse de Phyllosilicates en milieu acide et fluoré et leur Caractérisation.
- Huve, L.; Delmotte, L.; Martin, P.; Le Dred, R.; Baron, J.; Saehr, D. 19F MAS-NMR study of structural fluorine in some natural and synthetic 2:1 layer silicates. Clays Clay Miner. 1992, 40, 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Reinholdt, M. Synthèse en milieu fluoré et caractérisation de Phyllosilicates de type Montmorillonite. Etude Structurale par Spectroscopies d'Absorption des Rayons X et de Résonance Magnétique Nucléaire.
- Miehé-Brendlé, J.; Tuilier, M.-H.; Marichal, C.; Gallego, J.-C.; Reinholdt, M. Mg environments in the octahedral sheet of 2:1 talc-like hybrid phyllosilicates: A comparative XAFS study. Eur. J. Inor. Chem. 2010, 35, 5587–5591. [Google Scholar]
- Reinholdt, M.; Miehé-Brendlé, J.; Delmotte, L.; Tuilier, M.-H.; Le Dred, R. Si-Al-Mg and Si-Al-Zn Montmorillonite: Synthesis and Characterization by EXAFS and Quantitative 27Al MAS-NMR. In Proceedings of the 12th International Clay Conference, Bahía Blanca, Argentina, July 22–28, 2001; Domínguez, E.A., Mas, G.R., Cravero, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tsipursky, S.I.; Drits, V.A. The distribution of octahedral cations in the 2:1 layers of dioctahedral smectites studied by oblique-texture electron diffraction. Clay Miner. 1984, 19, 177–193. [Google Scholar]
- Massiot, D.; Favon, F.; Capron, M.; King, I.; Le Calvé, S.; Alonso, B.; Durand, J.-O.; Bujoli, B.; Gan, Z.; Hoatson, G. Modelling one- and two-dimensional solid-state NMR spectra. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2002, 40, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Rad. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newville, M. IFEFFIT: Interactive XAFS analysis and FEFF fitting. J. Synchrotron Rad. 2001, 8, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabinsky, S.I.; Rehr, J.J.; Ankudinov, A.; Albers, R.C.; Eller, M.J. Multiple-scattering calculations of X-ray-absorption spectra. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, 2995–3009. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Reinholdt, M.X.; Brendlé, J.; Tuilier, M.-H.; Kaliaguine, S.; Ambroise, E. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Characterization of Ni-Al Montmorillonite-Like Phyllosilicates. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 48-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3010048
Reinholdt MX, Brendlé J, Tuilier M-H, Kaliaguine S, Ambroise E. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Characterization of Ni-Al Montmorillonite-Like Phyllosilicates. Nanomaterials. 2013; 3(1):48-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleReinholdt, Marc X., Jocelyne Brendlé, Marie-Hélène Tuilier, Serge Kaliaguine, and Emmanuelle Ambroise. 2013. "Hydrothermal Synthesis and Characterization of Ni-Al Montmorillonite-Like Phyllosilicates" Nanomaterials 3, no. 1: 48-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3010048
APA StyleReinholdt, M. X., Brendlé, J., Tuilier, M.-H., Kaliaguine, S., & Ambroise, E. (2013). Hydrothermal Synthesis and Characterization of Ni-Al Montmorillonite-Like Phyllosilicates. Nanomaterials, 3(1), 48-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3010048