Unique Design of Functionalized Covalent Organic Frameworks for Highly Selective Removal of Cyano-Neonicotinoids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
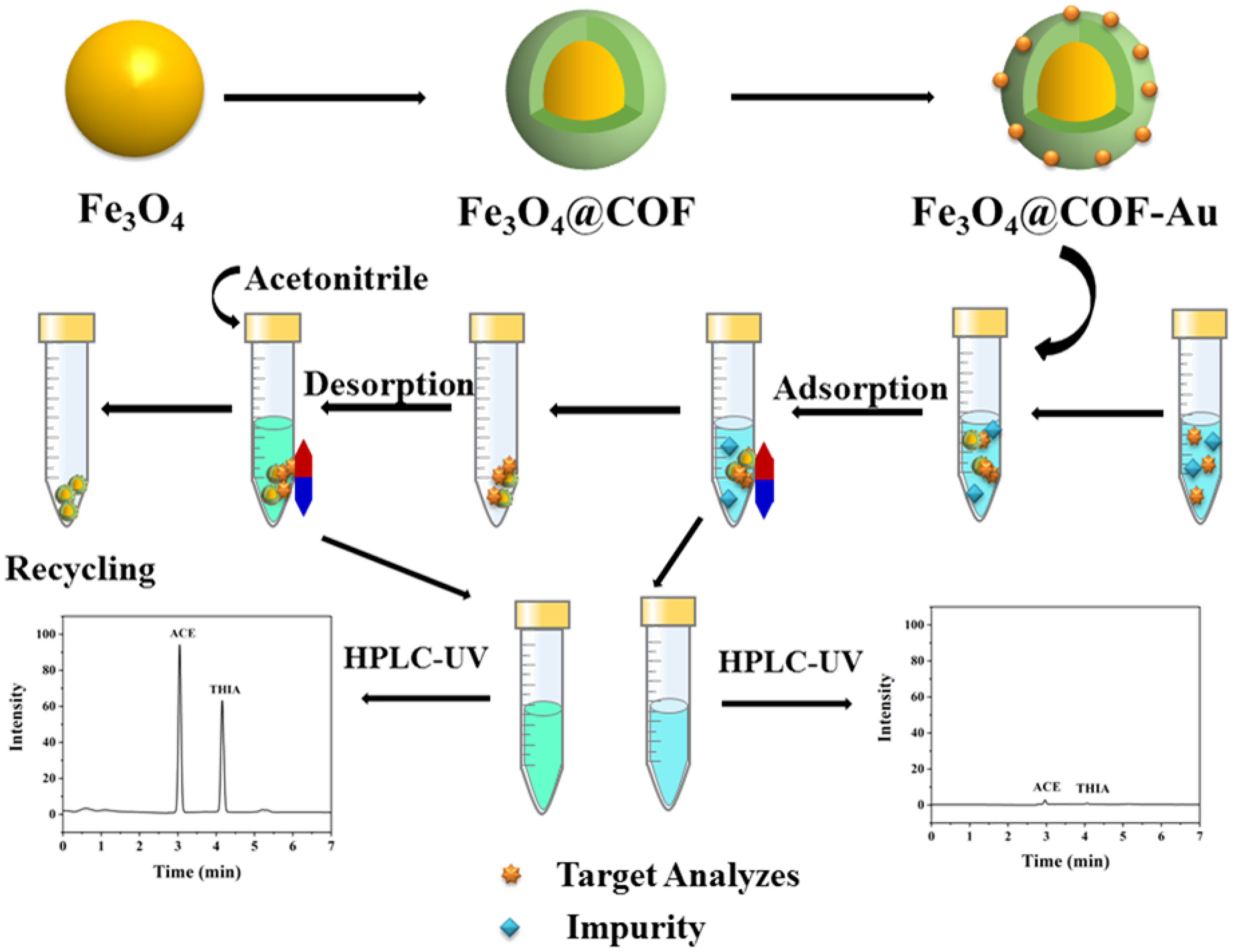
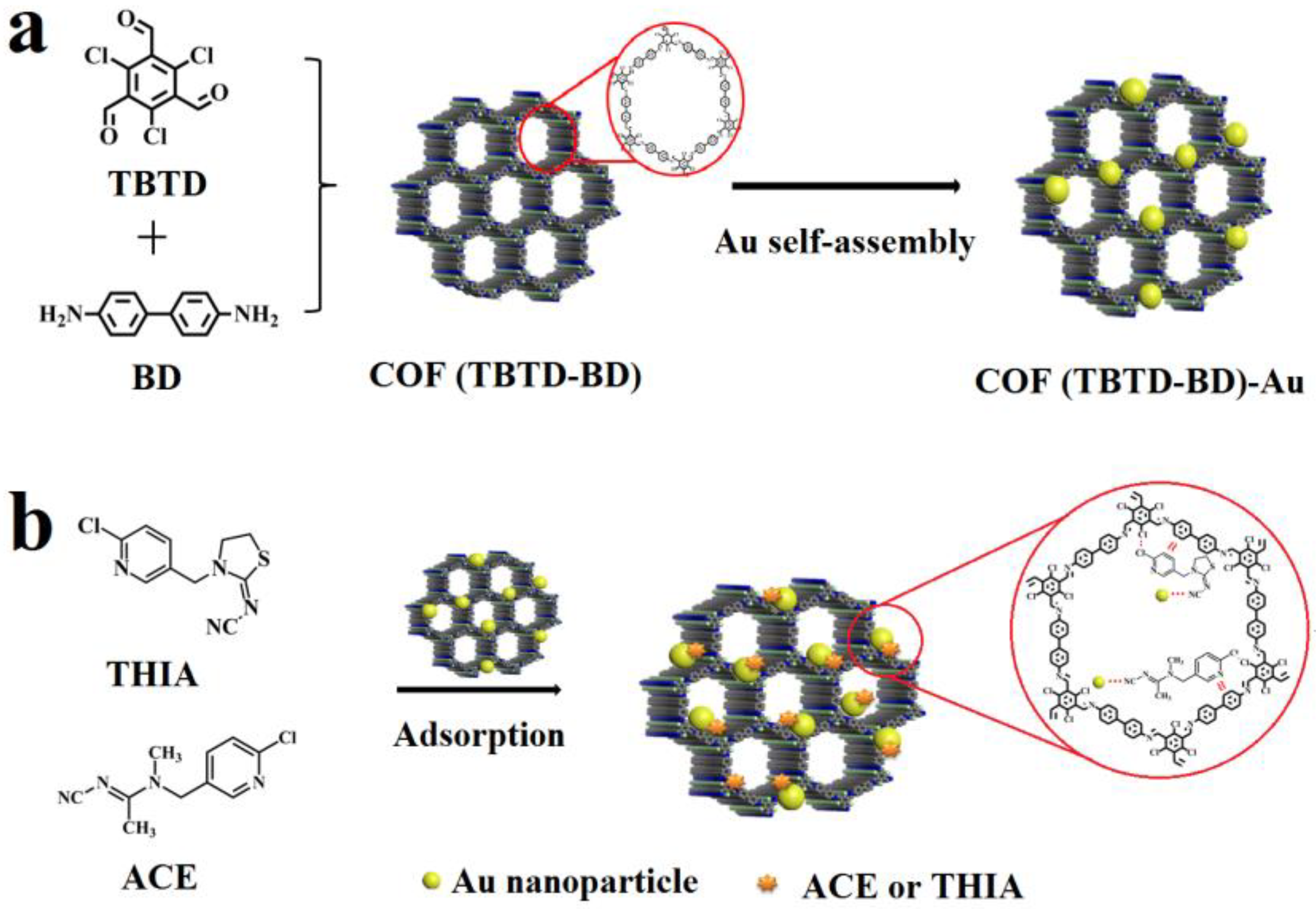
2.2. Preparation of Fe3O4, Fe3O4@COF, and Fe3O4@COF-Au
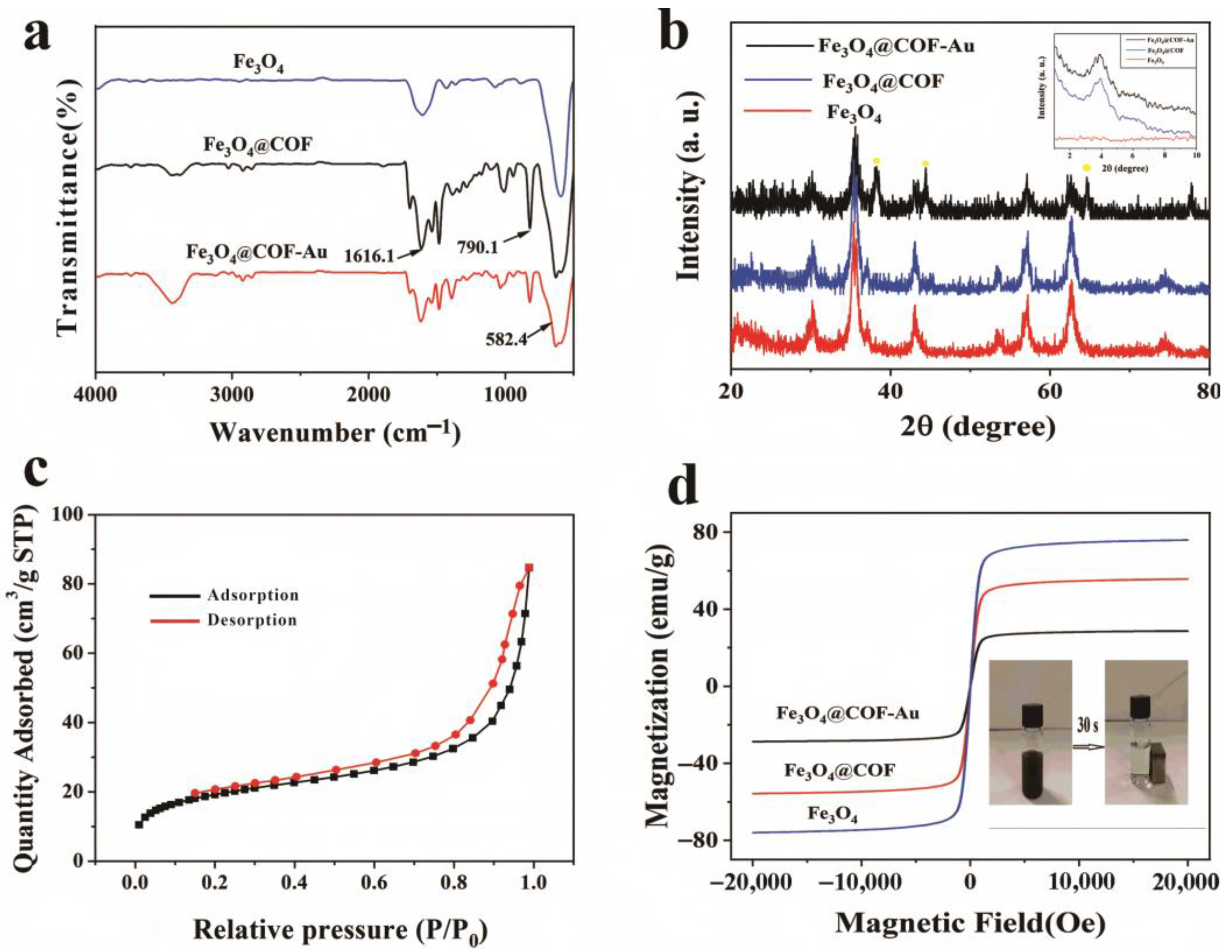
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Desorption and Reusability Experiments
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization
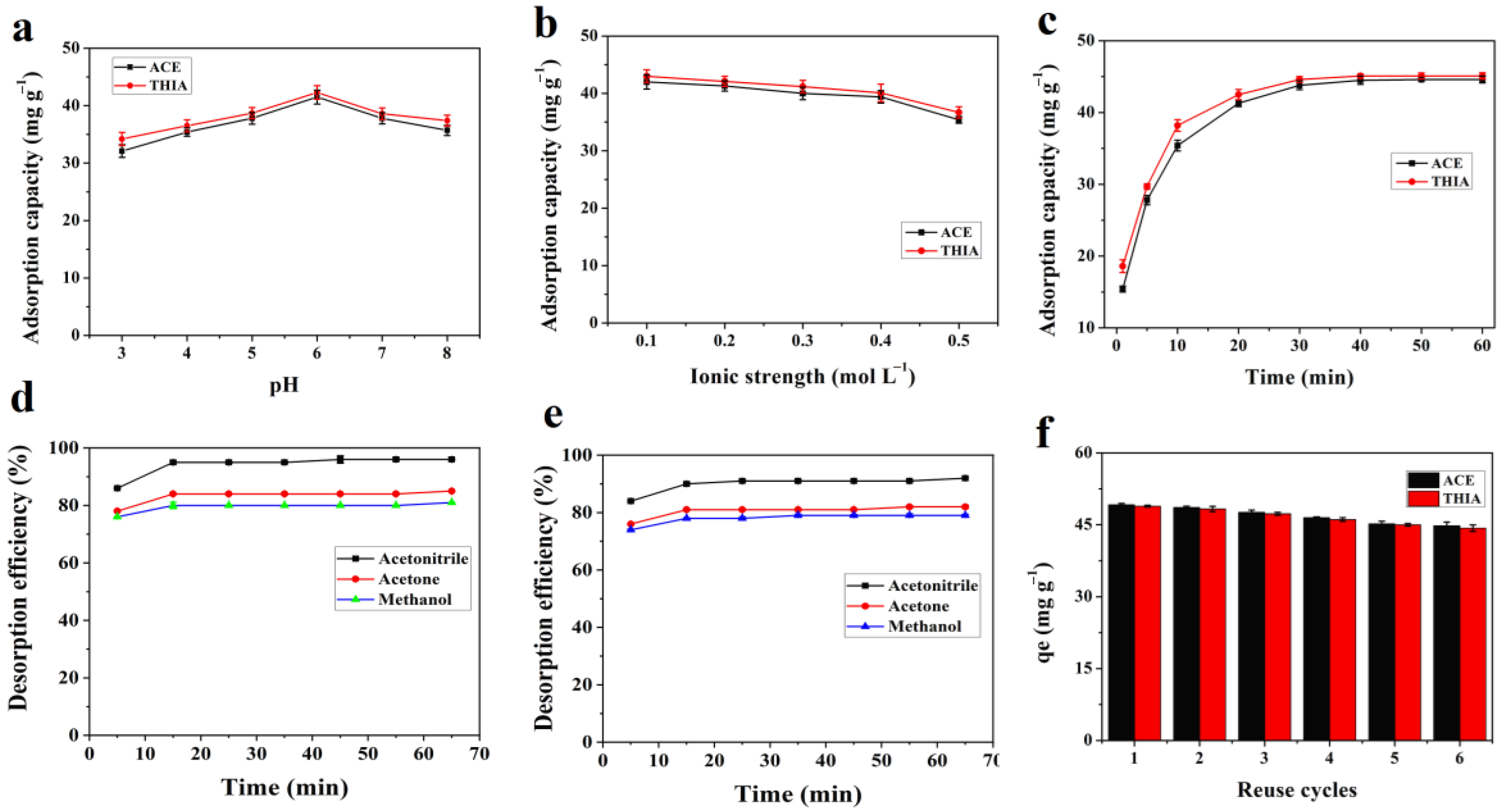
3.2. Effects of pH, Ionic Strength and Contact Time
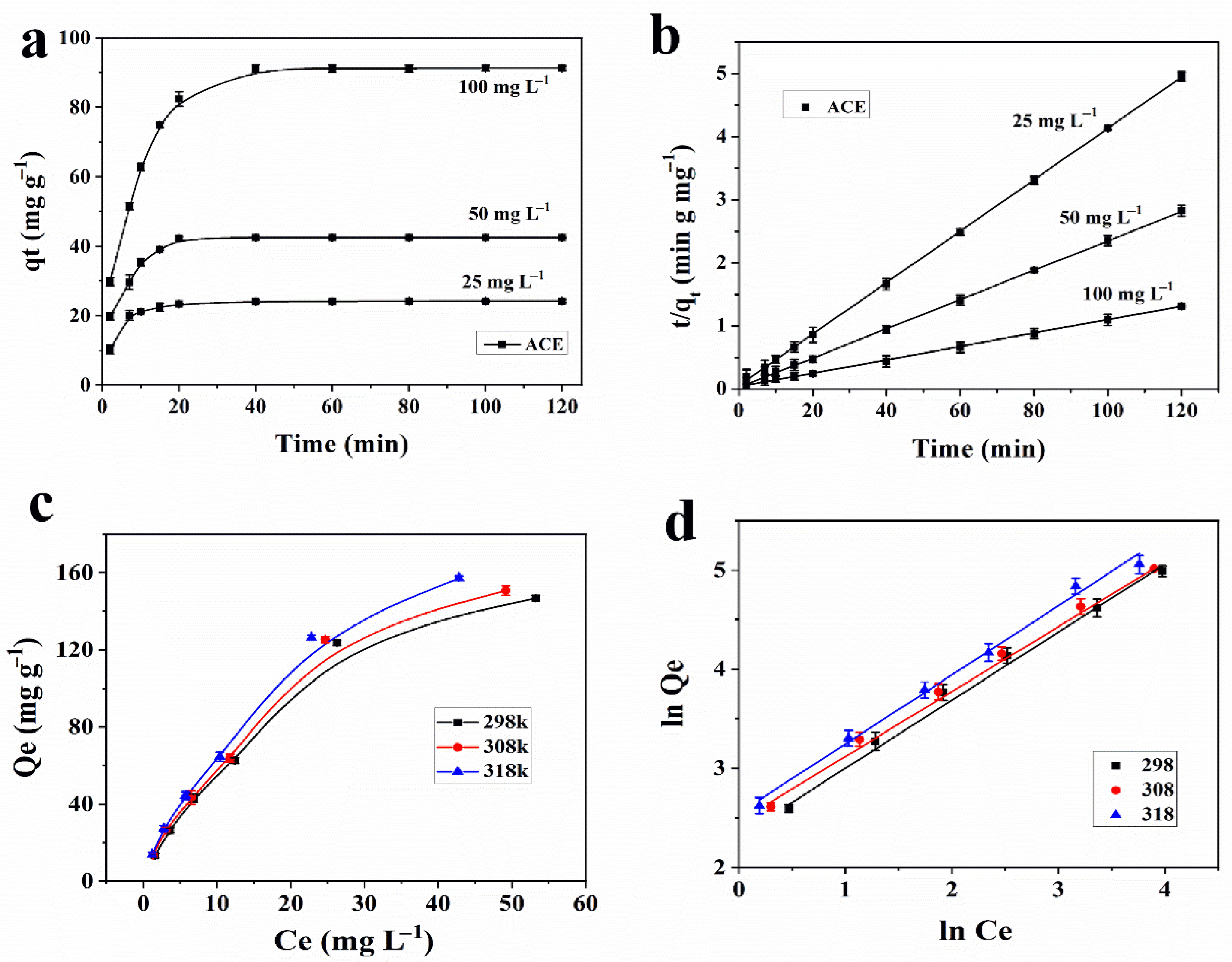
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms and Thermodynamics
3.5. Desorption and Reusability
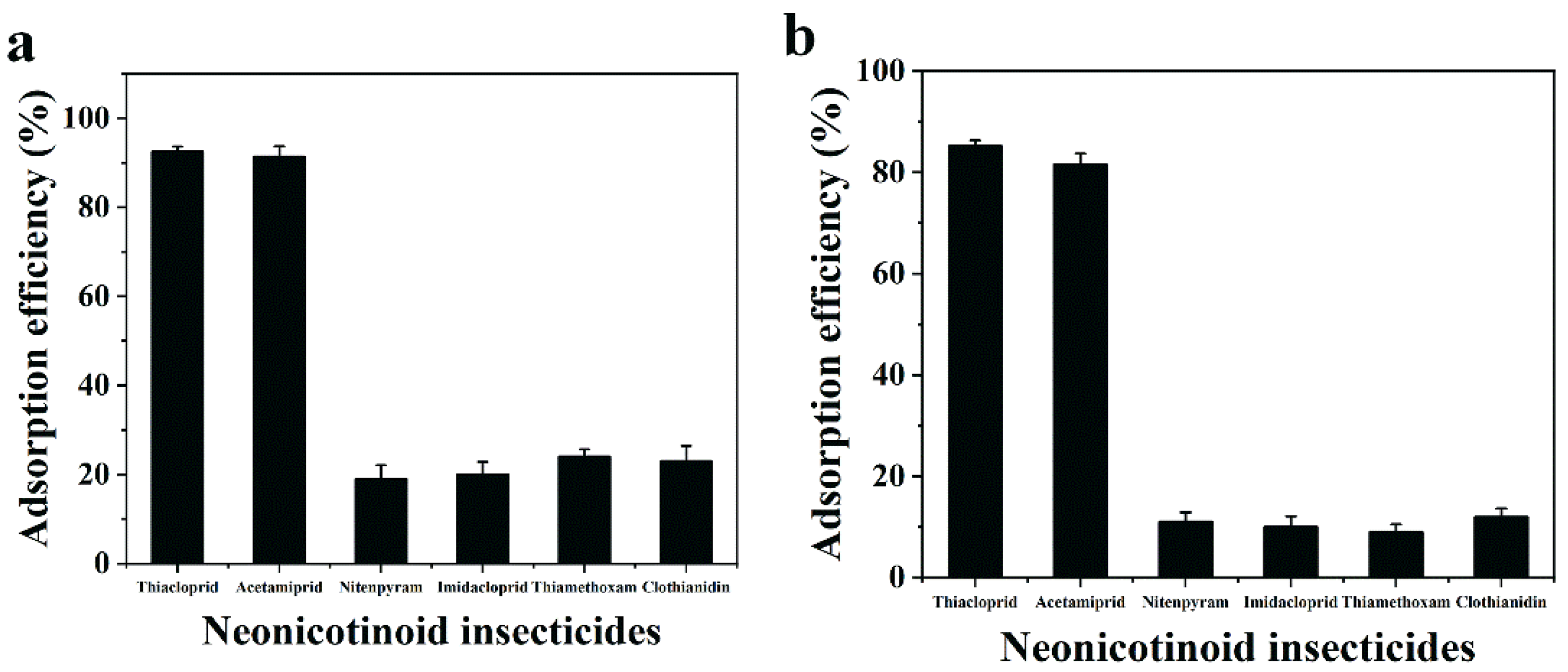
3.6. Removal Selectivity for ACE and THIA
3.7. Removal Mechanism
| Adsorbents | Adsorbate | Equilibrium Time | qm (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPP-MMIPs a | Paichongding | 150 min | 13.30 | [33] |
| AMCCP b | ACE | 100 min | 142.36 | [34] |
| Fe3O4/ZIF-67/GO | ACE and THIA | 50 min | - | [35] |
| Carbon cryogel | Imidacloprid | 24 h | 80–100 | [36] |
| Fe3O4@COF(TBTD-BD)-Au | ACE and THIA | 40 min | 157 | This work |
| GCA c (F-200) | Imidacloprid, Clothianidin, Thiamethoxam and Thiacloprid | 20 d | 60–150 | [37] |
3.8. Adsorption Performance in Beverages
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, F.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D.; Zhou, C.; Li, W.; Zeng, G.; Song, B.; Zeng, Z. Neonicotinoid insecticides in non-target organisms: Occurrence, exposure, toxicity, and human health risks. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 383, 125432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Kan, S.; Yang, G.; Yang, S.; Sun, T.; Zhang, H. From agrochemicals to thyroiditis: The alarming connection with neonicotinoid insecticides. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2025, 7, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimako, C.; Khidkhan, K.; Kulprasertsri, S.; Poapolathep, S.; Khunlert, P.; Yohannes, Y.B.; Ikenaka, Y.; Nakayama, S.M.M.; Ishizuka, M.; Poapolathep, A. Pollution and partitioning of neonicotinoid insecticides in free-grazing ducks and their eggs: Implications for human health. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, S.A.; Doherty, D.M.; Koch, H.M.; Käfferlein, H.U.; Bury, D.; Slattery, C.; Coggins, M.A.; Connolly, A. Characterising neonicotinoid insecticide exposures among the Irish population using human biomonitoring. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2025, 268, 114610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, J.L.; Real, F.J.; Javier Benitez, F.; Matamoros, E. Degradation of neonicotinoids by UV irradiation: Kinetics and effect of real water constituents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, E.; Munoz, M.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A. Fast oxidation of the neonicotinoid pesticides listed in the EU Decision 2018/840 from aqueous solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padervand, M.; Heidarpour, H.; Bargahi, A. A mechanistic study and in-vivo toxicity bioassay on acetamiprid photodegradation over the zeolite supported cerium-based photocatalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 395, 112526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Chen, Q.; Ke, S.; Yi, X.; Qiu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Bai, X.; Huang, M. Enhanced adsorption of neonicotinoids by MnCl2 and H3PO4 co-modified corn stover biochar: Performance and mechanism analysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. Elemental mercury removal by adsorbent CuO-modified MnO2 nano-hollow spheres: Performance, kinetics, and mechanism. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 3314–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, S.; Shaikh, H.; Solangi, A.R.; Batool, M.; Khan, M.Y.; Alqarni, N.D.; Alharthi, S.; Al-Shaalan, N.H. Fabrication of nanofiltration membrane with enhanced water permeability and dyes removal efficiency using tetramethyl thiourea-doped reduced graphene oxide. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 4461–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lin, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Xi, Y.; Li, X.; Ying, Y. Highly selective recovery of Au(III) from wastewater by thioctic acid modified Zr-MOF: Experiment and DFT calculation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.T.; Ghosh, S.; Wang, Z.; Wen, F.; Rodríguez-San-Miguel, D.; Feng, J.; Huang, N.; Wang, W.; Zamora, F.; Feng, X.; et al. Covalent organic frameworks. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2023, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, A.A.; Irshad, A.; Nazir, M.S.; Atif, M. A review on covalent organic frameworks as adsorbents for organic pollutants. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 400, 136737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, M. Covalent connections between metal–organic frameworks and polymers including covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 6379–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhao, Y. Covalent Organic Frameworks for Energy Conversion in Photocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202303086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, A.; Khosropour, A.; Khazdooz, L.; Amirjalayer, S.; Khojastegi, A.; Zadehnazari, A.; Zhao, Y.; Abbaspourrad, A. Substitution and Orientation Effects on the Crystallinity and PFAS Adsorption of Olefin-Linked 2D COFs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 9483–9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, S.; Yang, X.; Cui, C.-X.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; He, J.; Chen, G.Z.; Xu, Q.; Zeng, G. Post-synthetic modification of covalent organic frameworks for CO2 electroreduction. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Kaneko, Y.; Nishibori, E.; Nabeshima, T. Molecular recognition by multiple metal coordination inside wavy-stacked macrocycles. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wu, D.; Liu, J.; Hu, N.; Shi, X.; Dai, C.; Sun, Z.; Suo, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, Y. Magnetic covalent organic frameworks based on magnetic solid phase extraction for determination of six steroidal and phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals in food samples. Microchem. J. 2018, 143, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, A.; Li, G.; Wu, D.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, N.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y. Sulphonate functionalized covalent organic framework-based magnetic sorbent for effective solid phase extraction and determination of fluoroquinolones. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1612, 460651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, D.; Wen, A.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, X. β-Cyclodextrin-/AuNPs-functionalized covalent organic framework-based magnetic sorbent for solid phase extraction and determination of sulfonamides. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Yi, C.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, M.; Li, P.; Luo, X.; Li, Y. Magnetic organic frame material Fe3O4@Au/COF for sensitive SERS detection and photo-Fenton degradation of tetracycline. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 119472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhou, T.; Xu, J.; Li, F.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Guo, S.; Shen, X.; Zhang, W. AuPd Bimetallic Nanocrystals Embedded in Magnetic Halloysite Nanotubes: Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Reduction of Nitroaromatic Compounds. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Y.; Liu, G.; Dong, B.; Zhou, J.; Wang, A.; Wang, J.; Jin, R.; Lv, H.; Dou, Z.; Huang, W. Microbial synthesis of Pd/Fe3O4, Au/Fe3O4 and PdAu/Fe3O4 nanocomposites for catalytic reduction of nitroaromatic compounds. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorjanc, T.; Shetty, D.; Gándara, F.; Ali, L.; Raya, J.; Das, G.; Olson, M.A.; Trabolsi, A. Remarkably efficient removal of toxic bromate from drinking water with a porphyrin–viologen covalent organic framework. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Chuang, R.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Xia, N.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, L.; Rayan, A.M.; et al. Charge density of carboxymethyl cellulose affects depletion attraction-stabilized egg yolk Pickering emulsion gels: Rheological and interfacial properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 159, 110612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.-D.; Cui, Y.-Y.; Yang, C.-X.; Yan, X.-P. Core–Shell Magnetic Amino-Functionalized Microporous Organic Network Nanospheres for the Removal of Tetrabromobisphenol A from Aqueous Solution. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, U.; Chen, C.-C. Adsorption Thermodynamics for Process Simulation. Langmuir 2024, 40, 23583–23597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Ameen, S.S.; Hassan, D.D.; Mohammed, D.S.; Omer, K.M.; Latif, D.A.; Mohammad, Y.O. Natural-based chalcopyrite nanoparticles as high-performance mineral adsorbents for organic dye removal in water. Mater. Adv. 2025, 6, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-y.; Liu, Q.; Yang, C.; Wu, S.-c.; Cheng, J.-h. Magnetic aluminum-based metal organic framework as a novel magnetic adsorbent for the effective removal of minocycline from aqueous solutions. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Polo, M.; Velo-Gala, I.; López-Peñalver, J.J.; Rivera-Utrilla, J. Molecular imprinted polymer to remove tetracycline from aqueous solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 203, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, C.-X.; Yan, X.-P. Controllable preparation of core–shell magnetic covalent-organic framework nanospheres for efficient adsorption and removal of bisphenols in aqueous solution. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 2511–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, H.T.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.Y.; Zhang, H.; Dong, A.J. Preparation and characterization of surface molecularly imprinted film coated on a magnetic nanocore for the fast and selective recognition of the new neonicotinoid insecticide paichongding (IPP). RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3714–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Ma, Y. A higher efficiency removal of neonicotinoid insecticides by modified cellulose-based complex particle. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Hong, S.; Li, H.; Shao, Y.; She, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, F.; Jin, M. One-pot synthesis of magnetic zeolitic imidazolate framework/grapheme oxide composites for the extraction of neonicotinoid insecticides from environmental water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4747–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momčilović, M.Z.; Ranđelović, M.S.; Purenović, M.; Onjia, A.E.; Babić, B.M.; Matović, B.Z. Synthesis and characterization of resorcinol formaldehyde carbon cryogel as efficient sorbent for imidacloprid removal. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 7306–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, D.T.; Nagorzanski, M.R.; Powers, M.M.; Cwiertny, D.M.; Hladik, M.L.; LeFevre, G.H. Differences in Neonicotinoid and Metabolite Sorption to Activated Carbon Are Driven by Alterations to the Insecticidal Pharmacophore. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14694–14705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Analytes | C0 (mg L−1) | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg g−1) | K2 | R2 | ||
| ACE | 25 | 24.2 | 0.026 | 0.9908 |
| 50 | 42.7 | 0.013 | 0.9916 | |
| 100 | 91.3 | 0.0027 | 0.9932 | |
| THIA | 25 | 24.9 | 0.028 | 0.9917 |
| 50 | 44.3 | 0.014 | 0.9926 | |
| 100 | 92.9 | 0.0026 | 0.9955 | |
| Analytes | Temperature | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg g−1) | b (L mg−1) | R2 | Kf | 1/n | R2 | ||
| ACE | 298 K | 146.8 | 0.5978 | 0.8109 | 1.1858 | 0.6882 | 0.9985 |
| 308 K | 150.8 | 0.5961 | 0.8202 | 1.3972 | 0.7086 | 0.9982 | |
| 318 K | 157.2 | 0.6002 | 0.8314 | 1.5547 | 0.7144 | 0.9980 | |
| THIA | 298 K | 149.9 | 0.6243 | 0.8331 | 1.0422 | 0.6610 | 0.9982 |
| 308 K | 151.3 | 0.5981 | 0.8209 | 1.4353 | 0.7131 | 0.9964 | |
| 318 K | 156.1 | 0.5859 | 0.8241 | 1.7423 | 0.7292 | 0.9988 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Mai, W.; Wei, S.; Teng, G.; Pu, P.; Zhao, J.; Tian, Y. Unique Design of Functionalized Covalent Organic Frameworks for Highly Selective Removal of Cyano-Neonicotinoids. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201596
Yang Y, Wang S, Mai W, Wei S, Teng G, Pu P, Zhao J, Tian Y. Unique Design of Functionalized Covalent Organic Frameworks for Highly Selective Removal of Cyano-Neonicotinoids. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(20):1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201596
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yan, Shuojie Wang, Wenxin Mai, Shiyu Wei, Guixiang Teng, Peng Pu, Jiaxing Zhao, and Yongqiang Tian. 2025. "Unique Design of Functionalized Covalent Organic Frameworks for Highly Selective Removal of Cyano-Neonicotinoids" Nanomaterials 15, no. 20: 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201596
APA StyleYang, Y., Wang, S., Mai, W., Wei, S., Teng, G., Pu, P., Zhao, J., & Tian, Y. (2025). Unique Design of Functionalized Covalent Organic Frameworks for Highly Selective Removal of Cyano-Neonicotinoids. Nanomaterials, 15(20), 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201596






