Design of Electrostatic Nanocomplex of Semaglutide with Protamine and Zinc for Subcutaneous Prolonged Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
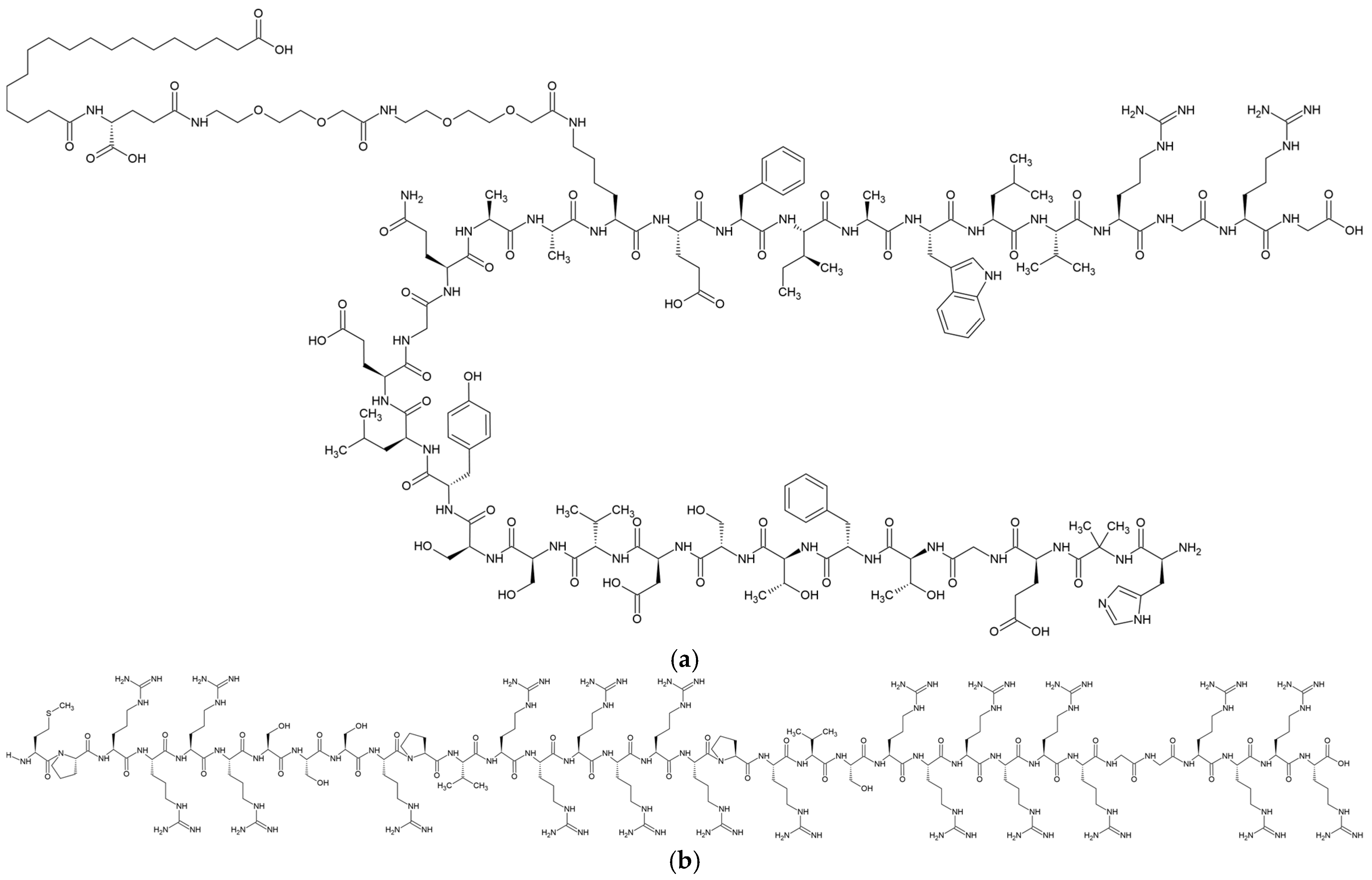
2.2. Preparation of SMG-PS-Zn Complexes
2.3. Determination of Lipophilicity of SMG-PS-Zn Complexes
2.4. HPLC Analysis
2.5. Particle Size and Zeta Potential of SMG-PS-Zn Complexes
2.6. Dispersibility of the Complexes After Centrifugation
2.7. Solid-State SMG (%) After Addition into Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS)
2.8. FT-IR Spectroscopy
2.9. Morphology and Physical Characteristics
2.9.1. Morphological Observation
2.9.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.9.3. Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) Analysis
2.10. In Vitro Dissolution Profile of SMG-Loaded Nanocomplexes
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
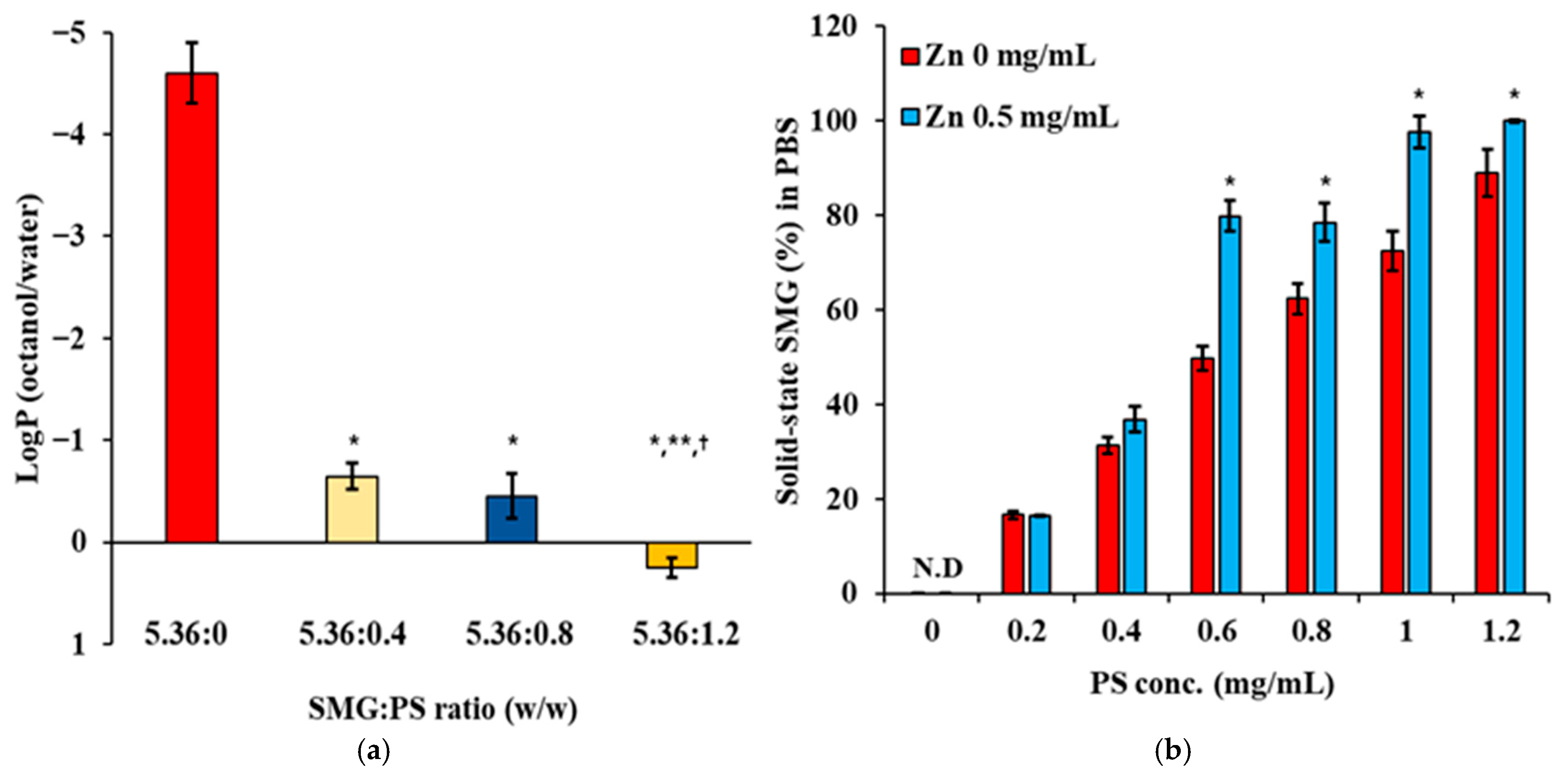
3.1. Effect of PS and Zn Concentration on logP and Solubility of SMG-PS-Zn Complexes
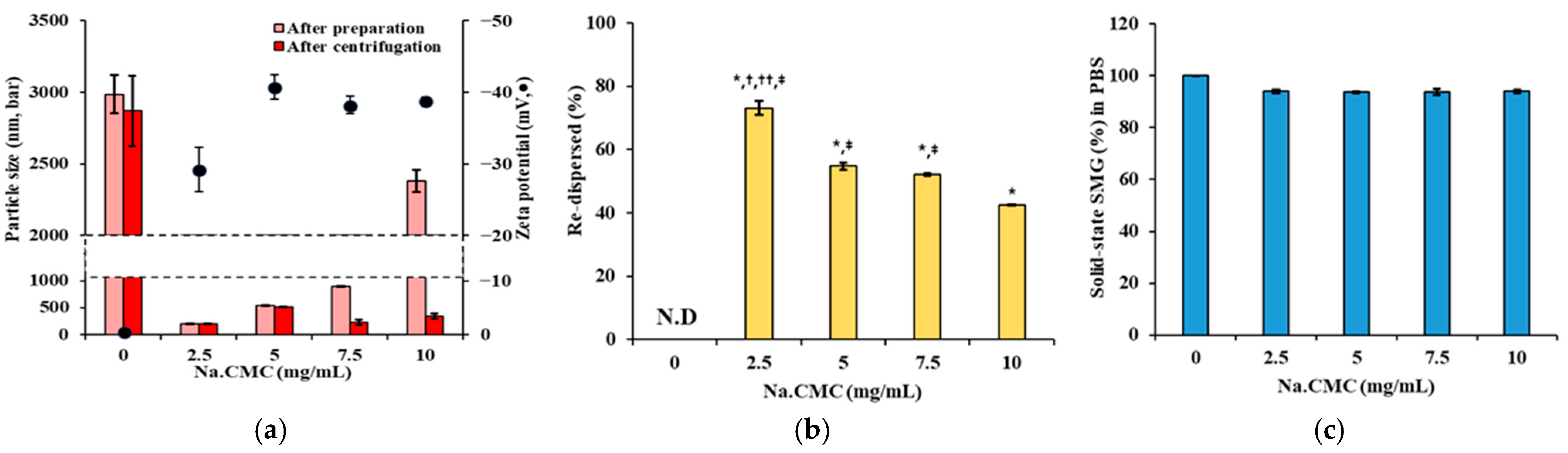
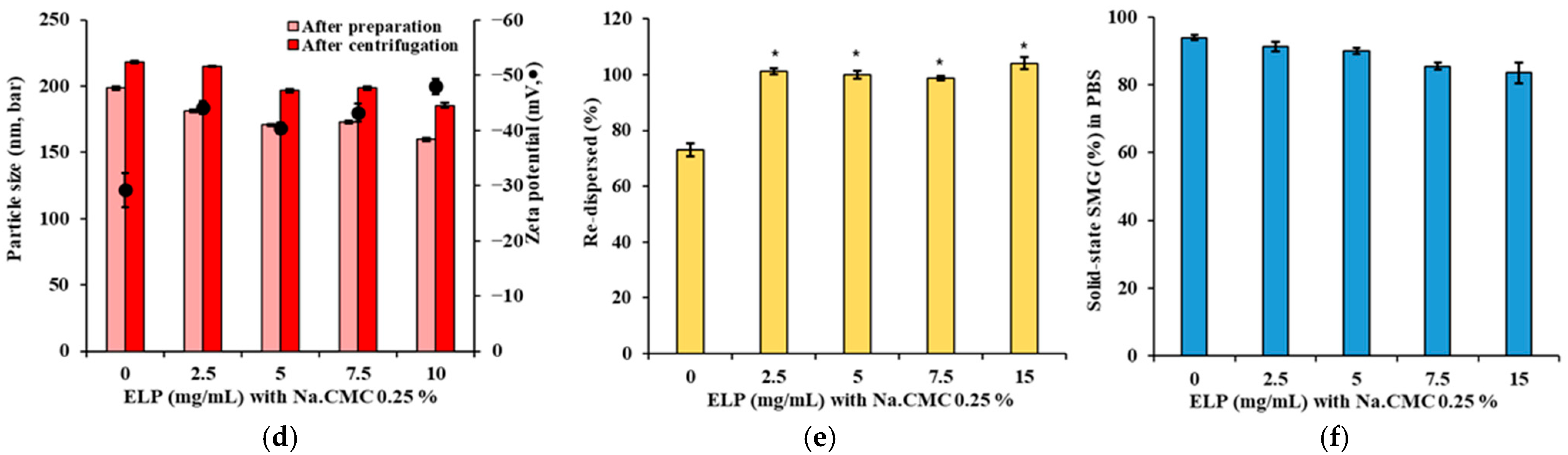
3.2. Effect of Suspending Agent on Size, Re-Dispersibility, and Solubility of SMG-PS-Zn Nanocomplexes
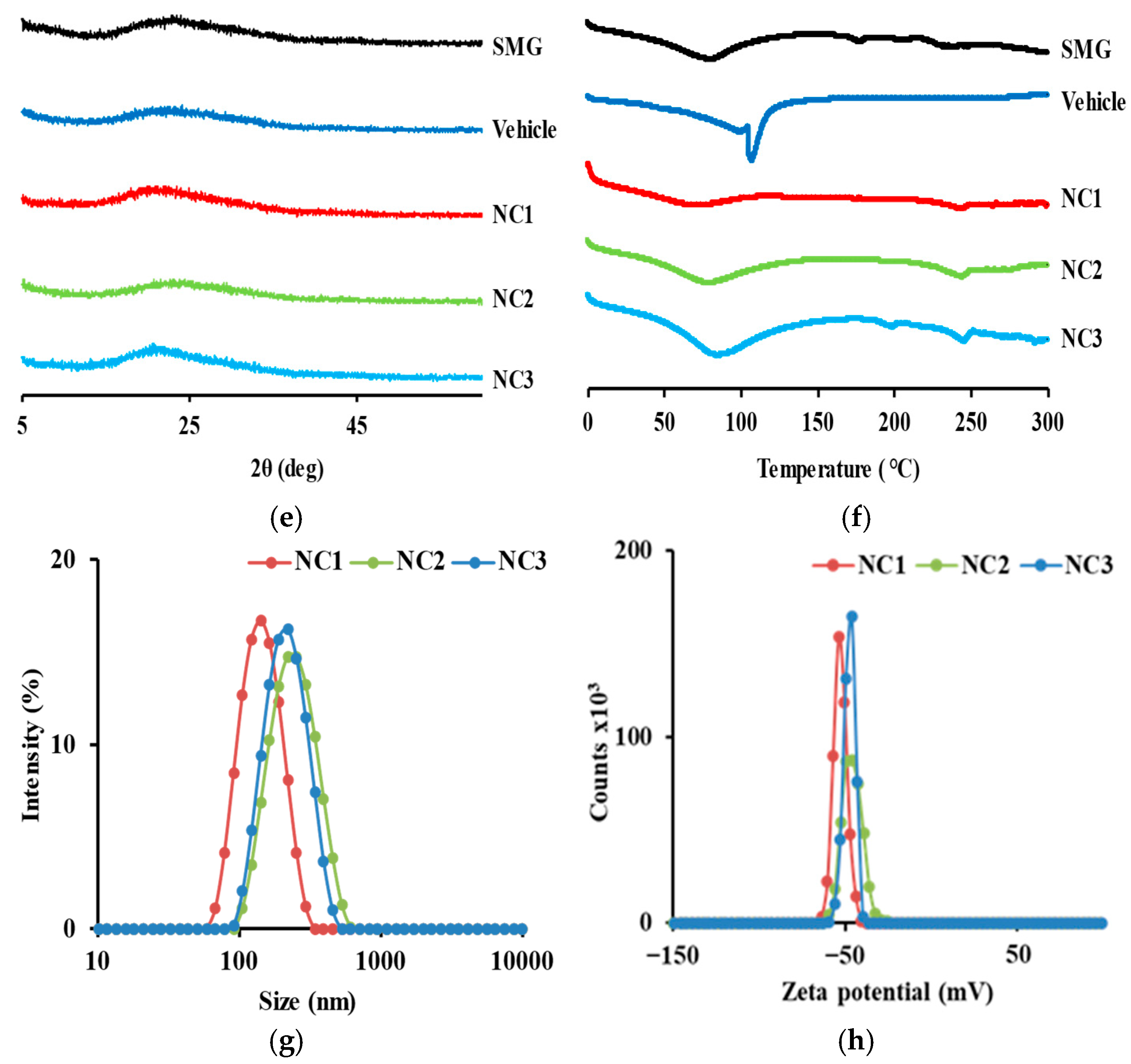
3.3. Optimization of SMG-PS-Zn Complexes
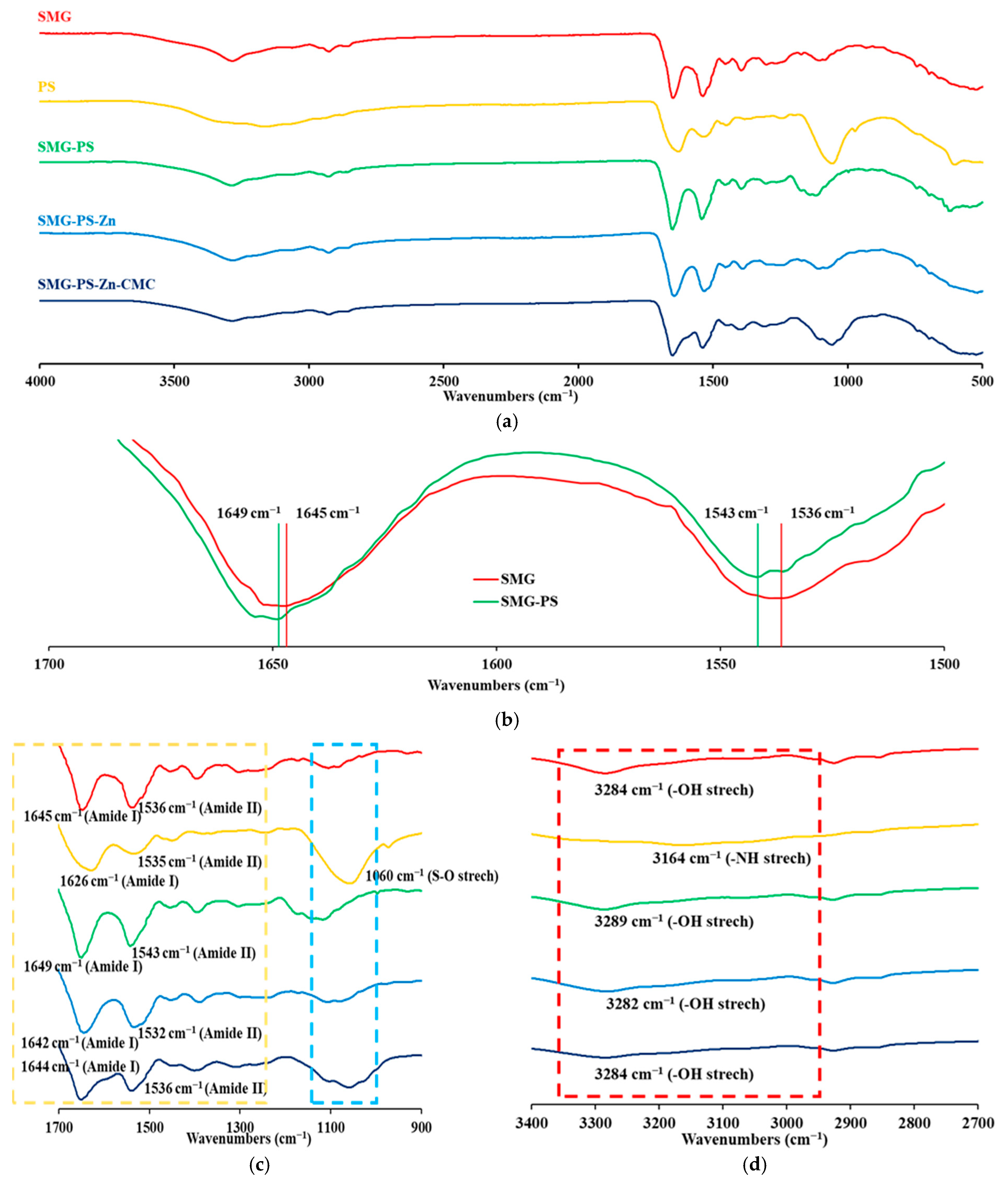
3.4. Interaction Between SMG, PS and Zn in Complexes
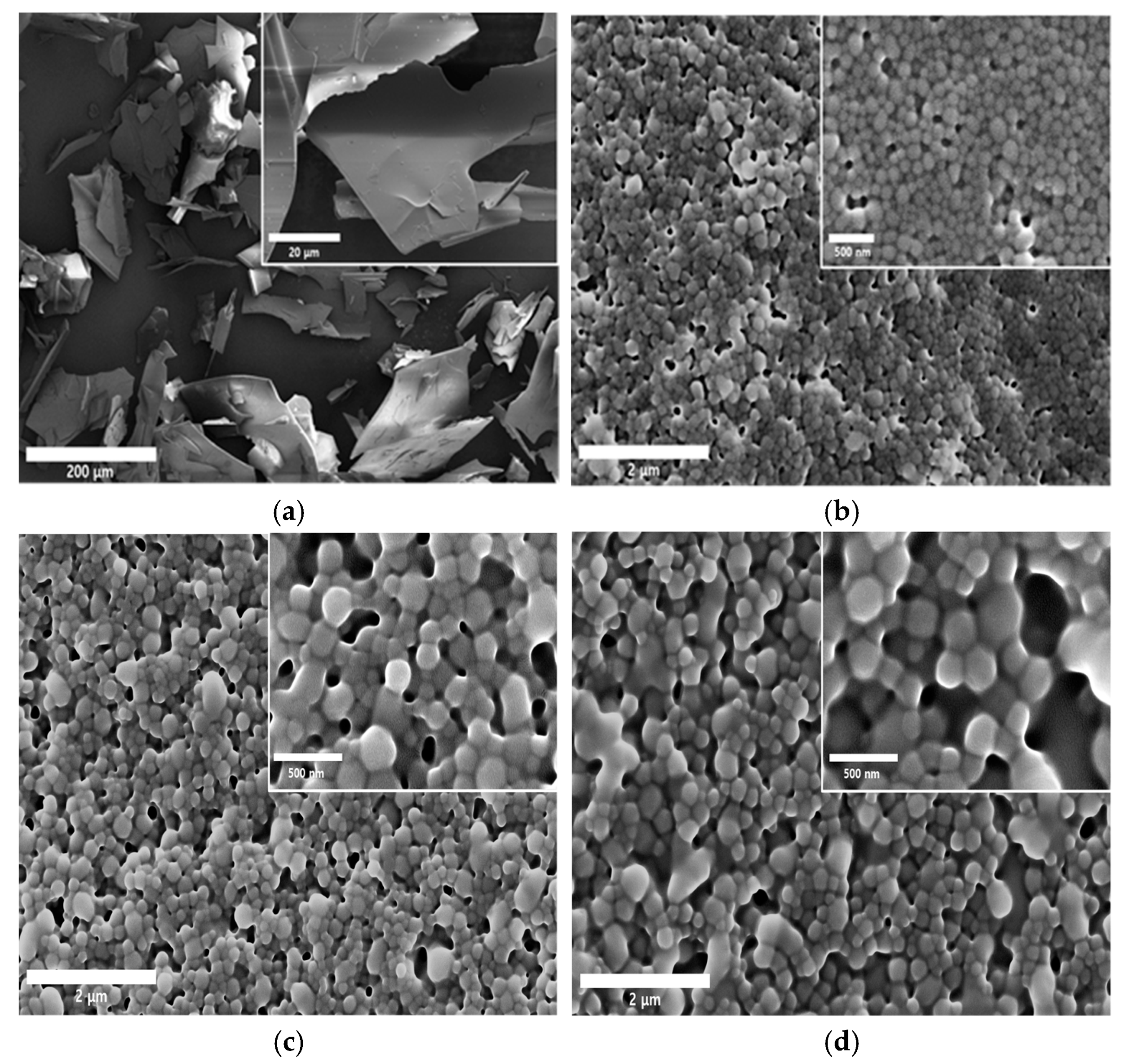
3.5. Morphological and Physical Characteristics of SMG-PS-Zn Nanocomplexes
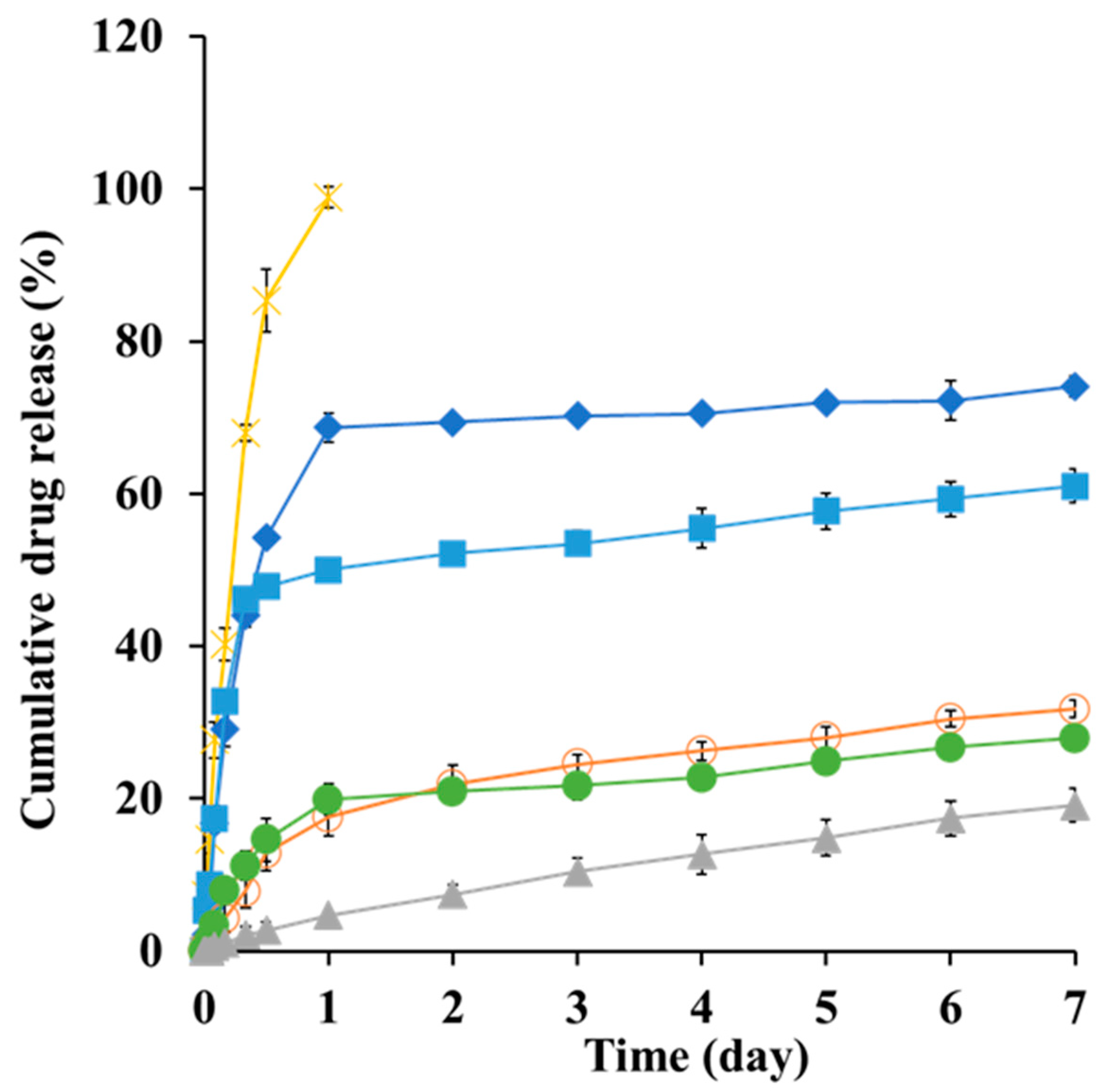
3.6. In Vitro Dissolution Profile of SMG–PS–Zn Nanocomplexes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nuha, A.E.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46 (Suppl. S1), S140–S157. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor: Mechanisms and Advances in Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.; Færch, L.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Paksseresht, A.; Pedersen, S.D.; Perreault, L.; Rosenstock, J.; Shimomura, I.; Viljoen, A.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. STEP 2 Study Group. Semaglutide 2·4 mg Once a Week in Adults with Overweight or Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes (STEP 2): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerre Knudsen, L.; Lau, J. The Discovery and Development of Liraglutide and Semaglutide. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.; Bloch, P.; Schäffer, L.; Pettersson, I.; Spetzler, J.; Kofoed, J.; Knudsen, L.B.; McGuire, J.; Steensgaard, D.B.; Strauss, H.M.; et al. Discovery of the Once-Weekly Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Analogue Semaglutide. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7370–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanselius, M.; Searle, S.; Rodler, A.; Tenje, M.; Abrahmsén-Alami, S.; Hansson, P. Microfluidics Platform for Studies of Peptide–Polyelectrolyte Interaction. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 621, 121785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellido, V.; Padín, C.A.; Catarig, A.-M.; Clark, A.; Pittol, S.B.; Delgado, E. Once-Weekly Semaglutide Use in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Results from the SURE Spain Multicentre, Prospective, Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.G.; Chang, S.G. Sustained-Release Formulation Development and Preclinical Evaluations of Monthly or Bimonthly Injectable Semaglutide and Tirzepatide. Diabetes 2023, 72 (Suppl. S1), 781-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, T.R.; Honorio, T.; Souza Domingos, T.F.; da Silva Candido de Paula, D.; Mendes Cabral, L.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Abrahim-Vieira, B.A. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modelling of Semaglutide in Children and Adolescents with Healthy and Obese Body Weights. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 89, 3175–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonora, B.M.; Russo, G.; Leonetti, F.; Strazzabosco, M.; Nollino, L.; Aimaretti, G.; Giaccari, A.; Broglio, F.; Consoli, A.; Avogaro, A.; et al. Effectiveness of Oral Semaglutide on Glucose Control and Body Weight up to 18 Months: A Multicenter Retrospective Real–World Study. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2024, 47, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo Nordisk Inc. Ozempic® (Semaglutide) Injection, Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.novo-pi.com/ozempic.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2025.).
- Yang, X.-D.; Yang, Y.-Y. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Semaglutide: A Systematic Review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 2567–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Yang, X. Semaglutide Sustained-Release Microspheres with Single-Phase Zero-Order Release Behavior: Effects of Polymer Blending and Surfactants. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 107, 106793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Esteban, S.; Alcalde, I.; Chacón, M.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; de la Fuente, M.; Csaba, N. Protamine Nanocapsules as Gene Delivery Carriers for the Treatment of Intraocular Tumors. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.; Lipiński, W.P.; Wang, J.; Spruijt, E. Peptide-based coacervates as biomimetic protocells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 3690–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sida, R.; Yuanyuan, G.; Liu, B.; Gao, H.; Hu, X.; Hao, H.; Jin, L.; Cai, T. Long-Acting Release Microspheres Containing Novel GLP-1 Analog as an Antidiabetic System. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2857–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, C.J.; Faulds, D. Nateglinide. Drugs 2000, 60, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohilla, K.K.; Pandey, M.K. Computational Approach to Elucidating Insulin–Protamine Binding Interactions and Dynamics in Insulin NPH Formulations. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 4857–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshargabi, R.; Harada, K.; Ishikado, A. Protamine: Current Insights and Evolving Applications. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2024, 11, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheicher, B.; Lorenzer, C.; Gegenbauer, K.; Partlic, J.; Andreae, F.; Kirsch, A.H.; Zimmer, A. Manufacturing of a Secretoneurin Drug Delivery System with Self-Assembled Protamine Nanoparticles by Titration. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Esteban, S.; Reimóndez-Troitiño, S.; Cabezas-Sainz, P.; de la Fuente, M.; Sánchez, L.; Rahman, R.; Alexander, C.; Garcia-Fuentes, M.; Csaba, N.S. Protamine-Based Nanotherapeutics for Gene Delivery to Glioblastoma Cells. Mol. Pharm. 2025, 22, 2466–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Weber, S.G. A High-Throughput Method for Lipophilicity Measurement. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Moon, S.; Lee, J.; Na, Y.; Jeong, H.; Lee, J.; Seol, E.; Lee, H. Sustained Release-Microsphere Formulation Comprising Semaglutide and Preparation Method Therefor. European Patent Application EP 4552634 A1, 14 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Na, Y.; Kim, H.; Oh, H.; Seol, E.; Lee, H. Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising Sustained-Release Microspheres Including GLP-1 Analogue or Pharmaceutically Acceptable Salt Thereof. World Intellectual Property Organization Patent Application WO 2021/162532 A3, 19 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shid, R.L.; Dhole, S.N.; Kulkarni, N.; Shid, S.L. Formulation and Evaluation of Nanosuspension Formulation for Drug Delivery of Simvastatin. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 7, 2648–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, C.; He, Y. The Inhibiting Role of Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose Acetate Succinate on Piperine Crystallization to Enhance Its Dissolution from Its Amorphous Solid Dispersion and Permeability. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 39523–39531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbeck, S.; Heise, H.M. Quality Assurance of Commercial Insulin Formulations: Novel Assay Using Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2021, 15, 885–892. [Google Scholar]
- Wolska, E.; Szymańska, M. Comparison of the In Vitro Drug Release Methods for the Selection of Test Conditions to Characterize Solid Lipid Microparticles. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Jha, P.K. Experiments and Modeling of Controlled Release Behavior of Commercial and Model Polymer–Drug Formulations Using Dialysis Membrane Method. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 10, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Tanwar, N.; Singh, A.; Munde, M. Formation of Protamine and Zn–Insulin Assembly: Exploring Biophysical Consequences. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 41044–41057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brange, J.; Langkjoer, L. Insulin Structure and Stability. In Stability and Characterization of Protein and Peptide Drugs; Ahern, T.J., Manning, M.C., Eds.; Pharmaceutical Biotechnology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; Volume 5, pp. 315–350. [Google Scholar]
- Motta, S.; Brocca, P.; Del Favero, E.; Rondelli, V.; Cantù, L.; Amici, A.; Pozzi, D.; Caracciolo, G. Nanoscale Structure of Protamine/DNA Complexes for Gene Delivery. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 053703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitaoja, M.; Valjakka, J.; Jänis, J. Zinc Coordination Spheres in Protein Structures. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 10983–10991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, S.; Geng, Y.; Wang, L. Coordination Behavior of Bis-Imidazole and Various Carboxylate Ligands towards Zn(II) and Cd(II) Ions: Synthesis, Structure, and Photoluminescence Study. Crystals 2018, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugsley, M.K.; Kalra, V.; Froebel-Wilson, S. Protamine Is a Low Molecular Weight Polycationic Amine That Produces Actions on Cardiac Muscle. Life Sci. 2002, 72, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, A.; Sullivan, M.J.; Lee, G.; Bartholomew, J.; Kapadia, S.; Aster, R.H.; Curtis, B.R. Protamine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia. Transfusion 2013, 53, 2158–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eli Lilly and Company. Humulin N (Insulin Isophane Human) Injection, Suspension, Prescribing Information; Eli Lilly and Company: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, S.; Kishimoto, S.; Nakamura, S.; Nambu, M.; Fujita, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Mori, Y.; Tagawa, M.; Maehara, T.; Ishihara, M. Fragmin/Protamine Microparticles as Cell Carriers to Enhance Viability of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells and Their Subsequent Effect on In Vivo Neovascularization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 92, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Ji, W.; Zhao, M.; Wang, M.; Yan, W.; Chen, M.; Ren, S.; Yuan, B.; Wang, B.; Chen, L. Protamine Zinc Insulin Combined with Sodium Selenite Improves Glycometabolism in Diabetic KKAy Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norrman, M.; Hubálek, F.; Schluckebier, G. Structural Characterization of Insulin NPH Formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, M.J.; Soetrisno, D.D.; Park, N.; Conrad, J.C. Aggregation and Gelation in a Tunable Aqueous Colloid–Polymer Bridging System. J. Chem. Phys. 2022, 157, 114903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, R. Bridging Flocculation by Polymers. KONA Powder Part. J. 2013, 30, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.; Shi, L.; Feng, X.; Xiao, L. Electrostatic and Electrosteric Stabilization of Aqueous Suspensions of Barite Nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2009, 192, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Xin, X.; Zhang, Y. Development and Characterization of Promising Cremophor EL-Stabilized o/w Nanoemulsions Containing Short-Chain Alcohols as a Cosurfactant. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 19815–19824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, K.; Kaplan, M.; Çalış, S. Effects of Nanoparticle Size, Shape, and Zeta Potential on Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 666, 124799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubashynskaya, N.V.; Gasilova, E.R.; Skorik, Y.A. Nano-Sized Fucoidan Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes: Effect of Protamine Ratio on Particle Size and Stability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umerska, A.; Paluch, K.J.; Santos-Martinez, M.J.; Tajber, L. Self-Assembled Hyaluronate/Protamine Polyelectrolyte Nanoplexes: Synthesis, Stability, Biocompatibility and Potential Use as Peptide Carriers. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 1090–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.R.; Chun, C.; Cho, C.S.; Song, S.C. Enhancement of Sustained and Controlled Protein Release by Polyelectrolyte Complexes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Chakravarthy, R.D.; Lin, H.-C. Influence of Metal Ion Crosslinking on the Nanostructures, Stiffness, and Biofunctions of Bioactive Peptide Hydrogels. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2022, 7, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meutter, J.; Goormaghtigh, E. Evaluation of Protein Secondary Structure from FTIR Spectra Improved after Partial Deuteration. Eur. Biophys. J. 2021, 50, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Yang, S.; Kong, J.; Dong, A.; Yu, S. Obtaining Information about Protein Secondary Structures in Aqueous Solution Using Fourier Transform IR Spectroscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xia, L.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, F.; Wu, H. A 2-D Zn(II) Coordination Polymer Based on 4,5-Imidazoledicarboxylate and Bis(benzimidazole) Ligands: Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Fluorescence Properties. Z. Naturforsch. B 2021, 76, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A. Infrared Spectroscopy of Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krimm, S.; Bandekar, J. Vibrational Spectroscopy and Conformation of Peptides, Polypeptides, and Proteins. Adv. Protein Chem. 1986, 38, 181–364. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz-Fonfría, V.A. Infrared Difference Spectroscopy of Proteins: From Bands to Bonds. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3466–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.; Mantsch, H.H. The Use and Misuse of FTIR Spectroscopy in the Determination of Protein Structure. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 30, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows, A.P.; Casford, M.T.L.; Davies, P.B. Spectral Analysis and Deconvolution of the Amide I Band of Proteins Presenting with High-Frequency Noise and Baseline Shifts. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 597–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awotwe-Otoo, D.; Agarabi, C.; Keire, D.; Lee, S.; Raw, A.; Yu, L.; Habib, M.J.; Khan, M.A.; Shah, R.B. Physicochemical Characterization of Complex Drug Substances: Evaluation of Structural Similarities and Differences of Protamine Sulfate from Various Sources. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Newman, A.; Engers, D.; Bates, S.; Ivanisevic, I.; Kelly, R.C.; Zografi, G. Characterization of Amorphous API:Polymer Mixtures Using X-ray Powder Diffraction. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4840–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, C.; Ladisa, M.; Altamura, D.; Siliqi, D.; Sibillano, T.; De Caro, L. X-ray Diffraction: A Powerful Technique for the Multiple-Length-Scale Structural Analysis of Nanomaterials. Crystals 2016, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.; Agrawal, S.; Cherumukkil, S.; Sharma, V.; Jasra, R.V.; Munshi, P. Revisiting Zeta Potential, the Key Feature of Interfacial Phenomena, with Applications and Recent Advancements. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 1234–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, W.; Dyba, M.; Szewczuk, Z.; Jeżowska-Bojczuk, M.; Kasprzak, K.S. Differential Zinc and DNA Binding by Partial Peptides of Human Protamine HP2. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 222, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.; Leung, D.; Famili, A.; Chang, D.; Nayak, P.; Al-Sayah, M. Accelerated In Vitro Release Testing Method for a Long-Acting Peptide–PLGA Formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 165, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochańczyk, T.; Drozd, A.; Krężel, A. Relationship between the Architecture of Zinc Coordination and Zinc Binding Affinity in Proteins—Insights into Zinc Regulation. Metallomics 2015, 7, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajanna, D.; Pushpadass, H.A.; Emerald, F.M.E.; Padaki, N.V.; Nath, B.S. Nanoencapsulation of Casein-Derived Peptides within Electrospun Nanofibres. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1684–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruseska, I.; Fresacher, K.; Petschacher, C.; Zimmer, A. Use of Protamine in Nanopharmaceuticals—A Review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboubian, A.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Valizadeh, H.; Zakeri-Milani, P.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Javadzadeh, Y. Preparation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Controlled Release Triptorelin Microspheres. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 641–649. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, L.; Helleberg, H.; Roffel, A.; van Lier, J.J.; Bjørnsdottir, I.; Pedersen, P.J.; Rowe, E.; Derving Karsbøl, J.; Pedersen, M.L. Absorption, Metabolism and Excretion of the GLP-1 Analogue Semaglutide in Humans and Nonclinical Species. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 104, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Ozempic (INN-Semaglutide)—EPAR Public Assessment Report; European Medicines Agency (EMA): London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, I.G.; Kim, J.-S.; Kang, M.J. Design of Electrostatic Nanocomplex of Semaglutide with Protamine and Zinc for Subcutaneous Prolonged Delivery. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181399
Yang IG, Kim J-S, Kang MJ. Design of Electrostatic Nanocomplex of Semaglutide with Protamine and Zinc for Subcutaneous Prolonged Delivery. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(18):1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181399
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, In Gyu, Jeong-Soo Kim, and Myung Joo Kang. 2025. "Design of Electrostatic Nanocomplex of Semaglutide with Protamine and Zinc for Subcutaneous Prolonged Delivery" Nanomaterials 15, no. 18: 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181399
APA StyleYang, I. G., Kim, J.-S., & Kang, M. J. (2025). Design of Electrostatic Nanocomplex of Semaglutide with Protamine and Zinc for Subcutaneous Prolonged Delivery. Nanomaterials, 15(18), 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181399





