The Influence of Light Rare-Earth Substitution on Electronic and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Morphology and Crystal Structure
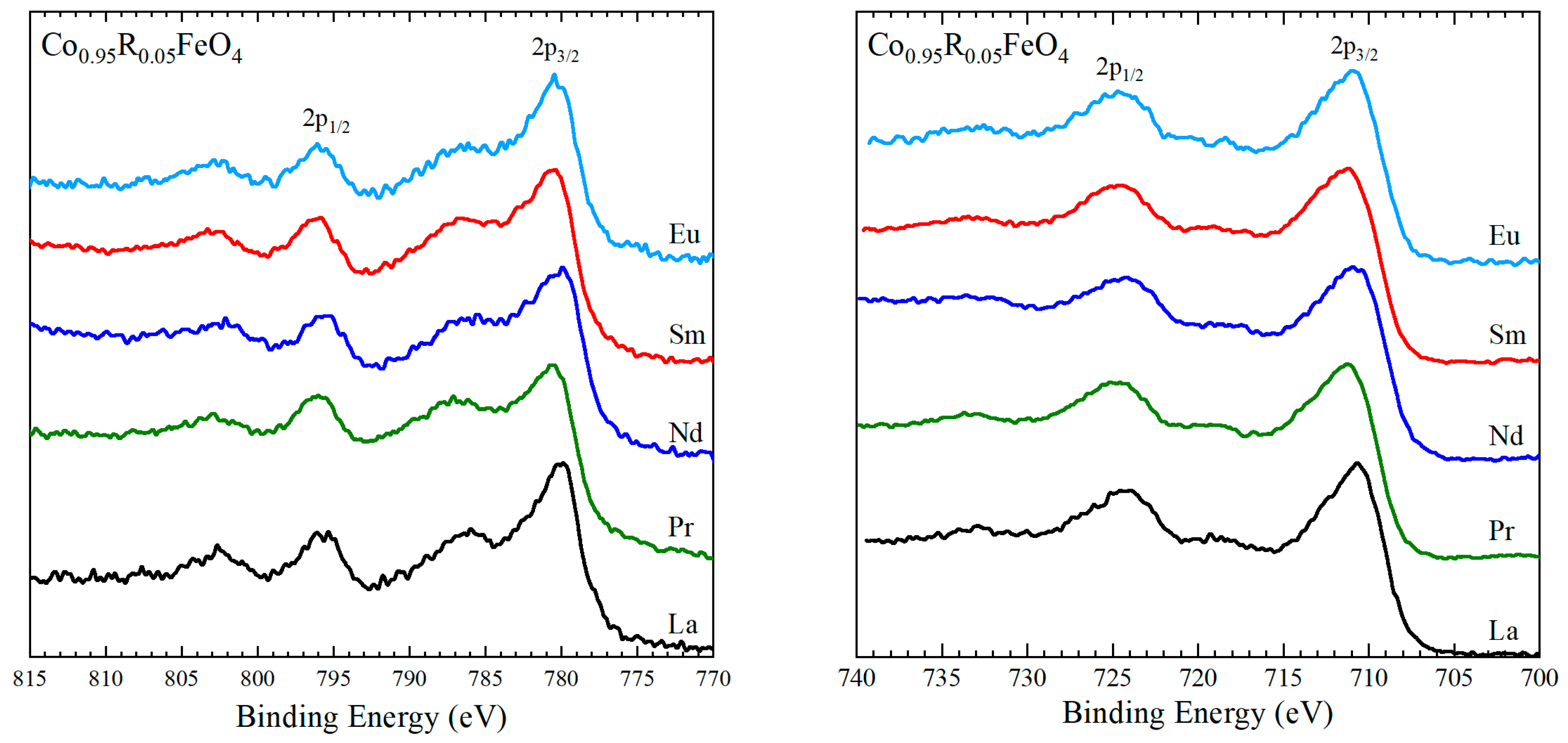
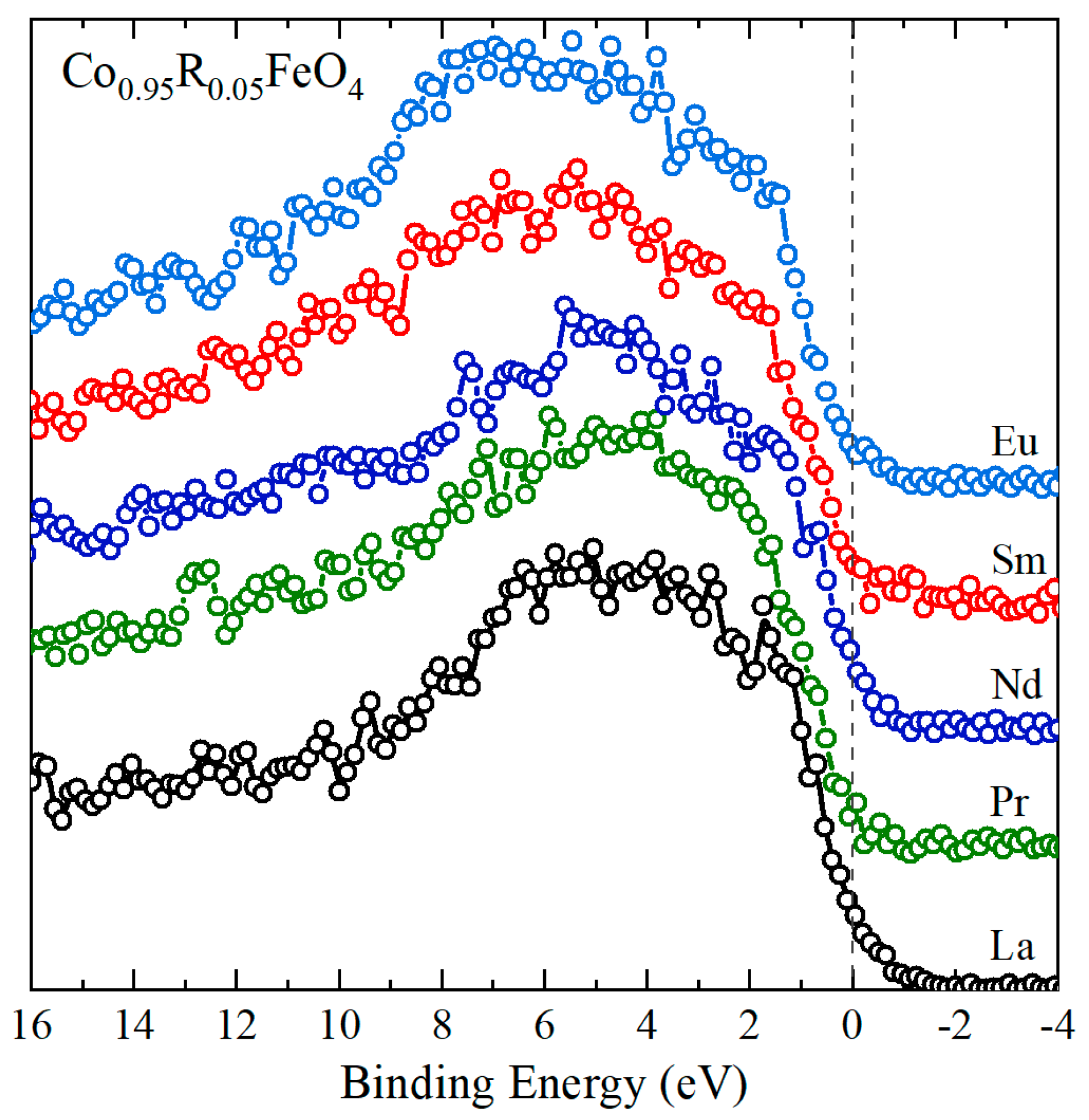
3.2. XPS Results
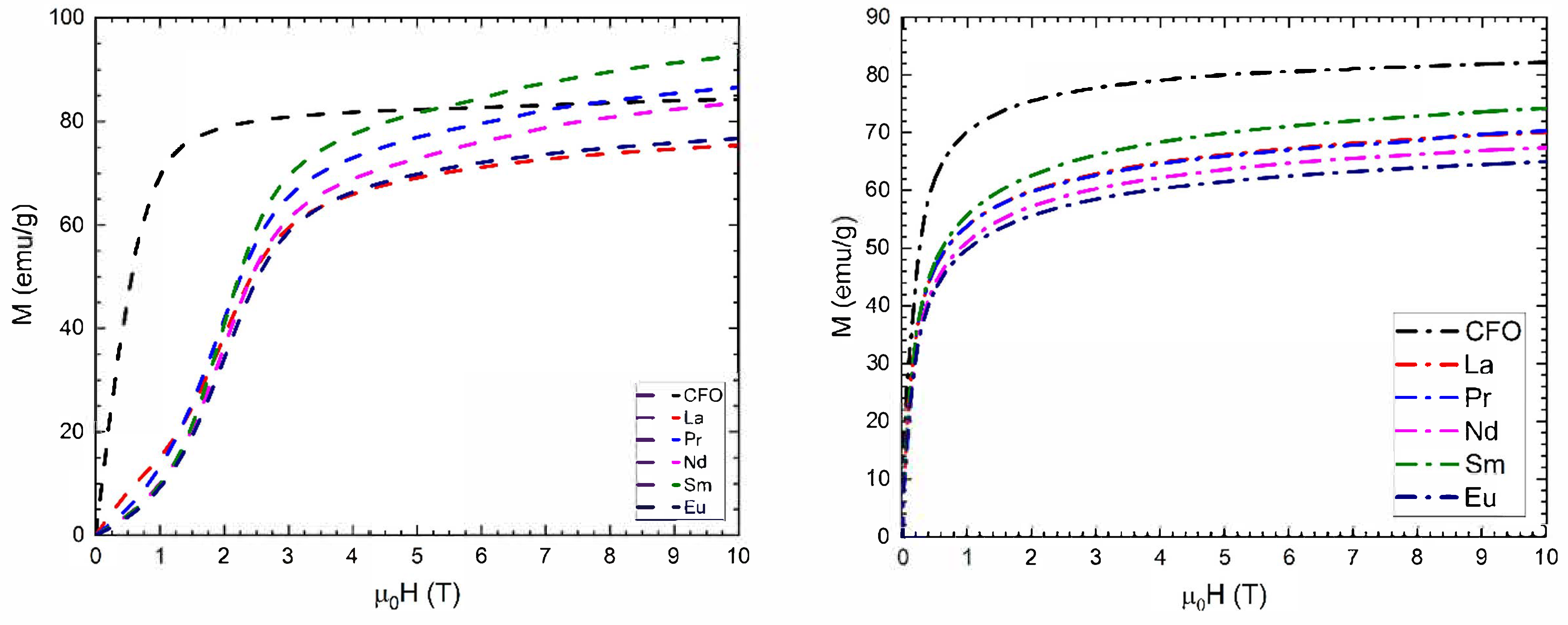
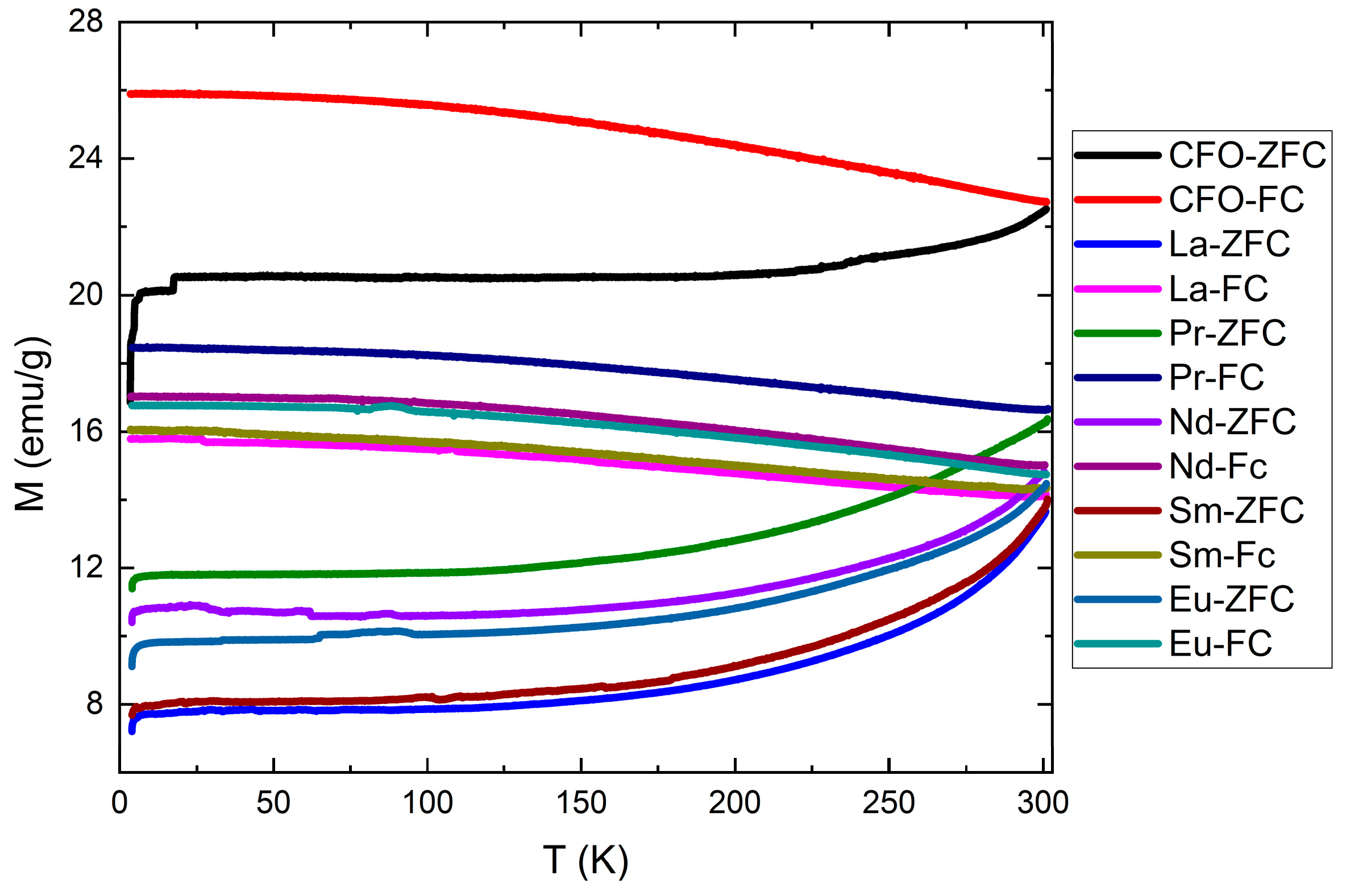
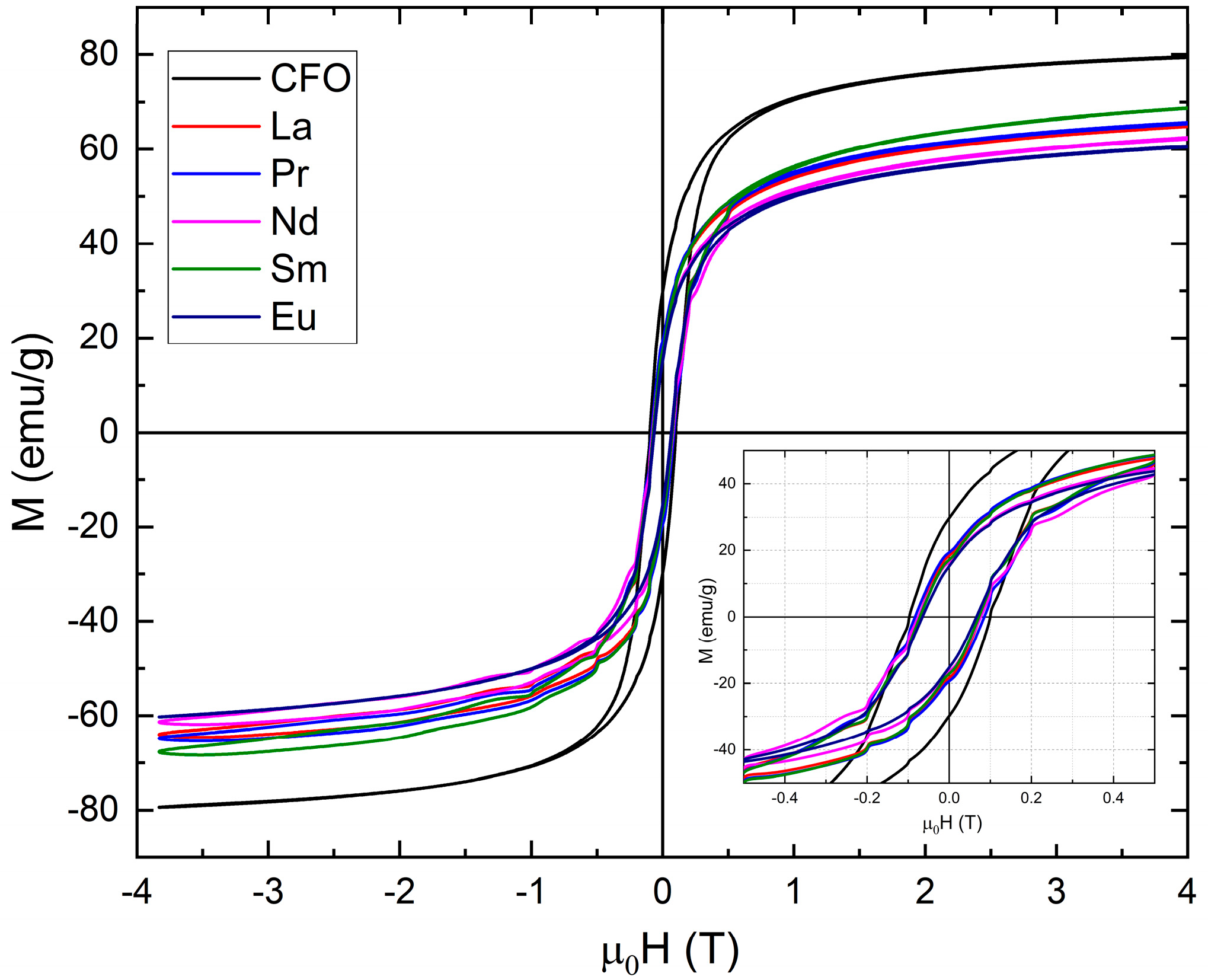
3.3. Magnetic Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, J.; Roy, S.; Xie, M.; Yang, X.; Guo, B. Contrast Agents of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Future Perspective. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karageorgou, M.-A.; Bouziotis, P.; Stiliaris, E.; Stamopoulos, D. Radiolabeled Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Dual Modality Contrast Agents in SPECT/MRI and PET/MRI. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, D.C.; Misra, M.; Das, A.R. Structure and Magnetization Studies of Ti-Substituted Ni0.3 Zn0.7Fe2O4. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, 2722–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodelalová, J.; Rittich, B.; Spanová, A.; Petrová, K.; Benes, M.J. Isolation of Genomic DNA Using Magnetic Cobalt Ferrite and Silica Particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1056, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, S.; Shokrollahi, H. The Role of Cobalt Ferrite Magnetic Nanoparticles in Medical Science. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Španová, A.; Rittich, B.; Beneš, M.J.; Horák, D. Ferrite Supports for Isolation of DNA from Complex Samples and Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1080, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aram, E.; Moeni, M.; Abedizadeh, R.; Sabour, D.; Sadeghi-Abandansari, H.; Gardy, J.; Hassanpour, A. Smart and Multi-Functional Magnetic Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment Applications: Clinical Challenges and Future Prospects. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.Y.; Paknikar, K.M.; Bodas, D.; Gajbhiye, V. Applications of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles in Biomedical Nanotechnology. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, W.; Torbett-Dougherty, M.; Islam, A.; Soleimani, S.; Bruce-Tagoe, T.A.; Johnson, J.A. Magnetic Nanoparticles and Drug Delivery Systems for Anti-Cancer Applications: A Review. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Chen, D.; Shang, P.; Yin, D.-C. A Review of Magnet Systems for Targeted Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2019, 302, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehere, A.C.; Jadhav, V.R.; Kasabe, S.M.; Rathod, S.M. Ni2+ Doped Cobalt Nano-Ferrite for Gas Sensing Application. Results Surf. Interfaces 2025, 18, 100461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Ravi, B.G.; Sampath, S.; Gambino, R.J. Atmospheric Plasma Sprayed Cobalt Ferrite Coatings for Magnetostrictive Sensor Applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 2391–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharamaiah, P.N.; Shashanka, H.M.; Srinivasan, S.; Das, D.; El-Gendy, A.A.; Ramana, C.V. Structural, Magnetic, and Magnetostriction Properties of Flexible, Nanocrystalline CoFe2O4 Films Made by Chemical Processing. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 43813–43819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himcinschi, C.; Vrejoiu, I.; Salvan, G.; Fronk, M.; Talkenberger, A.; Zahn, D.R.T.; Rafaja, D.; Kortus, J. Optical and Magneto-Optical Study of Nickel and Cobalt Ferrite Epitaxial Thin Films and Submicron Structures. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 084101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.-X.; Jia, J.-T.; Xu, Z.-G.; Zhou, B.; Liao, C.-S.; Yan, C.-H.; Chen, L.-Y.; Zhao, H.-B. Microstructure, Magnetic, and Magneto-Optical Properties of Chemical Synthesized Co–RE (RE=Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu) Ferrite Nanocrystalline Films. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 2727–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, M.R.; De Gouveia, G.L.; Dalla Costa, L.J.; De Oliveira, A.J.A.; Kiminami, R.H.G.A. Microwave Assisted Combustion Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystalline Nickel-Doped Cobalt Ferrites. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fannin, P.C.; Marin, C.N.; Malaescu, I.; Stefu, N.; Vlazan, P.; Novaconi, S.; Sfirloaga, P.; Popescu, S.; Couper, C. Microwave Absorbent Properties of Nanosized Cobalt Ferrite Powders Prepared by Coprecipitation and Subjected to Different Thermal Treatments. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1600–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.I. Nano Cobalt Ferrites: Doping, Structural, Low-Temperature, and Room Temperature Magnetic and Dielectric Properties—A Comprehensive Review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 562, 169840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayakvad, K.; Somdatta, K.; Mathe, V.; Dongale, T.; W, M.; Patankar, K. Spinel Ferrites for Resistive Random Access Memory Applications. Emergent Mater. 2024, 7, 103–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinosha, P.A.; Manikandan, A.; Ceicilia, A.S.J.; Dinesh, A.; Nirmala, G.F.; Preetha, A.C.; Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.; Baykal, A.; Xavier, B. Review on recent advances of zinc substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Synthesis characterization and diverse applications. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 10512–10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukoviene, A.; Ali, S.; Jagminas, A.; Ramanavicius, S. Magnetic Cobalt and Other Types of Ferrite Nanoparticles: Synthesis Aspects and Novel Strategies for Application in Wastewater Treatment (Review). Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, R.N.; Shih, J.C.; Chin, T.S. Magnetic Properties of Nano-Crystalline Gd- or Pr-Substituted CoFe2O4 Synthesized by the Citrate Precursor Technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 257, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirosh, E.; Shemer, G.; Markovich, G. Optimizing Cobalt Ferrite Nanocrystal Synthesis Using a Magneto-Optical Probe. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Guo, M.; Li, Z.; Qin, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Gong, H. Study on Structure and Magnetic Properties of Rare Earth Doped Cobalt Ferrite: The Influence Mechanism of Different Substitution Positions. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 14046–14056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasrotia, R.; Prakash, J.; Saddeek, Y.B.; Alluhayb, A.H.; Younis, A.M.; Lakshmaiya, N.; Prakash, C.; Aly, C.A.; Sillanpää, M.; Ismail, Y.A.M.; et al. Cobalt ferrites: Structural insights with potential applications in magnetics, dielectrics, and Catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 522, 216198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemasankari, S.; Priyadharshini, S.; Thangaraju, D.; Sathiyanarayanamoorthi, V.; Al Sdran, N.; Shkir, M. Effect of neodymium (Nd) doping on the photocatalytic organic dye degradation performance of sol-gel synthesized CoFe2O4 self-assembled microstructures. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2023, 660, 414870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulhakem, O.; Belaiche, M.; El Ansary, M.; Lemine, M.A.; Salameh, B.; Alsmadi, A.K.M.; Alaoui, K.B. (Y3+/Sm3+)-doped and co-doped CoFe2O4 for heterogeneous advanced oxidation process: Structural, magneto-optical, and photocatalytic investigations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 57623–57644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsath, S.E.; Kadam, R.H.; Patange, S.M.; Mane, M.L.; Ghasemi, A.; Morisako, A. Enhanced Magnetic Properties of Dy3+ Substituted Ni-Cu-Zn Ferrite Nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 042407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ederer, C.; Spaldin, N.A. Weak Ferromagnetism and Magnetoelectric Coupling in Bismuth Ferrite. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 060401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, I.A. Indirect Exchange for Rare Earths in Metals. J. Phys. F Met. Phys. 1972, 2, L47–L50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, H.; Kawabata, J.; Fujita, K.; Murai, S.; Tanaka, K. Magnetic Properties of Oxide Glasses Containing Iron and Rare-Earth Ions. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 144408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezlescu, E.; Rezlescu, N.; Popa, P.D.; Rezlescu, L.; Pasnicu, C. The Influence of R2O3 (R = Yb, Er, Dy, Tb, Gd, Sm and Ce) on the Electric and Mechanical Properties of a Nickel–Zinc Ferrite. Phys. Status Solidi A 1997, 162, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.A.; Wafk, A.H.; El-Shokroty, K.M.; El-Tabby, M.M. Magnetic Properties of Cu–Zn Ferrites Doped with Rare Earth Oxides. Phys. Status Solidi A 1999, 171, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.; Raghasudha, M.; Meena, S.S.; Shah, J.; Shirsath, S.E.; Kumar, S.; Ravinder, D.; Bhatt, P.; Alimuddin Kumar, R.; Kotnala, R.K. Influence of rare earth ion doping (Ce and Dy) on electrical and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 449, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.P.; Mukherjee, S. Disordered surface spins induced large exchange anisotropy in single-phase Sm3+ ions substituted nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 489, 165320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R.; Ghosh, M.P.; Mukherjee, S. Size dependent exchange bias in single-phase Zn0.3Ni0.7Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 458, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mang, C.; Ma, Z.; Luo, J.; Rao, M.; Zhang, X.; Peng, Z. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of cobalt-zinc ferrite nanoparticles doped with rare earth elements. J. Rare Earths 2020, 39, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Hojamberdiev, M.; Xu, Y.; Cao, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, H. Hydrothermal synthesis and magnetic properties of gadolinium-doped CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elayakumar, K.; Dinesh, A.; Manikandan, A.; Palanivelu, M.; Kavitha, G.; Prakash, S.; Thilak Kumar, R.; Jaganathan, S.K.; Baykal, A. Structural, morphological, enhanced magnetic properties and antibacterial bio-medical activity of rare earth element (REE) Cerium (Ce3+) doped CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 476, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaqat, A.; Almessiere, M.; Slimani, Y.; Guner, S.; Sertkol, M.; Albetran, H.; Baykal, A.; Shirsath, S.E.; Ozcelik, B.; Ercan, I. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Tb3+ substituted Co nanoferrites prepared via sonochemical approach. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 22538–22546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanbir, K.; Ghosh, M.P.; Singh, R.K.; Kar, M.; Mukherjee, S. Effect of doping different rare earth ions on microstructural, optical, and magnetic properties of nickel–cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugutkar, A.B.; Gore, S.K.; Tumberphale, U.B.; Jadhav, V.V.; Mane, R.S.; Patange, S.M.; Shirsath, S.E.; Jadhav, S.S. Role of composition and grain size to control the structure sensitive magnetic properties of Sm3+ substituted nanocrystalline Co-Zn ferrites. J. Rare Earths 2020, 38, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, R.H.; Shitole, R.; Kadam, S.B.; Desai, K.; Birajdar, A.P.; Barote, V.K.; Batoo, K.M.; Hussain, S.; Shirsath, S.E. A thorough Investigation of Rare-Earth Dy3+ Substituted Cobalt-Chromium Ferrite and Its Magnetoelectric Nanocomposite. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.A.; Demir Korkmaz, A.; Baykal, A.; Gondal, M.A.; Güngünes, H.; Shirsath, S.E.; Manikandan, A. Structural, morphological, and magnetic properties of (Ni0.5Co0.5)[GaxGdxFe2–2x]O4 nanoparticles prepared via sonochemical approach. J. Rare Earths 2023, 41, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascalu, G.; Popescu, T.; Feder, M.; Caltun, O.F. Structural, Electric and Magnetic Properties of CoFe1.8RE0.2O4 (RE=Dy, Gd, La) Bulk Materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 333, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daha, R.; Bouloudenine, M.; Khiat, A.; Gomez, C.V.; La Pietra, M.; Tibermacine, I.E.; Alleg, S.; Rabehi, A.; Bellucci, S. Enhancement of Cobalt Ferrite Properties through Rare Earth Ion Doping. Semiconductors 2024, 58, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounkachi, O.; Lamouri, R.; Abraime, B.; Ez-Zahraouy, H.; El Kenz, A.; Hamedoun, M.; Benyoussef, A. Exploring the Magnetic and Structural Properties of Nd-Doped Cobalt Nano-Ferrite for Permanent Magnet Applications. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 14401–14404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ding, Z.; Song, N.; Li, L.; Wang, W. Effect of the Rare-Earth Substitution on the Structural, Magnetic and Adsorption Properties in Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 4246–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachpinde, A.M.; Langade, M.M.; Lohar, K.S.; Patange, S.M.; Shirsath, S.E. Impact of Larger Rare Earth Pr3+ Ions on the Physical Properties of Chemically Derived PrxCoFe2−xO4 Nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. 2014, 429, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Mahmood, A.; Cheong, W.-C.; Ali, I.; Khan, M.A.; Chughtai, A.H.; Ashiq, M.N. Structural, Morphological and Magnetic Properties of Eu-Doped CoFe2O4 Nano-Ferrites. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 3203–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souca, G.; Dudric, R.; Iacovita, C.; Moldovan, A.; Frentiu, T.; Stiufiuc, R.; Lucaciu, C.M.; Tetean, R.; Burzo, E. Physical properties of Zn doped Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2020, 22, 298–302. Available online: https://joam.inoe.ro/articles/physical-properties-of-zn-doped-fe3o4-nanoparticles/fulltext (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Szatmari, A.; Bortnic, R.; Souca, G.; Hirian, R.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Nekvapil, F.; Iacovita, C.; Burzo, E.; Dudric, R.; Tetean, R. The Influence of Zn Substitution on Physical Properties of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatmari, A.; Bortnic, R.; Atanasov, R.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Nekvapil, F.; Dudric, R.; Tetean, R. Enhanced Magnetic Properties of Co1−xMnxFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2024, 15, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A Profile Refinement Method for Nuclear and Magnetic Structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, P.; Sullivan, J.L. A Study of the Core Level Electrons in Iron and Its Three Oxides by Means of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1983, 16, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graat, P.C.J.; Somers, M.A.J. Simultaneous Determination of Composition and Thickness of Thin Iron-Oxide Films from XPS Fe 2p Spectra. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1996, 100–101, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS Spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ Ions in Oxide Materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, T.; Naumkin, A.; Sidorov, A.; Eremenko, I.; Kiskin, M. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectra and Electron Structure of Polynuclear Cobalt Complexes. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2007, 156–158, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, A.; Yang, D.; Chin, W.K.; Tamang, B.; Sahoo, S.; Yancey, P.; Mahbub, R.; Shield, J.; Lai, R.Y.; Xu, X.; et al. An Interpretation for the Components of 2p3/2 Core Level X-Ray Photoelectron Spectra of the Cations in Some Inverse Spinel Oxides. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2024, 36, 285001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, S.R.; Salker, A.V. Change in the Magnetostructural Properties of Rare Earth Doped Cobalt Ferrites Relative to the Magnetic Anisotropy. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 2740–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, N.S.; Cook, M.G. X-Ray Photoelectron Studies on Some Oxides and Hydroxides of Cobalt, Nickel, and Copper. Anal. Chem. 1975, 47, 2208–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.Y.; Tsunemaru, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Takeichi, Y.; Harasawa, A.; Yaji, K.; Kim, S.; Kakizaki, A. Valence Band Structure and Magnetic Properties of Co-Doped Fe3O4(100) Films. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 123919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langell, M.A.; Anderson, M.D.; Carson, G.A.; Peng, L.; Smith, S. Valence-Band Electronic Structure of Co3O4 epitaxy on CoO(100). Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 4791–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, H.Y.; Han, W.Q.; Lee, T.-L.; Tadich, A.; Qi, D.-C.; Qiao, L.; et al. Electronic Structure Andp-Type Conduction Mechanism of Spinel Cobaltite Oxide Thin Films. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 100, 115301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Mao, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, P.; Tong, Y. Electrochemical synthesis of CoFe2O4 porous nanosheets for visible light driven photoelectrochemical applications. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 2965–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolotyrkin, Y.M.; Belova, I.D.; Roginskaya, Y.E.; Kozhevnikov, V.B.; Zakhar’in, D.S.; Venevtsev, Y.N. High-spin configuration of Co(III) in nonstoichiometric Co3O4 films. XPS investigations. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1984, 11, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Gahlawat, N.; Punia, P.; Kharbanda, S.; Ravelo, B.; Thakur, A. Cobalt Nanoferrites: A Review on Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications. J Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2022, 35, 2639–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhar, S.; Kaur, J.; Goyal, A.; Singhal, S. Tuning the Properties of Cobalt Ferrite: A Road towards Diverse Applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97694–97719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.P.; Kumar, H.; Srivastava, R.C.; Singhal, A.; Sarin, N.; Chae, K.H. Solubility Limit, Magnetic Interaction and Conduction Mechanism in Rare Earth Doped Spinel Ferrite. Appl. Sci. Lett. 2016, 2, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifianjazi, F.; Moradi, M.; Parvin, N.; Nemati, A.; Jafari Rad, A.; Sheysi, N.; Abouchenari, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Karbasi, S.; Ahmadi, Z.; et al. Magnetic CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles Doped with Metal Ions: A Review. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 18391–18412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lievanos, K.R.; Stair, J.L.; Knowles, K.E. Cation Distribution in Spinel Ferrite Nanocrystals: Characterization, Impact on their Physical Properties, and Opportunities for Synthetic Control. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 4291–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacovita, C.; Stiufiuc, G.F.; Dudric, R.; Vedeanu, N.; Tetean, R.; Stiufiuc, R.I.; Lucaciu, C.M. Saturation of Specific Absorption Rate for Soft and Hard Spinel Ferrite Nanoparticles Synthesized by Polyol Process. Magnetochemistry 2020, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtan, U.; Topkaya, R.; Baykal, A.; Toprak, M.S. Temperature Dependent Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4/CTAB Nanocomposite Synthesized by Sol–Gel Auto-Combustion Technique. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 6551–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
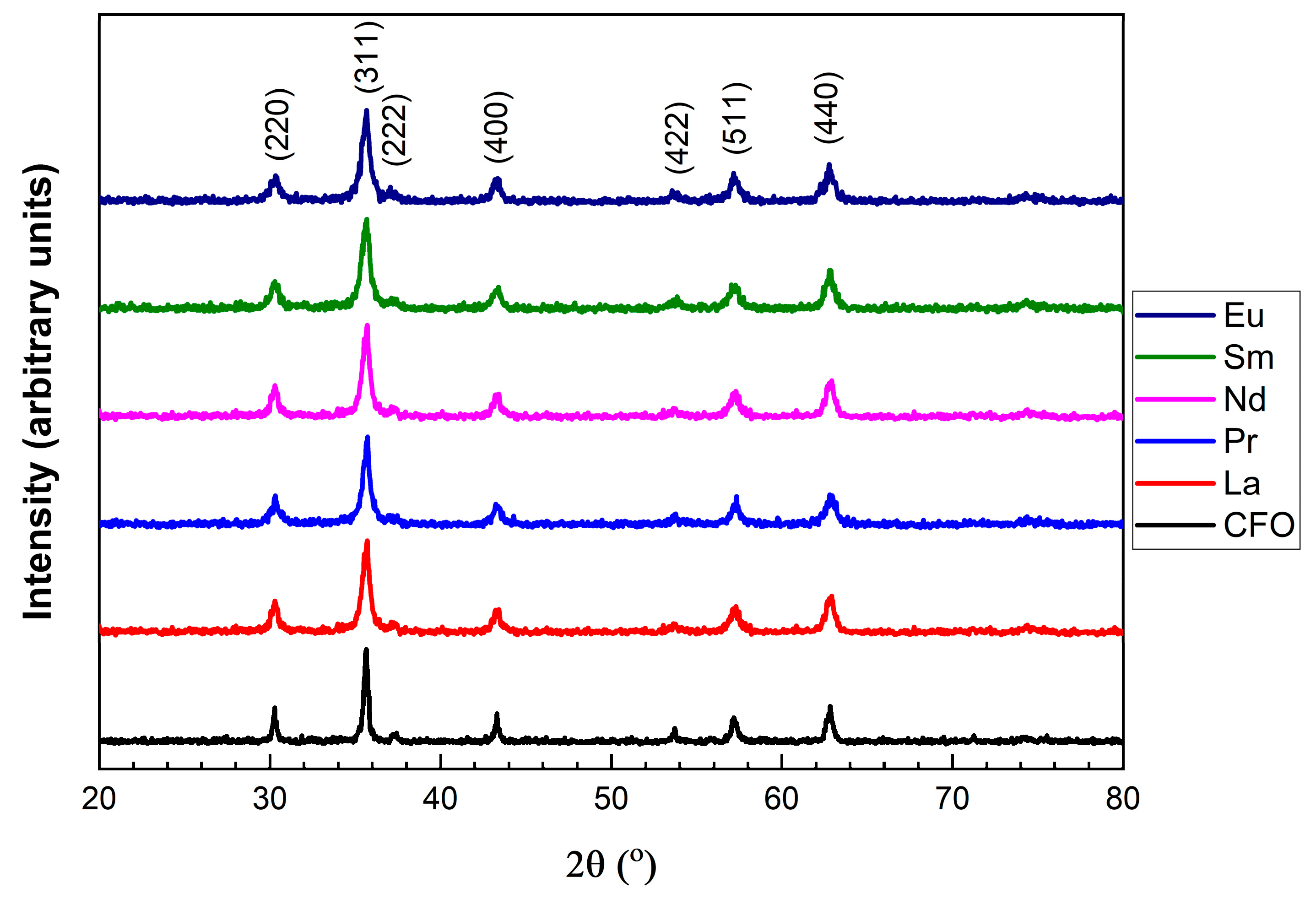
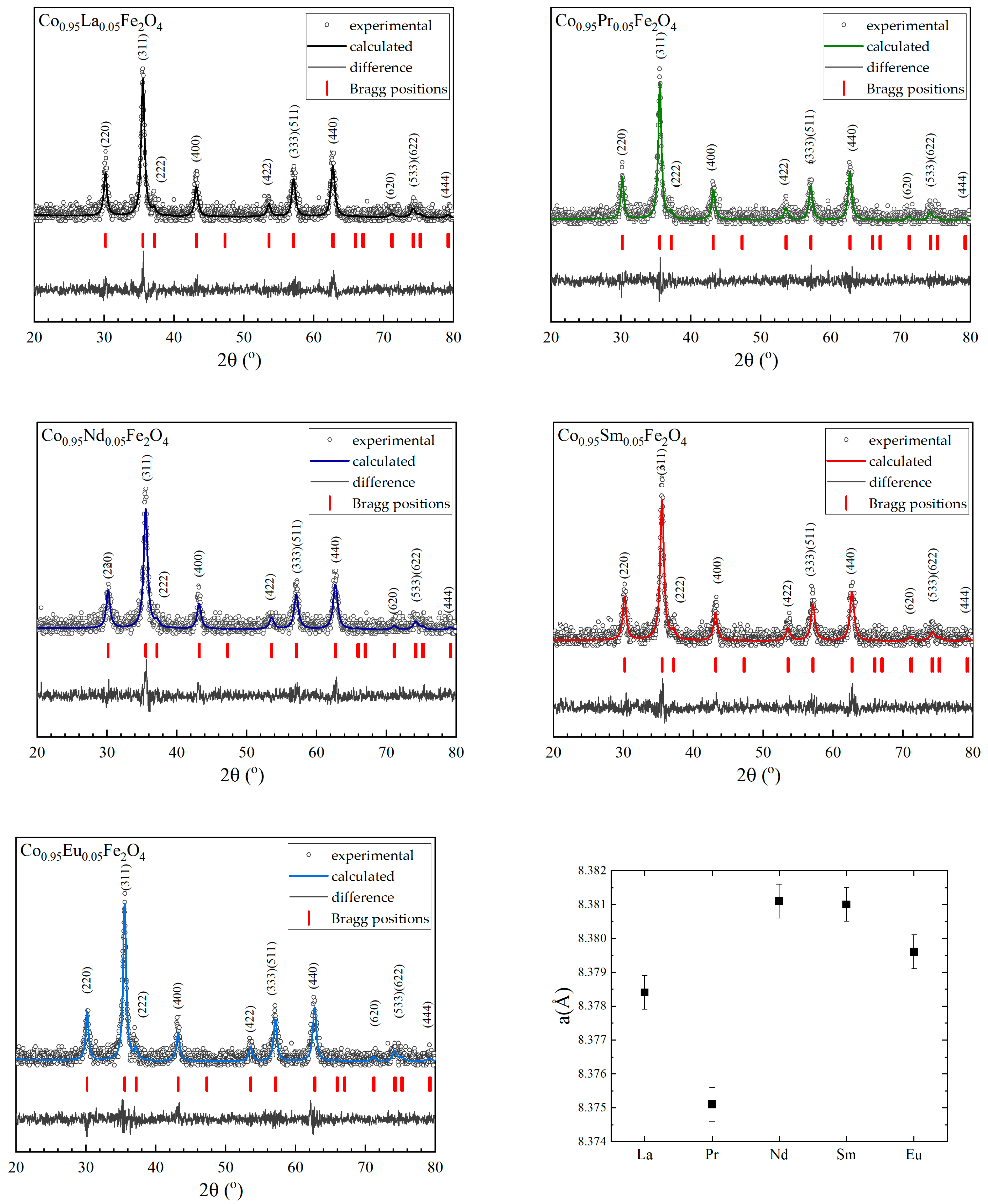
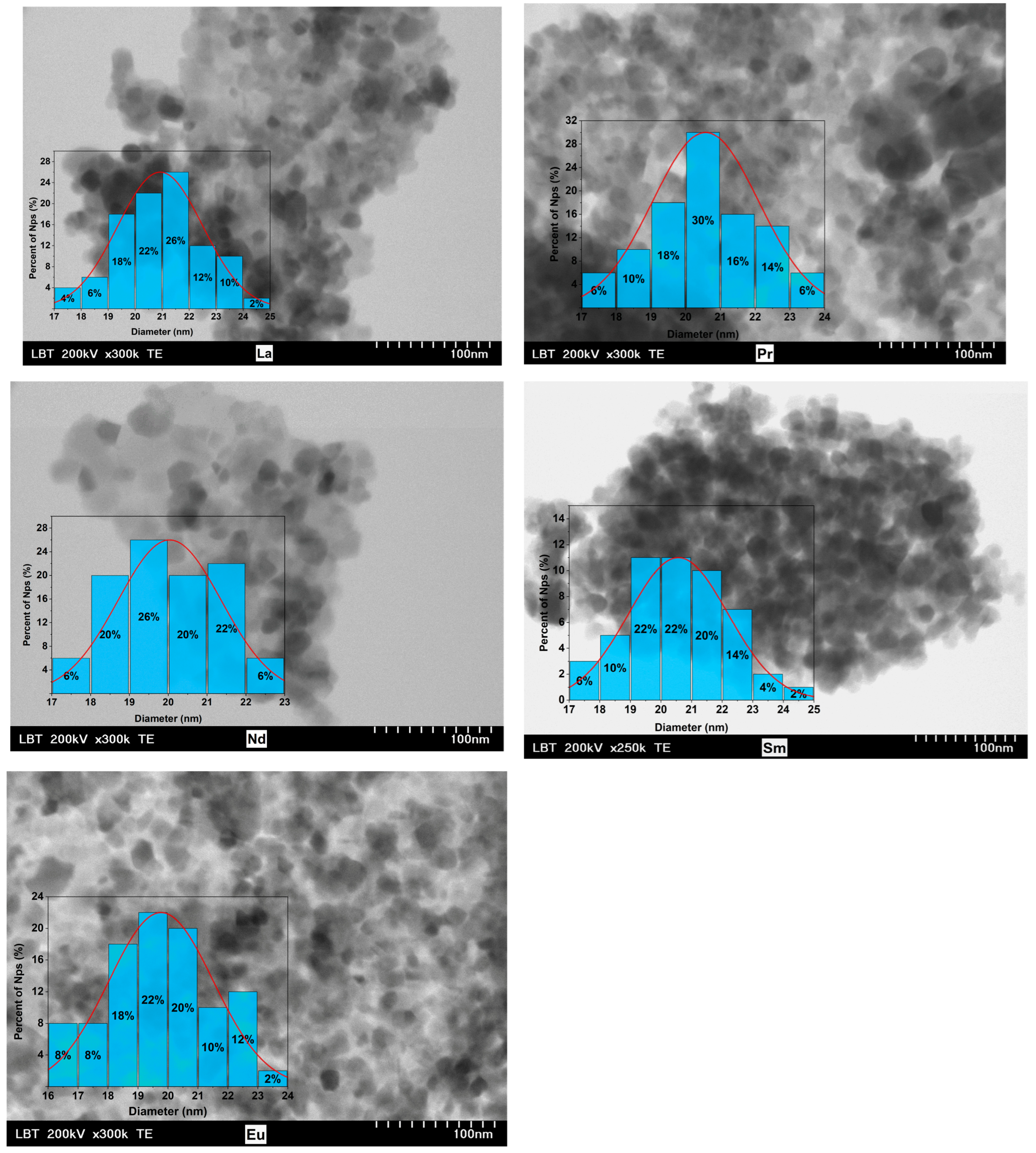
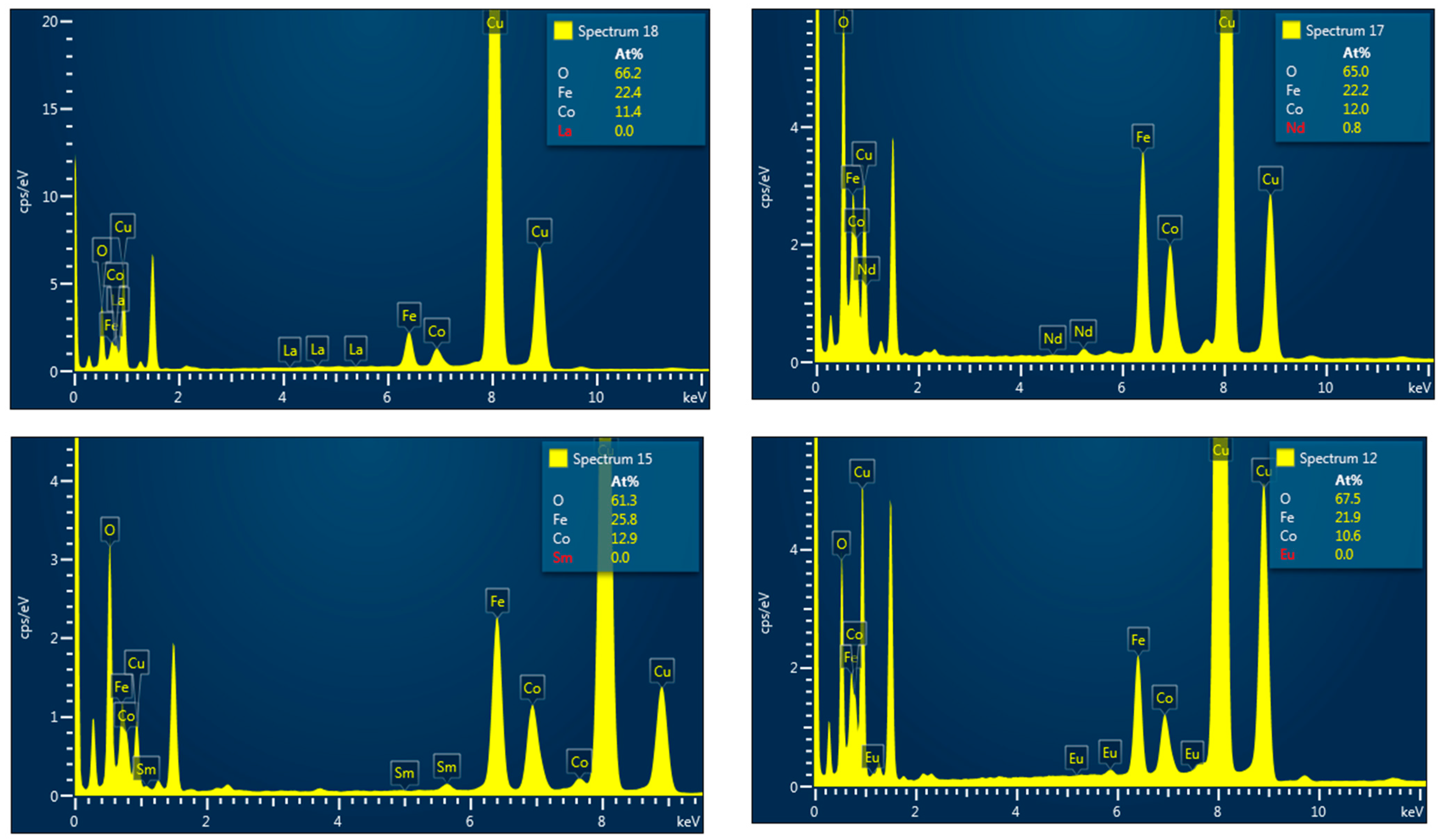
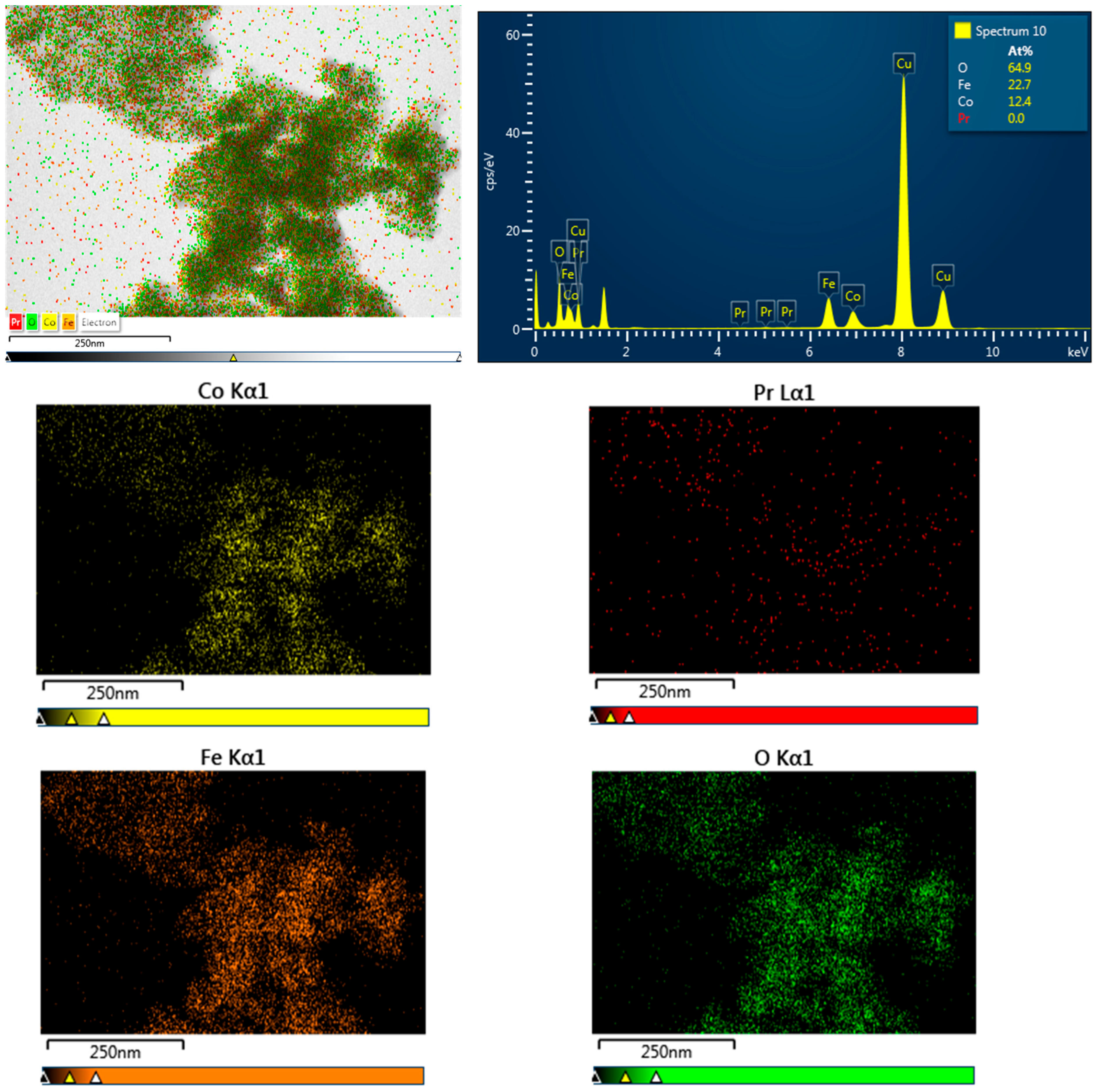
| R | a (Å) | χ2 | d (nm) XRD | d (nm) TEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | 8.378(4) | 1.22 | 20.7(1) | 20.929 ± 1.573 |
| Pr | 8.375(1) | 1.23 | 20.0(2) | 20.574 ± 1.529 |
| Nd | 8.381(1) | 1.22 | 17.9(0) | 20.035 ± 1.329 |
| Sm | 8.381(0) | 1.17 | 19.5(2) | 20.567 ± 1.623 |
| Eu | 8.379(6) | 1.26 | 19.3(7) | 19.032 ± 2.046 |
| R | 2p3/2 (eV) | 2p1/2 (eV) | ΔSO (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| La | 780.2 ± 0.2 | 795.6 ± 0.2 | 15.4 |
| Pr | 780.6 ± 0.2 | 795.9 ± 0.2 | 15.3 |
| Nd | 780.4 ± 0.2 | 795.7 ± 0.2 | 15.3 |
| Sm | 780.6 ± 0.2 | 796.0 ± 0.2 | 15.4 |
| Eu | 780.4 ± 0.2 | 795.8 ± 0.2 | 15.4 |
| R | Cation Distribution | MS (μB) th T = 4.2 K | MS (emu/g) exp. T = 4.2 K | MS (μB) exp. T = 4.2 K | MS (emu/g) exp. T = 300 K | MS (μB) exp. T = 300 K | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetrahedral Sites | Octahedral Sites | |||||||||||
| Fe3+ | Fe2+ | R3+ | Co3+ | Co2+ | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | ||||||
| La | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.95 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 3 | 70.2597 | 3 | 63.54 | 2.72 |
| Pr | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.95 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 3.16 | 73.4661 | 3.14 | 61.7 | 2.64 |
| Nd | 1 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.95 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2.96 | 69.3367 | 2.97 | 61.3 | 2.62 |
| Sm | 0.78 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.94 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.77 | 3.28 | 76.6135 | 3.28 | 66.62 | 2.85 |
| Eu | 1 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.95 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2.8 | 66.8424 | 2.87 | 59.02 | 2.53 |
| R | m0Hc (T) | Mr (emu/g) | SR = Mr/Ms | K (KJ/m3) | TB (K) XRD | TB (K) TEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | 0.065 | 17.45 | 0.27 | 21.84823 | 293.95 | 303.82 |
| Pr | 0.0733 | 18.469 | 0.3 | 23.92461 | 290.33 | 316.05 |
| Nd | 0.0659 | 15.439 | 0.25 | 21.36985 | 185.91 | 260.69 |
| Sm | 0.0612 | 16.095 | 0.24 | 21.56809 | 242.59 | 284.63 |
| Eu | 0.0654 | 15.212 | 0.26 | 20.41891 | 222.67 | 213.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bortnic, R.; Szatmari, A.; Dragoiu, T.; Hategan, R.G.; Atanasov, R.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Tiusan, C.; Lucacel-Ciceo, R.; Dudric, R.; Tetean, R. The Influence of Light Rare-Earth Substitution on Electronic and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15151152
Bortnic R, Szatmari A, Dragoiu T, Hategan RG, Atanasov R, Barbu-Tudoran L, Tiusan C, Lucacel-Ciceo R, Dudric R, Tetean R. The Influence of Light Rare-Earth Substitution on Electronic and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(15):1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15151152
Chicago/Turabian StyleBortnic, Rareș, Adam Szatmari, Tiberiu Dragoiu, Radu George Hategan, Roman Atanasov, Lucian Barbu-Tudoran, Coriolan Tiusan, Raluca Lucacel-Ciceo, Roxana Dudric, and Romulus Tetean. 2025. "The Influence of Light Rare-Earth Substitution on Electronic and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 15, no. 15: 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15151152
APA StyleBortnic, R., Szatmari, A., Dragoiu, T., Hategan, R. G., Atanasov, R., Barbu-Tudoran, L., Tiusan, C., Lucacel-Ciceo, R., Dudric, R., & Tetean, R. (2025). The Influence of Light Rare-Earth Substitution on Electronic and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 15(15), 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15151152







