CdSe/ZnS Quantum Rods (QRs) and Phenyl Boronic Acid BODIPY as Efficient Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) Donor–Acceptor Pair
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dynamic Light Scattering
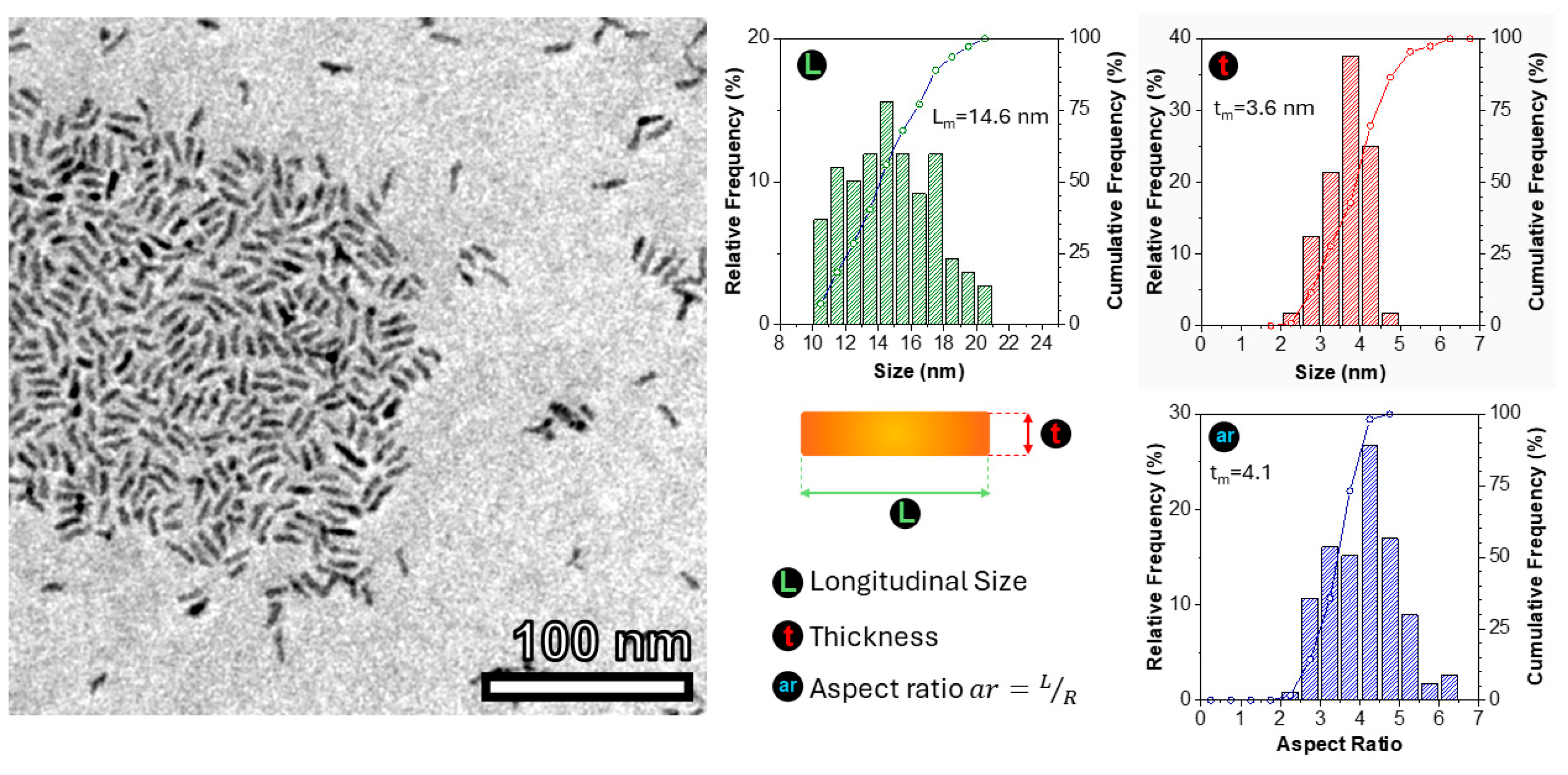
2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (STEM)
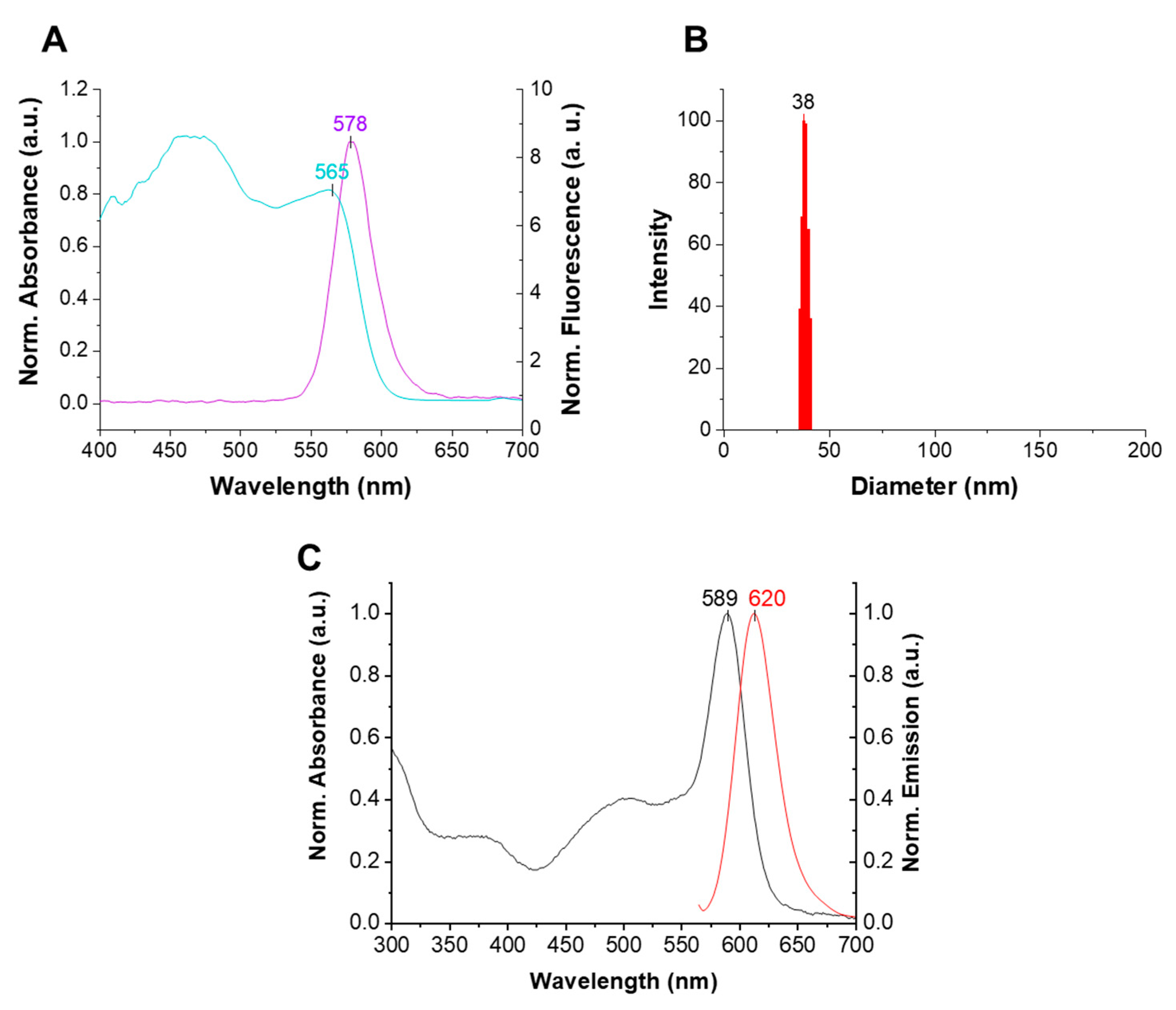
2.3. UV–Visible and Fluorescence Emission Spectroscopy
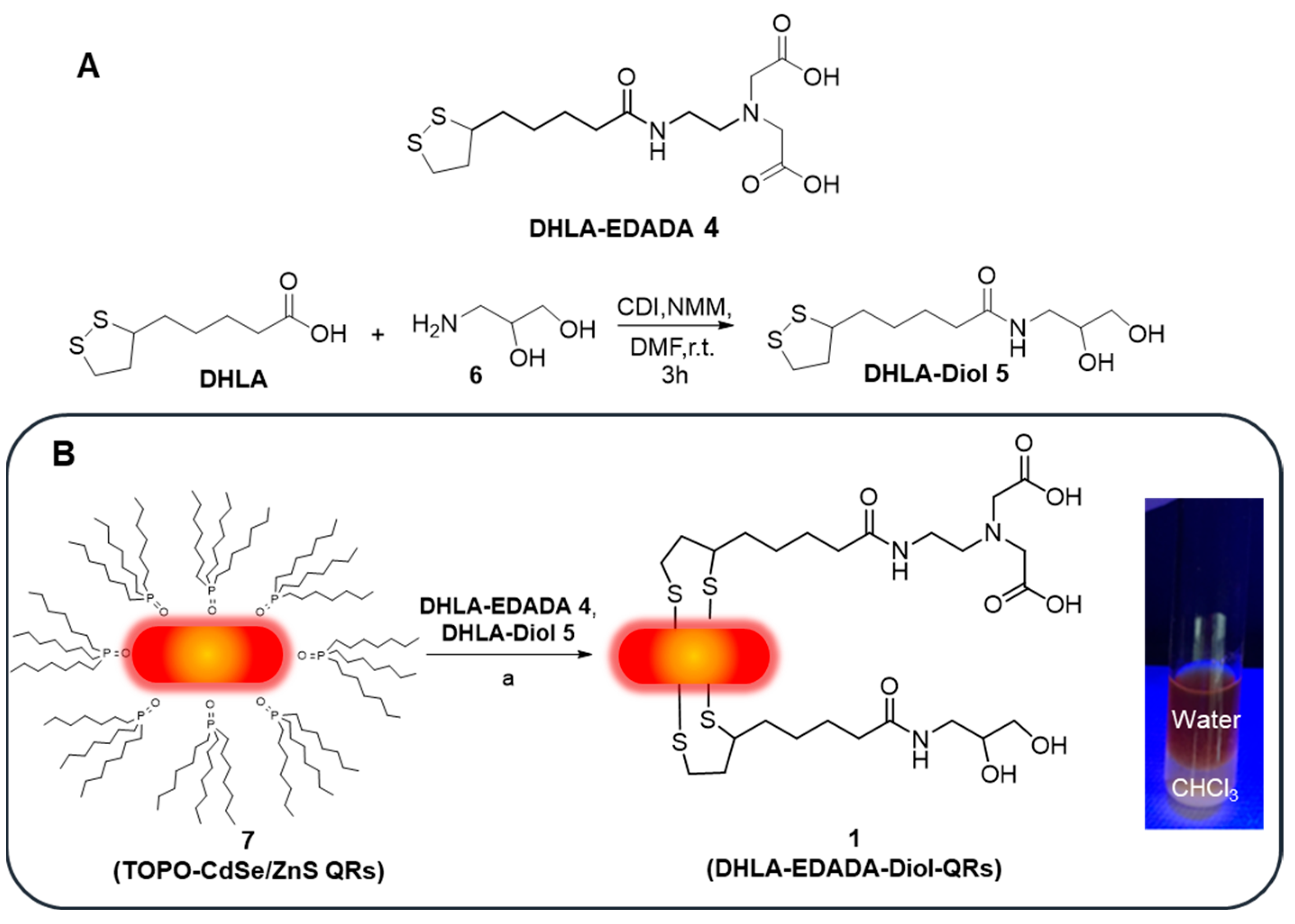
2.3.1. Synthesis of 5
2.3.2. Synthesis of CdSe/ZnS QRs 7
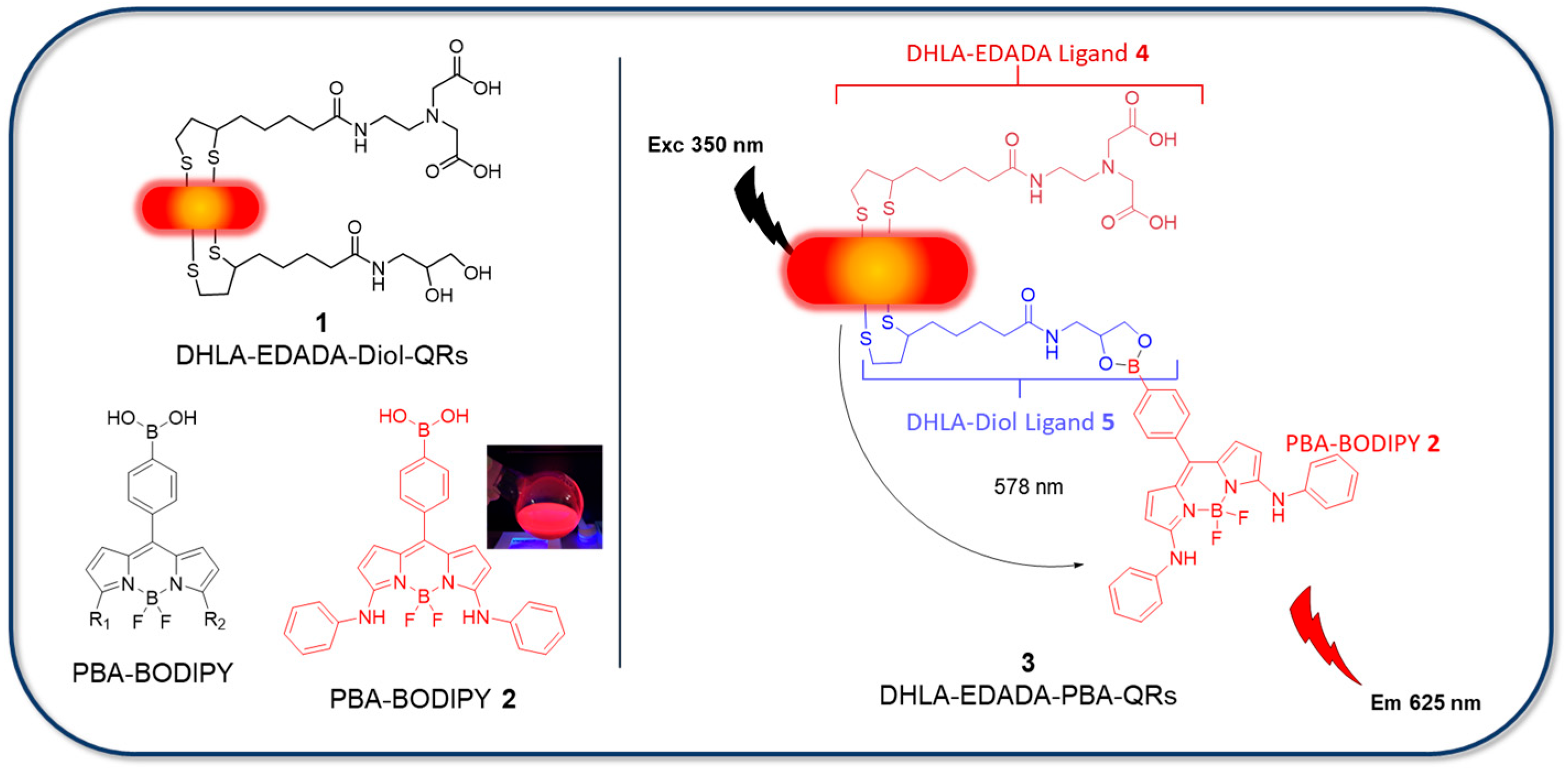
2.3.3. Synthesis of QRs 1
2.3.4. Synthesis of QRs 3
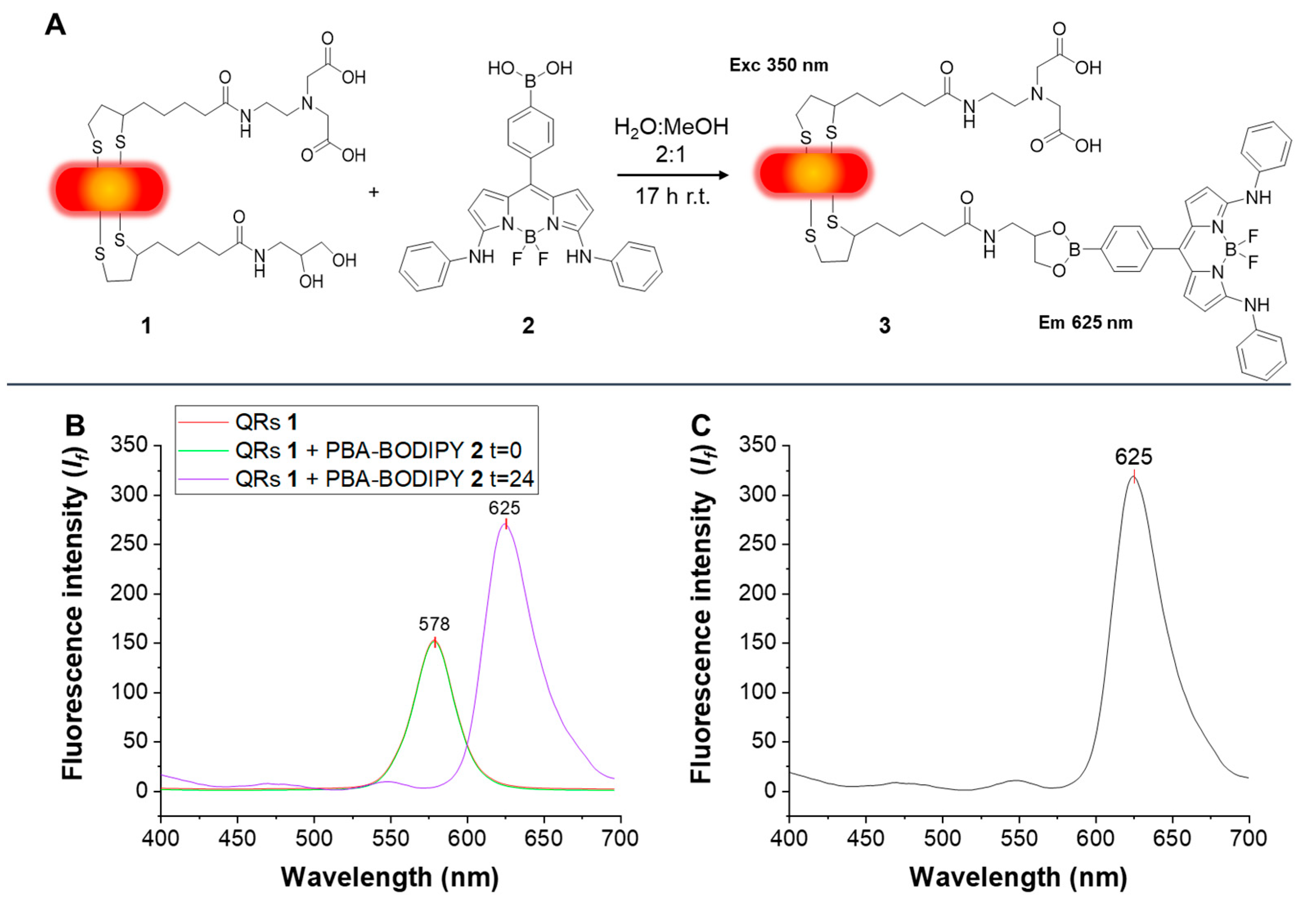
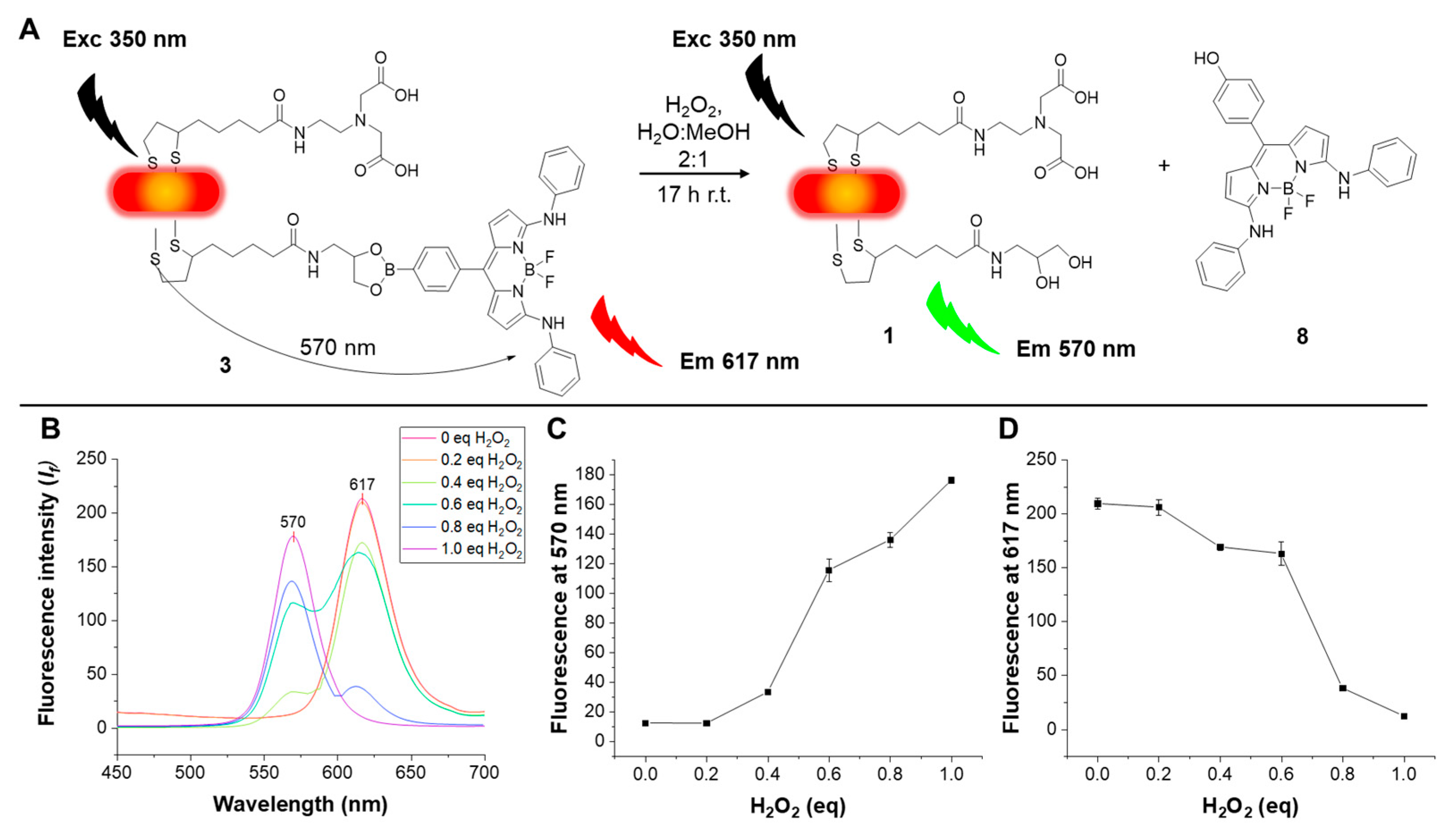
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chatterjee, S.; Tripathi, N.M.; Bandyopadhyay, A. The Modern Role of Boron as a ‘Magic Element’ in Biomedical Science: Chemistry Perspective. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 13629–13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chen, X.-X.; Jiang, Y.-B. Recent Advances in Boronic Acid-Based Optical Chemosensors. Analyst 2017, 142, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Wang, H.; Bian, Z.; Sun, J.; Liu, A.; Fang, H.; Liu, B.; Yao, Q.; Wu, Z. Recent Development of Boronic Acid-Based Fluorescent Sensors. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 29400–29427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinaro, W.A.; Prankerd, R.; Kinnari, K.; Stella, V.J. Interaction of Model Aryl- and Alkyl-Boronic Acids and 1,2-Diols in Aqueous Solution. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, W.L.A.; Deng, C.C.; Sumerlin, B.S. Structure–Reactivity Relationships in Boronic Acid–Diol Complexation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 17863–17870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Francés-Soriano, L.; Guo, J.; Hallaj, T.; Qiu, X.; Hildebrandt, N. Energy Transfer with Nanoparticles for In Vitro Diagnostics. Front. Nanosci. 2020, 16, 25–65. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, M.; Lu, Q.; Qing, G.; Sun, T. Sialic Acid-Targeted Biointerface Materials and Bio-Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Stephenson-Brown, A.J.; Khan, T.; Miyazawa, T.; Cabral, H.; Kataoka, K.; Miyahara, Y. Heterocyclic Boronic Acids Display Sialic Acid Selective Binding in a Hypoxic Tumor Relevant Acidic Environment. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6165–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Li, D.; Yu, M.; Guo, J.; Wang, C. Benzoboroxole-Functionalized Magnetic Core/Shell Microspheres for Highly Specific Enrichment of Glycoproteins under Physiological Conditions. Small 2014, 10, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Bie, Z. Branched Polyethyleneimine-Assisted Boronic Acid-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for the Selective Enrichment of Trace Glycoproteins. Analyst 2017, 142, 4494–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wu, J.; Ju, H.; Chen, Y. Ultra-Galactocation to Sialic Acid on Tumor Cells with A Penta-Functional Dendritic Probe for Enhanced Immuno-Killing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, e202319849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, P.; Tamberi, L.; Tasca, E.; Giacomazzo, G.E.; Martinez, M.; Severi, M.; Marradi, M.; Cicchi, S.; Moya, S.; Biagiotti, G.; et al. The B & B Approach: Ball-Milling Conjugation of Dextran with Phenylboronic Acid (PBA)-Functionalized BODIPY. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2272–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Gao, X.; Song, F.; Wang, C.; Chu, F.; Wu, S. A Sensing Approach for Dopamine Determination by Boronic Acid-Functionalized Molecularly Imprinted Graphene Quantum Dots Composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.A.; Gillis, K.D.; Glass, T.E. A High-Affinity Fluorescent Sensor for Catecholamine: Application to Monitoring Norepinephrine Exocytosis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7611–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reina, G.; Ruiz, A.; Richichi, B.; Biagiotti, G.; Giacomazzo, G.E.; Jacquemin, L.; Nishina, Y.; Ménard-Moyon, C.; Al-Jamal, W.T.; Bianco, A. Design of a Graphene Oxide-BODIPY Conjugate for Glutathione Depletion and Photodynamic Therapy. 2D Mater. 2022, 9, 015038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, G.; Beneventi, G.M.; Kaur, R.; Biagiotti, G.; Cadranel, A.; Ménard-Moyon, C.; Nishina, Y.; Richichi, B.; Guldi, D.M.; Bianco, A. Graphene Oxide-BODIPY Conjugates as Highly Fluorescent Materials. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e2023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Anslyn, E.V.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Boronic Acid Based Dynamic Click Chemistry: Recent Advances and Emergent Applications. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 1585–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Kusuyama, D.; Sugaya, T.; Iwatsuki, S.; Inamo, M.; Takagi, H.D.; Ishihara, K. Reactivity of Boronic Acids toward Catechols in Aqueous Solution. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 5255–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, D.G. Boronic Acid Catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3475–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomazzo, G.E.; Palladino, P.; Gellini, C.; Salerno, G.; Baldoneschi, V.; Feis, A.; Scarano, S.; Minunni, M.; Richichi, B. A Straightforward Synthesis of Phenyl Boronic Acid (PBA) Containing BODIPY Dyes: New Functional and Modular Fluorescent Tools for the Tethering of the Glycan Domain of Antibodies. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 30773–30777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Qian, X.; da Silva, G.C.Q.; Gabellini, C.; Lucherelli, M.A.; Biagiotti, G.; Richichi, B.; Ménard-Moyon, C.; Gao, H.; Posocco, P.; et al. Unveiling Liquid-Phase Exfoliation of Graphite and Boron Nitride Using Fluorescent Dyes Through Combined Experiments and Simulations. Small 2024, 2307817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, T.; Uhlikova, N.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Egap, E.; Lian, T. Competition of Dexter, Förster, and Charge Transfer Pathways for Quantum Dot Sensitized Triplet Generation. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 214702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekar, R.B.; Periasamy, A. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) Microscopy Imaging of Live Cell Protein Localizations. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso Dos Santos, M.; Algar, W.R.; Medintz, I.L.; Hildebrandt, N. Quantum Dots for Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET). TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 125, 115819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.A.; Peng, X. Nearly Monodisperse and Shape-Controlled CdSe Nanocrystals via Alternative Routes: Nucleation and Growth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 3343–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, S.; Rani, M.; Dubey, R.B.; Mahajan, J. Synthesis of CdSe crystal using hot injection method. Int. J. Latest Res. Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 518–521. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.A.; Peng, X. Formation of High-Quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS Nanocrystals Using CdO as Precursor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.B.; Norris, D.J.; Bawendi, M.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Nearly Monodisperse CdE (E = Sulfur, Selenium, Tellurium) Semiconductor Nanocrystallites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8706–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, G.; Scarano, S.; Mamusa, M.; Consumi, M.; Giuntini, S.; Macagnano, A.; Nativi, S.; Fragai, M.; Minunni, M.; Berti, D.; et al. A Small Heterobifunctional Ligand Provides Stable and Water Dispersible Core–Shell CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots (QDs). Nanoscale 2018, 10, 19720–19732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, J.V.; Chenoweth, D.M.; Petersson, E.J. Rational Design of Small Molecule Fluorescent Probes for Biological Applications. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 5747–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolcott, A.; Fitzmorris, R.C.; Muzaffery, O.; Zhang, J.Z. CdSe Quantum Rod Formation Aided by in Situ TOPO Oxidation. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 2814–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Li, L.; Yang, W.; Manna, L.; Wang, L.; Alivisatos, A.P. Linearly Polarized Emission from Colloidal Semiconductor Quantum Rods. Science 2001, 292, 2060–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panniello, A.; Trapani, M.; Cordaro, M.; Dibenedetto, C.N.; Tommasi, R.; Ingrosso, C.; Fanizza, E.; Grisorio, R.; Collini, E.; Agostiano, A.; et al. High-Efficiency FRET Processes in BODIPY-Functionalized Quantum Dot Architectures. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiró Cadahiá, J.; Previtali, V.; Troelsen, N.S.; Clausen, M.H. Prodrug Strategies for Targeted Therapy Triggered by Reactive Oxygen Species. Medchemcomm 2019, 10, 1531–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.W.; Albers, A.E.; Pralle, A.; Isacoff, E.Y.; Chang, C.J. Boronate-Based Fluorescent Probes for Imaging Cellular Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 16652–16659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salerno, G.; Palladino, P.; Marelli, M.; Polito, L.; Minunni, M.; Berti, D.; Scarano, S.; Biagiotti, G.; Richichi, B. CdSe/ZnS Quantum Rods (QRs) and Phenyl Boronic Acid BODIPY as Efficient Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) Donor–Acceptor Pair. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14090794
Salerno G, Palladino P, Marelli M, Polito L, Minunni M, Berti D, Scarano S, Biagiotti G, Richichi B. CdSe/ZnS Quantum Rods (QRs) and Phenyl Boronic Acid BODIPY as Efficient Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) Donor–Acceptor Pair. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(9):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14090794
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalerno, Gianluca, Pasquale Palladino, Marcello Marelli, Laura Polito, Maria Minunni, Debora Berti, Simona Scarano, Giacomo Biagiotti, and Barbara Richichi. 2024. "CdSe/ZnS Quantum Rods (QRs) and Phenyl Boronic Acid BODIPY as Efficient Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) Donor–Acceptor Pair" Nanomaterials 14, no. 9: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14090794
APA StyleSalerno, G., Palladino, P., Marelli, M., Polito, L., Minunni, M., Berti, D., Scarano, S., Biagiotti, G., & Richichi, B. (2024). CdSe/ZnS Quantum Rods (QRs) and Phenyl Boronic Acid BODIPY as Efficient Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) Donor–Acceptor Pair. Nanomaterials, 14(9), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14090794








