A High-Performance and Durable Direct-Ammonia Symmetrical Solid Oxide Fuel Cell with Nano La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.7Ni0.2Mo0.1O3−δ-Decorated Doped Ceria Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Synthesis
2.2. Cell Fabrication
2.3. Characterisation Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
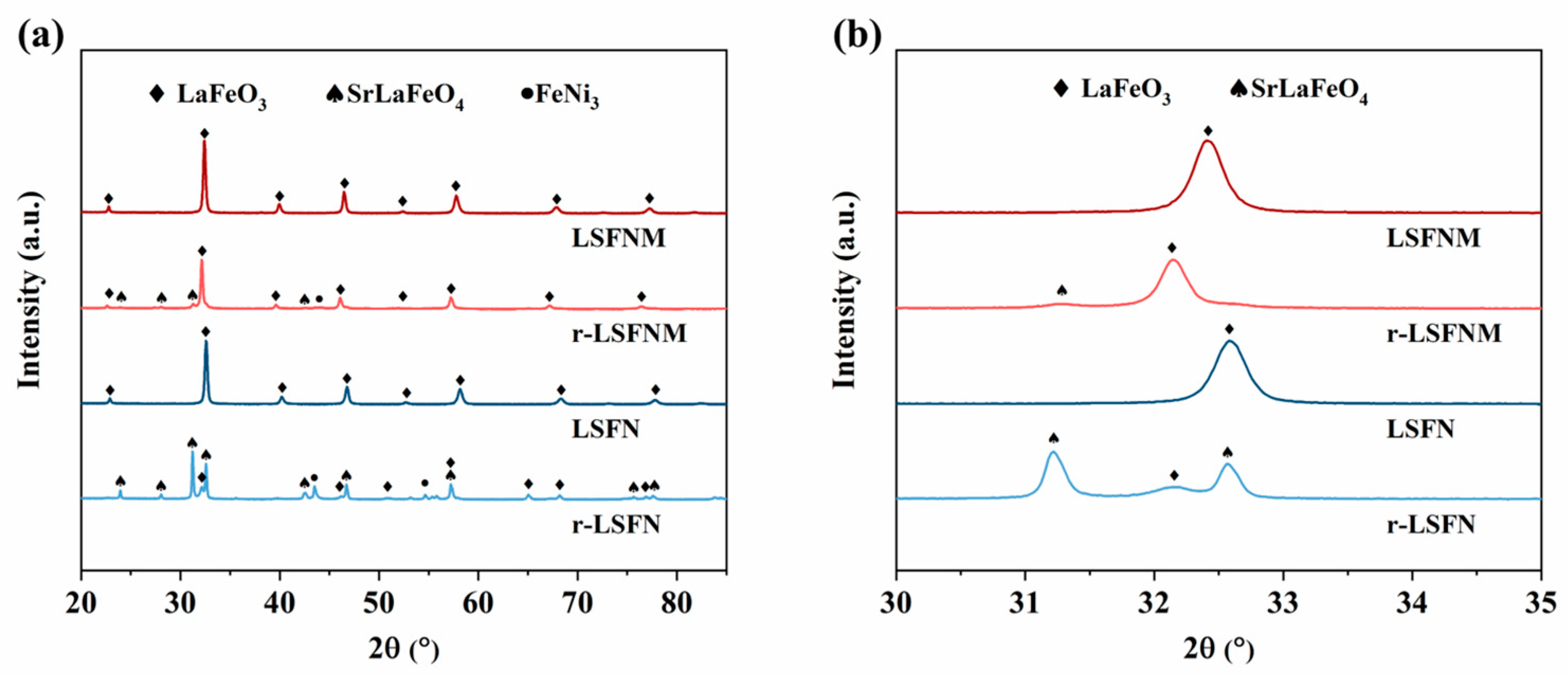
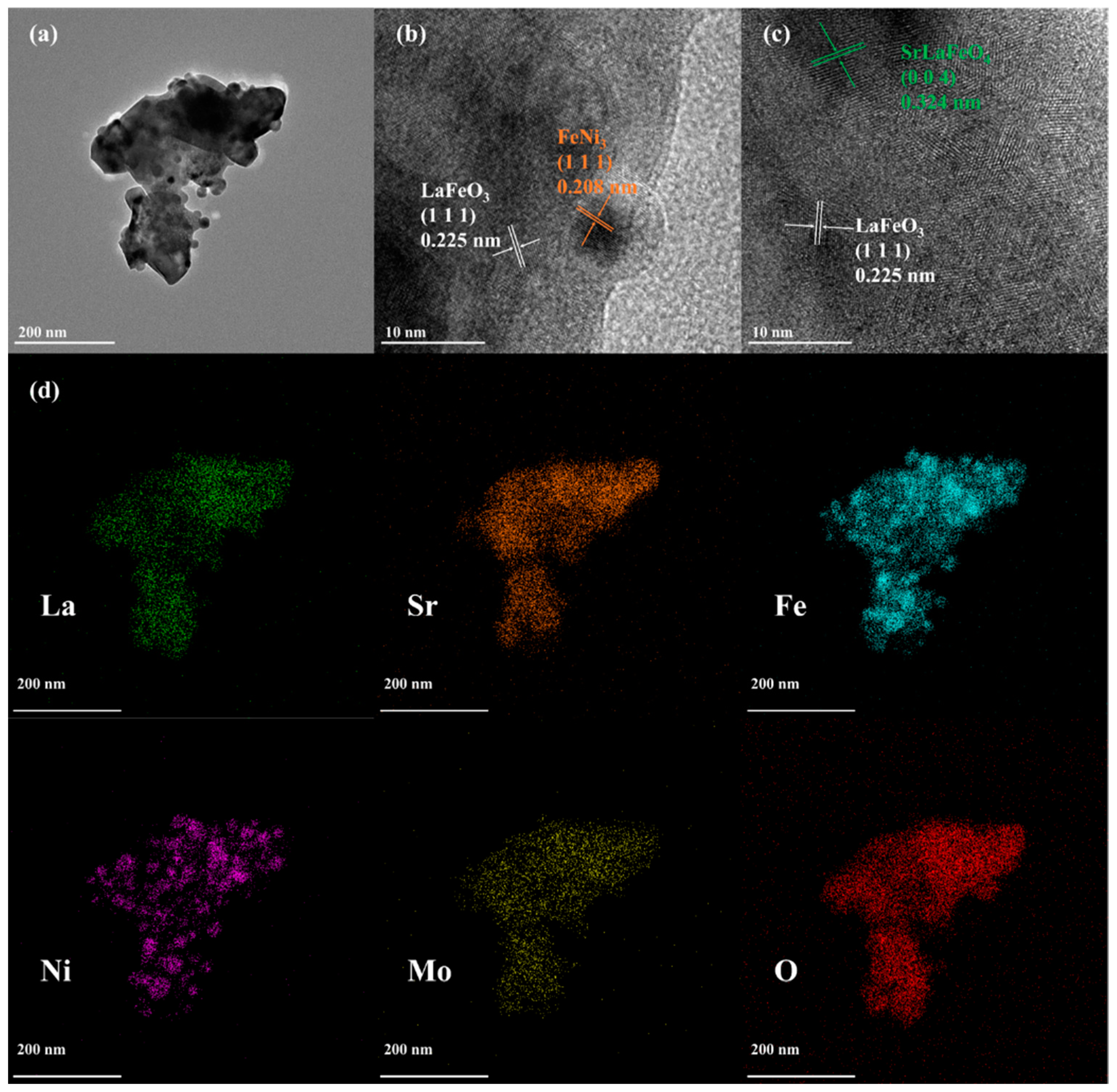
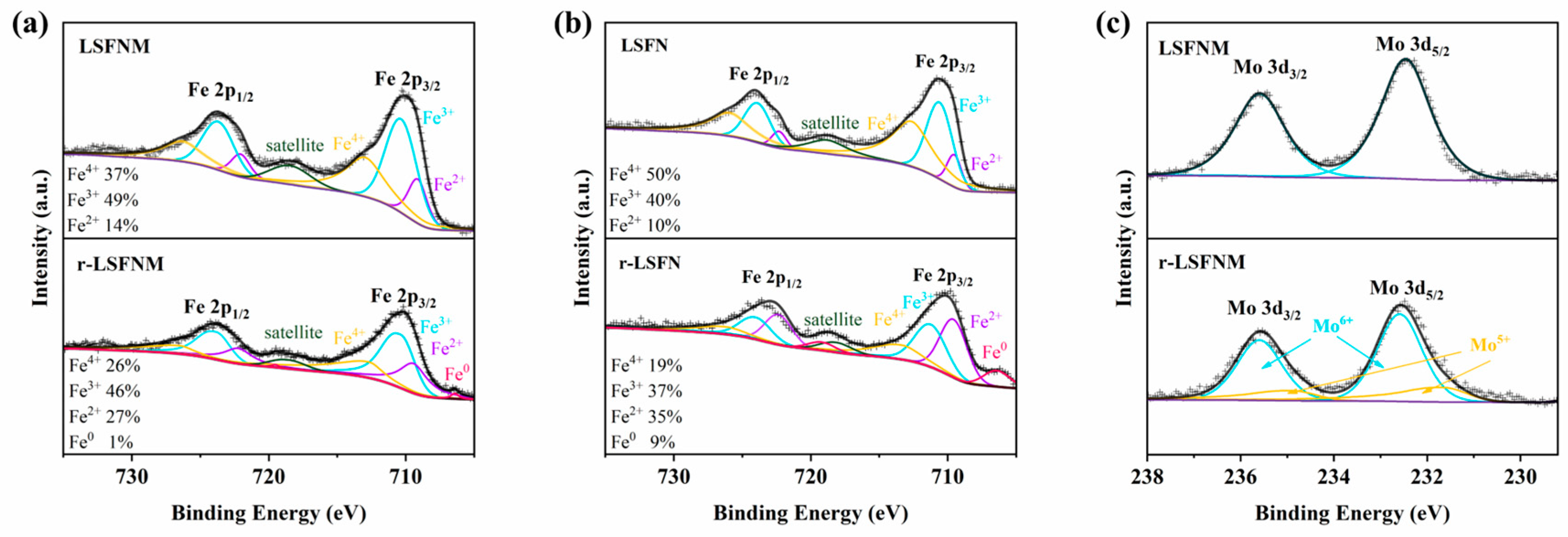
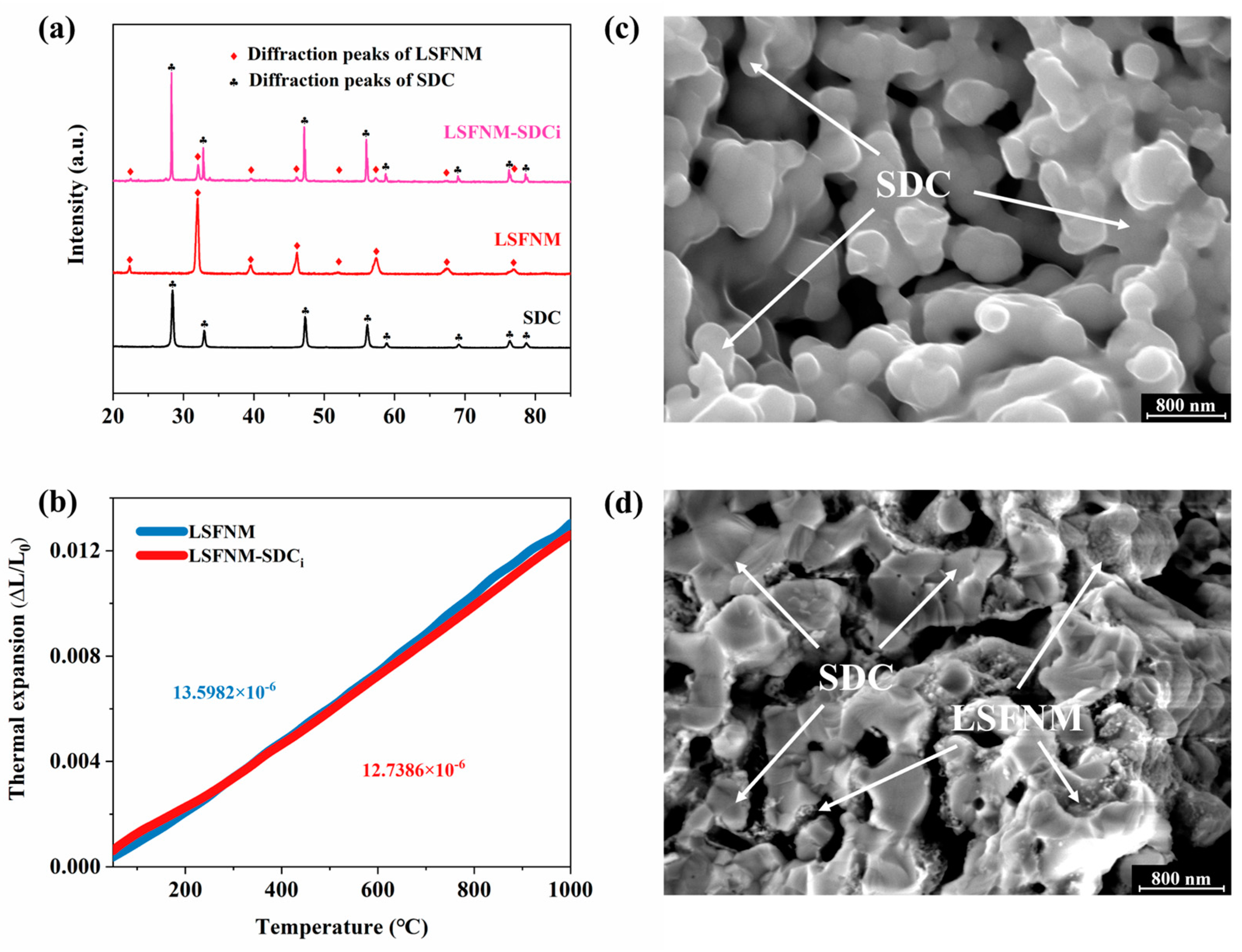
3.1. Basic Characterisation of LSFNM
3.2. Basic Characterisation of LSFNM-Infiltrated SDC
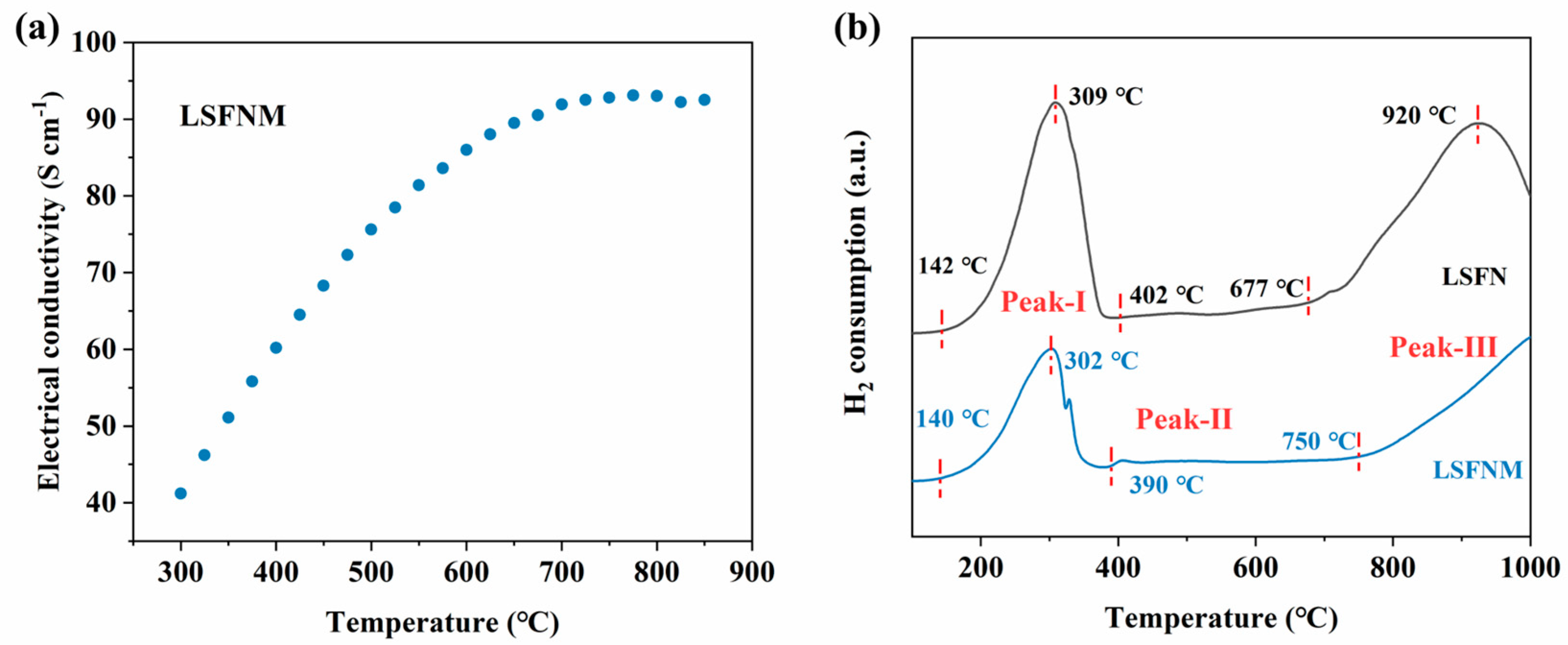
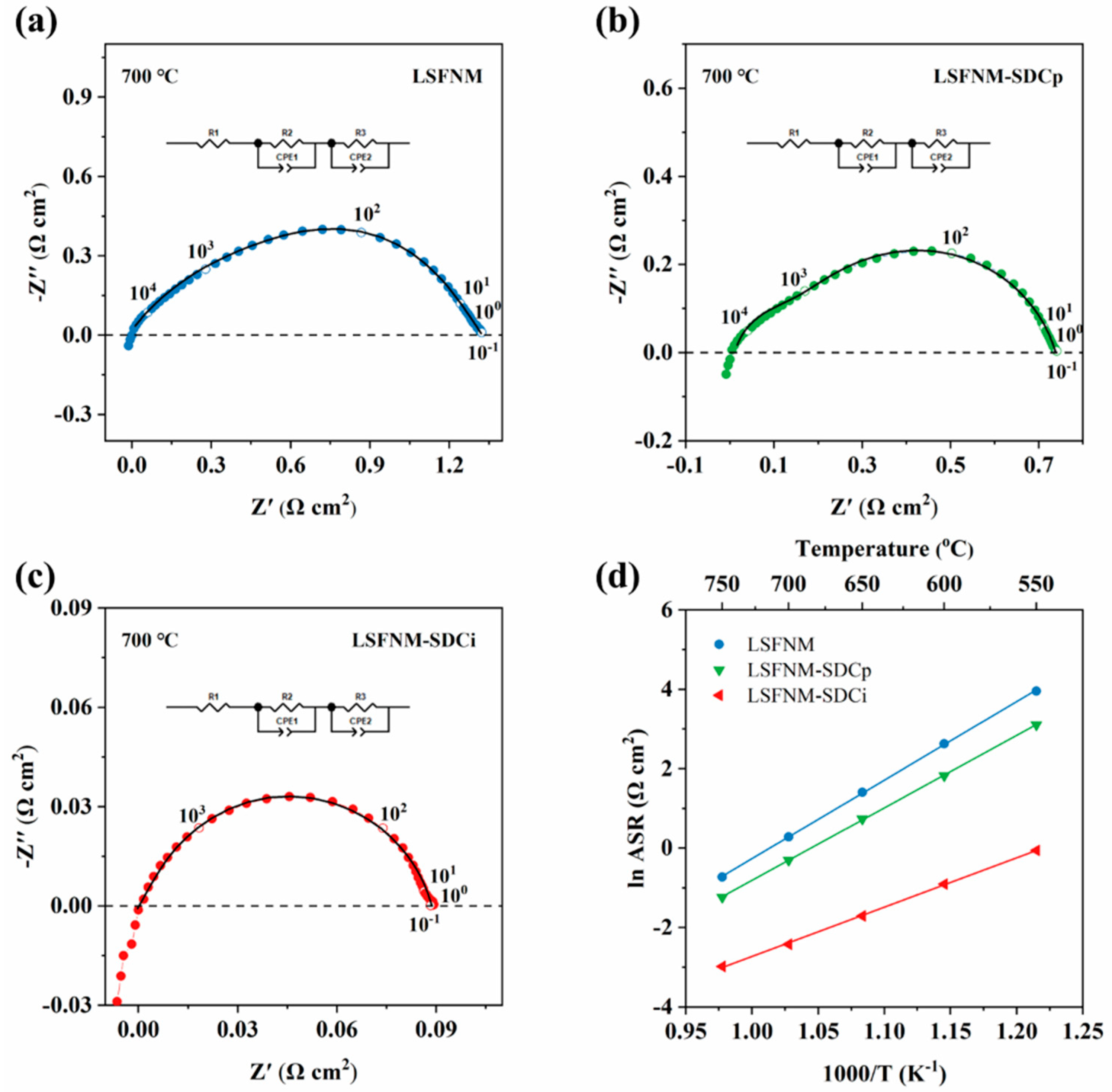
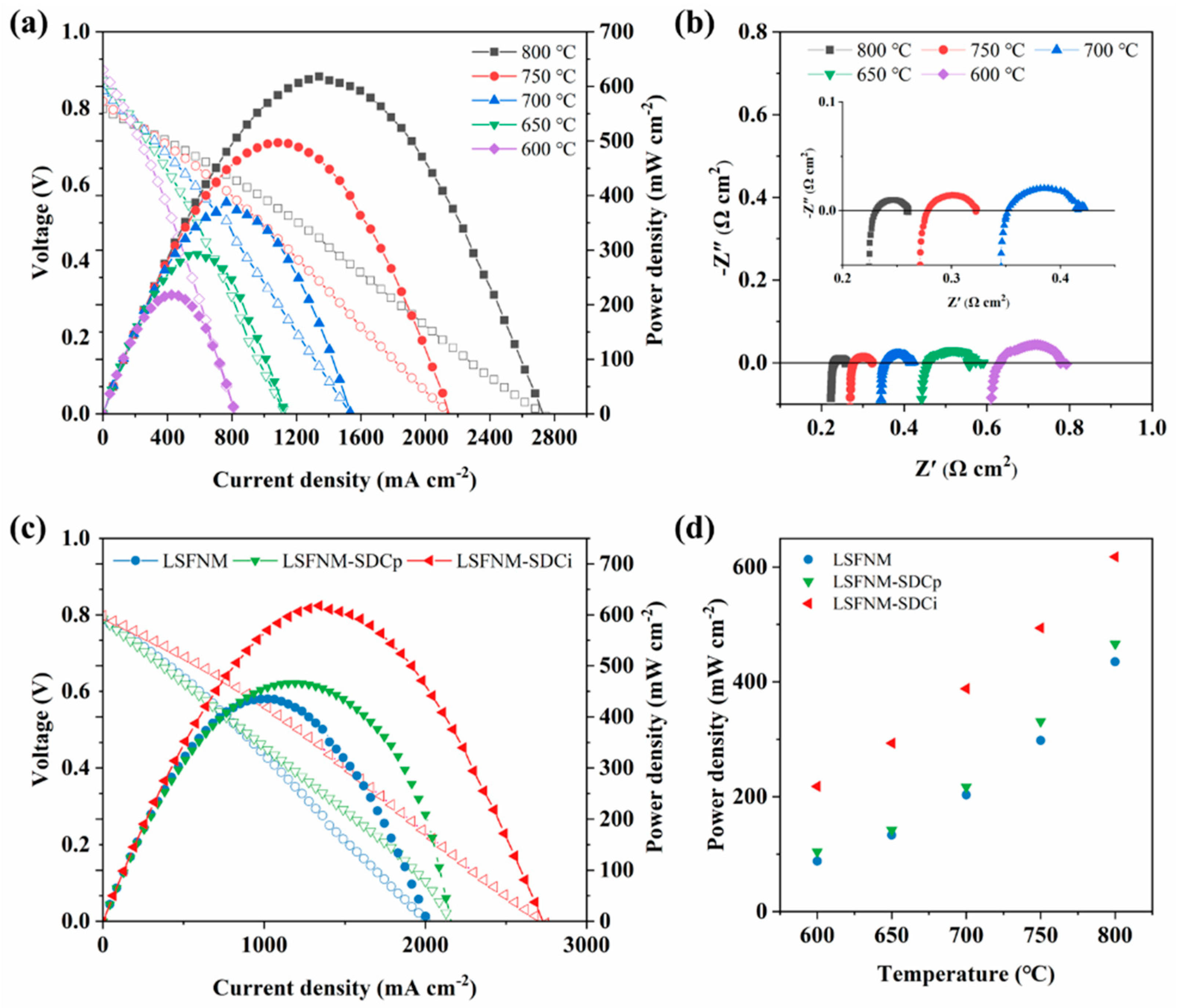
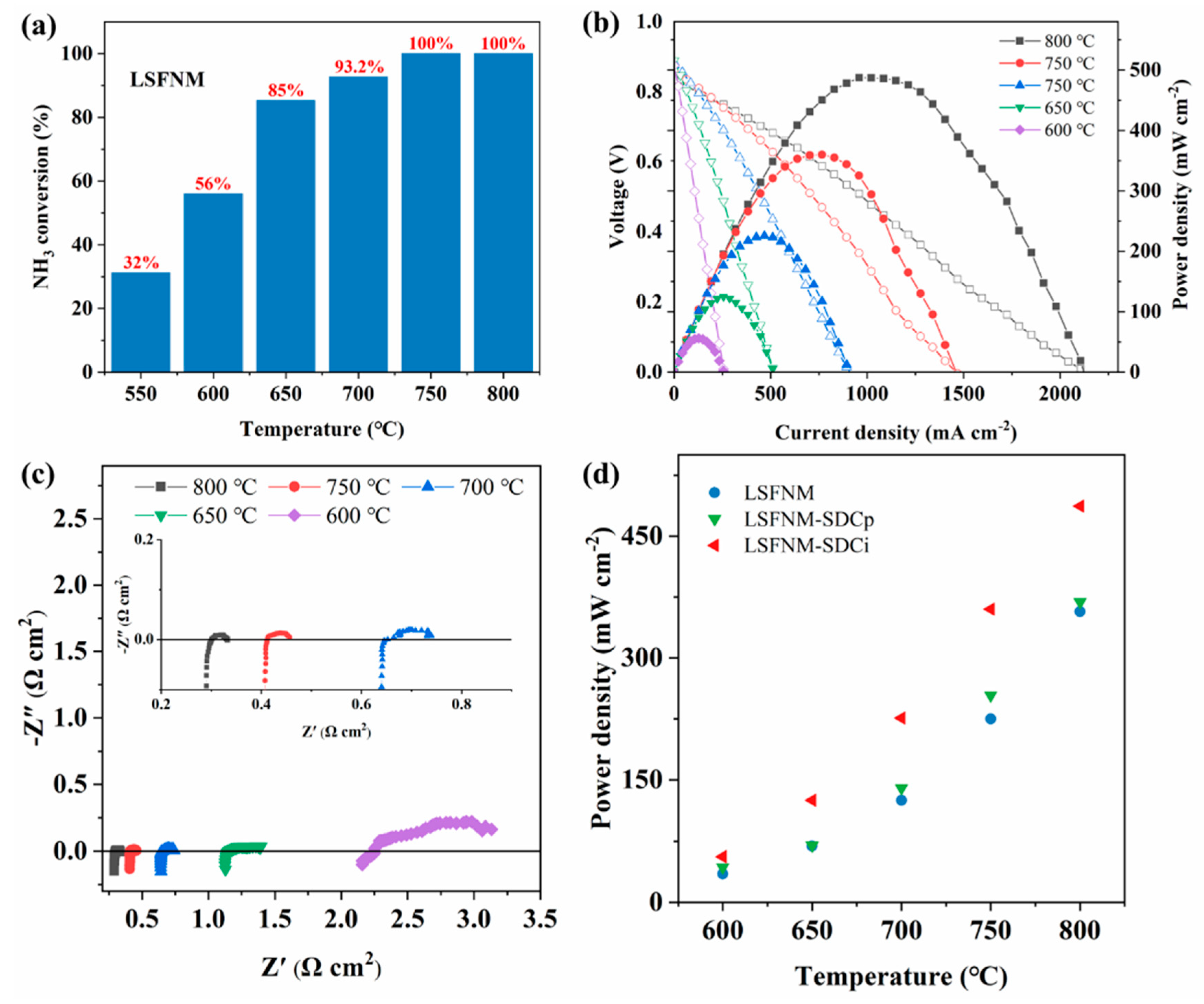
3.3. Electrocatalytic Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Ru, X.; Yang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, S.; Hong, C.; Peng, F.; Qu, M.; Xue, C.; Lu, J.; et al. Flexible silicon solar cells with high power-to-weight ratios. Nature 2024, 626, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Wang, W.; Shao, Z. Cation-deficient perovskites for clean energy conversion. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Pang, Y.P.; Su, C.; Jiang, S.S.; Ge, L. Toward High Performance Mixed Ionic and Electronic Conducting Perovskite-Based Oxygen Permeable Membranes: An Overview of Strategies and Rationales. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 7042–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Su, C.; Zhu, Z.H.; Wang, H.; Ge, L. Composite cathodes for protonic ceramic fuel cells: Rationales and materials. Compos. B. Eng. 2022, 238, 109881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qiu, H.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, D.; Su, C. Enhanced ORR activity of A-site-deficient SrCo0.8Nb0.1Ti0.1O3−δ as a bifunctional air electrode for low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 6740–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, T.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, T.; Dong, D.; Wang, Z. Direct ethanol solid oxide fuel cells integrated with internal reforming for renewable power generation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.T.; Wu, Y.X.; Li, L.; Xie, Z.H.; Xie, Y.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Meng, X.X.; Yu, F.Y.; Yang, N.T. A high-performance direct carbon solid oxide fuel cell powered by barium-based catalyst-loaded biochar derived from sunflower seed shell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 38747–38756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawale, D.S.; Biswas, S.; Kaur, G.; Giddey, S. Challenges and advancement in direct ammonia solid oxide fuel cells: A review. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 6176–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Sun, W.; Luo, H.; Li, C.M. Recent progress in electrochemical synthesis of carbon-free hydrogen carrier ammonia and ammonia fuel cells: A review. Mater. Rep. Energy 2022, 2, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhongde, V.; Singh, A.; Kala, J.; Anjum, U.; Haider, M.A.; Basu, S. Radio-frequency magnetron sputtered thin-film La0.5Sr0.5Co0.95Nb0.05O3−δ perovskite electrodes for intermediate temperature symmetric solid oxide fuel cell (IT-SSOFC). Mater. Rep. Energy 2022, 2, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, T.; Gong, F.; Othman, M.H.D.; Xiao, R. Ammonia as a green energy carrier: Electrochemical synthesis and direct ammonia fuel cell—A comprehensive review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 235, 107380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.S.; Biswas, S.; Fini, D.; Kulkarni, A.P.; Giddey, S. Direct ammonia solid-oxide fuel cells: A review of progress and prospects. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 35365–35384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, S.; Gotsch, T.; Klotzer, B. Increasing complexity approach to the fundamental surface and interface chemistry on SOFC anode materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Molouk, A.F.S.; Okanishi, T.; Muroyama, H.; Matsui, T.; Eguchi, K. A stability study of Ni/Yttria-stabilized zirconia anode for direct ammonia solid oxide fuel cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 28701–28707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yu, J.; Huang, X.; Zou, D.; Song, Y.; Xu, M.; Ran, R.; Wang, W.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z. Slightly ruthenium doping enables better alloy nanoparticle exsolution of perovskite anode for high-performance direct-ammonia solid oxide fuel cells. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 125, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazzani, J.; Squizzato, E.; Brusamarello, E.; Glisenti, A. Exsolution in Ni-doped lanthanum strontium titanate: A perovskite-based material for anode application in ammonia-fed solid oxide fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 13921–13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, M.; Yang, G.; Shao, Z. Infiltrated NiCo alloy nanoparticle decorated perovskite oxide: A highly active, stable, and antisintering anode for direct-ammonia solid oxide fuel cells. Small 2020, 16, 2001859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istomin, S.Y.; Lyskov, N.V.; Mazo, G.N.; Antipov, E.V. Electrode materials based on complex d-metal oxides for symmetrical solid oxide fuel cells. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2021, 90, 644–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuterbekov, K.A.; Nikonov, A.; Bekmyrza, K.Z.; Pavzderin, N.B.; Kabyshev, A.M.; Kubenova, M.M.; Kabdrakhimova, G.D.; Aidarbekov, N. Classification of solid oxide fuel cells. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Sun, C.; Ma, C.; Wu, H.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, L. Ni doped La0.6Sr0.4FeO3-δ symmetrical electrode for solid oxide fuel cells. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zuo, Y.; Zsurzsan, G.; Zhang, Z. La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3−δ perovskite with in-situ exsolved Ni-Fe nanoparticles as high activity catalyst for symmetric solid oxide electrolysis cells. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 156, 111984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jia, L.; Yang, J.; Chi, B.; Pu, J.; Li, J. Cobalt-free perovskite oxide La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3−δ as active and robust oxygen electrode for reversible solid oxide cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Xi, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Medvedev, D.; Luo, J.; Fu, X. In-situ exsolved FeNi nanoparticles on perovskite matrix anode for co-production of ethylene and power from ethane in proton conducting fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 393, 139096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.M.; Su, C.; Shi, H.G.; Zhu, Y.L.; Song, Y.F.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z.P. Toward reducing the operation temperature of solid oxide fuel cells: Our past 15 years of efforts in cathode development. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 15169–15194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Bian, L.; Chen, N.; Chou, K. High performance of Mo-doped La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.9Ni0.1O3−δ perovskites as anode for solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 292, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xuan, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, S.; Xia, C. Hollow La0.6Sr0.4Ni0.2Fe0.75Mo0.05O3−δ electrodes with exsolved FeNi3 in quasi-symmetrical solid oxide electrolysis cells for direct CO2 electrolysis. Electrochem. Commun. 2022, 134, 107188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, Q.; Tian, D.; Yu, W.; Lin, B. Mo-doped Pr0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3−δ as potential electrodes for intermediate-temperature symmetrical solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 227, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Komvokis, V.G.; Amiridis, M.D.; Heyden, A.; Ma, S.; Chen, F. Synthesis and characterization of Mo-doped SrFeO3−δ as cathode materials for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2012, 202, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tian, Y.; Pu, J.; Chi, B. Anion fluorine-doped La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3−δ perovskite cathodes with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for solid oxide electrolysis cell direct CO2 electrolysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Xi, X.; Medvedev, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Luo, J.-L.; Fu, X.-Z. Emerging anode materials architectured with NiCoFe ternary alloy nanoparticles for ethane-fueled protonic ceramic fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2021, 515, 230634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.B.; Huang, Y.-H. Alternative anode materials for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 173, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S. Solid oxide fuel cell: Materials for anode, cathode and electrolyte. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 23988–24013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, M.; Song, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Cai, H.; Su, X.; Han, X.; Wang, S.; et al. In situ growth of LaSr(Fe,Mo)O4 ceramic anodes with exsolved Fe-Ni nanoparticles for SOFCs: Electrochemical performance and stability in H2, CO, and syngas. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 4537–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Rath, M.K.; Kwak, H.H.; Kim, H.J.; Han, J.W.; Hong, S.-T.; Lee, K.T. A highly active and redox-stable SrGdNi0.2Mn0.8O4±δ anode with in situ exsolution of nanocatalysts. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y. Molybdenum modified CeAlOx catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014, 386, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deganello, F.; Liotta, L.F.; Marcì, G.; Fabbri, E.; Traversa, E. Strontium and iron-doped barium cobaltite prepared by solution combustion synthesis: Exploring a mixed-fuel approach for tailored intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell cathode materials. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2013, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Su, C.; Chen, Y.; Tadé, M.O.; Shao, Z. Nano La0.6Ca0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3−δ decorated porous doped ceria as a novel cobalt-free electrode for “symmetrical” solid oxide fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 19526–19535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Qiu, H.; Wang, W.; Miller, E.; Su, C. Fluorine anion-doped Ba0.6Sr0.4Co0.7Fe0.2Nb0.1O3−δ as a promising cathode for protonic ceramic fuel cells. Catalysts 2023, 13, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, W.; Qu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z. Rational design of perovskite-vased anode with decent activity for hydrogen electro-oxidation and beneficial effect of sulfur for promoting power generation in solid oxide fuel cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41257–41267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Li, P.; Zhu, Q.; Kumar, A.; Sun, K.; Tian, S.; Sun, X. Atomically precise electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem 2023, 9, 280–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsdottir, A.E.; Erdosy, D.P.; Costentin, C.; Mason, J.A.; Nocera, D.G. Enhanced activity for the oxygen reduction reaction in microporous water. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.C.; Pei, K.; Pan, Y.X.; Xu, K.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, B.T.; Sasaki, K.; Choi, Y.M.; Chen, Y.; et al. An efficient and durable anode for ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, K.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yuan, W.; Sasaki, K.; Choi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. A high-performance and durable direct NH3 tubular protonic ceramic fuel cell integrated with an internal catalyst layer. Appl. Catal. B 2022, 306, 121071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Oh, M.J.; Hong, J.; Yoon, K.J.; Ji, H.I.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, H.; Son, J.W.; Yang, S. A comprehensive investigation of direct ammonia-fueled thin-film solid-oxide fuel cells: Performance, limitation, and prospects. iScience 2022, 25, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.Y.; Kwon, O.; Gorte, R.J.; Vohs, J.M. Metal exsolution to enhance the catalytic activity of electrodes in solid oxide fuel cells. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, W.; Fujimoto, T.; Saito, M.; Inaba, M.; Yoshida, H.; Inagaki, T. Ni-Fe/Sm-doped CeO2 anode for ammonia-fueled solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 2014, 256, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, G.G.M.; Cumming, I.W.; Hellgardt, K. High performance direct ammonia solid oxide fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yin, Y.-M.; Zhou, N.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Z.-F. Sulfur tolerant redox stable layered perovskite SrLaFeO4−δ as anode for solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 76, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, T. Improved thermal expansion and electrochemical performance of La1−δSrδFe0.7Ni0.3O3−δ cathodes for intermediate-temperature SOFCs. Solid State Sci. 2020, 108, 106356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Electrolyte | Anode | Cathode | Electrolyte Thickness (µm) | PPD at 800 °C (mW cm−2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDC | LSFNM-SDCi | LSFNM-SDCi | 300 | 487 | This work |
| SDC | Pr0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.78O3−δ | BaCo0.4Fe0.4Zr0.1Y0.1O3−δ | 400 | 288 | [15] |
| SDC | Pr0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.75Ru0.05O3−δ | BaCo0.4Fe0.4Zr0.1Y0.1O3−δ | 400 | 374 | [15] |
| SDC | La0.52Sr0.28Ti0.94Ni0.06O3−δ-SDC | Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δ | 350 | 161 | [17] |
| SDC | La0.52Sr0.28Ti0.94Co0.06O3−δ-SDC | Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δ | 350 | 98 | [17] |
| SDC | La0.52Sr0.28Ti0.94Ni0.03Co0.03O3−δ-SDC | Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δ | 350 | 361 | [17] |
| La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2O2.85 | Ni-SDC | Sm0.5Sr0.5CoO3−δ | 500 | 118 | [46] |
| La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2O2.85 | Ni(40)Fe(60)-SDC | Sm0.5Sr0.5CoO3−δ | 500 | 250 | [46] |
| 6mol% YSZ | Ni-YSZ | Ag | 400 | 75 | [47] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Liang, Z.; Qiu, H.; Yi, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Su, C.; Yang, T. A High-Performance and Durable Direct-Ammonia Symmetrical Solid Oxide Fuel Cell with Nano La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.7Ni0.2Mo0.1O3−δ-Decorated Doped Ceria Electrode. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080673
Jiang H, Liang Z, Qiu H, Yi Y, Jiang S, Xu J, Wang W, Su C, Yang T. A High-Performance and Durable Direct-Ammonia Symmetrical Solid Oxide Fuel Cell with Nano La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.7Ni0.2Mo0.1O3−δ-Decorated Doped Ceria Electrode. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(8):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080673
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Hao, Zhixian Liang, Hao Qiu, Yongning Yi, Shanshan Jiang, Jiahuan Xu, Wei Wang, Chao Su, and Tao Yang. 2024. "A High-Performance and Durable Direct-Ammonia Symmetrical Solid Oxide Fuel Cell with Nano La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.7Ni0.2Mo0.1O3−δ-Decorated Doped Ceria Electrode" Nanomaterials 14, no. 8: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080673
APA StyleJiang, H., Liang, Z., Qiu, H., Yi, Y., Jiang, S., Xu, J., Wang, W., Su, C., & Yang, T. (2024). A High-Performance and Durable Direct-Ammonia Symmetrical Solid Oxide Fuel Cell with Nano La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.7Ni0.2Mo0.1O3−δ-Decorated Doped Ceria Electrode. Nanomaterials, 14(8), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080673








