The Catalytic Role of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as a Support Material for TiO2 and ZnO on Chlorpyrifos Photodegradation in an Aqueous Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Fe3O4-NP
2.2. Synthesis of SPION@SiO2
2.3. Synthesis of SPION@SiO2@TiO2 and SPION@SiO2@ZnO Nanocomposites
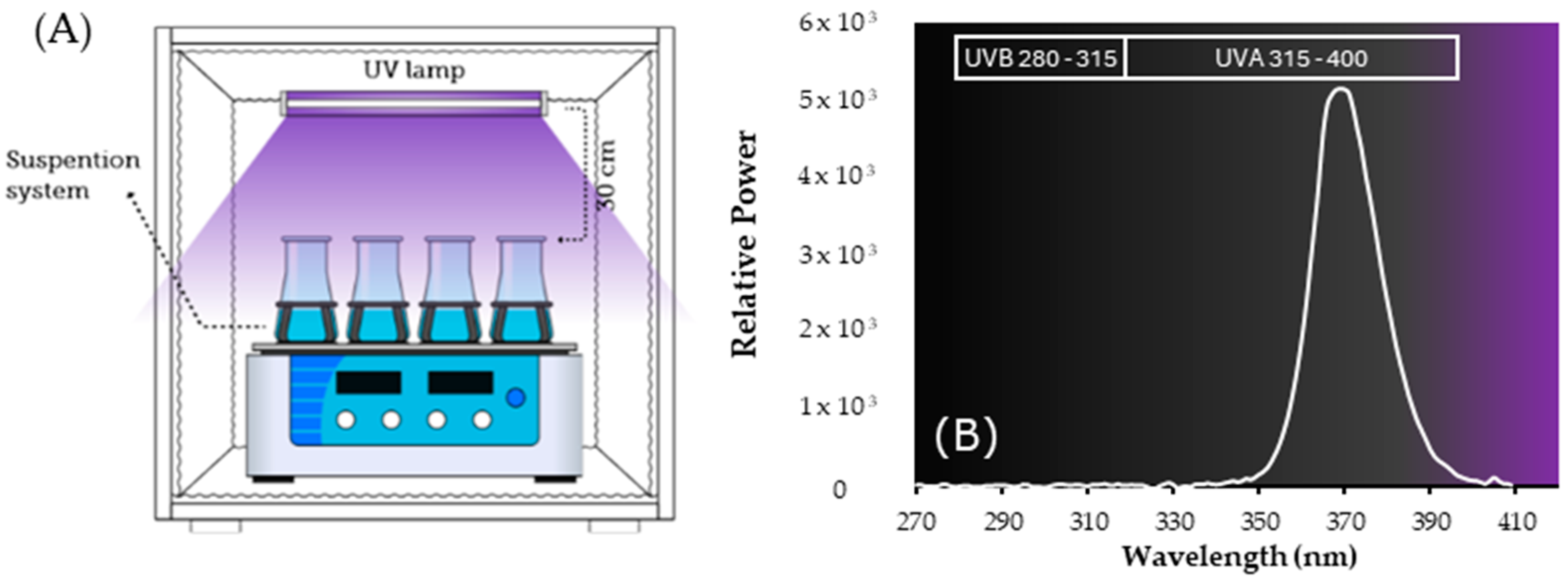
2.4. Photocatalytic Degradation
2.5. Kinetic Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analyses
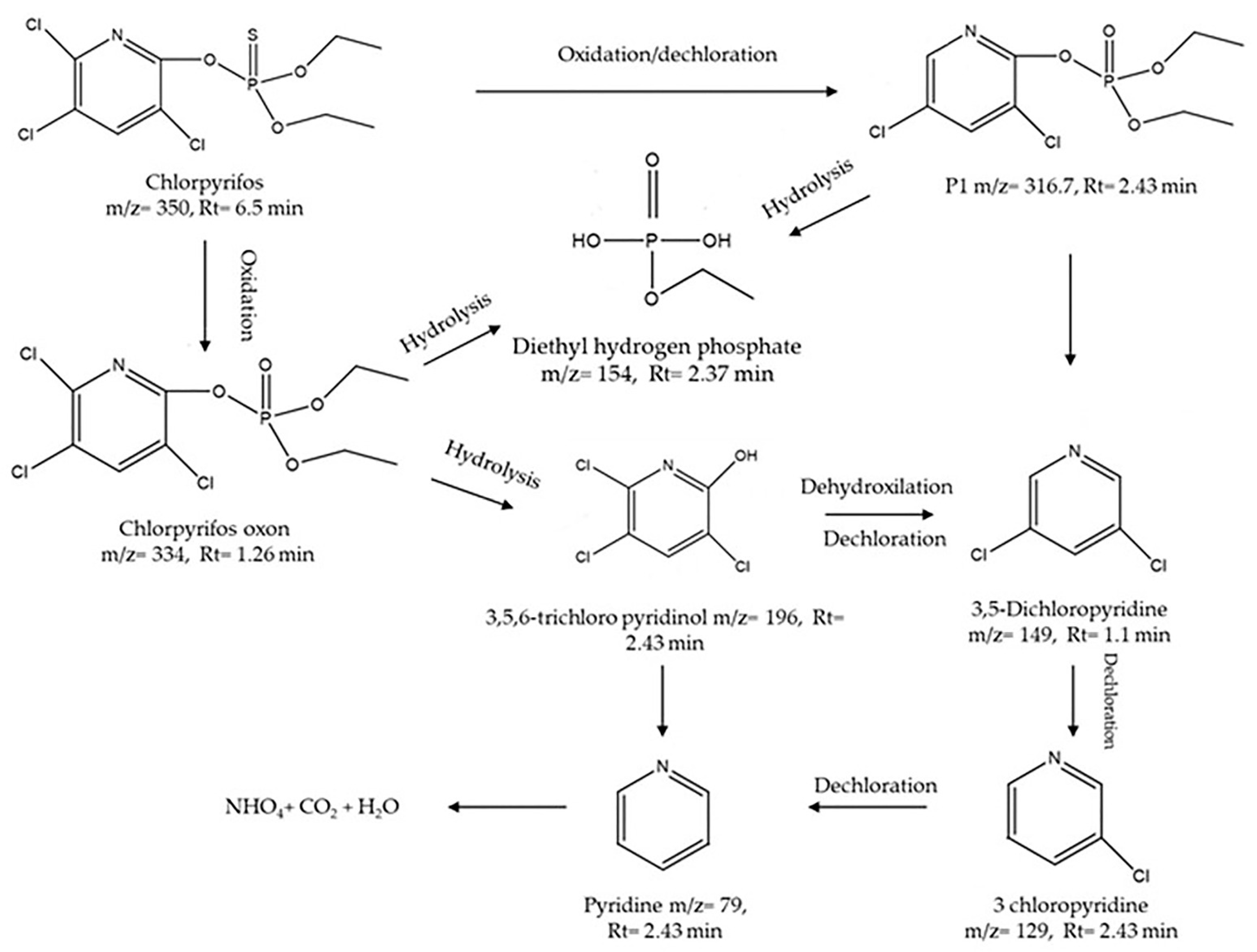
2.7. Proposed Degradation Pathway of Chlorpyrifos by SPION@SiO2@TiO2
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Synthesized Nanoparticles
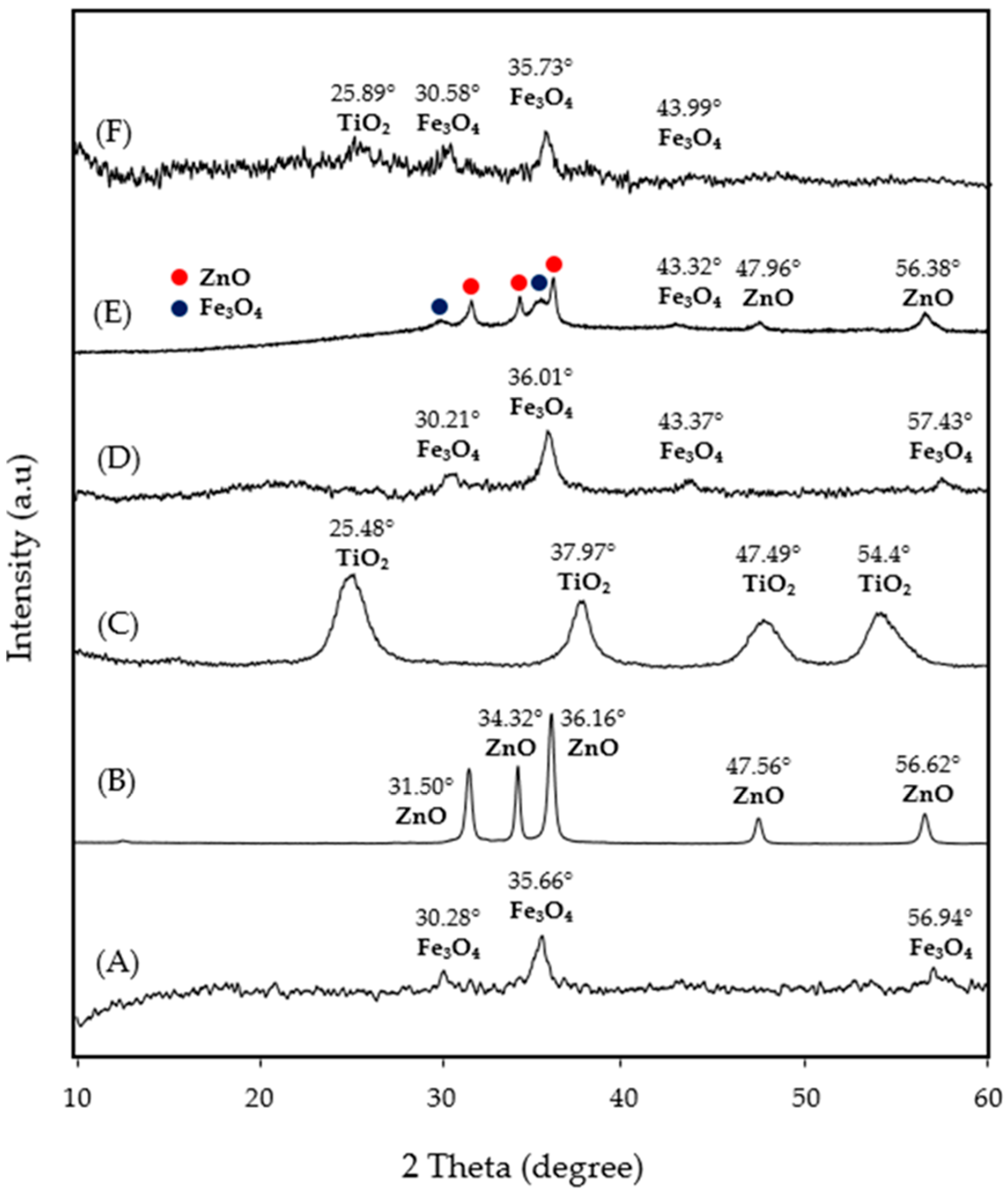
3.1.1. XRD Analysis
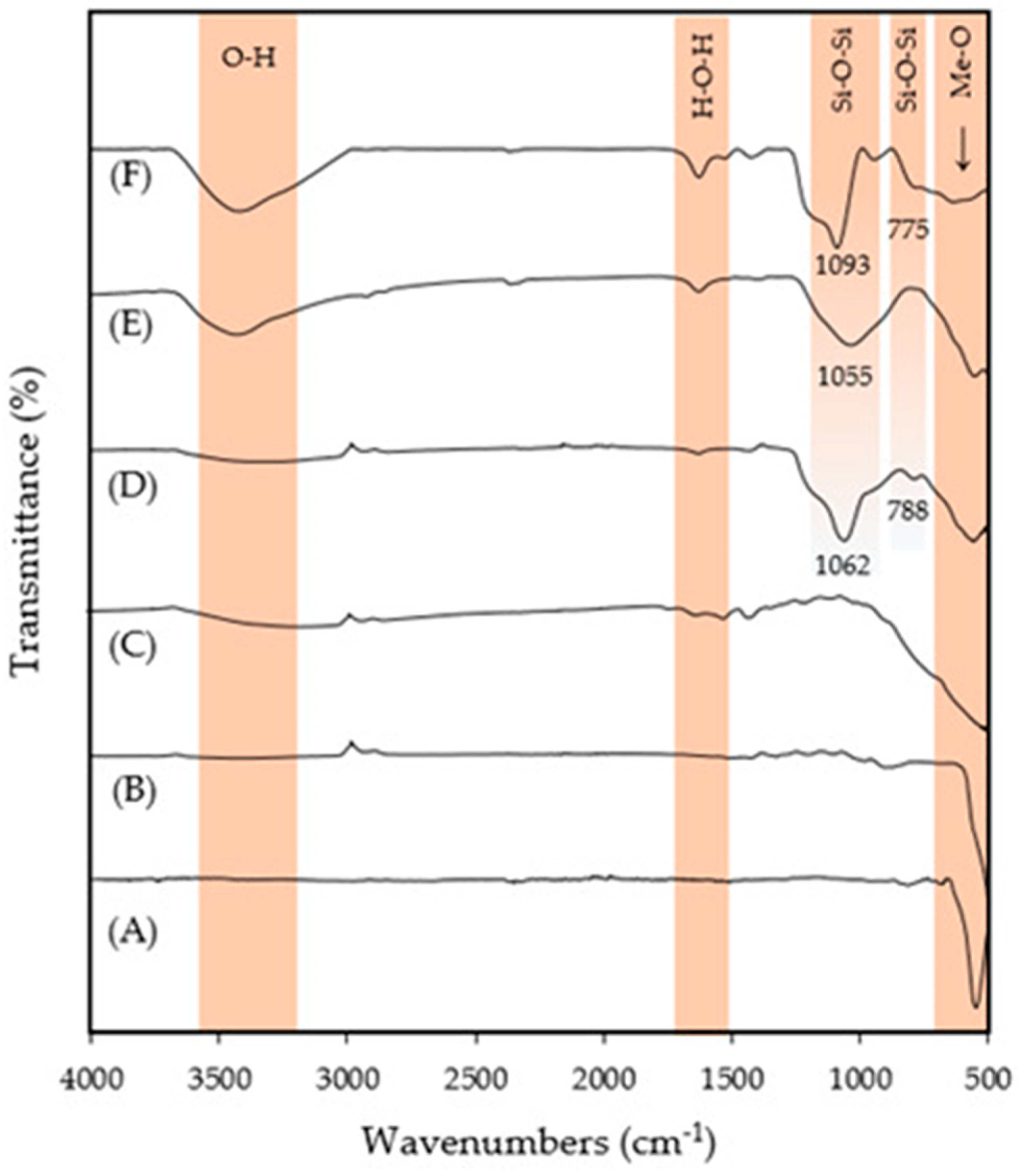
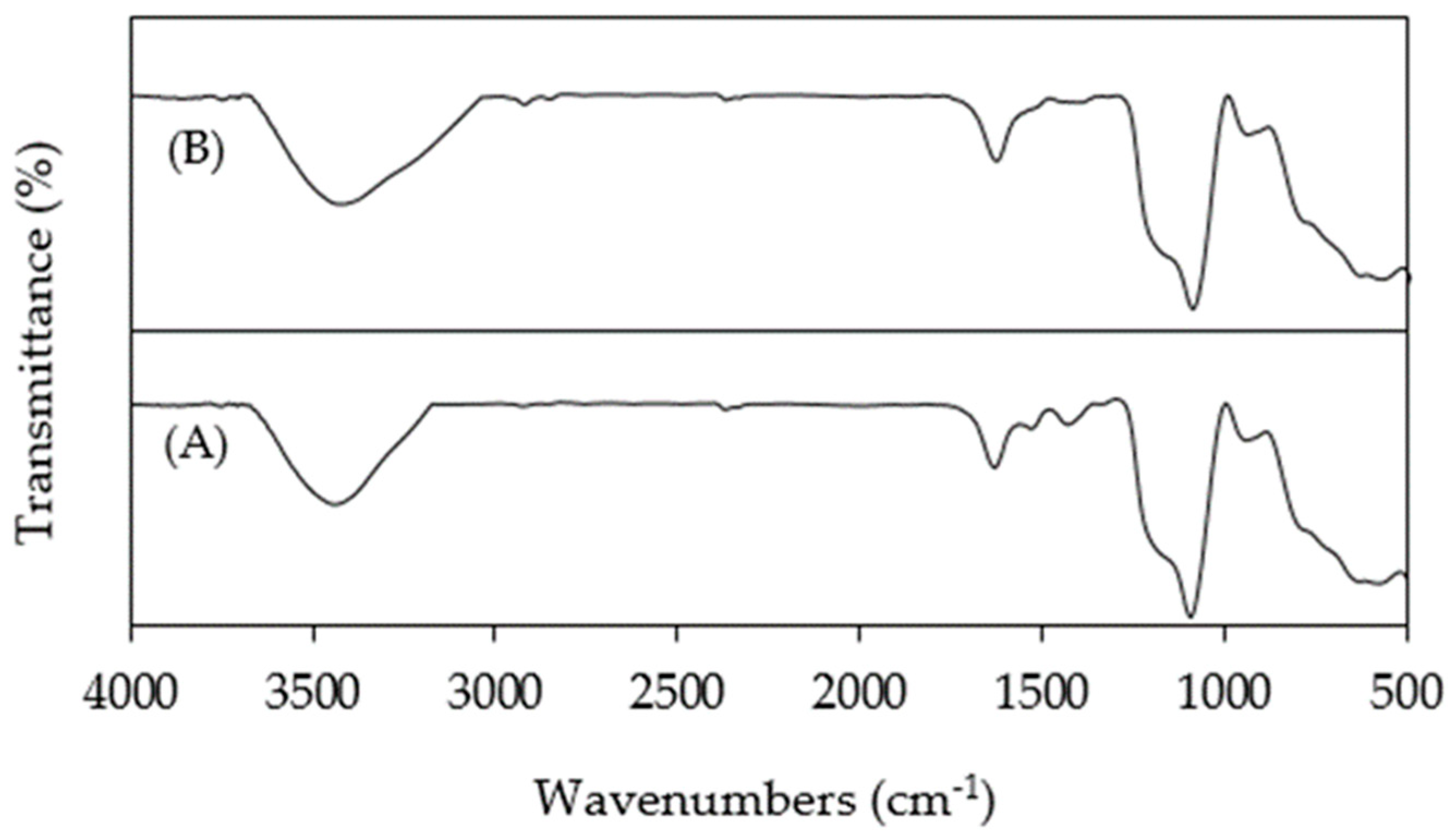
3.1.2. FT-IR Analysis
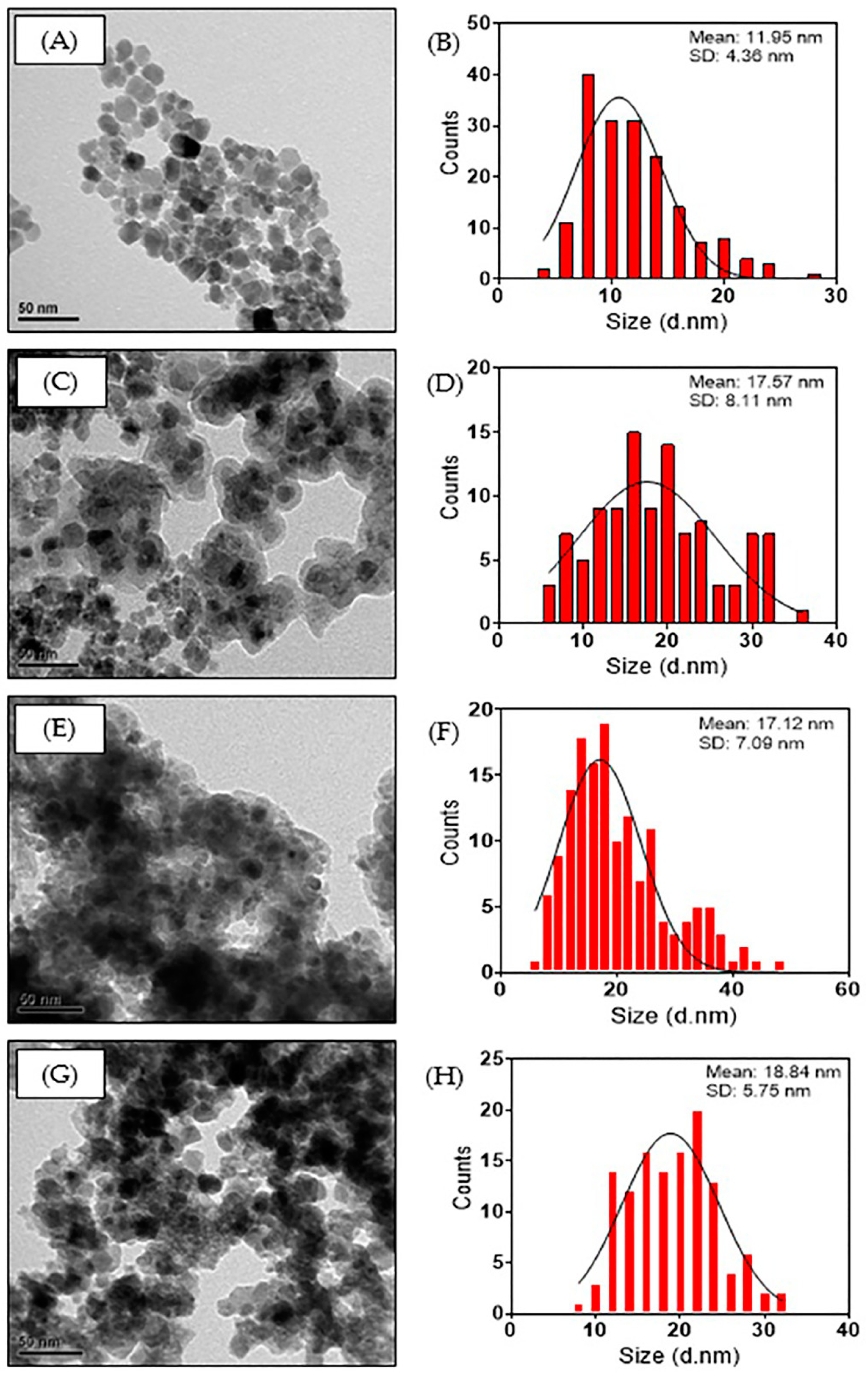
3.1.3. TEM Analysis
3.1.4. Porosity and Surface Area of SPION@SiO2@TiO2 and SPION@SiO2@ZnO Nanocomposites
3.2. Photocatalytic Degradation
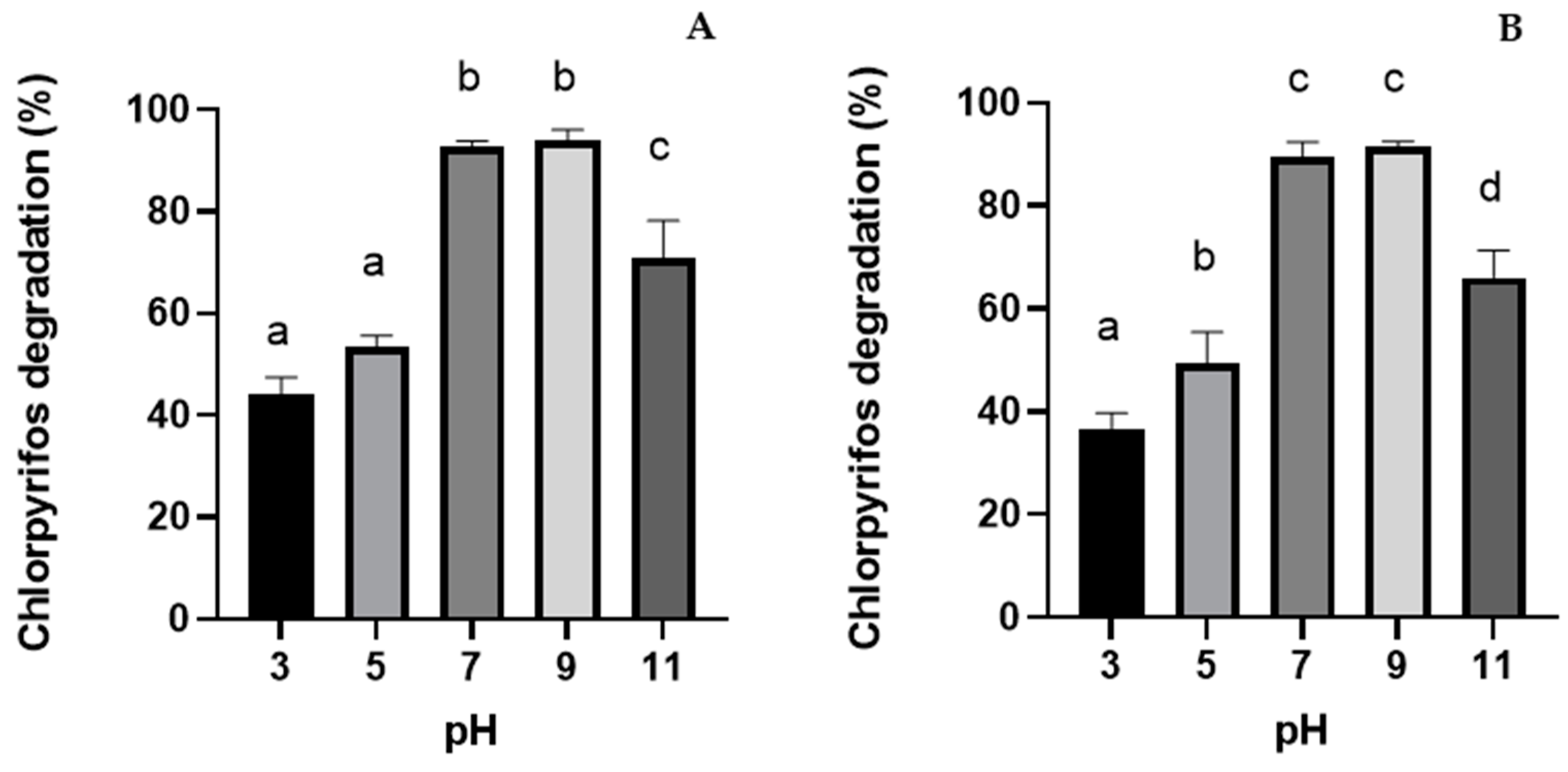
3.2.1. Initial pH Effect
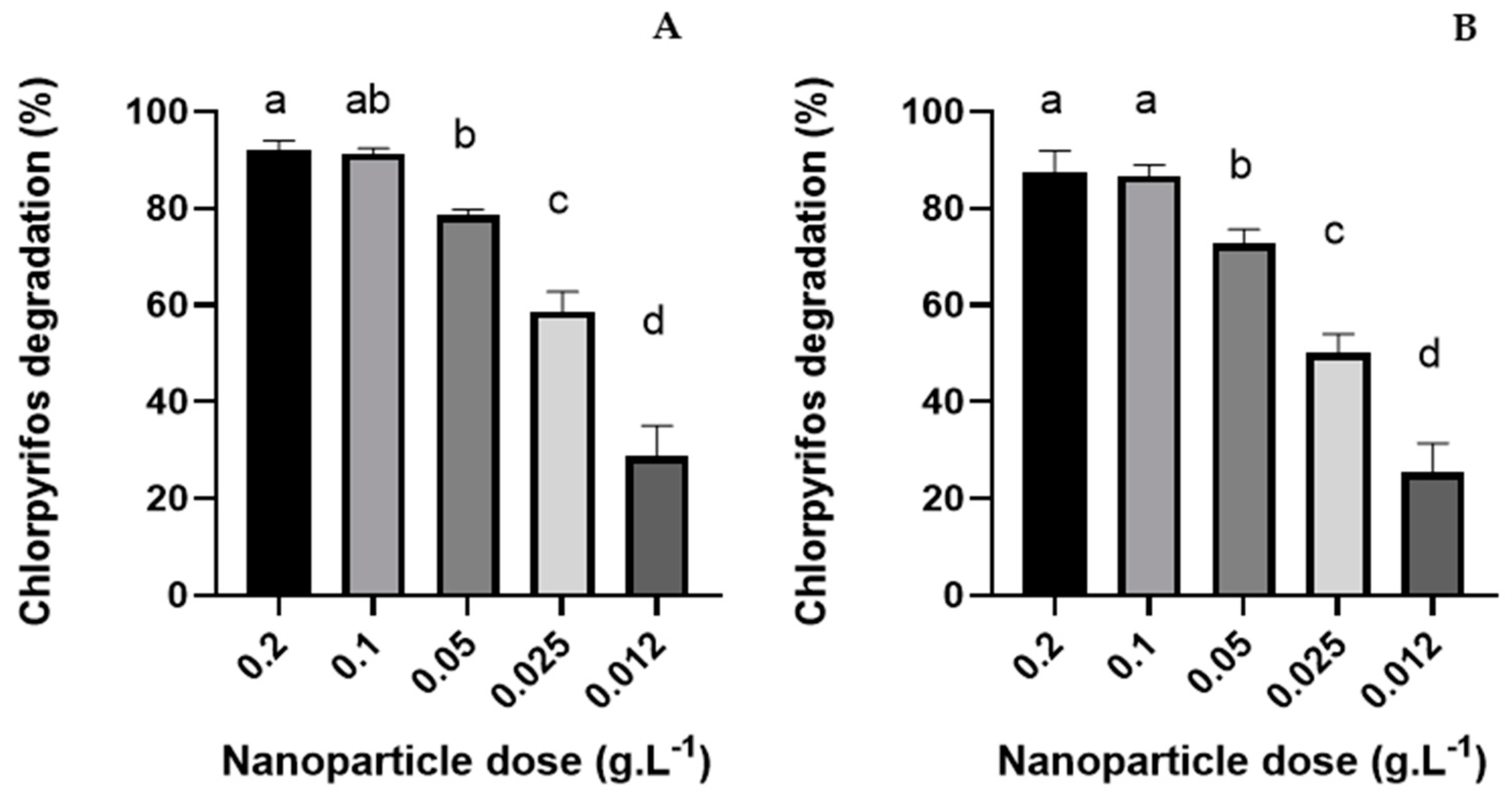
3.2.2. Nanoparticle Dose Effect
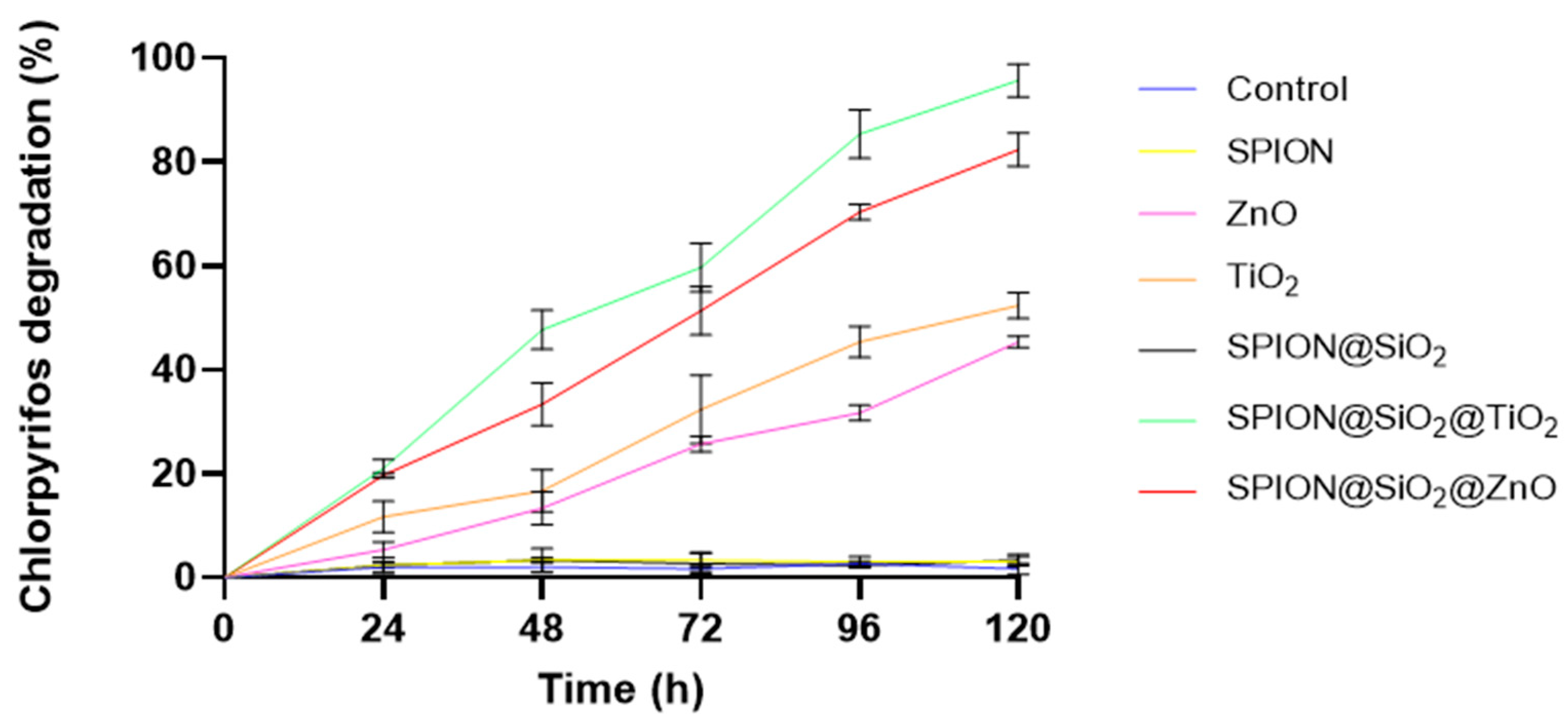
3.2.3. Effect of Catalyst Type on CP and TCP Degradation
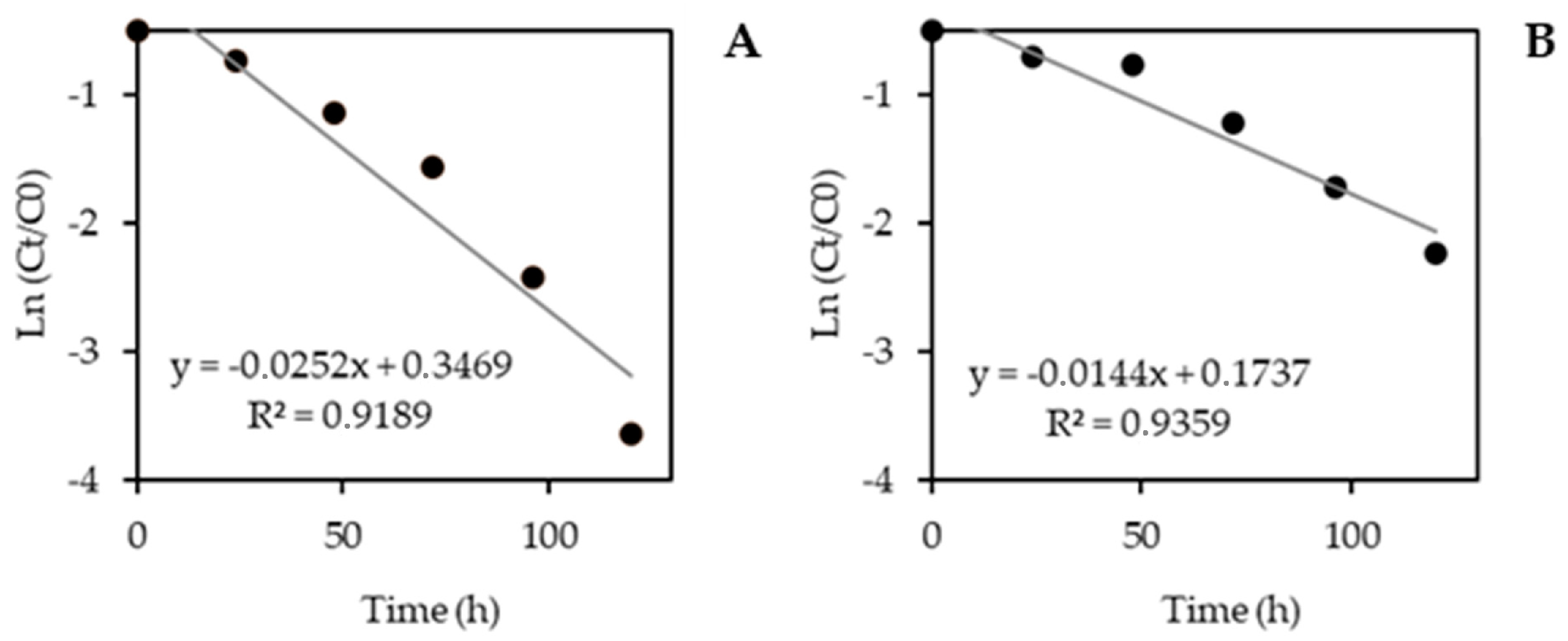
3.2.4. Kinetic Study
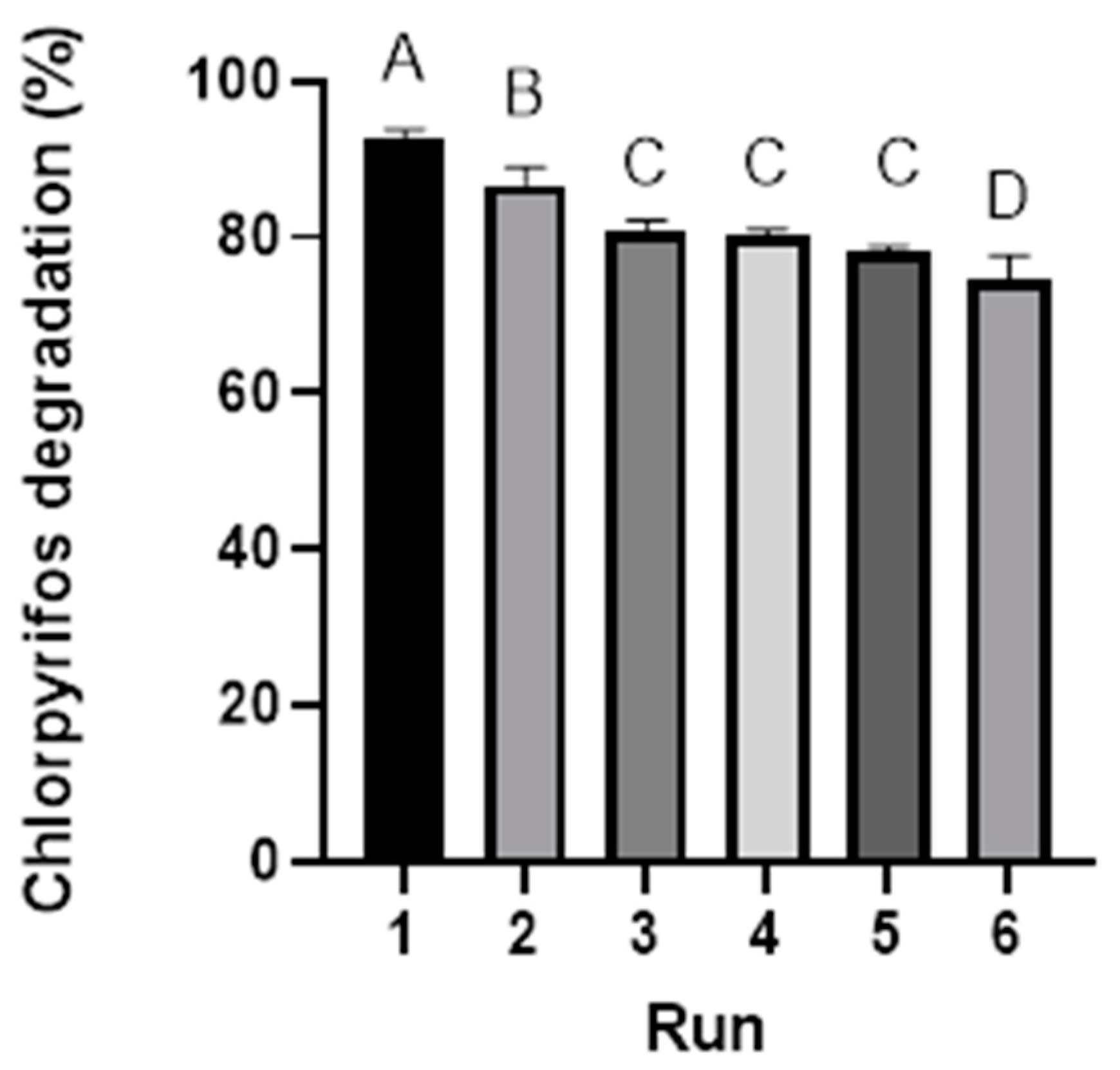
3.2.5. Reuse and Stability of Photocatalysts
3.2.6. Proposed Degradation Pathway
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grung, M.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Steen, A.O.; Huang, J.; Zhang, G.; Larssen, T. Pesticide Levels and Environmental Risk in Aquatic Environments in China—A Review. Environ. Int. 2015, 81, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in Glyphosate Herbicide Use in the United States and Globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, H.; Shah, C.; Patel, D.H.; Trivedi, U.; Subramanian, R.B. Degradation Insight of Organophosphate Pesticide Chlorpyrifos through Novel Intermediate 2,6-Dihydroxypyridine by Arthrobacter sp. HM01. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.G.; Blitzer, E.J.; Gibbs, J.; Losey, J.E.; Danforth, B.N.; Park, M.G. Negative Effects of Pesticides on Wild Bee Communities Can Be Buffered by Landscape Context. Proc. R. Soc. B 2015, 282, 20150299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, F.P. Pesticides, Environment, and Food Safety. Food Energy Secur. 2017, 6, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Agrochemicals, Health and Environment: Directory of Resources. Available online: http://www.who.int/heli/risks/toxics/chemicalsdirectory/en/index1.html (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Fernández-Alberti, S.; Rubilar, O.; Tortella, G.R.; Diez, M.C. Chlorpyrifos Degradation in a Biomix: Effect of Pre-Incubation and Water Holding Capacity. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2012, 12, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tortella, G.R.; Rubilar, O.; Castillo, M.D.P.; Cea, M.; Mella-Herrera, R.; Diez, M.C. Chlorpyrifos Degradation in a Biomixture of Biobed at Different Maturity Stages. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Peng, C.; Liu, H.; Hu, M.; Zhong, G. Biodegradation of Chlorpyrifos and Its Hydrolysis Product 3,5,6-Trichloro-2-Pyridinol by a New Fungal Strain Cladosporium Cladosporioides Hu-01. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farner Budarz, J.; Cooper, E.M.; Gardner, C.; Hodzic, E.; Ferguson, P.L.; Gunsch, C.K.; Wiesner, M.R. Chlorpyrifos Degradation via Photoreactive TiO2 Nanoparticles: Assessing the Impact of a Multi-Component Degradation Scenario. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 372, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sud, D.; Kumar, J.; Kaur, P.; Bansal, P. Toxicity, Natural and Induced Degradation of Chlorpyrifos. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2020, 65, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo, E.; Villaverde, J. Advanced Technologies for the Remediation of Pesticide-Contaminated Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 576–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootharaju, M.S.; Pradeep, T. Understanding the Degradation Pathway of the Pesticide, Chlorpyrifos by Noble Metal Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dârjan, A.; Drăghici, C.; Perniu, D.; Duţă, A. Degradation of Pesticides by TiO2 Photocatalysis. In Environmental Security Assessment and Management of Obsolete Pesticides in Southeast Europe. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C: Environmental Security; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Žabar, R.; Komel, T.; Fabjan, J.; Kralj, M.B.; Trebše, P. Photocatalytic Degradation with Immobilised TiO2 of Three Selected Neonicotinoid Insecticides: Imidacloprid, Thiamethoxam and Clothianidin. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affam, A.C.; Chaudhuri, M. Degradation of Pesticides Chlorpyrifos, Cypermethrin and Chlorothalonil in Aqueous Solution by TiO2 Photocatalysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 130, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Li, J.; Mu, Z.; Li, L.; Hao, Z. Effect of PH on DDT Degradation in Aqueous Solution Using Bimetallic Ni/Fe Nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 66, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, D.L.; Cao, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wang, Y. Enhanced Photodegradation Activity of Organic Pollutants Contained in Sewage Through Construction of a CuO/Ag Composite Nanostructure. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.J.; Moussavi, G.; Hossaini, H. Degradation and Mineralization of Diazinon Pesticide in UVC and UVC/TiO2 Process. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 3782–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.N.; Dhabbe, R.S.; Kokate, M.R.; Gaikwad, Y.B.; Garadkar, K.M. Preparation of N Doped TiO2 via Microwave-Assisted Method and Its Photocatalytic Activity for Degradation of Malathion. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 133, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Ilyas, M.; Basheer, C.; Tariq, M.; Daud, M.; Baig, N.; Shehzad, F. Impact of Nanoparticles on Human and Environment: Review of Toxicity Factors, Exposures, Control Strategies, and Future Prospects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4122–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shee, N.K.; Park, B.H.; Kim, H.J. Hybrid Composite of Sn(IV)-Porphyrin and Mesoporous Structure for Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes. Molecules 2023, 28, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saljooqi, A.; Shamspur, T.; Mostafavi, A. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity of Porous ZnO Stabilized by TiO2 and Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Investigation of Pesticide Degradation Reaction in Water Treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9146–9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, R.; Khan, M.M.; Gupta, V.K.; Mosquera, E.; Gracia, F.; Narayanan, V.; Stephen, A. ZnO/Ag/Mn2O3 Nanocomposite for Visible Light-Induced Industrial Textile Effluent Degradation, Uric Acid and Ascorbic Acid Sensing and Antimicrobial Activity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 34645–34651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Gupta, U. A Review on Applications of Nanoparticles for the Preconcentration of Environmental Pollutants. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8279–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, R.; Veerapandian, M.; Yun, K.S. Nanoparticles: Functionalization and Multifunctional Applications in Biomedical Sciences. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 4559–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dakdouki, M.; El-Boubbou, K.; Xia, J.; Kavunja, H.; Huang, X. Methods for Magnetic Nanoparticle Synthesis. In Chemistry of Bioconjugates: Synthesis, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications; Narain, R., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Published: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 281–314. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Qian, T.; Jiang, H. Bimetallic Fe Nanoparticles: Recent Advances in Synthesis and Application in Catalytic Elimination of Environmental Pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, W.; Vera, J.; Aponte, H.; Hermosilla, E.; Fincheira, P.; Parada, J.; Tortella, G.; Seabra, A.B.; Diez, M.C.; Rubilar, O. Meta-Analysis of Metal Nanoparticles Degrading Pesticides: What Parameters Are Relevant? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 60168–60179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Hasan, A.; Iqbal, N.; Alam, S.; Saini, M.K.; Raza, S.K. Synthesis and Surface Engineering of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Environmental Cleanup and Pesticide Residue Analysis: A Review. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 1805–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesus, A.C.B.; Jesus, J.R.; Lima, R.J.S.; Moura, K.O.; Almeida, J.M.A.; Duque, J.G.S.; Meneses, C.T. Synthesis and Magnetic Interaction on Concentrated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Obtained by the Co-Precipitation and Hydrothermal Chemical Methods. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 11149–11153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiari, N.; Kashefi, M.; Afsharnezhad, S.; Mirjalili, M. Insight into Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity of Fe3O4–SiO2–TiO2 Core-Multishell Nanoparticles on the Elimination of Escherichia coli. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 244, 122633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ferreira-Neto, E.P.; Pasa, A.A.; Alcântara, C.C.J.; Acuña, J.J.S.; Bilmes, S.A.; Martínez Ricci, M.L.; Landers, R.; Fermino, T.Z.; Rodrigues-Filho, U.P. Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties of Core@shell SiO2@TiO2 Nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 179, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, A.; Esquivel, K. SiO2@TiO2 Composite Synthesis and Its Hydrophobic Applications: A Review. Catalysts 2020, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Yan, W. Magnetically Separable Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2-Ag Microspheres with Well-Designed Nanostructure and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariani, P.L.; Salni, S.; Said, M.; Farahdiba, R. Core-Shell Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2 Magnetic Modified Ag for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Congo Red Dye and Antibacterial Activity. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2023, 18, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, W.; Yin, Y. Synthesis and Properties of Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2 Nanocomposites by Hydrothermal Synthetic Method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2012, 15, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaagac, O.; Köçkar, H. Improvement of the Saturation Magnetization of PEG Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 551, 169140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALOthman, Z. A Review: Fundamental Aspects of Silicate Mesoporous Materials. Materials 2012, 5, 2874–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, N.; Jayakrishnan, R.; Abraham, R. Role of Pore Size on the Photocatalytic Dilapidation of Organic Pollutant SRB in Mesoporous In2S3. J. Chem. Sci. 2023, 135, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foletto, E.L.; Battiston, S.; Simões, J.M.; Bassaco, M.M.; Pereira, L.S.F.; De Moraes Flores, É.M.; Müller, E.I. Synthesis of ZnAl2O4 Nanoparticles by Different Routes and the Effect of Its Pore Size on the Photocatalytic Process. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 163, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Guan, R.; Zheng, J. Effect of the Pore Size of TiO2-Loaded Activated Carbon Fiber on Its Photocatalytic Activity. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingmongkol, Y.; Trinh, D.T.T.; Phuinthiang, P.; Channei, D.; Ratananikom, K.; Nakaruk, A.; Khanitchaidecha, W. Enhanced Photocatalytic and Photokilling Activities of Cu-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanjwani, M.F.; Khuhawar, M.Y.; Khuhawar, T.M.J.; Lanjwani, A.H.; Memon, S.Q.; Soomro, W.A.; Rind, I.K. Photocatalytic Degradation of Eriochrome Black T Dye by ZnO Nanoparticles Using Multivariate Factorial, Kinetics and Isotherm Models. J Clust. Sci. 2023, 34, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaei, A.; Kargar, M. Photocatalytic Degradation of Chlorpyrifos in Water Using Titanium Dioxide and Zinc Oxide. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2013, 22, 2442–2447. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, R.J.; Molina, R.; Xu, J.; Dobson, P.J.; Thompson, I.P. Comparison of TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue and the Correlated Inactivation of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, C. Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Contaminants in Water by ZnO Nanoparticles: Revisited. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 304, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekaran, L.; Rajendran, S.; Qin, J.; Lütfi Yola, M.; Atar, N.; Gracia, F. Nanosized Fe3O4 Incorporated on a TiO2 Surface for the Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 287, 110967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshypany, R.; Selim, H.; Zakaria, K.; Moustafa, A.H.; ASadeek, S.; Sharaa, S.; Raynaud, P.; Nada, A.A. Elaboration of Fe3O4/ZnO Nanocomposite with Highly Performance Photocatalytic Activity for Degradation Methylene Blue under Visible Light Irradiation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourinia, H.; Alshamsi, H.A.; Al-nayili, A.; Gholami, M. Photocatalytic Degradation of Chlorpyrifos Using Ag Nanoparticles-Doped g-C3N5 Decorated with Dendritic CdS. Chemosphere 2023, 344, 140325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemer, H.; Sharpless, C.M.; Linden, K.G. Photodegradation of 3,5,6-Trichloro-2-Pyridinol in Aqueous Solution. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 168, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žabar, R.; Sarakha, M.; Lebedev, A.T.; Polyakova, O.V.; Trebše, P. Photochemical Fate and Photocatalysis of 3,5,6-Trichloro-2-Pyridinol, Degradation Product of Chlorpyrifos. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. Fabrication of Black TiO2/TiO2 Homojunction for Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 14320–14329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, A.; Iqbal, T.; Ashraf, M.; Nazir, A.; Ali, F.; Ranjha, Q.A.; Hussain, M.; Al-Harbi, F.F.; Galal, A.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Visible Light Driven Catalytic Removal of MB and RhB Dye: Experimental and Computational Analysis. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2023, 33, 1841–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhika, L.N.; Suryaningsih, S.; Aprilia, A. Photoactivity Enhancement of TiO2 Nanoparticle-Decorated ZnO as a Photocatalyst in Methylene Blue Degradation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2376, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Romain, S.J.; Basirico, L.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Armbrust, K.L. Impacts of Salinity on the Hydrolysis of Chlorpyrifos. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulić Petrić, A.; Stipičević, S.; Mešić, A. Stability of Malathion, Diazinon and Chlorpyrifos in Different Water Types—A Review. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2023, 24, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayodhya, D.; Veerabhadram, G. Fabrication of Schiff Base Coordinated ZnS Nanoparticles for Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Chlorpyrifos Pesticide and Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. J. Mater. 2019, 5, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahbakhsh, S.; Parvari, R.; Zare, A.; Mahdizadeh, H.; Faizi, V.; Saljooqi, A. Preparation of Biochar Based on Grapefruit Peel and Magnetite Decorated with Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic Degradation of Chlorpyrifos. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 126, 109130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | ABET (m2·g−1) | Pore Diameter (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPiON@SiO2@TiO2 | 243.22 | 3.84 | 0.19 |
| SPiON@SiO2@ZnO | 108.79 | 3.27 | 0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera, W.; Vera, J.; Hermosilla, E.; Diaz, M.; Tortella, G.R.; Dos Reis, R.A.; Seabra, A.B.; Diez, M.C.; Rubilar, O. The Catalytic Role of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as a Support Material for TiO2 and ZnO on Chlorpyrifos Photodegradation in an Aqueous Solution. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030299
Herrera W, Vera J, Hermosilla E, Diaz M, Tortella GR, Dos Reis RA, Seabra AB, Diez MC, Rubilar O. The Catalytic Role of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as a Support Material for TiO2 and ZnO on Chlorpyrifos Photodegradation in an Aqueous Solution. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(3):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030299
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera, Wence, Joelis Vera, Edward Hermosilla, Marcela Diaz, Gonzalo R. Tortella, Roberta Albino Dos Reis, Amedea B. Seabra, María Cristina Diez, and Olga Rubilar. 2024. "The Catalytic Role of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as a Support Material for TiO2 and ZnO on Chlorpyrifos Photodegradation in an Aqueous Solution" Nanomaterials 14, no. 3: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030299
APA StyleHerrera, W., Vera, J., Hermosilla, E., Diaz, M., Tortella, G. R., Dos Reis, R. A., Seabra, A. B., Diez, M. C., & Rubilar, O. (2024). The Catalytic Role of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as a Support Material for TiO2 and ZnO on Chlorpyrifos Photodegradation in an Aqueous Solution. Nanomaterials, 14(3), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030299










