Microwave Kinetic Inductance Detector Made of Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE)-Grown MgB2 Film
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
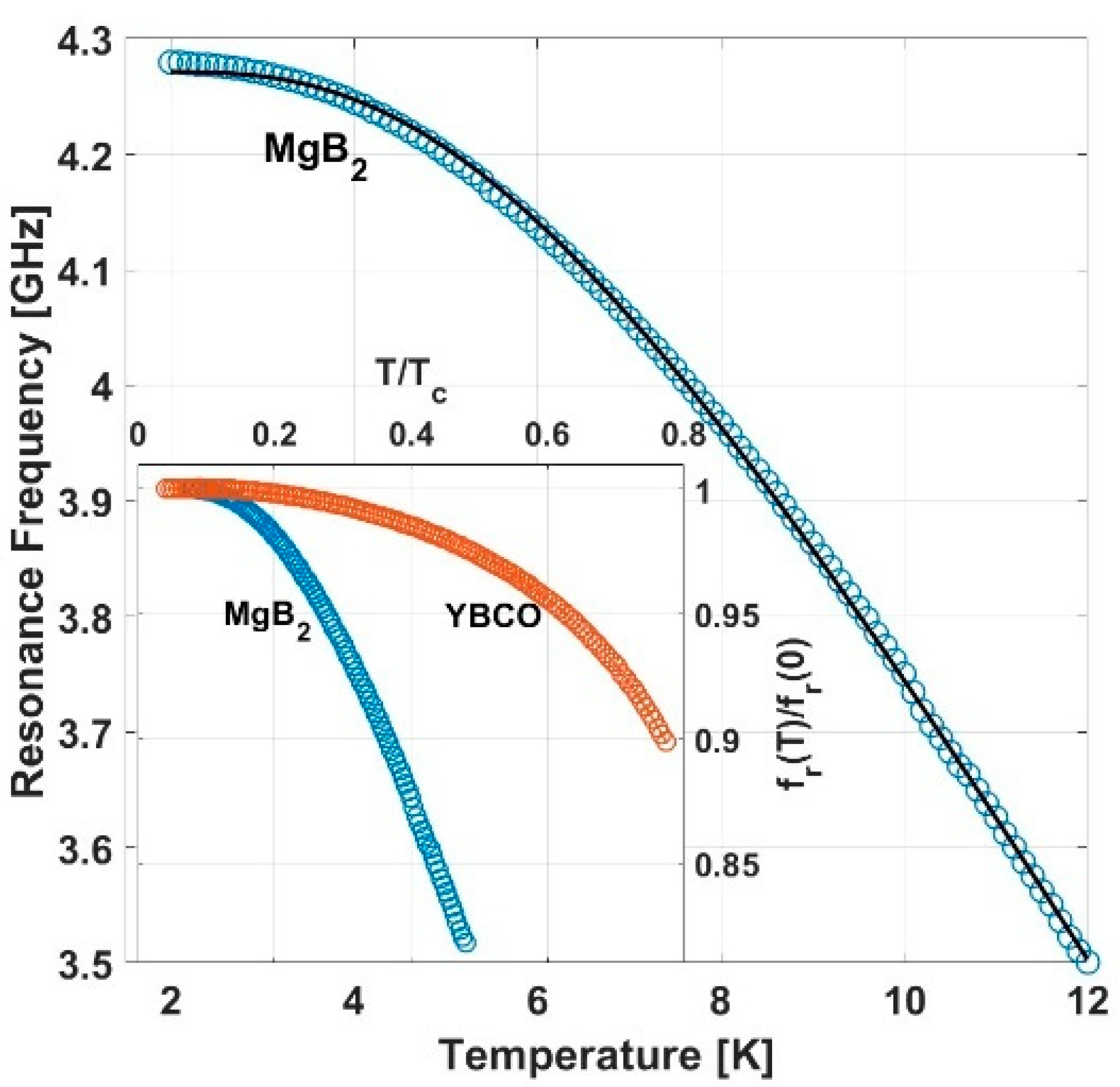
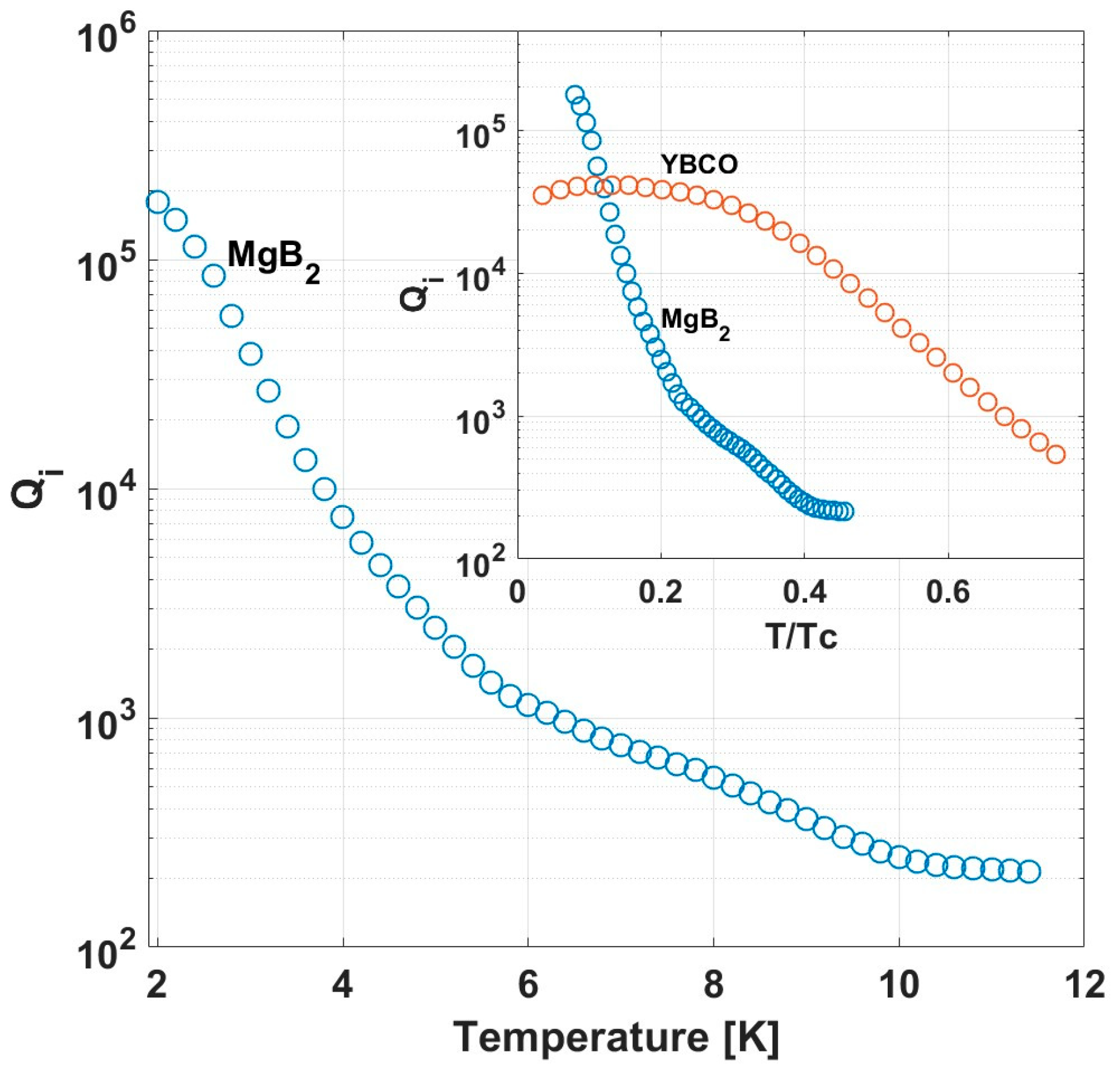
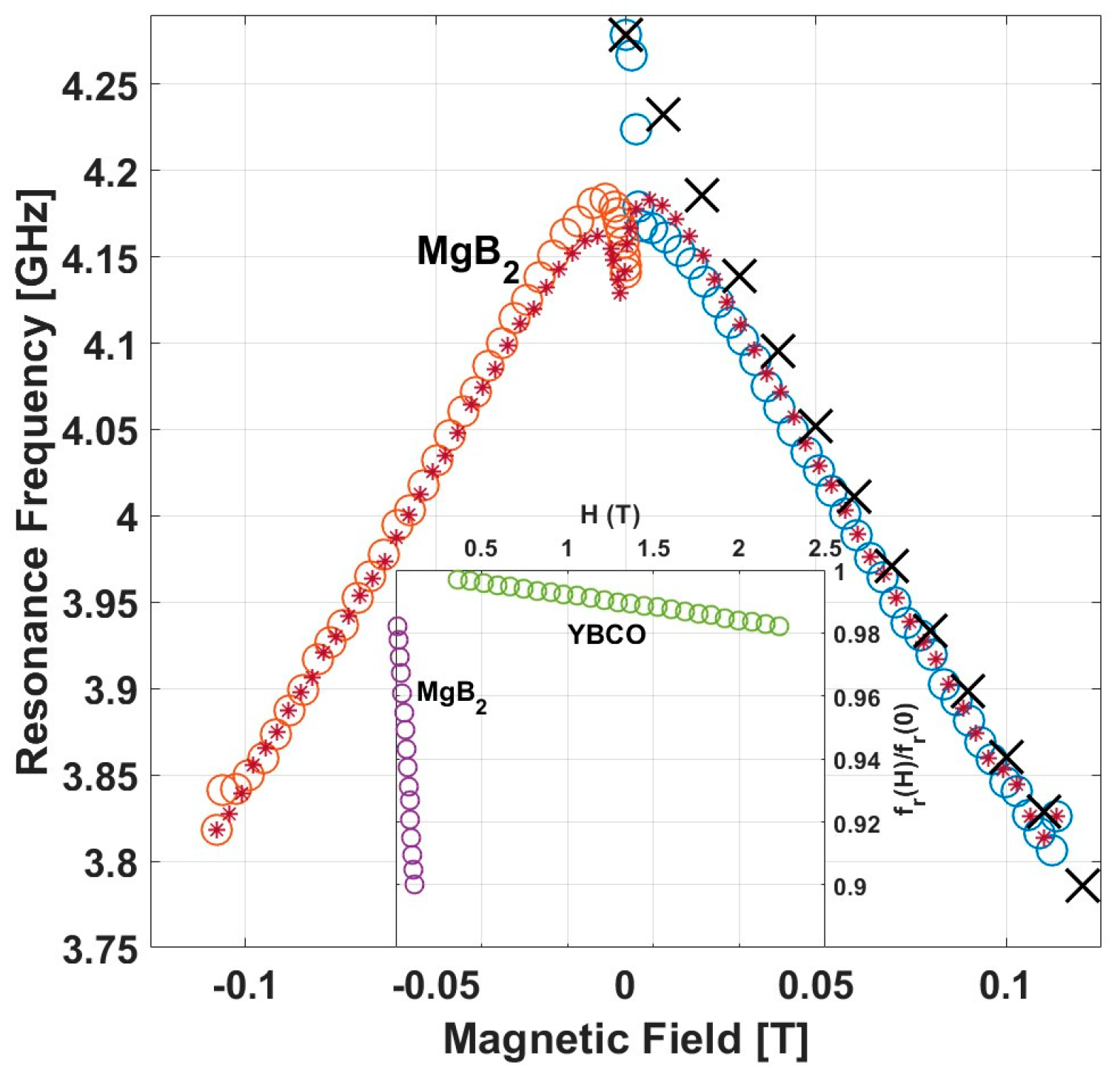
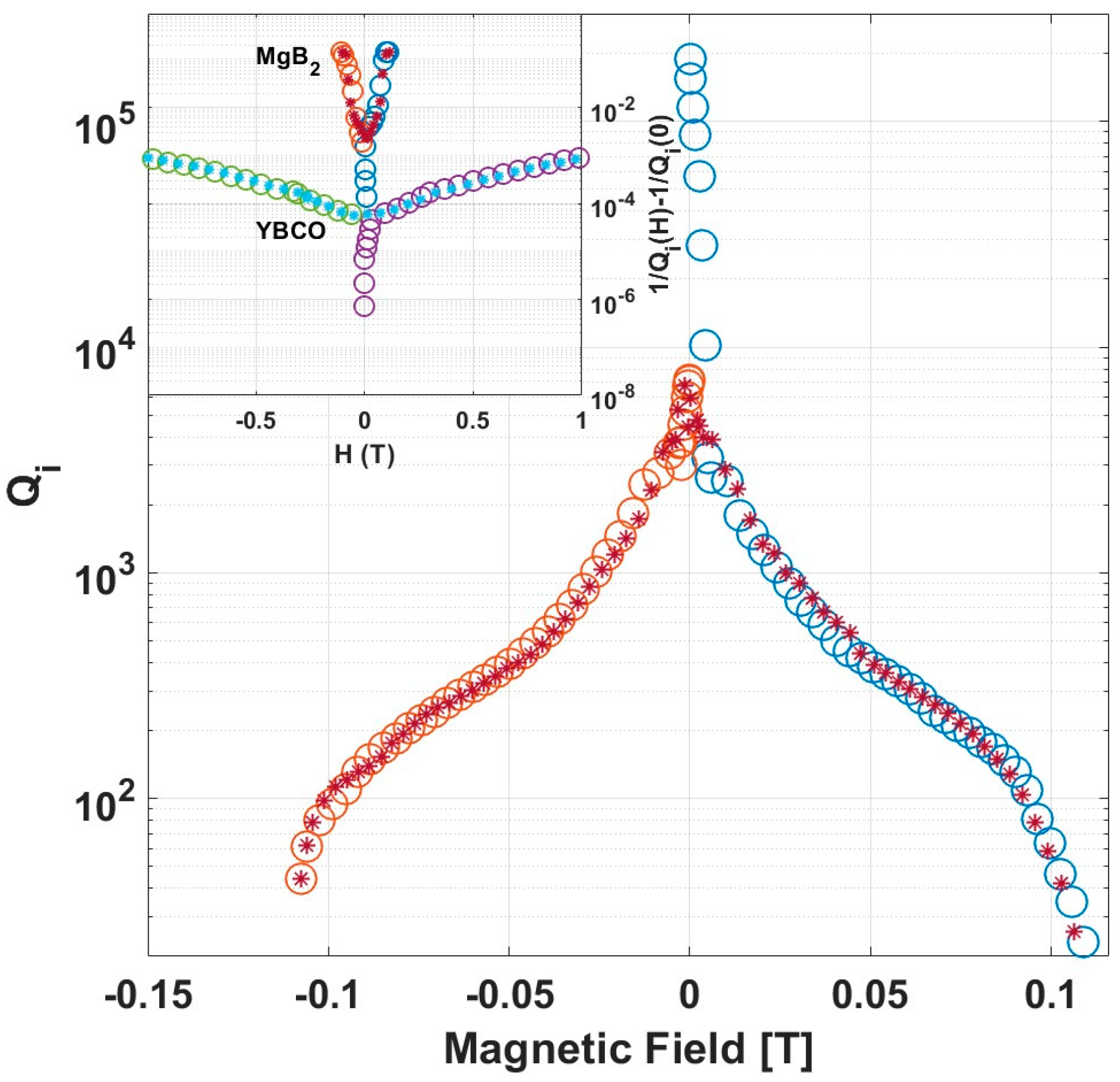
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zmuidzinas, J. Superconducting Microresonators: Physics and Applications. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2012, 3, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazin, B.A.; Young, B.; Cabrera, B.; Miller, A. Microwave Kinetic Inductance Detectors: The First Decade. AIP Conf. Proc. 2009, 1185, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ulbricht, G.; De Lucia, M.; Baldwin, E. Applications for Microwave Kinetic Induction Detectors in Advanced Instrumentation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünhaupt, L.; Maleeva, N.; Skacel, S.T.; Calvo, M.; Levy-Bertrand, F.; Ustinov, A.V.; Rotzinger, H.; Monfardini, A.; Catelani, G.; Pop, I.M. Loss Mechanisms and Quasiparticle Dynamics in Superconducting Microwave Resonators Made of Thin-Film Granular Aluminum. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Vale, L.R.; Mates, J.A.B.; Schmidt, D.R.; Hilton, G.C.; Irwin, K.D.; Mallet, F.; Castellanos-Beltran, M.A.; Lehnert, K.W.; Zmuidzinas, J.; et al. Strongly quadrature-dependent noise in superconducting microresonators measured at the vacuum-noise limit. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 232508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazin, B.A. H4.3 Superconducting Materials for Microwave Kinetic Inductance Detectors. In Handbook of Superconductivity: Characterization and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Ariyoshi, S.; Negishi, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Mikami, H.; Nakajima, K.; Tanaka, S. Evaluation of YBa2Cu3O7-δ based microwave kinetic inductance detectors with rewound spiral resonators. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1054, 12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roitman, A.; Shaulov, A.; Yeshurun, Y. Characterization of YBa2Cu3O7-δ coplanar resonator for microwave kinetic inductance detectors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2023, 36, 15002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamatsu, J.; Nakagawa, N.; Muranaka, T.; Zenitani, Y.; Akimitsu, J. Superconductivity at 39 K in magnesium diboride. Nature 2001, 413, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Niu, R.R.; Guo, Z.S.; Cai, X.W.; Chu, H.M.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Q.R.; Gan, Z.Z. Lumped element kinetic inductance detectors based on two-gap MgB2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 22601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghigo, G. MgB2 Thin Films for Radiation Detectors Operating at Microwave Frequencies. AIP Conf. Proc. 2006, 824, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- Cherednichenko, S.; Acharya, N.; Novoselov, E.; Drakinskiy, V. Low kinetic inductance superconducting MgB 2 nanowires with a 130 ps relaxation time for single-photon detection applications. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2021, 34, 44001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Fujita, Y.; Okayasu, S.; Katagiri, M.; Satoh, K.; Yotsuya, T.; Shimakage, H.; Miki, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Superconducting MgB2 Thin Film Detector for Neutrons. J. Low Temp. Phys. 2008, 151, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, V.G.; Zhelezina, N.V. Penetration-depth anisotropy in two-band superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 69, 132506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Naito, M. In Situ growth of superconducting MgB2 thin films by molecular-beam epitaxy. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Kuroha, M.; Iriuda, H.; Nakanishi, Y.; Izumida, F.; Endo, H.; Yoshizawa, M. Fabrication of as-grown MgB2 films on ZnO (0001) substrates by molecular beam epitaxy. Phys. C Supercond. Appl. 2006, 445–448, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido, H.; Yoshida, T.; Ishida, T. Ambient temperature epitaxial growth of MgB2 thin films with a Mg buffer layer. Appl. Phys. Express 2015, 8, 113101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, C.; Petit-Watelot, S.; Andrieu, S.; Pasquier, L.; Ghanbaja, J.; Mangin, S.; Dumesnil, K.; Hauet, T. Spin injection at MgB2-superconductor/ferromagnet interface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2024, 125, 102601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothner, D.; Gaber, T.; Kemmler, M.; Koelle, D.; Kleiner, R.; Wünsch, S.; Siegel, M. Magnetic hysteresis effects in superconducting coplanar microwave resonators. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 014517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roitman, A.; Shaulov, A.; Yeshurun, Y. Effect of Magnetic Fields on Superconducting Microwave Coplanar Resonators. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2023, 33, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahl, P.; Wordenweber, R. Nonlinear microwave properties of HTS thin film coplanar devices. IEEE Trans. Appiled Supercond. 2003, 13, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothner, D.; Clauss, C.; Koroknay, E.; Kemmler, M.; Gaber, T.; Jetter, M.; Scheffler, M.; Michler, P.; Dressel, M.; Koelle, D.; et al. Reducing vortex losses in superconducting microwave resonators with microsphere patterned antidot arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Heitmann, T.W.; DeFeo, M.P.; Yu, K.; McDermott, R.; Neeley, M.; Martinis, J.M.; Plourde, B.L.T. Microwave response of vortices in superconducting thin films of Re and Al. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 174512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieke, G.H. Detection of Light: From the Ultraviolet to the Submillimeter, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzocchi, F.; Driessen, E.; Shu, S.; Merker, M.; Ilin, K.; Siegel, M.; Meier, A.; Straus, D.; Scherer, T. Design of NbN Based Kinetic Inductance Detectors for Polarimetric Plasma Diagnostics. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2021, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J. The Physics of Superconducting Microwave Resonators. Ph.D. Thesis, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Askerzade, I.N.; Gencer, A. London penetration depth l(T) in two-band Ginzburg–Landau theory: Application to MgB2. Solid State Commun. 2002, 123, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larbalestier, D.C.; Cooley, L.D.; Rikel, M.O.; Polyanskii, A.A.; Jiang, J.; Patnaik, S.; Cai, X.Y.; Feldmann, D.M.; Gurevich, A.; Squitieri, A.A.; et al. Strongly linked current flow in polycrystalline forms of the superconductor MgB2. Nature 2001, 410, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghigo, G.; Botta, D.; Chiodoni, A.; Gozzelino, L.; Gerbaldo, R.; Laviano, F.; Mezzetti, E.; Monticone, E.; Portesi, C. Effective gap at microwave frequencies in MgB2 thin films with strong interband scattering. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 214522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Skinta, J.A.; Lemberger, T.R.; Kang, W.N.; Kim, H.-J.; Choi, E.-M.; Lee, S.-I. Reflection of a two-gap nature in penetration-depth measurements of MgB2 film. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 64511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, S. Lumped Element Kinetic Inductance Detectors. Ph.D. Thesis, Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Souma, S.; Machida, Y.; Sato, T.; Takahashi, T.; Matsui, H. The origin of multiple superconducting gaps in MgB2. Nature 2003, 423, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, A.; Sanna, A.; Lüders, M.; Profeta, G.; Lathiotakis, N.N.; Marques, M.A.L.; Franchini, C.; Gross, E.K.U.; Continenza, A.; Massidda, S. Superconducting properties of MgB2 from first principles. Phys. C Supercond. 2007, 456, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenov, A.; Loidl, A.; Krasnosvobodtsev, S.I. Energy gap and London penetration depth of MgB2 films determined by microwave resonator measurements. arXiv 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshchalkov, V.; Menghini, M.; Nishio, T.; Chen, Q.H.; Silhanek, A.V.; Dao, V.H.; Chibotaru, L.F.; Zhigadlo, N.D.; Karpinski, J. Type-1.5 Superconductivity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agassi, Y.D.; Oates, D.E. Theoretical and experimental evidence for a nodal energy gap in MgB2. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2017, 30, 115015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisterer, M. Magnetic properties and critical currents of MgB2. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2007, 20, R47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrando, V.; Bernini, C.; Manfrinetti, P.; Marré, D.; Putti, M.; Tarantini, C.; Ferdeghini, C. Upper critical fields of MgB2 thin films. Phys. C Supercond. 2004, 408–410, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bud’ko, S.L.; Canfield, P.C. Superconductivity of magnesium diboride. Phys. C Supercond. Its Appl. 2015, 514, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, C.; Courtois, T.; Koblischka, M.R.; Andrieu, S.; Lin, J.-X.; Hehn, M.; Mangin, S.; Dumesnil, K.; Hauet, T. Magnetic moment of thin film superconductors: When thickness matters. Phys. Rev. B 2024, 110, 94502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grissonnanche, G.; Cyr-Choinière, O.; Laliberté, F.; René De Cotret, S.; Juneau-Fecteau, A.; Dufour-Beauséjour, S.; Delage, M.-È.; LeBoeuf, D.; Chang, J.; Ramshaw, B.J.; et al. Direct measurement of the upper critical field in cuprate superconductors. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekitani, T.; Miura, N.; Ikeda, S.; Matsuda, Y.H.; Shiohara, Y. Upper critical field for optimally-doped YBa2Cu3O7-δ. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2004, 346–347, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, C.P. Handbook of Superconductivity; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Vissers, M.R.; Hubmayr, J.; Sandberg, M.; Chaudhuri, S.; Bockstiegel, C.; Gao, J. Frequency-tunable superconducting resonators via nonlinear kinetic inductance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 62601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Han, X.; Fu, W.; Zou, C.-L.; Tang, H.X. Frequency-tunable high-Q superconducting resonators via wireless control of nonlinear kinetic inductance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 192601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollitsch, C.W.; O’Sullivan, J.; Kennedy, O.; Dold, G.; Morton, J.J.L. Tuning high-Q superconducting resonators by magnetic field reorientation. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 125225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, D.E.; Dionne, G.F. Magnetically tunable superconducting resonators and filters. IEEE Trans. Appiled Supercond. 1999, 9, 4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roitman, A.; Pfaff, C.; Hauet, T.; Shaulov, A.; Yeshurun, Y. Microwave Kinetic Inductance Detector Made of Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE)-Grown MgB2 Film. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14211731
Roitman A, Pfaff C, Hauet T, Shaulov A, Yeshurun Y. Microwave Kinetic Inductance Detector Made of Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE)-Grown MgB2 Film. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(21):1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14211731
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoitman, Ariel, Corentin Pfaff, Thomas Hauet, Avner Shaulov, and Yosef Yeshurun. 2024. "Microwave Kinetic Inductance Detector Made of Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE)-Grown MgB2 Film" Nanomaterials 14, no. 21: 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14211731
APA StyleRoitman, A., Pfaff, C., Hauet, T., Shaulov, A., & Yeshurun, Y. (2024). Microwave Kinetic Inductance Detector Made of Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE)-Grown MgB2 Film. Nanomaterials, 14(21), 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14211731







