Sub-ppb H2S Sensing with Screen-Printed Porous ZnO/SnO2 Nanocomposite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
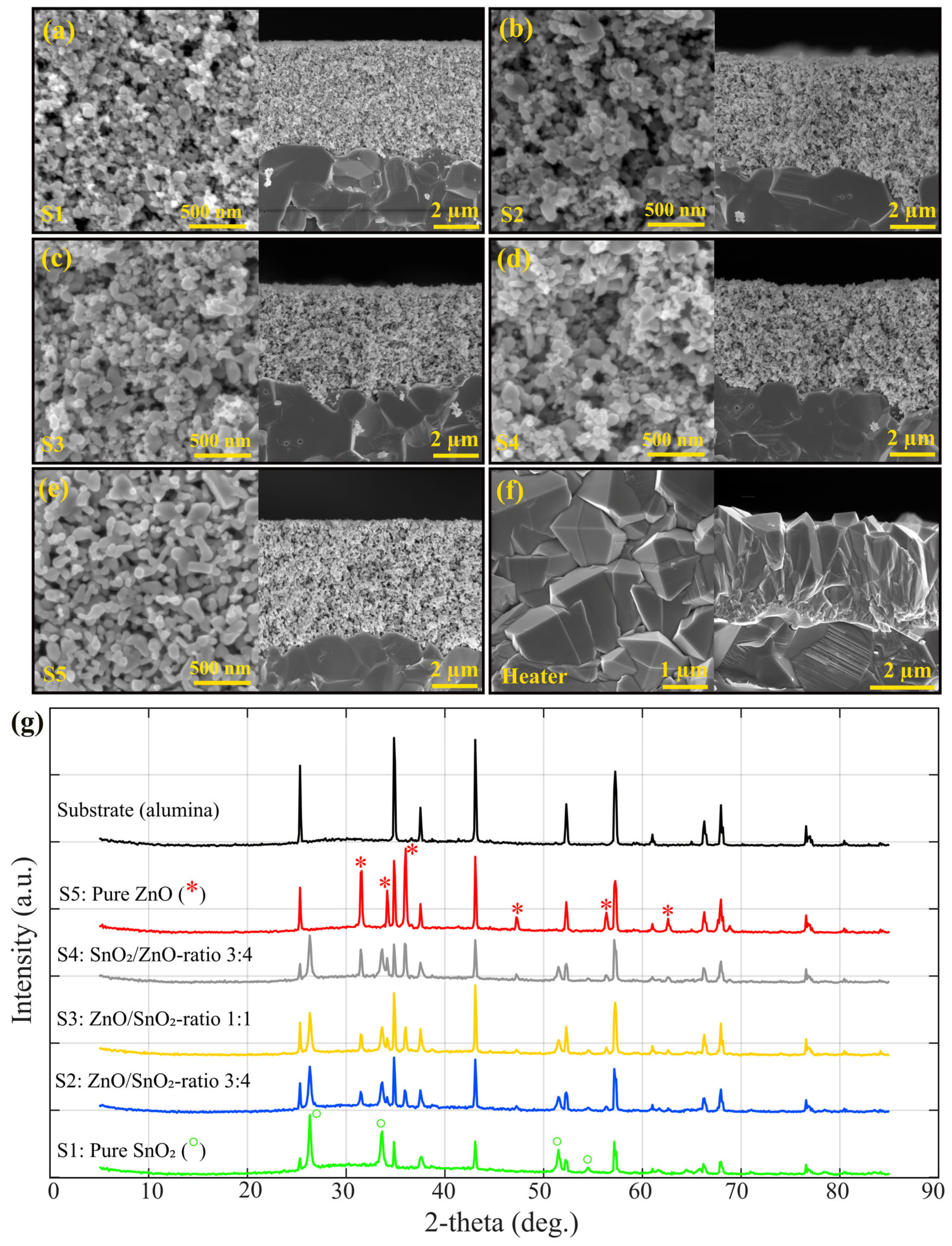
3. Results and Discussion
Sensing Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Shaik, R.; Kishore, R.; Kumar, A.; Shekhar, C.; Kumar, M. Metal oxide nanofibers based chemiresistive H2S gas sensors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 471, 214752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari-Saatlu, M.; Procek, M.; Mattsson, C.; Thungström, G.; Nilsson, H.-E.; Xiong, W.; Xu, B.; Li, Y.; Radamson, H.H. Silicon Nanowires for Gas Sensing: A Review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; O’Nils, M.; Lundgren, J.; Saatlu, M.A.; Hamrin, R.; Mattsson, C. A Deep Learning Approach for Classification and Measurement of Hazardous Gases Using Multi-Sensor Data Fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium, SAS 2023, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 18–20 July 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Babaei, F.; Masoumi, S.; Aghili, S.; Shokrani, M. Atmospheric Dependence of Thermoelectric Generation in SnO2Thin Films with Different Intergranular Potential Barriers Utilized for Self-Powered H2S Sensor Fabrication. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Xie, Z.; Wang, M.; Xu, J.; San, X.; Qi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Jin, Q. In Situ Fabrication of SnS2/SnO2 Heterostructures for Boosting Formaldehyde−Sensing Properties at Room Temperature. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.Y.; Zhang, M.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Deng, Z.P.; Huo, L.H.; Gao, S. Highly selective ppb-level H2S sensor for spendable detection of exhaled biomarker and pork freshness at low temperature: Mesoporous SnO2 hierarchical architectures derived from waste scallion root. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 307, 127662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari-Saatlu, M.; Schalk, M.; Pokhrel, S.; Mattsson, C.; Mädler, L.; Procek, M.; Radamson, H.H.; Thungström, G. Ultra-sensitive H2S and CH3SH Sensors Based on SnO2 Porous Structures Utilizing Combination of Flame and Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Methods. IEEE Sens. J. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, L.; Feng, Z.; Gao, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Shao, J.; Sun, C.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Metal-organic framework-derived ZnO decorated with CuO for ultra-high response and selectivity H2S gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 366, 131995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari-Saatlu, M.; Procek, M.; Thungström, G.; Mattsson, C.; Radamson, H.H. H2S gas sensing based on SnO2thin films deposited by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis on Al2O3 substrate. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS), Sundsvall, Sweden, 23–25 August 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yu, C.; Xin, C.; Xing, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, H.; Fei, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T. Increasing the Catalytic Activity of Co3O4 via Boron Doping and Chemical Reduction for Enhanced Acetone Detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2314174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Bala, H.; Zhang, Z. Pt-modified nanosheet-assembled SnS2 hollow microspheres for low temperature NO2 sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 417, 136118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, M. Ultrasensitive H2S Gas Sensor Based on SnO2 Nanoparticles Modified WO3 Nanocubes Heterojunction. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 27031–27037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yin, G.; Chen, J.; Ge, M.; Lu, J.; Yang, Z.; He, D. An olive-shaped SnO2 nanocrystal-based low concentration H2S gas sensor with high sensitivity and selectivity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 20537–20542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yin, W.; Gao, S.; Sun, Y.; Xu, P.; Wu, S.; Kong, H.; Yang, G.; Wei, G. The Combination of Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials with Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Gas Sensors: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.D.; Nikam, H.A.; Sharma, Y.C.; Yadav, R.S.; Kumar, D.; Singh, A.K.; Patil, D.R. Highly selective ppm level LPG sensors based on SnO2-ZnO nanocomposites operable at low temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 377, 133080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Z. Enhanced NO2 Sensing Performance of ZnO-SnO2 Heterojunction Derived from Metal-Organic Frameworks. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.H.; Di Chio, R.; Movlaee, K.; Amsalem, P.; Koch, N.; Barsan, N.; Neri, G.; Pinna, N. Role of Heterojunctions of Core−Shell Heterostructures in Gas Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 22041–22052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Feng, B.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, D.; Wei, J. Wireless Gas Sensor Based on the Mesoporous ZnO-SnO2 Heterostructure Enables Ultrasensitive and Rapid Detection of 3-Methylbutyraldehyde. ACS Sensors 2024, 9, 2585–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Chen, Y. Two-dimensional net-like SnO2/ZnO heteronanostructures for high-performance H2S gas sensor. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.W.; Lee, S.C.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jung, S.Y.; Lee, D.D.; Huh, J.S.; Kim, J.C. High sensitivity and recoverable SnO2-based sensor promoted with Fe2O3 and ZnO for sub-ppm H2S detection. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2017, 12, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Kim, S.Y.; Hwang, B.W.; Jung, S.Y.; Lee, S.U.; Lee, D.D.; Kim, J.C. New SnO2-based gas sensor promoted with ZnO and MoO3 for the detection of H2S. Sens. Lett. 2014, 12, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari-Saatlu, M.; Procek, M.; Mattsson, C.; Thungström, G.; Törndahl, T.; Li, B.; Su, J.; Xiong, W.; Radamson, H.H. Nanometer-Thick ZnO/SnO2 Heterostructures Grown on Alumina for H2S Sensing. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 6954–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.-Y.; Yuan, K.-P.; Yang, J.-H.; Hang, C.-Z.; Ma, H.-P.; Ji, X.-M.; Devi, A.; Lu, H.-L.; Zhang, D.W. Hierarchical highly ordered SnO2 nanobowl branched ZnO nanowires for ultrasensitive and selective hydrogen sulfide gas sensing. Microsystems Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Mei, L.; Wen, J.; Ma, J. High-response H2S sensor based on ZnO/SnO2 heterogeneous nanospheres. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 15048–15053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, G.; Duan, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, Z.; Dong, F.; Tai, H. Lever-inspired triboelectric respiration sensor for respiratory behavioral assessment and exhaled hydrogen sulfide detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.M.; Phuong, H.V.; Van Thinh, V.; Hong, L.T.; Thang, N.T.; Hanh, N.H.; Dich, N.Q.; Van Duy, N.; Van Hieu, N.; Hoa, N.D. Au doped ZnO/SnO2 composite nanofibers for enhanced H2S gas sensing performance. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 317, 112454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuoc, P.H.; Viet, N.N.; Thong, L.V.; Hung, C.M.; Hoa, N.D.; Van Duy, N.; Hong, H.S.; Hieu, N. Van Comparative study on the gas-sensing performance of ZnO/SnO2 external and ZnO–SnO2 internal heterojunctions for ppb H2S and NO2 gases detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 334, 129606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.T.; Thao, D.T.H.; Hung, N.M.; Van Hoang, N.; Hoat, P.D.; Van Thin, P.; Lee, J.H.; Heo, Y.W. H2S gas sensing properties of ZnO–SnO2 branch–stem nanowires grown on a copper foil. Scr. Mater. 2025, 255, 116372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Mirzaei, A.; Bang, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Selective H2S sensing without external heat by a synergy effect in self-heated CuO-functionalized SnO2-ZnO core-shell nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 300, 126981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh Le, D.T.; Trung, D.D.; Chinh, N.D.; Thanh Binh, B.T.; Hong, H.S.; Van Duy, N.; Hoa, N.D.; Van Hieu, N. Facile synthesis of SnO2–ZnO core–shell nanowires for enhanced ethanol-sensing performance. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoang, N.D.; Trung, D.D.; Van Duy, N.; Hoa, N.D.; Van Hieu, N. Design of SnO2/ZnO hierarchical nanostructures for enhanced ethanol gas-sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, C.; Wei, Z.; Xu, L.; Gui, Y. Electrospun ZnO–SnO2 Composite Nanofibers and Enhanced Sensing Properties to SF6 Decomposition Byproduct H2S. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.S.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, J.K.; Choi, J.; Ji, H.; Kim, G.T.; Cao, G.; Lee, J.H. Synthesis and gas sensing characteristics of highly crystalline ZnO–SnO2 core–shell nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 148, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, A.A.; Pisliakov, A.V.; Sokolov, A.V.; Samotaev, N.N.; Soloviev, S.A.; Oblov, K.; Guarnieri, V.; Lorenzelli, L.; Brunelli, J.; Maglione, A.; et al. Non-silicon MEMS platforms for gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, I.; Bârsan, N.; Bauer, M.; Weimar, U. Micromachined metal oxide gas sensors: Opportunities to improve sensor performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 73, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharesi, M.; Ansari, M.; Akbari-Saatlu, M. Transparent heaters made by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis of nanograined SnO2 layers on soda-lime glass substrates. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 076303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Babaei, F.; Akbari-Saatlu, M. Growing continuous zinc oxide layers with reproducible nanostructures on the seeded alumina substrates using spray pyrolysis. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 8567–8574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Babaei, F.; Akbari-Saatlu, M. Growth of ZnO nanorods on the surface and edges of a multilayer graphene sheet. Scr. Mater. 2017, 139, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, S.; Shokrani, M.; Aghili, S.; Hossein-Babaei, F. Zinc oxide-based direct thermoelectric gas sensor for the detection of volatile organic compounds in air. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 294, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Babaei, F.; Gharesi, M.; Ansari, M. Ten micron-thick undoped SnO2 layers grown by spray pyrolysis for microheater fabrication. Mater. Lett. 2017, 196, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Babaei, F.; Gharesi, M. Intense thermal shock generators made of micron-thick SnO2 layers for the on-chip rapid thermal processing in air. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 108719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simion, C.E.; Junker, B.; Weimar, U.; Stanoiu, A.; Bârsan, N. Sensing mechanisms of CO and H2 with NiO material–DRIFTS investigations. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 390, 134028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demello, A.J. I’m Sensitive about Sensitivity. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 1235–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’amico, A.; Natale, C. Di A Contribution on Some Basic Definitions of Sensors Properties. IEEE Sens. J. 2001, 1, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoufi, D.; Raoufi, T. The effect of heat treatment on the physical properties of sol–gel derived ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5812–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhage, S.B.; Patil, V.L.; Yelpale, A.M.; Malghe, Y.S. Farming of ZnO–SnO2 Nanocubes for Chemiresistive NO2 Gas Detection. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202303578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Yan, R.; Li, J. Hydrogenation effect on 2D ZnO single crystal/ZnO–SnO2 two phase ceramics and its enhanced mechanism in H2 gas sensing. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 6441–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Li, Y. The hydrothermal synthesis of 3D hierarchical porous MoS2 microspheres assembled by nanosheets with excellent gas sensing properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 749, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.A.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.C.; Park, J.S.; Lee, H.N. Effects of porosity and particle size on the gas sensing properties of SnO2 films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 481, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degler, D.; Weimar, U.; Barsan, N. Current Understanding of the Fundamental Mechanisms of Doped and Loaded Semiconducting Metal-Oxide-Based Gas Sensing Materials. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2228–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahrizjani, R.T.; Maleki, R.M.; Ghafarkani, M.; Esmaeili, A.; Ameri, M.; Mohajerani, E.; Safari, N.; Dou, Y.; Dou, S.X. Highly sensitive H2S gas sensor containing simultaneously UV treated and self-heated Ag-SnO2 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 391, 134045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Chen, Y.; Ma, J. Gas Sensing of SnO2 Nanocrystals Revisited: Developing Ultra-Sensitive Sensors for Detecting the H2S Leakage of Biogas. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, srep06028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bârsan, N.; Hübner, M.; Weimar, U. Conduction mechanisms in SnO2 based polycrystalline thick film gas sensors exposed to CO and H2 in different oxygen backgrounds. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 157, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerz, A.; Weimar, U.; Barsan, N. Current state of knowledge on the metal oxide based gas sensing mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Concentration (ppb) | Response (Ra/Rg) | T (°C) | Target Gas | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO/SnO2 | 5 | 9.7 | 325 | H2S | This work |
| SnO2/ZnO | 500 | 11.5 | 100 | H2S | [19] |
| ZnO/SnO2 | 500 | 30 | 450 | H2S | [22] |
| SnO2 promoted with ZnO | 500 | 4.5 | 350 | H2S | [20] |
| ZnO/SnO2 heterogeneous nanospheres | 500 | 3.94 | 300 | H2S | [24] |
| SnO2 promoted with ZnO | 500 | 0.71 | 350 | H2S | [21] |
| Au-doped ZnO/SnO2 nanofibers | 1000 | 73.3 | 350 | H2S | [26] |
| ZnO/SnO2 heterostructure | 1000 | 317 | 350 | H2S | [27] |
| SnO2 nanobowls branched ZnO NWs | 1000 | 6.24 | 250 | H2S | [23] |
| ZnO/SnO2 nanowires | 10,000 | 319.6 | 225 | H2S | [28] |
| CuO functionalized SnO2-ZnO core-shell NWs | 10,000 | 1.69 | RT | H2S | [29] |
| SnO2-ZnO core-shell NWs | 25,000 | 3.08 | 400 | Ethanol | [30] |
| SnO2/ZnO hierarchical nanostructures | 25,000 | 3 | 400 | Ethanol | [31] |
| ZnO/SnO2 nanofibers | 50,000 | 63.3 | 250 | H2S | [32] |
| SnO2-ZnO core-shell NWs | 200,000 | 280 | 400 | Ethanol | [33] |
| Sensors | Composition Powder Weight Ratio | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | Pure SnO2 | Only SnO2 powder |
| S2 | ZnO/SnO2 3:4 | The weight of ZnO powder was three-quarters (3/4) of the weight of SnO2 powder |
| S3 | ZnO/SnO2 1:1 | The weight of SnO2 powder was the same as the weight of ZnO powder |
| S4 | SnO2/ZnO 3:4 | The weight of SnO2 powder was three-quarters (3/4) of the weight of ZnO powder |
| S5 | Pure ZnO | Only ZnO powder |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akbari-Saatlu, M.; Heidari, M.; Mattsson, C.; Zhang, R.; Thungström, G. Sub-ppb H2S Sensing with Screen-Printed Porous ZnO/SnO2 Nanocomposite. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14211725
Akbari-Saatlu M, Heidari M, Mattsson C, Zhang R, Thungström G. Sub-ppb H2S Sensing with Screen-Printed Porous ZnO/SnO2 Nanocomposite. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(21):1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14211725
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkbari-Saatlu, Mehdi, Masoumeh Heidari, Claes Mattsson, Renyun Zhang, and Göran Thungström. 2024. "Sub-ppb H2S Sensing with Screen-Printed Porous ZnO/SnO2 Nanocomposite" Nanomaterials 14, no. 21: 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14211725
APA StyleAkbari-Saatlu, M., Heidari, M., Mattsson, C., Zhang, R., & Thungström, G. (2024). Sub-ppb H2S Sensing with Screen-Printed Porous ZnO/SnO2 Nanocomposite. Nanomaterials, 14(21), 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14211725






