The Fabrication of Gold Nanostructures as SERS Substrates for the Detection of Contaminants in Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Cleaning the Glass Substrate
2.2. Fabrication of SERS Substrate
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
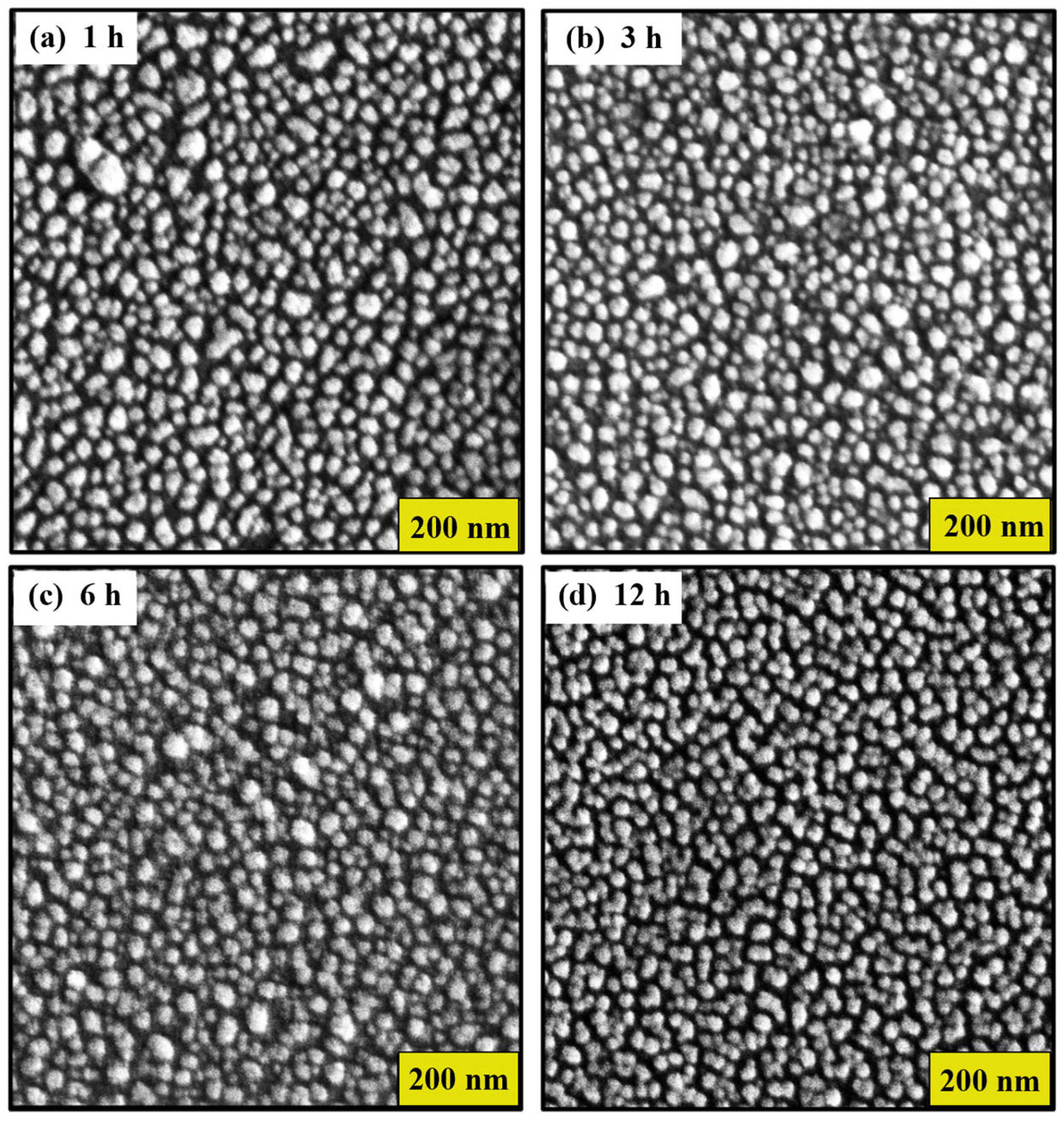
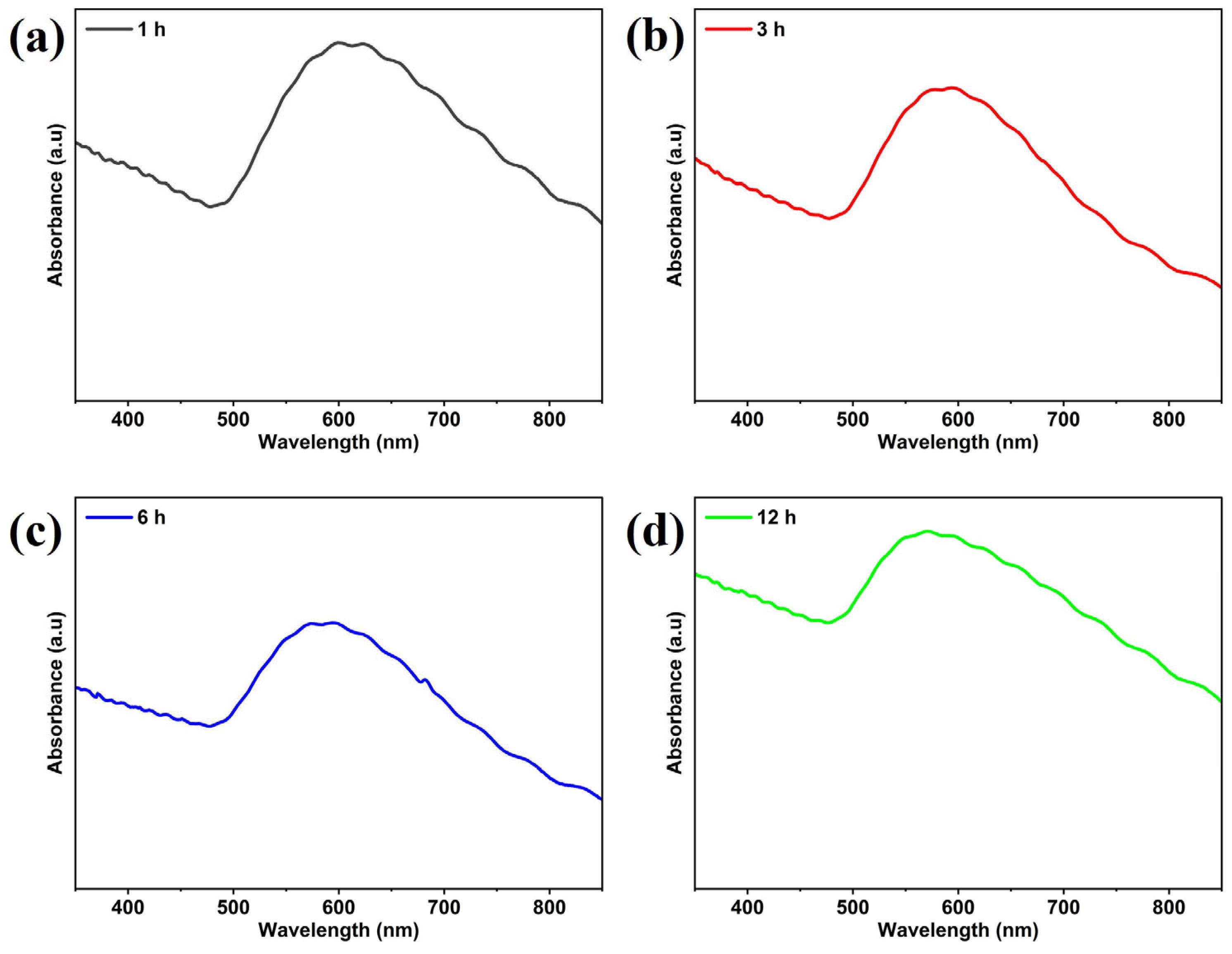
3.1. Characterization of Gold SERS Substrates
Effect of Thermal Treatment Time
3.2. SERS Spectra of RhB Adsorbed on AuNSs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, A.H.A.; Barros, R. Pharmaceuticals in Water: Risks to Aquatic Life and Remediation Strategies. Hydrobiology 2023, 2, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bhattacharya, A. Drinking water contamination and treatment techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1043–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of Emerging Concern in Aquatic Systems: Chemistry, Occurrence, Effects, and Removal Methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Pharmaceuticals in Drinking-Water. 2012. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241502085 (accessed on 17 May 2024).
- Marcela, E.; Bambague, J. Technological Coupling of Advanced Oxidation Processes and High Rate Algal Pond for Removal of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Urban Wastewater; Universidad del Valle: Santiago de Cali, Colombia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, M.; Sandoval, M.; Pineda, H.R. Remoción de Compuestos Farmacéuticos Activos en Aguas Residuales Industriales, Mediante un Reactor Electroquímico de Compartimentos Separados. Master’s Thesis, Universidad de Manizales, Manizales, Columbia, 2021. Available online: https://ridum.umanizales.edu.co/xmlui/handle/20.500.12746/5488 (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Moreno-Ortiz, V.C.; Martínez-Núñez, J.M.; Kravzov-Jinich, J.; Pérez-Hernández, L.A.; Moreno-Bonett, C.; Altagracia-Martínez, M. Los medicamentos de receta de origen sintético y su impacto en el medio ambiente. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Farm. 2013, 44, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Bambague, E.M.; Madera-Parra, C.A.; Machuca-Martinez, F. The occurrence of emerging compounds in real urban wastewater before and after the COVID-19 pandemic in Cali, Colombia. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 33, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulkifli, S.N.; Rahim, H.A.; Lau, W.-J. Detection of contaminants in water supply: A review on state-of-the-art monitoring technologies and their applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 2657–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadadou, D.; Tizani, L.; Alsafar, H.; Hasan, S.W. Analytical methods for determining environmental contaminants of concern in water and wastewater. MethodsX 2024, 12, 102582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatta, D.; Achilleos, A.; Nikolaou, A.; Meriç, S. Analytical methods for tracing pharmaceutical residues in water and wastewater. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, N. Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 41, 2256–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, D. Nanomaterial-based SERS sensing technology for biomedical application. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3755–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneipp, K. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Phys. Today 2007, 60, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, C.L.; McFarland, A.D.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 338A–346A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, D.; Dong, X.; Huang, Q. A review: Research progress of SERS-based sensors for agricultural applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 128, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbillon, G.; Cheap-Charpentier, H. Advances in Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Sensors of Pollutants in Water Treatment. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier-Boss, P.A. Review of SERS Substrates for Chemical Sensing. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, R.C. SERS Hot Spots. In Raman Spectroscopy for Nanomaterials Characterization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 9783642206207, pp. 215–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, A.M.; Nirmal, M.; Brus, L.E. Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy of Individual Rhodamine 6G Molecules on Large Ag Nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 9932–9939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadal, P.A.; Fraire, J.C.; Coronado, E.A. Simple Approach to Assess the Maximum Hot Spot SERS Enhancement Factors in Colloidal Dispersions of Gold Nanoparticle Aggregates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 10524–10533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, N.; Anslin, T.M. New trends in gold nanostructure-based SERS substrate: From fundamental to biomedical applications. Vib. Spectrosc. 2023, 124, 103477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Pei, F.; Feng, S.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, P.; Tong, Z.; Mu, X.; Lei, W.; Liu, B. Detection of trace Rhodamine B using stable, uniformity, and reusable SERS substrate based on Ag@SiO2-Au nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 657, 130595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Jin, D.; Ma, P.; Wang, D.; Yang, Q.; Song, D.; Wang, X. Rapid Determination of Rhodamine B in Chili Powder by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 1918–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-M.; Cui, Y.; Xu, Y.-H.; Ren, B.; Tian, Z.-Q. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Substrate-related issues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1729–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brust, M.; Walker, M.; Bethell, D.; Schiffrin, D.J.; Whyman, R. Synthesis of thiol-derivatised gold nanoparticles in a two-phase Liquid–Liquid system. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Particle size and sol stability in metal colloids. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1972, 250, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broens, M.I.; Pérez, O.E.L. Highly ordered TiO2 nanotube films photo-decorated with Ag nanoparticles as SERS platforms: Relationship between morphology and enhancement. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 7627–7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrikaitė, V.; Ignatjev, I.; Selskis, A.; Niaura, G.; Stankevičius, E. Hybrid gold-silver nanoparticles synthesis on a glass substrate using a nanosecond laser-induced dewetting of thin bimetallic films and their application in SERS. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 168, 109956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuzdak, K.; Macewicz, Ł.; Skiba, F.; Szkoda, M.; Karczewski, J.; Burczyk, Ł.; Śliwiński, G. Nanostructuring of thin Au films deposited on ordered Ti templates for applications in SERS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 418, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupa, D.; Oćwieja, M.; Piergies, N.; Baliś, A.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Adamczyk, Z. Gold nanoparticles deposited on silica microparticles—Electrokinetic characteristics and application in SERS. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2018, 33, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Yamaguchi, I.; Kobayashi, T. Local plasmon sensor with gold colloid monolayers deposited upon glass substrates. Opt. Lett. 2000, 25, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, B.; Gui, X.; Ma, J.; Chu, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Qin, W.; Qin, Z.; Yao, H.; et al. Planting gold nanoflower for harvesting reproducible SERS substrate. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 308, 123793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Shrivastav, A.M.; Vashistha, N.; Abdulhalim, I. 3D plasmonic hot spots network via gold decorated deep micro-porous silicon exhibiting ultrahigh-SERS enhancement with application to explosives detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 374, 132813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.S.; Yang, M. Sensitive and Reproducible Gold SERS Sensor Based on Interference Lithography and Electrophoretic Deposition. Sensors 2018, 18, 4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Ma, Q.; Qu, C.-X.; Zhou, H.-T.; Cao, M.; Wang, S.-D. Review on 3D Fabrication at Nanoscale. Autex Res. J. 2022, 23, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ji, Z.; Shang, L. Top-Down Fabrication of Nanostructures. In Nanotechnology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, Y.; Srolovitz, D.J.; Bao, W. Solid-state dewetting on curved substrates. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2018, 2, 113401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, H.A.; Horwood, C.A.; Owusu-Ansah, E.; Shi, Y.J.; Birss, V.I. Gold nanoparticle array formation on dimpled Ta templates using pulsed laser-induced thin film dewetting. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 11062–11069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.V. Solid-State Dewetting of Thin Films. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2012, 42, 399–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hu, W.; Song, X.-N.; Wang, C.-K. Density Functional Theory Study on Raman Spectra of Rhodamine Molecules in Different Forms. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 27, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Fu, S.; Yang, T.; Wen, Y.; Yang, H. Optimized core-shell Au@Ag nanoparticles for label-free Raman determination of trace Rhodamine B with cancer risk in food product. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.H.; Wang, M.L.; Feng, Q.; Liu, W.; Xu, C.X. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) study on Rhodamine B adsorbed on different substrates. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 89, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xiang, R.; Lee, Y.; Otsuka, K.; Ho, Y.-L.; Chiashi, S.; Delaunay, J.-J.; Maruyama, S. Fabrication, characterization, and high temperature surface enhanced Raman spectroscopic performance of SiO2 coated silver particles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 5449–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Meneghetti, M. Size Evaluation of Gold Nanoparticles by UV−vis Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 4277–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, D.-W.; Li, Y.; Fossey, J.S.; Long, Y.-T. Cyclic electroplating and stripping of silver on Au@SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles for sensitive and recyclable substrate of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Hasi, W.-L.; Lin, X.; Han, S.-Q.; Lou, X.-T.; Yang, F.; Lin, D.-Y.; Lu, Z.-W. Rapid and sensitive SERS method for determination of Rhodamine B in chili powder with paper-based substrates. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 5289–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Agarwal, A.; Buddharaju, K.D.; Khalid, N.M.; Salim, S.M.; Widjaja, E.; Garland, M.V.; Balasubramanian, N.; Kwong, D.-L. DNA detection using nanostructured SERS substrates with Rhodamine B as Raman label. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechalany, M.; Maeder, X.; Riesterer, J.; Hankache, J.; Lerose, D.; Christiansen, S.; Micheler, J.; Pilippe, L. Synthesis Mechanisms of Organized Gold Nanoparticles: Influence of Annealing Temperature and Atmosphere. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, A.S.; Lin, X.M.; Curtiss, L.A. Equilibrium Morphology of Face-Centered Cubic Gold Nanoparticles >3 nm and the Shape Changes Induced by Temperature. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 24465–24472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Han, Y.; Zhu, B.; Gao, Y. Exploration of structure sensitivity of gold nanoparticles in low-temperature CO oxidation. Ind. Chem. Mater. 2024, 2, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ru, E.C.; Blackie, E.; Meyer, M.; Etchegoin, P.G. Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Enhancement Factors: A Comprehensive Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 13794–13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

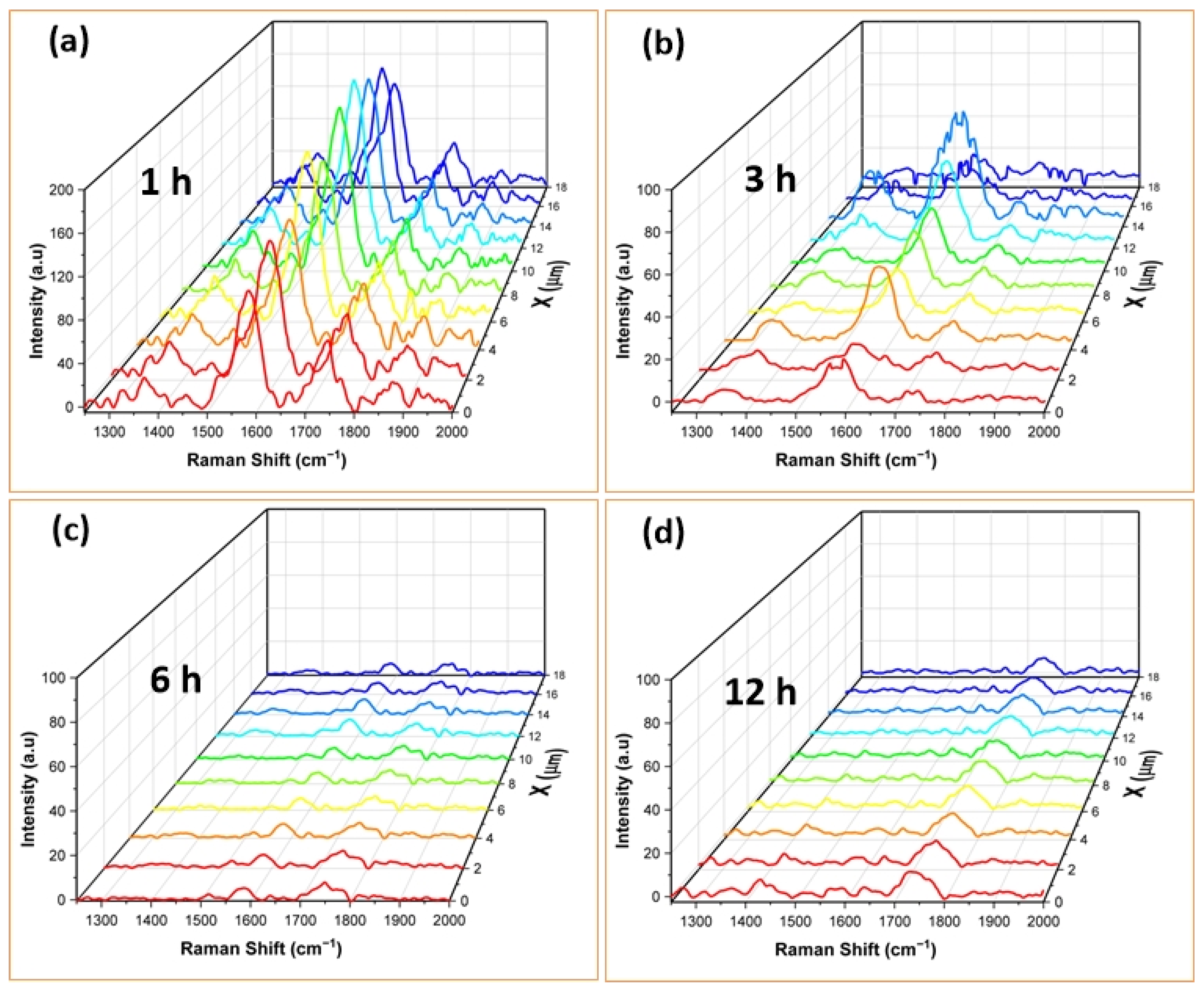
| Observed Raman Shifts | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other Reported RhB SERS Modes | SERS (RhB/AuNPs) | Assignment | References | |||
| 1 h | 3 h | 6 h | 12 h | |||
| 1355, 1361, 1362 | 1370 w | 1364 m | -- | -- | arom C–C str | [41,43,46,47,48] |
| 1503, 1504, 1510, 1512 | 1514 sh | -- | -- | -- | arom C–C str | [41,43,46,47,48] |
| 1526, 1532, 1533 | 1522 sh | -- | -- | -- | C–H str | [43,46,47] |
| 1560, 1572, 1575, 1580, 1585 | 1583 vs | 1583 vs | 1584 vw | -- | arom C–C str | [43,46,48] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Visbal, C.A.; Cervantes, W.R.; Marín, L.; Betancourt, J.; Pérez, A.; Diosa, J.E.; Rodríguez, L.A.; Mosquera-Vargas, E. The Fabrication of Gold Nanostructures as SERS Substrates for the Detection of Contaminants in Water. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14181525
Visbal CA, Cervantes WR, Marín L, Betancourt J, Pérez A, Diosa JE, Rodríguez LA, Mosquera-Vargas E. The Fabrication of Gold Nanostructures as SERS Substrates for the Detection of Contaminants in Water. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(18):1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14181525
Chicago/Turabian StyleVisbal, Cristhian A., Wilkendry Ramos Cervantes, Lorena Marín, John Betancourt, Angélica Pérez, Jesús E. Diosa, Luis Alfredo Rodríguez, and Edgar Mosquera-Vargas. 2024. "The Fabrication of Gold Nanostructures as SERS Substrates for the Detection of Contaminants in Water" Nanomaterials 14, no. 18: 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14181525
APA StyleVisbal, C. A., Cervantes, W. R., Marín, L., Betancourt, J., Pérez, A., Diosa, J. E., Rodríguez, L. A., & Mosquera-Vargas, E. (2024). The Fabrication of Gold Nanostructures as SERS Substrates for the Detection of Contaminants in Water. Nanomaterials, 14(18), 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14181525








