Chitosan Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery of Curcumin Suppresses Tumor Growth in Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culturing of the Cell Line and Primary Culture
2.2. Preparation of Nanoparticles
2.3. Size and Zeta Potential Characterization
2.4. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.6. Encapsulation Efficiency (EE)
2.7. In Vitro Cellular Uptake
2.8. Wound-Healing Assay
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Antitumor Efficacy of Cur-CHNPs
2.11. Biodistribution and Tumor Homing of CHNPs Using NOD/SCID Mice Model
2.12. In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy Studies in Orthotopic Breast Cancer NOD/SCID Mice Models
2.13. Assessment of the Acute and Subchronic Toxicities of Cur-CHNPs in BALB/c Mice
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
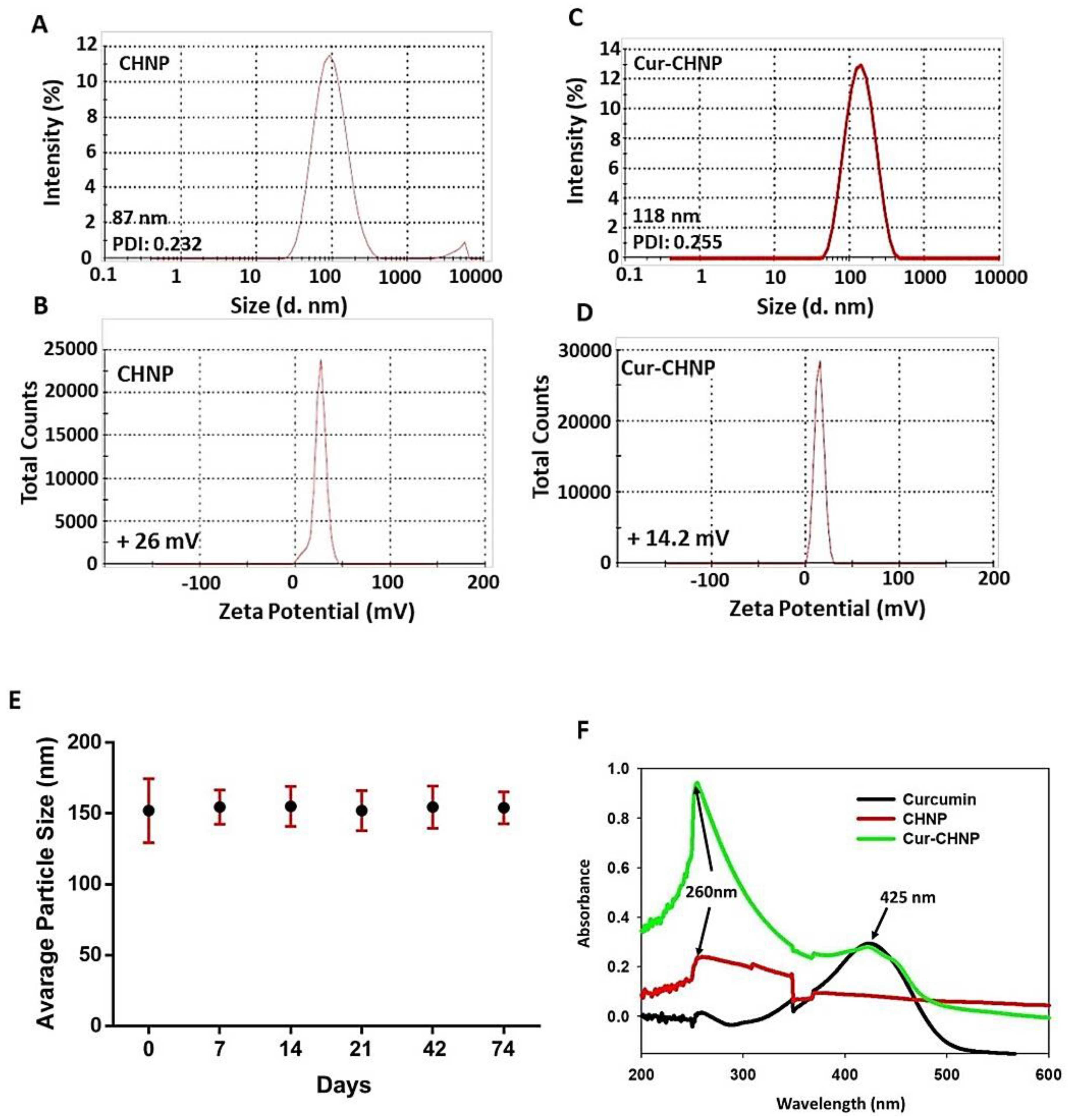
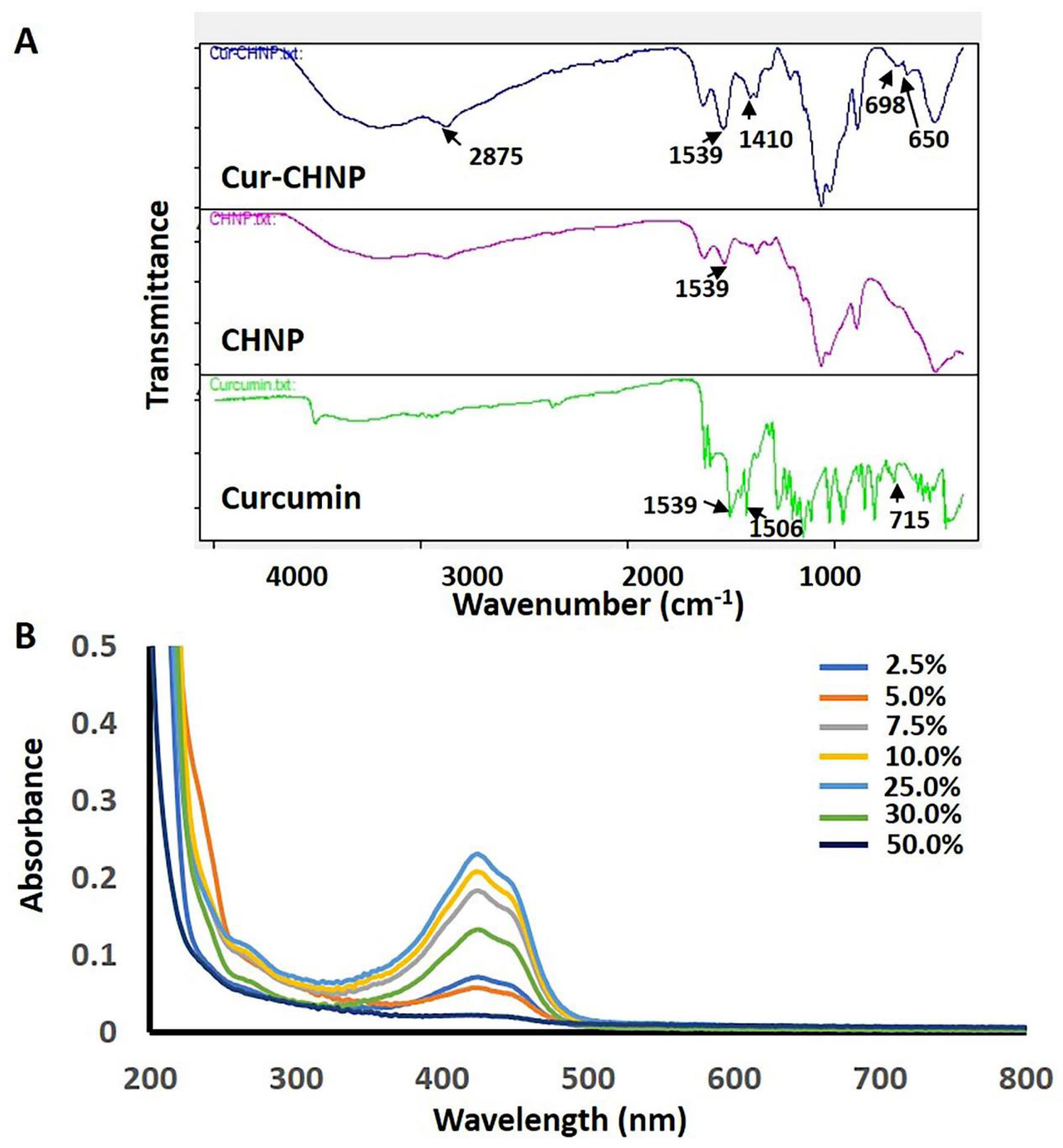
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Nanoparticles
3.2. In Vitro Cellular Uptake of CHNPs
3.3. Assessment of the In Vitro Antitumor Efficacy of Cur-CHNPs
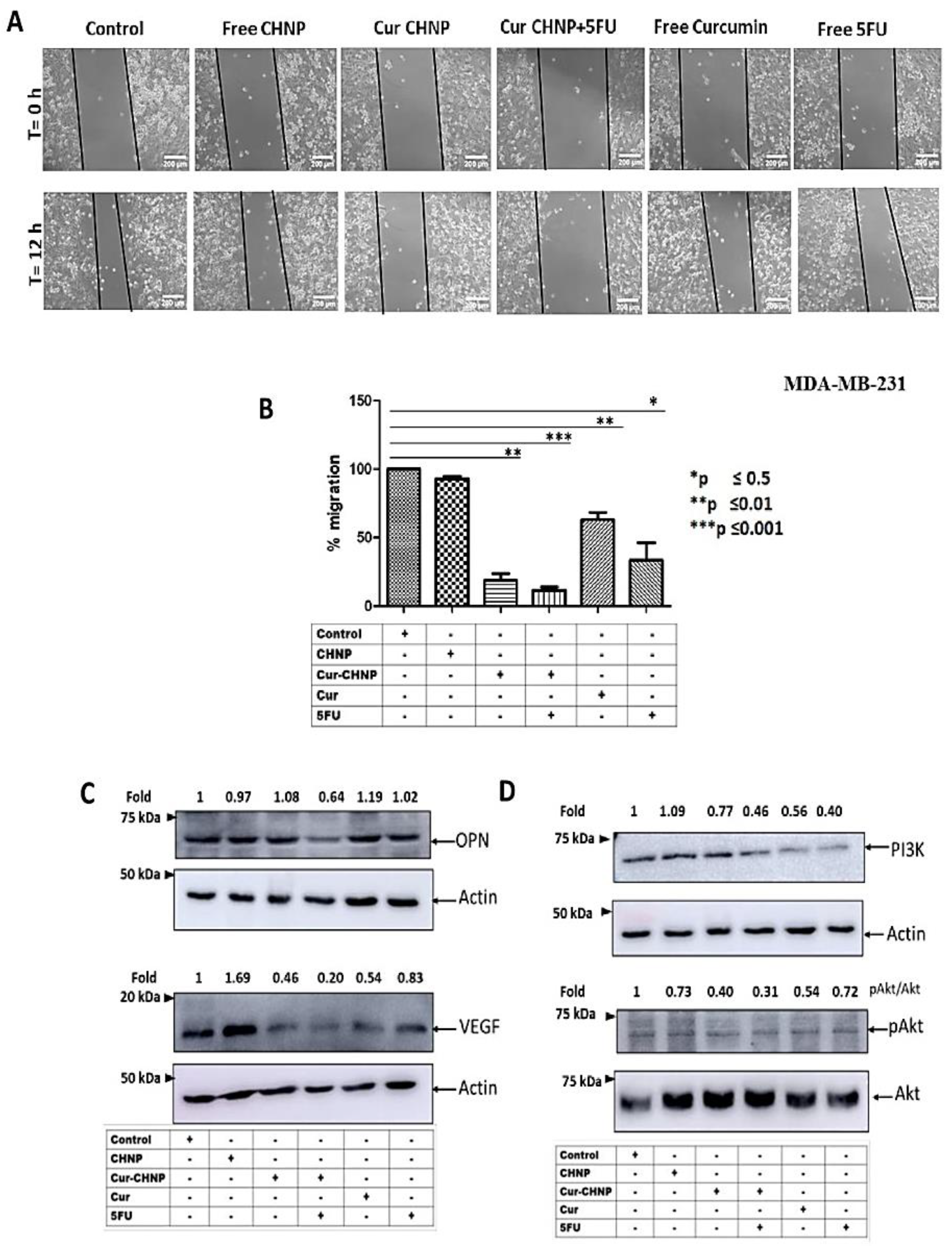
3.4. Effect of Cur-CHNPs on Breast Cancer Cell Migration
3.5. Effect of Cur-CHNPs on PI3K and Akt Activation and OPN and VEGF Expression
3.6. In Vivo Biodistribution and Tumor Homing of CHNPs
3.7. In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy of CHNPs
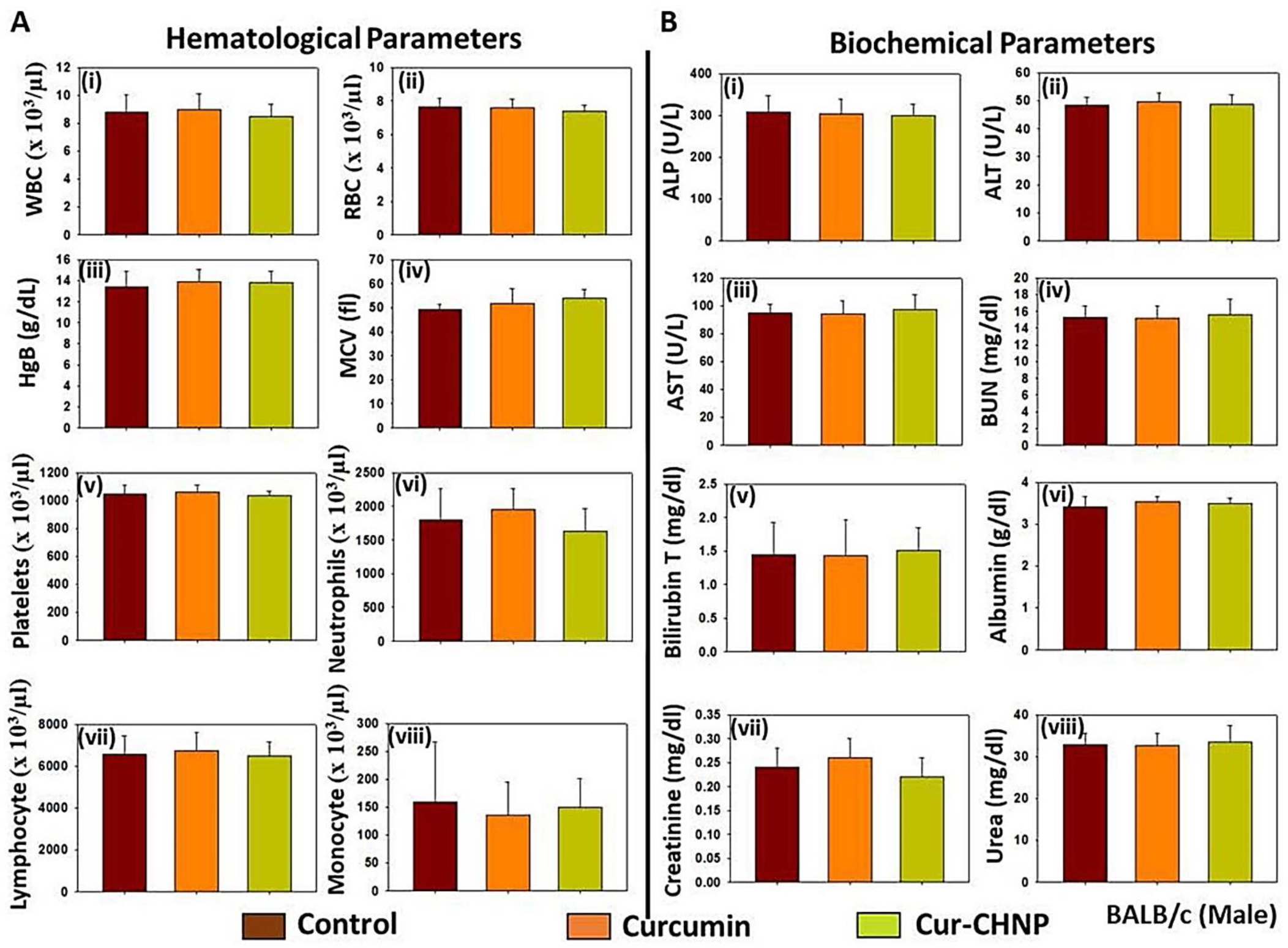
3.8. In Vivo Toxicity Assessment
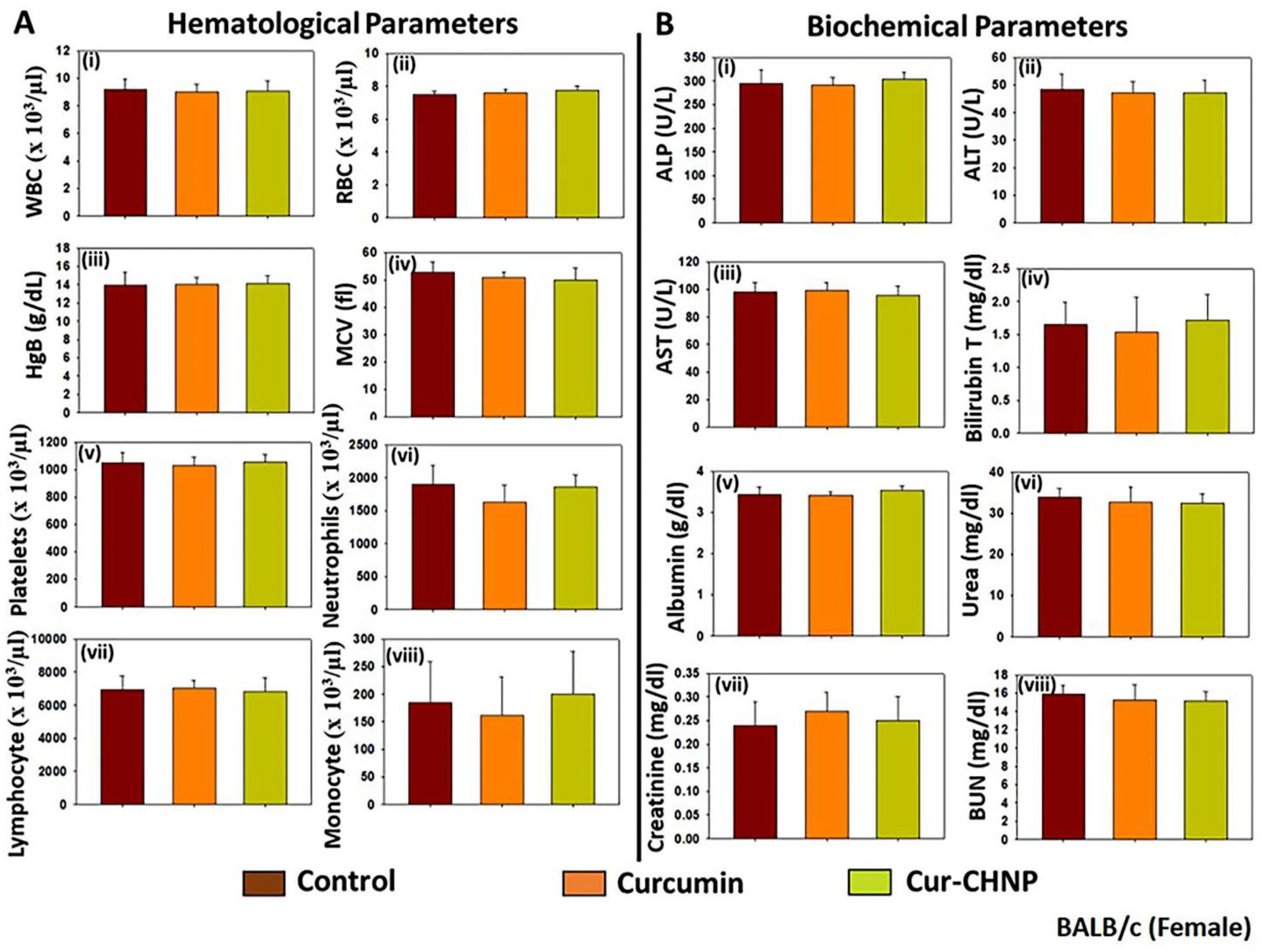
3.8.1. Acute Toxicity
3.8.2. Subchronic Toxicity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moo, T.A.; Sanford, R.; Dang, C.; Morrow, M. Overview of Breast Cancer Therapy. PET Clin. 2018, 13, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinotti, S.; Calabrese, G.; Ranzato, E. Honeydew honey: Biological effects on skin cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 435, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmeier, B.E.; Melchart, D. Therapeutic Effects of Curcumin-From Traditional Past to Present and Future Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, K.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Daneshkhah, A.; Abolfathi, S.; Salari, N.; Mohammadi, M.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Shabani, S. Clinical effects of curcumin in enhancing cancer therapy: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, A.; Innao, V.; Russo, S.; Gerace, D.; Alonci, A.; Musolino, C. Anticancer Activity of Curcumin and Its Analogues: Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Cancer Investig. 2017, 35, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, P.A.; Panati, K.; Narala, V.R. Curcumin Nanotechnologies and Its Anticancer Activity. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, U.; Chauhan, S.; Nagaich, U.; Jain, N. Current Advances in Chitosan Nanoparticles Based Drug Delivery and Targeting. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Yan, W.; Xu, Z.; Ni, H. Formation mechanism of monodisperse, low molecular weight chitosan nanoparticles by ionic gelation technique. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, J.; Raichura, Z.; Khan, T.; Momin, M.; Omri, A. Chitosan Nanoparticles-Insight into Properties, Functionalization and Applications in Drug Delivery and Theranostics. Molecules 2021, 26, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.S.; Radharani, N.N.V.; Gorain, M.; Bulbule, A.; Shetti, D.; Roy, G.; Baby, T.; Kundu, G.C. RGD functionalized chitosan nanoparticle mediated targeted delivery of raloxifene selectively suppresses angiogenesis and tumor growth in breast cancer. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 10664–10684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandhakumar, S.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Ramkumar, K.M.; Raichur, A.M. Preparation of collagen peptide functionalized chitosan nanoparticles by ionic gelation method: An effective carrier system for encapsulation and release of doxorubicin for cancer drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 70, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooneh-Farahani, S.; Naghib, S.M.; Naimi-Jamal, M.R. A Novel and Inexpensive Method Based on Modified Ionic Gelation for pH-responsive Controlled Drug Release of Homogeneously Distributed Chitosan Nanoparticles with a High Encapsulation Efficiency. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 1917–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, E.; De Benedittis, S.; Qualtieri, A.; Muzzalupo, R. Actively Targeted and Redox Responsive Delivery of Anticancer Drug by Chitosan Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2019, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, M.A.; Madni, A.; Rehman, M.; Rahim, M.A.; Jabar, A. Ionically Cross-Linked Chitosan Nanoparticles for Sustained Delivery of Docetaxel: Fabrication, Post-Formulation and Acute Oral Toxicity Evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 10035–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.S.; Morris, A.; Billa, N.; Leong, C.O. An Evaluation of Curcumin-Encapsulated Chitosan Nanoparticles for Transdermal Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019, 20, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almutairi, F.M.; El Rabey, H.A.; Tayel, A.A.; Alalawy, A.I.; Al-Duais, M.A.; Sakran, M.I.; Zidan, N.S. Augmented anticancer activity of curcumin loaded fungal chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omer, A.M.; Ziora, Z.M.; Tamer, T.M.; Khalifa, R.E.; Hassan, M.A.; Mohy-Eldin, M.S.; Blaskovich, M.A.T. Formulation of Quaternized Aminated Chitosan Nanoparticles for Efficient Encapsulation and Slow Release of Curcumin. Molecules 2021, 26, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Luo, Y. Chitosan-based nanocarriers for encapsulation and delivery of curcumin: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 179, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.M.; Dahlin, J.L.; Bisson, J.; Graham, J.; Pauli, G.F.; Walters, M.A. The Essential Medicinal Chemistry of Curcumin. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1620–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xu, Y.; Meng, L.; Huang, L.; Sun, H. Curcumin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.D.; Liu, X.P.; Zhao, W.J.; Dong, Q.; Li, F.N.; Wang, H.B.; Kong, B. Curcumin induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Zhang, M.; Dai, E.; Luo, Y. Molecular targets of curcumin in breast cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, G.; Jain, S.; Kale, S.; Raja, R.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, R.; Kundu, G.C. Curcumin suppresses breast tumor angiogenesis by abrogating osteopontin-induced VEGF expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2008, 1, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Gupta, S.C.; Sung, B. Curcumin: An orally bioavailable blocker of TNF and other pro-inflammatory biomarkers. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1672–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, A.; Maya, S.; Deepa, N.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Curcumin-loaded N, O-carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles for cancer drug delivery. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 1381–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzali, E.; Eslaminejad, T.; Yazdi Rouholamini, S.E.; Shahrokhi-Farjah, M.; Ansari, M. Cytotoxicity Effects of Curcumin Loaded on Chitosan Alginate Nanospheres on the KMBC-10 Spheroids Cell Line. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Su, X.; Gregory, D.A.; Li, W.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, X. Magnetic Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Curcumin into Human Breast Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfandiarpour-Boroujeni, S.; Bagheri-Khoulenjani, S.; Mirzadeh, H.; Amanpour, S. Fabrication and study of curcumin loaded nanoparticles based on folate-chitosan for breast cancer therapy application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Deepagan, V.G.; Divya Rani, V.V.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Preparation, characterization, in vitro drug release and biological studies of curcumin loaded dextran sulphate–chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaumet, M.; Vargas, A.; Gurny, R.; Delie, F. Nanoparticles for drug delivery: The need for precision in reporting particle size parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Dutta, S.; Sarkar, A.; Kundu, M.; Sil, P.C. Targeted delivery of curcumin in breast cancer cells via hyaluronic acid modified mesoporous silica nanoparticle to enhance anticancer efficiency. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpoor, Z.; Mostafaie, A.; Nikokar, I.; Hassan, Z.M. Curcumin-human serum albumin nanoparticles decorated with PDL1 binding peptide for targeting PDL1-expressing breast cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xia, K.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, D.; Xu, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z. Multifunctional CaCO3@Cur@QTX125@HA nanoparticles for effectively inhibiting growth of colorectal cancer cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matloubi, Z.; Hassan, Z. HSA-curcumin nanoparticles: A promising substitution for Curcumin as a Cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Daru 2020, 28, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanda, M.; Getti, G.; Nandi, U.; Mithu, M.S.; Douroumis, D. Bioconjugated solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) for targeted prostate cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honarvari, B.; Karimifard, S.; Akhtari, N.; Mehrarya, M.; Moghaddam, Z.S.; Ansari, M.J.; Jalil, A.T.; Matencio, A.; Trotta, F.; Yeganeh, F.E.; et al. Folate-Targeted Curcumin-Loaded Niosomes for Site-Specific Delivery in Breast Cancer Treatment: In Silico and In Vitro Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, S.; Xie, Z.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Xiao, H.; Song, Y. Hyaluronic acid coating on the surface of curcumin-loaded ZIF-8 nanoparticles for improved breast cancer therapy: An in vitro and in vivo study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 203, 111759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, J.; Dilnawaz, F.; Sahoo, S.K.; Singh, D.V.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Hussain, T.; Pati, S. Curcumin Encapsulated into Biocompatible Co-Polymer PLGA Nanoparticle Enhanced Anti-Gastric Cancer and Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Effect. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Sharma, N.; Manchanda, R.; Gupta, N.; Syed, A.; Bahkali, A.H.; Nimesh, S. PGMD/curcumin nanoparticles for the treatment of breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idoudi, S.; Bedhiafi, T.; Sahir, F.; Hijji, Y.; Uddin, S.; Merhi, M.; Dermime, S.; Billa, N. Studies on anti-colon cancer potential of nanoformulations of curcumin and succinylated curcumin in mannosylated chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Mishra, L.; Li, S. Technologies for deriving primary tumor cells for use in personalized cancer therapy. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajappa, S.; Joshi, A.; Doval, D.C.; Batra, U.; Rajendranath, R.; Deo, A.; Biswas, G.; Bajpai, P.; Tilak, T.V.S.; Kane, S.; et al. Novel formulations of docetaxel, paclitaxel and doxorubicin in the management of metastatic breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 3757–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Ramos-Medina, R.; Bernat, R.; García-Saenz, J.A.; Del Monte-Millan, M.; Alvarez, E.; Cebollero, M.; Moreno, F.; Gonzalez-Haba, E.; Bueno, O.; et al. Activity of docetaxel, carboplatin, and doxorubicin in patient-derived triple-negative breast cancer xenografts. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeweiss, A.; Möbus, V.; Tesch, H.; Hanusch, C.; Denkert, C.; Lübbe, K.; Huober, J.; Klare, P.; Kümmel, S.; Untch, M.; et al. Intense dose-dense epirubicin, paclitaxel, cyclophosphamide versus weekly paclitaxel, liposomal doxorubicin (plus carboplatin in triple-negative breast cancer) for neoadjuvant treatment of high-risk early breast cancer (GeparOcto-GBG 84): A randomised phase III trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 106, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanazadeh, M.; Babaahmadi Rezaei, H.; Rashidi, M. Quercetin synergistically potentiates the anti-metastatic effect of 5-fluorouracil on the MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 24, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.A.; Beaumont, K.; Maurer, T.S.; Di, L. Volume of Distribution in Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 5691–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghadani, R.; Naidu, R. Curcumin: Modulator of Key Molecular Signaling Pathways in Hormone-Independent Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Chen, G.; Shi, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ou, J.; Zhu, H.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Lv, L. Curcumin and its nano-formulations: Defining triple-negative breast cancer targets through network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental verification. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 920514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, G.; Dattatrya, S.; Yadav, A.S.; Kundu, G.C. Nanomedicine: Therapeutic applications and limitations. In Handbook of Research on Diverse Applications of Nanotechnology in Biomedicine, Chemistry, and Engineering; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 64–89. [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal, K.; Singh, S.K.; Mishra, D.N. Chitosan nanoparticles: A promising system in novel drug delivery. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafy, A.S.; Farid, R.M.; Helmy, M.W.; ElGamal, S.S. Pharmacological, toxicological and neuronal localization assessment of galantamine/chitosan complex nanoparticles in rats: Future potential contribution in Alzheimer’s disease management. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3111–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kean, T.; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, F.; Oveisi, Z.; Samani, S.M.; Amoozgar, Z. Chitosan based hydrogels: Characteristics and pharmaceutical applications. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Islam, N.; Dmour, I.; Taha, M.O. Degradability of chitosan micro/nanoparticles for pulmonary drug delivery. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Curcumin (w/w%) | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Appearance | EE % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5 | 92.96 | 0.334 | Clear Suspension | 63.14 ± 4.10 |
| 5 | 94.55 | 0.376 | Clear Suspension | 82.46 ± 5.28 |
| 7.5 | 93.14 | 0.312 | Clear Suspension | 53.62 ± 2.45 |
| 10 | 95.72 | 0.401 | Clear Suspension | 79.17 ± 2.23 |
| 25 | 106.5 | 0.348 | Clear Suspension | 77.14 ± 0.23 |
| 30 | 1364 | 1.0 | Precipitate | 90.28 ± 1.76 |
| 50 | 1315 | 1.0 | Precipitate | 94.42 ± 0.31 |
| Nature of Curcumin Nanoparticles | Cancer Types | Specific Molecular Target | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSN-HA-C (Hyaluronic acid functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with curcumin) | Breast Cancer | NF-κB and Bax | [32] |
| Peptide-HSA/Cur NPs (PDL1 binding peptide conjugated–Human serum albumin–curcumin nanoparticles) | Breast Cancer | PDL1, Apoptosis | [33] |
| CaCO3@Cur@QTX125@HA (CaCO3 nanoparticles loaded with curcumin (Cur) and Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, QTX125, and coated with hyaluronic acid) | Colorectal cancer | Apoptosis | [34] |
| HSA-Curcumin NPs (Human serum albumin-conjugated curcumin NPs) | Breast cancer | Apoptosis | [35] |
| Tf-CRC-SLNs (Curcumin-loaded transferrin-bioconjugated solid lipid nanoparticles) | Prostate cancer | Apoptosis | [36] |
| PEG-FA@Nio-Cur (Folate-targeted curcumin-loaded niosomes) | Breast cancer | Bax, Bcl2, p53 | [37] |
| Cur@ZIF-8@HA (Hyaluronic acid-coated curcumin-loaded ZIF-8 nanoparticles) | Breast cancer | Apoptosis and induction of ROS | [38] |
| Cur-NPs (Curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles) | Gastric cancer | Cell cycle arrest and Apoptosis | [39] |
| PGMD-Cur nanoparticles (poly-glycerol–malic acid–dodecanedioic acid)/curcumin nanoparticles) | Breast cancer | Caspase 9 | [40] |
| Cur.SA-loaded CM nanoparticles (Succinylated Cur-encapsulated mannosylated-chitosan nanoparticles) | Colon cancer | PARP, Caspase 8 | [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mishra, B.; Yadav, A.S.; Malhotra, D.; Mitra, T.; Sinsinwar, S.; Radharani, N.N.V.; Sahoo, S.R.; Patnaik, S.; Kundu, G.C. Chitosan Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery of Curcumin Suppresses Tumor Growth in Breast Cancer. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14151294
Mishra B, Yadav AS, Malhotra D, Mitra T, Sinsinwar S, Radharani NNV, Sahoo SR, Patnaik S, Kundu GC. Chitosan Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery of Curcumin Suppresses Tumor Growth in Breast Cancer. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(15):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14151294
Chicago/Turabian StyleMishra, Barnalee, Amit Singh Yadav, Diksha Malhotra, Tandrima Mitra, Simran Sinsinwar, N. N. V. Radharani, Saroj Ranjan Sahoo, Srinivas Patnaik, and Gopal C. Kundu. 2024. "Chitosan Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery of Curcumin Suppresses Tumor Growth in Breast Cancer" Nanomaterials 14, no. 15: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14151294
APA StyleMishra, B., Yadav, A. S., Malhotra, D., Mitra, T., Sinsinwar, S., Radharani, N. N. V., Sahoo, S. R., Patnaik, S., & Kundu, G. C. (2024). Chitosan Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery of Curcumin Suppresses Tumor Growth in Breast Cancer. Nanomaterials, 14(15), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14151294






