Carbon Nanotube Immunotoxicity in Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells Is Mediated by Physical Contact-Independent Cell–Cell Interaction with Macrophages as Demonstrated in an Optimized Air–Liquid Interface (ALI) Coculture Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Reagents
2.2. CNT Preparation and Characterization
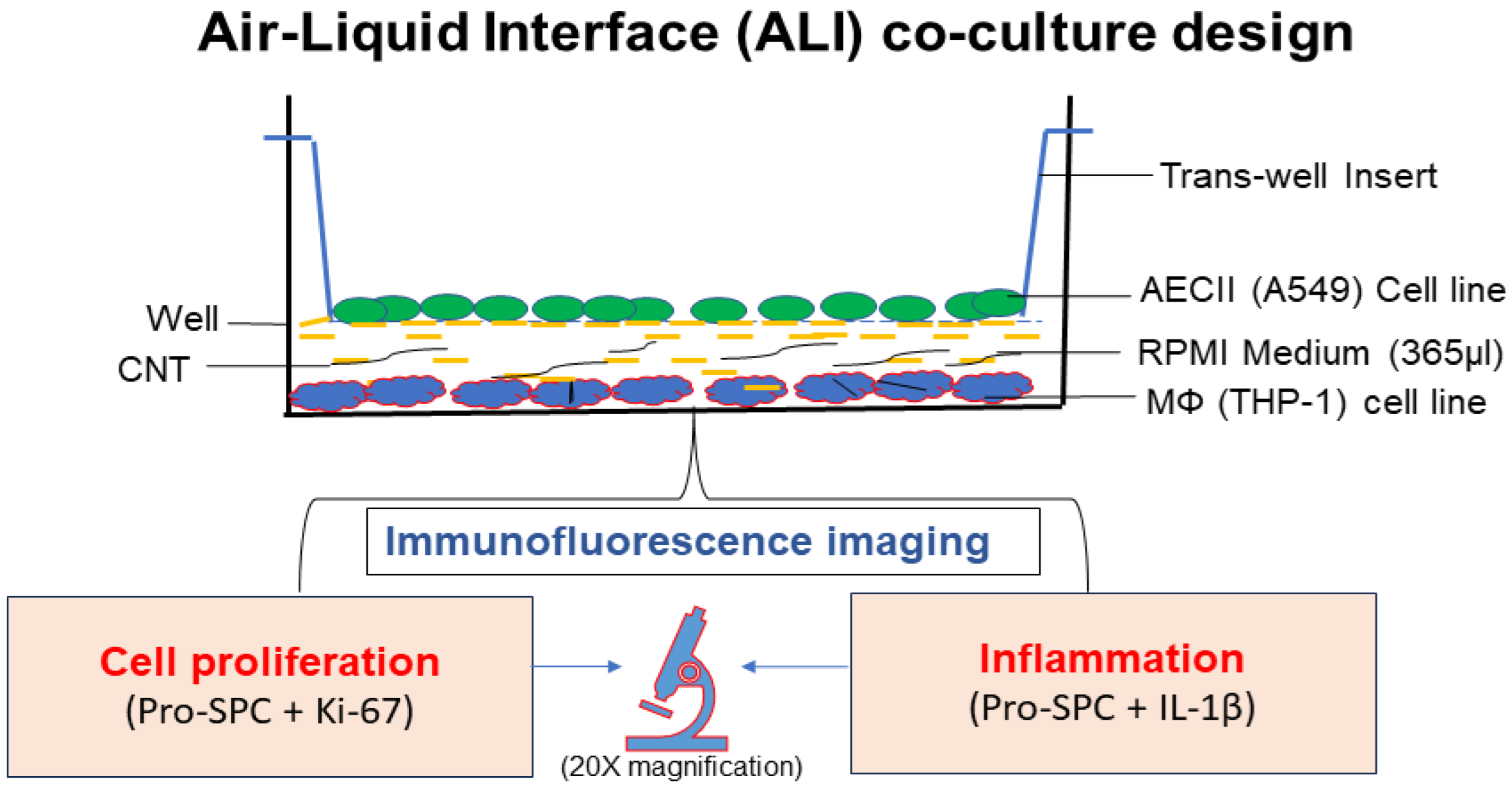
2.3. In Vitro Air–Liquid Interface (ALI) Coculture Setup
2.3.1. THP-1 Monocyte Cell Line Differentiation into Macrophages and Culturing
2.3.2. Human Alveolar Type-II Epithelial Cell Line (A549) Culture
2.3.3. ALI Transwell Coculture Set Up
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining and Confocal Microscopy
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of ALI Coculture Model to Screen for MWCNT Immunotoxicity Potential
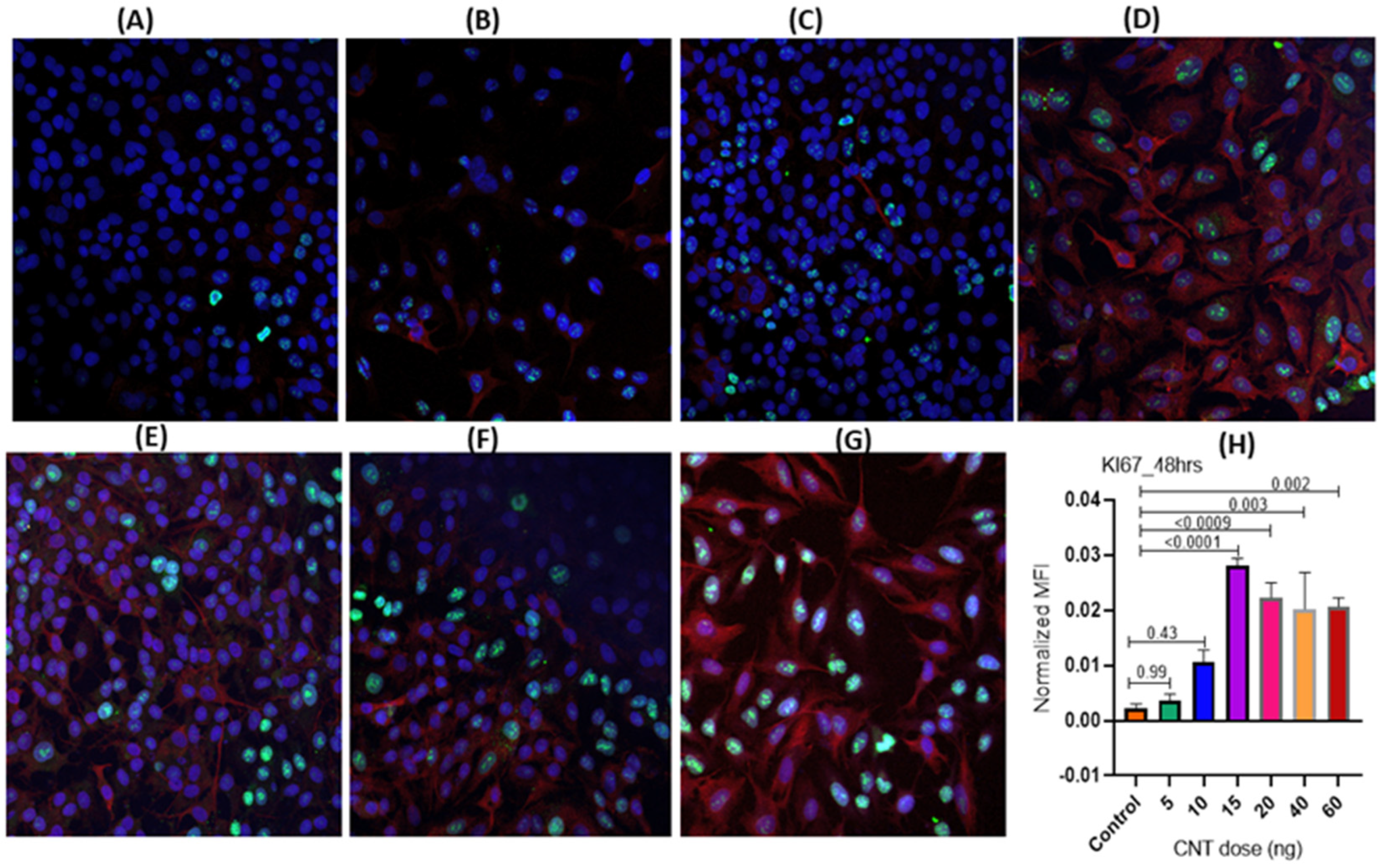
3.1.1. Dose-Dependence of CNT-Induced Proliferation of Human AECII Cells (A549) in the Presence of Human Macrophages (THP-1) in ALI Coculture
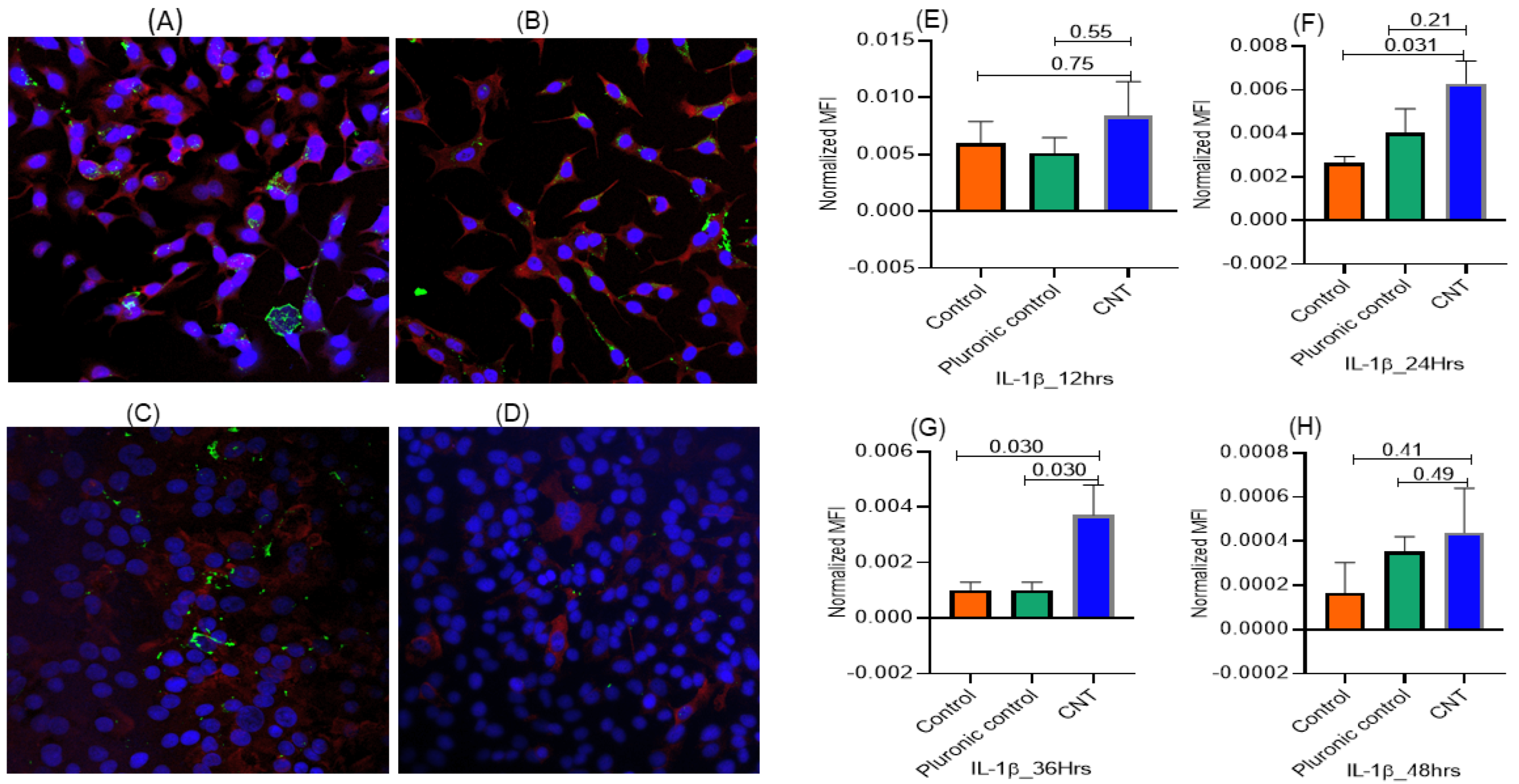
3.1.2. Temporal Pattern of CNT-Induced Proliferative- and Inflammatory-Responses in Human AECII Cells (A549) in the Presence of Human Macrophages (THP-1) in ALI Coculture
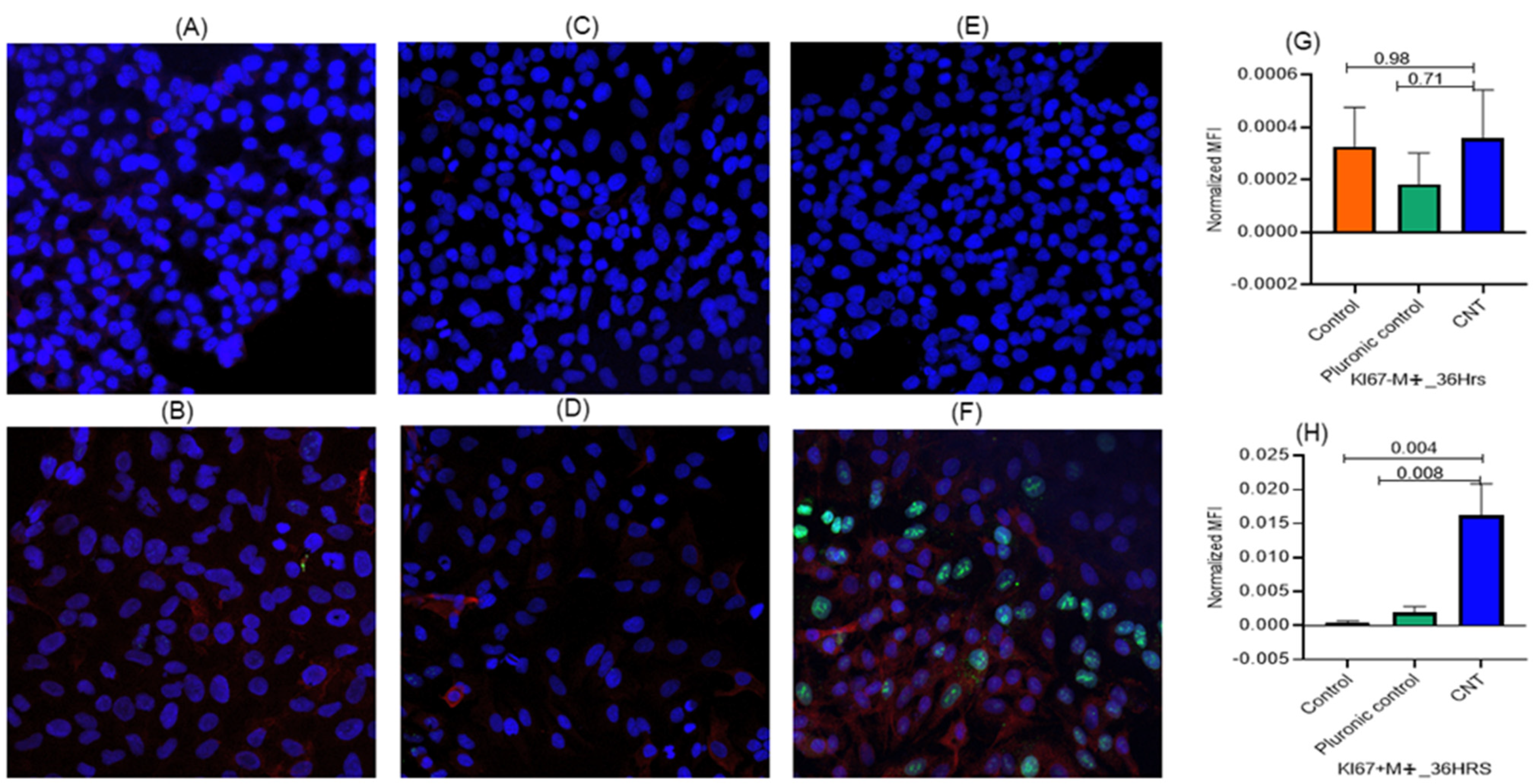
3.2. Macrophages Found Indispensable for CNT-Induced Response (Ki-67, IL-1β) in AECII Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bonner, J.C. Carbon Nanotubes as Delivery Systems for Respiratory Disease: Do the Dangers Outweigh the Potential Benefits? Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2011, 5, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safdar, M.; Kim, W.; Park, S.; Gwon, Y.; Kim, Y.-O.; Kim, J. Engineering Plants with Carbon Nanotubes: A Sustainable Agriculture Approach. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Zhang, Q. Advances and Frontiers in Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Electronics. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2102860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almstrand, A.-C.; Ljungström, E.; Lausmaa, J.; Bake, B.; Sjövall, P.; Olin, A.-C. Airway Monitoring by Collection and Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Exhaled Particles. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakand, S.; Hayes, A.; Dechsakulthorn, F. Nanoparticles: A Review of Particle Toxicology Following Inhalation Exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 2012, 24, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Cellular Toxicity and Immunological Effects of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2019, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortune Business Insights. Carbon Nanotubes Market Size, Share & Global Report; Report ID FBI 102700; Fortunebusinessinsights.Com: Pune, India, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- IMRAC. Carbon Nanotubes Market Report by Product (Multi Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNT), Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNT)), Method (Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Catalytic Chemical Vapor Deposition (CCVD), High-Pressure Carbon Monoxide Reaction, and Others), Application (Polymers, Electrical and Electronics, Energy, and Others), and Region 2024–2032; Marker Research Report. Report ID: SR112024A5191; IMRAC: London, UK, 2023; Available online: https://www.imarcgroup.com/carbon-nanotubes-market (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- De Volder, M.F.L.; Tawfick, S.H.; Baughman, R.H.; Hart, A.J. Carbon Nanotubes: Present and Future Commercial Applications. Science 2013, 339, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, K.; Andón, F.T.; El-Sayed, R.; Fadeel, B. Mechanisms of Carbon Nanotube-Induced Toxicity: Focus on Pulmonary Inflammation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 2087–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Noga, R.; Shanov, V.; Ryu, H.; Chandra, H.; Yadav, B.; Yadav, J.; Chae, S. Electrically Heatable Carbon Nanotube Point-of-Use Filters for Effective Separation and in-Situ Inactivation of Legionella Pneumophila. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.S.; Yadav, B.; Rosen, L.; Nagpal, R.; Yadav, H.; Yadav, J.S. Crosstalk between Gut Microbiota and Lung Inflammation in Murine Toxicity Models of Respiratory Exposure or Co-Exposure to Carbon Nanotube Particles and Cigarette Smoke Extract. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 447, 116066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.S.; Yadav, B.; Yadav, E.; Hus, A.; Yadav, N.; Kaur, P.; Rosen, L.; Jandarov, R.; Yadav, J.S. Differential Modulation of Lung Aquaporins among Other Pathophysiological Markers in Acute (Cl2 Gas) and Chronic (Carbon Nanoparticles, Cigarette Smoke) Respiratory Toxicity Mouse Models. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 880815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, E.A.; Carreira, V.S.; Birch, M.E.; Yadav, J.S. Carbon Nanotube and Asbestos Exposures Induce Overlapping but Distinct Profiles of Lung Pathology in Non-Swiss Albino CF-1 Mice. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 44, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, B.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Rosen, L.; Nagpal, R.; Yadav, H.; Yadav, J.S. Oro-Respiratory Dysbiosis and Its Modulatory Effect on Lung Mucosal Toxicity during Exposure or Co-Exposure to Carbon Nanotubes and Cigarette Smoke. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomäki, J.; Karisola, P.; Pylkkänen, L.; Savolainen, K.; Alenius, H. Engineered Nanomaterials Cause Cytotoxicity and Activation on Mouse Antigen Presenting Cells. Toxicology 2010, 267, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebsch, M.; Grune, B.; Seiler, A.; Butzke, D.; Oelgeschläger, M.; Pirow, R.; Adler, S.; Riebeling, C.; Luch, A. Alternatives to Animal Testing: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 841–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaus, P.W.F.; Karmaus, A.L. Challenges for Integrating Immunotoxicology into the Twenty-First-Century Toxicology Testing Paradigm. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1803, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, S.; Okazaki, Y.; Ito, D.; Asakawa, A.; Nagai, H.; Tajima, M.; Toyokuni, S. Asbestos and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Generate Distinct Oxidative Responses in Inflammatory Cells. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2015, 56, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepen, T.; Van Rooijen, N.; Kraal, G. Alveolar Macrophage Elimination in Vivo Is Associated with an Increase in Pulmonary Immune Response in Mice. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 170, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, B.E.; Valdez, Y.E.; Tietjen, G.L. Alveolar Macrophage-Particle Relationships during Lung Clearance. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1989, 1, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, E.A.; Birch, M.E.; Yadav, J.S. MyD88 Mediates In Vivo Effector Functions of Alveolar Macrophages in Acute Lung Inflammatory Responses to Carbon Nanotube Exposure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 288, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Ferin, J.; Gelein, R.; Soderholm, S.C.; Finkelstein, J. Role of the Alveolar Macrophage in Lung Injury: Studies with Ultrafine Particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 1992, 97, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillot, L.; Nathan, N.; Tabary, O.; Thouvenin, G.; Le Rouzic, P.; Corvol, H.; Amselem, S.; Clement, A. Alveolar Epithelial Cells: Master Regulators of Lung Homeostasis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitsett, J.A.; Weaver, T.E. Alveolar Development and Disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, H.; Kwon, S. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Induced Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress in a Dynamic Cell Growth Environment. J. Biol. Eng. 2012, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, A.; Dierker, C.; Rommel, C.; Hahn, D.; Wohlleben, W.; Schulze-Isfort, C.; Göbbert, C.; Voetz, M.; Hardinghaus, F.; Schnekenburger, J. Cytotoxicity Screening of 23 Engineered Nanomaterials Using a Test Matrix of Ten Cell Lines and Three Different Assays. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, A.-G.; Karg, E.; Brendel, E.; Hinze-Heyn, H.; Maier, K.L.; Eickelberg, O.; Stoeger, T.; Schmid, O. Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Responses of an Alveolar Epithelial Cell Line to Airborne Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles at the Air-Liquid Interface: A Comparison with Conventional, Submerged Cell-Culture Conditions. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 652632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loret, T.; Peyret, E.; Dubreuil, M.; Aguerre-Chariol, O.; Bressot, C.; le Bihan, O.; Amodeo, T.; Trouiller, B.; Braun, A.; Egles, C.; et al. Air-Liquid Interface Exposure to Aerosols of Poorly Soluble Nanomaterials Induces Different Biological Activation Levels Compared to Exposure to Suspensions. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balis, J.U.; Bumgarner, S.D.; Paciga, J.E.; Paterson, J.F.; Shelley, S.A. Synthesis of Lung Surfactant-Associated Glycoproteins by A549 Cells: Description of an in Vitro Model for Human Type II Cell Dysfunction. Exp. Lung Res. 1984, 6, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagre, N.; Cong, X.; Pearson, A.C.; Zhao, X. Alveolar Macrophage Phagocytosis and Bacteria Clearance in Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 145, e59088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuyama, A.; Kanno, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Hirano, S. Extrapulmonary Translocation of Intratracheally Instilled Fine and Ultrafine Particles via Direct and Alveolar Macrophage-Associated Routes. Arch. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Chen, R.; Kan, H. Ambient Fine Particulate Matter Induce Toxicity in Lung Epithelial-Endothelial Co-Culture Models. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 301, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, M.J.; Brandão, F.; Fokkens, P.H.B.; Leseman, D.L.A.C.; Boere, A.J.F.; Cassee, F.R.; Salmatonidis, A.; Viana, M.; Vulpoi, A.; Simon, S.; et al. In Vitro Toxicity of Industrially Relevant Engineered Nanoparticles in Human Alveolar Epithelial Cells: Air-Liquid Interface versus Submerged Cultures. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The Inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Sangtian, S.; Anderson, S.M.; Snyder, R.J.; Marshburn, J.D.; Rice, A.B.; Bonner, J.C.; Garantziotis, S. Inflammasome Activation in Airway Epithelial Cells after Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Exposure Mediates a Profibrotic Response in Lung Fibroblasts. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ong, S.L.; Tran, L.M.; Jing, Z.; Liu, B.; Park, S.J.; Huang, Z.L.; Walser, T.C.; Heinrich, E.L.; Lee, G.; et al. Chronic IL-1β-Induced Inflammation Regulates Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Memory Phenotypes via Epigenetic Modifications in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, C.; Pereira, J.F.S.; Matos, P.; Marques, B.; Jordan, P.; Sousa-Uva, A.; Silva, M.J. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of MWCNT-7 and Crocidolite: Assessment in Alveolar Epithelial Cells versus Their Coculture with Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 479–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visalli, G.; Bertuccio, M.P.; Iannazzo, D.; Piperno, A.; Pistone, A.; Di Pietro, A. Toxicological Assessment of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on A549 Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Ma, J.; Gao, J.; Zuo, Y.Y.; Liu, S. Mesoporous Carbon Nanomaterials Induced Pulmonary Surfactant Inhibition, Cytotoxicity, Inflammation and Lung Fibrosis. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 62, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.N.; Yadav, N.; Kaur, P.; Jandarov, R.; Yadav, J.S. Immunomodulation of Susceptibility to Pneumococcal Pneumonia Infection in Mouse Lungs Exposed to Carbon Nanoparticles via Dysregulation of Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2024, 483, 116820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Zou, X.-B.; Chai, Y.-F.; Yao, Y.-M. Macrophage Polarization in Inflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Martinez, F.O. Alternative Activation of Macrophages: Mechanism and Functions. Immunity 2010, 32, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, F.A.; Schinwald, A.; Poland, C.A.; Donaldson, K. The Mechanism of Pleural Inflammation by Long Carbon Nanotubes: Interaction of Long Fibres with Macrophages Stimulates Them to Amplify pro-Inflammatory Responses in Mesothelial Cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.-W.; Braakhuis, H.M.; Vandebriel, R.J.; Staal, Y.C.M.; Gremmer, E.R.; Fokkens, P.H.B.; Kemp, C.; Vermeulen, J.; Westerink, R.H.S.; Cassee, F.R. Optimization of an Air-Liquid Interface in Vitro Cell Co-Culture Model to Estimate the Hazard of Aerosol Exposures. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 153, 105703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yadav, B.; Yadav, J.S. Carbon Nanotube Immunotoxicity in Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells Is Mediated by Physical Contact-Independent Cell–Cell Interaction with Macrophages as Demonstrated in an Optimized Air–Liquid Interface (ALI) Coculture Model. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14151273
Yadav B, Yadav JS. Carbon Nanotube Immunotoxicity in Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells Is Mediated by Physical Contact-Independent Cell–Cell Interaction with Macrophages as Demonstrated in an Optimized Air–Liquid Interface (ALI) Coculture Model. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(15):1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14151273
Chicago/Turabian StyleYadav, Brijesh, and Jagjit S. Yadav. 2024. "Carbon Nanotube Immunotoxicity in Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells Is Mediated by Physical Contact-Independent Cell–Cell Interaction with Macrophages as Demonstrated in an Optimized Air–Liquid Interface (ALI) Coculture Model" Nanomaterials 14, no. 15: 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14151273
APA StyleYadav, B., & Yadav, J. S. (2024). Carbon Nanotube Immunotoxicity in Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells Is Mediated by Physical Contact-Independent Cell–Cell Interaction with Macrophages as Demonstrated in an Optimized Air–Liquid Interface (ALI) Coculture Model. Nanomaterials, 14(15), 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14151273





