Exploring the Microstructural Effect of FeCo Alloy on Carbon Microsphere Deposition and Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of f-Fe(OH)3/Co(OH)2 Precursor
2.3. Preparation of f-FeCo Alloy
2.4. Preparation of f-FeCo@CM and s-FeCo@CM
2.5. Characterization
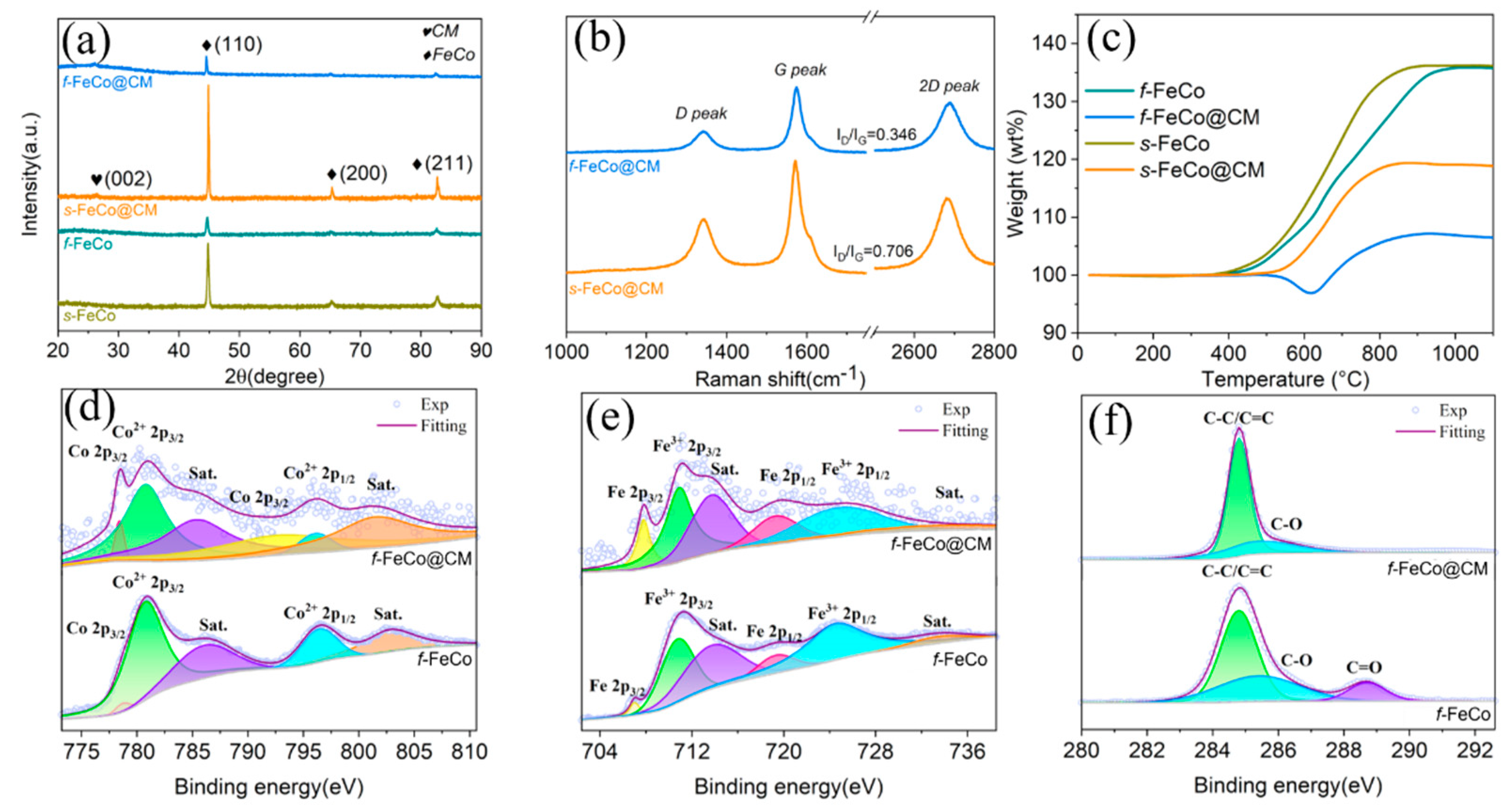
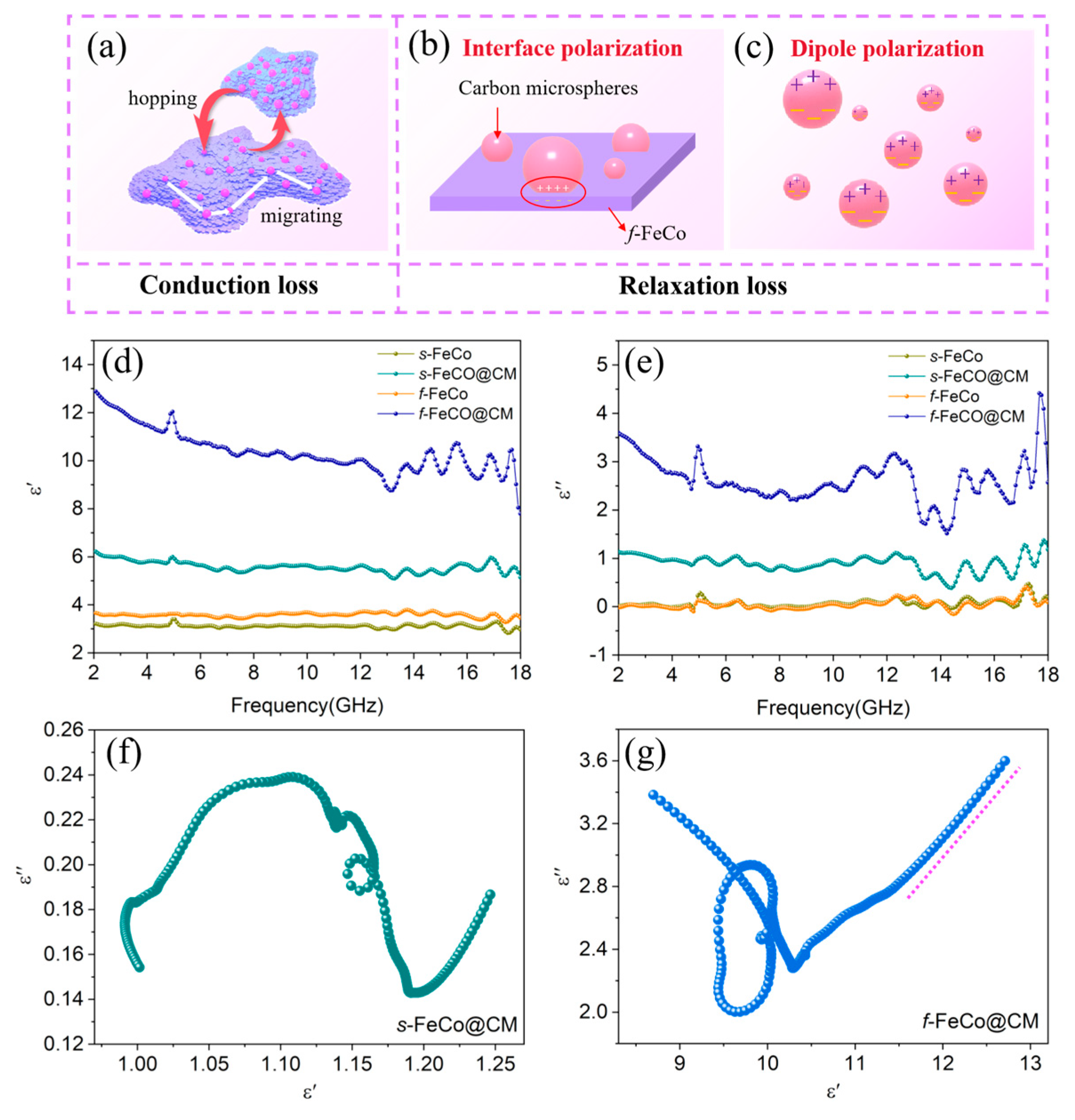
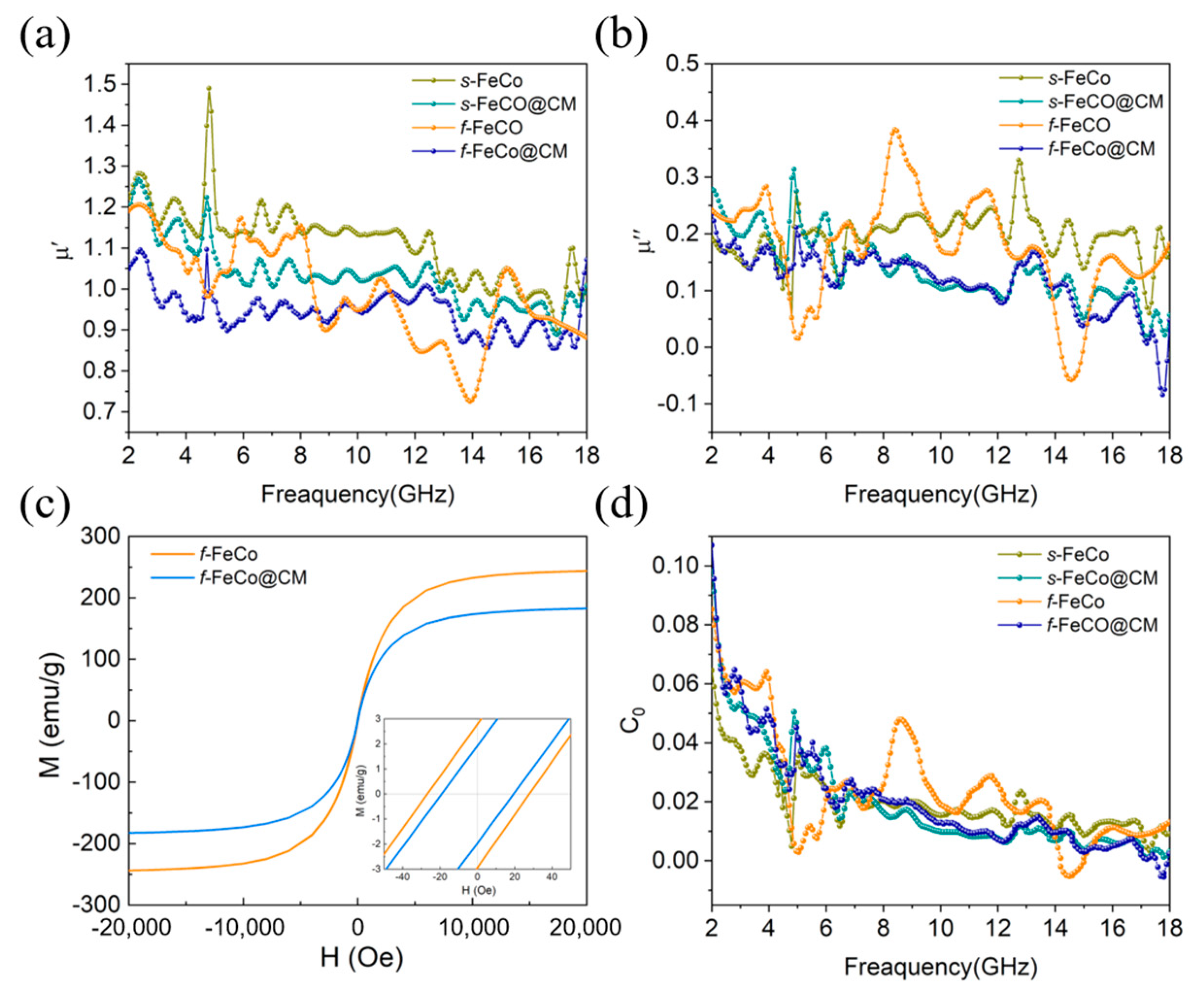
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Han, M.; Liu, W.; Wu, N.; Liu, J. Hydrogel-based composites beyond the porous architectures for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 9614–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, B.; Han, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, L.; Cao, M. Nature-inspired 3D hierarchical structured “vine” for efficient microwave attenuation and electromagnetic energy conversion device. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Hu, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Min, Z.; Zhang, R. N-doped honeycomb-like Ag@N-Ti3C2Tx foam for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Han, L.; Wang, X.; Gao, F.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J. MOF-derived CoNC@rGO/amine-rich@rGO/fluorinated-epoxy nanocomposites with EMI shielding, mechanical robustness, superamphiphobicity and long-term anticorrosion properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cui, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, X.; Wang, X. Polypyrrole chains decorated on CoS spheres: A core-shell like heterostructure for high-performance microwave absorption. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Cao, M. VSe2/CNTs nanocomposites toward superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon 2023, 212, 118159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qin, Y.; Peng, L.; Pan, M.; Xu, H. Lightweight and anti-corrosive carbon nanotubes (CNTs)/bamboo fiber/HDPE composite for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Colloid Surf. A 2023, 672, 131746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Yi, E.; Zhou, X.; He, G. Quantum dots with Mott-Schottky effect embedded in crystal-amorphous carbon for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 929, 167246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.; Peng, L.; Duan, X.; Chen, Q.; Liang, X. Microwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of Fe encapsulated within carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P.L.; Ji, G.; Song, J.; Zheng, L.; Xu, Z.J. A voltage-boosting strategy enabling a low-frequency, flexible electromagnetic wave absorption device. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cao, Q.; Bi, H.; Liang, C.; Yuan, K.; She, W.; Yang, Y.; Che, R. CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@ Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Wang, X.; Cao, W.; Fang, X.; Wen, B.; Yuan, J. Thermally driven transport and relaxation switching self-powered electromagnetic energy conversion. Small 2018, 14, 1800987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sista, K.; Dwarapudi, S.; Kumar, D.; Sinha, G.; Moon, A. Carbonyl iron powders as absorption material for microwave interference shielding: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 853, 157251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Ning, M.; Raza, H.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, G.; Zheng, Q.; Che, R. Emerging materials and designs for low- and multi-band electromagnetic wave absorbers: The search for dielectric and magnetic synergy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, J.; Gu, J. New generation electromagnetic materials: Harvesting instead of dissipation solo. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 1413–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Wang, S.; Kuang, D. Facile synthesis and excellent microwave absorption properties of FeCo-C core–shell nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 085604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Ji, G.; Wang, M. Hexagonal-cone like of Fe50Co50 with broad frequency microwave absorption, Effect of ultrasonic irradiation time. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Jiang, J.; Xu, C. Co7Fe3 and Co7Fe3@SiO2 nanospheres with tunable diameters for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017, 9, 21933–21941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, D.; Hou, L.; Wang, S. Large-scale synthesis and outstanding microwave absorption properties of carbon nanotubes coated by extremely small FeCo-C core-shell nanoparticles. Carbon 2019, 153, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Liu, H.; Cao, Z. Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance of amorphous CoxFe10−x alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 726, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ji, G.; Li, Z. Facile synthesis of FeCo alloys with excellent microwave absorption in the whole Ku-band, Effect of Fe/Co atomic ratio. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 704, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; You, W.; Xiong, X. Morphology-evolved succulent-like FeCo microarchitectures with magnetic configuration regulation for enhanced microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 32369–32378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zong, Y. Carbon nanofibers supported by FeCo nanocrystals as difunctional magnetic/dielectric composites with broadband microwave absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 824, 153980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ding, M.; Shao, C. Facile synthesis of CoxFey@C nanocomposite fibers derived from pyrolysis of cobalt/iron chelate nanowires for strong broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajia, S.; Asa, H.; Toyoda, Y. Development of an alternative approach for electromagnetic wave absorbers using Fe–Cr–Co alloy powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 903, 163920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jiao, Q.; Fu, R. Cu/NC@Co/NC composites derived from core-shell Cu-MOF@Co-MOF and their electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2022, 613, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, M.; Kamkar, M.; Rahmani, F. Multilayer structures of a Zn0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4-reduced graphene oxide/PVDF nanocomposite for tunable and highly efficient microwave absorbers. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 5514–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, R. High-density anisotropy magnetism enhanced microwave absorption performance in Ti3C2Tx MXene@Ni microspheres. ACS Nano 2021, 16, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, R.; Du, Y.; Zhao, H. Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13426–13434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Cao, M.; Chen, Y.; Cao, W.; Liu, J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Yuan, J. Multiscale assembly of grape-like ferroferric oxide and carbon nanotubes: A smart absorber prototype varying temperature to tune intensities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19408–19415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Shi, T.; Wu, G.; Lu, Y. One pot green synthesis and EM wave absorption performance of MoS2@nitrogen doped carbon hybrid decorated with ultrasmall cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Carbon 2020, 163, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, M. High efficiency microwave absorption nanocomposites of multiple-phase core-shell CoNi alloy@C loaded on rGO conducting network. Compos. Part A-Appl. S. 2018, 115, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hou, Y.; Li, L. Synthesis of the SiO2@C composites with high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. Powder Technol. 2019, 343, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qiang, R.; Du, Y. Prussian blue analogues derived magnetic FeCo alloy/carbon composites with tunable chemical composition and enhanced microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2018, 514, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, Y. Hierarchically porous carbon sheets/Co nanofibers derived from corncobs for enhanced microwave absorbing properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 534, 147510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Miao, P.; Chen, K. Highly effective electromagnetic wave absorbing Prismatic Co/C nanocomposites derived from cubic metal-organic framework. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2020, 182, 107613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wen, B.; Yang, H. Hierarchical nest-like structure of Co/Fe MOF derived CoFe@C composite as wide-bandwidth microwave absorber. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. 2020, 135, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, N.; Han, X. Core-shell FeCo@carbon nanoparticles encapsulated in polydopamine-derived carbon nanocages for efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 2019, 145, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Hu, T.; Yang, L. Facile fabrication of electroactive microporous Co3O4 through microwave plasma etching for supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 771, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, N.; Fonseca, A.; Konya, Z.; Nagy, J. Alumina and silica supported metal catalysts for the production of carbon nanotubes. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2002, 181, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, I.; Kónya, Z.; Colomer, J.; Tendeloo, G.; Nagaraju, N.; Fonseca, A.; Nagy, J. Control of the outer diameter of thin carbon nanotubes synthesized by catalytic decomposition of hydrocarbons. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 317, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kónya, Z.; Kiss, J.; Oszkó, A.; Siska, A.; Kiricsi, I. XPS characterization of catalysts during production of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Chu, W.; Jiang, C.; Tong, D. Growth of carbon nanotubes on the novel FeCo-Al2O3 catalyst prepared by ultrasonic coprecipitation. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2010, 19, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yu, F.; Ma, C.; Xue, X.; Fu, H.; Yuan, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, G.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L. Effective Oxygen reduction reaction performance of FeCo alloys in situ anchored on nitrogen-doped carbon by the microwave-assistant carbon bath method and subsequent plasma etching. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Q.; Zhang, F.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Piao, M. One-step synthesis of cobalt nanosheets depositing with carbon microsphere by microwave plasma assisted reduction chemical vapor deposition technique against electromagnetic pollution. Carbon 2023, 214, 118322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Zou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Dryfe, R.A.W.; Huang, X.; Dou, S.; Dai, L.; Wang, S. Oxygen reduction reaction in a droplet on graphite, direct evidence that the edge is more active than the basal plane. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2014, 53, 10804–10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivkov, D.; Petrova, O.; Mingaleva, A.; Ob’edkov, A.; Kaverin, B.; Gusev, S.; Vilkov, I. The structure and chemical composition of the Cr and Fe pyrolytic coatings on the MWCNTs’ surface according to NEXAFS and XPS Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ding, X.; Liu, Q.; Pang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T. Safety assessment of graphene oxide and microcystin-LR complex, a toxicological scenario beyond physical mixture. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, D.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Ren, H.; Meng, F. A review of three-dimensional graphene-based aerogels, synthesis, structure and application for microwave absorption. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 211, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, H.; Cheng, J.; Han, C.; Yang, X.; Xu, J. Conductive WS2-NS/CNTs hybrids based 3D ultra-thin mesh electromagnetic wave absorbers with excellent absorption performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 528, 147052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wei, B.; Wang, M.; Yao, Z.; Chen, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, Z. Three dimensional flowerlike ZnFe2O4 ferrite loaded graphene, enhancing microwave absorption performance by constructing microcircuits. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 889, 161734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Guo, F.; Luo, J.; Hao, G.; Liu, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Guo, H.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, W. Designed 3D heterostructure with 0D/1D/2D hierarchy for low-frequency microwave absorption in the S-band. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Feng, X.; Zhu, K.; Lin, G.; Bai, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X. Phthalocyanine-mediated interfacial self-assembly of magnetic graphene nanocomposites toward low-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption. Chen. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Geng, L.; Jiang, S.; Bai, W.; Dai, L.; Jiang, S.; Hu, J.; Ren, E.; Guo, R. Construction of hierarchical carbon fiber Aerogel@Hollow Co9S8 polyhedron for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption at low-frequency. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Zhao, B.; Which, C.; Pei, K.; Money, L.; Zhang, R.; You, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Che, R. Remarkable magnetic exchange coupling via constructing bi-magnetic interface for broadband lower-frequency microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2203161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, W.; Qiang, R.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Ma, J.; Xu, P. Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core-shell Fe3O4@C composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Liang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, D.; Zhang, B.; Ji, G.; Du, Y. Coin-like α-Fe2O3@CoFe2O4 Core–Shell Composites with Excellent Electromagnetic Absorption Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4744–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjipanayis, G.; Kim, A. Domain wall pinning versus nucleation of reversed domains in R-Fe-B magnets (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63, 3310–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, D.; Geng, D.; An, J.; He, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z. Microwave absorption properties of core double-shell FeCo/C/BaTiO3 nanocomposites. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 3967–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Dong, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Lei, J.; Sun, J. Microwave absorption properties of the core/shell-type iron and nickel nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Garg, A.; Ketterson, J. Ferromagnetic resonance modes in the exchange-dominated limit in cylinders of finite length. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 16, 064007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Ji, G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Du, W. Achieving hierarchical hollow carbon@Fe@Fe3O4 nanospheres with superior microwave absorption properties and lightweight features. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10232–10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, P.; Yun, J. A novel MOF-drived self-decomposition strategy for CoO@N/C-Co/Ni-NiCo2O4 multi-heterostructure composite as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, B.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Tao, X. Constructing FeCo@C core-shell structure with strong polarization behavior towards excellent microwave absorption performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 300, 127553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; Yi, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Piao, M. Exploring the Microstructural Effect of FeCo Alloy on Carbon Microsphere Deposition and Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141194
Jia X, Zhang H, Liu F, Yi Q, Li C, Wang X, Piao M. Exploring the Microstructural Effect of FeCo Alloy on Carbon Microsphere Deposition and Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(14):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141194
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Xiaoshu, Heng Zhang, Fang Liu, Qiaojun Yi, Chaolong Li, Xiao Wang, and Mingxing Piao. 2024. "Exploring the Microstructural Effect of FeCo Alloy on Carbon Microsphere Deposition and Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption" Nanomaterials 14, no. 14: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141194
APA StyleJia, X., Zhang, H., Liu, F., Yi, Q., Li, C., Wang, X., & Piao, M. (2024). Exploring the Microstructural Effect of FeCo Alloy on Carbon Microsphere Deposition and Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Nanomaterials, 14(14), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141194







