Temperature-Induced Irreversible Structural Transition in Fe1.1Mn1.9O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Combustion Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Fe1.1Mn1.9O4 Nanoparticles
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Structural and Magnetic Properties of the As-Synthesized Sample
3.2. Temperature-Dependent Magnetization Measurements
3.3. Effect of High-Temperature Measurements on the Structural and Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amiri, M.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Akbari, A. Magnetic nanocarriers: Evolution of spinel ferrites for medical applications. Adv. Colloid Int. Sci. 2019, 265, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seehra, M.; Spinels, M. Properties and Applications; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kirankumar, V.S.; Sumathi, S. A review on photodegradation of organic pollutants using spinel oxide. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 18, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revia, R.A.; Zhang, M. Magnetite nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis, treatment, and treatment monitoring: Recent advances. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Mendoza-Garcia, A.; Li, Q.; Sun, S. Organic Phase Syntheses of Magnetic Nanoparticles and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10473–10512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Ding, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, L.; Fu, Z.; Qin, C.; Wang, F.; Tao, X. Micro-tube biotemplate synthesis of Fe3O4/C composite as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 425, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, L.; Gaete, J.; Alfaro, I.; Ide, V.; Valenzuela, F.; Parada, J.; Basualto, C. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles functionalized with organophosphorus compounds and its application as an adsorbent for La (III), Nd (III) and Pr (III) ions from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 275, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cao, H.; Shao, J.; Qu, M.; Warner, J.H. Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanocrystals@graphene composites for energy storage devices. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 5069–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Liang, X.; He, Z.; Liao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Liu, P.; Ji, S.; He, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, J. Heterogeneous activation of Oxone by substituted magnetites Fe3−xMxO4 (Cr, Mn, Co, Ni) for degradation of Acid Orange II at neutral pH. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 398, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaobushi, J.; Ishikawa, M.; Ueda, S.; Ikenaga, E.; Kim, J.-J.; Kobata, M.; Takeda, Y.; Saitoh, Y.; Yabashi, M.; Nishino, Y.; et al. Electronic structures of Fe3−xMxO4 (M = Mn, Zn) spinel oxide thin films investigated by x-ray photoemission spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 205108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emídio, E.S.; Hammer, P.; Nogueira, R.F.P. Simultaneous degradation of the anticancer drugs 5-fluorouracil and cyclophosphamide using a heterogeneous photo-Fenton process based on copper-containing magnetites (Fe3−xCuxO4). Chemosphere 2020, 241, 124990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penoyer, R.F.; Shafer, M.W. On the Magnetic Anisotropy in Manganese-Iron Spinels. J. Appl. Phys. 1959, 30, 315S–316S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Mizoguchi, T.; Aiyama, Y. Mössbauer Effect in MnxFe3−xO4. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1963, 18, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, N.U.; Bergamasco, R.; Hamoudi, S. Magnetic MnFe2O4—Graphene hybrid composite for efficient removal of glyphosate from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 295, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, Q.; Wang, T.; Gong, Y.-S.; Han, B.; Xia, K.-S.; Zhou, C.-G. Solvothermal synthesis of MnxFe3−xO4 nanoparticles with interesting physicochemical characteristics and good catalytic degradation activity. Mater. Des. 2016, 97, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yu, C.; Jiao, L.; Chen, J. MnFe2O4@C nanofibers as high-performance anode for sodium-ion batteries. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Ali, J.A.; Akbari, V.; Aghazadeh, M.; Paran, S.M.R.; Naderi, G.; Saeb, M.R.; Ranjbar, Z.; Ganjali, M.R. Curing epoxy with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) surface-functionalized MnxFe3-xO4 magnetic nanoparticles. Progr. Organ. Coat. 2019, 136, 105247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikdeli, M.; Dorraji, M.S.S.; Hosseini, S.F.; Hajimiri, I.; Rasoulifard, M.H.; Amani-Ghadim, A.R. High performance microwave shielding in green nanocomposite coating based on polyurethane via nickel oxide, MnxFe3−xO4 and polyaniline nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2020, 262, 114728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunaryono; Hidayat, M.F.; Kholifah, M.N.; Hidayat, S.; Mufti, N.A. Taufiq Magneto-thermal behavior of MnxFe3−xO4-PVA/PVP magnetic hydrogel and its potential application. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2228, 030018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdick, S.D.; Abdelgawad, A.; Moya, C.; Mesbahi-Vasey, S.; Kepaptsoglou, D.; Lazarov, V.K.; Evans, R.F.L.; Meilak, D.; Skoropata, E.; van Lierop, J.; et al. Spin canting across core/shell Fe3O4/MnxFe3−xO4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, S.; Jasrotia, R.; Kumari, N.; Singh, V.P.; Singh, P.; Kumar, R. A Current Review on Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Pure and Doped Manganese Ferrites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2357, 050007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, I.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Elovitz, M.; Mills, M.; Boulanger, B. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic manganese ferrites. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.S.; Yoon, H.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Wu, J.H.; Kim, Y.K. Synthesis and magnetic properties of size-tunable MnxFe3−xO4 ferrite nanoclusters. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17B517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.; Liao, J.; Ye, M.; Li, Y.; Peng, X. Preparation of Nano-MnFe2O4 and Its Catalytic Performance of Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium Perchlorate. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 19, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, A.; Nakano, J.; Seetharaman, S. Synthesis of nano-manganese ferrite by an oxalate method and characterization of its magnetic properties. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2015, 106, 1264–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabers, V.A.M.; Migration, C. Cation Valencies and the Cubic-Tetragonal Transition in MnxFe1−xO4. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1971, 32, 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, K.; Inaba, H.; Yagi, H. Heat capacity measurements of MnxFe3−xO4. J. Solids State Chem. 1981, 36, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, R.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, S.; Tian, W.; Nagler, S.E.; Jin, R. Structural and magnetic transitions in spinel FeMn2O4 single crystals. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 024410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, P.; Sengupta, S.K. Physico-chemical properties and catalytic activities of the spinel series MnxFe3–xO4 towards peroxide decomposition. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Transac. 1995, 91, 3489–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamuthu, S.; Vijayakumar, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Ryu, K.-S. Hybrid supercapacitor devices based on MnCo2O4 as the positive electrode and FeMn2O4 as the negative electrode. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.H.; Mosavi, V. Synthesis and characterization of Fe2O3/Mn2O3/FeMn2O4 nano composite alloy coated glass for photo-catalytic degradation of Reactive Blue 222. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 11078–11083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidan, I. The Development of FeMn2O4 Gas Sensors at Room Temperature. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; Volume 605, pp. 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Brabers, V.A.M. Infrared Spectra of Cubic and Tetragonal Manganese Ferrites. Phys. State Solids 1969, 33, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillot, B.; Laarj, M.; Kacim, S. Reactivity towards oxygen and cation distribution of manganese iron spinel Mn3−xFexO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 3) fine powders studied by thermogravimetry and IR spectroscopy. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, J. Crystal Distortion in Magnetic Compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 1960, 31, 14S–23S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, V.; Aggarwal, S.; Mandal, U.K.; Kotnala, R.K. Synthesis of nanocrystalline Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 ferrite and study of its magnetic behavior at different temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 166, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheeshkumar, M.K.; Kumar, E.R.; Srinivas, C.; Suriyanarayanan, N.; Deepty, M.; Prajapat, C.L.; Rao, T.V.C.; Sastry, D.L. Study of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Ag substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by honey assisted combustion method and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 469, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, I.; Šepelák, V.; Feldhoff, A.; Heitjans, P.; Becker, K.D. Particle size dependent cation distribution in lithium ferrite spinel LiFe5O8. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2008, 18, 375–378. [Google Scholar]
- Zhandun, V.S.; Nemtsev, A.V. Ab initio comparative study of the magnetic, electronic and optical properties of AB2O4 (A, B = Mn, Fe) spinels. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 259, 124065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Wu, X.C.; Zou, B.S.; Wang, Y.J. Magnetic properties of nanosized MnFe2O4 particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1998, 183, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, N.S.; Balaji, G.; Ghafari, M. Magnetic Properties of Nanostructured MnFe2O4 Synthesized by Precursor Technique. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2002, 189, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhong, Y.; Liang, X.; Tan, W.; Zhu, J.; Wang, C.Y. Natural Magnetite: An efficient catalyst for the degradation of organic contaminant. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakshi, M.; Mitchell, D.R.G.; Prince, K. Incorporation of TiB2 additive into MnO2 cathode and its influence on rechargeability in an aqueous battery system. Solid State Ion. 2008, 179, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, A.; Das, D.P.; Minakshi, M.; Ghosh, M.K.; Padhi, D.K. Probing Environmental Remediation of RhB Organic Dye Using α-MnO2 under Visible- Light Irradiation: Structural, Photocatalytic and Mineralization Studies. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 4277–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Z.; Lu, M.; Peng, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Formation mechanism of MnxFe3−xO4 by solid-state reaction of MnO2 and Fe2O3 in air atmosphere: Morphologies and properties evolution. Powder Technol. 2017, 313, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, S.T.; Iranmanesh, P.; Saeednia, S.; Mehran, M. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of MnxFe3−xO4 nanoferrites synthesized by a simple capping agent-free coprecipitation route. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2019, 245, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amighian, J.; Karimzadeh, E.; Mozaffari, M. The effect of Mn2+ substitution on magnetic properties of MnxFe3xO4 nanoparticles prepared by coprecipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 332, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.; John, A.M.; Nair, S.S.; Joy, P.A.; Anantharaman, M.R. Finite size effects on the structural and magnetic properties of sol–gel synthesized NiFe2O4 powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 302, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, O.L.; Monsalve, O.I.K.A.G.; Wable, D.; Savliwala, S.; Grooms, N.W.F.; Nacea, C.; Tuitt, O.R.; Dobson, J. Evaluation of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic fluid hyperthermia. Int. J. Hypertherm. 2019, 36, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.J.; Shinde, A.B.; Krishna, P.S.R.; Kalarikkal, N. Cation distribution and micro level magnetic alignments in the nanosized nickel zinc ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 546, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Sorensen, C.M.; Klabunde, K.J.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Devlin, E.; Kostikas, A. Size-dependent magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 fine particles synthesized by coprecipitation. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 9288–9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, A.E.; Rodriguez, G.F.; Hong, J.I.; An, K.; Hyeon, T.; Agarwal, N.; Smith, D.J.; Fullerton, E.E. Antiferromagnetic MnO nanoparticles with ferrimagnetic Mn3O4 shells: Doubly inverted core-shell system. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 024403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, R.; Depeyrot, J.; Sousa, M.H.; Tourinho, F.A.; Dubois, E.; Perzynski, R. Magnetization temperature dependence and freezing of surface spins in magnetic fluids based on ferrite nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 184435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.D.; Babu, P.D.; Rayaprol, S.; Murari, M.S.; Mendonca, L.D.; Daivajna, M. Size control on the magnetism of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 797, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
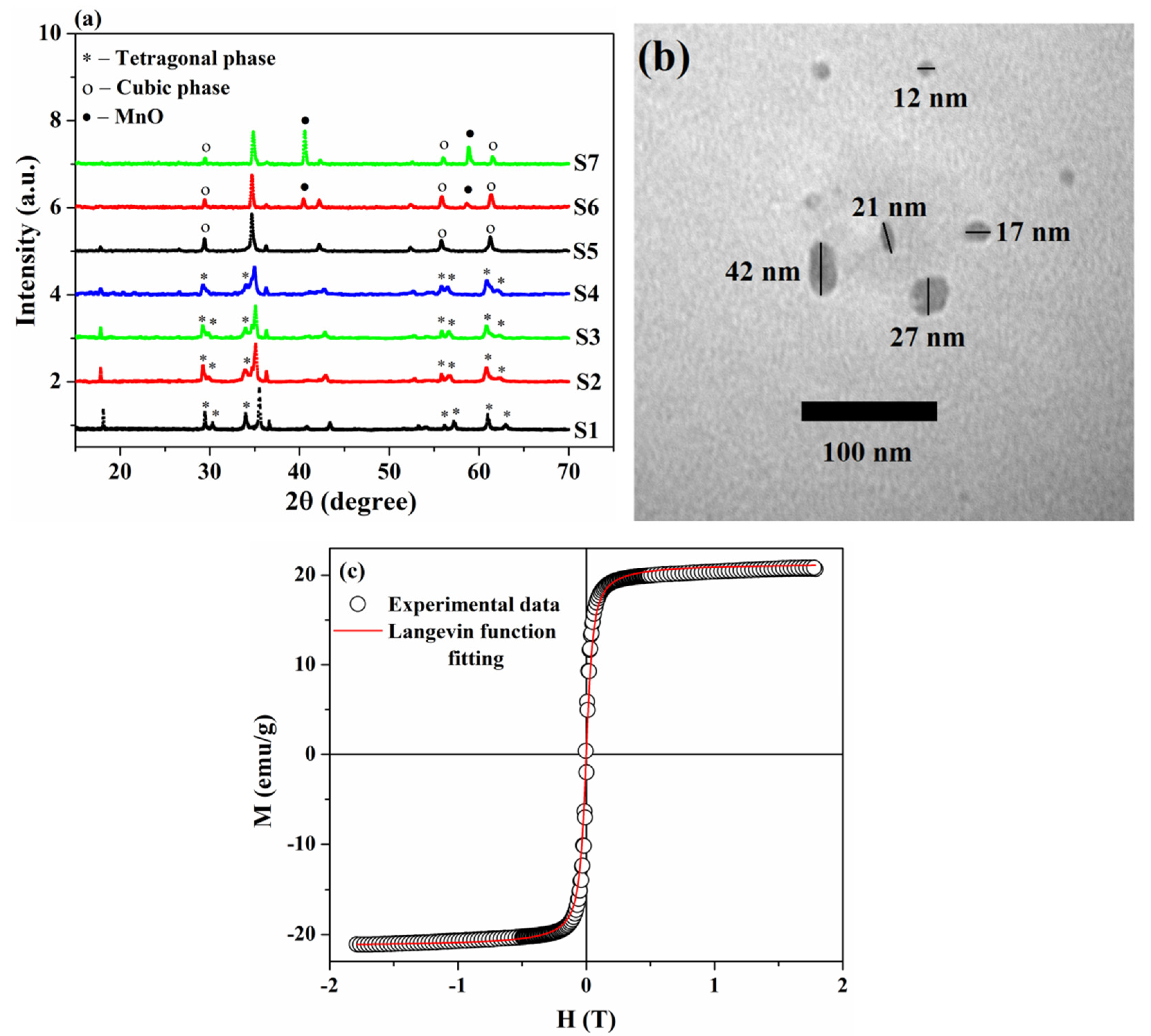
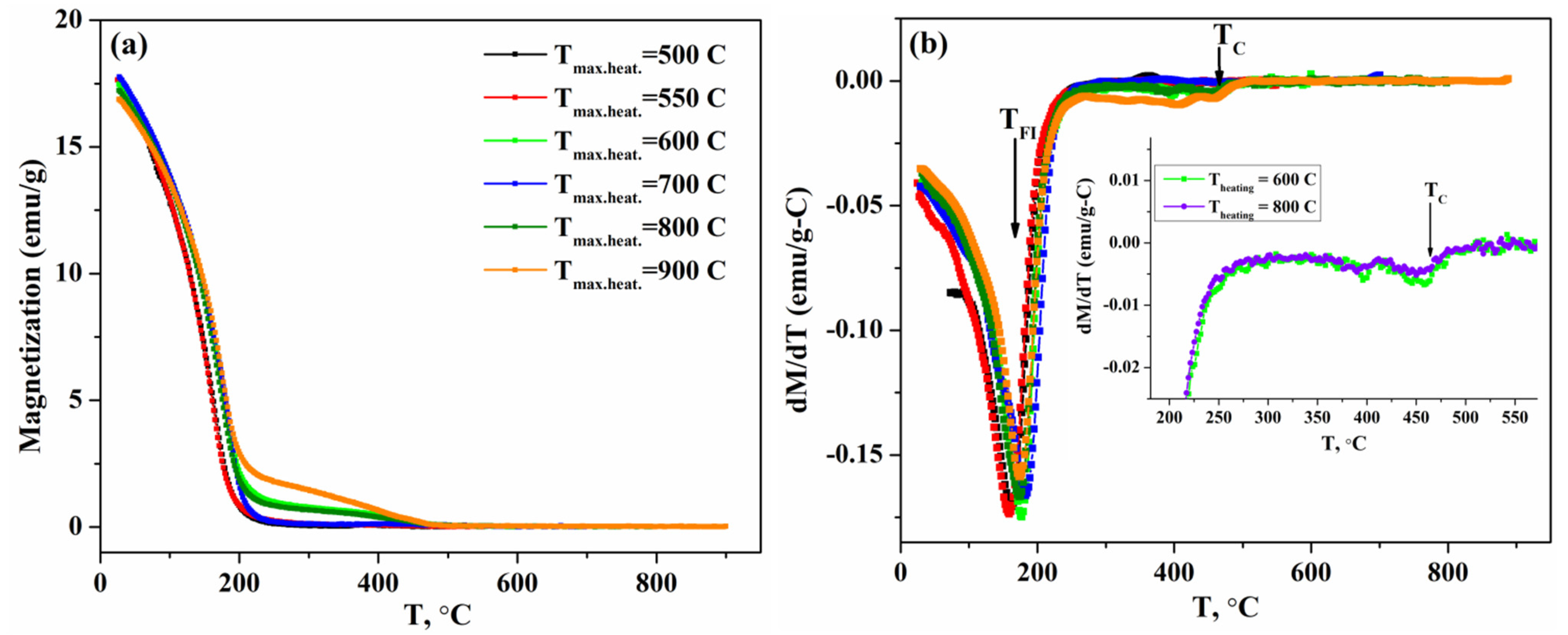
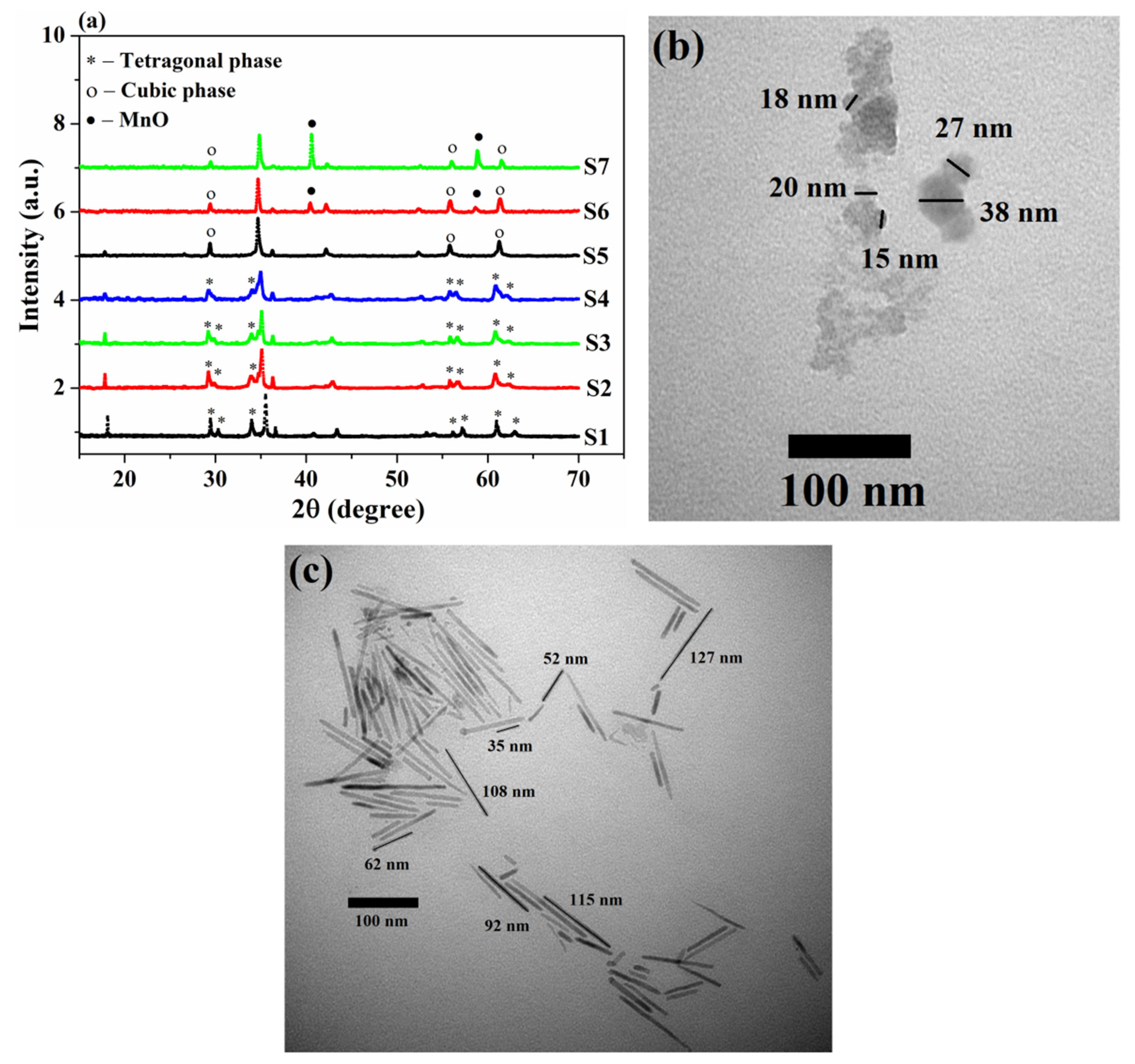
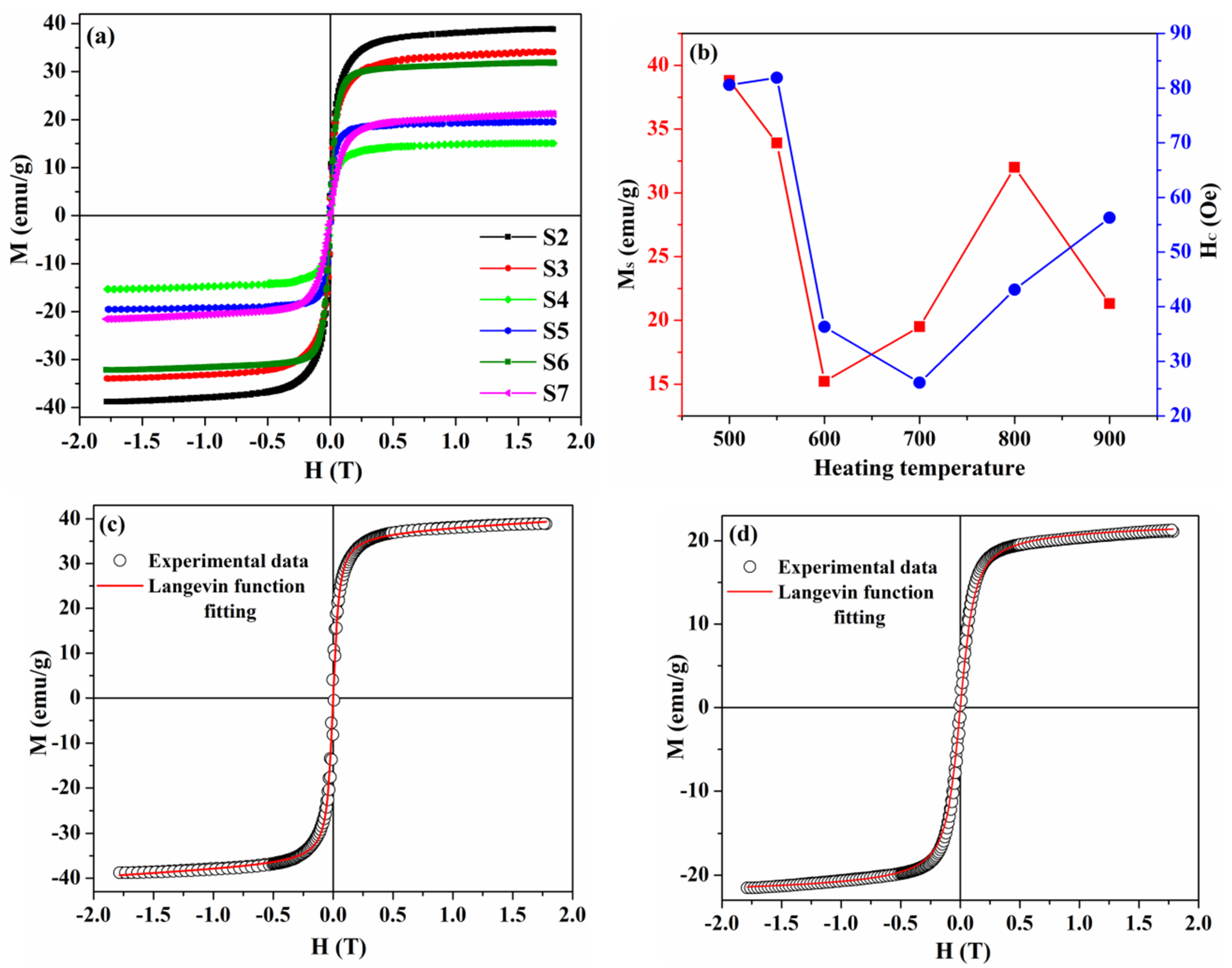
| Sample | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D, nm | 20.5 | 33.1 | 29.5 | 19.4 | - | - | - |
| MS, emu/g | 20.9 | 38.8 | 33.9 | 15.2 | 19.5 | 32 | 21.3 |
| , emu/g | 21.5 | 36.2 | 32.1 | 15.1 | 20.3 | 32.2 | 21.5 |
| MR, emu/g | 2.3 | 6.4 | 6.1 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 2.7 | 1.14 |
| HC, Oe | 38.8 | 80.6 | 81.9 | 36.3 | 26.1 | 43.1 | 56.3 |
| μ, μB | 20,644 | 28,551 | 26,794 | 18,448 | 14,934 | 14,055 | 9224 |
| dS, nm | 12.4 | 11.6 | 11.9 | 13.3 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spivakov, A.A.; Lin, C.-R.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Huang, L.-H. Temperature-Induced Irreversible Structural Transition in Fe1.1Mn1.9O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Combustion Method. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071273
Spivakov AA, Lin C-R, Chen Y-Z, Huang L-H. Temperature-Induced Irreversible Structural Transition in Fe1.1Mn1.9O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Combustion Method. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(7):1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071273
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpivakov, Aleksandr A., Chun-Rong Lin, Ying-Zhen Chen, and Li-Huai Huang. 2023. "Temperature-Induced Irreversible Structural Transition in Fe1.1Mn1.9O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Combustion Method" Nanomaterials 13, no. 7: 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071273
APA StyleSpivakov, A. A., Lin, C.-R., Chen, Y.-Z., & Huang, L.-H. (2023). Temperature-Induced Irreversible Structural Transition in Fe1.1Mn1.9O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Combustion Method. Nanomaterials, 13(7), 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071273





